Londoners spend more time in mobile signal not-spots, or coverage gaps, and experience slower 5G speeds than residents of other UK cities—resulting in poorer performance in everyday tasks such as web browsing.
London is the sprawling metropolis at the heart of the UK economy, home to one of the world’s largest and most lucrative service hubs, supporting a vast network of finance and technology firms. Beyond its strategic time zone and English-language advantage for accessing both American and Asian markets, London’s prosperity has been founded on the availability of world-class infrastructure that facilitates doing business.
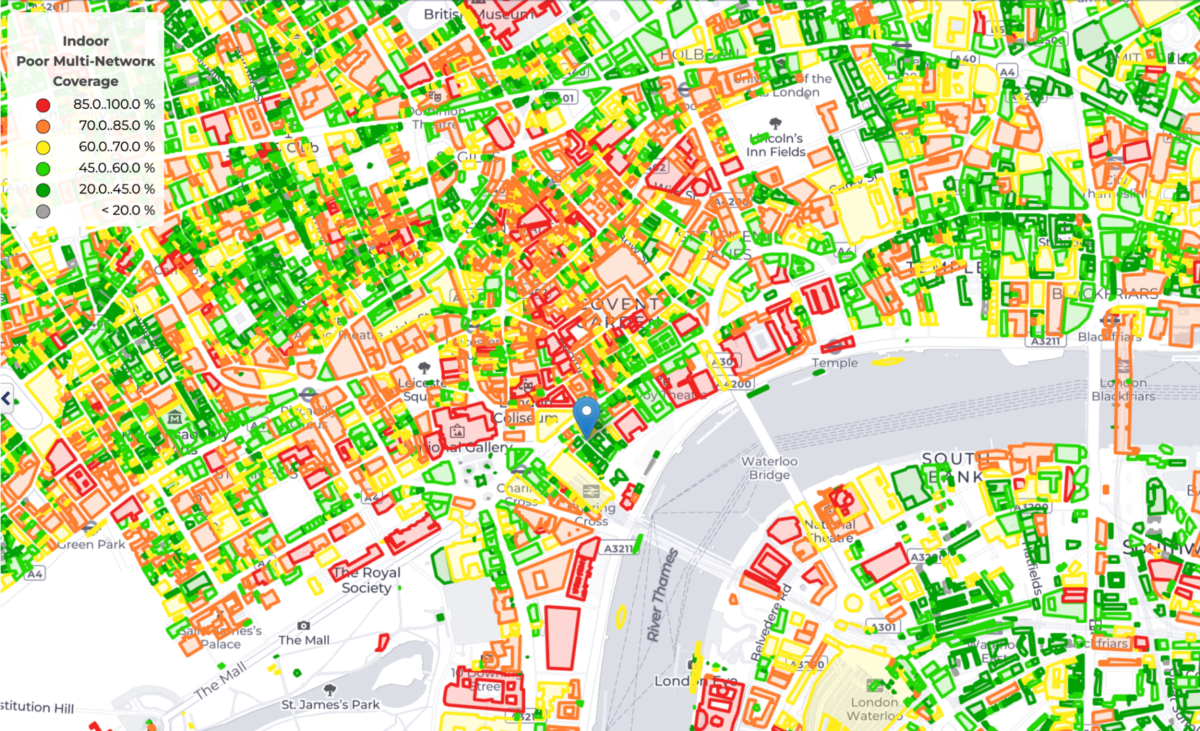
The city’s reputation for international competitiveness has not, however, been matched by the quality of its telecommunications infrastructure. In recent years, a flurry of media reports has highlighted the frustrations of Londoners—and visitors alike—that experience frequent issues using mobile devices indoors, underground, and in busy areas. These problems, reported as being more pronounced than in other UK and European cities, typically manifest as poor quality of experience in everyday tasks such as web browsing, video streaming, and gaming.
This article is the first and a high-level prelude to a series exploring the competitiveness of mobile networks in European towns and cities—starting in the UK with city-level comparisons to London, and followed by a deeper, more comprehensive analysis among international peers coming in research later this year.
Key Takeaways:
- London lags behind the UK’s largest cities across key 5G performance indicators, and the gap to top-performing Glasgow is widening. In Q1 2025, London trailed other UK cities in 5G network consistency—a key indicator of performance at the lower end of the user experience—as well as in median download and upload speeds. Mobile users in London and Belfast experienced the weakest outcomes among UK cities, with median 5G download speeds of approximately 115 Mbps in both cities, significantly behind Glasgow’s 185 Mbps. London’s marked underperformance makes the UK unique in Western European terms—not only are the disparities between its major cities wider, but it is also unusual for the capital to be the primary laggard.
- Mobile users in London spend more time in signal not-spots with no service than residents of other UK cities, reflecting lingering coverage gaps indoors and across key transport routes. The proportion of Londoners spending the majority of their time in locations with no service (0.7%) remained higher than in other UK cities in Q1 2025, but has improved significantly from 3.7% in Q1 2023. This progress reflects operator investments in network densification through small cells and the ongoing rollout of mobile coverage across the London Underground—historically one of the city’s largest mobile not-spots—which have together enhanced overall network availability in the capital. Time spent on 2G networks increased, however, across several UK cities over the last year, including Birmingham and Manchester, as the advancement of the 3G sunset in the UK contributed to greater propensity for 2G fallback.
- The gap in 5G availability between the UK’s major cities and the national average has significantly narrowed over the past year. In Q1 2024, Leeds led UK cities in 5G availability, with a 21 percentage point gap above the national average. By Q1 2025, London had taken the lead in 5G availability among major UK cities, and that gap above the national average had narrowed to 13 percentage points. This trend reflects progress in 5G network expansion in smaller UK towns and rural areas in recent months, which has moved at a faster pace than coverage improvements in larger cities. Overall, median 5G download speeds fell by more than 7% on average across major UK cities between Q1 2024 and Q1 2025, likely reflecting the impact of shifting network load from older technologies onto 5G, which contributed to broader improvements in overall mobile network performance in most UK cities in the same period.
A confluence of factors has created unique headwinds for mobile network deployments in UK cities in recent years, particularly in dense urban settings like London
The deployment of 5G networks in higher-frequency spectrum—most commonly the 3.5 GHz band—continues to present significant challenges for operators globally. Like their counterparts across Europe, UK mobile operators have had to invest heavily in network densification during the 5G cycle. The widespread deployment of small cells at street level across UK cities illustrates the scale of effort required to increase network capacity and overcome the more limited propagation attributes of mid-band spectrum.
Over time, the city environment itself has become increasingly hostile to the operation of high-performing mobile networks. Across developed markets, advancements in building design and stricter regulations have led to a proliferation of highly insulated, airtight structures. These developments often incorporate low-E glass, metal cladding, and reinforced concrete—materials that, collectively, turn new and retrofitted buildings into de facto Faraday cages. London, in particular, presents unique challenges among UK cities, with a high concentration of high-rise buildings featuring deep floorplates.
While the UK’s Part L Building Regulations are not unique or unusually stringent by European standards, they have evolved alongside a set of factors particular to the UK context that have significantly hindered mobile operators’ ability to deliver high-performing 5G networks in dense urban environments. The roots of these factors stem as far back as 2017, well before the commercialization of the country’s first 5G networks, when the UK government introduced changes to the Electronics Communications Code (ECC) in an effort to accelerate mobile network rollouts and reduce costs by streamlining access to land for telecommunications deployments.
The Digital Economy Act, which reformed the ECC, granted mobile operators and tower companies greater rights to access land on more favorable financial terms in the UK. The intention was to curb inflated lease costs, particularly in cases where landowners appeared to demand “ransom rents.” However, rather than accelerating network rollouts, the reforms triggered widespread legal disputes, uncertainty in lease negotiations, and delays in site access and upgrades.
The impact of these land access reforms has been especially acute in dense urban settings such as London, where rooftop deployments play a disproportionate role due to limited ground-level space for mobile equipment. In London, the sheer number of individual property owners—including private landlords, commercial building managers, and housing associations—results in highly fragmented land ownership, making rooftop sites significantly more complex to manage, both legally and logistically, than rural ground leases.
The EEC further compounded this complexity by disrupting long-standing rooftop leasing arrangements in cities like London, leading to thousands of disputes since 2017 over issues such as ransom rents, blocked site upgrades, and non-renewals. The regulation reduced potential rental income by as much as 80% to 90% for some landlords, significantly discouraging the availability of rooftop space for mobile network deployments. This effect was particularly pronounced in London, where building owners have seen greater commercial value in alternative uses for scarce rooftop space, such as bars, gardens, or solar panel installations, hindering the ability of operators to densify their networks.
The UK is the only European country to have adopted such a unilateral price-cutting approach to site access during the 5G cycle. To ease tensions between operators and land owners, the UK government introduced further changes in the “2022 Product Security and Telecommunications Infrastructure Act.” These updates aimed to encourage alternative dispute resolution, simplify lease renewals, and extend the provisions from the EEC to agreements signed before 2017. However, the reforms retained the reduced rental model, meaning while procedural barriers were reduced, incentives for property owners to host rooftop sites remained weak, failing to stem the decline in rooftop site availability in cities like London in recent years.
Combined with the UK’s decision to impose stricter controls on the use of telecom equipment from non-European vendors than those seen elsewhere in Europe, which diverted time and resources toward network rebuilds rather than expansion and upgrades, UK operators have faced significant headwinds in deploying mobile network infrastructure during the 5G cycle.
Progress in the 5G rollout belies lingering performance disparities among the UK’s major cities
Despite significant progress countrywide in improving 5G networks with additional sites, more spectrum availability (some of it from the refarming of 3G), and an expanded 5G standalone (SA) footprint, disparities continue to exist among the UK’s cities. The gap between the best- and worst-performing major cities in median 5G download and upload speeds, for example, widened between Q1 2024 and Q1 2025, based on analysis of Speedtest Intelligence® data.
The Gap in 5G Download Speeds Between Glasgow and Other UK Cities Has Widened
Speedtest Intelligence® | Q1 2024 – Q1 2025
In Q1 2025, Glasgow led the UK with median 5G download speeds reaching 185 Mbps, which was as much as 47% higher than in London, the slowest major city, and 24% higher than in Birmingham, the next best performer. This ranking profile extended to 5G network consistency, which measures the proportion of Speedtest samples that meet a minimum download and upload speed threshold of 25 Mbps and 3 Mbps. While more than 85% of Speedtest samples met this threshold in Glasgow, fewer than 75% did in London, which exhibited the lowest consistency rate among major UK cities and was the only one aligned with the national average that includes both rural and urban areas.
London’s underperformance at the lower percentiles of measures like download speeds is particularly notable, as it strongly reflects the experience of mobile users in more challenging conditions—such as at the network edge, during peak hours, or in congested areas. The city’s lower consistency score and weaker 10th percentile download and upload speeds suggest that Londoners are more likely to encounter poor mobile performance compared to residents of other major UK cities.
The UK stands out in Western Europe for both the scale of the performance gap between its major cities and the unusual fact that its capital is the lagging city. Most regional peers more closely resemble the profile of neighboring France, where Paris ranks among the top three cities nationally for 5G network consistency, as well as median download and upload speeds. In France, the gap in 5G network consistency between the best- and worst-performing cities was as narrow as 5 percentage points in Q1 2025—a disparity that is half that of the UK.
The UK's Cities Exhibit a Greater Range in 5G Consistency Than Other Western European Countries
Speedtest Intelligence® | Q1 2025
In practical terms, London’s underperformance in metrics like 5G download speed and consistency translates into poorer QoE outcomes in everyday tasks like web browsing. In Q1 2025, for example, median web page load times to popular global websites were higher in London than in nine out of ten other major UK cities.
Mobile not-spots continue to be a fixture of everyday life in UK cities, particularly in London
The combination of factors outlined earlier, including the shift toward insulation materials that inhibit signal propagation, the collapse in rooftop rental fees reducing access to mobile sites, and the use of higher-frequency spectrum for 5G, has posed challenges for mobile operators across all UK cities seeking to reduce the prevalence of mobile not-spots. These challenges have been particularly pronounced in the cities with the highest levels of density, most notably London.
Deep indoor and underground spaces (e.g., transport systems like the London Underground network) remain the primary contributors to time spent with no mobile signal or fallback to 2G networks. These cell edge scenarios are highly disruptive for the end-user, resulting in limited access to basic telephony features like texting and calling and a substantial increase in device-side power consumption.
Londoners Spend More Time in Mobile Not-Spots Than the UK Average
Speedtest Intelligence® | Q1 2024 – Q1 2025
The proportion of mobile users in London spending the majority of their time in locations with no network access at all (0.7%) was higher than in other major UK cities in Q1 2025 (an observation related to the capital city that again defies Western European norms). By contrast, less than 0.3% of mobile users in Belfast, Bristol and Sheffield spent the majority of their time in not-spots in the same period. Overall, time spent with no service accounted for as much as 2.6% of quarterly network usage in Q1 2025 in London, significantly higher than the national average.
Despite the disproportionate scale of mobile not-spots lingering in London, recent operator investments in network densification and progress in the ongoing rollout of 4G and 5G coverage throughout the London Underground network are driving dramatic improvements in outcomes. The proportion of Londoners spending the majority of their time in locations with no service has more than halved over the last two years, reflecting a much more pronounced pace of improvement than other UK cities and putting the capital on course to fall into line with other large cities like Birmingham and Manchester.
The advancement of the UK’s 3G sunset, which is set to be substantially complete by the end of this year, is reflected in a sharp reduction in the proportion of mobile users spending the majority of their time on 3G networks. In London, for example, this proportion fell from over 4.5% in Q1 2023 to less than 0.7% in Q1 2025.
The 3G sunset has, however, contributed to an increase in 2G fallback in UK cities at the cell edge where 4G and 5G networks are unavailable. Time spent on 2G increased across several UK cities over the last year, including Liverpool, where this trend has resulted in a larger share of users spending the majority of their time on 2G than in areas with no service at all (a rarity among UK cities).
The Decline in 3G Usage Has Been Similarly Rapid Across UK Cities
Speedtest Intelligence® | Q1 2023 – Q1 2025
Cities that take a proactive approach to telecoms feature the best 5G outcomes
Glasgow’s position as the leading UK city in key 5G performance indicators is unlikely to be an outcome achieved by mere chance. Beyond the contribution of inherent structural factors related to building composition, such as a lower prevalence of high-rise developments relative to other major UK cities, Glasgow’s 5G leadership is also likely rooted in its early and proactive approach to supporting telecoms infrastructure.
The city was among the first in Europe to establish a dedicated “Telecoms Unit”, which streamlined access to city-owned assets for telecom deployments, provided standardized agreements for rental fees, and consolidated telecoms functions within the local authority to reduce departmental siloes. This proactive approach facilitates inward investment in network infrastructure and better 5G outcomes.
Ookla retains ownership of this article including all of the intellectual property rights, data, content graphs and analysis. This article may not be quoted, reproduced, distributed or published for any commercial purpose without prior consent. Members of the press and others using the findings in this article for non-commercial purposes are welcome to publicly share and link to report information with attribution to Ookla.

