5G continues to offer new and exciting ways of rethinking everything from streaming video to performing remote surgery. However, not everyone shares equally in these possibilities as many countries do not have access to 5G and even those that do, do not experience the same level of performance from their 5G connections. We examined Speedtest Intelligence® data from Q3 2021 Speedtest® results to see how 5G speeds have changed, where download speeds are the fastest at the country and capital level, where 5G deployments have increased and what worldwide 5G Availability looked like in Q3 2021. We also looked at countries that don’t yet have 5G to understand where consumers are seeing improvements in 4G access.
5G slowed down at the global level
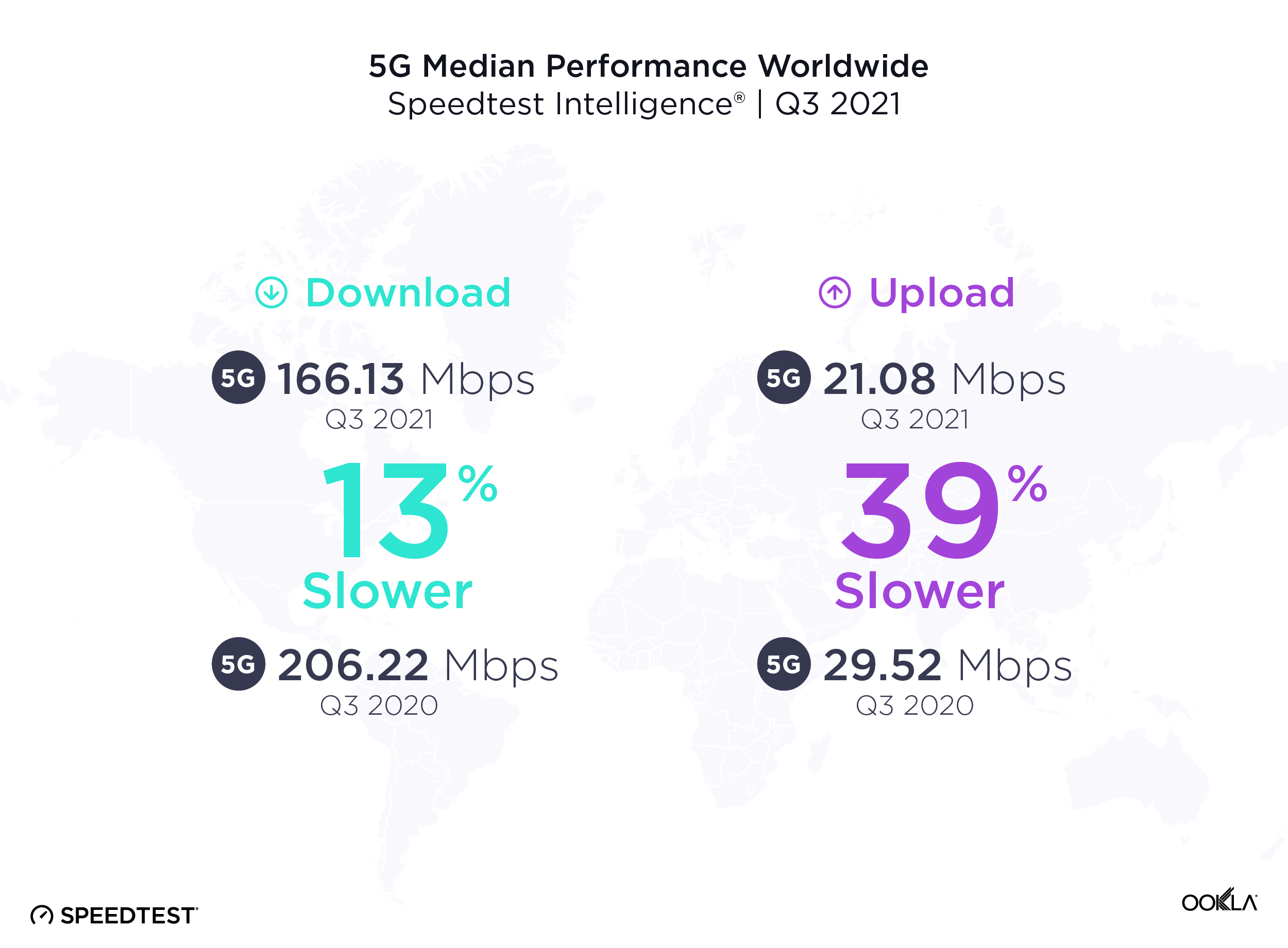
It’s common to see new mobile access technologies slow down as adoption scales, particularly early on in the tech cycle. Over the past year from Q3 2020 to Q3 2021, the median global 5G download speed fell to 166.13 Mbps, down from 206.22 Mbps in Q3 2020. Median upload speed over 5G also slowed to 21.08 Mbps (from 29.52 Mbps) during the same period.
More users are logging on to existing 5G networks, and we’re also at the stage in the evolution of 5G where countries that have historically had slower speeds are starting to offer 5G. In addition, the widespread use of dynamic spectrum sharing that has been used to boost early 5G coverage weighs on 5G download speeds. While the dip in speeds looks like a letdown, it’s more of a compromise to enable broader access. With additional spectrum and further deployments slated for 2022, we anticipate speeds will begin to pick up again.
South Korea had the fastest 5G in the world

South Korea had the fastest median download speed over 5G during Q3 2021, leading a top 10 list that included Norway, United Arab Emirates, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Kuwait, Sweden, China, Taiwan and New Zealand. Sweden, China, Taiwan and New Zealand were new to the top 10 in 2021 while South Africa (whose 5G was brand new last year), Spain and Hungary fell out of the top 10.
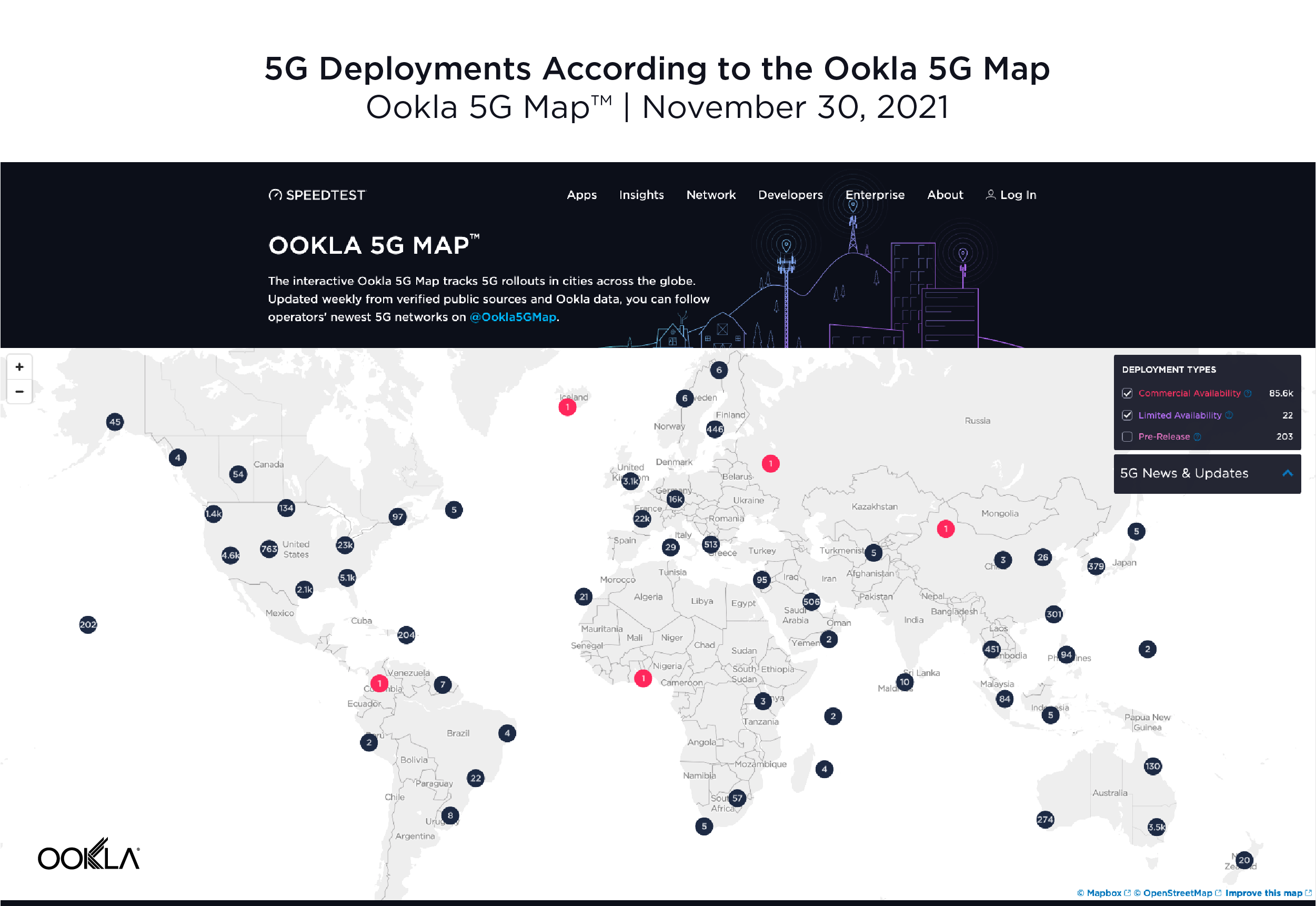
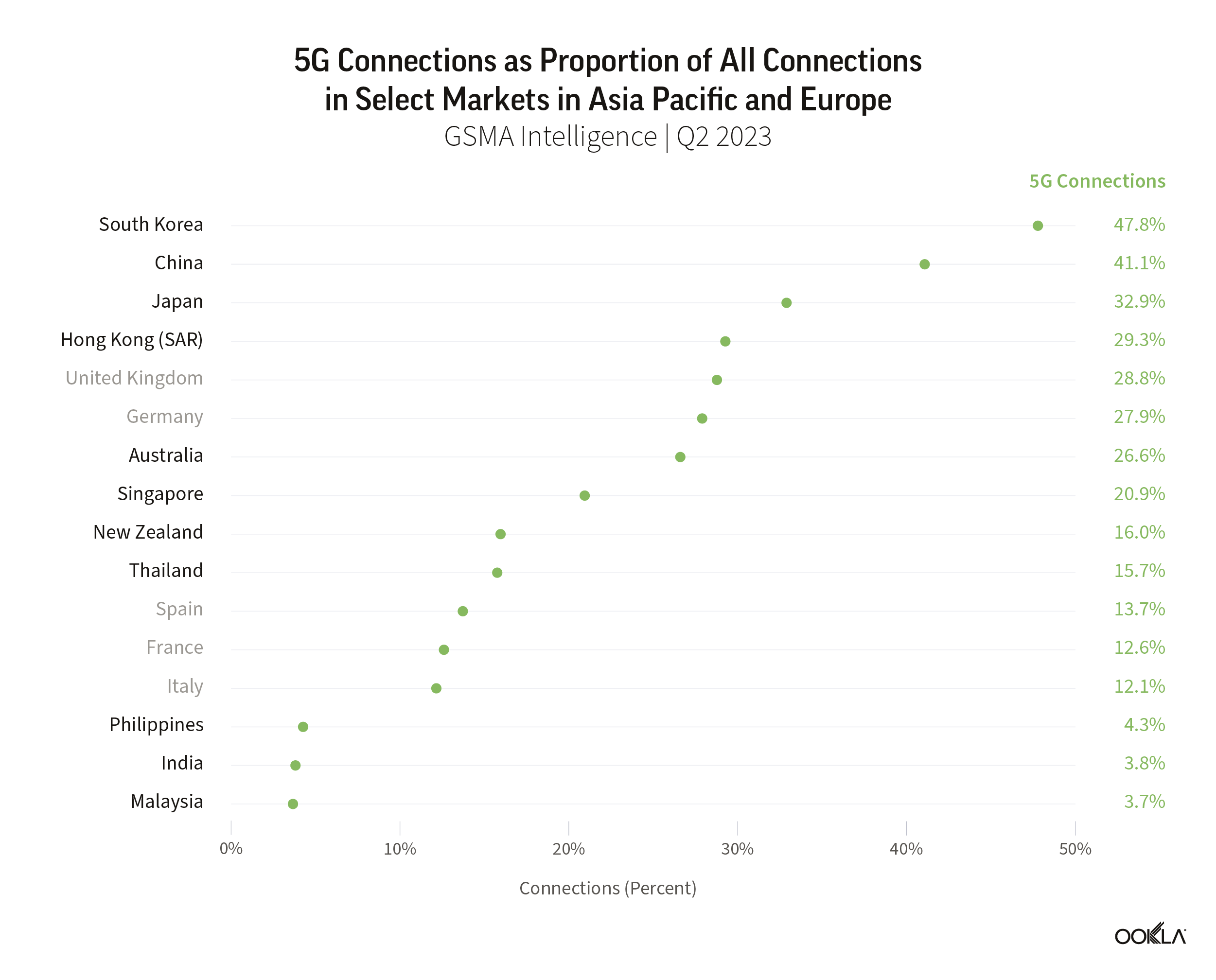
5G expanded to 13 additional countries
According to the Ookla® 5G Map™, there were 5G deployments in 112 countries as of November 30, 2021. That’s up from 99 countries on the same date a year ago. The total number of deployments increased dramatically during the same time period with 85,602 deployments on November 30, 2021 compared to 17,428 on November 30, 2020, highlighting the degree to which 5G networks scaled during the year. Note that there are often multiple deployments in a given city.
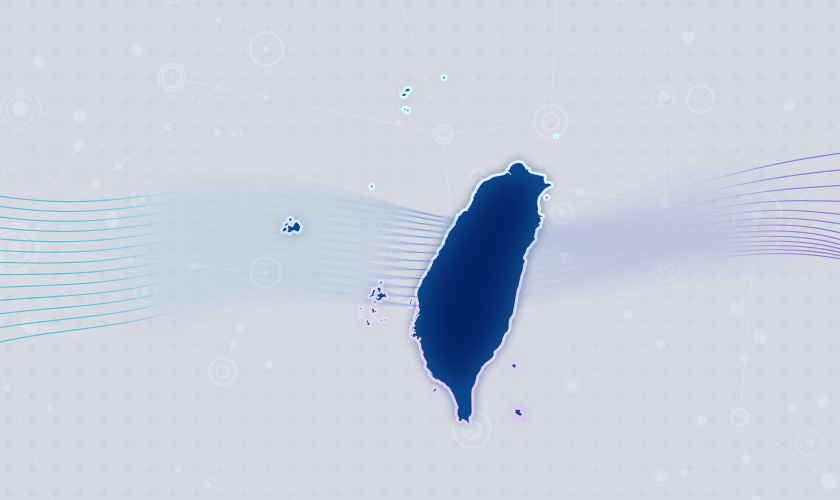
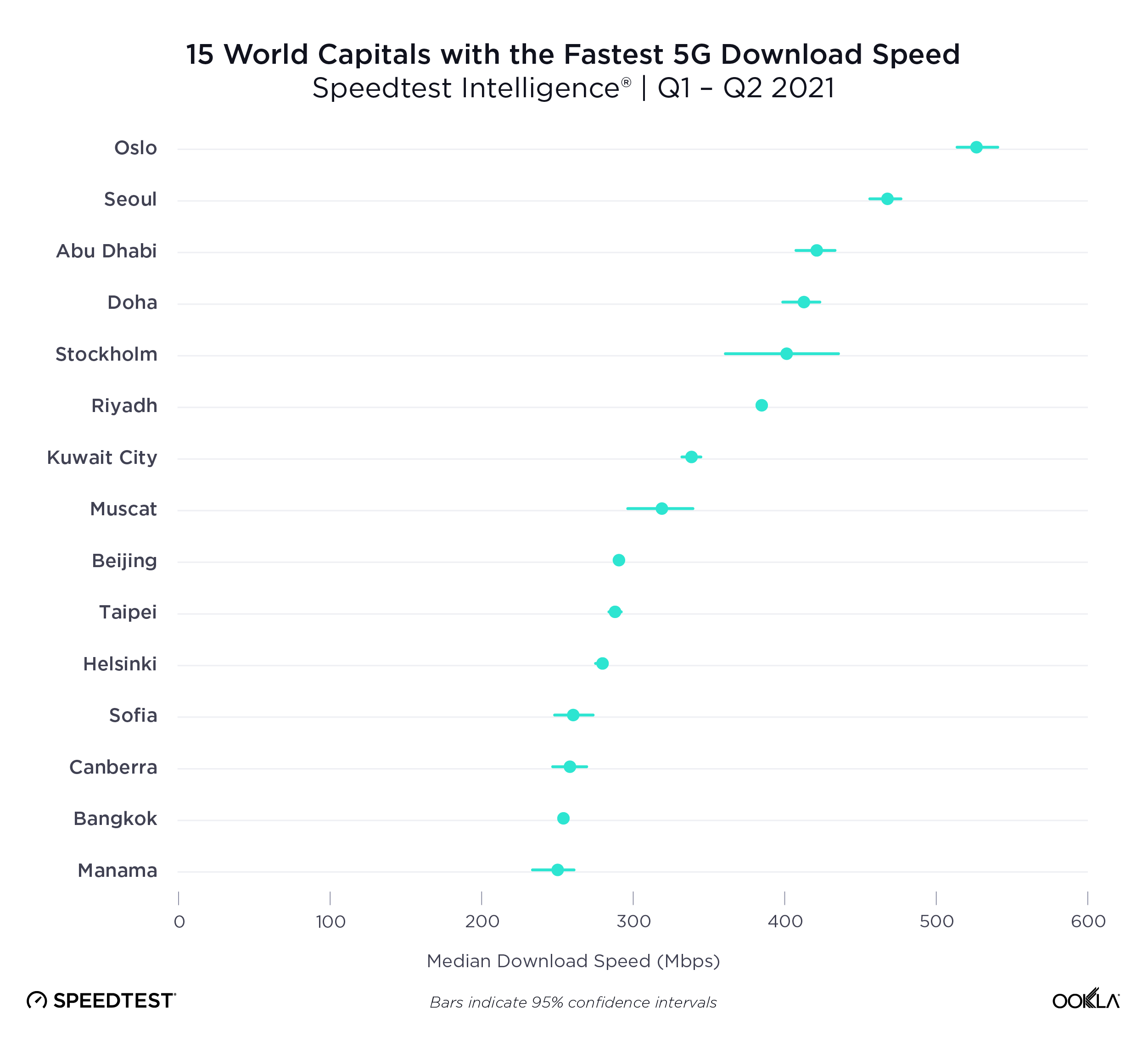
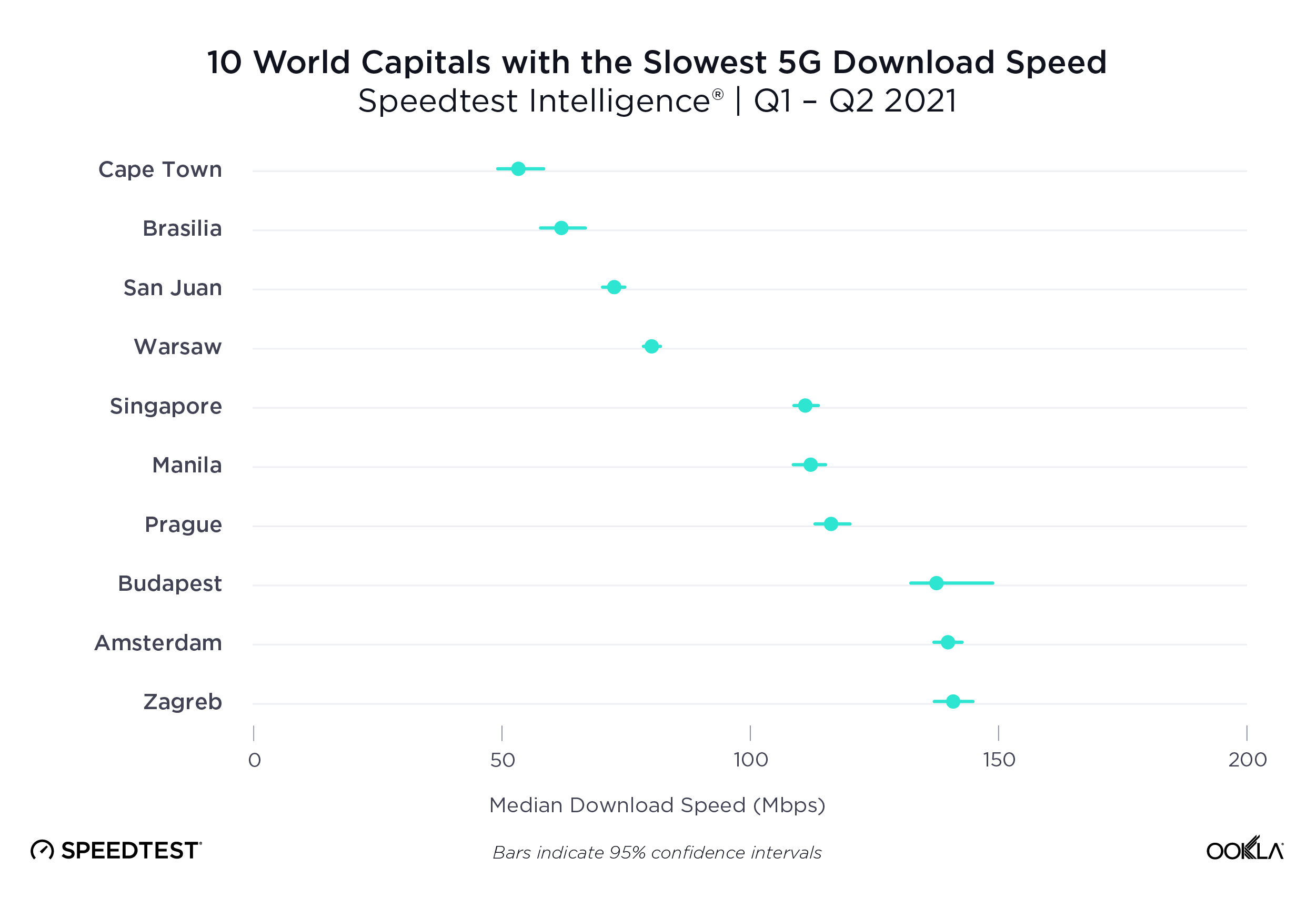
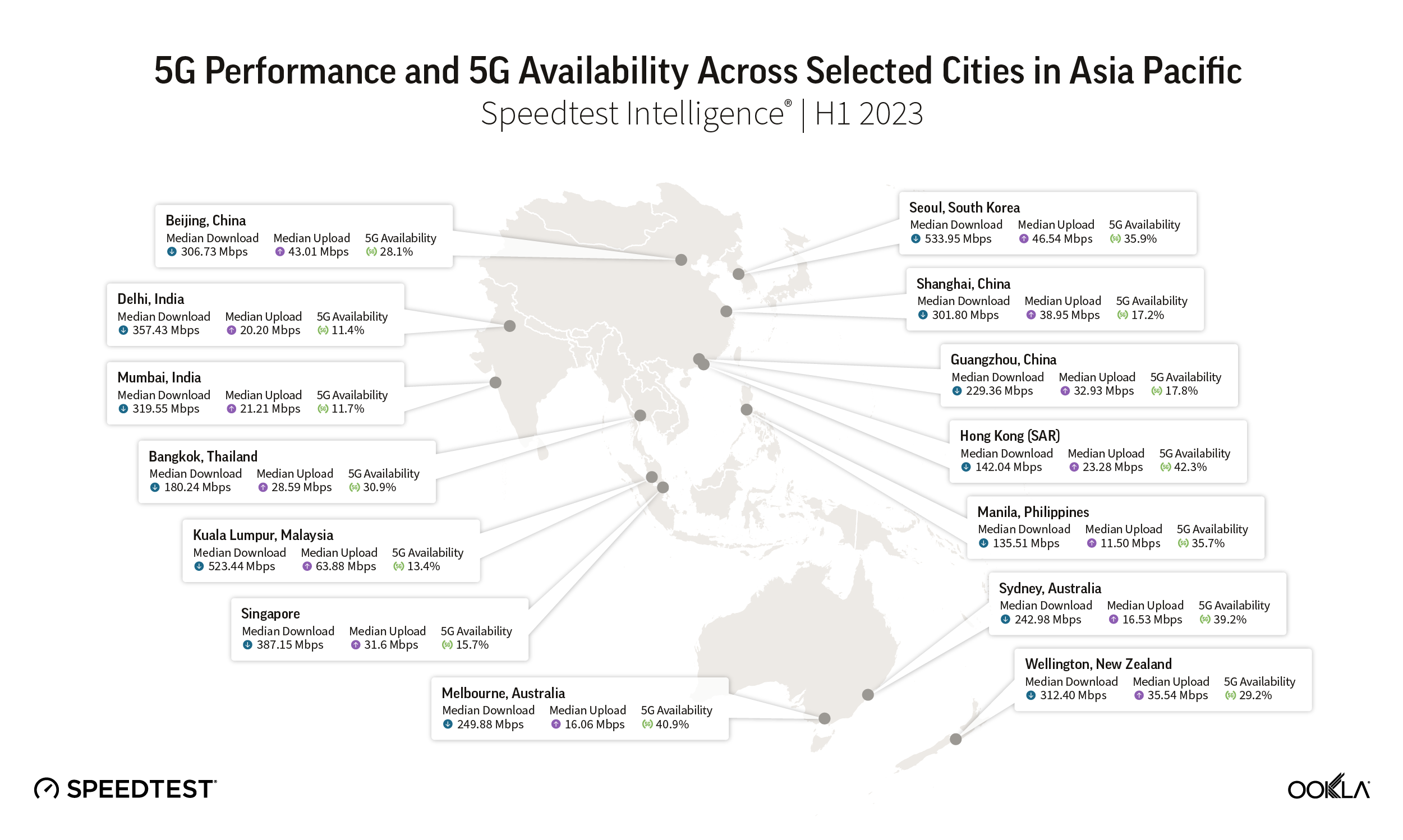
Seoul and Oslo lead world capitals for 5G
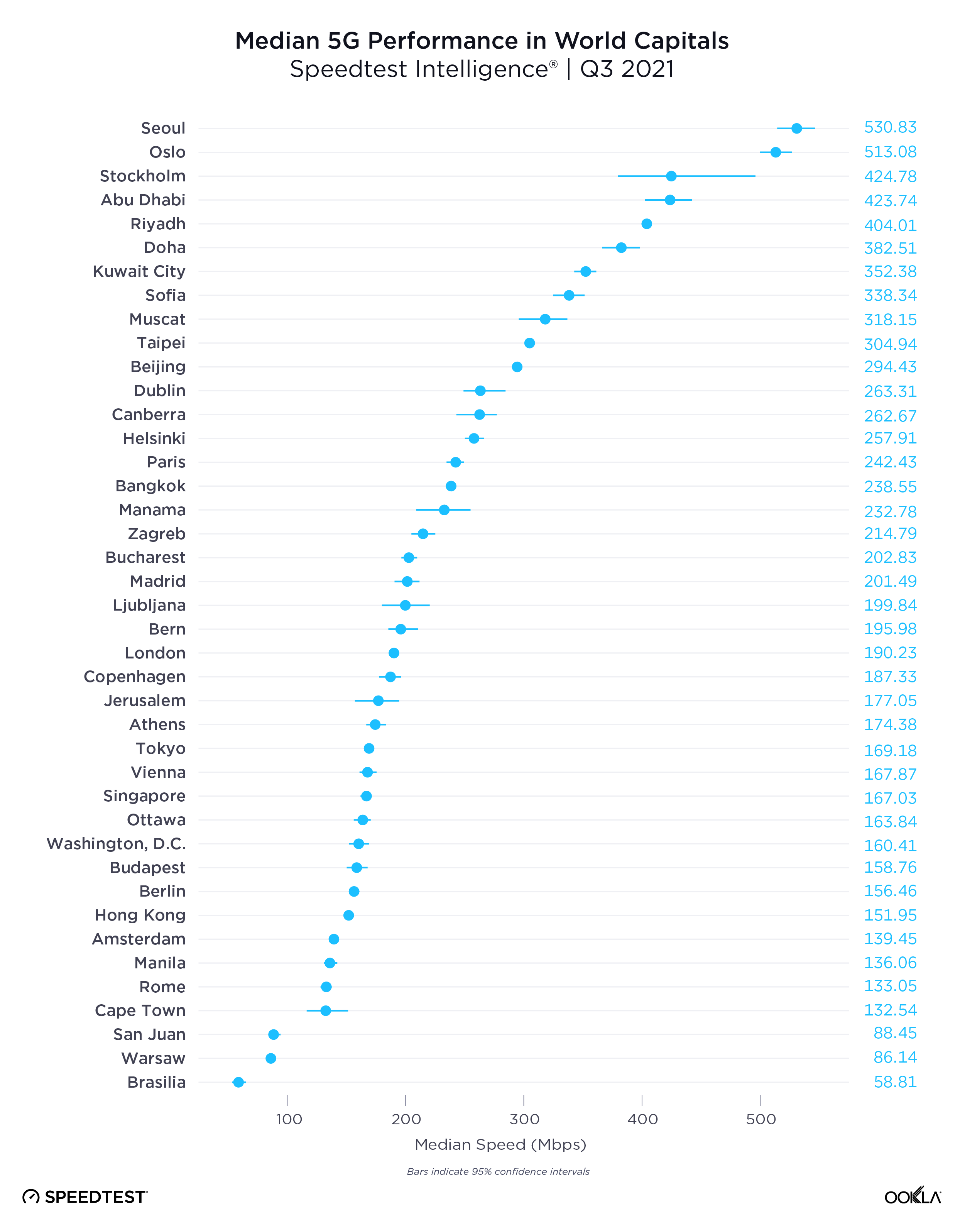
Speedtest Intelligence data from Q3 2021 shows a wide range of median 5G speeds among global capitals. Seoul, South Korea and Oslo, Norway were in the lead with 530.83 Mbps and 513.08 Mbps, respectively; Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates; Riyadh, Saudi Arabia and Doha Qatar followed. Brasilia, Brazil had the slowest median download speed over 5G on our list, followed by Warsaw, Poland; Cape Town, South Africa and Rome, Italy. Stockholm, Sweden and Oslo, Norway had some of the the fastest median upload speeds over 5G at 56.26 Mbps and 49.95 Mbps, respectively, while Cape Town had the slowest at 14.53 Mbps.
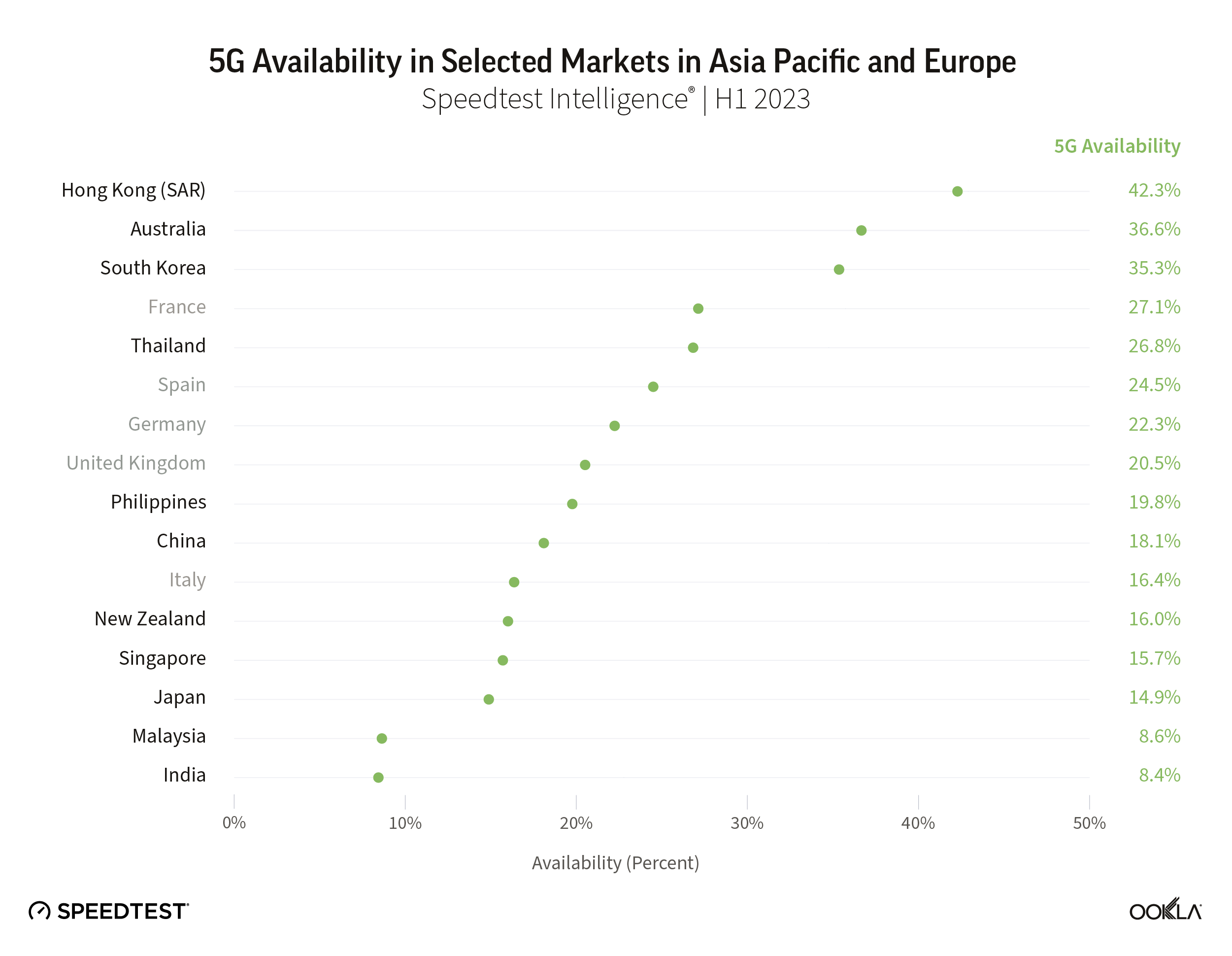
The U.S. had the highest 5G Availability
The presence of 5G is only one indicator in a market, because even in markets where 5G has launched, coverage and adoption can be pretty low. We analyzed 5G Availability to see what percent of users on 5G-capable devices spent the majority of their time on 5G, both roaming and on-network during Q3 2021.
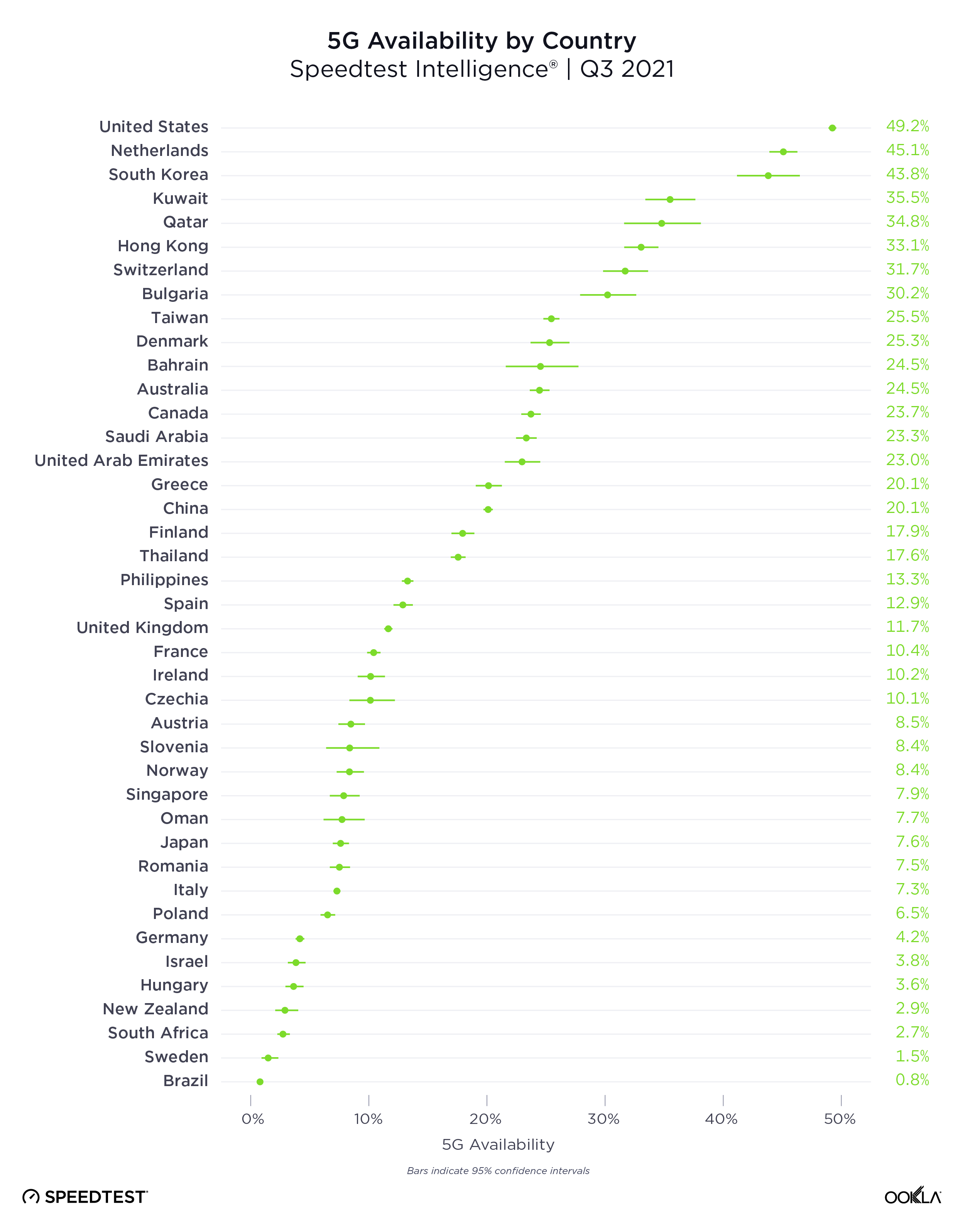
The United States had the highest 5G Availability at 49.2%, followed by the Netherlands (45.1%), South Korea (43.8%), Kuwait (35.5%) and Qatar (34.8%). Brazil had the lowest 5G Availability on our list at 0.8%, followed by Sweden (1.5%), South Africa (2.7%), New Zealand (2.9%) and Hungary (3.6%).
Not all 5G networks are created equal
Ookla Speedtest Intelligence data shows a growing disparity in the performance of 5G networks worldwide, even among the pioneer markets who were among the first to launch the new technology. We see leading markets such as South Korea, Norway, the UAE and China pulling well ahead of key European markets, the U.S. and Japan on 5G download speeds, creating what increasingly looks like two tiers of 5G markets.
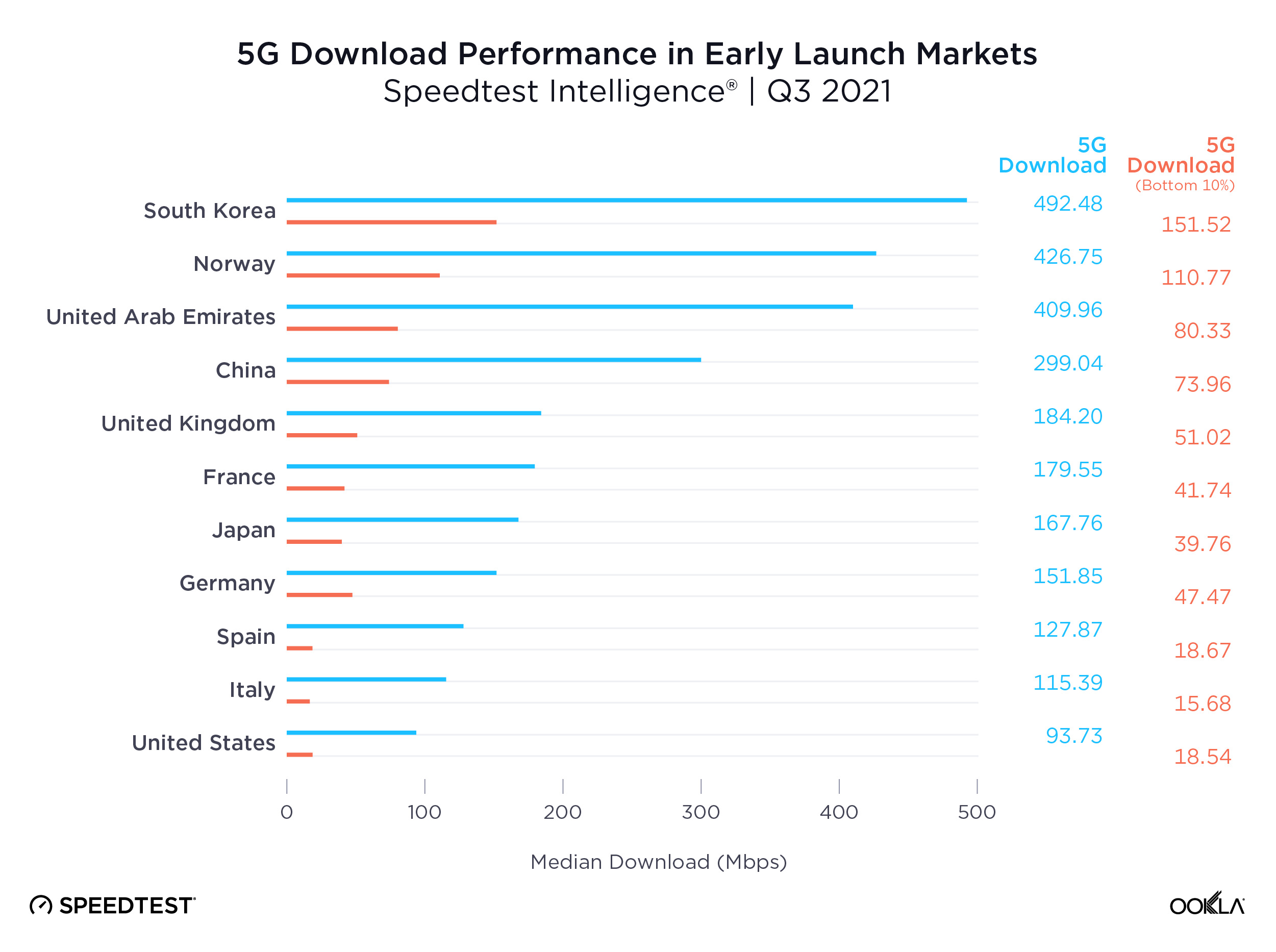
Part of the reason for this divergence is access to key 5G spectrum bands, with Verizon and AT&T in the U.S. for example, soon to deploy their C-band spectrum holdings for 5G use. However, what really seems to separate these markets is the level of 5G network densification. The number of people per 5G base station ranges from 319 in South Korea and 1,531 in China, to 4,224 in the EU and 6,590 in the US, according to the European 5G Observatory’s International Scoreboard during October 2021.
Despite the noise around 6G, 5G still has a long way to run
Median 5G mobile download speeds across these markets are respectable relative to the International Telecommunication Union’s (ITU) IMT-2020 target of 100 Mbps for user experienced download data rates. However, 5G Speedtest® results in each market demonstrate significant variability, with the bottom 10th percentile only recording speeds in excess of the IMT-2020 target in South Korea and Norway, and falling significantly short in many other markets, with Spain, Italy and the U.S. below 20 Mbps.
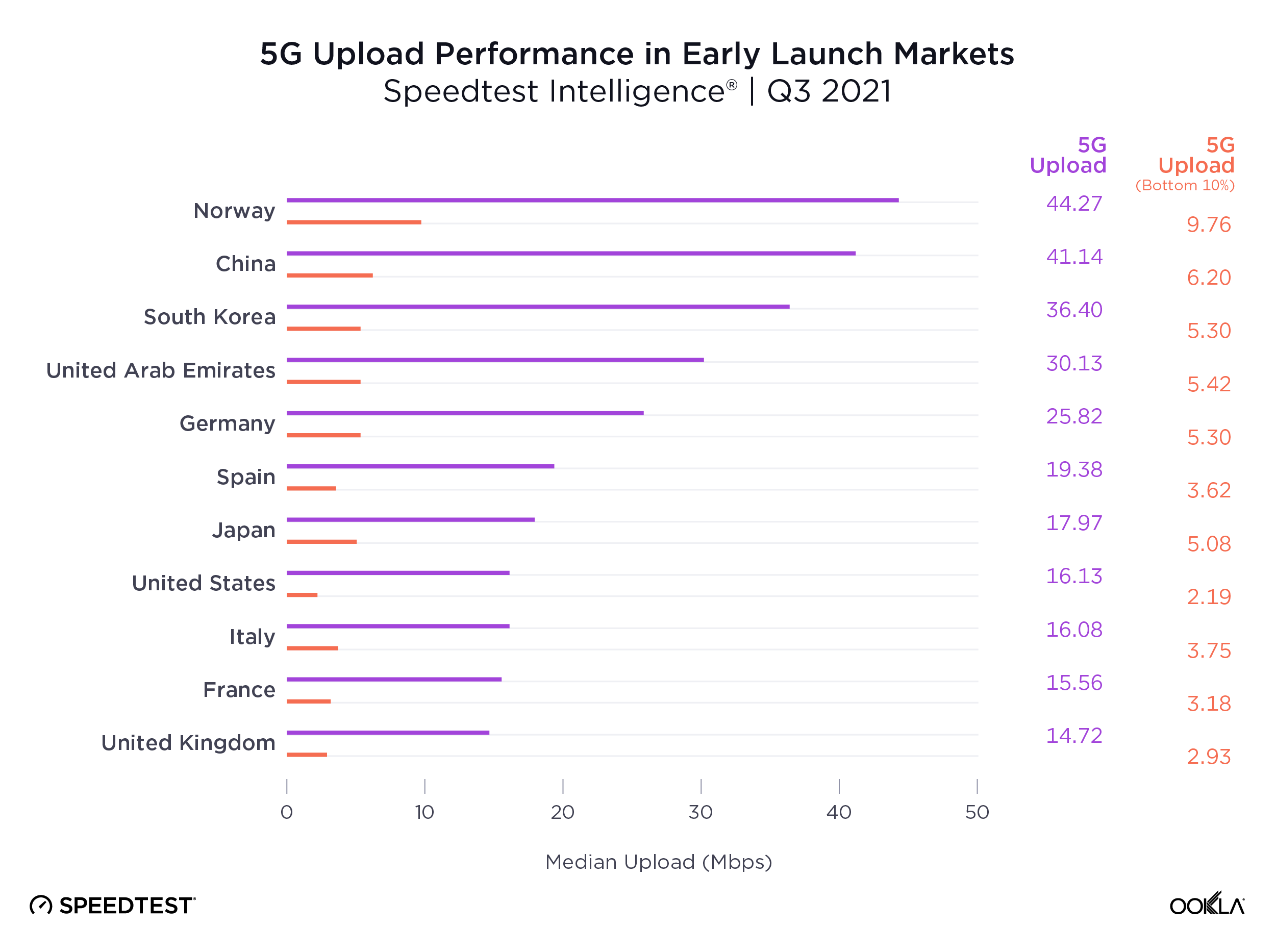
The story gets worse for upload speeds, where no market’s median speed broke the IMT-2020 recommended 50 Mbps, and where the bottom 10th percentile lay in single digits across the board. Operators are clearly prioritizing download speeds over upload, which makes sense given the asymmetric nature of demand, with most consumer applications requiring higher download speeds. However, as operators increasingly look to target the enterprise market with 5G connectivity and consumer demand for services such as video calling and mobile gaming continues to rise, operators will need to boost upload speeds.
Demand for mobile internet bandwidth continues to grow, up 43% year-on-year in Q3 2021 according to Ericsson’s latest mobility report. Looking ahead to 2022, operators will need to increase the capacity of their 5G networks to tackle this growing demand while driving network speeds to new heights. We’ve seen the impact the deployment of new spectrum can have on congested networks during 2021, with Reliance Jio witnessing a bump in 4G LTE performance and consumer sentiment following its acquisition of additional spectrum in India.
Where 5G still fails to reach
Speedtest Intelligence showed 70 countries in the world where more than 20% of samples were from 2G and 3G connections (combined) during Q3 2021 and met our statistical threshold to be included. These are mostly countries where 5G is still aspirational for a majority of the population. As excited as we are about the expansion of 5G, we do not want to see these countries left behind. Not only are 2G and 3G decades old, they are only sufficient for basic voice and texting, social media and navigation apps. To deliver rich media experiences or video calling, users need access to 4G or higher. Having so many consumers on 2G and 3G also prevents mobile operators from refarming that spectrum to make 4G and 5G networks more efficient.
Countries That Still Rely Heavily on 2G and 3G Connections
Speedtest IntelligenceⓇ | Q3 2021
| Country | 2G & 3G Samples |
|---|---|
| Central African Republic | 89.9% |
| Palestine | 84.7% |
| Yemen | 72.4% |
| Turkmenistan | 71.8% |
| Micronesia | 56.3% |
| Madagascar | 55.0% |
| Belarus | 53.2% |
| Rwanda | 51.7% |
| Kiribati | 48.4% |
| Equatorial Guinea | 47.6% |
| Afghanistan | 44.4% |
| South Sudan | 43.4% |
| Guyana | 42.3% |
| Guinea | 37.0% |
| Angola | 36.8% |
| Cape Verde | 35.9% |
| Tajikistan | 35.6% |
| Zimbabwe | 34.7% |
| Benin | 34.4% |
| Togo | 33.8% |
| Ghana | 33.0% |
| Sierra Leone | 31.7% |
| Antigua and Barbuda | 30.2% |
| Vanuatu | 30.1% |
| Lesotho | 30.0% |
| Syria | 29.6% |
| Moldova | 29.4% |
| Saint Kitts and Nevis | 28.9% |
| Mozambique | 28.8% |
| Sudan | 28.4% |
| Palau | 28.3% |
| Grenada | 28.1% |
| Tanzania | 27.6% |
| Uganda | 27.5% |
| Niger | 27.5% |
| Gabon | 27.5% |
| Haiti | 27.4% |
| Suriname | 27.4% |
| Tonga | 27.3% |
| Liberia | 27.0% |
| Namibia | 26.7% |
| Swaziland | 26.5% |
| The Gambia | 26.3% |
| Saint Vincent and the Grenadines | 26.3% |
| Dominica | 26.3% |
| Somalia | 26.1% |
| Cook Islands | 26.0% |
| Zambia | 25.9% |
| Barbados | 25.7% |
| Armenia | 25.5% |
| Algeria | 25.4% |
| Papua New Guinea | 25.2% |
| Jamaica | 24.5% |
| Venezuela | 24.2% |
| Ethiopia | 24.1% |
| Uzbekistan | 24.0% |
| El Salvador | 23.5% |
| Honduras | 23.1% |
| Nigeria | 23.0% |
| Solomon Islands | 22.8% |
| Caribbean Netherlands | 22.7% |
| Botswana | 22.3% |
| Anguilla | 21.7% |
| Mauritania | 20.6% |
| Saint Lucia | 20.5% |
| Bosnia and Herzegovina | 20.3% |
| Burundi | 20.3% |
| Ecuador | 20.2% |
| Ukraine | 20.1% |
| Trinidad and Tobago | 20.0% |
We were pleased to see the following countries come off the list from last year, having dropped below the 20% threshold: Azerbaijan, Bangladesh, Belize, Burkina Faso, Cameroon, Costa Rica, Côte d’Ivoire, DR Congo, Iraq, Kenya, Laos, Libya, Maldives, Mali, Mauritius, Mongolia, Nicaragua, Paraguay and Tunisia. While countries like Palestine, Suriname, Ethiopia, Haiti and Antigua and Barbuda are still on this list, they have improved the percentage of their samples on these outmoded technologies when compared to last year (dropping 10-15 points, respectively), 2G and 3G samples in Belarus increased 6.7 points when comparing Q3 2021 to Q3 2020.
We’re excited to see how performance levels will normalize as 5G expands to more and more countries and access improves. Keep track of how well your country is performing on Ookla’s Speedtest Global Index™.
Ookla retains ownership of this article including all of the intellectual property rights, data, content graphs and analysis. This article may not be quoted, reproduced, distributed or published for any commercial purpose without prior consent. Members of the press and others using the findings in this article for non-commercial purposes are welcome to publicly share and link to report information with attribution to Ookla.










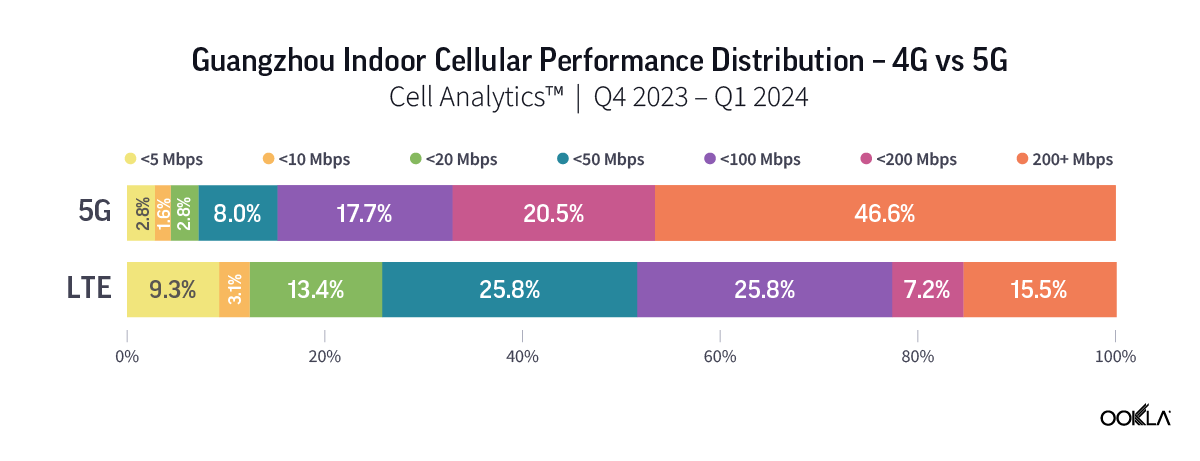
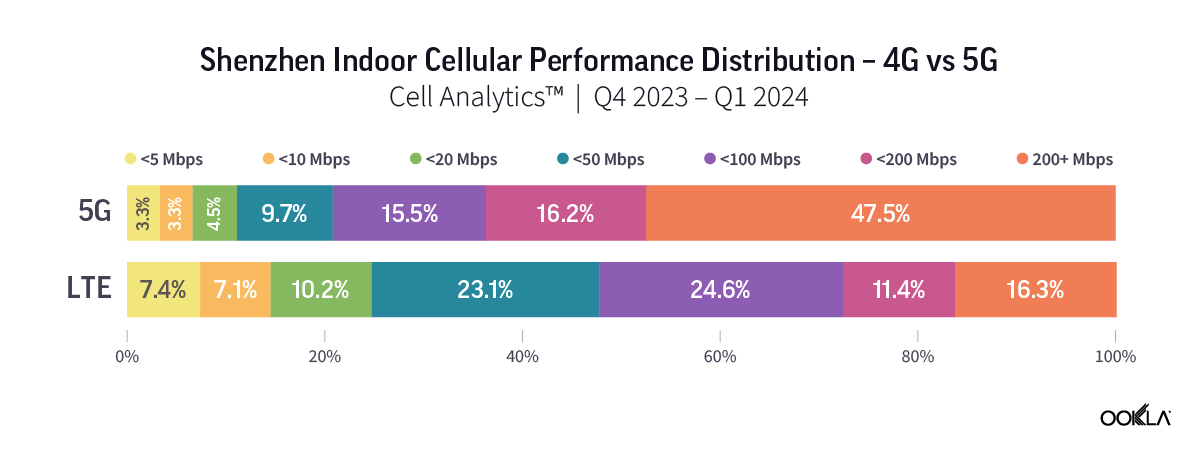
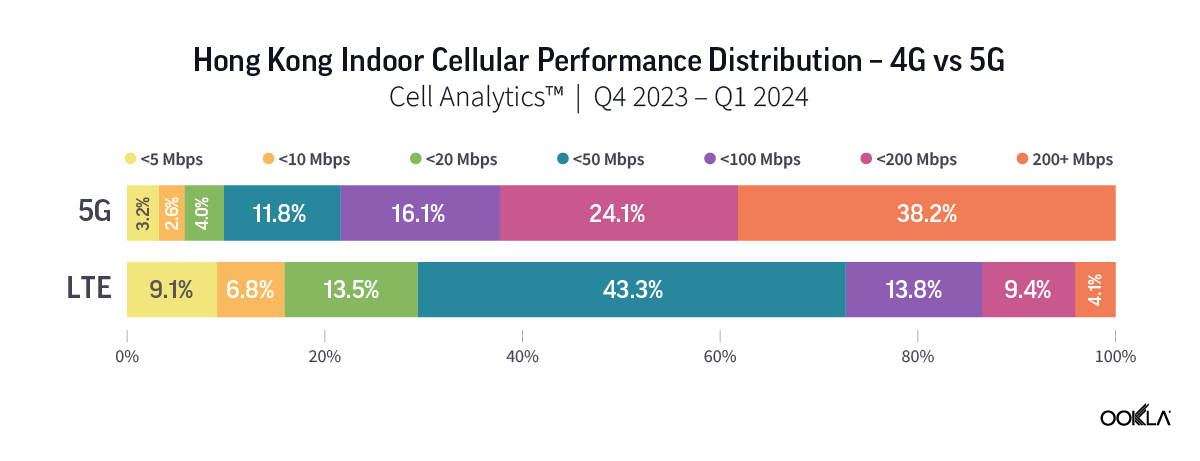
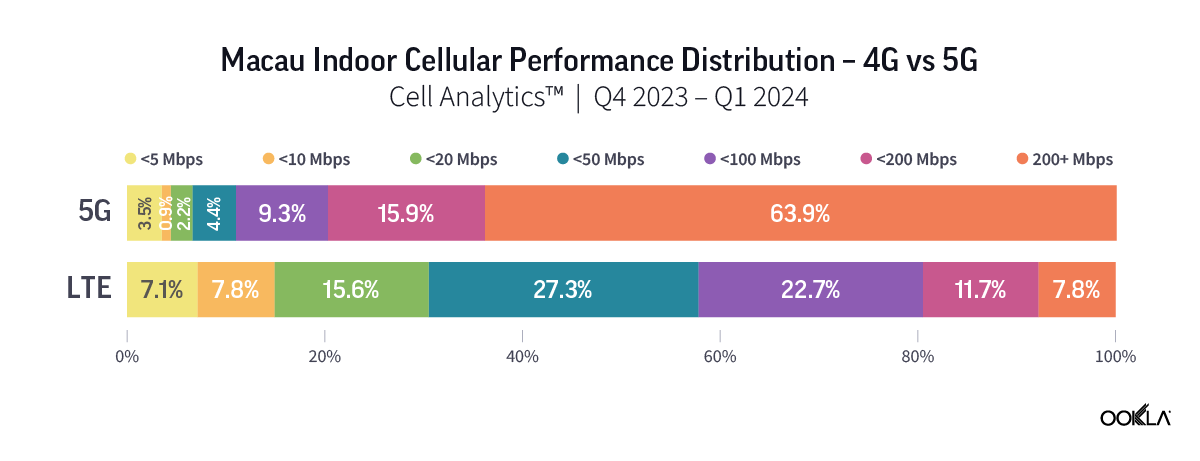
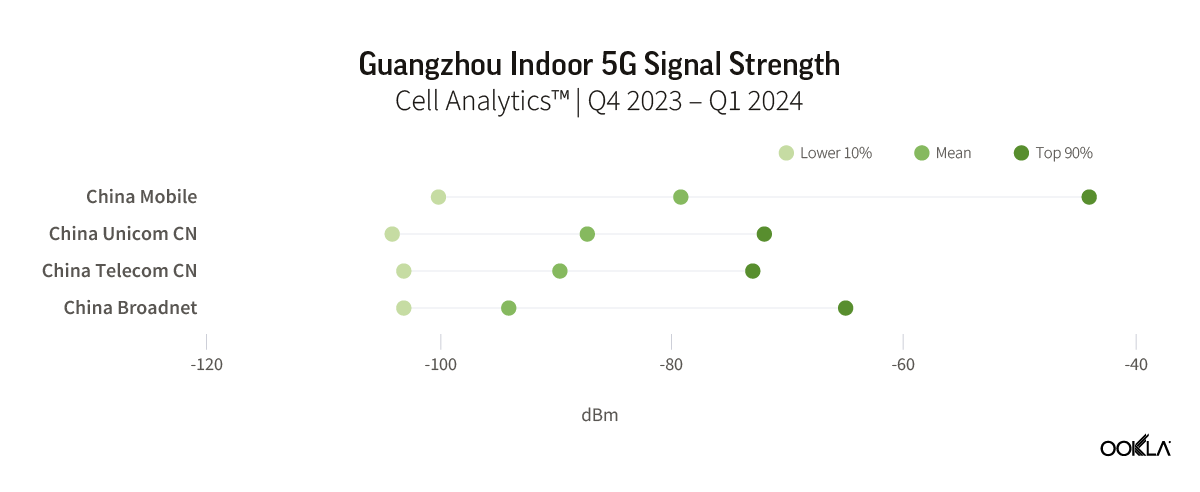
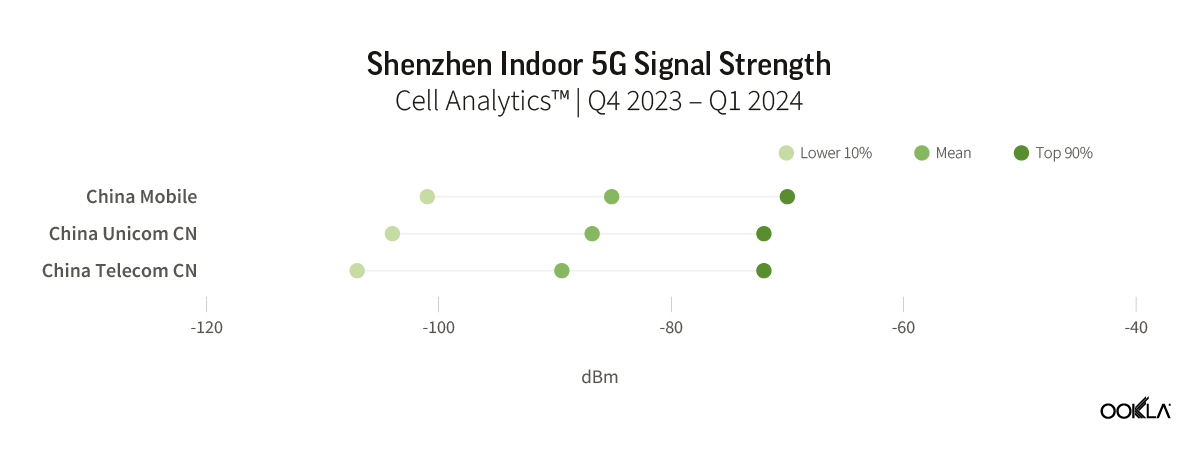
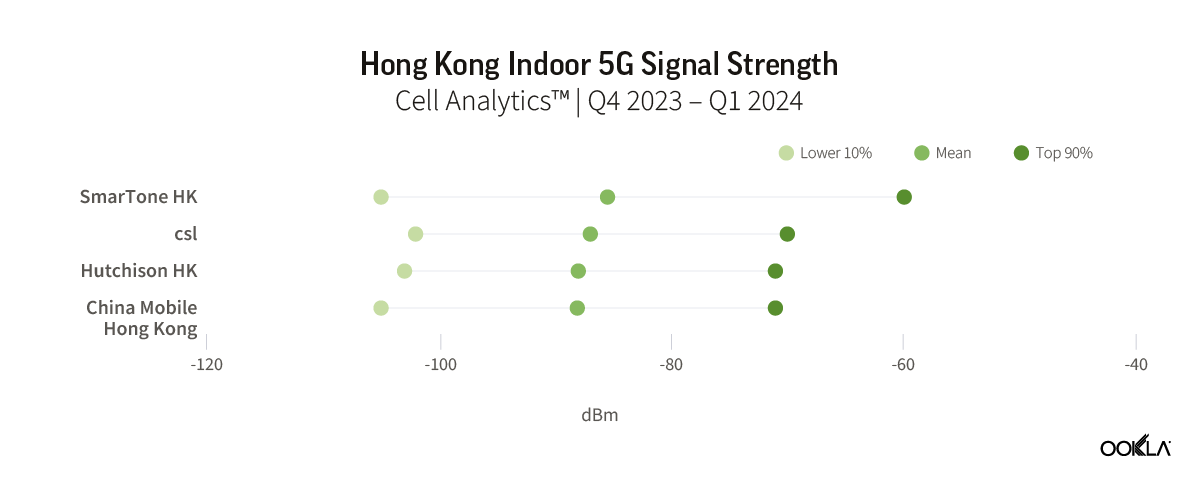
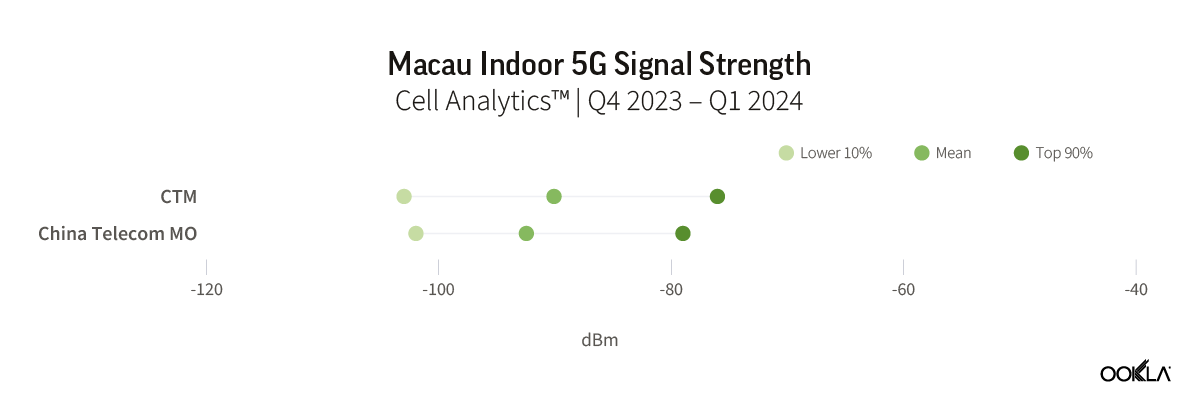

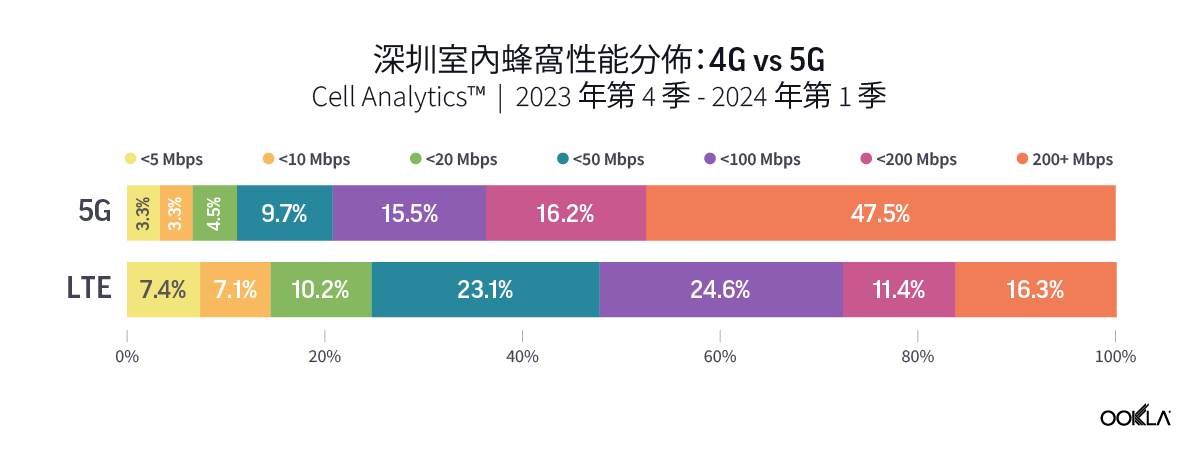
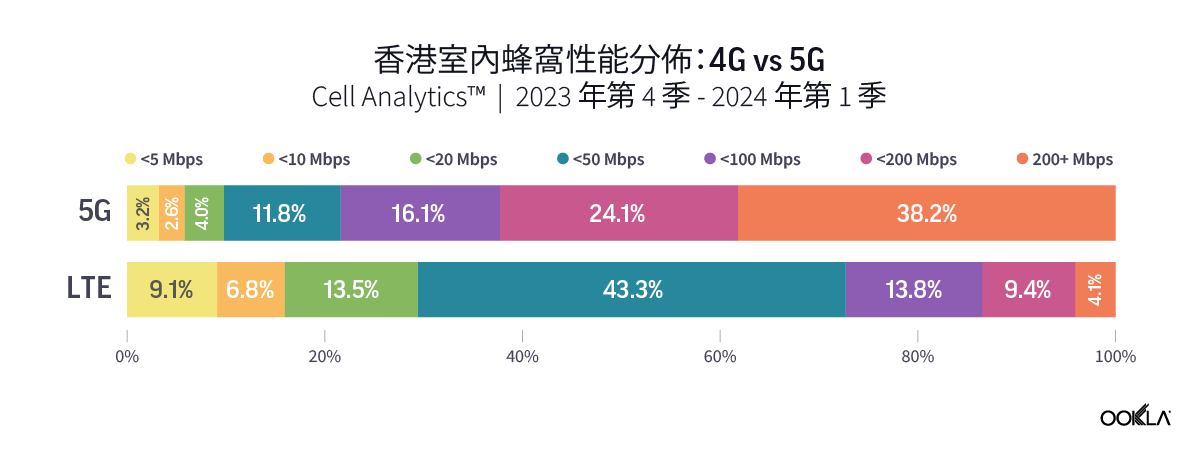
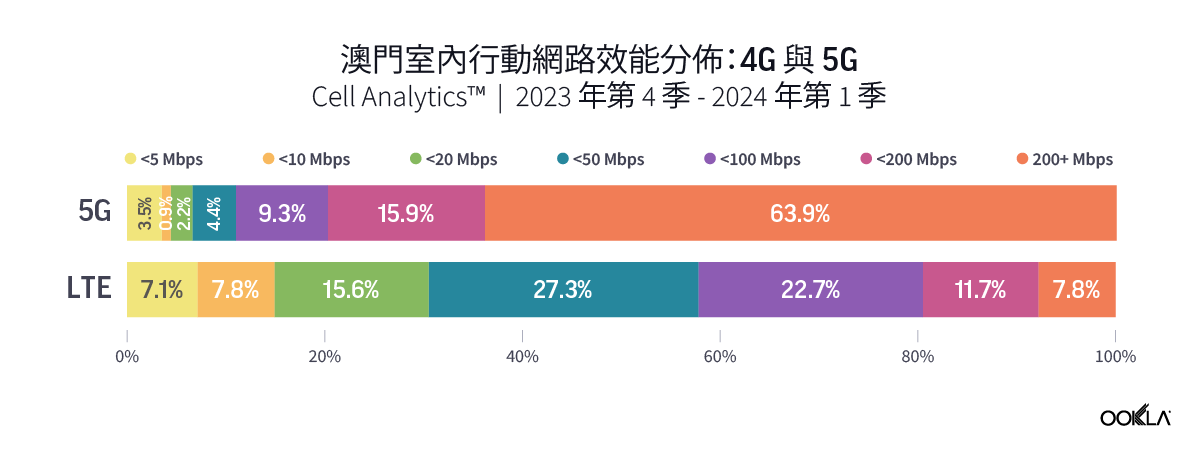
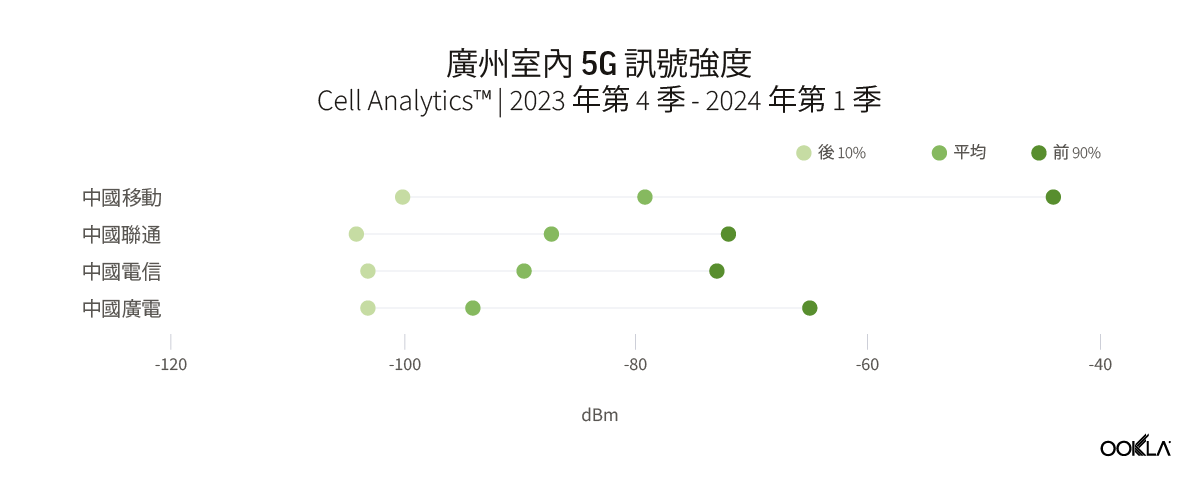
 Speedtest Global Index™ Market Analyses from Ookla® identify key data about internet performance in countries across the world. This quarter we’ve provided updated analyses for 21 markets about top mobile and fixed broadband providers as well as device and chipset manufacturers and some city-level data. Click a country in this list to see highlights or scroll through the article to learn about all 21 markets:
Speedtest Global Index™ Market Analyses from Ookla® identify key data about internet performance in countries across the world. This quarter we’ve provided updated analyses for 21 markets about top mobile and fixed broadband providers as well as device and chipset manufacturers and some city-level data. Click a country in this list to see highlights or scroll through the article to learn about all 21 markets: