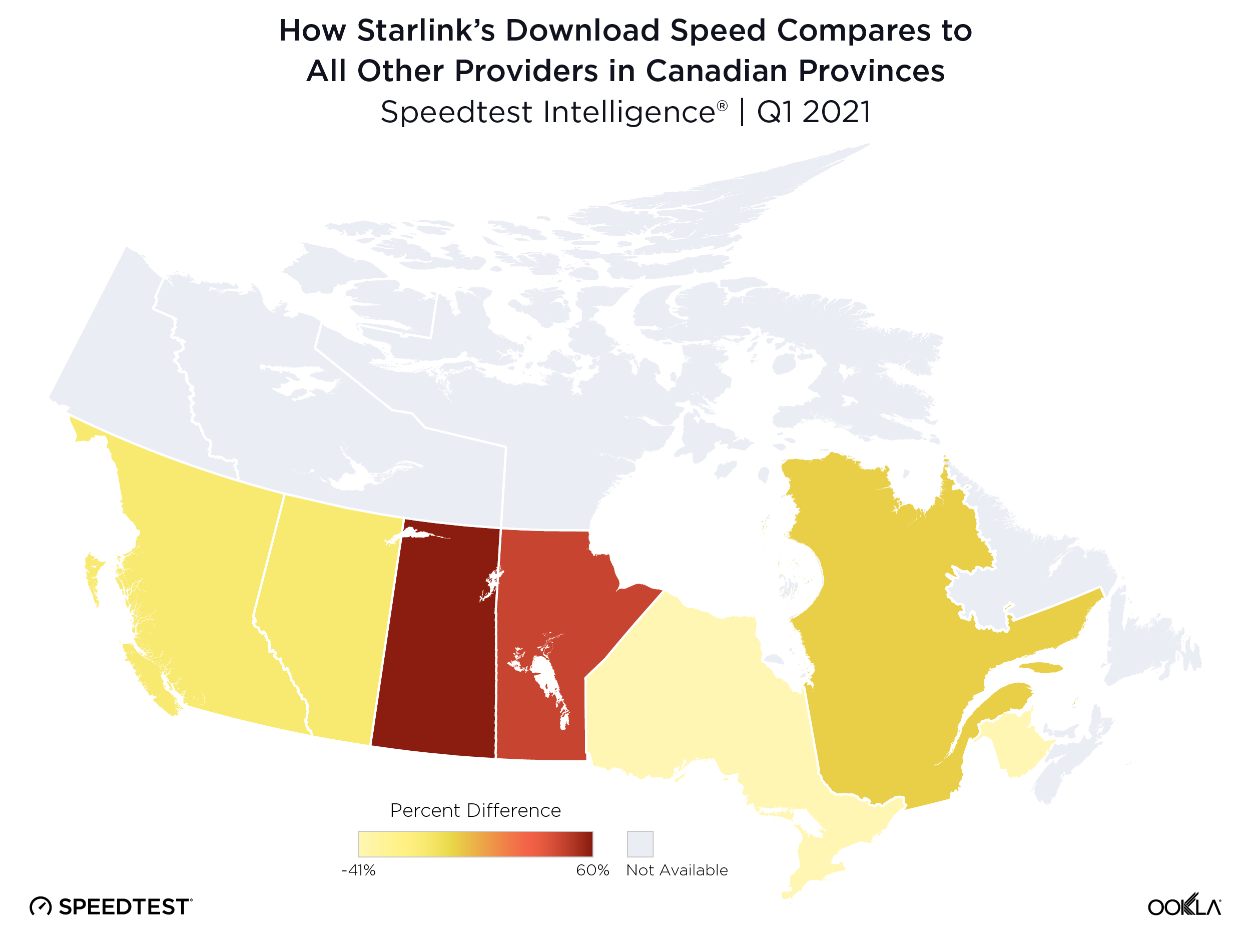
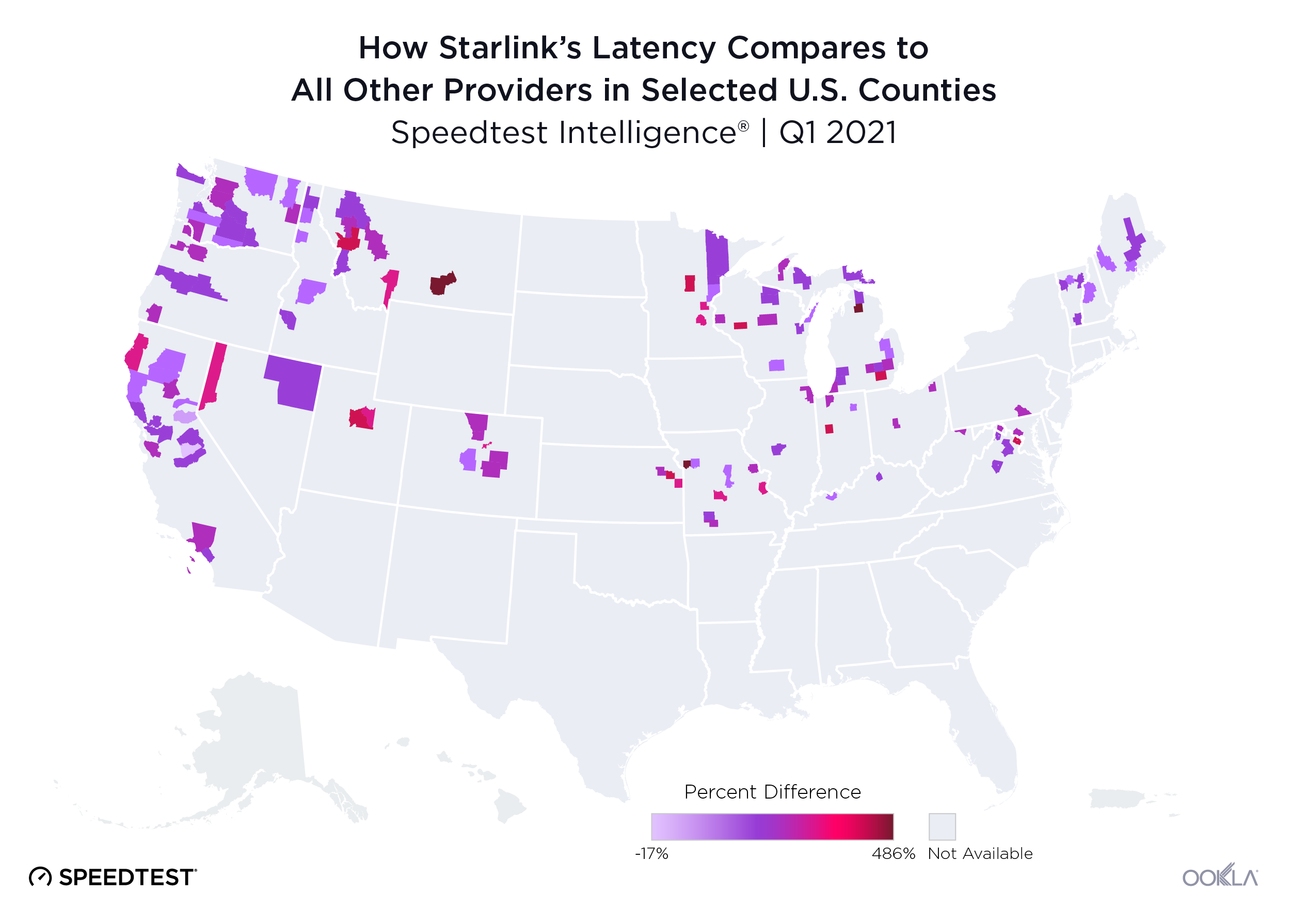
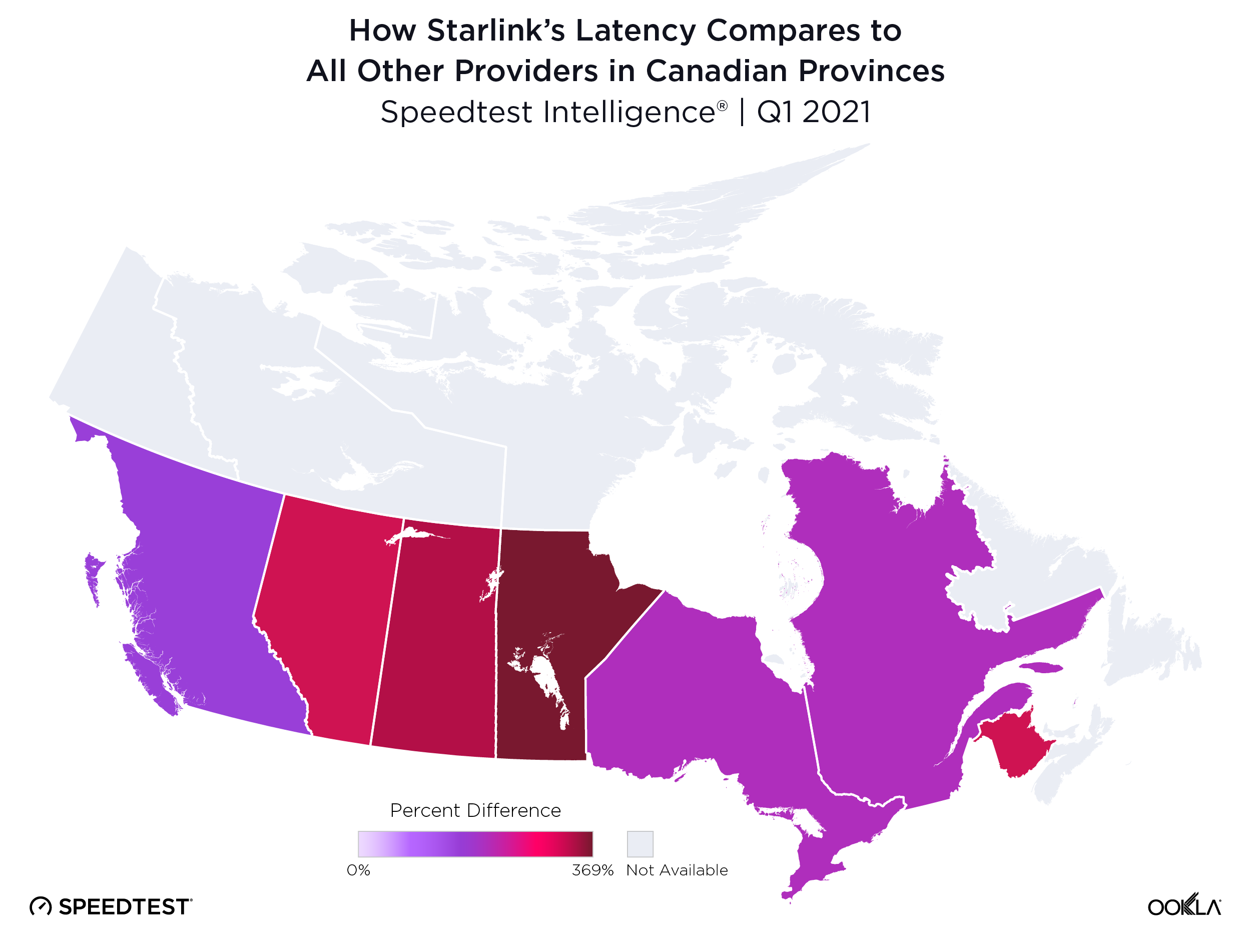
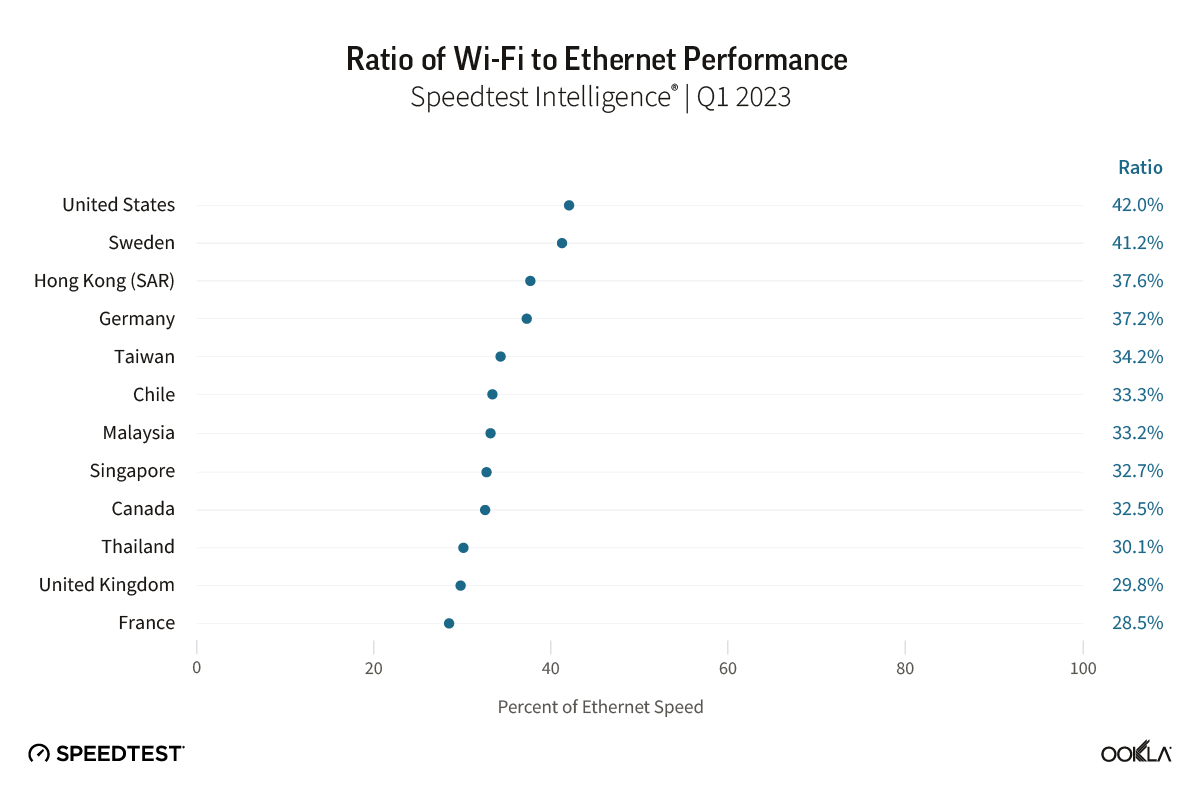
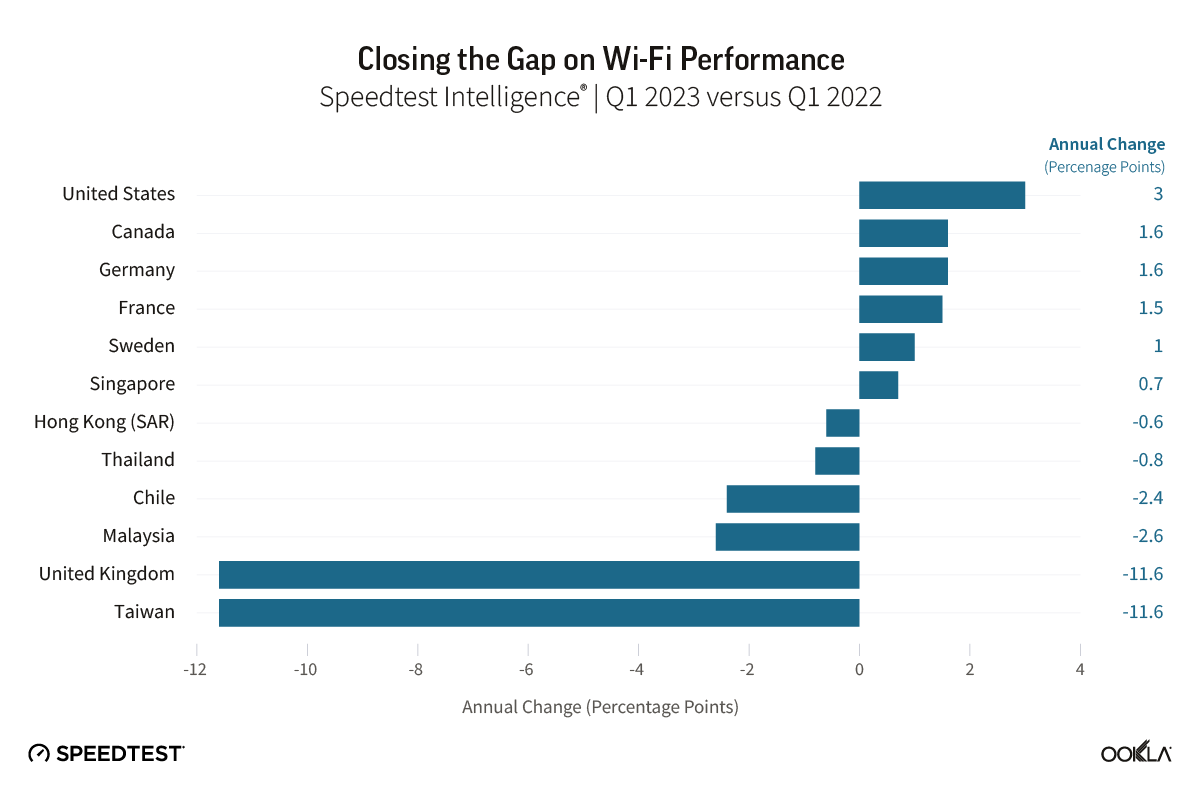
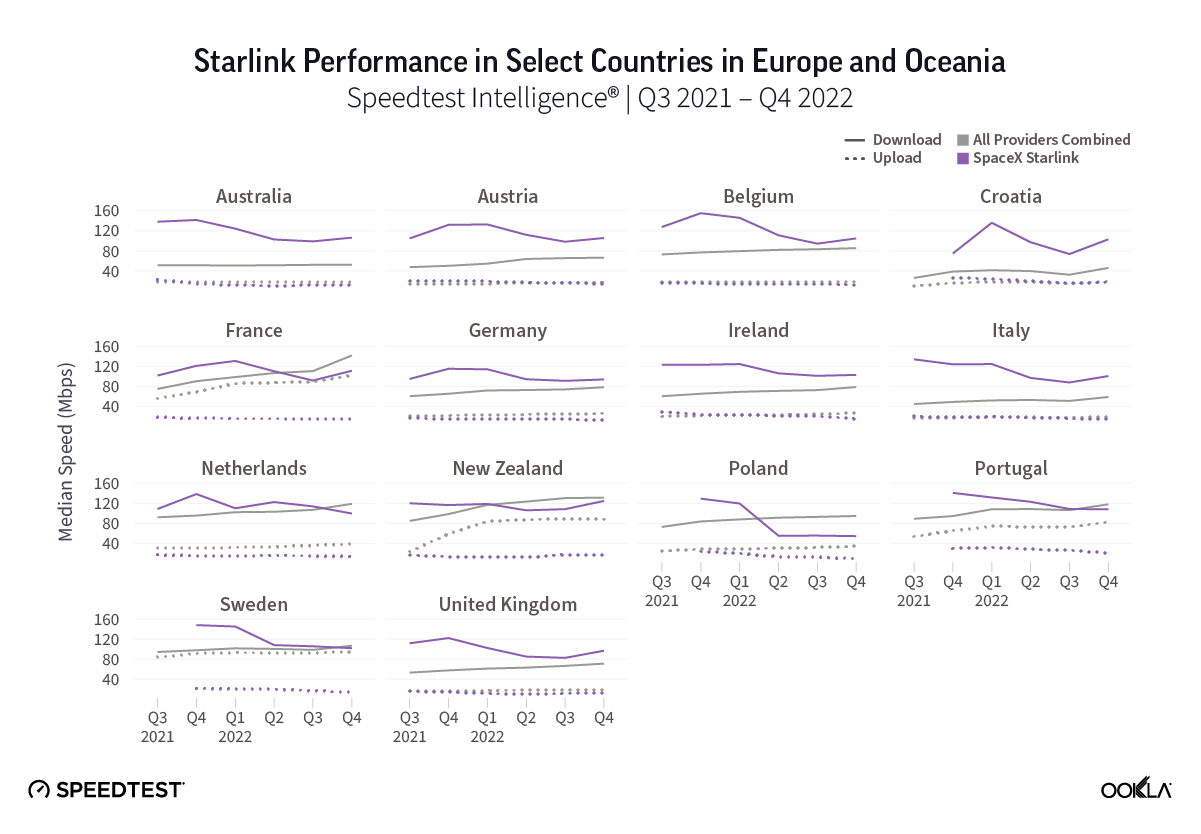
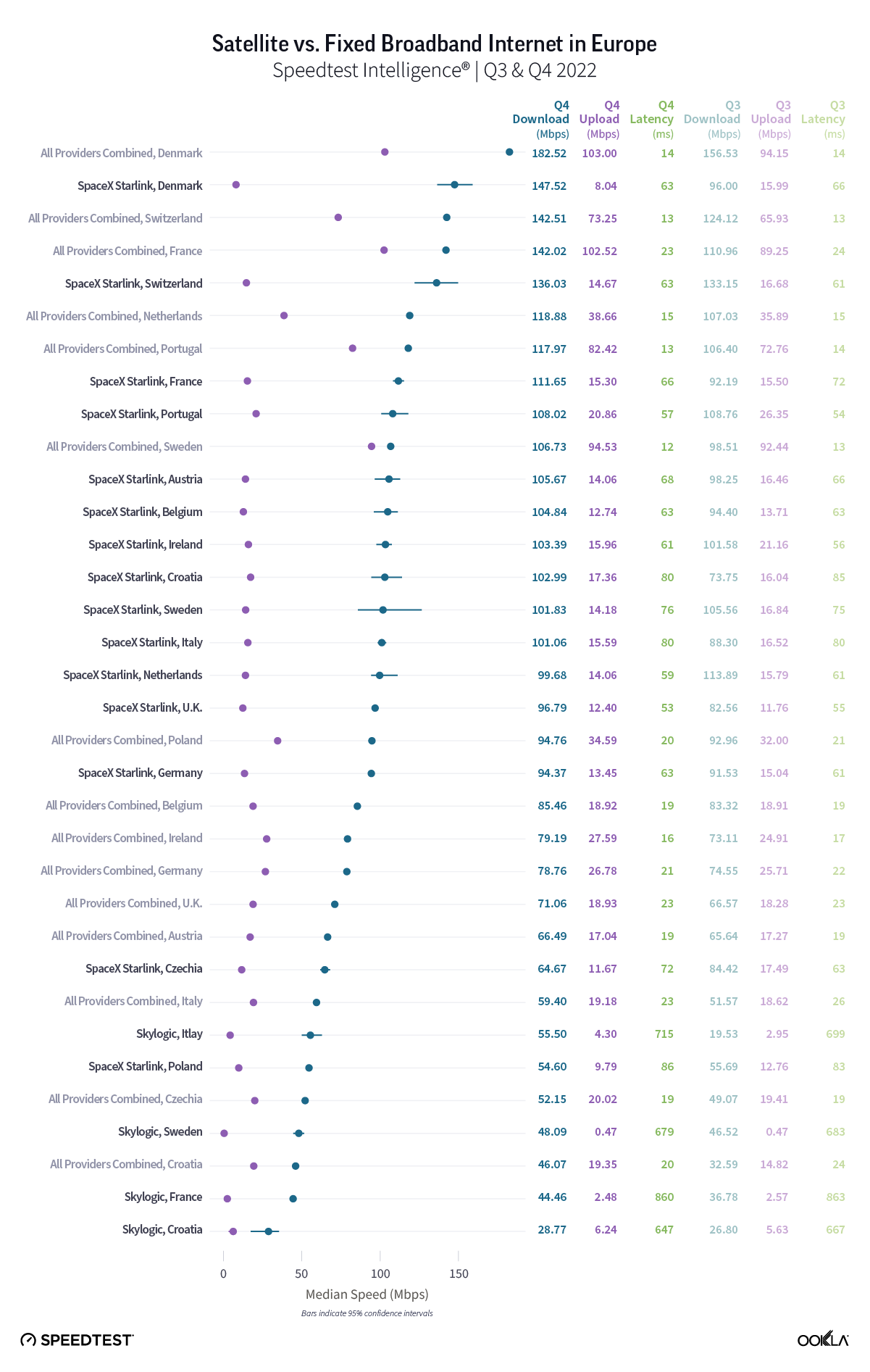
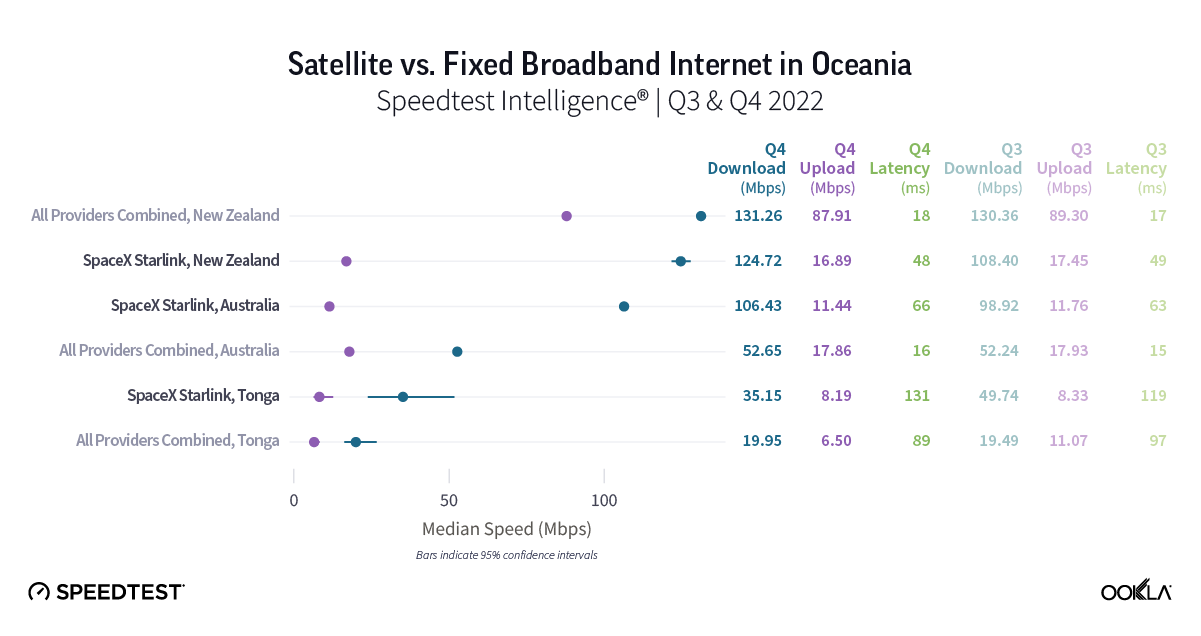
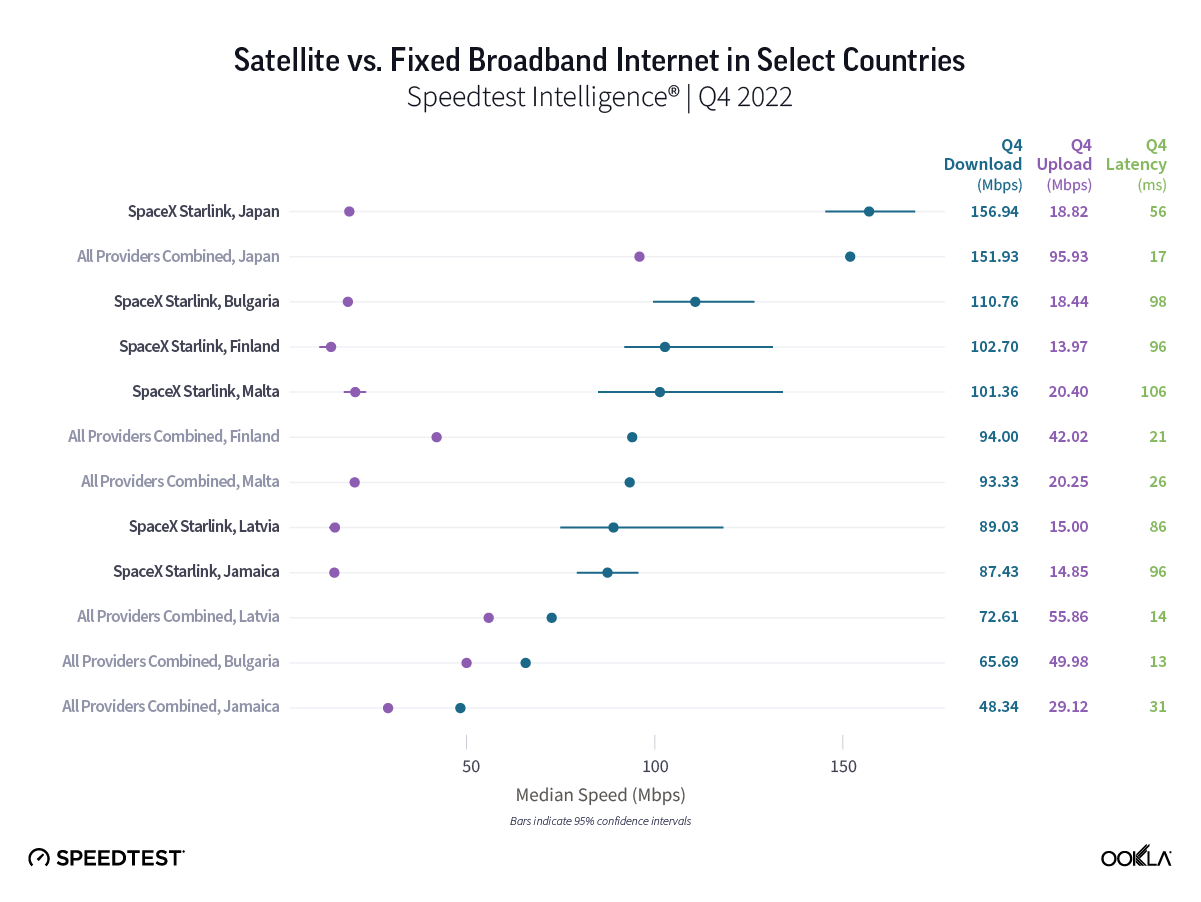
Wireless ISPs face a growing threat from LEO satellite providers like Starlink that can reach rural users with faster download speeds.
There are around 2,000 U.S. wireless internet service providers (WISPs) and about nine million Americans get their internet service from these companies, according to the Wireless ISP Association (WISPA). Many of these WISPs are very small and provide service to just a few hundred customers.
WISPs have become more prevalent over the past few years largely due to the introduction of vendor equipment that makes it possible to more cost-effectively deliver better coverage using unlicensed spectrum and commercial off-the-shelf hardware.
WISPs deliver their services using fixed wireless access (FWA) but they tend to be smaller and focused on certain markets such as rural areas or apartment complexes than the large telcos like Verizon, T-Mobile or AT&T, which also use FWA technology to deliver broadband services across the country. However, unlike the WISPs, these operators don’t consider broadband to be their primary business.
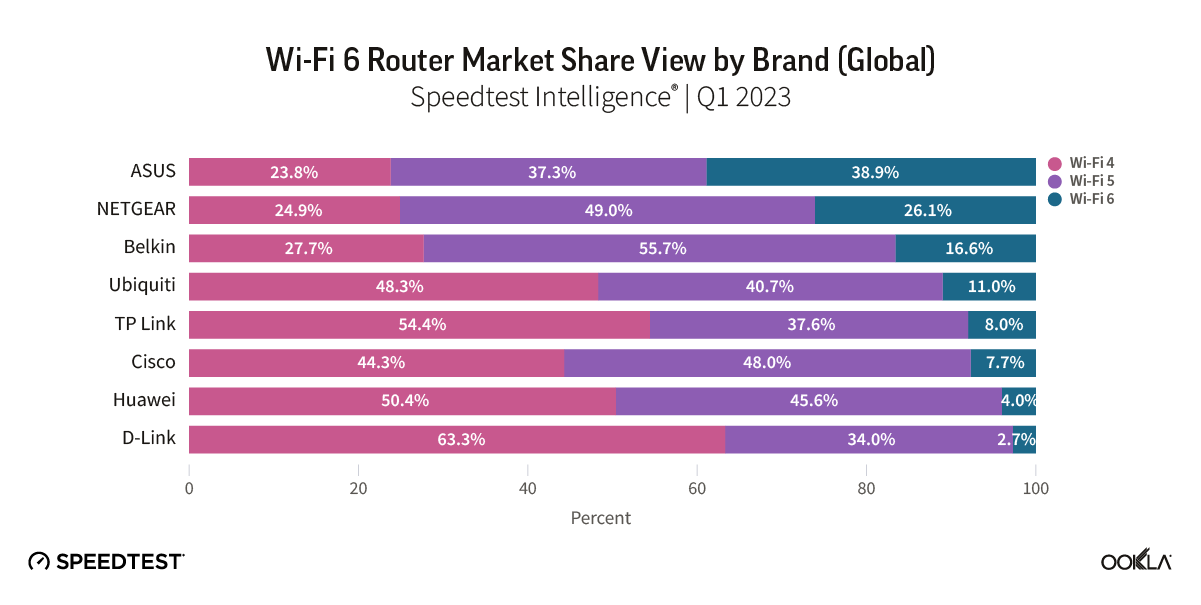
Using Ookla’s Speedtest Intelligence® data, we examined the performance of eight of the larger U.S. WISPs—Etheric Networks, GeoLinks, NextLink Internet, Resound Networks, Rise Broadband, Starry, Unwired Broadband, and Wisper Internet — from Q1 2021 through Q2 2025. For those providers that offer both FWA and fiber, we categorized users with upload speeds under 100 Mbps as FWA customers to distinguish them from fiber users. While all eight of the WISPs that we monitored improved their median download speeds during that time period, their performance varies greatly.
Key Takeaways
- Starry, which is being acquired by Verizon, delivered the highest median download speeds (202.25 Mbps in Q2 2025) of all eight U.S. WISPs that we studied.
- GeoLinks delivered the slowest median download speeds (22.74 Mbps in Q2 2025) of the WISPs we reviewed. Its users in the 75th percentile (those in the upper end of the typical speed range) experienced download speeds of 56.58 Mbps in Q2 2025. We measured GeoLinks customers in its California markets where the company currently uses an older platform on 5 GHz spectrum.
- Because of Starry’s faster speeds, the WISP was able to deliver the FCC’s minimum requirement for broadband speeds of 100/20 Mbps to 66.88% of Speedtest users in Q2 2025.
- WISPs face a growing threat from low-Earth orbit (LEO) satellite providers like Starlink, which can reach rural users with download speeds that are often faster than WISPs.
- To continue to compete in the broadband space, WISPs need to find ways to secure more spectrum to avoid network congestion and interference.
The Many Flavors of WISPs
The performance of WISPs in the U.S. is under scrutiny right now because of recent changes that the National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA) made to the Broadband Equity and Deployment (BEAD) program. In June 2025 the NTIA revamped BEAD to provide a technology-neutral approach and prioritize cost-per-location.This means that instead of favoring fiber, other technologies such as low-Earth orbit (LEO) satellite and FWA can compete with fiber for BEAD funding. The revisions also include a rule to ensure that bids go to the lowest-cost bidders.
States revised their BEAD applications and re-submitted them using the new guidance. Early indications are that many states plan to use FWA for at least a portion of their BEAD eligible locations. Connected Nation, a non-profit that monitors the digital divide, found that states have awarded 11.7% of eligible locations to FWA providers, and many of those FWA providers are categorized as wireless ISPs (WISPs).
We analyzed the performance of eight of the largest U.S. WISPs over several quarters from Q1 2021 until Q2 2025. However, it’s important to note that all of these companies vary greatly in terms of their spectrum holdings, their business models, their coverage areas, and their vendor equipment, which drives a large variance in performance outcomes.
Nevertheless, it’s notable that all eight of the WISPs we monitored improved their median download speeds during that time period. They also improved their median upload speeds, but to a much lesser extent.
Starry outpaced all the others and recorded the highest median download speeds. In Q2 2025 Starry’s median download speed was 202.25 Mbps, which is more than double that of the Resound Networks with a median download speed of 99.41 Mbps in Q2 2025. Starry also was nearly nine times higher in median download speeds than the slowest of the eight WISPs, GeoLinks, which had a median download speed of just 22.74 Mbps in Q2 2025.
A Comparison of WISPs Median Download and Upload Speeds
Q1 2021 through Q2 2025
A comparison of WISPs median download and upload speed over time.
The eight WISPs and their coverage areas
| Name | States where WISP operates | Spectrum used |
| Etheric Networks | California | 2.4 MHz, 5.8 GHz unlicensed and 28 GHz licensed |
| GeoLinks | California, Arizona, and Nevada | unlicensed 5 GHz, LMDS 29-31 GHz spectrum, unlicensed 59-71 GHz spectrum |
| NextLink | Texas, Oklahoma, Illinois, Iowa, Kansas, and Nebraska | 2.4 MHz, 5 GHz, and 6 GHz |
| Resound Networks | Texas, New Mexico, Arizona, Colorado, Oklahoma, Arkansas, Kansas | 6 GHz unlicensed, 5 GHz unlicensed, and 3.65 GHz licensed |
| Rise Broadband | 16 states including Colorado, Nebraska, Illinois, Iowa, Texas and Southern Wisconsin | unlicensed 5 GHz, unlicensed 3.65 GHz, licensed 2.5 GHz, and some TV white space spectrum at 470-698 MHz |
| Starry Broadband | Major cities such as Boston, Denver, Los Angeles, New York City and Washington, DC | 37 GHz licensed, 24 GHz licensed, some 5 GHz unlicensed |
| Unwired Broadband | California | unlicensed 6 GHz |
| Wisper Wireless | Oklahoma, Kansas, Indiana, and Illinois | 3.5 GHz (CBRS), 5.1 GHz, and maybe 6 GHz |
Most WISPs struggle to deliver the FCC’s minimum broadband speeds to their customers
All of the eight WISPs use a different configuration of spectrum licenses. Most are reliant upon some combination of low-, mid-, or high-band licensed and unlicensed spectrum. In addition, many have deployed fiber either as an alternative to their FWA service or to use to carry backhaul or middle-mile traffic.
While using unlicensed spectrum means that a WISP can launch services quickly without having to purchase costly spectrum licenses, it also means that congestion and interference can result in the WISP having to carefully manage demand for their services.
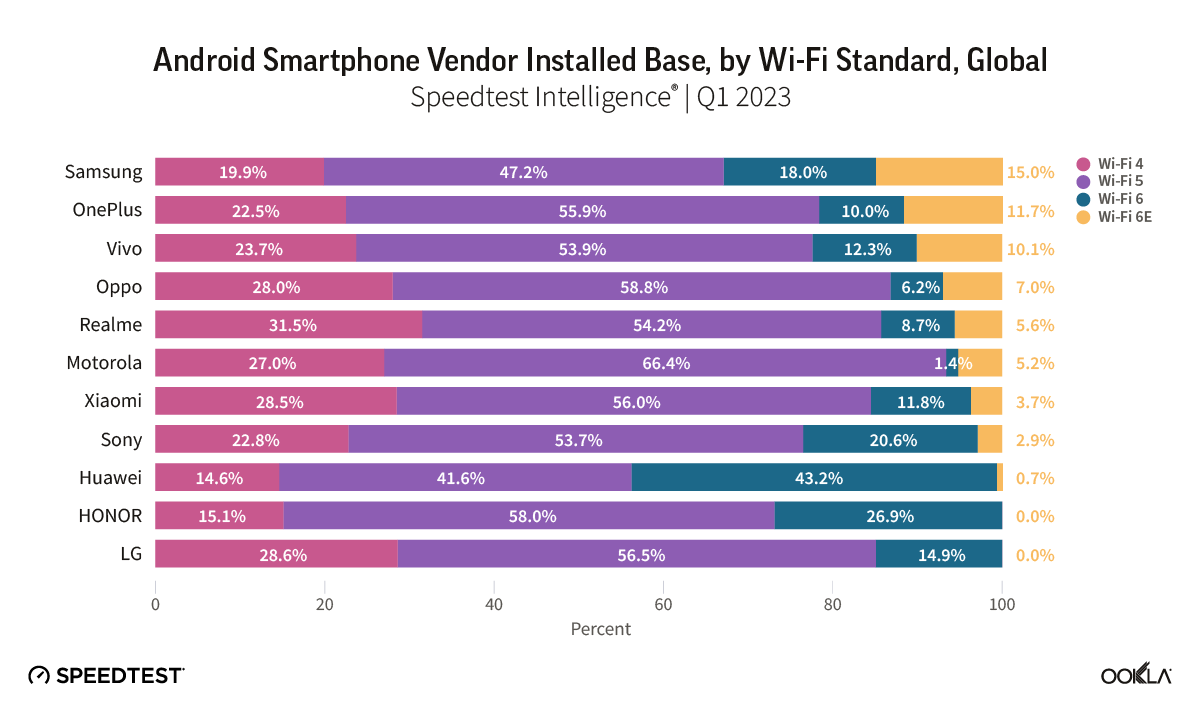
Using Speedtest data collected in Q2 2025 we compared the median download and upload speeds of the eight WISPs to determine what percentage of their Speedtest users were receiving the FCC’s minimum standard for fixed broadband speeds (100 Mbps downstream/20 Mbps upstream).
Starry, which has mmWave spectrum licenses and uses proprietary equipment, is able to provide the FCC’s minimum standard for broadband to the highest percentage of users at 66.9%. In contrast Rise Broadband, which primarily operates with unlicensed spectrum in the 5 GHz band and in the 3.55 GHz to 3.7 GHz bands (CBRS), but also uses some licensed spectrum in the 2.5 GHz band, is able to provide the FCC’s minimum requirement for broadband to just 6.7% of its users.
| WISPs | % of Speedtest users achieving wireless broadband speeds of 100/20 Mbps |
| Starry | 66.9% |
| Resound Networks | 41.5% |
| Wisper Internet | 26.0% |
| NextLink | 24.4% |
| Unwired | 21.8% |
| GeoLinks | 8.7% |
| Etheric | 8.4% |
| Rise Broadband | 6.7% |
mmWave’s bigger pipe doesn’t always equal faster speeds
Starry, GeoLinks and Etheric all use some combination of high-band spectrum to deliver their FWA services. The benefits of this spectrum is it can deliver faster speeds and carry bandwidth-intensive applications. But it also requires line-of-sight or near-line-of-sight to work because of potential interference from buildings, trees, and even rain.
Among the three providers that use mmWave spectrum we saw dramatic differences with Starry significantly outperforming GeoLinks and Etheric, which suggest that Starry has a greater penetration of mmWave spectrum among its customer base that is benefitting the WISP.
Starry
Starry uses a proprietary technology with base stations that cover a radius of about one mile and its system operates on shared spectrum licenses in the 37.1, 37.3 and 37.5 GHz mmWave bands. It also acquired 104 licenses in the 24 GHz band that cover 51 partial economic areas.
The company targets large apartment buildings with its service. Its setup consists of a rooftop base station that broadcasts a signal to multiple building-mounted receivers, allowing a single base station to serve dozens of buildings. Although it uses proprietary equipment it’s based upon modified 802.11ac/ax standards that takes advantage of the Wi-Fi chipset ecosystem.
The company, which is currently being acquired by Verizon, offers service to about 100,000 subscribers in apartment buildings in five markets; Boston, Denver, Los Angeles, New York/New Jersey, and Washington, D.C./Virginia.
Starry offers a variety of rate plans: $30 per month for up to 200 Mbps; $55 per month for up to 500 Mbps; and $75 per month for up to 1 Gbps.
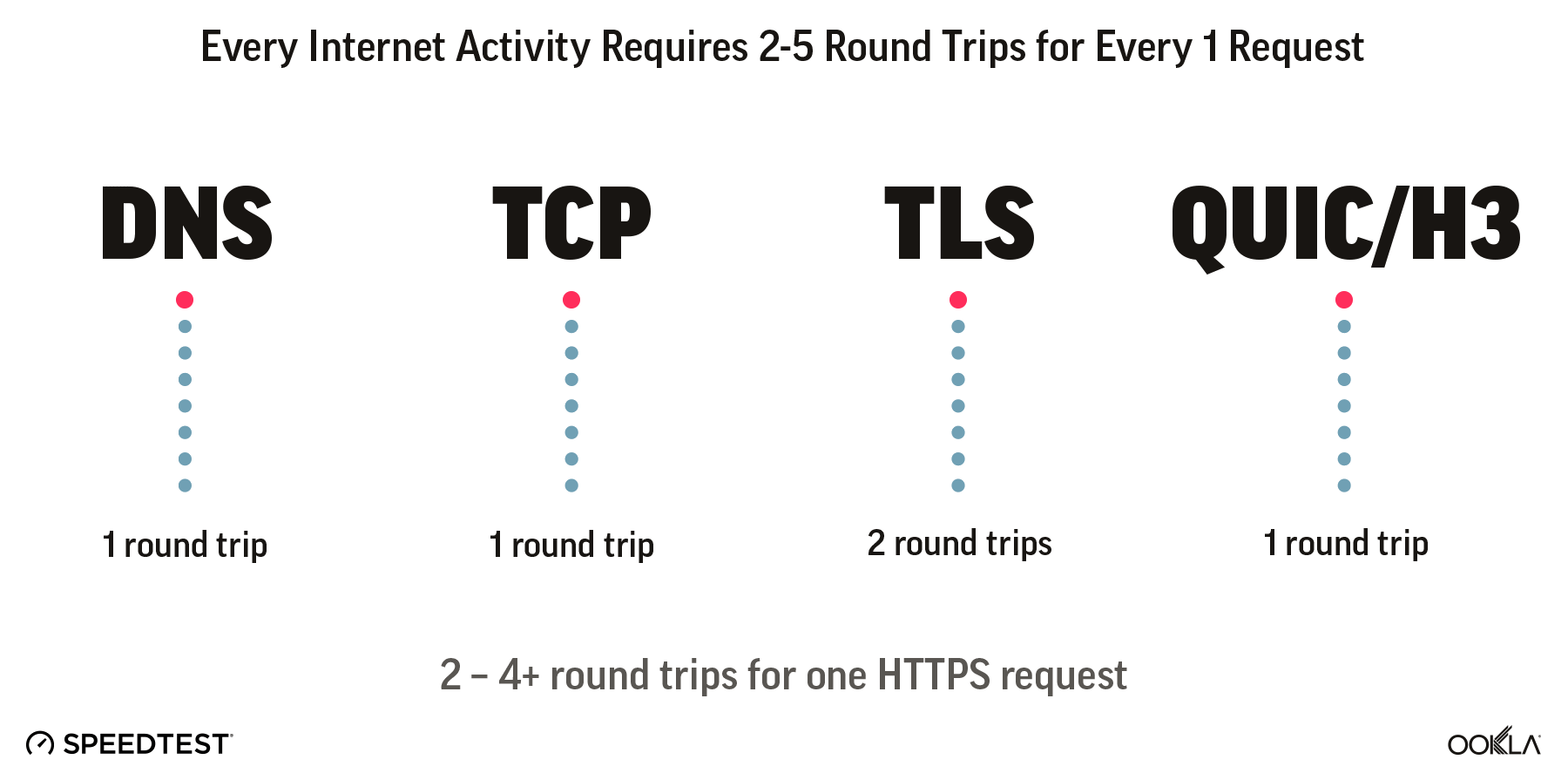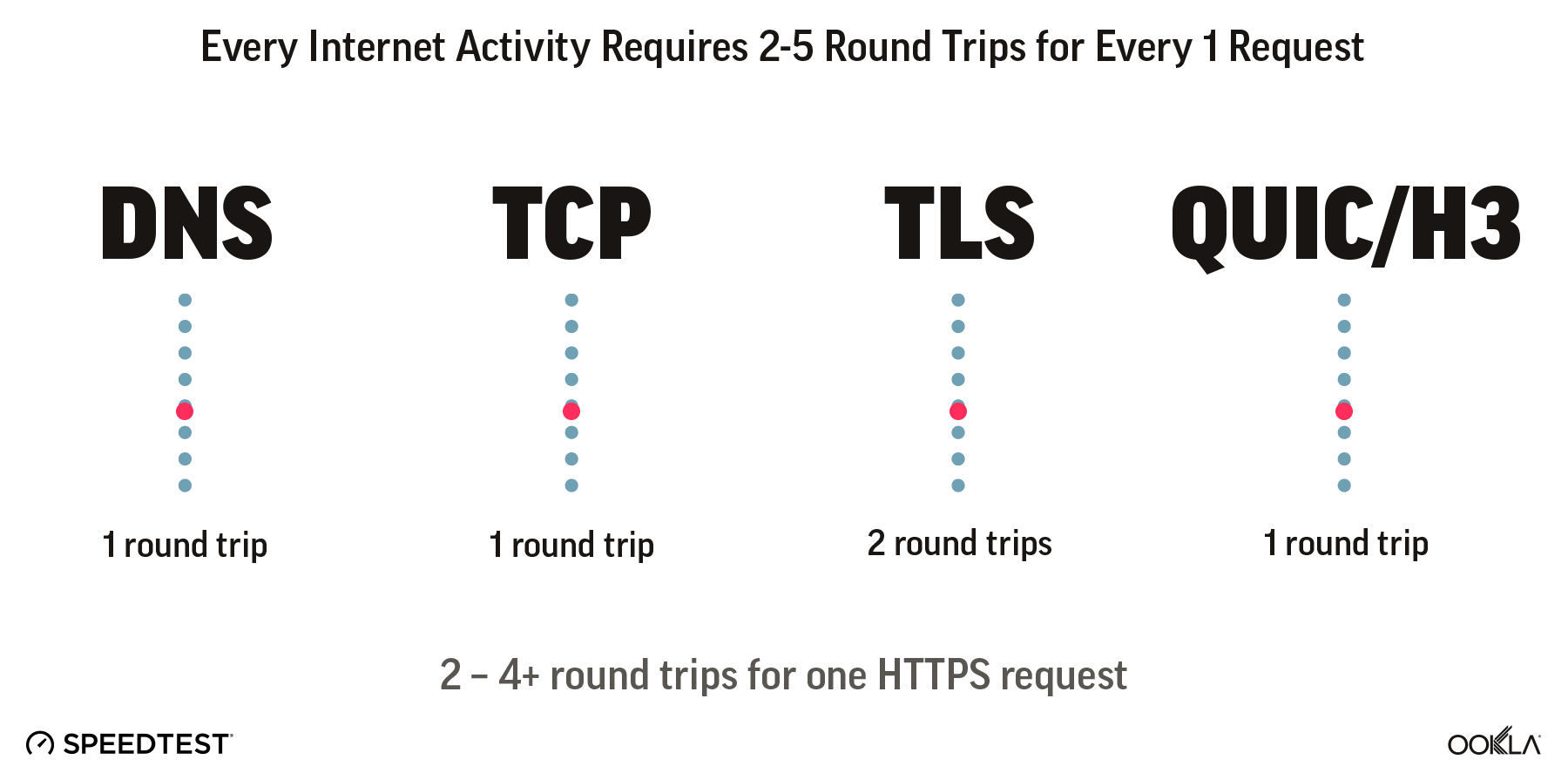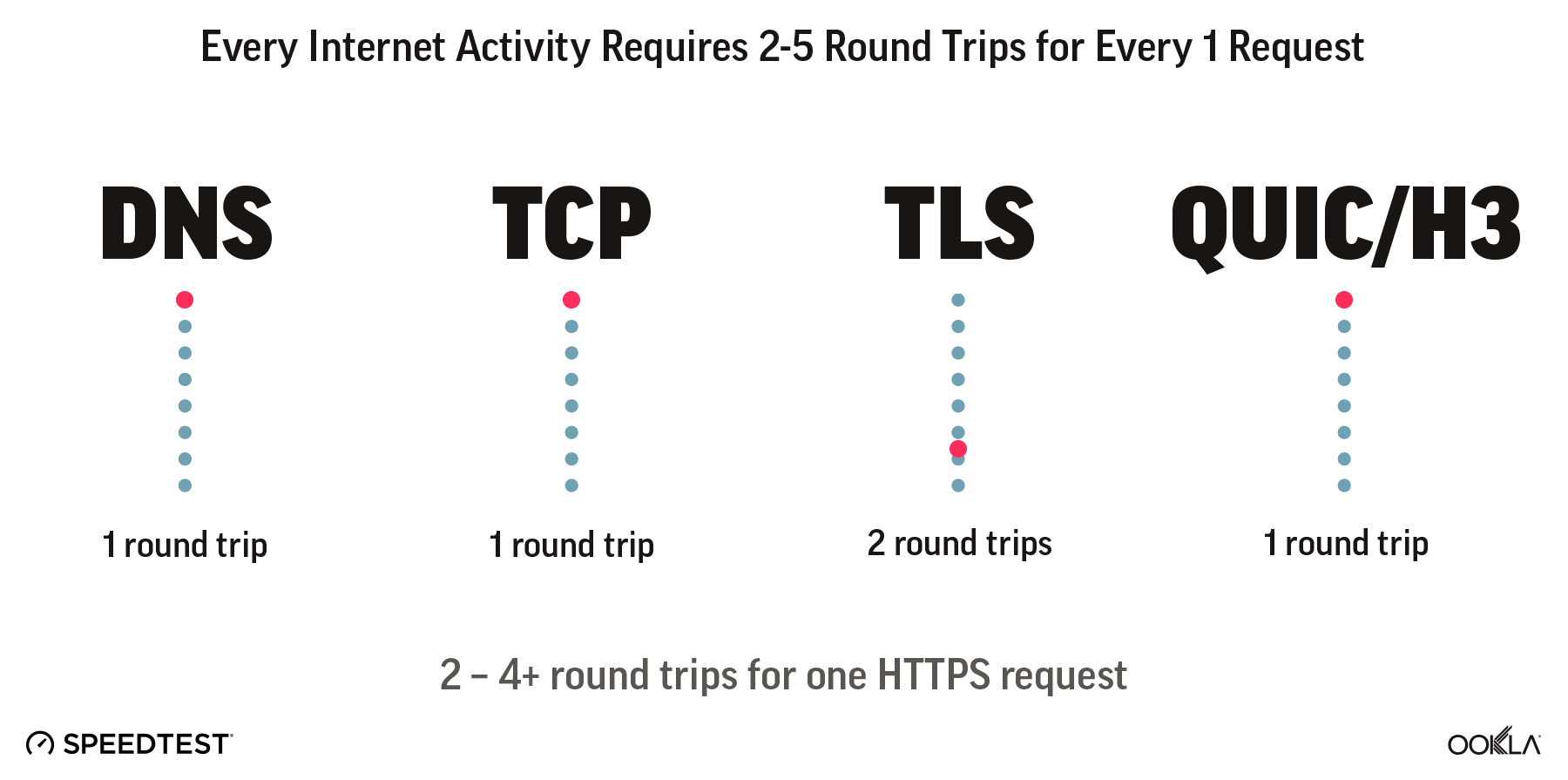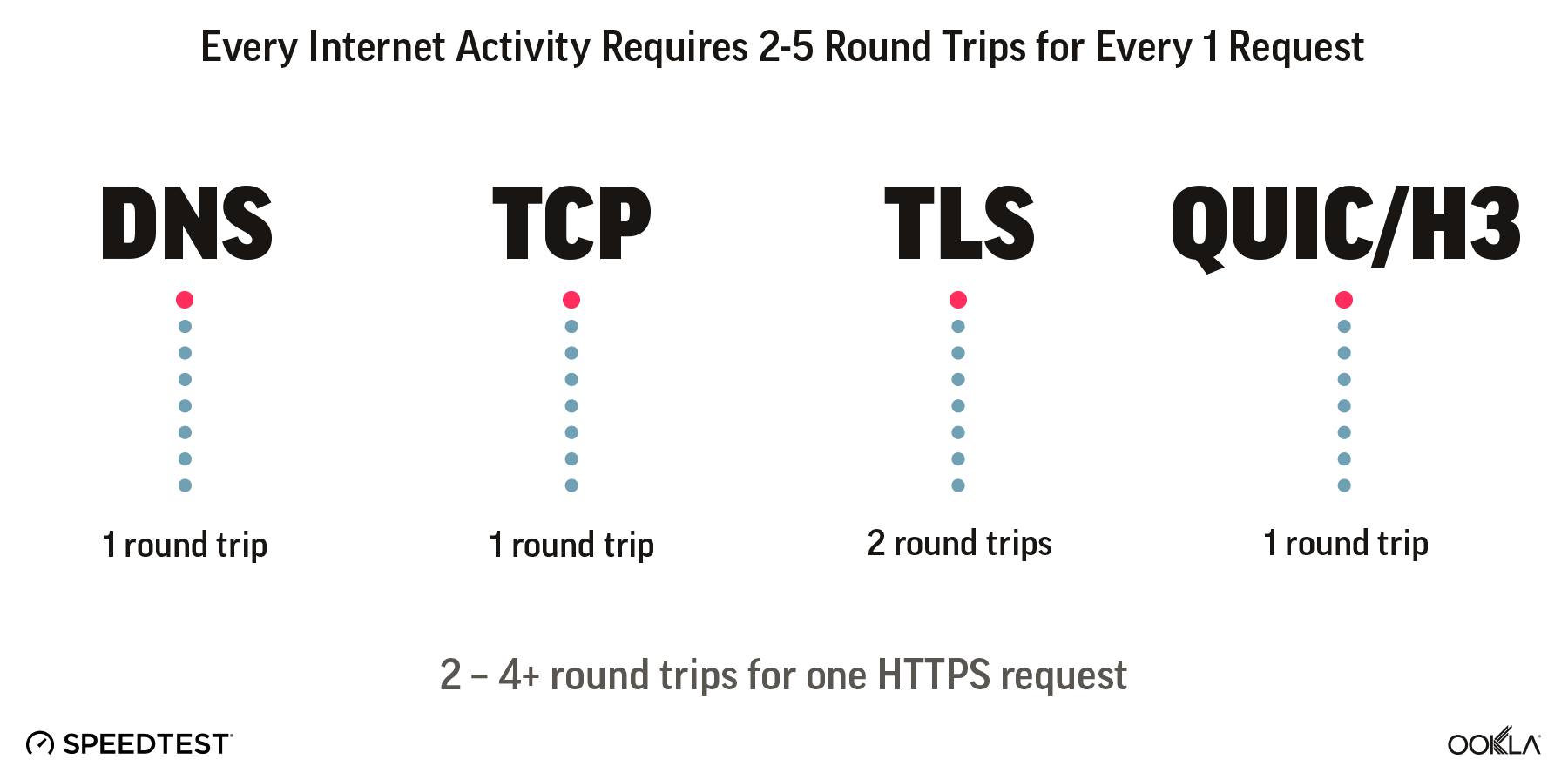
Ookla’s Speedtest® data shows that Starry has nearly doubled its median download speeds in its markets from 102.74 Mbps in Q1 2022 to 202.25 Mbps in Q2 2025. The company’s upload speed also increased, but not as dramatically from 52.29 Mbps in Q1 2022 to 54.34 Mbps in Q2 2025. The company saw the biggest increase in speeds from Q1 2024 to Q2 2025, which is likely due to some network upgrades, including the deployment of the 2.0 version of its Comet receiver. Starry said the upgrades would expand its coverage range as well as provide better spectral efficiency.
Starry's Median Download, 75th Percentile Download, and Median Upload Speeds
Q1 2021 through Q2 2025
Starry's median download, median upload and 75th percentile speeds over time.
GeoLinks
GeoLinks uses local multipoint distribution services (LMDS) spectrum that it acquired from Verizon in 2021 as well as some unlicensed 5 GHz and unlicensed 59-61 GHz spectrum. Those 208 LMDS licenses are in the 29/31 GHz bands and cover several markets. However, GeoLinks currently offers service primarily in California and has a few deployments in Arizona and Nevada, but our Speedtest data samples were all collected from the company’s California deployment where it is currently using the unlicensed 5 GHz spectrum and an older platform..
The company recently tested Intracom Telecom’s point-to-multipoint equipment to demonstrate multi-gigabit FWA using its 29/31GHz mmWave spectrum. In addition, it has indicated that it is interested in leasing its spectrum to other enterprises and operators that can then use its spectrum holdings to develop their own FWA services.
GeoLinks offers a variety of price plans: $25.99 per month for speeds of 10/10 Mbps; $38.99 per month for 25/10 Mbps; $45.99 per month for 30/30 Mbps; and $69.99 per month for speeds of 100/25 Mbps. The company’s web site indicates that the $45.99 per month plan that delivers 30/30 Mbps is the most popular plan with its customers.
Speedtest data shows Geolinks delivering median download speeds of just 22.74 Mbps in Q2 2025 with 75th percentile download speeds of 56.58 Mbps. Its users experience median upload speeds of 19.82 Mbps in Q2 2025.
GeoLink's Median Download, 75th Percentile Download, and Median Upload Speeds
Q1 2021 through Q2 2025
GeoLink's median download, median upload and 75th percentile speeds over time.
Etheric Networks
Etheric Networks provides FWA service to the California Bay Area. The company has a fiber ring stretching from San Francisco to Monterey, California that connects its FWA towers and eight data centers. Etheric uses a mix of spectrum including unlicensed 2.4 GHz and 5.8 GHz spectrum. However, in 2024 Etheric partnered with BroadbandOne to leverage BroadbandOne’s 28 GHz mmWave spectrum. The company said this partnership will allow it to enhance its connectivity and serve more rural and agricultural areas.
The company offers three residential price plans: $79 per month for speeds up to 100 Mbps; $99 per month for speeds up to 250 Mbps and $169 per month for 1 Gbps speeds.
Speedtest data shows Etheric has nearly doubled its median download speeds from 21.34 Mbps in Q1 2021 to 41.09 Mbps in Q2 2025. Its users in the 75th percentile (those in the upper end of the typical speed range) saw speeds of 65.45 Mbps in Q2 2025.The company’s median upload speeds also increased over time from 13.6 Mbps in Q1 2021 to 29.5 Mbps in Q2 2025.
Etheric Networks' Median Download, 75th Percentile Download, and Median Upload Speeds
Q1 2021 through Q2 2025
Etheric Networks' median download, median upload and 75th percentile speeds over time.
WISPs make the most of mid-band with CBRS licenses
Many WISPs take advantage of the mid-band CBRS spectrum, which is a 150 MHz shared spectrum in the 3.5 GHz to 3.7 GHz band that allows for flexible use by three different groups that are managed by a Spectrum Access System (SAS). The SAS can dynamically grant access to different users. The band is shared by these three parties: incumbent users such as the U.S. Navy that have priority access to the band; licensed users with Priority Access Licenses (PAL) that have exclusive use of a portion of the band in a specific geographic location; and the General Authorized Access (GAA) group who can access the spectrum but have no protection from interference from the other two groups.
Several of the WISPs we analyzed deploy their services in the CBRS spectrum and primarily use the GAA portion of the band. Others have acquired CBRS PAL and some use a combination of both. Some WISPS also use unlicensed bands such as 5 GHz.
NextLink
Nextlink spent $28.4 million in FCC’s Auction 105 to purchase over 1,100 CBRS PAL licenses covering 491 counties in eleven states including Texas, Oklahoma, Kansas, Nebraska, Iowa, Minnesota, Wisconsin, Indiana, Wyoming, and Missouri. The company uses that spectrum to deliver its FWA service to its more than 100,000 subscribers (as of August 2025). NextLink also has deployed fiber to more than 100,000 locations and has 20,000 fiber customers.
Nextlink secured Connect America Fund II funding and participated in the FCC’s Rural Digital Opportunity Fund so much of its FWA expansion has been driven by those commitments. In August Nextlink said it has completed five of the six states as part of its CAF II funding and is halfway through its RDOF buildout.
The company offers a variety of FWA plans: The Next50, which offers up to 50 Mbps speeds for $30 per month; the Next100 that offers speeds up to 100 Mbps for $40 per month; The Next300 that offers speeds up to 300 Mbps for $60 per month; and the Next500 that offers speeds up to 500 Mbps for $75 per month.
Speedtest data shows NextLink has more than tripled its median download speeds from 19.45 Mbps in Q1 2021 to 68.47 Mbps in Q2 2025. The WISP also increased its median upload speeds significantly from 4.72 Mbps in Q1 2021 to 18.26 Mbps in Q2 2025. NextLink users in the 75th percentile (those in the upper end of the typical speed range) get much higher speeds of 122.88 Mbps in Q2 2025.
NextLink's Median Download, 75th Percentile Download, and Median Upload Speeds
Q1 2021 through Q2 2025
NextLink's median download, median upload and 75th percentile speeds over time.
Resound Networks
Resound Networks provides FWA service in Texas, New Mexico, Arkansas, Arizona and Oklahoma and uses Tarana Wireless gear in the unlicensed 5 GHz and 6 GHz spectrum bands. It also offers fiber service in some locations and is planning to expand its fiber footprint. Like many WISPs, Resound is focused specifically on rural communities that have historically been overlooked by larger ISPs. In 2022 the company was awarded $303 million through the FCC’s RDOF program to deliver FWA and fiber to 214,000 rural locations.
Resound offers both residential and enterprise rate plans. Its residential plans start at 75 Mbps for $55 per month and go up to 1 Gbps for $130 per month.
The company’s customers experienced a steady increase in their download and upload speeds from mid-2023 until Q2 2025 from a median download speed of 38.94 Mbps in Q3 2023 to 99.41 Mbps in Q2 2025. Its users in the 75th percentile (those in the upper end of the typical speed range) experienced an even greater climb in download speeds from 62.99 Mbps in Q3 2023 to 190.76 Mbps in Q2 2025. During this time period Resound was expanding its network.
Resound Network's Median Download, 75th Percentile Download, and Median Upload Speeds
Q1 2021 through Q2 2025
Resound's median download, median upload and 75th percentile speeds over time.
Rise Broadband
Rise Broadband claims to be the country’s largest WISP with around 200,000 customers. It may also be one of the longest living WISPs because it dates back to 2006 when it started as JAB Broadband and its goal was to consolidate many of the country’s smaller WISPs to create one big WISP with a large footprint.
Today Rise offers FWA service in16 states, mostly in the Midwest. Rise offers service primarily in rural areas and it uses a mix of unlicensed spectrum in the 5 GHz band and in the 3.55 GHz to 3.7 GHz bands (CBRS), but also uses some licensed spectrum in the 2.5 GHz band, to deliver its service.
Like NextLink, the company is actively deploying fiber in addition to FWA. The company’s strategy is to deploy FWA initially to capture market share and then roll out fiber to the densest FWA coverage areas.
Rise’s price plans start as low as $30 per month for 50 Mbps and reach up to 400 Mbps for $55 per month.
Rise users logged median download speeds of 42.58 Mbps in Q2 2025, which is a significant jump from Q1 2021 when users experienced median download speeds of just 16.01 Mbps. Rise’s users in the 75th percentile (those in the upper end of the typical speed range) were able to achieve download speeds of 65.97 Mbps in Q2 2025. The company’s median upload speeds also increased from 4.05 Mbps in Q1 2021 to 18.38 Mbps Q2 2025. Rise saw a big jump in median upload speeds between Q2 2022 when users logged median upload speeds of 5.86 Mbps and Q3 2022 when users experienced median upload speeds of 13.68 Mbps.
Rise Broadband's Median Download, 75th Percentile Download, and Median Upload Speeds
Q1 2021 through Q2 2025
Rise Broadband's median download, median upload and 75th percentile speeds over time.
Wisper Internet
Wisper Internet offers FWA in six midwestern states including Illinois, Missouri, Kansas, Oklahoma, Arkansas and Indiana. The company uses unlicensed spectrum in the 5 GHz, and a mix of unlicensed and licensed spectrum in the 2.5 GHz and 3.65 GHz bands. Like NextLink and Rise, the company also has deployed fiber in a few select areas.
Wisper offers a variety of rate plans including 25 Mbps for $70 per month; 50 Mbps for $75 per month; 100 Mbps for $80 per month; 200 Mbps for $110 per month and 400 Mbps for $140 per month.
Similar to the other WISPs, Wisper’s median download speeds increased over time but it increased dramatically from Q3 2023 to Q2 2025 when its median download speeds increased from 33.74 Mbps to 52.90 Mbps. Likewise, the download speeds for users in the 75th percentile also increased, climbing from 55.12 Mbps in Q3 2023 to 107.90 Mbps in Q2 2025. This jump in speeds was likely due to Wisper’s deployment of additional FWA gear from Tarana Wireless on 180 more towers in its footprint.
Wisper Internet's Median Download, 75th Percentile Download, and Median Upload Speeds
Q1 2021 through Q2 2025
Wisper Internet's median download, median upload and 75th percentile speeds over time.
Unwired
Unwired Broadband provides FWA coverage in rural and underserved areas in central and northern California. The company said it has a network of more than 200 towers and a coverage area of about 17,000 square miles. Besides FWA, Unwired also provides some fiber service but It’s early in its deployment process.
Unwired uses a combination of licensed and unlicensed spectrum to deliver its FWA service, including the licensed 2.5 GHz band and the unlicensed 6 GHz band.
The company offers both business and residential FWA service and its pricing starts at $59.99 per month for 100 Mbps.
Unwired users experienced increases in download and upload speeds over time but between Q3 2024 and Q4 2024 the jump was more dramatic. Median download speeds jumped from 27.22 Mbps in Q3 to 44.25 Mbps in Q4. Similarly median upload speeds increased from 9.7 Mbps in Q3 2024 to 15.9 Mbps in Q4.
Unwired's Median Download, 75th Percentile Download, and Median Upload Speeds
Q1 2021 through Q2 2025
Unwired's median download, median upload and 75th percentile speeds over time.
WISPs’ performance is improving but competitive threats lurk
Although the WISPs we studied are improving their networks and delivering better performance for their customers, the broadband market is rapidly changing. In the past many WISPs, particularly those in rural areas, faced little or no competition. But that’s no longer the case.
As LEO satellite constellations such as Starlink become more powerful and more prevalent (Amazon’s Kuiper now has 153 satellites in orbit and is expected to launch late this year), WISPs will face growing competition from these companies.
A recent Ookla report on Starlink found that Starlink’s network saw its median download speeds nearly double from 53.95 Mbps in Q3 2022 to 104.71 Mbps in Q1 2025, making its median download speeds on par or better than seven of the eight WISPs we reviewed (Starry was the only exception). With Starlink residential price plans starting around $80 per month, the company’s introductory price plan is a bit more expensive than some introductory price plans from WISPs but Starlink is aggressively promoting its services and offering large discounts on its equipment to entice new customers.
To continue to play in the broadband space, WISPs need to try to secure more spectrum–licensed or unlicensed— to avoid network congestion and interference and also invest in network upgrades so their services remain competitive.
To find out more about Speedtest Intelligence® data and insights, visit our website.
Ookla retains ownership of this article including all of the intellectual property rights, data, content graphs and analysis. This article may not be quoted, reproduced, distributed or published for any commercial purpose without prior consent. Members of the press and others using the findings in this article for non-commercial purposes are welcome to publicly share and link to report information with attribution to Ookla.