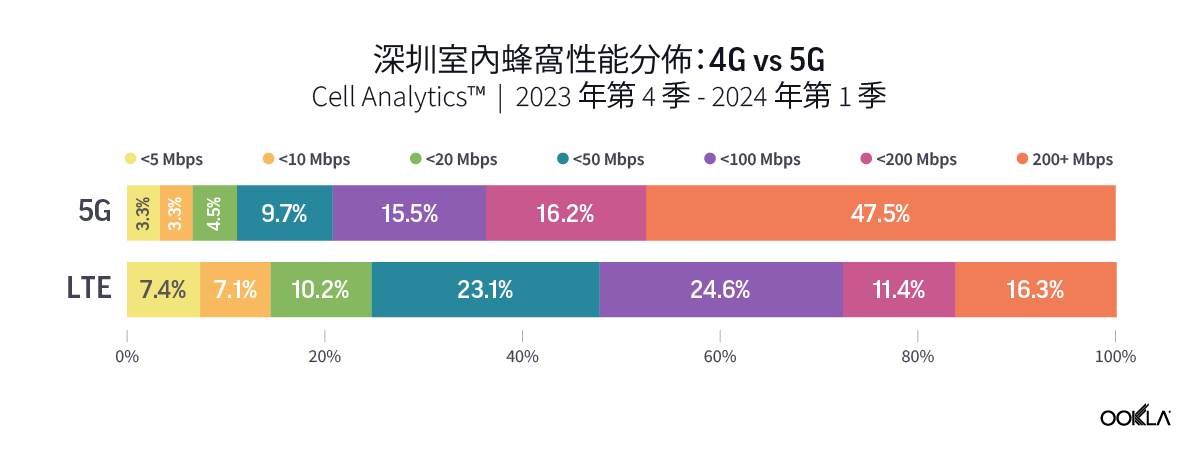
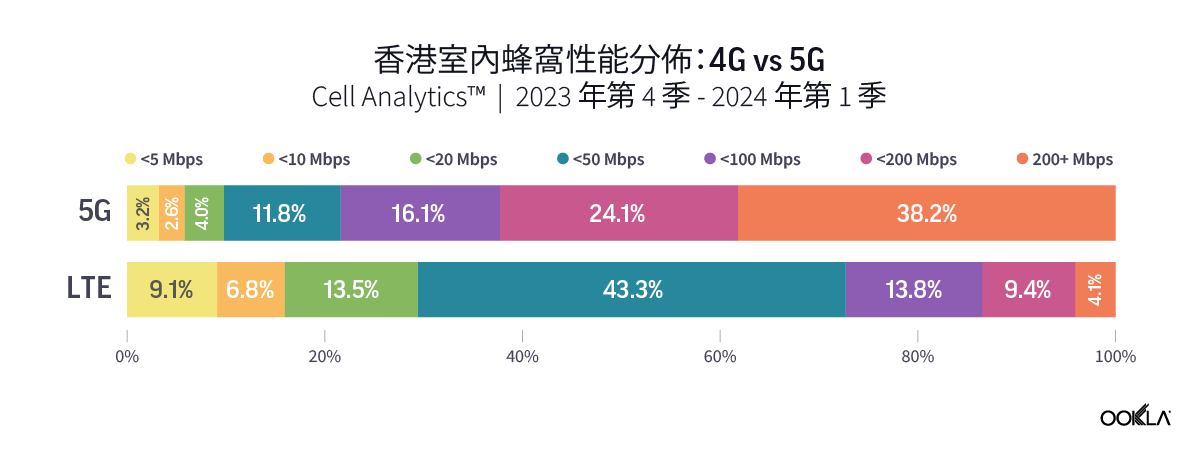
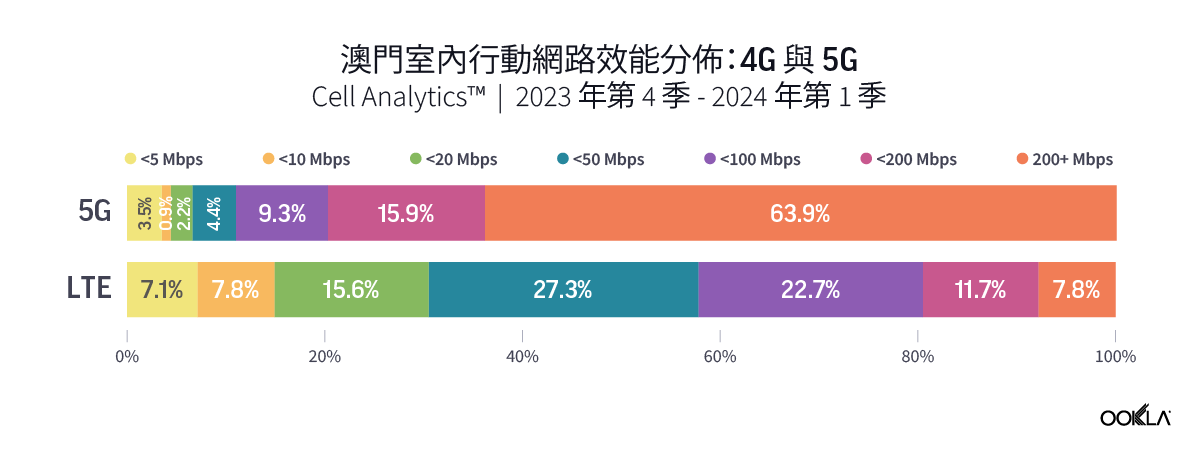
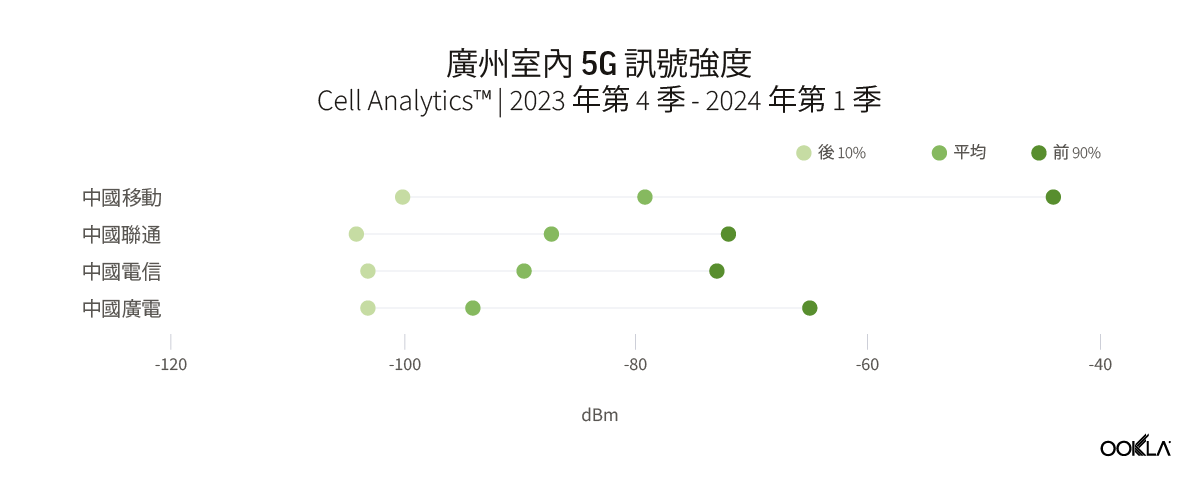
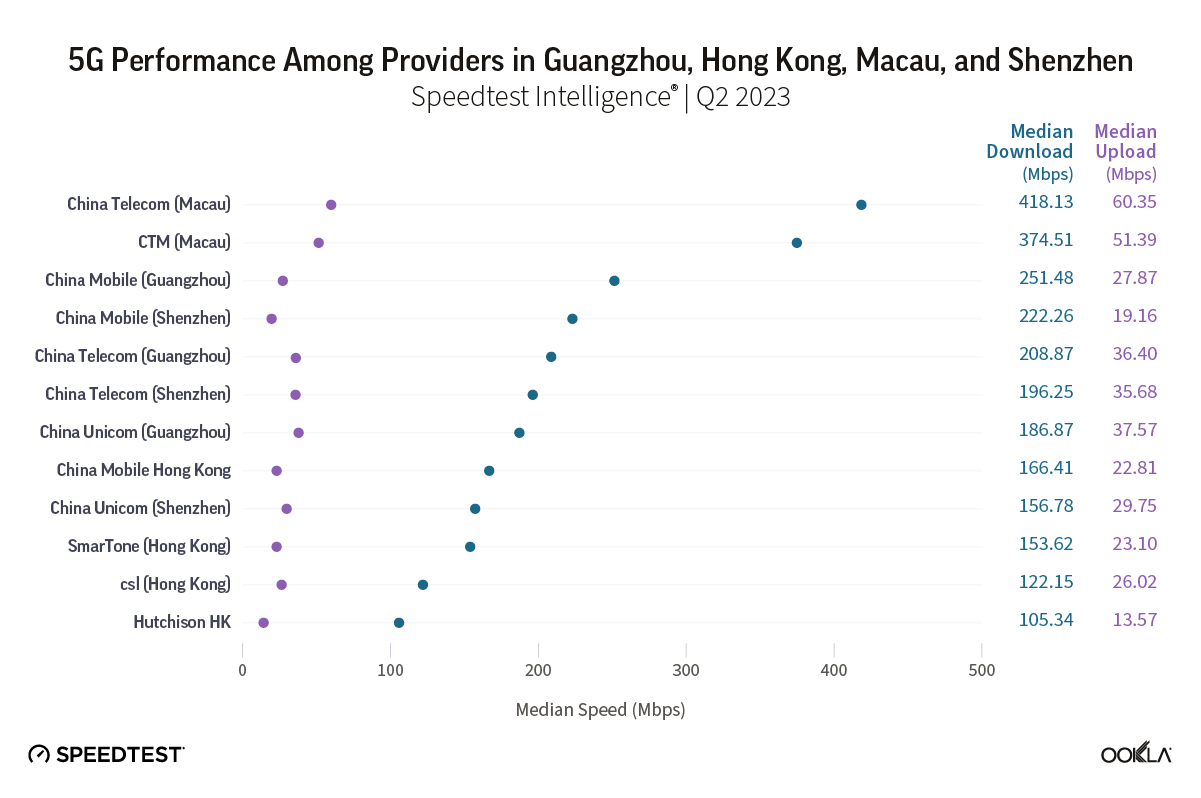
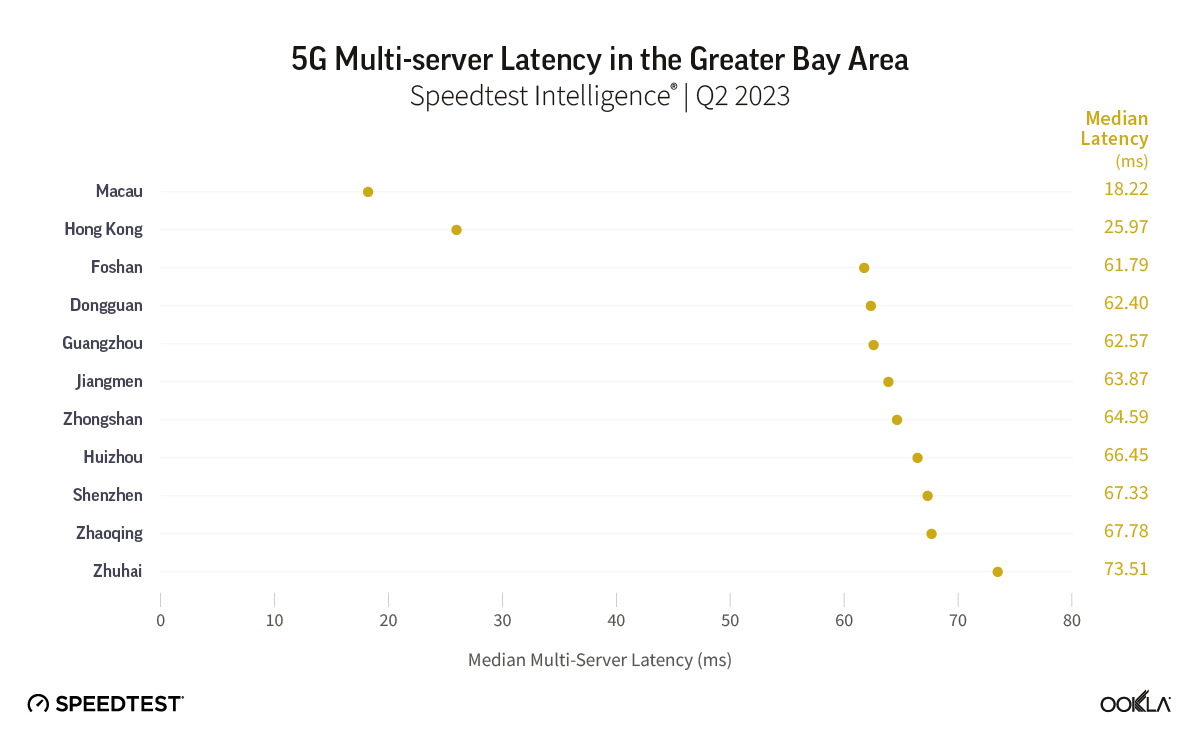
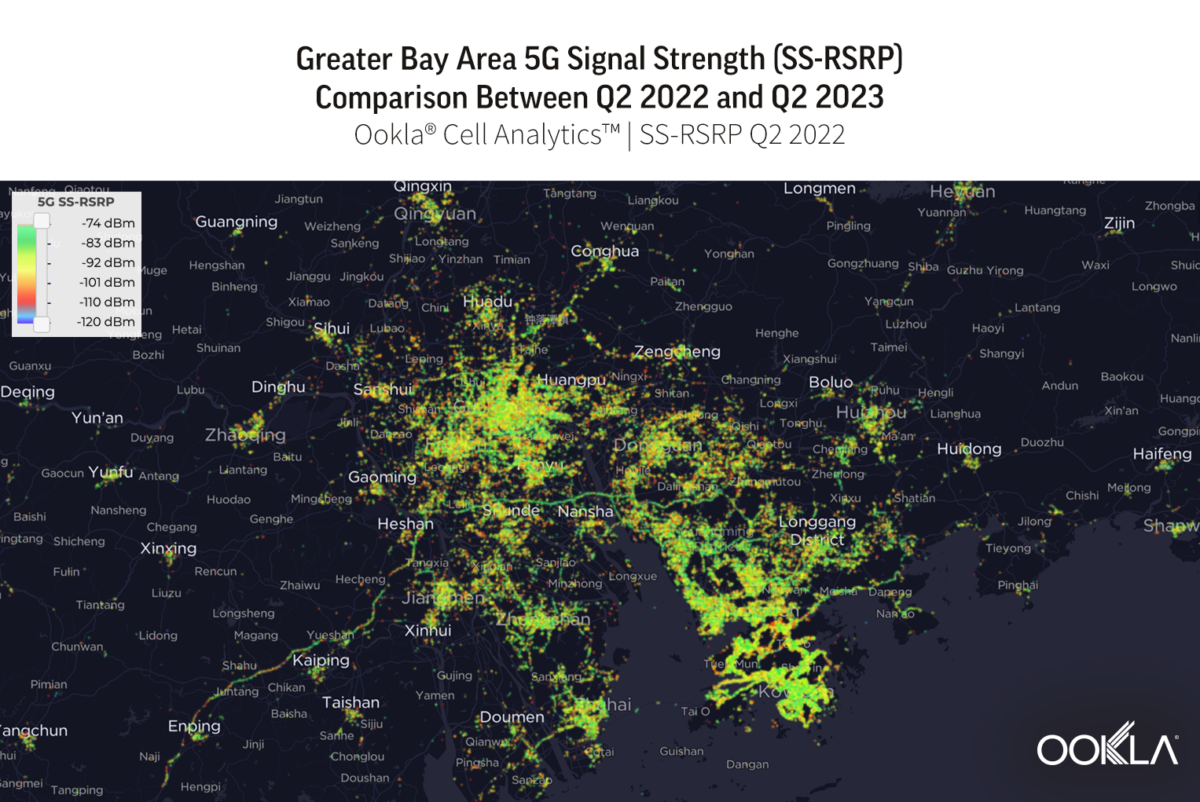
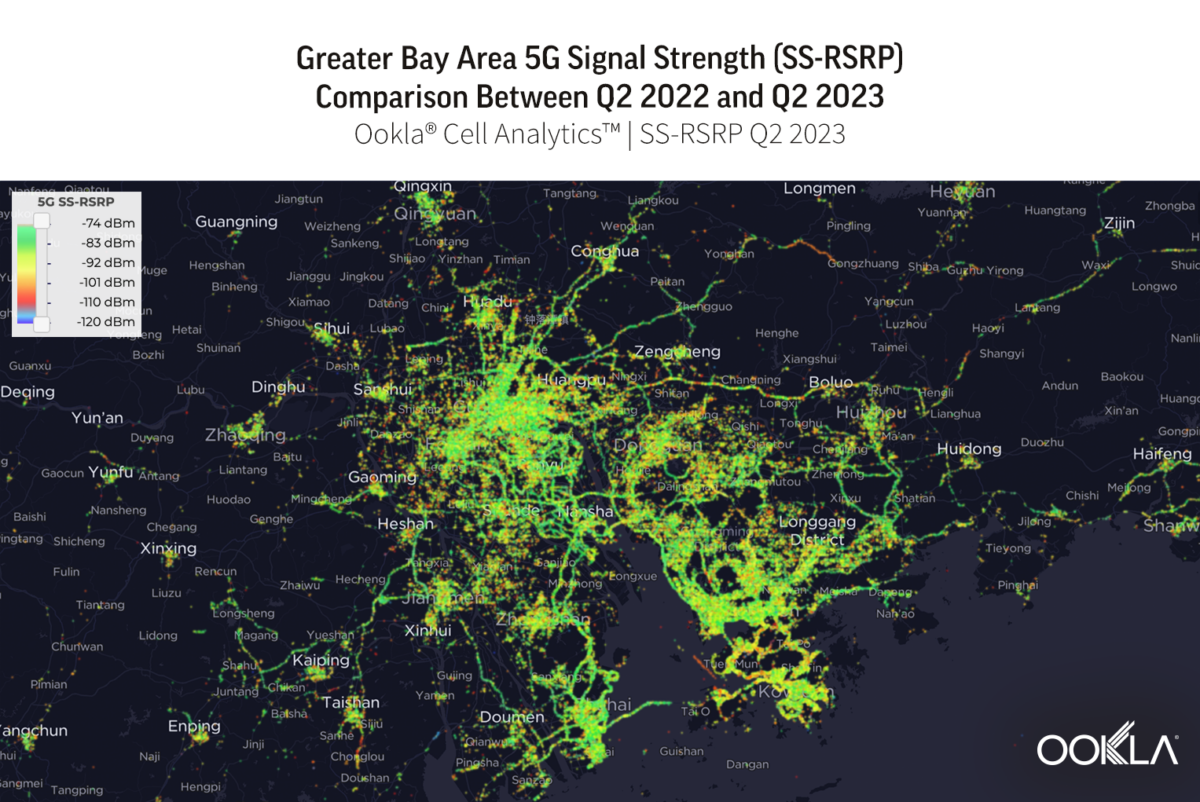
To gain insight into the current performance of networks, we analyzed Speedtest® data in Q3 2023. Our analysis compares changes in 5G performance to the previous year, identifies the top 10 countries with the best performance, and discusses customer satisfaction with 5G. We also ranked countries based on the performance of their fixed networks and investigated the connectivity gap across the world.
5G | Fixed | Connectivity for All
Key takeaways
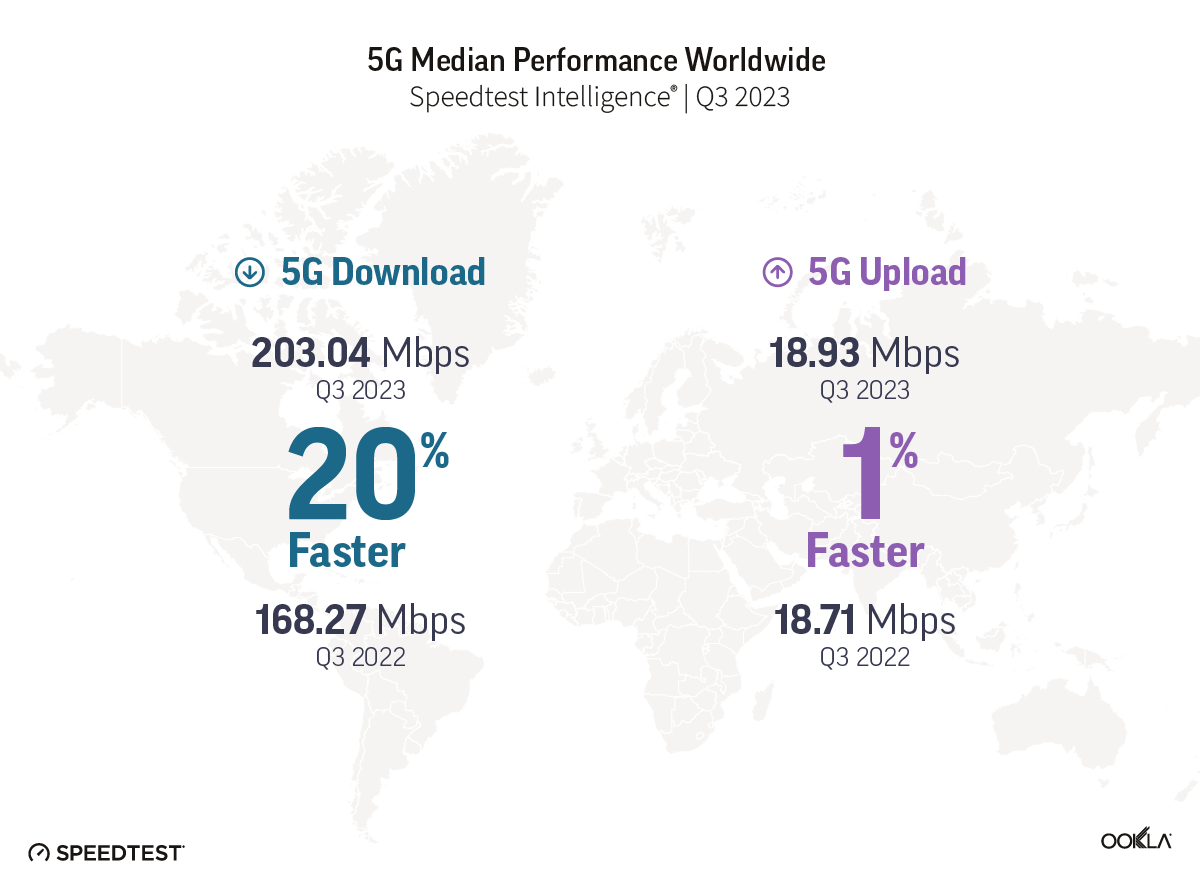
- Global 5G download speed improved. The median global 5G download speed experienced a substantial 20% increase in Q3 2023, reaching 203.04 Mbps, compared to 168.27 Mbps in Q3 2022. This improvement aligns with a significant rise in global 5G subscriptions, indicating positive progress in user adoption of 5G and the performance of 5G networks.
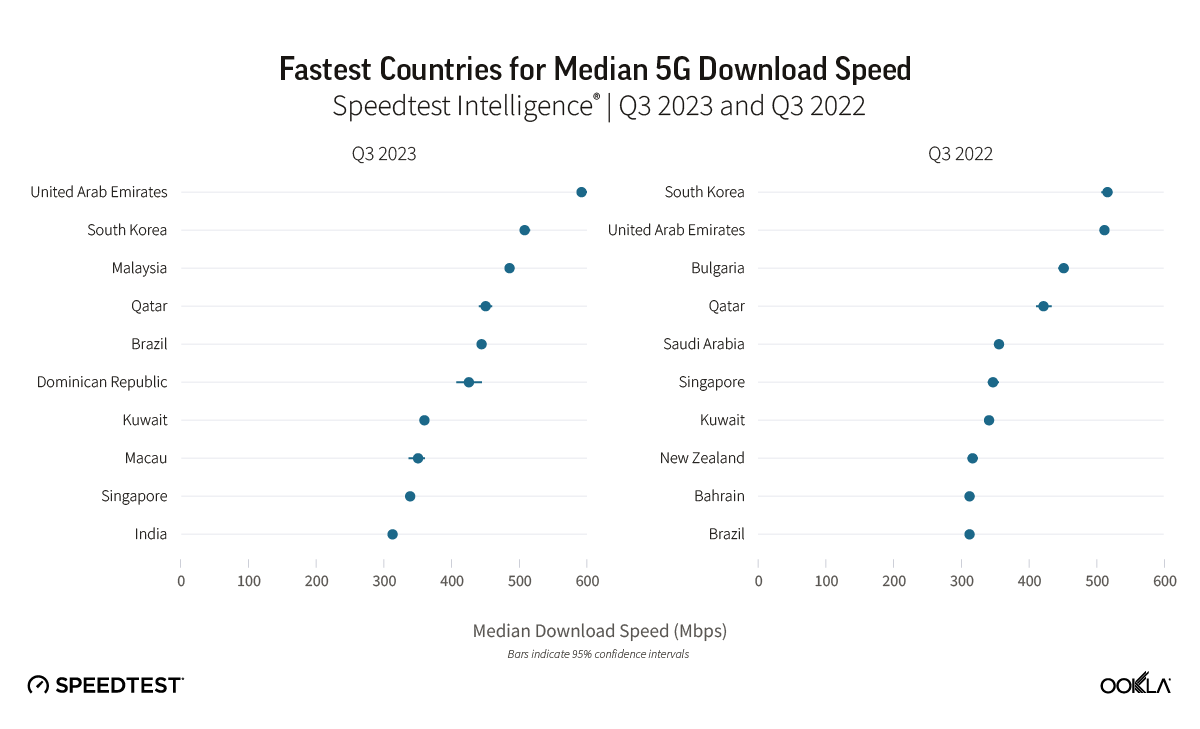
- Top 5G performers have shifted. The top 10 countries for 5G performance witnessed notable changes, with the United Arab Emirates claiming the top spot, surpassing South Korea. Malaysia, India, and the Dominican Republic also made significant strides, showcasing a dynamic shift in the global 5G landscape.
- Speedtest user ratings indicate room for 5G improvement. Despite advancements in 5G technology, there has been a decline in the Net Promoter Score (NPS) among 5G users. Factors contributing to this dissatisfaction could include unmet expectations and discrepancies between actual 5G speeds and advertised speeds.
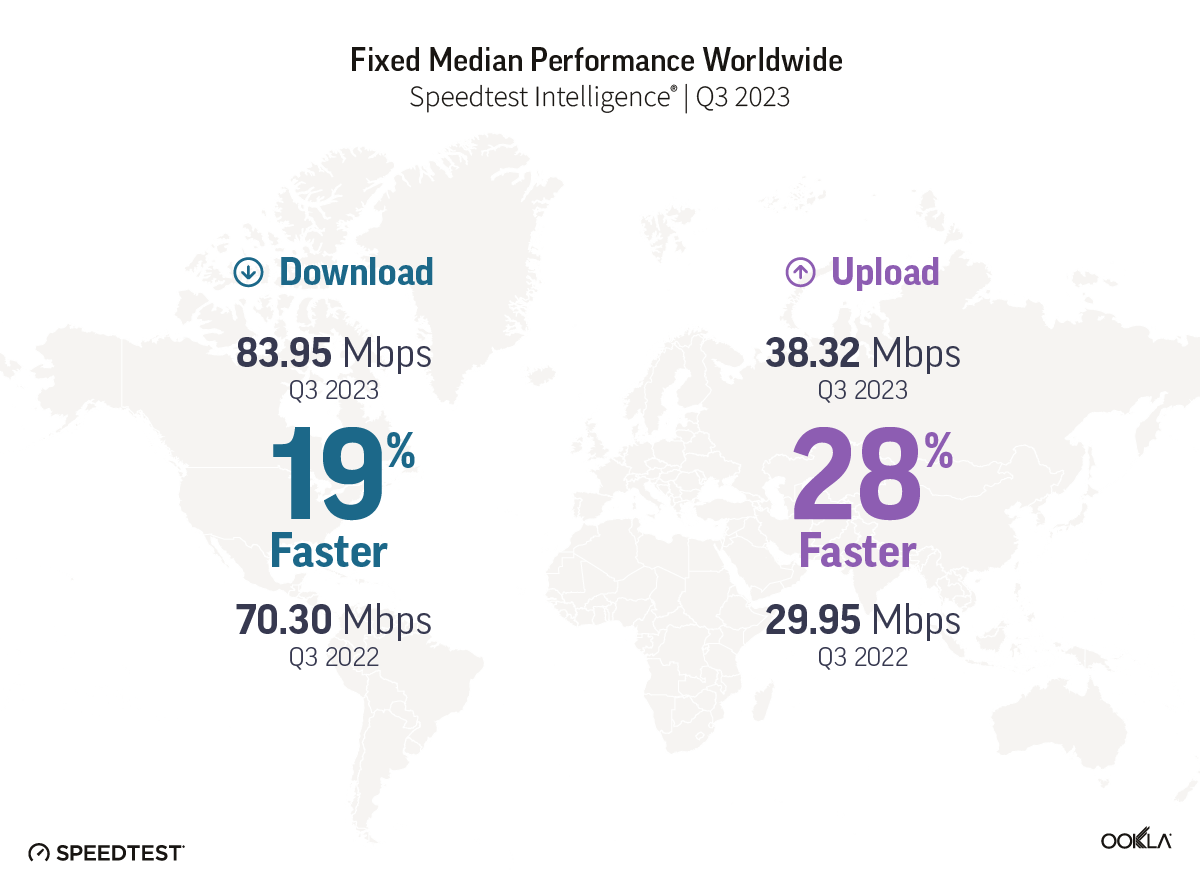
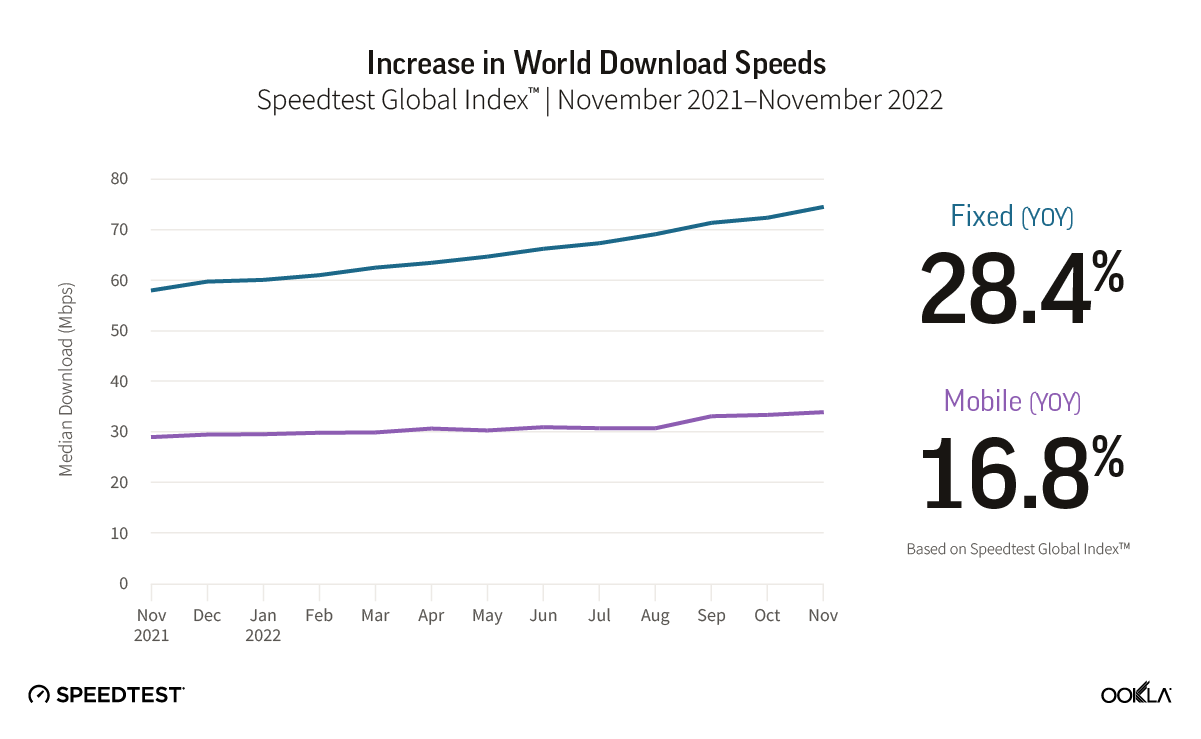
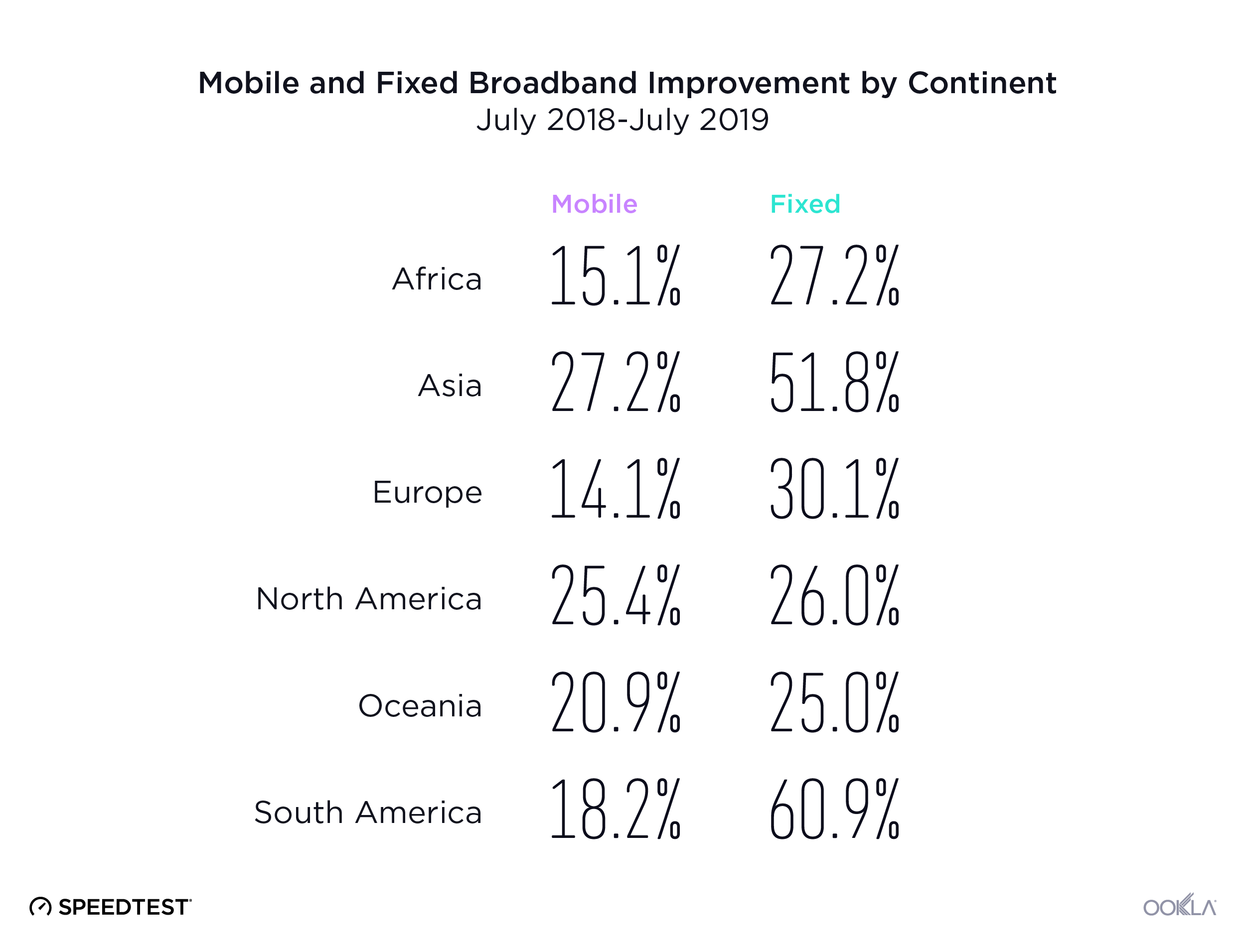
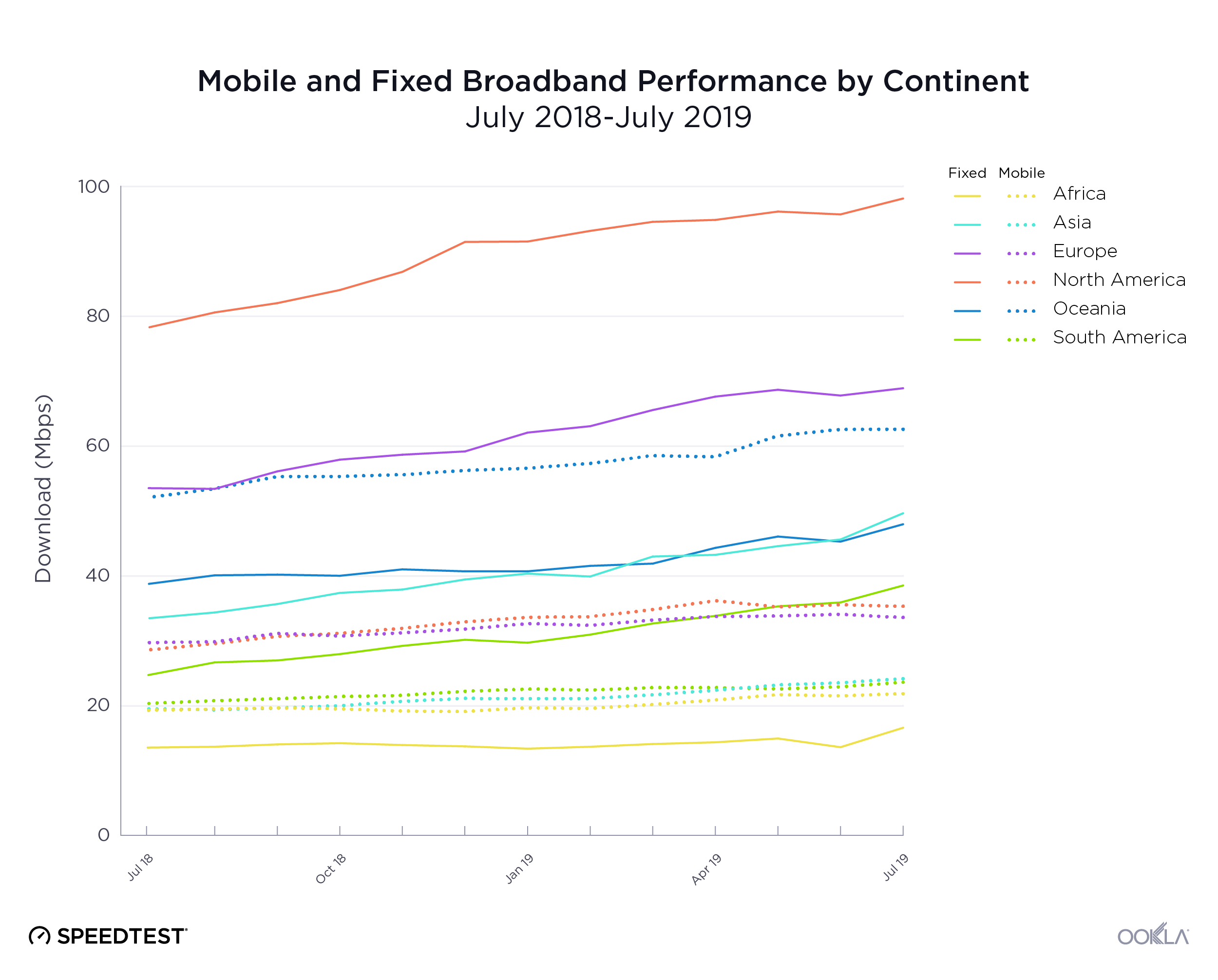
- Fixed Networks Advancements. On a global scale, fixed networks demonstrated significant performance improvement, with a 19% increase in median download speed (83.95 Mbps) and a 28% increase in upload speed (38.32 Mbps) in Q3 2023 compared to the previous year. This highlights the ongoing transition to more advanced broadband technologies, particularly Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH).
- The imperative of closing the connectivity gaps. Despite improvements in global connectivity, there are still areas that fall outside of network coverage. Speedtest® data highlights disparities in internet performance between fixed and mobile networks across different regions, emphasizing the importance of addressing connectivity challenges worldwide.
5G Networks
Global 5G download speed improvements
The median global 5G download speed has experienced a noteworthy surge, registering a 20% increase and reaching 203.04 Mbps in Q3 2023, compared to 168.27 Mbps in Q3 2022, according to Speedtest Intelligence® data. This improvement coincides with a substantial rise in global 5G connections, reaching 1.4 billion according to GSMA Intelligence, representing a 65% year-on-year increase from 872 million a year ago.
In terms of upload speed and latency, only a very modest improvement of 1% occurred. Median 5G upload speeds reached 18.93 Mbps in Q3 2023, compared to 18.71 Mbps in the same period last year; multi-server latency, a critical metric for network responsiveness, improved from 45 ms in Q3 2022 to 44 ms in Q3 2023.
Speedtest users experiencing the top 10% of 5G download speeds globally have seen a 9% increase, rising from 525.54 Mbps in Q3 2022 to 573.12 Mbps in Q3 2023. However, speeds have not yet reached Gigabit levels, primarly because of network economics. 5G was originally designed to deliver peak data rates of up to 20 Gbps based on IMT-2020 requirements, but we are still a ways off before gigabit speeds become the new normal. For instance, symmetrical download, upload speeds, and ultra-low latency haven’t been realized, partially because the vast majority of 5G networks are not ‘true 5G’ as they have been deployed in Non-Standalone (NSA) mode, meaning they rely on a 4G LTE network core. According to GSA, over 40 operators have launched 5G standalone (SA) in public networks, but the rollout is not yet complete. Nevertheless, the industry is actively exploring the prospect of 5G Advanced, which promises symmetrical upload and download speeds and ultra-low latency, signaling a proactive stance ahead of the eventual transition to 6G.
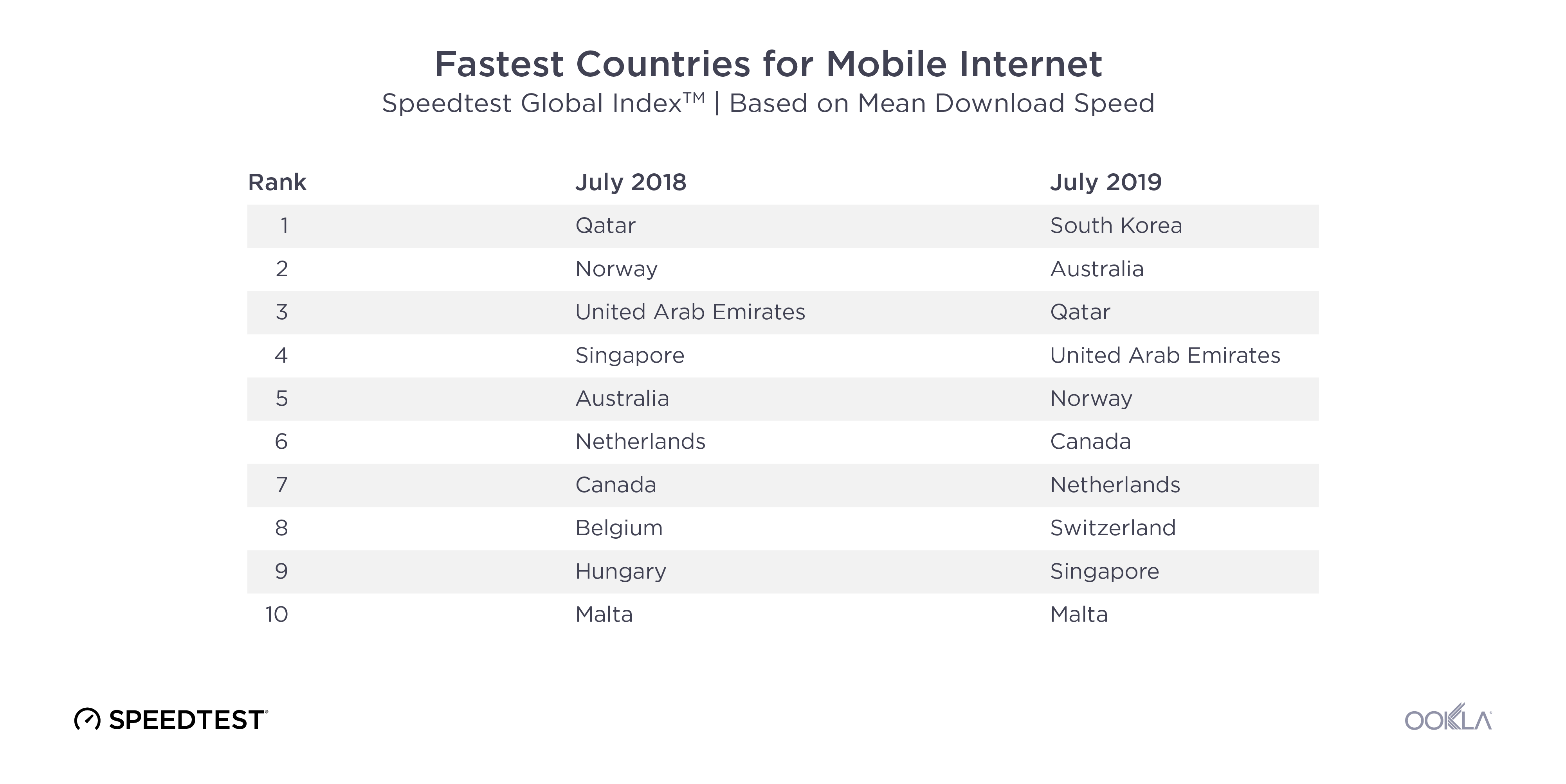
Malaysia joined South Korea and the U.A.E at 5G speeds podium
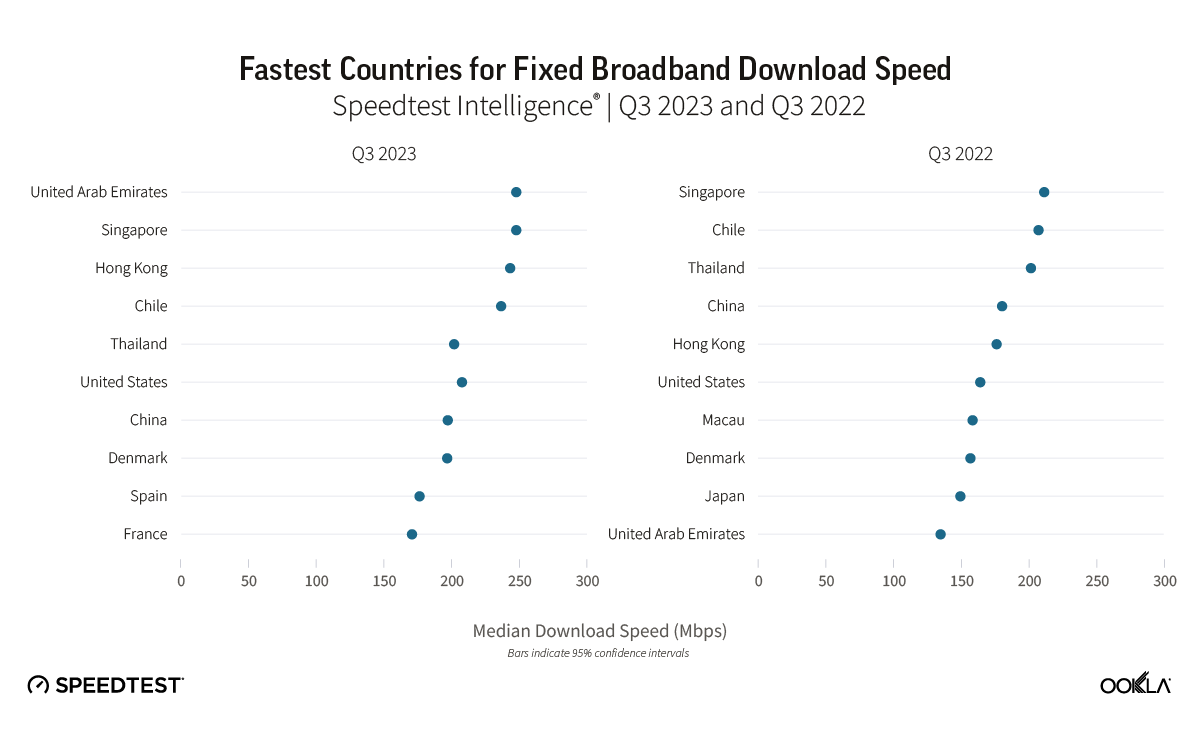
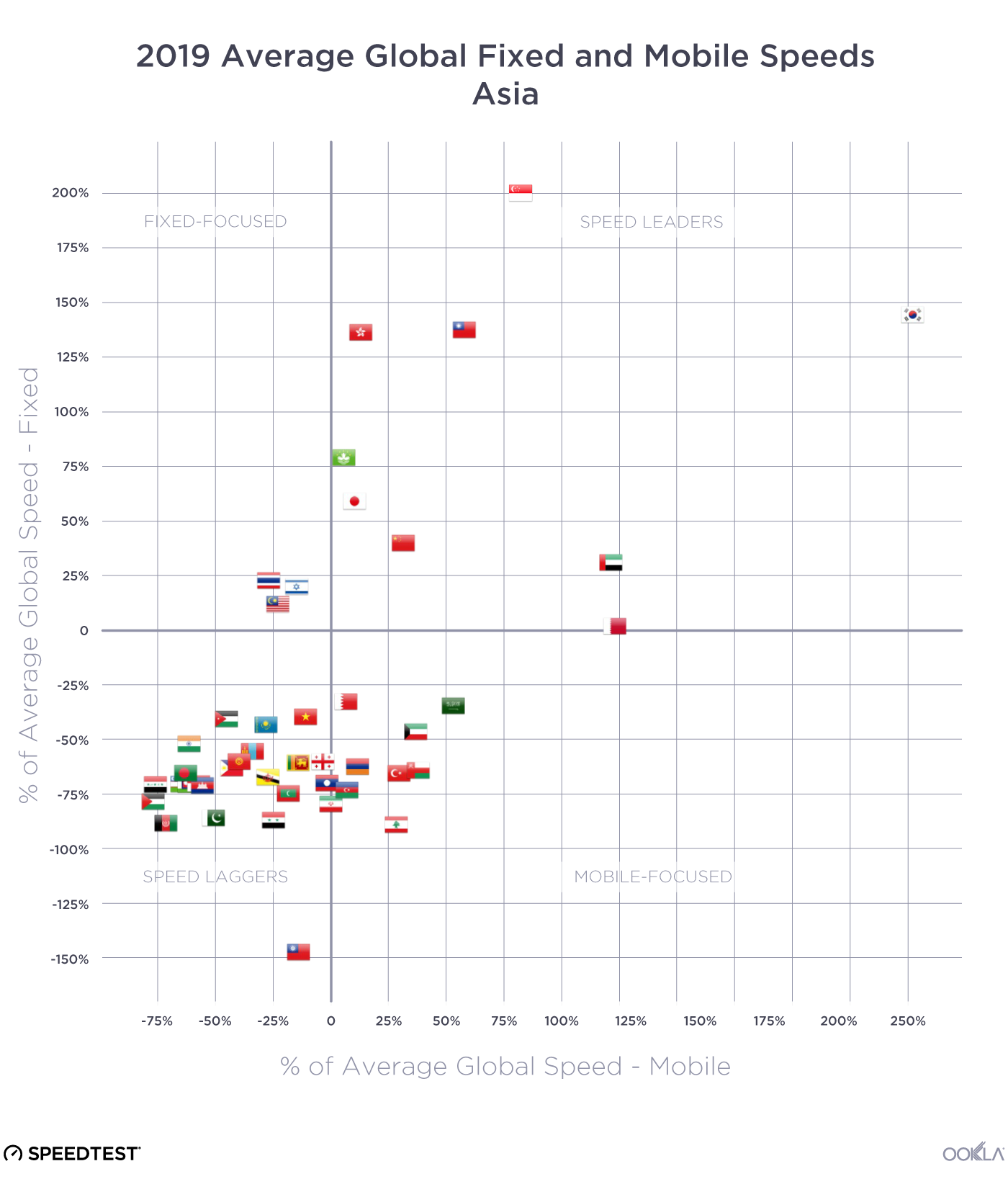
During Q3 2023, the United Arab Emirates and South Korea stood out as leaders in 5G performance, boasting the fastest median 5G download speeds globally at 592.01 Mbps and 507.59 Mbps, respectively. Our top 10 list also includes Malaysia, Qatar, Brazil, the Dominican Republic, Kuwait, Macau, Singapore, and India. The shift in the top 10 rankings reveals dynamic changes, with Malaysia, the Dominican Republic, and India making significant strides, while Bulgaria, Saudi Arabia, New Zealand, and Bahrain dropped out of the rankings.
The U.A.E showcased a 14% increase in its median 5G download speed, reaching 592.01 Mbps in Q3 2023, up from 511.68 Mbps in Q3 2022, allowing the U.A.E to take the top spot from South Korea. Key factors contributing to the U.A.E.’s 5G leadership include fierce market competition driven by Etisalat and du, resulting in extensive 5G coverage and widespread access to 5G services. Additionally, the allocation of a 100 MHz of contiguous spectrum, as discussed in our 5G spectrum article, has played a pivotal role in achieving faster speeds, lower latency, and improved spectral efficiency.
The regional shift in 5G performance leadership is noteworthy. In 2022, half of the top 10 countries were from the Middle East, while in 2023, the same proportion hailed from the Asia Pacific region. Our analysis suggests that early adopters in the Asia Pacific region have outperformed major European markets in 5G performance, due to factors such as early spectrum availability and supportive government policies.
Malaysia’s remarkable achievement in reaching the third spot globally for 5G download speed, with a reported speed of 485.24 Mbps in Q3 2023, is particularly noteworthy. Despite launching its nationwide 5G network less than two years ago, Malaysia’s unconventional deployment strategy has proven effective. India has also made a significant leap, with its median 5G download speed of 312.26 Mbps allowing India to reach the top 10 worldwide. The country’s climb of 72 places on the Speedtest Global Index™ between September 2022 and August 2023 is primarily credited to the launch of 5G. Following a 5G spectrum auction in India, operators have successfully addressed network congestion issues by offloading 4G traffic onto 5G networks.
In Brazil, 5G download speed increased 1.4 times, jumping from 312.09 Mbps in Q3 2022 to 443.93 Mbps in Q3 2023. Before Brazil’s 5G spectrum auction, operators had offered 5G using DSS since July 2020. While DSS can provide broad 5G coverage, its speeds are often similar to those on 4G LTE networks. In November of 2021, however, Brazil’s multi-band 5G spectrum auction closed, which not only generated BRL47.2 billion ($8.5 billion) in total commitments, but it also allowed operators to deliver much faster speeds on dedicated 5G spectrum compared to DSS. National operators – Telefonica Brasil (Vivo), Claro Brazil, and TIM Brazil – ended up with 40 MHz or 50 MHz in the 2.3 GHz spectrum band and 100 MHz each in the 3.5 GHz band. The subsequent simultaneous activation of 5G networks in July 2022 marked a transformative moment with the continuous expansion of 5G services to 623 municipalities by December 2023. An upcoming spectrum auction expects to improve Brazil’s 5G standing even further.
The Dominican Republic’s entry into the top 10 fastest 5G countries was marked by its official launch of 5G services in December 2021, making it the first Caribbean nation and the third in Latin America to adopt a 5G network.
Disparity Between 5G Performance and Consumer Perception
The Net Promoter Score (NPS) is a tool that gauges customer loyalty and satisfaction. At the end of Speetest, users may be asked to answer “How likely is it that you would recommend [provider] to a friend or colleague?” on a scale from 0-10. Net Promoter Scores are applied to both users and providers. Users are categorized into Detractors (score 0-6), Passives (score 7-8), and Promoters (score 9-10). NPS is the percent of Promoters minus the percent of Detractors and is displayed in the range from -100 to 100. Providers are ranked in descending order of NPS. NPS categorizes users into Detractors (those that score 0-6), Passives (scores between 7 and 8), and Promoters (scores of 9-10). NPS represents the percentage of Promoters minus the percent of Detractors displayed in the range from -100 to 100.
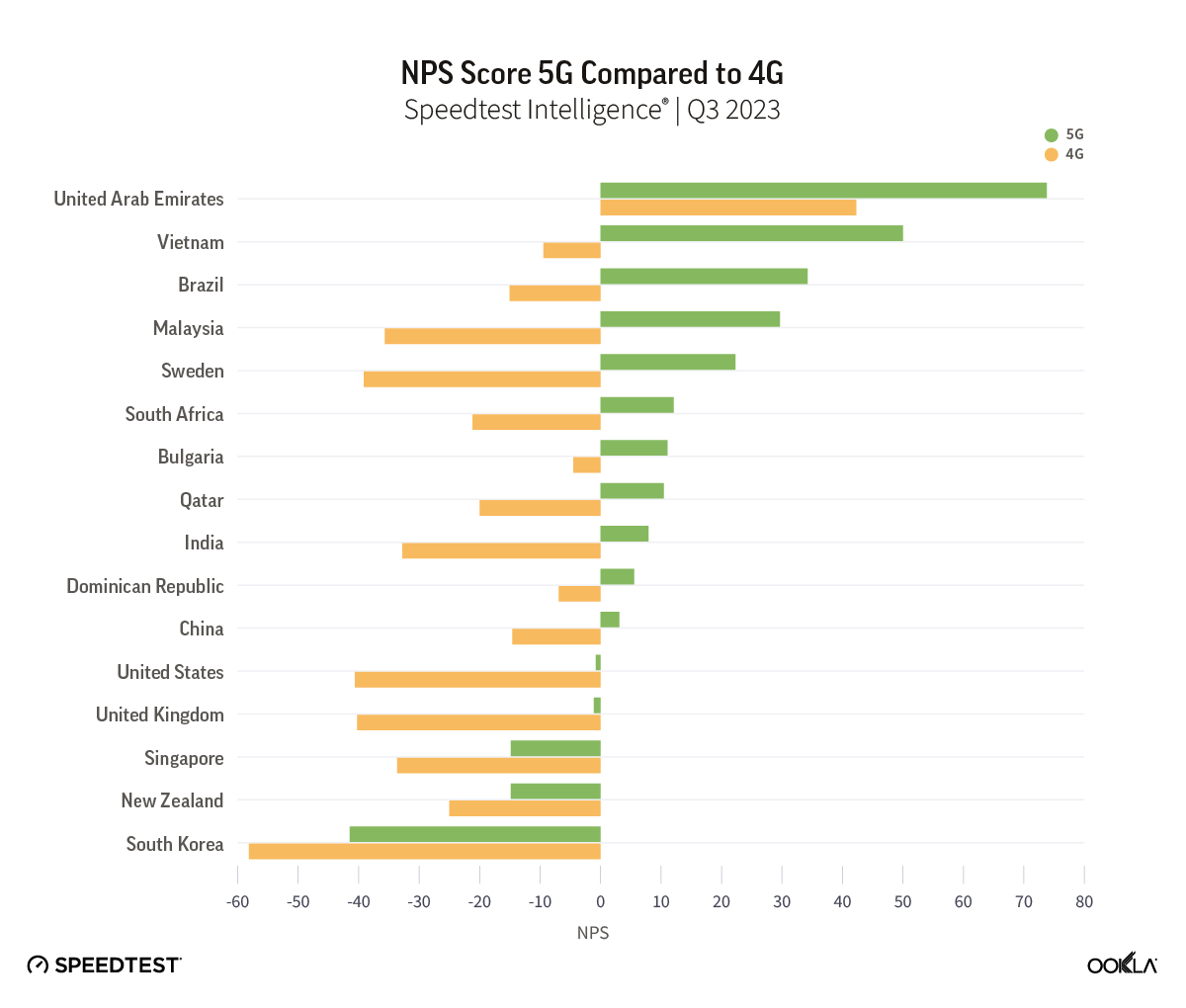
In our article discussing whether 5G was meeting customer expectations, we found that 5G users typically rate their network operator with NPS scores universally higher than those for 4G LTE users. In Q3 2023, that trend continued, as 5G users that were on 5G network when answering the NPS question still scored higher than those on 4G across all markets analyzed. It isn’t surprising given that at a global level, 5G had a 637% better median download speed than 4G and a 130% better median upload speed.
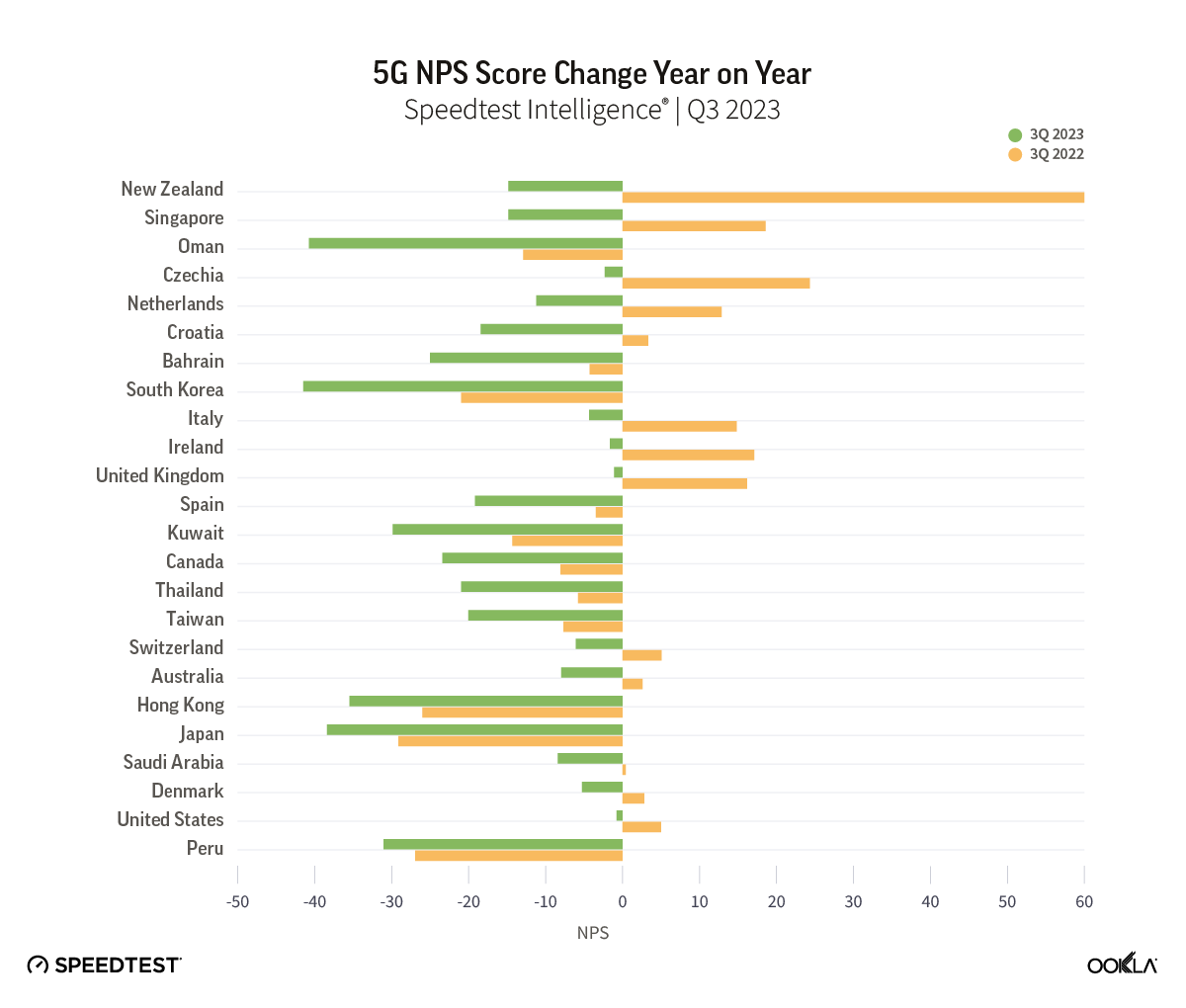
While 5G NPS still outpaces scores on 4G, our data shows that 5G NPS has been decreasing annually. This could point to the fact that excitement about 5G as a new technology is waning as users become used to faster speeds, or as customers await new use cases that can take advantage of the faster speeds that 5G can provide. After all, we are still waiting for that killer app for 5G, the way the video and streaming were for 4G.
While it is difficult to fully explain the reasons behind the 5G NPS decrease without further research, we can clearly see that network performance isn’t the only factor at play influencing NPS declines. Others can include customer care, pricing, and other services. For example, in South Korea, one of the first countries to launch 5G with one of the world’s fastest speeds, consumers scored 5G networks -41.47 in Q3 2023 compared to -20.51 in Q3 2022.
In March 2021, South Korean consumers launched a class action suit against operators because they felt they were being misled by the promises of 5G in the country. Recently, South Korea’s antitrust regulator fined three 5G operators a total of 33.6 billion won ($25.06 million) for making exaggerated claims about the level of performance their networks could achieve. South Korean operators claimed consumers could experience theoretical 5G speeds, which are not practically achievable in a “real world” environment, as factors such as spectrum usage, network densification, user location, and device capability significantly affect actual performance. Our data shows that the top 10% of 5G users in South Korea experienced speeds of 1.004 Gbps in Q3 2023, which, although impressive, are far lower than the advertised 20 Gbps speeds.
Fixed Networks
Fiber driving fixed performance gains
On a global scale, fixed networks have demonstrated significant advancements, achieving a median download speed of 83.95 Mbps and an upload speed of 38.32 Mbps in Q3 2023, per Speedtest Intelligence data. This signifies a substantial 19% improvement in download speed and an impressive 28% enhancement in upload speed compared to those in 2022. This also indicates that more fixed connections have migrated to fiber networks.
According to the World Broadband Association (WBBA) report titled “Next Generation Broadband Roadmap 2023 to 2030” Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH) is identified as the natural progression from copper-based xDSL broadband networks. The shift towards FTTH varies across different countries and regions, but the industry is committed to embracing more advanced and efficient broadband technologies.
Oftentimes, despite improvement in underlying broadband technology, Wi-Fi is the bottleneck that reduces customer experience. Our research has shown that Wi-Fi performance can lag behind ethernet in markets where advanced cable and fiber connections are replacing legacy broadband technology (such as DSL or coax cable). Wi-Fi speeds typically range from 30-40% of ethernet, indicating a need to accelerate the adoption of more advanced Wi-Fi technologies and optimize the home network environment.
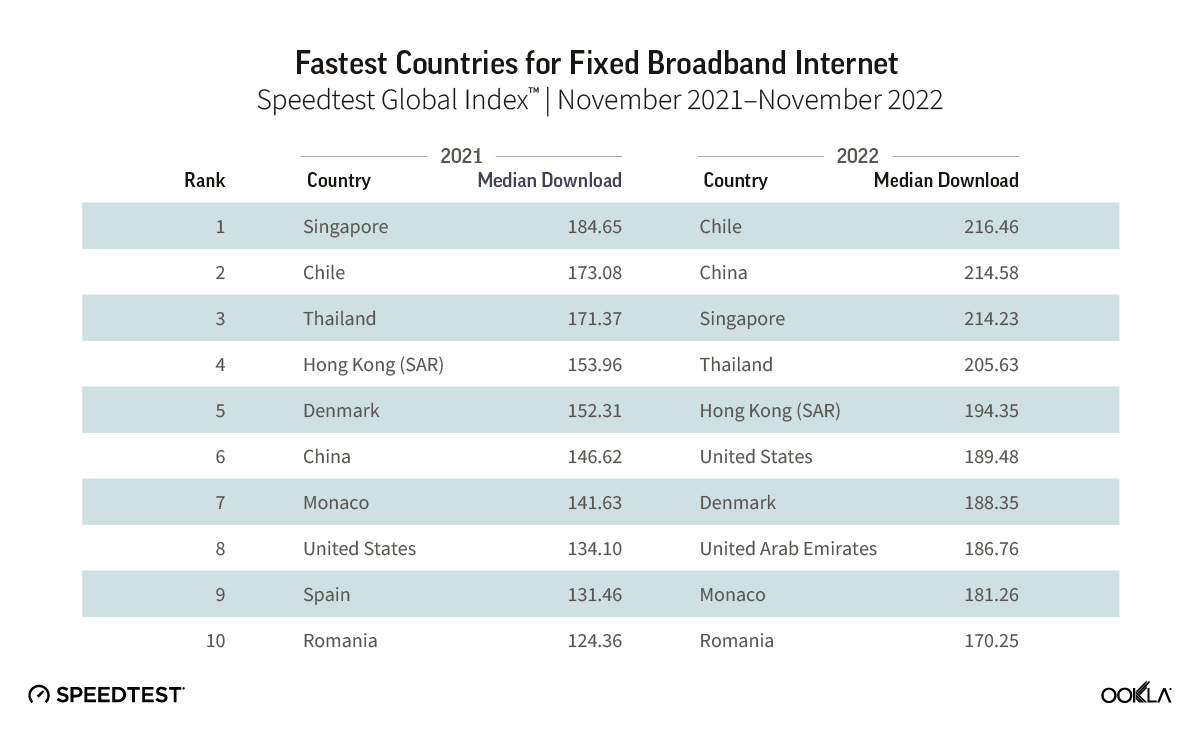
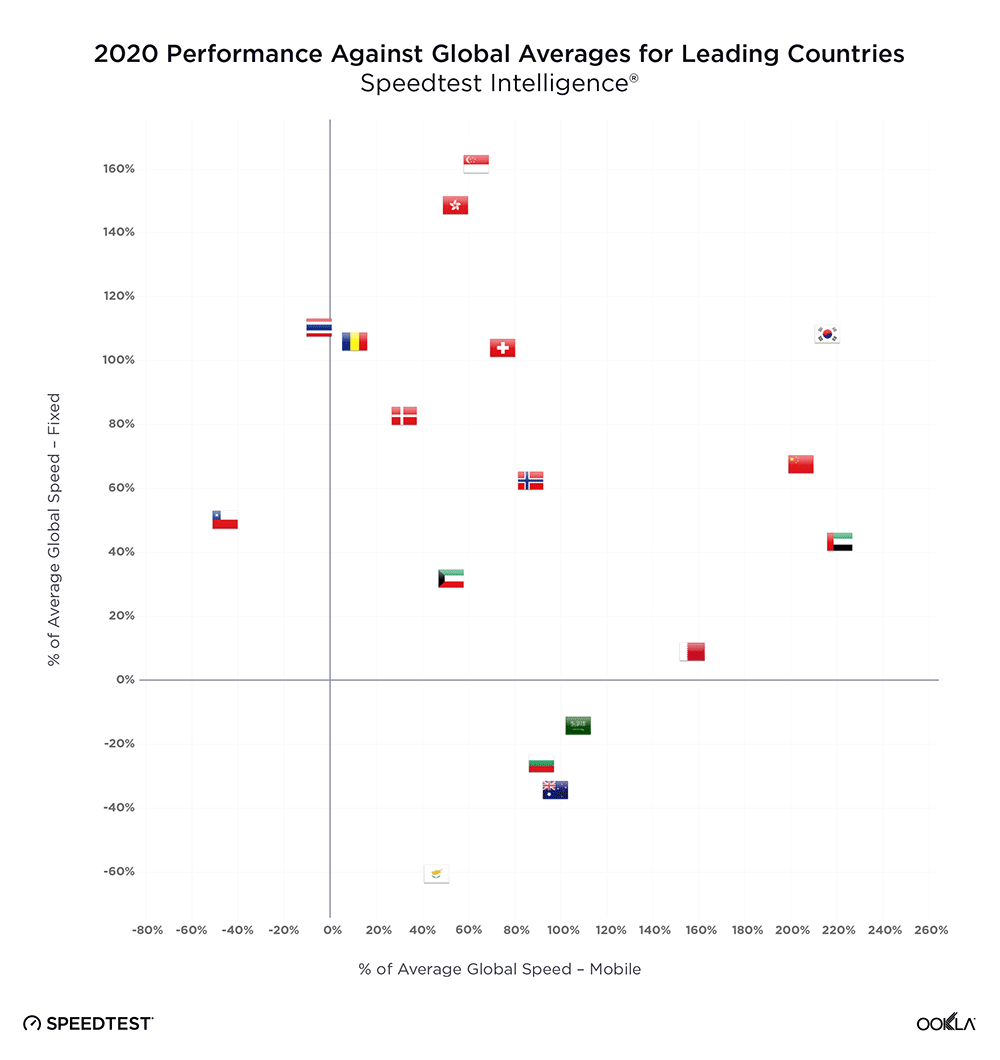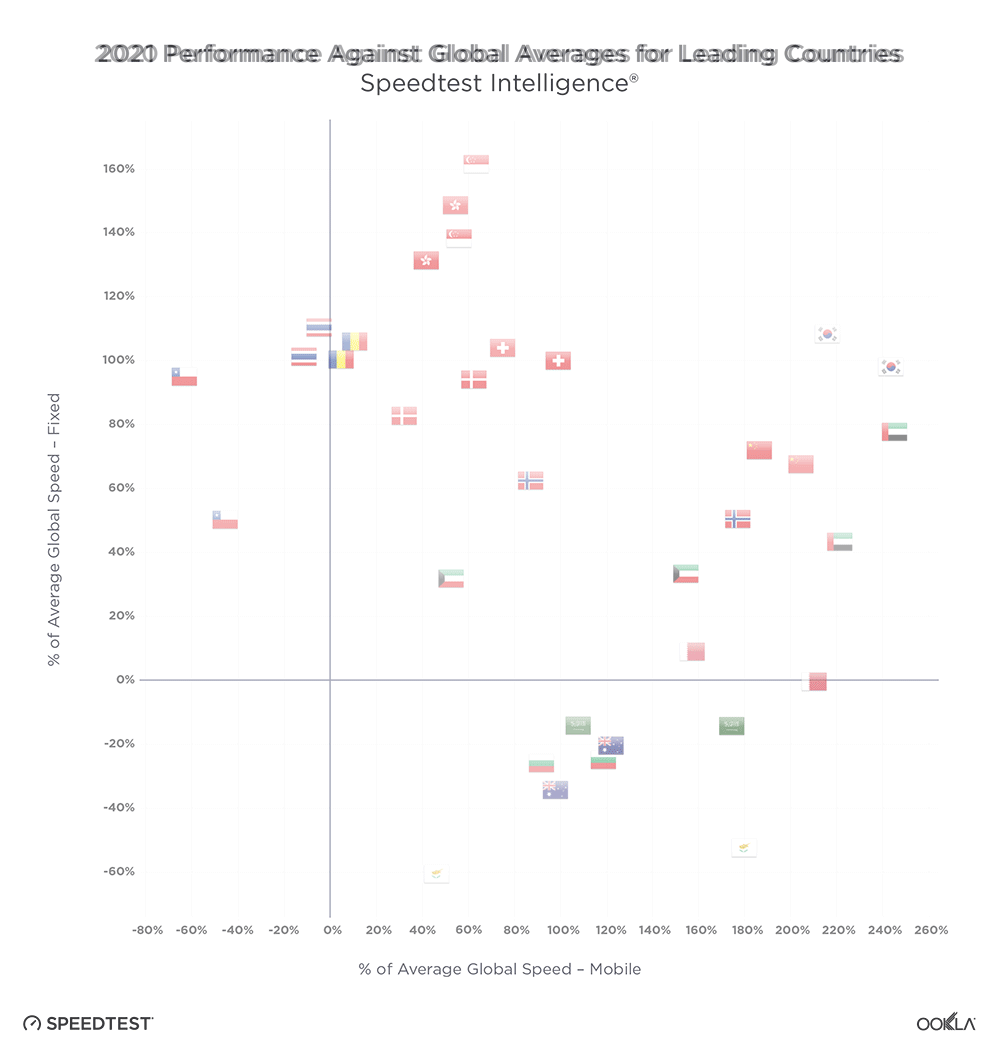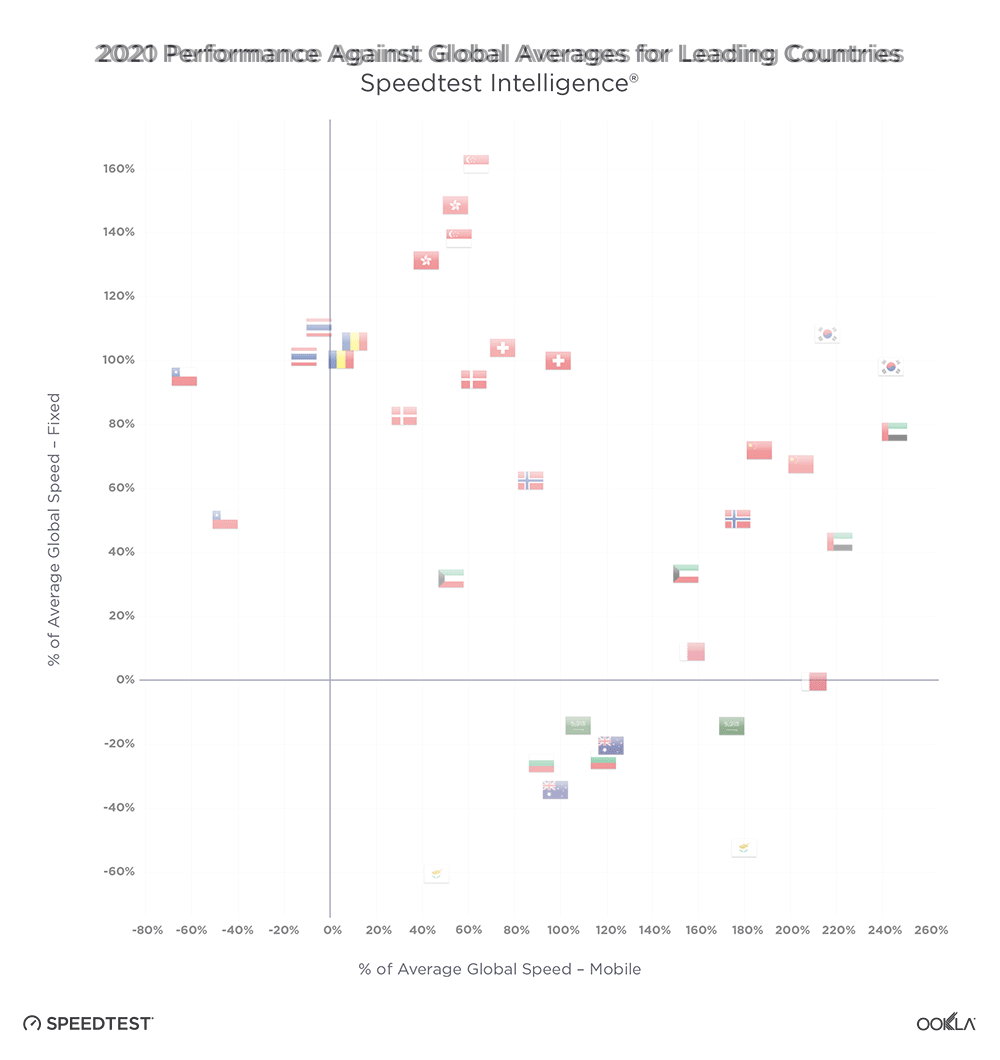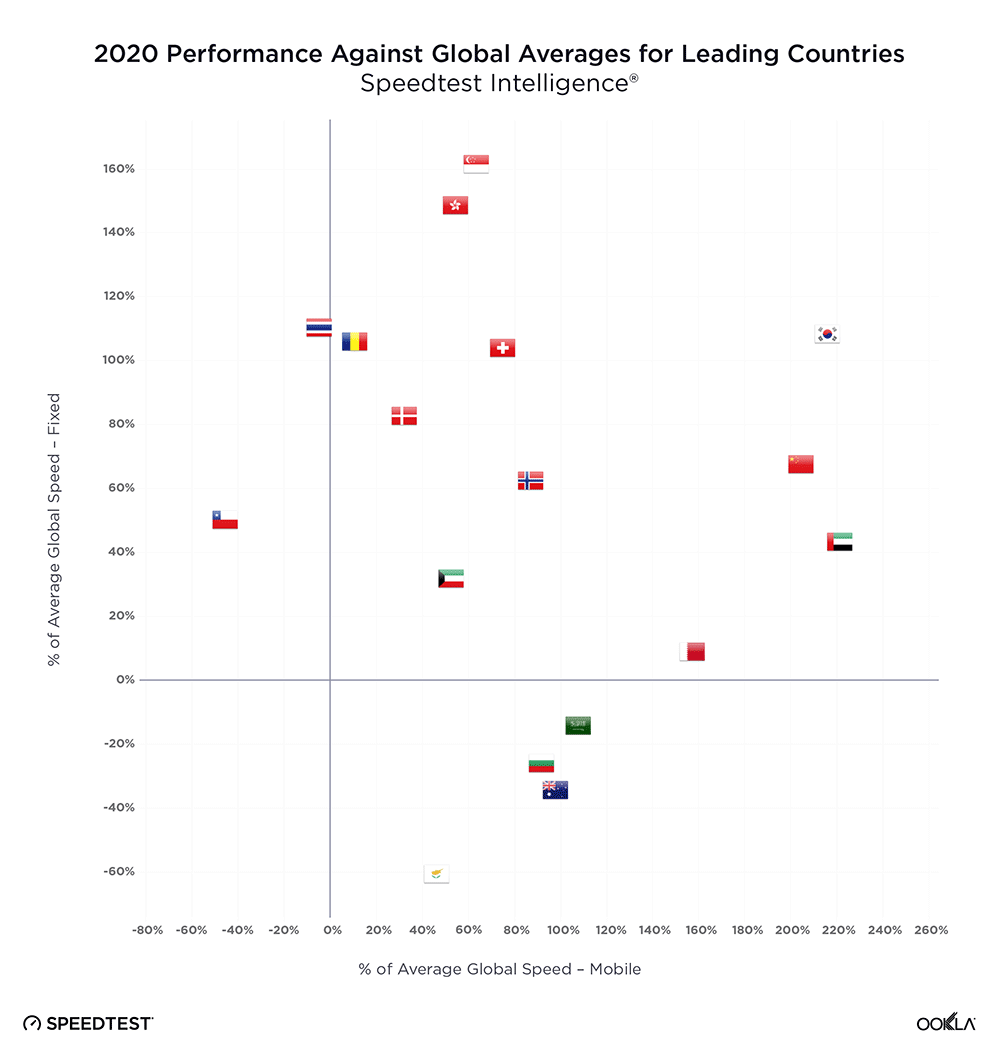
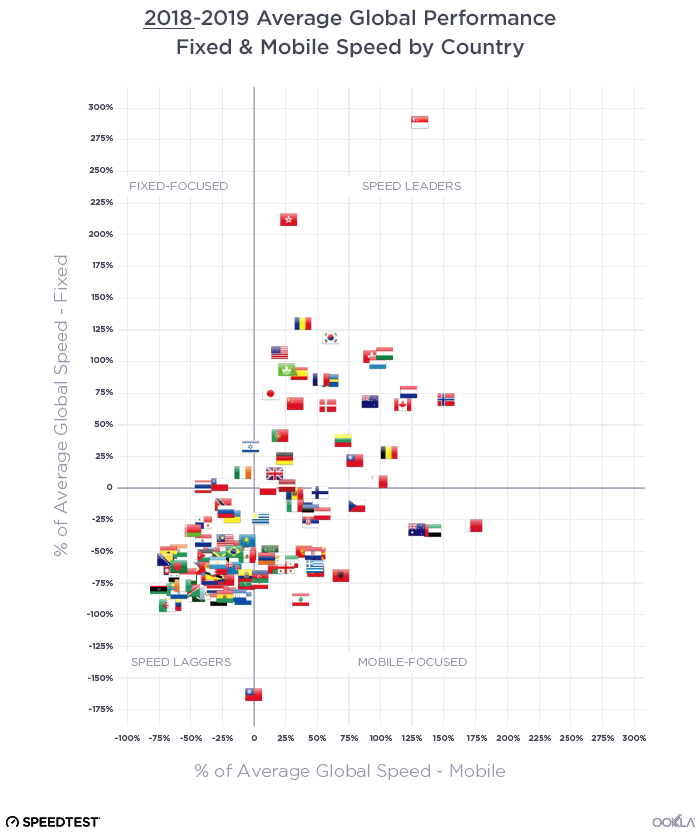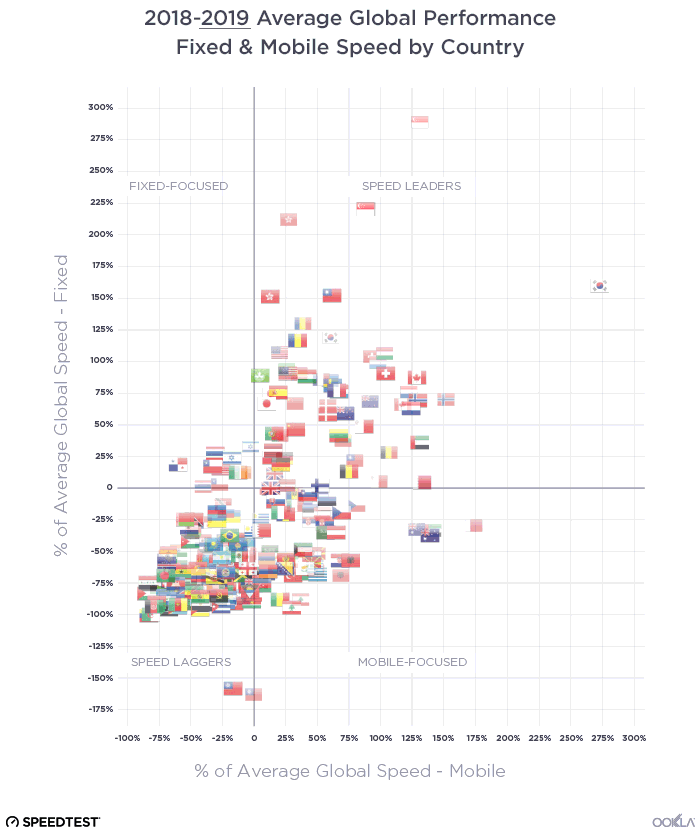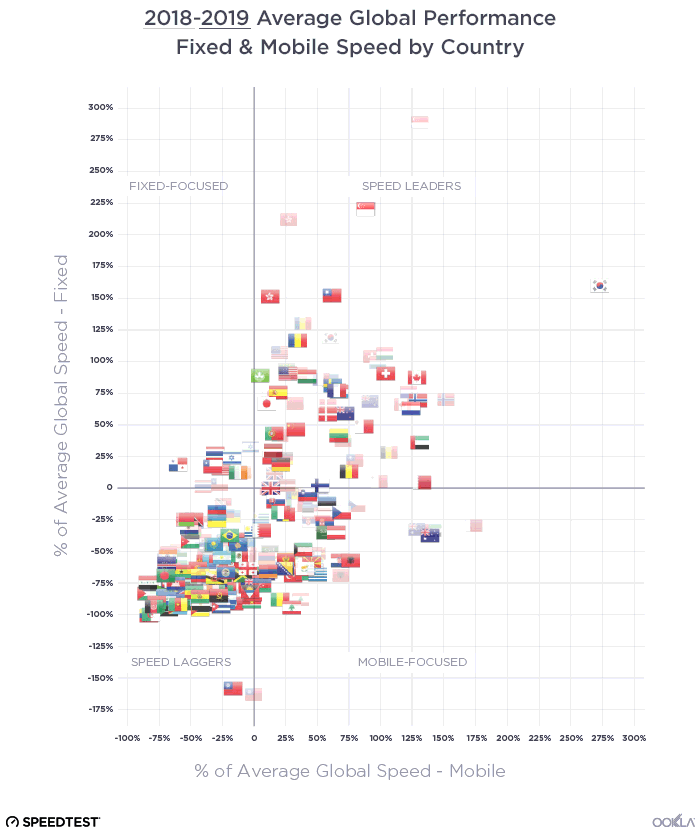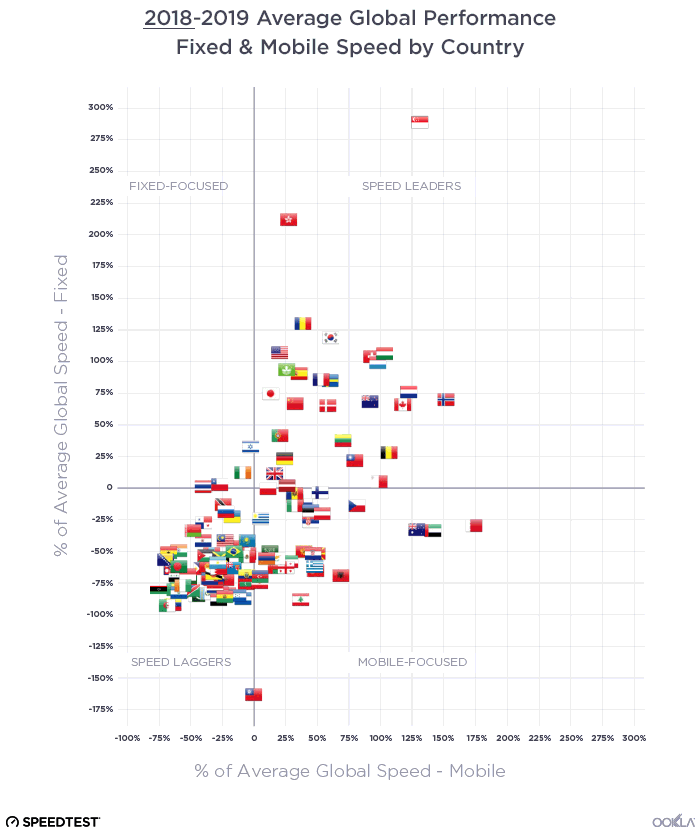
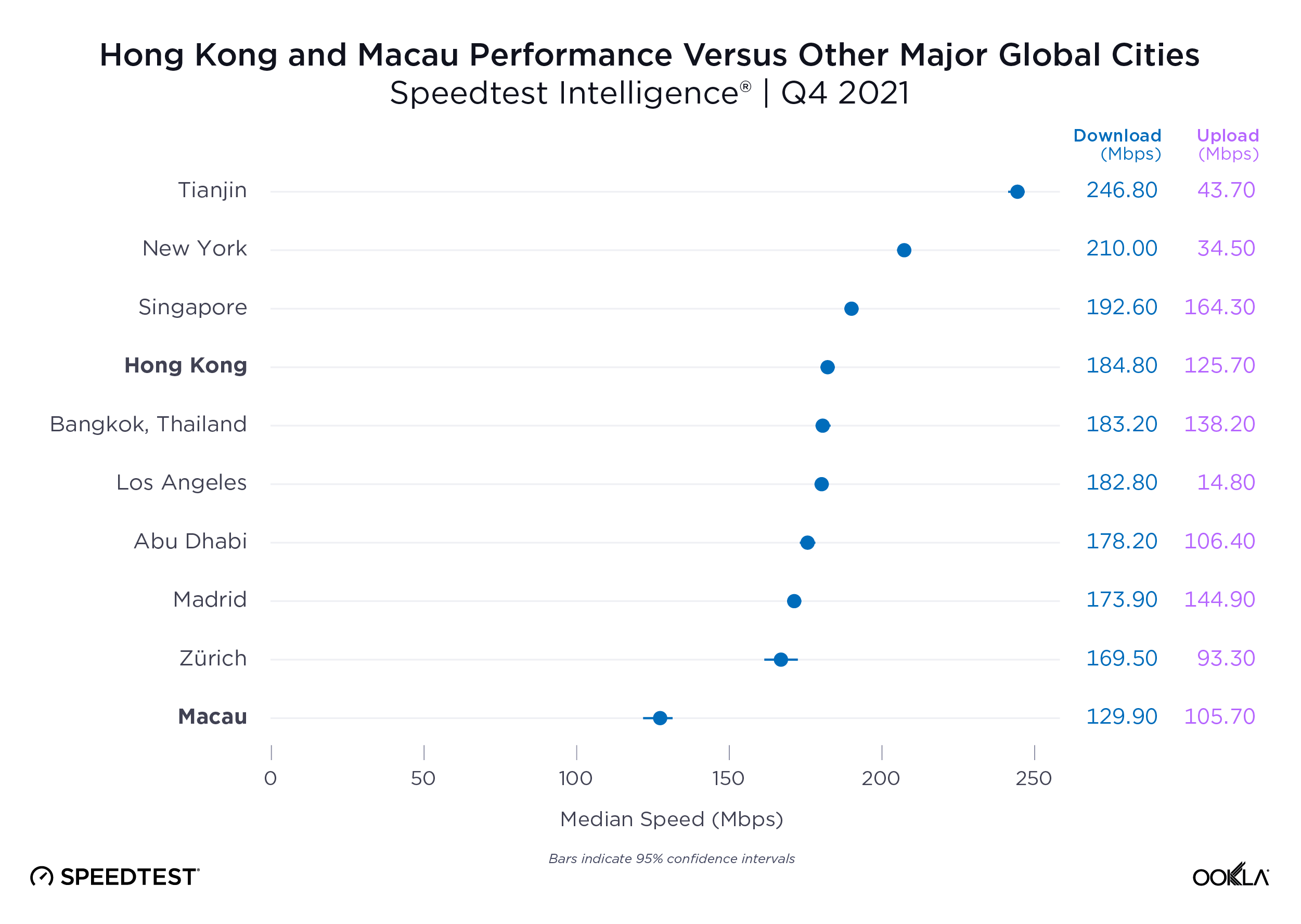
The UAE, Singapore, and Hong Kong are in the lead for fixed
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) and Singapore led the way in fixed network performance.
The UAE achieved a median download speed of 247.63 Mbps in Q3 2023, representing a notable 1.83 times increase compared to the previous year. Most customers in the UAE have access to fiber networks, and additional measures have been implemented by operators in the region to enhance internet speeds, such as increasing the minimum download speed from 250 Mbps to 500 Mbps and offering price discounts to incentivize users to upgrade to higher-tier plans.
Singapore also leads on the 2023 Fiber Development Index (FDI), with maximum scores in seven of the nine metrics. Singapore, along with Qatar and South Korea, has achieved 100% FTHH coverage. One of the reasons for this success, besides having a smaller area, is that Singapore’s regulator mandates building owners and real estate developers to provide adequate space, facilities, and accessibility for network operators to pre-install fiber networks.
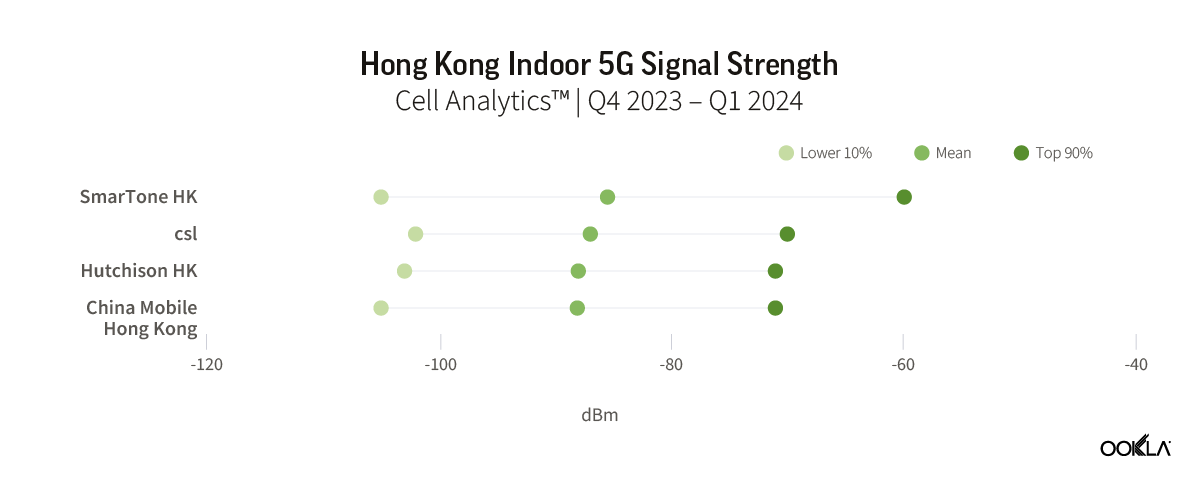
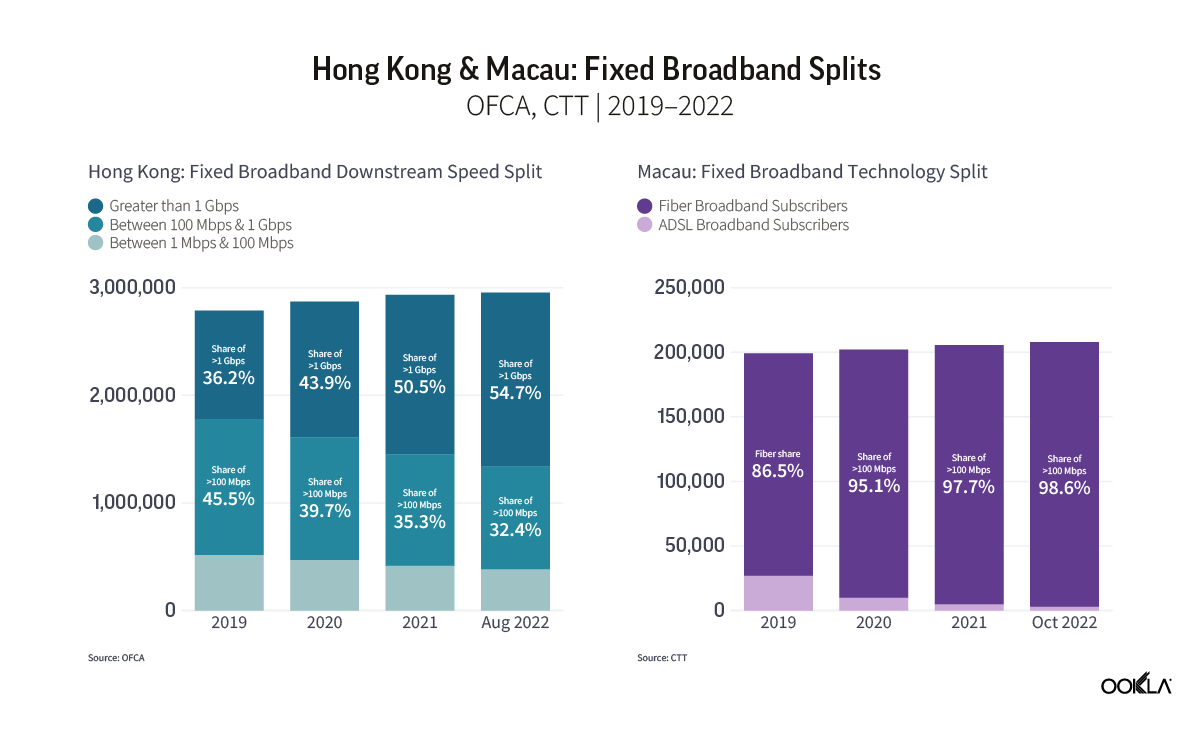
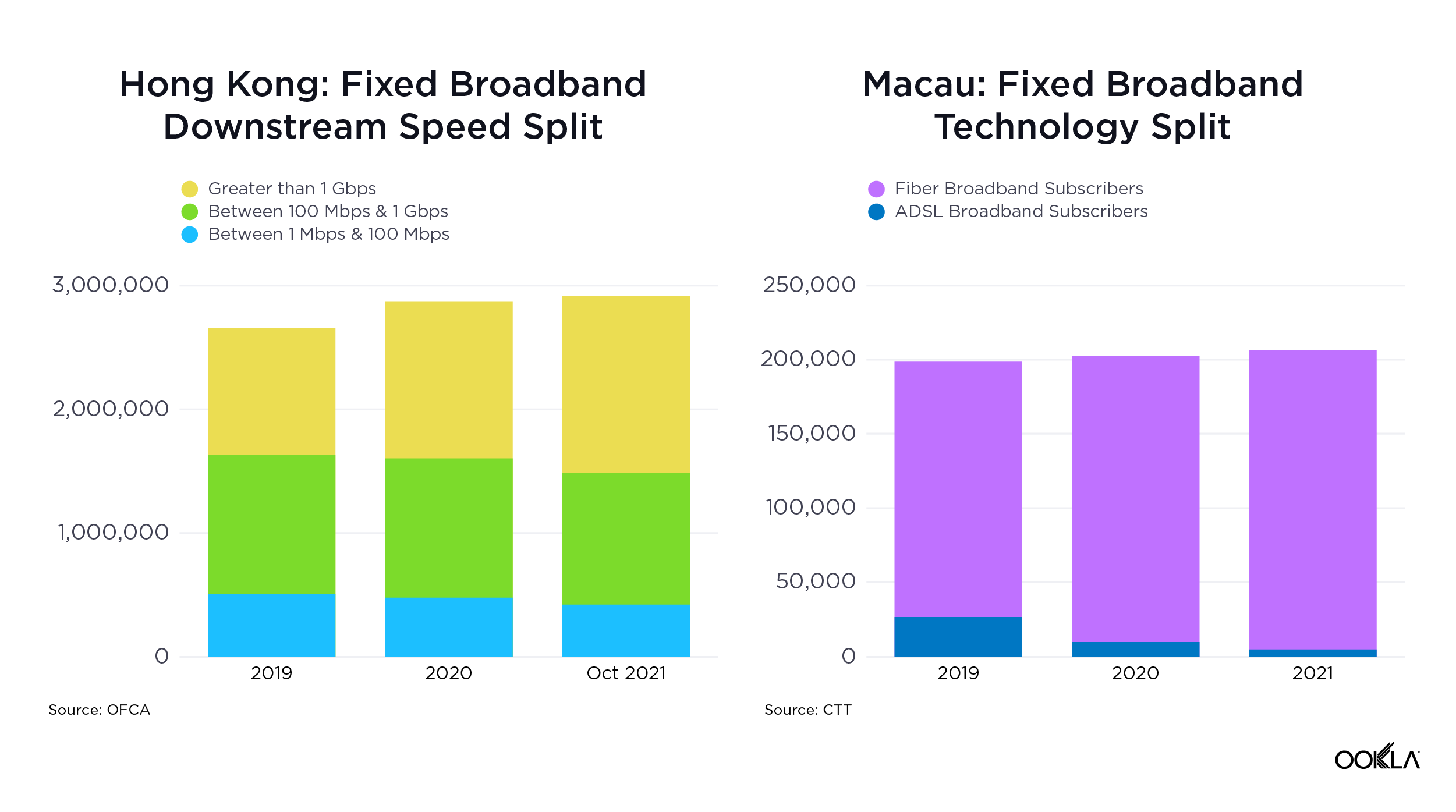
Hong Kong also demonstrated significant progress, with a 37% increase in median download speed and a 40% increase in upload speed. To track broadband adoption, the Office of the Communications Authority (OFCA) in Hong Kong monitors broadband adoption by advertised speed and technology mix; as of August 2023, 66% of residential clients already subscribed to the Internet with a download speed equal to or greater than 1 Gbps.
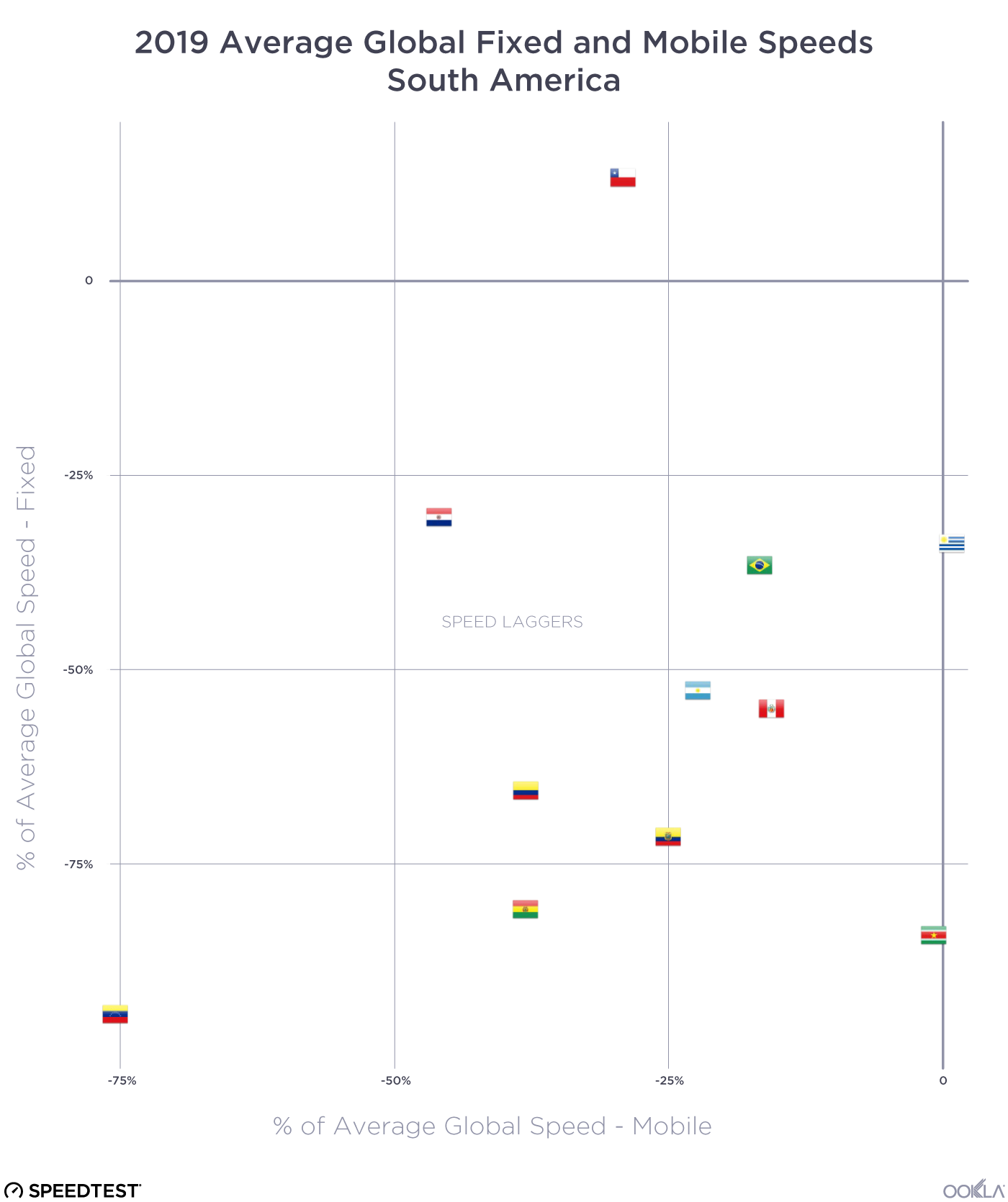
Chile has seen a 14% improvement in median download speed and a 29% improvement in upload speed on the back of a greater fiber adoption. Chile has been the top-performing fixed broadband market across Latin America, consistently outperforming other regional markets but over the last three years, it has also closed the performance gap with other leading markets globally. Chile’s strong fixed broadband performance — an anomaly in the region — is primarily due to strong competition among Chilean ISPs. Chile has seven ISPs with over 5% market share, all heavily focused on migrating customers to fiber.
Thailand is a newcomer to the ranking as FTTH continues to grow strongly. FTTH constitutes an impressive 95% of fixed broadband users in Thailand, equivalent to around 58.96% of household penetration. Operators have been actively rolling out fiber in adherence to the Digital Thailand National Policy.
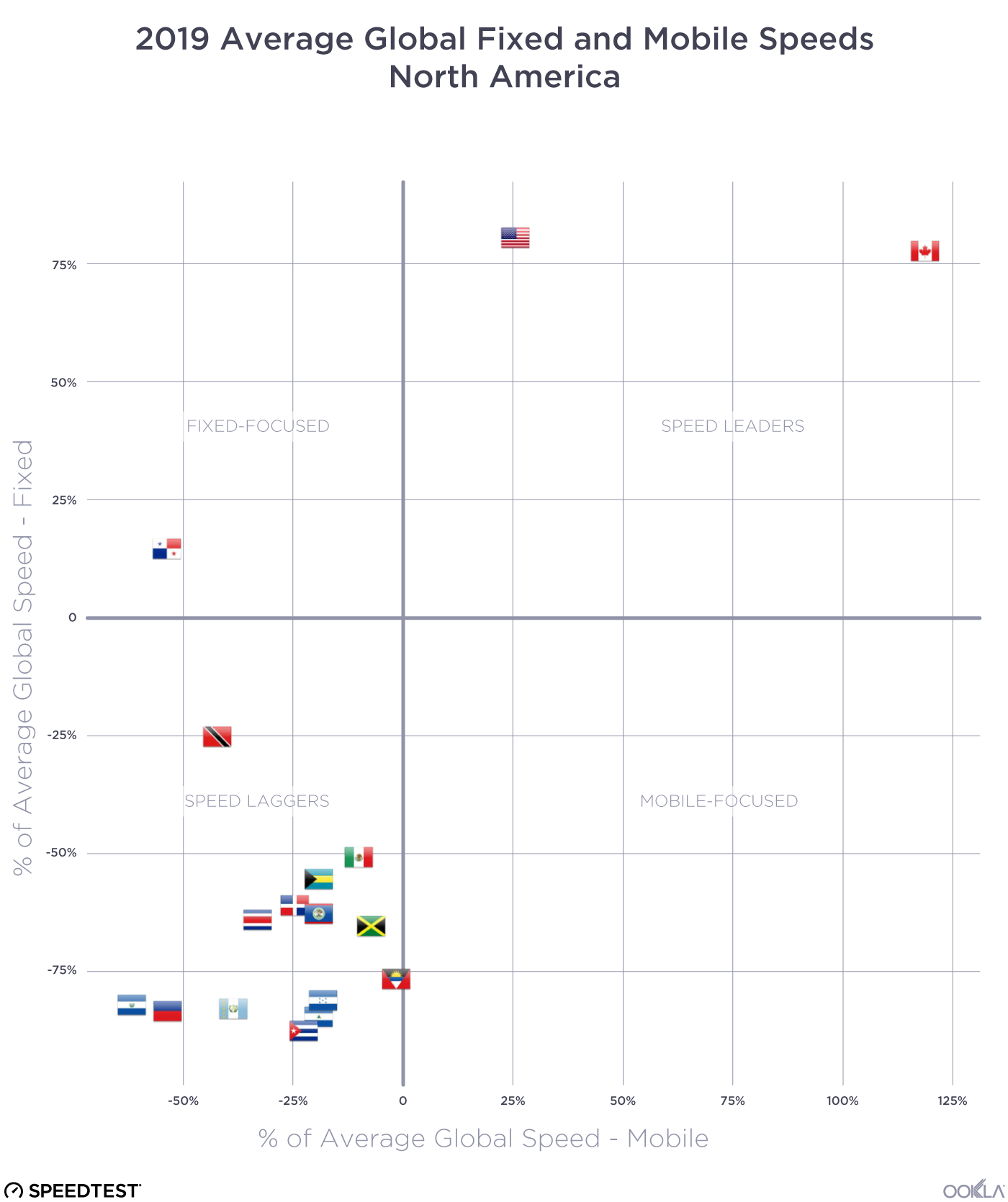
In the United States, there has been a 26% improvement in median download speed and a 7% improvement in upload speed. In this very competitive market, with a range of access technologies vying for customers, a combination of migration to fiber, 5G fixed-wireless access (FWA), and faster cable connections is helping drive higher performance levels. In line with the demand for faster network performance in the market, the FCC recently announced that it is seeking input on a planned increase to its definition of broadband/high-speed internet to 100 Mbps download and 20 Mbps upload, up from the current 25 Mbps download and 3 Mbps upload standard.
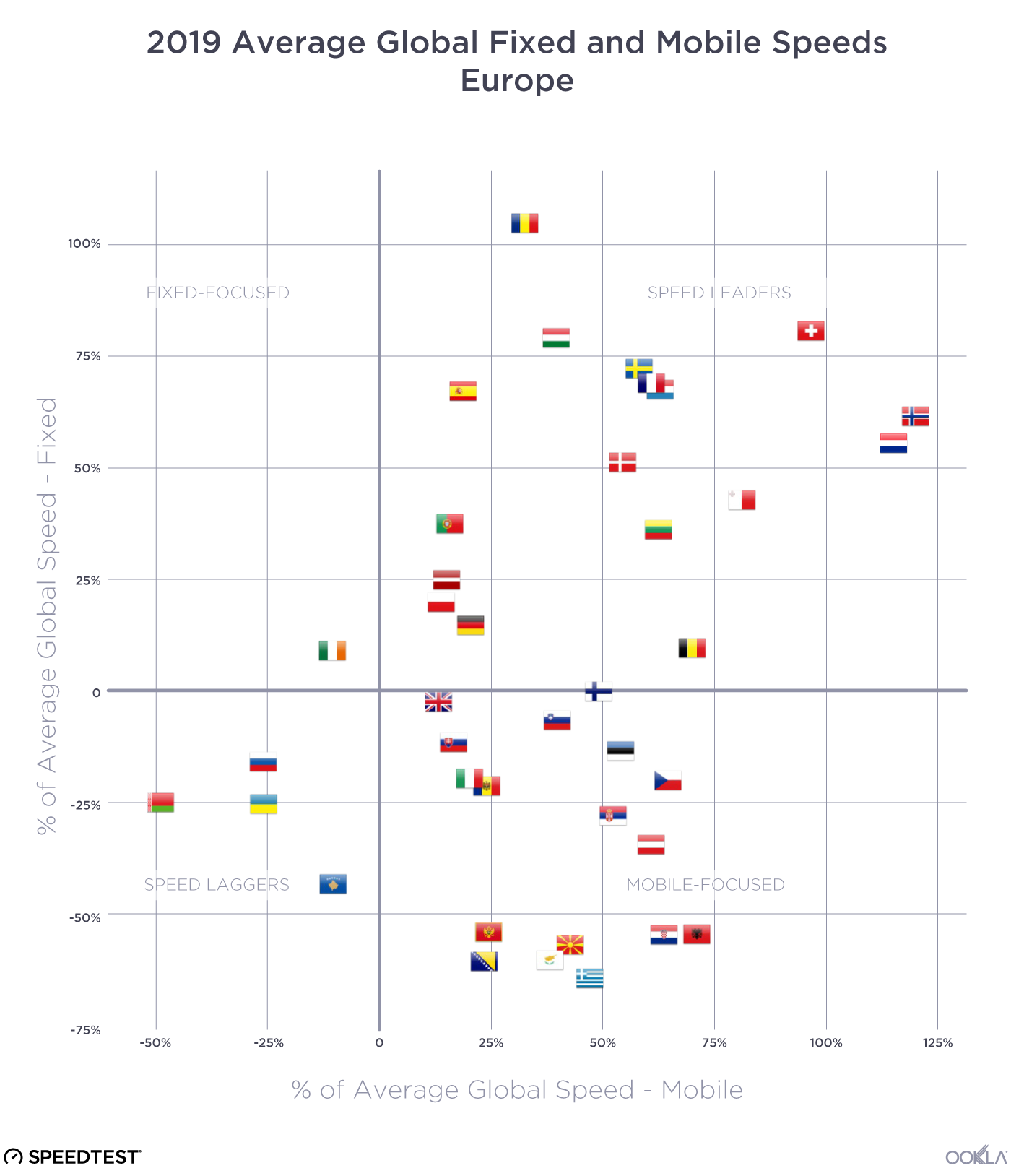
As discussed in our recent article, several European countries are making substantial progress in offering high-speed broadband. Across Europe, Denmark had the fastest median download speed for fixed broadband (196.43 Mbps), followed by Spain (176.08 Mbps) and France (170.51 Mbps). Denmark experienced a 25% improvement in median download speed and a 16% improvement in upload speed. Spain also showed significant improvement, with a 32% increase in median download speed and a 29% increase in upload speed. France exhibited even stronger progress, with a 53% increase in median download speed and a 41% increase in upload speed. The speed gains we’ve seen in Spain and France are correlated with an increase in fiber adoption; for example, Spain boasts nearly 90% fiber optic coverage, thanks to private initiatives and government support, while France expects a full-fiber rollout by 2025.
Connectivity for All
The imperative of closing the connectivity gap
Massive investments are being made to bridge the connectivity gap as recognition of connectivity as a fundamental human right is growing. According to a WBBA Whitepaper, a high level of broadband penetration is critical to the country’s socioeconomic development. However, it’s not only about being connected to the network per se; the quality of that broadband connection is equally crucial. Unlike other utility services like gas and electricity, where quality is generally stable, with broadband, the quality of the network experience is crucial to ensure users can benefit fully from multiple applications.
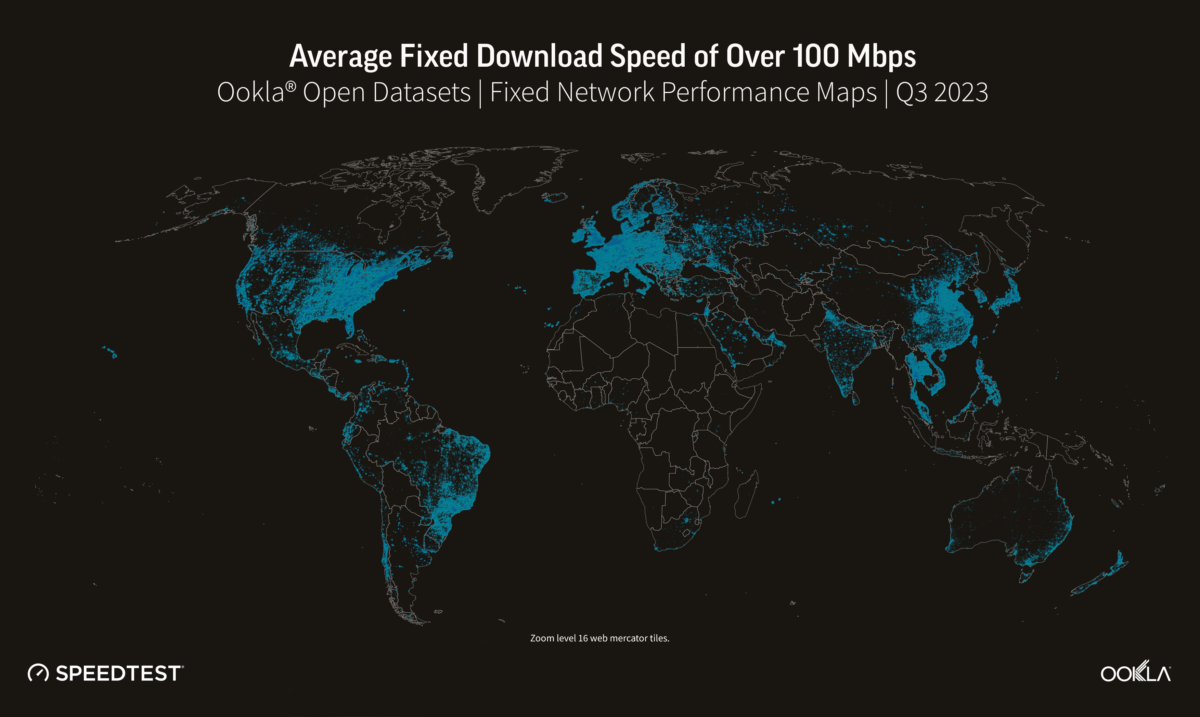
To assess the digital divide, we mapped mobile and fixed internet performance using data from the Open Data Initiative, which Ookla provides as part of Ookla for Good.
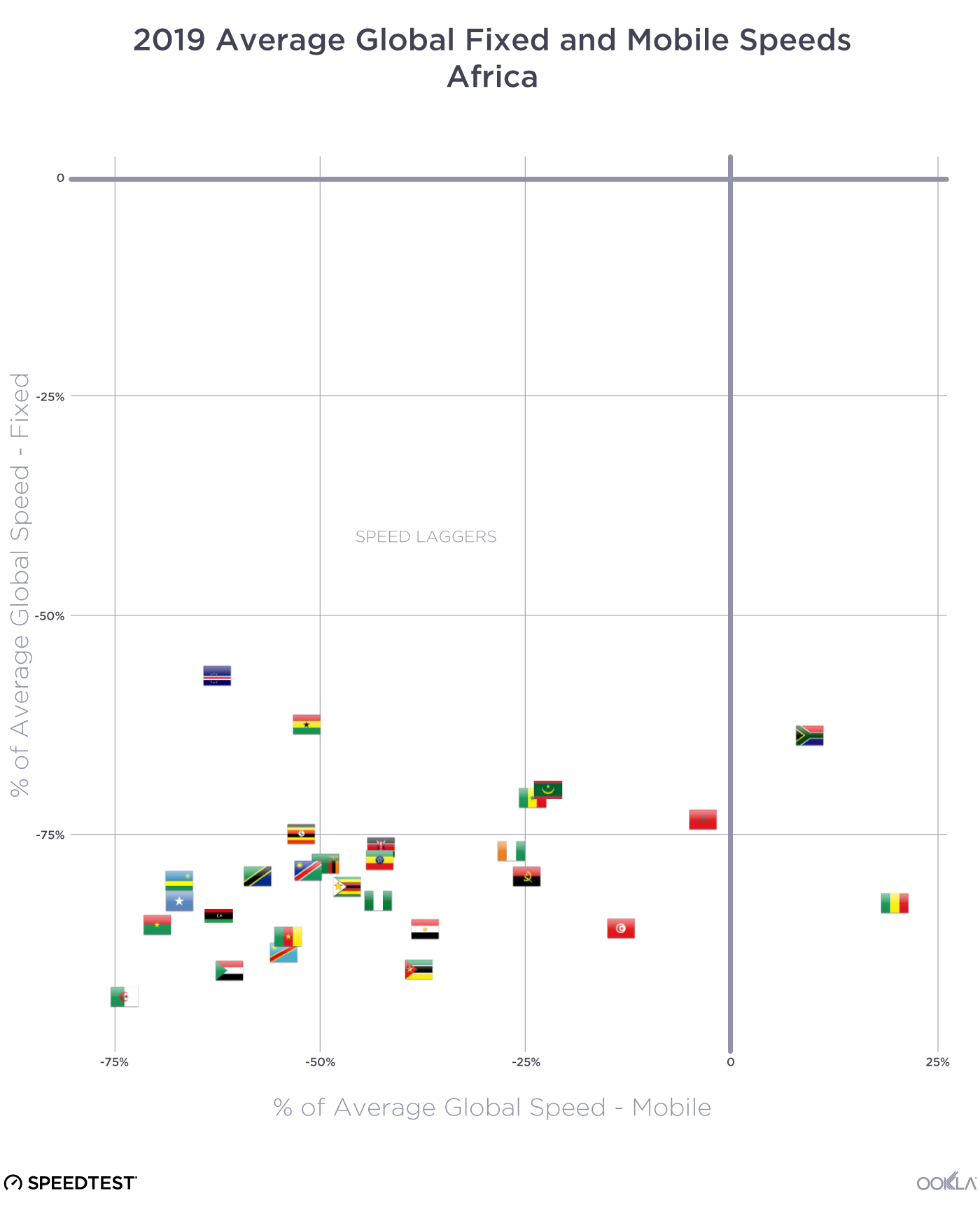
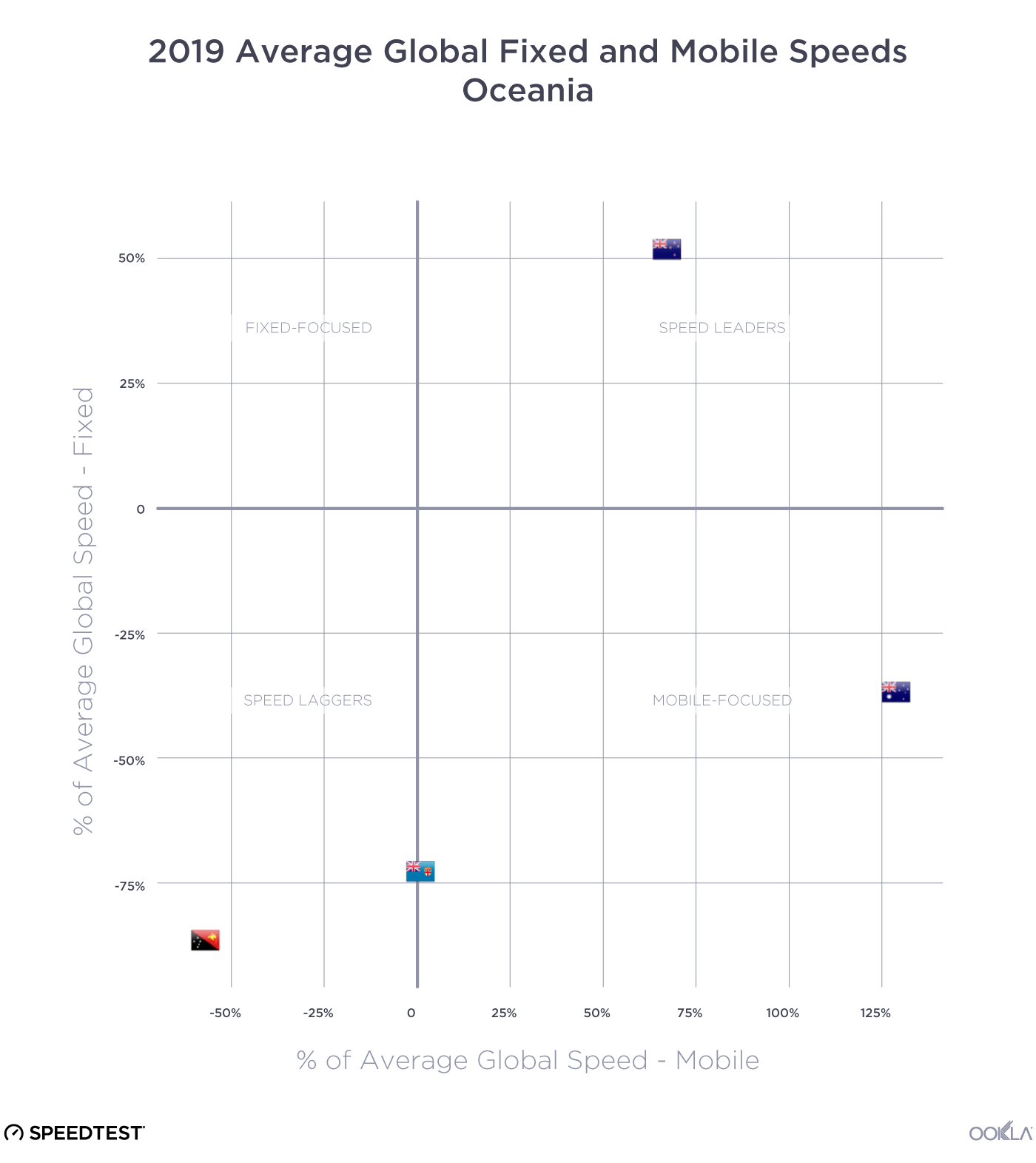
Determining where a digital divide exists is a complex issue that involves identifying where network infrastructure is located, where people need connectivity, and how affordable it is. Although it can be challenging to dig into a specific location, it is evident that there are varying levels of Internet performance worldwide. A quick glance at our data shows that fixed broadband customers are more likely to experience faster networks (measured as an average download speed of 100 Mbps and above) than mobile across the Americas and Europe. The opposite is true for mobile networks across Africa and APAC, where mobile networks are often the primary means of connectivity. Compared to urban areas, rural communities are often ill-equipped for broadband access. Due to a lack of bandwidth (and therefore slower speeds), people in these areas need help doing many things on the internet, such as streaming videos. The US regulator FCC defines broadband in the United States as access to 25 Mbps download and 3 Mbps upload speeds. Areas without those speeds are classified as broadband “digital deserts,” even if those areas have internet access. Although broadband definitions can vary considerably from country to country, we can see in the next section that many areas fall outside any standards of connectivity globally.
Despite the world becoming increasingly connected, many rural and remote areas still struggle to access the internet. For example, large swathes of South America and Africa fall outside terrestrial network coverage. As discussed in our recent article, cellular networks are critical to connecting individuals and businesses as internet access in Africa is predominantly mobile. Before we can start discussing 5G, connecting communities with the internet in general is a priority. Affordable 4G smartphones and targeted financing for under-served demographics are key for bridging the digital divide and reducing poverty, as a World Bank study found that 4G coverage can help cut poverty by up to 4.3%.
5G technology can potentially replace fixed internet access in situations where the cost of fiber deployments is high and rolling out traditional fixed broadband networks isn’t commercially viable. However, in countries like Indonesia, satellite technology may be a more effective solution for connecting remote areas. While 5G Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) and satellite technology can complement each other, the adoption of satellite technology is currently limited by factors such as coverage, device affordability, and service cost. As revealed in our recent article, Starlink outperforms GEO satellites and is a suitable replacement for fixed networks in rural areas. While it may not match the leading cable or fiber providers in terms of median speeds or multi-server latency, satellite internet provides a viable alternative in places where cable and fiber access networks are unavailable. This is mainly due to a more consistent distribution of download performance across Speedtest samples, unlike FWA and DSL-based services, where performance is impacted by the distance from the cell site or exchange/DSLAM.
Fixed and mobile network operators across the globe widely use Speedtest data to enhance Internet quality, improve accessibility, and inform network expansion. The United States Federal Communications Commission and the Malaysian Communications and Multimedia Commission rely on Speedtest data to ensure accountability of telecommunications entities and allocate funds for rural and urban connectivity development. Ookla also licenses data to NGOs and educational institutions to help bridge the digital divide between areas with and without modern Internet access. Our mapping data is used to track results and determine whether broadband infrastructure can handle growth as more people connect devices and technologies demand more bandwidth. We are also actively involved in discussing best practices for ensuring digital transformation and connectivity for all in the APAC region, Central Asia, and Europe. If you are interested in working with us, please reach out.
Keep track of how well your country is performing on Ookla’s Speedtest Global Index™ and get advice on how to plan and optimize your network.
Ookla retains ownership of this article including all of the intellectual property rights, data, content graphs and analysis. This article may not be quoted, reproduced, distributed or published for any commercial purpose without prior consent. Members of the press and others using the findings in this article for non-commercial purposes are welcome to publicly share and link to report information with attribution to Ookla.