The Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area (GBA) is one of the regions with the fastest urbanization process in China in the past 4 decades. With the highest concentration of skyscrapers in the world, operators in the region must prioritize seamless indoor and outdoor 5G coverage to optimize services and meet customer needs.
In this report, we use data from Cell Analytics™ to examine the 5G indoor performance and signal quality across Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Hong Kong, and Macau, the four major cities in GBA.
Key Takeaways
- Guangzhou and Shenzhen showed better city-wide indoor 5G coverage and quality compared to Hong Kong and Macau. Guangzhou reported a mean RSRP of -82.89 dBm, with Shenzhen slightly lower at -86.96 dBm. Additionally, both cities boast better 5G indoor quality with scores of 10.09 dB and 10.98 dB, respectively. In contrast, Hong Kong’s mean RSRP was at -87.36 dBm, while Macau’s was at -91.02 dBm.
- China Mobile in Guangzhou stands out for offering better indoor 5G coverage in the city. The operator reported a mean RSRP of -79.17 dBm, which is significantly better by approximately 8 dB compared to China Unicom’s mean RSRP of -87.2 dBm. There were only minor differences in 5G indoor signal strength between operators in the other cities, but in Macau, the operators had significantly weaker indoor signal strength than almost all other operators in the other selected cities.
Indoor 5G Traffic Continue to Rise Among the Greater Bay Area Cities
The Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area, commonly known as the Greater Bay Area (GBA), comprises nine cities in the Guangdong region of China and the two Special Administrative Regions (SAR) of Hong Kong and Macau. These cities are connected by an extensive transportation network, including high-speed rail, bridges, and tunnels, due to their proximity. As a key economic and technological hub in China, the adoption of 5G technology has become a key driver in the region, enabling the transformation of various industries and promoting automation and digitalization. In our recent article, we delved into the factors driving the rollout of 5G technology and examined its performance in the GBA region.
Indoor coverage is particularly important for the major “core” cities of GBA; Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Hong Kong, and Macau, where high-rise buildings dominate the skyline and indoor spaces play essential roles in commercial and tourist activities. In this recent article, we touched on the different technical solutions to address indoor cellular coverage challenges.
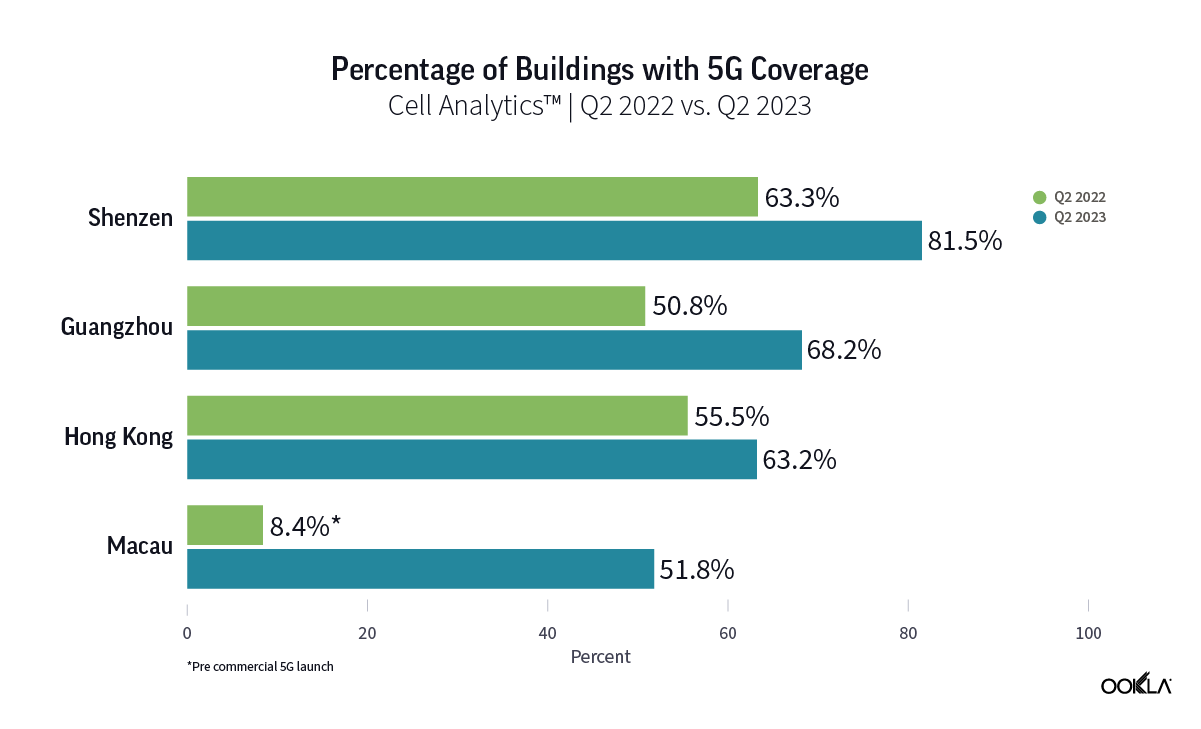
In order to assess the reach of 5G coverage inside buildings, we analyzed data from Ookla® Cell Analytics™ to measure the percentage of buildings in Hong Kong, Macau, Shenzhen, and Guangzhou with reported indoor 5G samples between Q1 2023 to Q4 2023. In this analysis, we have only considered buildings taller than 10 meters, which is the height of a typical three-story building or more.

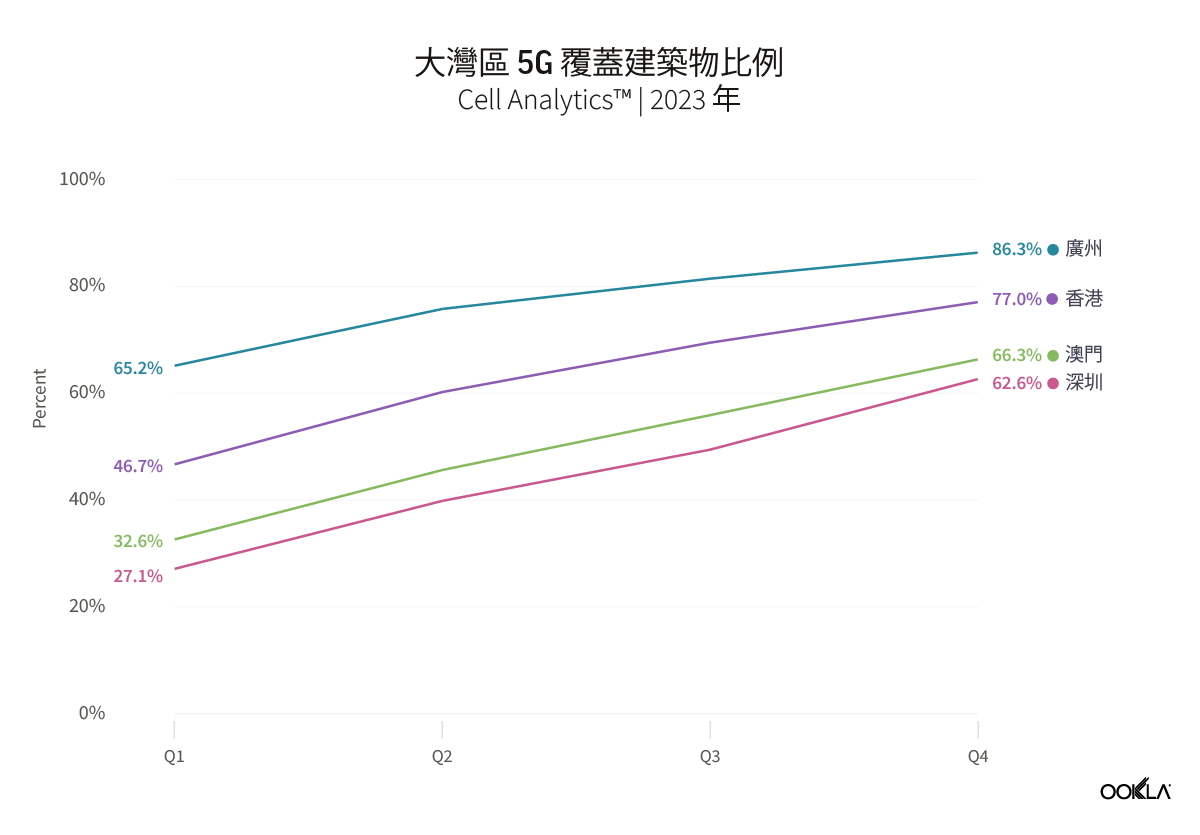
The chart shows an increase in the number of buildings with detected indoor 5G samples for every quarter from Q1 2023 to Q4 2023 across all four cities. Guangzhou, Shenzhen, and Macau all had an increase of more than 30 percentage points between Q1 2023 and Q4 2023, while Hong Kong saw a rise of 21 percentage points within the same period. The significant increase in the number of 5G base stations in China and its Special Administrative Regions has been the driving force behind the growth of indoor traffic. The Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) of China announced that there were 3.38 million 5G sites in China at the end of 2023, which would have included a significant number of dedicated 5G indoor sites.
As 5G traffic continues to proliferate, subscribers are increasingly demanding optimal indoor coverage to ensure a seamless experience. Meeting these expectations requires a comprehensive strategy by the service providers that accounts for the unique challenges of the different indoor environments in each city.
5G indoor coverage and quality differs across the core cities of the Greater Bay Area
Drilling down into Cell Analytics data at the city level from Q4 2023 to Q1 2024, we evaluated subscribers’ 5G indoor experience by measuring the average Reference Signal Received Power (RSRP) and Reference Signal Received Quality (RSRQ). RSRP represents the network signal strength received by a mobile phone. An RSRP value that exceeds -90 dBm indicates superior coverage. If the signal strength is between -90 dBm and -100 dBm, then network coverage is considered good. Below this range, expect slower download speeds and potential network disconnections. RSRQ is a metric used to evaluate the quality of the reference signal received by a device. A value of -10 dB or higher indicates excellent network quality while a value between -10 dB and -15 dB is considered good. An RSRQ value lower than -15 dB is poor or indicates no signal at all.
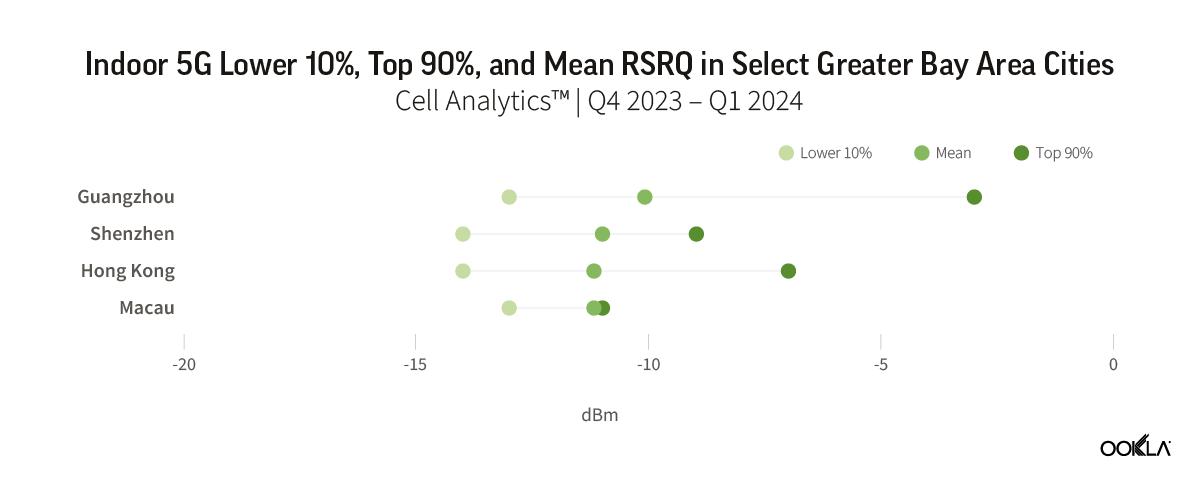
We compared the average RSRP and RSRQ for each of the four major cities in GBA and plotted out the range between the values of the Lower 10% and the Top 90% to examine the variations in the signal strength and quality of each city.
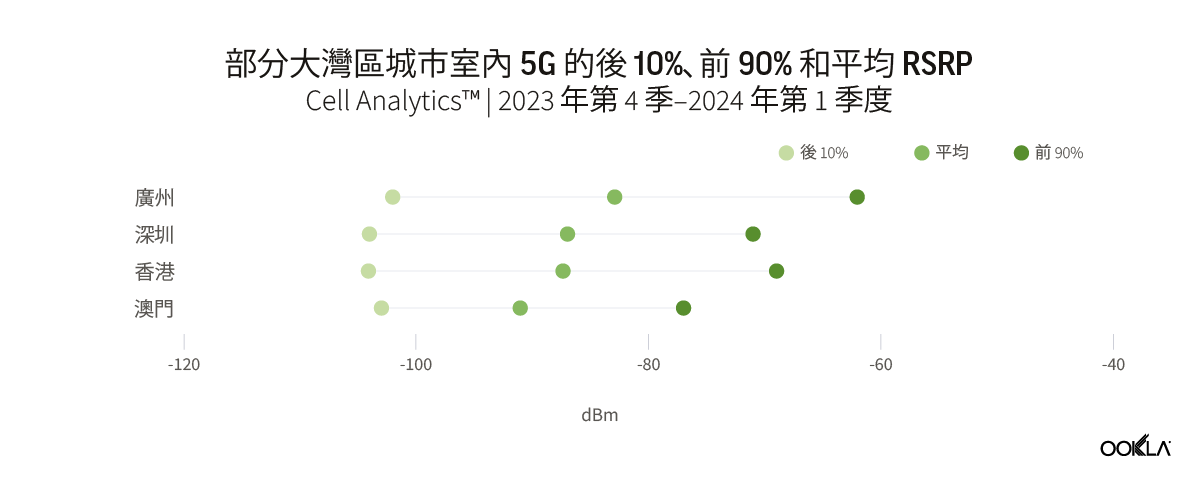
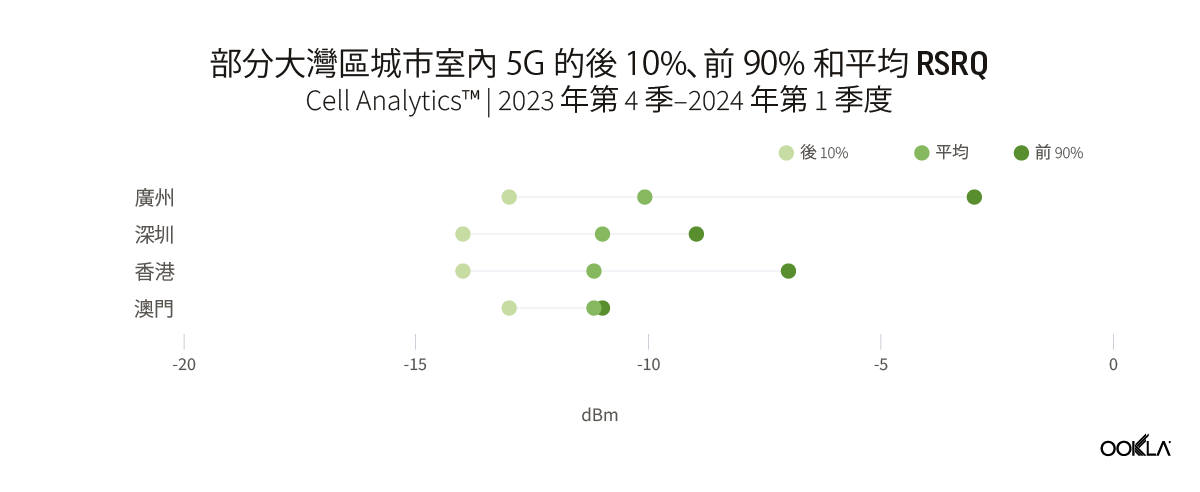
Overall, the Chinese cities of Guangzhou and Shenzhen reported better city-wide 5G indoor coverage than those of Hong Kong and Macau. Guangzhou reported a weighted average RSRP of -82.9 dBm of all samples detected inside buildings, followed by Shenzhen with RSRP of -87.0 dBm. Both cities also reported better city-wide 5G indoor quality compared to Hong Kong and Macau, at -10.1 dB and -11.0 dB, respectively.
The data shows a substantial variance in performance and quality between the top and bottom 10% of users when connected to 5G indoors in these cities. The Upper 90% of samples in all cities had extremely good RSRP, ranging from -77 dBm in Macau to -62 dBm in Guangzhou. While the Lower 10% reported signal strength of around -104 dBm. This indicates that while, in general, users were experiencing reasonable 5G average speeds indoors, there are still hotspots with a concentration of users who are experiencing poor performance and coverage.
5G performance uplift accentuates the need for better indoor coverage
While today’s indoor 4G and Wi-Fi networks may meet the current connectivity demands, having dedicated in-building 5G networks provides a more seamless and efficient connectivity experience, bridging the gap between 4G’s inherent limitations in terms of latency and performance with the requirements of newer data-intensive use cases and low-latency applications.
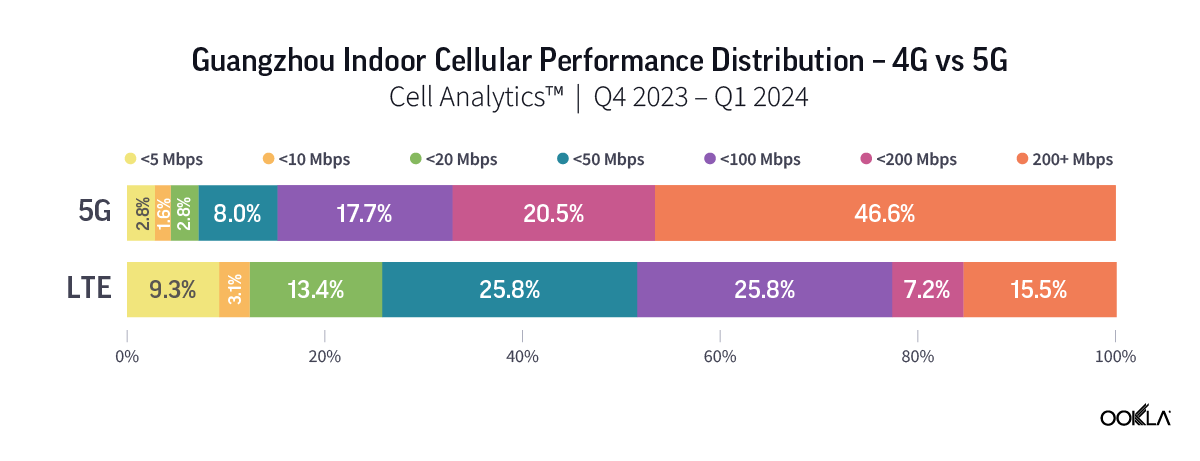
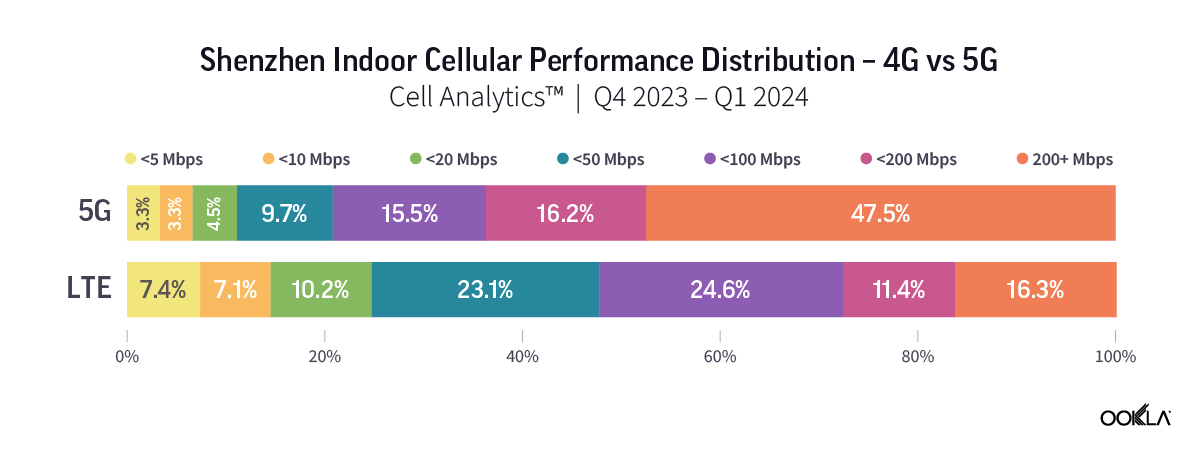
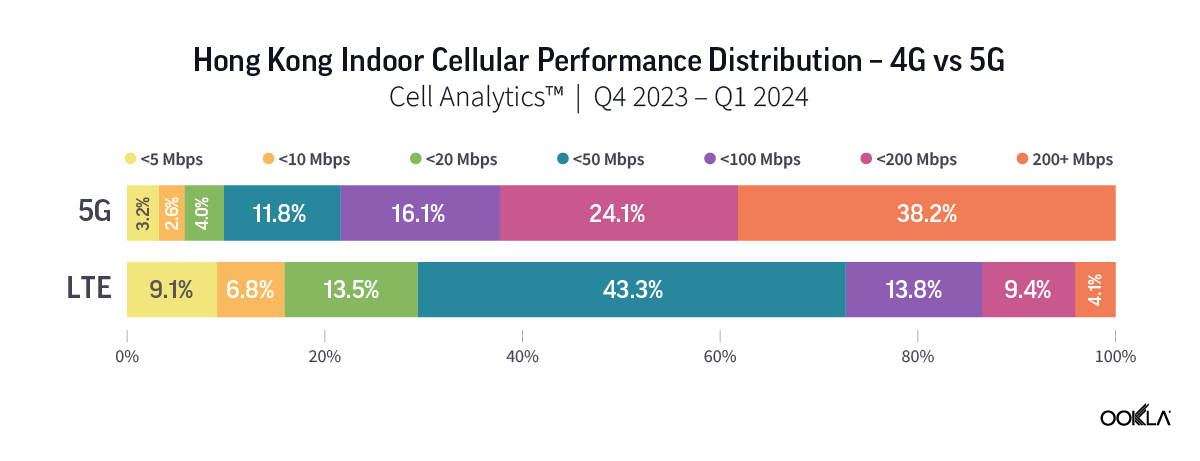
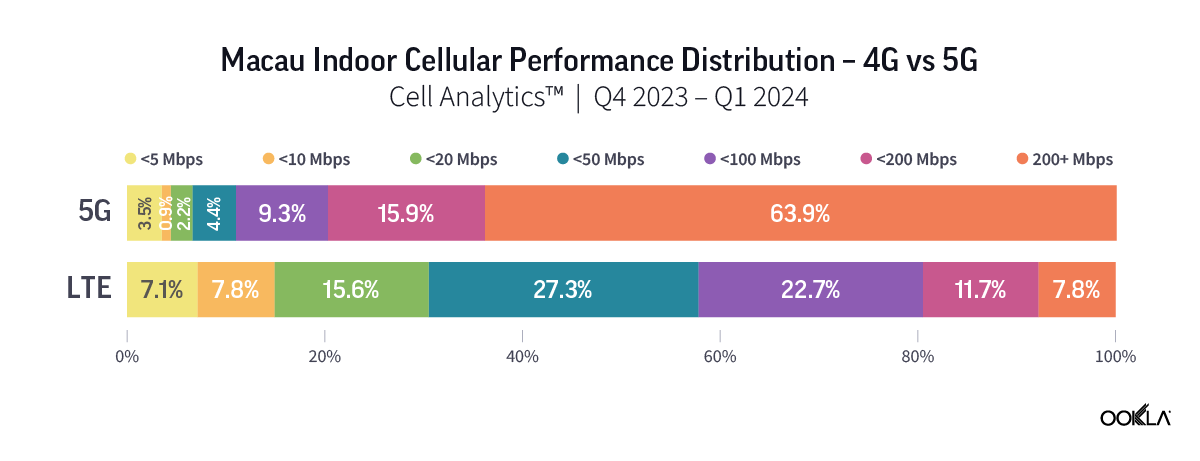
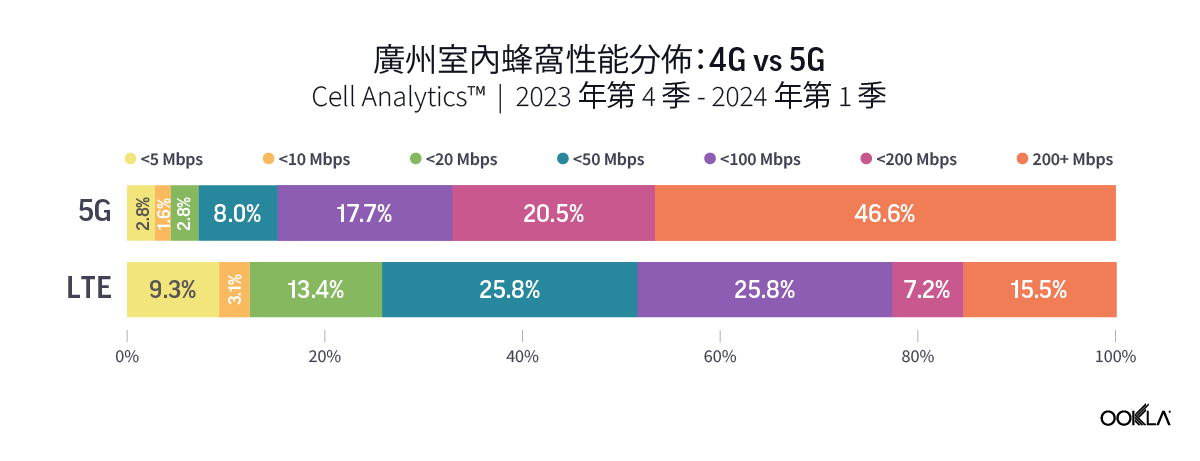
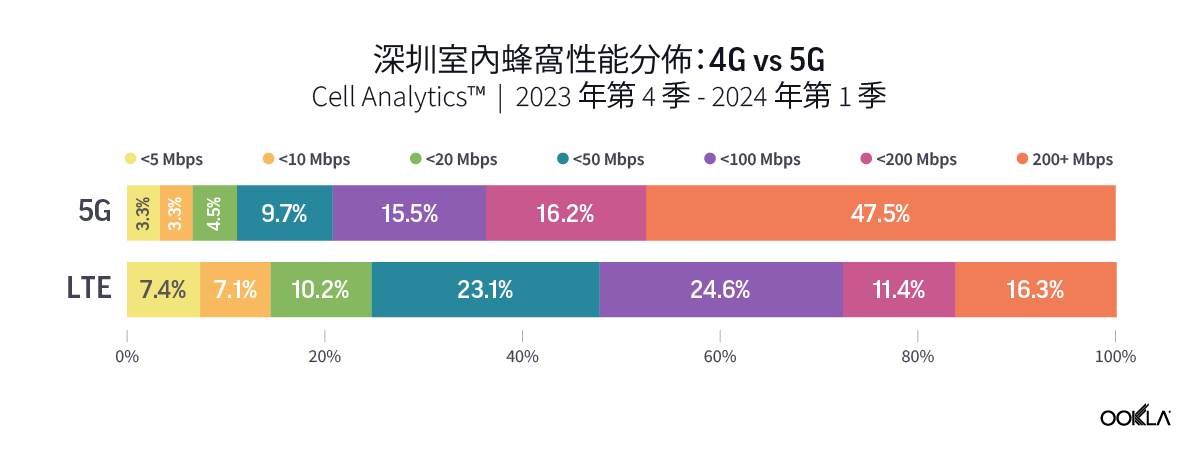
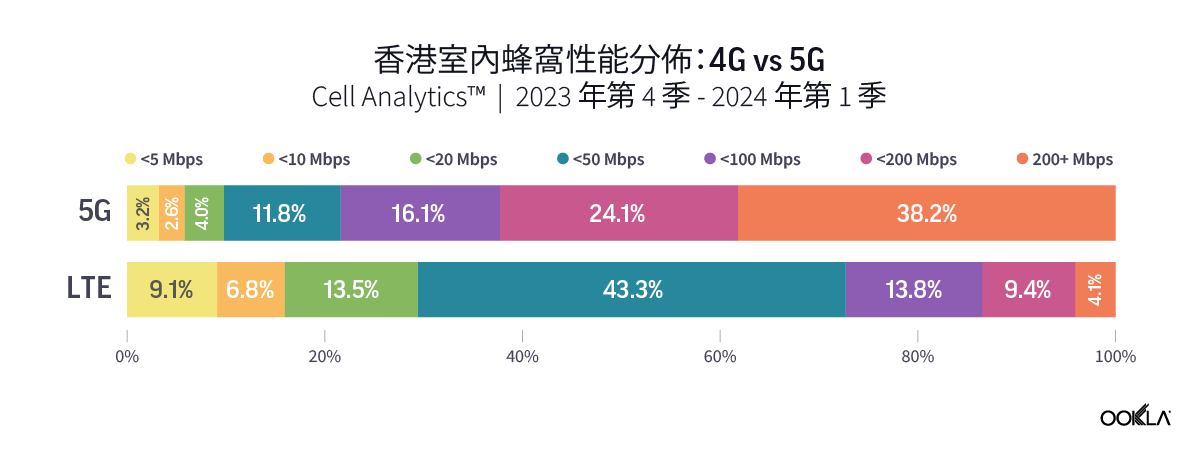
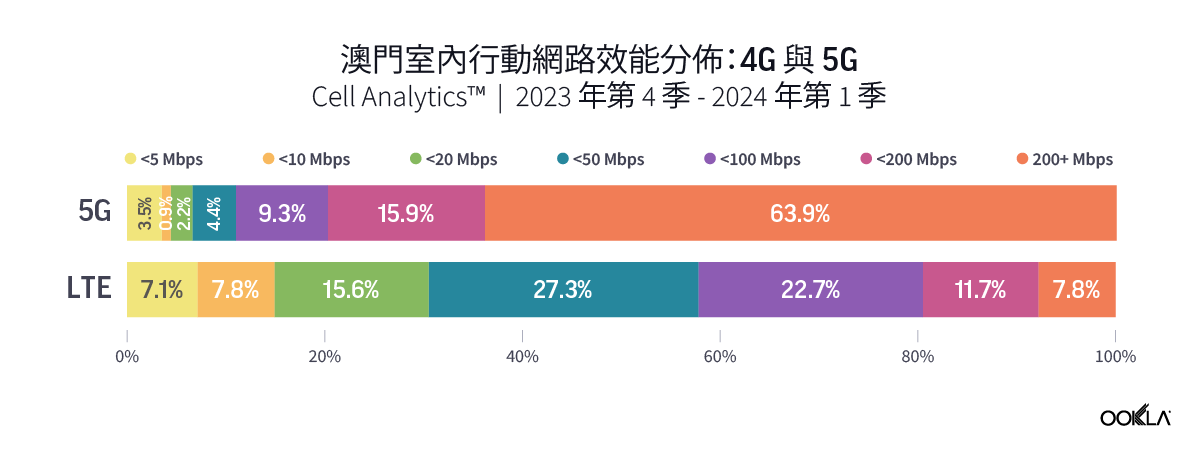
Ookla’s data for Q4 2023 to Q1 2024 reveal a higher percentage of users experiencing significant performance improvement when connected to 5G networks indoors. In Guangzhou and Shenzhen, over 45% of indoor 5G samples achieved speeds of 200 Mbps or higher, while only approximately 15% of 4G users experienced the same speed. The percentage is much higher in Macau, where more than 60% of indoor 5G users were on speeds of more than 200 Mbps, as compared to only 7.8% for those on 4G indoor networks.
Significant variations in 5G coverage among operators in Guangzhou, while operators in other cities exhibit only minor differences
Given the increasing reliance on mobile services for commercial transactions, ensuring uninterrupted 5G connectivity within buildings is paramount for service providers and building owners, particularly in buildings with a high concentration of users. This can be achieved by deploying advanced technologies such as small cells, distributed antenna systems (DAS), and network function virtualization (NFV). This enhances the consumer experience and adds substantial value to businesses by enabling various digital services, such as 8K video, augmented and virtual reality, and the Internet of Things (IoT). The building tenants can also leverage the 5G network to connect video cameras, point-of-sale (PoS) devices, and signage systems, which can attract customers who rely on mobile services for digital store deals and commercial transactions.
Through Cell Analytics data, we compared the 5G signal strength (RSRP) of top operators in Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Hong Kong, and Macau from Q4 2023 to Q1 2024. For each location, we compare operators’ RSRP values of samples detected inside buildings with a height of more than 10 meters to determine which ones offer better 5G coverage.
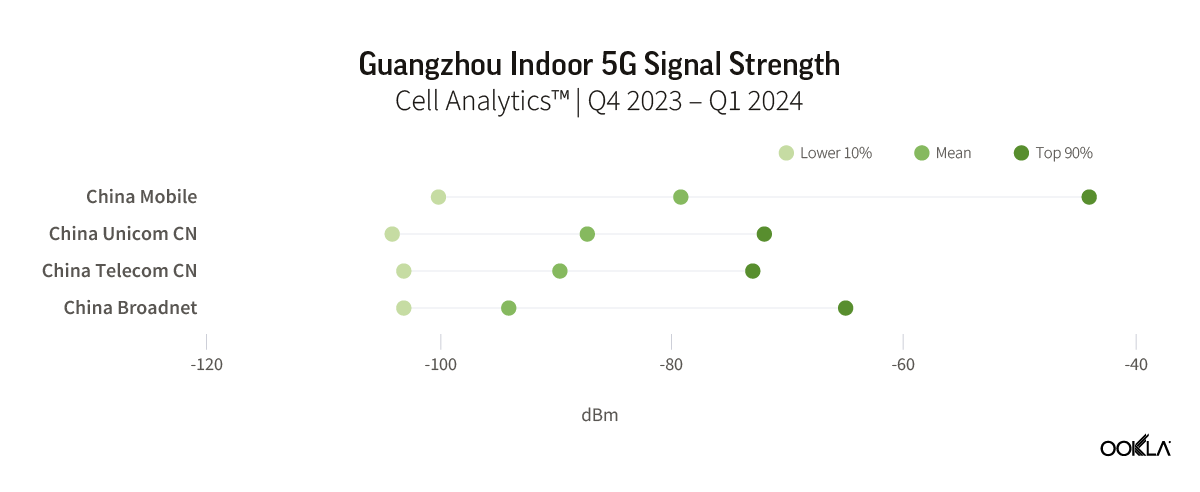
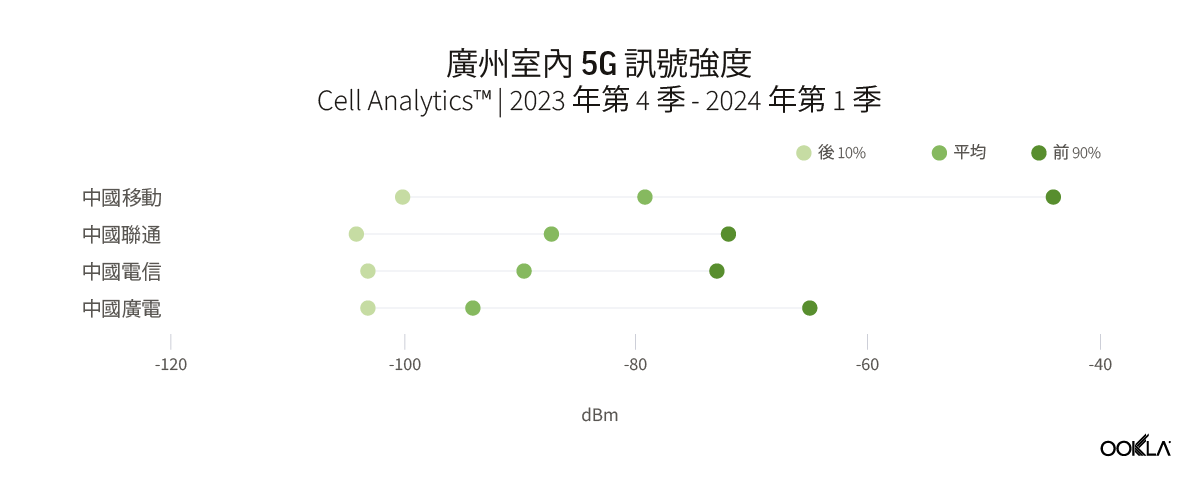
In Guangzhou, China Mobile had the best indoor 5G coverage across the city. Their weighted mean RSRP was -79.2 dBm, which is around 8 dB stronger than China Unicom’s mean RSRP of -87.2 dBm. The Upper 90% of China Mobile’s 5G network users reported a strong signal strength with an RSRP of -44 dBm when they were indoors. This indicates that there could be more buildings with dedicated wireless 5G networks in the city.
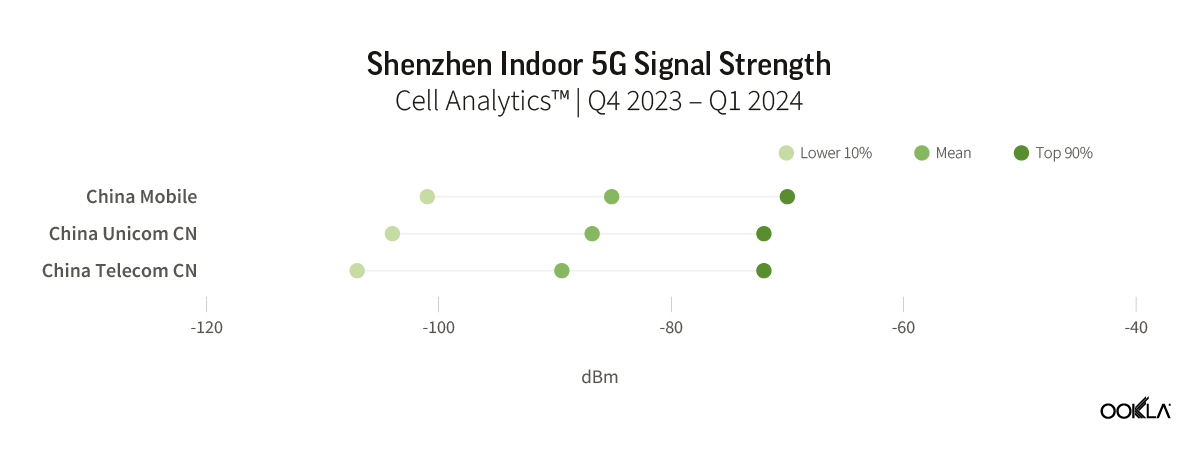
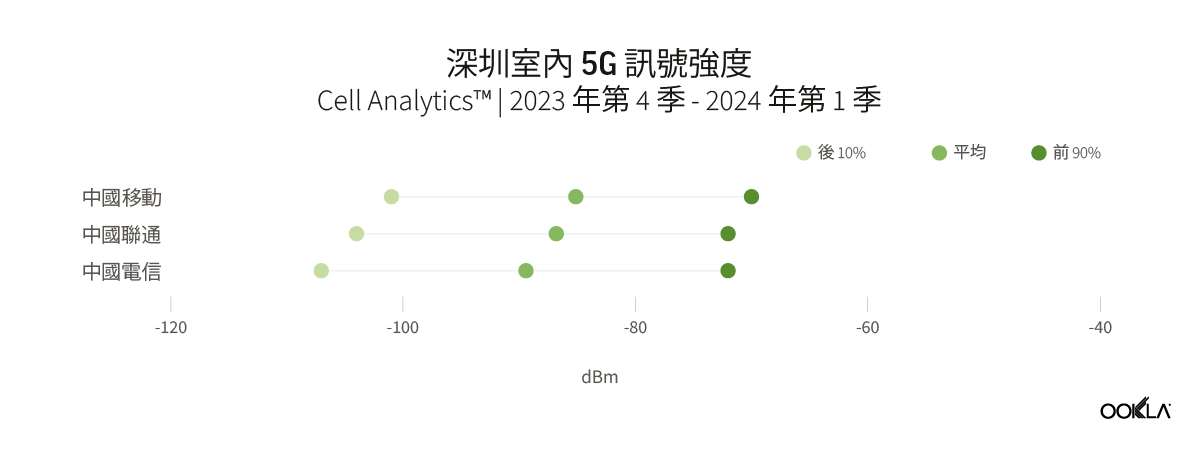
The three service providers in Shenzhen reported a small variation in their 5G indoor signal strength. China Mobile had a slightly better mean RSRP at -85.1 dBm, compared to China Unicom’s -86.8 dBm and China Telecom’s -89.4 dBm. Overall, there is unlikely to be a significant difference in 5G coverage when indoors, and consumers in the city may not notice any major differences. During the period, there were insufficient samples available for China Broadnet to be included in the analysis.
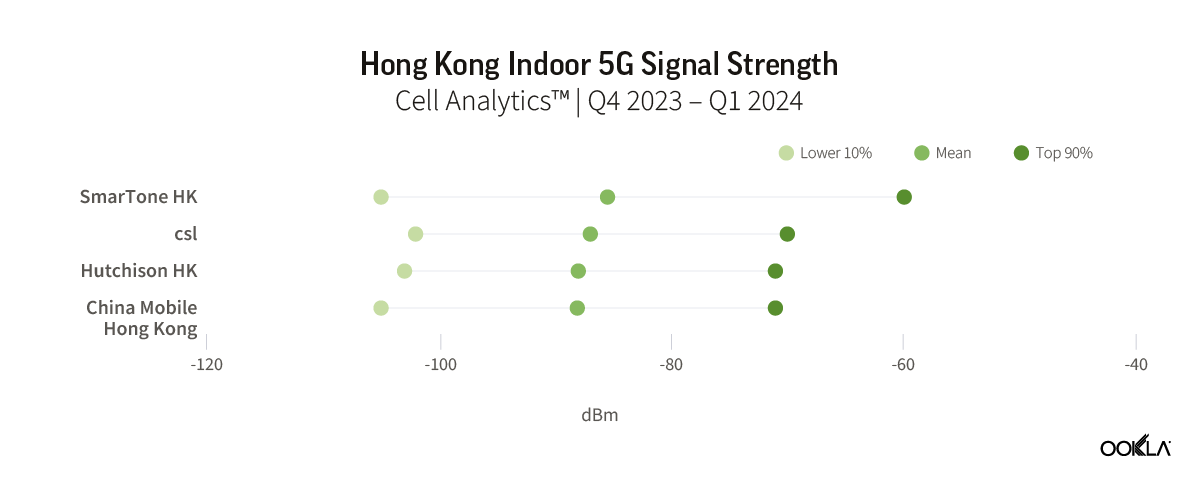
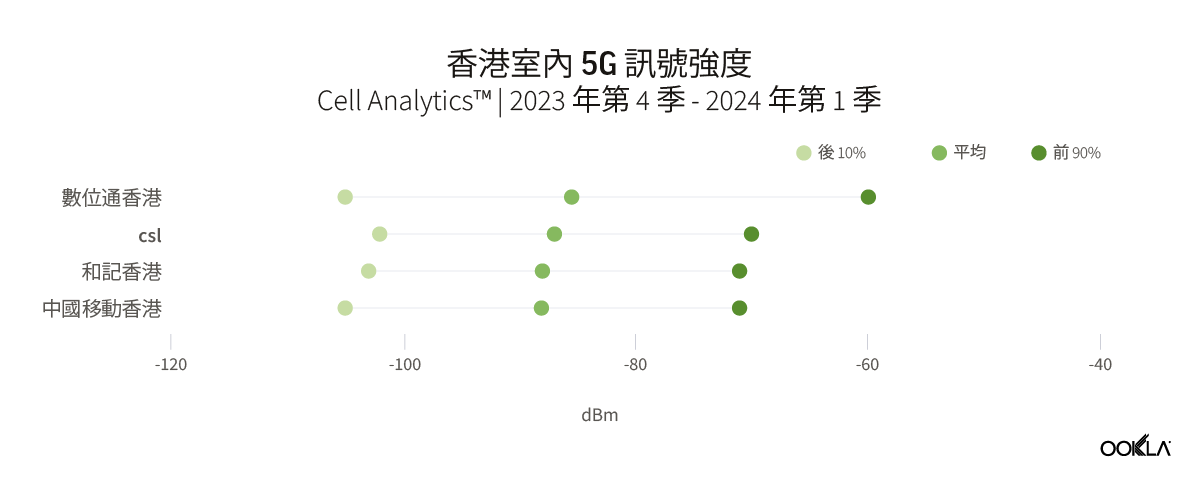
In Hong Kong, much like what was observed in Shenzhen, the difference in average signal strength among the top four telecom operators was marginal. Between Q4 2023 and Q1 2024, the difference in the mean RSRP between the carriers was only 1.5 dB. SmarTone stood out slightly by having the highest RSRP at -85.5 dBm. This indicates a competitive and closely matched performance among the operators, with opportunities for further improvements in indoor connectivity and quality.
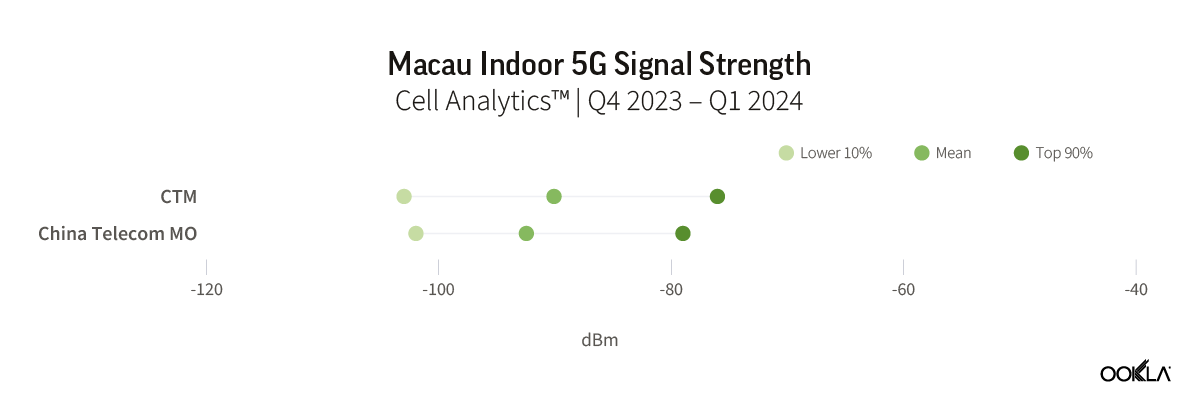
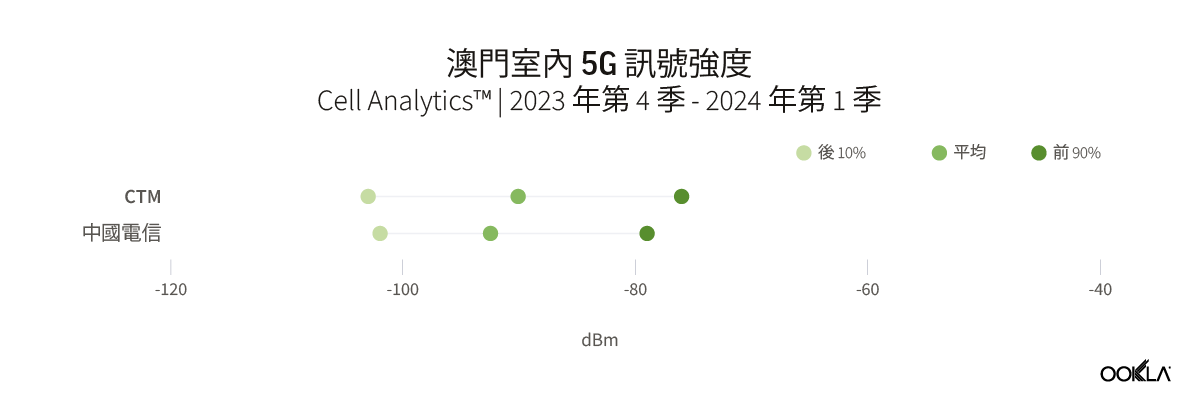
Macau is the most recent city in GBA to launch its 5G network, with CTM and China Telecom Macau receiving their 5G licenses in November 2022. In our previous report, we discussed how Macau, being a newly launched network, was rated higher than the other three cities in terms of overall 5G performance. However, the latest data reveals that in terms of indoor 5G signal strength, both operators are trailing behind other operators in the selected cities, except for China Broadnet in Guangzhou. Both CTM and China Telecom Macau reported 5G indoor mean RSCP lower than -90 dBm, with CTM at -90.1 dBm and China Telecom Macau at -92.5 dBm.
The imperative of 5G indoor network expansion
With the increasing adoption of 5G technology, consumers are expecting faster network speeds and consistent connectivity. As most 5G data traffic is expected to occur indoors, prioritizing the expansion of indoor coverage is crucial for operators to meet users’ expectations. 5G indoor deployments are a strategic avenue for operators to monetize their investments through advances such as massive IoT (IoT), enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB), and fixed wireless access (FWA), which will all play an important role in transformation across sectors such as industrial automation, retail applications, and smart cities. The primary challenge lies in delivering consistent performance and quality across various indoor settings, where issues may be confined to certain floors or sections.
Regulators can have a proactive role in reducing bureaucratic hurdles and encouraging government-industry collaboration, such as promoting the parallel development of indoor and outdoor 5G coverage across the country. As a step towards prioritizing 5G indoor coverage, China’s Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) mandated that operators share the mid-band spectrum (3.3-3.4 GHz) for indoor coverage to promote co-development and cost-sharing.
There is also a significant push in the GBA to extend 5G coverage, making it readily available in public transport infrastructures. One such example is CSL, which provides 5G network coverage along the MTR lines in Hong Kong, with some routes utilizing dedicated 5G spectrum.
Ookla can assist operators in identifying buildings or indoor venues with coverage or capacity issues using crowdsourced data and diagnosis. Powered by millions of signal measurements collected daily by Speedtest®, Cell Analytics provides intelligence about wireless service quality, RF measurements, data usage, user density, cell site locations, and much more. It helps operators to track their own and competitors’ performance and understand how new 5G deployments are affecting user experience and quality of service. To find out more about Cell Analytics, please get in touch.
探索大灣區 5G 網路室內鏈接
粵港澳大灣區 (GBA) 是過去 40 多年來,中國都市化最快的地區之一。該地區是全球摩天大樓最集中的地區,營運商必須優先考慮室內外 5G 無縫覆蓋,以優化服務並滿足客戶需求。
在本報告中,我們使用 Cell Analytics™ 的資料,檢驗廣州、深圳、香港和澳門這四個 GBA 主要城市的 5G 室內效能和訊號品質。
關鍵摘要
- 與香港和澳門相比,廣州和深圳的全市室內 5G 覆蓋範圍和品質更好。廣州報告的平均 RSRP 為 -82.9 dBm,深圳略低,為 -87.0 dBm。此外,兩個城市的 5G 室內品質均較好,得分分別為 10.1 dB 和 11.0 dB。相比之下,香港的平均 RSRP 為 -87.4 dBm,而澳門為 -91.0 dBm。
- 廣州移動因在該市提供更好的室內 5G 覆蓋而脫穎而出。該營運商的平均 RSRP 為 -79.17 dBm,以 8 dB 的差距,明顯優於中國聯通的平均 RSRP -87.2 dBm。其他城市營運商之間的 5G 室內訊號強度僅有微小差異,但在澳門,營運商的室內訊號強度明顯弱於其他選定城市的幾乎所有其他營運商。
大灣區城市室內 5G 流量持續上升
粵港澳大灣區普遍稱為大灣區 (GBA),由中國廣東地區九個城市及香港、澳門兩個特別行政區組成。由於鄰近,這些城市由廣泛的交通網絡連接起來,包括高鐵、橋樑和隧道。這裡是中國重要的經濟和技術中心,而 5G 技術的採用已成為該地區的關鍵驅動力,推動著各行各業轉型,並促進自動化和數位化。在我們最近的 文章中,我們深入研究了推動 5G 技術推出的因素,並研究了其在大灣區的表現。
室內涵蓋率對於 GBA 主要「中心」城市尤為重要,廣州、深圳、香港和澳門的高樓大廈主宰著天際線,室內空間在商業和旅遊活動中扮演著重要角色。在最近的這篇文章中,我們探討了解決室內蜂窩覆蓋挑戰的不同技術解決方案。
為了評估建築物內的 5G 涵蓋率,我們分析了 Ookla® Cell Analytics™ 的資料,以衡量在 2023 年第 1 季到 2023 年第 4 季期間,香港、澳門、深圳和廣州回報室內 5G 樣本的建築物比例。在此分析中,我們只考慮了高於 10 公尺的建築物,亦即典型三層樓以上建築的高度。
圖表顯示,從 2023 年第 1 季到 2023 年第 4 季,四個城市偵測到室內 5G 樣本的建築物數量,每一季均有增加。廣州、深圳和澳門在 2023 年第 1 季到 2023 年第 4 季期間的成長幅度均超過 30 個百分點,而香港在同一期間的成長幅度為 21 個百分點。 中國和特別行政區 5G 基地台數量大幅成長,是室內流量成長的驅動力。根據中國工業和資訊化部 (MIIT) 公告,在 2023 年底,中國有 338 萬座 5G 基地台,其中包括大量專用的 5G 室內基地台。
隨著 5G 流量持續激增,訂閱用戶為了獲得無縫的體驗,對最佳室內涵蓋率的要求也愈來愈高。滿足這些期望需要服務提供者制定全面的策略,以應對每個城市不同室內環境的獨特挑戰。
大灣區中心城市的 5G 室內涵蓋率與品質各不相同
我們深入研究 2023 年第四季至 2024 年第一季城市層級的 Cell Analytics 數據,透過測量平均參考訊號接收功率 (RSRP) 和參考訊號接收品質 (RSRQ) 來評估使用者的 5G 室內體驗。RSRP 代表手機接收到的網路訊號強度。RSRP 值超過 -90 dBm,表示涵蓋率優異。如果訊號強度在 -90 dBm 和 -100 dBm 之間,則認為網路覆蓋範圍良好。 低於此範圍,下載速度會變慢,並且可能會出現網路連線中斷的情況。RSRQ 是用於評估設備接收的參考訊號品質的指標。-10 dB 或更高的值表示網路品質極佳,介於 -10 dB 和 -15 dB 之間的值則是尚可。RSRQ 值低於 -15 dB 表示訊號較差或根本沒有訊號。
我們比較了 GBA 四個主要城市的平均 RSRP 和 RSRQ,並繪製出後 10% 與前 90% 之間的範圍,以檢視每個城市訊號強度和品質的差異。
整體而言,中國城市廣州和深圳的 5G 室內覆蓋範圍優於香港和澳門。廣州報告在建築物內檢測到的所有樣本的加權平均 RSRP 為 -82.9 dBm,其次是深圳,RSRP 為 -87.0 dBm。與香港和澳門相比,這兩個城市的全市 5G 室內品質也更好,分別為 -10.1 dB 和 -11.0 dB。
資料顯示,這些城市中,前 10% 使用者和後 10% 的使用者在室內連接 5G 時,效能和品質有顯著差異。所有城市上 90%的樣本都具有非常好的 RSRP,範圍從澳門的-77 dBm 到廣州的-62 dBm。後 10% 的樣本則顯示訊號強度約為 -104 dBm。這說明雖然整體而言,使用者在室內能體驗到合理的 5G 平均速度,但在使用者集中的熱點,效能和涵蓋率體驗仍然不佳。
5G 性能提升凸顯對更好室內覆蓋的需求
雖然現在的室內 4G 和 Wi-Fi 網路可以滿足目前的連線需求,但擁有專用的室內 5G 網路,能夠提供更順暢、有效率的連線體驗,以滿足新的資料密集型使用案例和低延遲應用需求,彌補 4G 在延遲和效能方面的固有限制。
Ookla 2023 年第四季至 2024 年第一季的數據顯示,在室內連接 5G 網路時,體驗到效能顯著提升的用戶比例更高。在廣州和深圳,超過 45% 的室內 5G 樣本實現了 200 Mbps 或更高的速度,而只有約 15% 的 4G 使用者體驗到了相同的速度。該比例在澳門高出許多,室內 5G 使用者速度超過 200 Mbps 的比例超過 60%,4G 室內網路的使用者則僅有 7.8%。
廣州業者 5G 覆蓋差異較大,其他城市業者差異較小
由於商業交易愈來愈依賴行動服務,因此對服務提供者和建築物擁有者而言,確保建築物內的 5G 連線不中斷是首要之務,在使用者密集高的建築物中更是如此。這可以透過部署小型蜂窩、分散式天線系統 (DAS) 和網路功能虛擬化 (NFV) 等先進技術來實現。如此一來,就能夠提供 8K 影片、擴增實境和虛擬實境及物聯網 (IoT) 等多種數位服務,藉此提升用戶體驗,並為企業增加巨大價值。大樓租戶還可以利用 5G 網路連接攝影機、銷售點 (PoS) 設備和標牌系統,這可以吸引依賴行動服務進行數位商店交易和商業交易的客戶。
透過 Cell Analytics 資料,我們比較了廣州、深圳、香港和澳門頂尖營運商在 2023 年第 4 季到 2024 年第 1 季的 5G 訊號強度 (RSRP)。在每個地點,我們利用在超過 10 公尺高的建築物內偵測到的樣本,比較了營運商 RSRP 值,以判斷哪些城市提供的 5G 涵蓋率更佳。
在廣州,中國移動擁有全市最好的室內 5G 覆蓋範圍。他們的加權平均 RSRP 為 -79.2 dBm,比中國聯通的平均 RSRP -87.2 dBm 高出約 8 dB。中國移動前 90% 5G 網路使用者回報的室內訊號強度較強,為 RSRP -44 dBm。這表明該市可能會有更多擁有專用無線 5G 網路的建築物。
深圳的三家服務提供者報告其 5G 室內訊號強度略有差異。與中國聯通的 -86.8 dBm 和中國電信的 -89.4 dBm 相比,中國移動的平均 RSRP 略高,為 -85.1 dBm。總體而言,室內 5G 覆蓋範圍不太可能出現顯著差異,城市消費者可能不會注意到任何重大差異。在此期間,中國廣電沒有足夠的樣本可供分析。
在香港,與深圳的情況非常相似,四大電信業者之間的平均訊號強度差異微乎其微。2023 年第四季和 2024 年第一季之間,各載波之間的平均 RSRP 差異僅為 1.5 dB。SmarTone 的 RSRP 最高為 -85.5 dBm,稍微突出。這表明運營商之間的競爭和緊密匹配的表現,以及進一步改善室內連接和品質的機會。
澳門是 GBA 最晚推出 5G 網路的城市,CTM 和中國電信 (澳門) 於 2022 年 11 月獲得 5G 執照。我們先前的報告討論過,澳門新推出的網路整體 5G 效能為何比其他三個城市更優異。然而,最新資料顯示,就室內 5G 訊號強度而言,除了廣州的中國廣電之外,這兩家營運商都落後於選定城市的其他營運商。CTM 和中國電信澳門均報告 5G 室內平均 RSCP 低於-90 dBm,其中 CTM 為-90.1 dBm,中國電信澳門為-92.5 dBm。
5G 室內網路擴容勢在必行
5G 技術日益普及,消費者對網路速度和連線穩定度的期望也隨之提高。由於大部分 5G 數據流量預計發生在室內,因此優先擴大室內覆蓋範圍對於營運商滿足用戶期望至關重要。營運商能夠經由 5G 室內部署這個策略途徑,透過大規模物聯網 (IoT)、增強型行動寬頻 (eMBB) 和固定無線接取 (FWA) 等先進技術,將投資變現。這些技術將在工業自動化、零售應用和智慧城市等領域的轉型中,佔有一席之地。主要挑戰在於在各種室內環境中提供一致的性能和質量,其中問題可能僅限於某些樓層或部分。
監管機構可以在減少官僚障礙和鼓勵政府與行業合作方面發揮積極作用,例如促進全國室內和室外 5G 覆蓋的並行發展。中國工業和資訊化部 (MIIT) 為了優先發展 5G 室內涵蓋率,要求營運商共享中頻段頻譜 (3.3-3.4 GHz),以促進共同開發和成本分攤。
大灣區也大力推動擴大 5G 覆蓋範圍,使其在公共交通基礎設施中隨時可用。其中一個例子是 CSL,他們在香港地鐵沿線提供 5G 網路涵蓋率,其中幾個路線使用了專用的 5G 頻譜。
Ookla 可以利用群眾外包的資料和診斷,協助營運商識別有涵蓋率或容量問題的建築物或室內場所。Cell Analytics 利用 Speedtest® 每天收集的數百萬個訊號測量資料,提供有關無線服務品質、RF 測量值、資料使用量、使用者密度、行動網路基地台位置等資訊的相關情報。它可以幫助營運商追蹤自己和競爭對手的表現,並了解新的 5G 部署如何影響用戶體驗和服務品質。要了解有關 Cell Analytics 的更多信息,請 與我們聯繫。
Ookla retains ownership of this article including all of the intellectual property rights, data, content graphs and analysis. This article may not be quoted, reproduced, distributed or published for any commercial purpose without prior consent. Members of the press and others using the findings in this article for non-commercial purposes are welcome to publicly share and link to report information with attribution to Ookla.