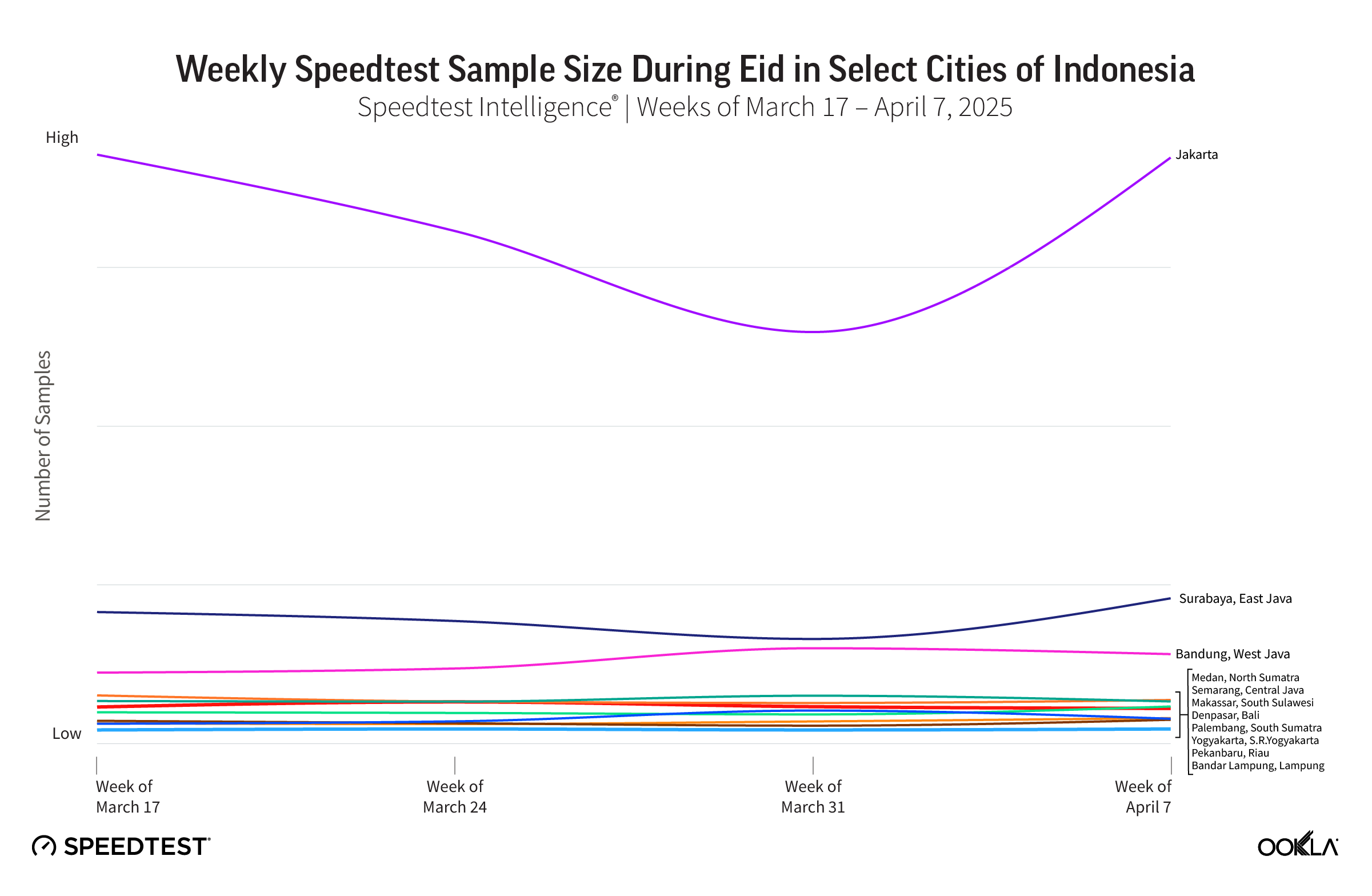
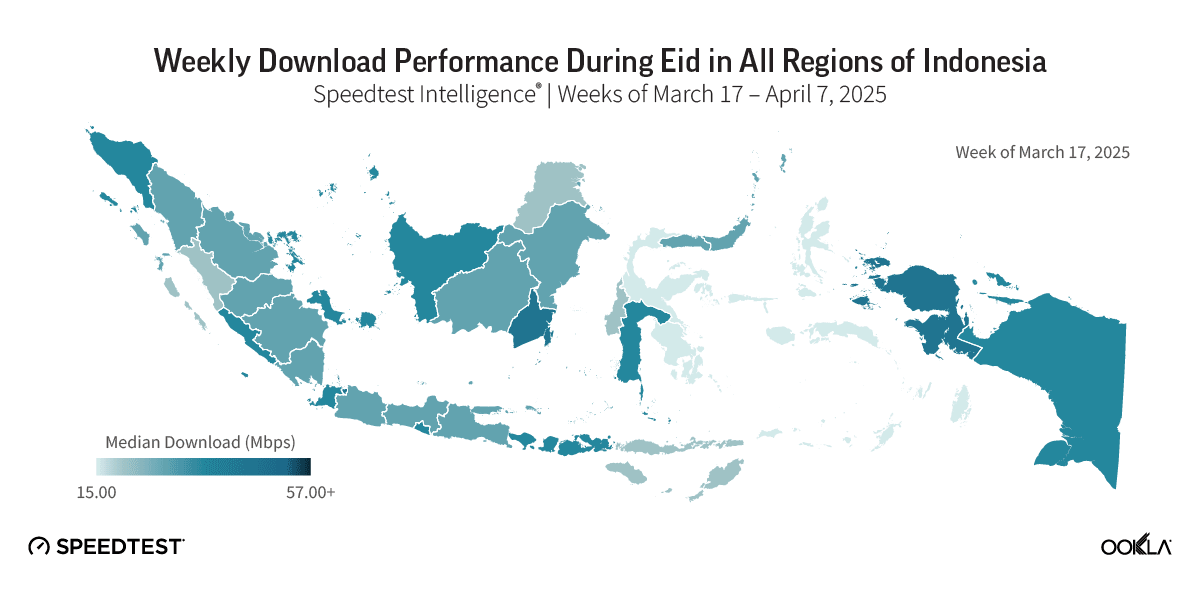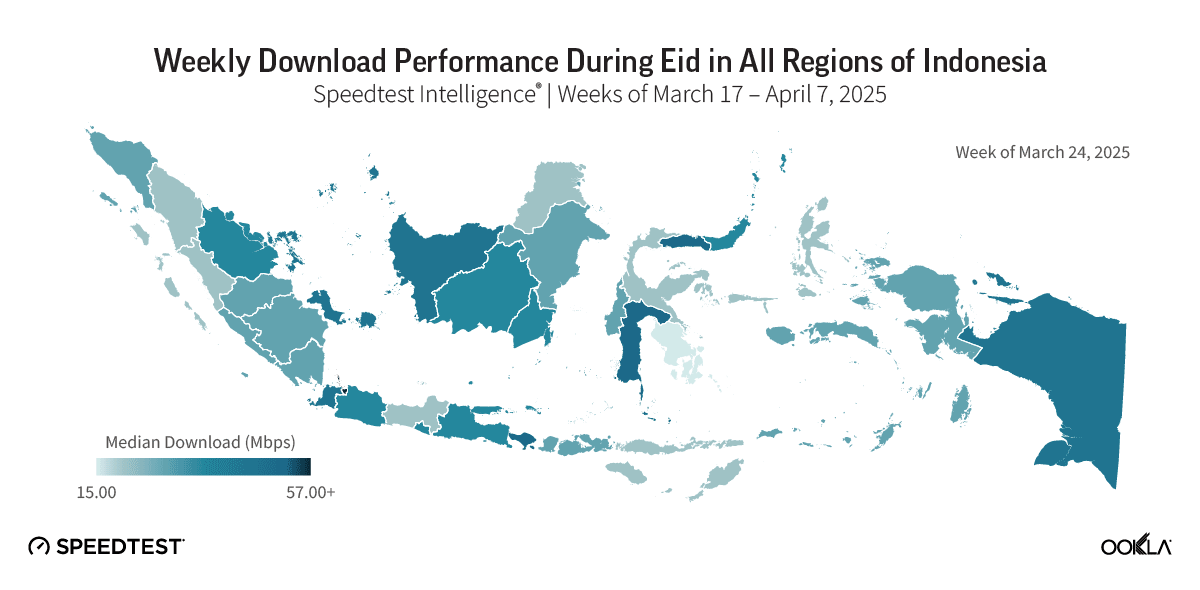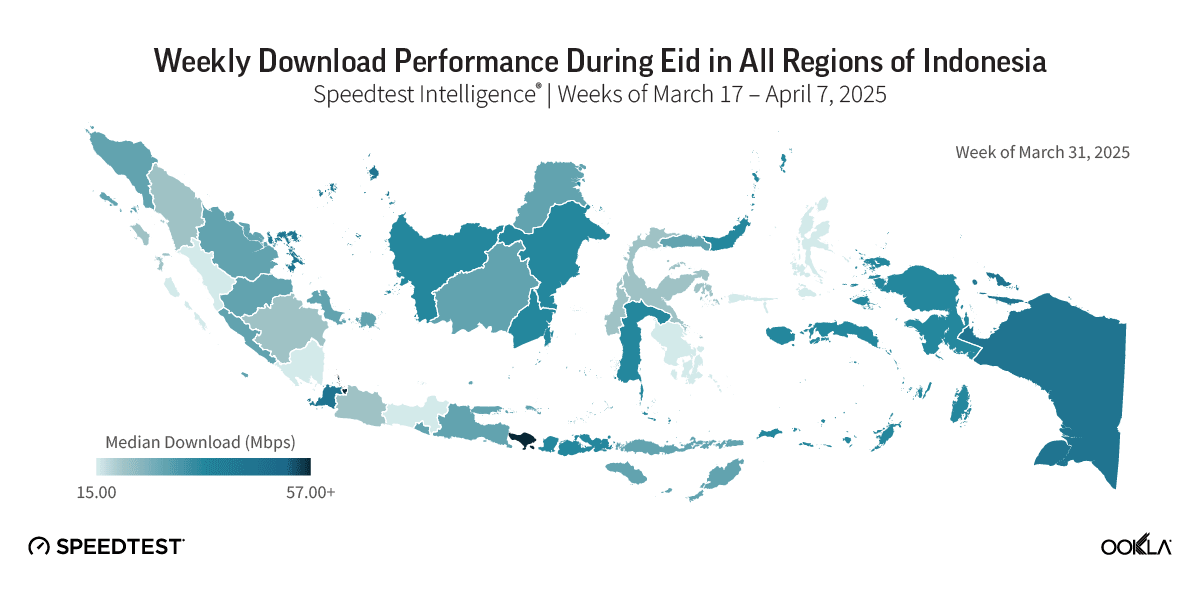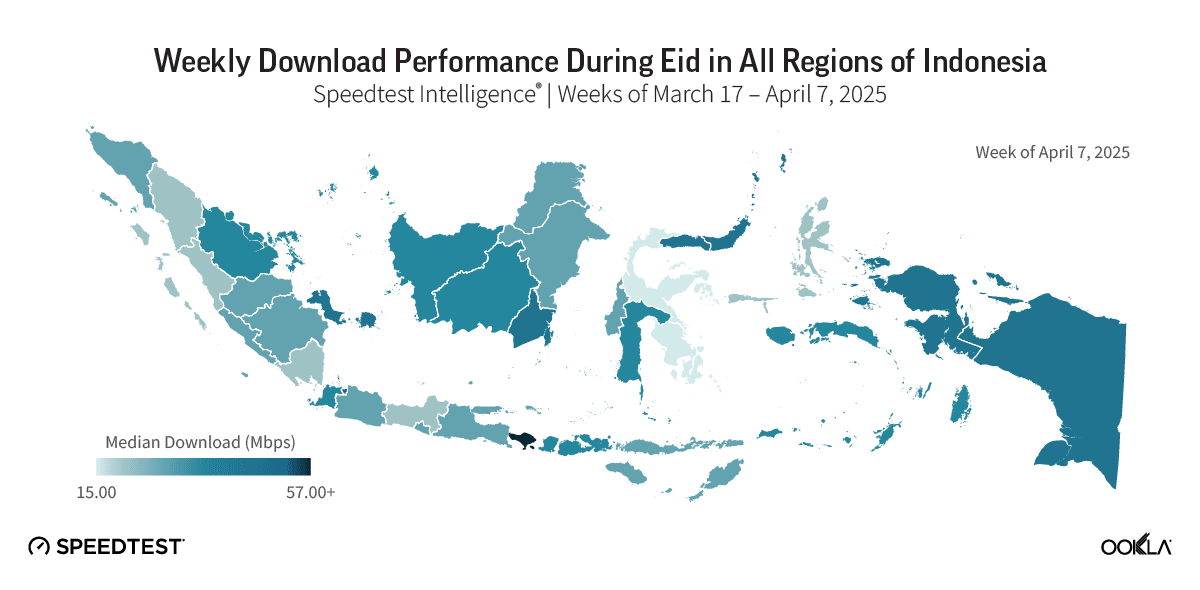
Japan’s mobile market is one of the world’s most dynamic and technologically advanced, characterized by intense competition among four major operators: NTT DOCOMO, KDDI (au), SoftBank, and Rakuten Mobile. Each operator employs distinct strategies to secure market share in this highly competitive landscape. This report assesses 5G network performance and availability across Japan’s competitive mobile market.
Key Takeaways
- 4G remains the essential mobile connectivity service nationwide, while 5G access is geographically segmented. 5G Availability varies dramatically by location, ranging nearly fourfold from a high of 35.2% in Osaka to a low of 9.1% in Yamanashi. Conversely, the 4G network provides a stable and highly reliable foundation, with 4G Availability consistently clustered above the 97% mark across all major operators.
- Japan’s mobile market is strategically split, with operators prioritizing distinct performance goals. SoftBank and au lead in median download speed across all technologies, at 62.05 Mbps and 57.85 Mbps, respectively. Conversely, Rakuten Mobile achieved the fastest median 5G download speed at 128.39 Mbps.
- Operators’ 10th percentile download speeds across prefectures show that highly urbanized prefectures consistently receive higher minimum speeds, reflecting greater site density and capacity investment. NTT DOCOMO maintained the most consistent lower 10th percentile speed across prefectures, peaking at 41 Mbps in Ishikawa. SoftBank’s lower 10th percentile speeds show a significant variation that directly correlates with the urban-rural divide, peaking at 49 Mbps in Aomori but dropping to 4 Mbps in Nagano.
SoftBank leads all technologies in median download speed, while Rakuten Mobile achieves highest 5G speeds
Japan’s mobile telecommunications landscape features highly competitive networks and accelerating technology migration, which is reflected in operator performance data. Speedtest Intelligence®data from Q3 2025 shows SoftBank leading in median download speed across all technologies combined, at 62.05 Mbps, slightly surpassing au’s 57.85 Mbps. SoftBank’s leading performance stems from its notable network modernization and optimization initiatives, which aim to ensure reliable service delivery. Rakuten Mobile and NTT DOCOMO followed with median download speeds of 52.45 Mbps and 50.50 Mbps, respectively.
Conversely, Rakuten Mobile led in median 5G performance during the same period. Although its median download speed for all technologies combined was 52.45 Mbps (ranking third), Rakuten’s 5G median download and upload speeds were significantly higher at 128.39 Mbps and 22.34 Mbps, respectively. SoftBank followed with a median download speed of 127.45 Mbps and upload speed of 17.51 Mbps.
Nationwide availability data confirms extensive 4G baseline and differing 5G investment priorities
The Japanese mobile market operates under near-universal adoption, with approximately 194 million cellular connections and a penetration rate of 157% as of early 2025. This saturation dictates that competition is driven primarily by quality of service, speed, and next-generation network availability. According to the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications (MIC), the national 5G population coverage reached 98.4% by the end of fiscal year 2024.
Analysis of Network Availability using Ookla Speedtest Intelligence data from Q3 2025 measures how frequently mobile users connect to 4G and/or 5G networks. The data demonstrate the robust, widespread coverage of the 4G network across all major carriers, with scores clustered above 97%.
Mobile Operators 4G/5G Network Availability, Japan
Source: Speedtest Intelligence® | Q3 2025
5G Availability—the percentage of time users with 5G-capable devices spent connected to a 5G network—showed a more varied result. NTT DOCOMO led in 5G Availability with 38.4%, exceeding au by almost 6 percentage points. SoftBank recorded the lowest 5G Availability at 26.5%, despite achieving the fastest median download speed across all technologies. This outcome suggested a strategic trade-off, common across the industry due to Japan’s geographical challenges: operators often prioritize mid-band capacity and speed in accessible, high-traffic urban areas, while relying on their 4G networks for broader national coverage.
Disparity in 5G footprint across prefectures
Japan’s mobile network strategy is fundamentally shaped by its unique geography and extreme population concentration. While approximately 92.1% of the population resides in urban areas, this density necessitates operators covering vast, geographically challenging territories for the remaining users. The Japanese Government, through the MIC, imposes strict mandates tied to 5G spectrum licensing to ensure equitable service access. These requirements compel operators to invest significantly beyond major urban centers, including mandatory coverage obligations across all 47 prefectures.
Speedtest Intelligence data reveals significant disparities in 5G Availability across Japan’s prefectures. This variation is largely due to the nation’s unique population distribution and the economics associated with network build-out. The 5G Availability percentages vary dramatically, from a high of 35.2% in Osaka to a low of 9.1% in Yamanashi. This disparity means users are nearly four times less likely to access 5G connectivity in the lowest-ranking prefecture (Yamanashi) than in the highest (Osaka).
5G Availability (%) Across Prefectures
Source: Speedtest Intelligence® | Q3 2025
The prefectures with the highest 5G Availability results correspond to Japan’s most populated and economically vital regions, led by Osaka (35.2%), Tokyo (33.7%), Aichi (30.6%), and Kanagawa (29.1%). Operators have strategically prioritized these high-density areas for 5G deployment to maximize capacity of more advanced technology, and secure high-value customers. Conversely, largely inland or mountainous prefectures with scattered populations, such as Yamanashi (9.1%) and Nagano (9.8%), recorded the lowest 5G Availability. This minimal 5G presence underscores the significant challenge of deploying 5G in regions with low population density and difficult terrain, compelling operators to continue relying on their existing 4G networks.
Median 5G Download Speed (Mbps) Across Prefectures
Source: Speedtest Intelligence® | Q3 2025
The data shows a regional digital divide, marked by a substantial disparity in 5G Availability between the prefectures with the highest and lowest network access. This inequality is compounded by the fact that users in more rural prefectures not only spend significantly less time connected to the 5G network but also experience lower median 5G download speeds, widening the gap between urban and rural areas.
Osaka for instance, recorded 35.2% 5G Availability and a median 5G download speed of 172 Mbps, while Tokyo achieved 33.7% 5G Availability and 128 Mbps median 5G download speed. The dense site deployment in these centers confirms substantial infrastructure investment, and a more robust spectrum strategy. This strategic metropolitan focus directly supports the recorded higher speeds.
However, several prefectures contradict this correlation. Yamagata, for example, is a clear exception to this trend, recording the nation’s highest speed at 181 Mbps despite low 5G Availability at 13.9%. This suggests a scenario where operators deployed 5G infrastructure to meet regulatory coverage commitments, but low user density prevents network contention.
Operators’ 10th percentile 5G performance underscores the urban-rural quality divide
The analysis of the 10th percentile 5G download speeds across the 47 Japanese prefectures in Q3 2025 provides a crucial measure of minimum quality of performance, representing the speeds experienced by the bottom 10% of all users.
NTT DOCOMO generally recorded higher download speeds at the 10th percentile, securing the highest (peaking at 41 Mbps in Ishikawa) or near-highest scores across the widest array of prefectures. Conversely, SoftBank recorded the single highest minimum 10th percentile download speed across all prefectures, reaching 49 Mbps in Aomori. However, SoftBank’s 10th percentile performance varied significantly, dropping to 4 Mbps in Nagano, and 6 Mbps in Chiba. au and Rakuten Mobile generally showed lower and more tightly grouped minimum speeds, suggesting greater performance vulnerability, typically observed at the cell edge or during times of congestion.
The data shows a clear link between 10th percentile download speeds and urbanization. Highly urbanized prefectures or those serving as regional capitals consistently show higher minimum speeds across all operators. This is likely due to higher site density and focused mid-band spectrum deployment to manage greater user volume. For instance, in Osaka, all operators reported narrower 10th percentile speed ranges, from 18 Mbps to 28 Mbps.
Speedtest data also reveals a positive correlation between the median 5G download speed and the 5G Consistency Score across Japan’s prefectures. Ookla’s 5G Consistency metric measures the network’s ability to consistently provide a high-quality user experience, such as for 4K video streaming. Specifically, it quantifies the proportion of user samples that meet or exceed the performance threshold of 25 Mbps download and 3 Mbps upload. Prefectures with higher median download speeds consistently demonstrate a proportionally higher probability of users experiencing a reliable service.
SoftBank recorded the highest 5G Consistency in many prefectures across all regions, demonstrating superior baseline reliability, particularly in Hokkaido and Tōhoku. Notable examples include Aomori in Tōhoku and Nagasaki in Kyūshū, both recording 90.9% consistency, and Iwate (Tōhoku) at 90.7%. NTT DOCOMO and au also demonstrated strong, consistent performance, reflecting the benefits of their mature, optimized infrastructure.
Significant regional disparities persist, highlighting specific areas that require immediate infrastructure improvement. The highest 5G Consistency scores were concentrated in the Chūgoku and Shikoku regions, with several operators exceeding 80%. Conversely, the lowest consistency scores are primarily found in rural or challenging prefectures, such as the northern Kanto region (Ibaraki, Gunma, Tochigi).
Japan’s 5G rollout has been a success, achieving high national coverage due to proactive regulatory policies and substantial investment from operators. The main policy goal of universal population coverage has clearly been met. However, an analysis of 5G performance shows a measurable disparity between urban and rural areas, likely influenced by strategic operator deployment decisions and geographical challenges. To ensure universal, high-quality digital connectivity across all of Japan’s 47 prefectures by the 2030 target, continued targeted investment in extending 5G infrastructure, coupled with the strategic integration of innovative technologies such as Non-Terrestrial Networks (NTN), is critical for bridging the digital divide.
モバイルパワープレイ:日本の5Gネットワークパフォーマンスを形作る戦略的なトレードオフ
日本のモバイル市場は、NTTドコモ、KDDI (au)、ソフトバンク、楽天モバイルという4つの主要な通信事業者の間で激しい競争が繰り広げられる、世界で最もダイナミックで技術的に進んだ市場の1つです。各事業者は、この競争の激しい環境で市場シェアを確保するために、明確な戦略を採用しています。本レポートは、日本の競争的なモバイル市場における5Gネットワークの性能と利用可能性を評価します。
主なポイント
- 4Gは全国的に不可欠なモバイル接続サービスである一方、5Gアクセスは地理的に分断されています。 5Gの利用可能性は場所によって劇的に異なり、大阪の35.2%を最高に、山梨の9.1%を最低として、約4倍の開きがあります。対照的に、4Gネットワークは、すべての主要な通信事業者で4Gの利用可能性が一貫して97%以上に集約されており、安定した信頼性の高い基盤を提供しています。
- 日本のモバイル市場は戦略的に二分されており、通信事業者は明確なパフォーマンス目標を優先しています。 SoftBankとauは、全技術のメディアンダウンロード速度でそれぞれ62.05 Mbpsと57.85 Mbpsを記録し、リードしています。一方、楽天モバイルは128.39 Mbpsで最速の5Gメディアンダウンロード速度を達成しました。
- 都道府県ごとの通信事業者の10パーセンタイルダウンロード速度は、高度に都市化された都道府県が一貫してより高い最低速度を受け取っていることを示しており、 これはより高いサイト密度と容量投資を反映しています。NTTドコモは、石川県で41 Mbpsをピークとする、都道府県全体で最も一貫した低い10パーセンタイル速度を維持しました。SoftBankの低い10パーセンタイル速度は、都市と地方の格差に直接相関する大きな変動を示しており、青森県で49 Mbpsをピークに、長野県では4 Mbpsにまで落ち込んでいます。
SoftBankが全技術のメディアンダウンロード速度でリード、Rakutenが最高の5G速度を達成
日本のモバイル通信環境は、競争の激しいネットワークと加速する技術移行が特徴であり、これは通信事業者のパフォーマンスデータに反映されています。Speedtest Intelligence®の2025年第3四半期のデータによると、SoftBankが全技術を合わせたメディアンダウンロード速度で62.05 Mbpsを記録し、auの57.85 Mbpsをわずかに上回りリードしています。SoftBankの優れたパフォーマンスは、信頼性の高いサービス提供を目指した、注目すべきネットワーク近代化および最適化の取り組みに起因しています。楽天モバイルとNTT DOCOMOは、それぞれ53.54 Mbpsと50.50 Mbpsのメディアンダウンロード速度でそれに続きました。
逆に、同期間の5GのメディアンパフォーマンスではRakuten Mobileがリードしました。全技術を合わせたメディアンダウンロード速度は52.45 Mbps(3位)でしたが、Rakutenの5Gメディアンダウンロード速度とアップロード速度はそれぞれ128.39 Mbpsと22.34 Mbpsと著しく高くなっています。SoftBankがこれに続き、メディアンダウンロード速度は127.45 Mbps、アップロード速度は17.51 Mbpsでした。
全国的な可用性データは、広範囲にわたる4Gベースラインと異なる5G投資の優先順位を裏付けています
日本のモバイル市場は、ほぼ普遍的な普及の状況下で運営されており、2025年初頭時点で約1億9400万の携帯電話接続と157%の普及率があります。この飽和状態により、競争は主にサービスの品質、速度、次世代ネットワークの可用性によって推進されています。総務省(MIC)によると、全国の5G人口カバー率は2024年度末までに98.4%に達しました。
2025年第3四半期のOokla Speedtest Intelligenceデータを使用したネットワーク可用性の分析は、モバイルユーザーが4Gまたは5Gネットワークに接続する頻度を測定しています。このデータは、すべての主要なキャリアで4Gネットワークが堅牢かつ広範囲にカバーされており、スコアが97%以上に集約されていることを明確に示しています。
携帯電話事業者による4G/5Gネットワーク可用性、日本
Source: Speedtest Intelligence® | Q3 2025
5G Availability—5G対応デバイスを持つユーザーが5Gネットワークに接続して過ごした時間の割合—は、より多様な結果を示しました。NTT DOCOMOが38.4%で5G Availabilityをリードし、auをほぼ6パーセントポイント上回りました。SoftBankは、全技術のメディアンダウンロード速度で最速を達成したにもかかわらず、26.5%で最も低い5G Availabilityを記録しました。この結果は、日本の地理的課題により業界全体で一般的な戦略的トレードオフを示唆しています。すなわち、通信事業者は、アクセスしやすくトラフィックの多い都市部でミッドバンドの容量と速度を優先する一方で、より広範な全国カバレッジには4Gネットワークに依存しているということです。
都道府県全体での5Gフットプリントの格差
日本のモバイルネットワーク戦略は、その独自の地理と極端な人口集中によって根本的に形成されています。人口の約92.1%が都市部に居住している一方で、この密度により、通信事業者は残りのユーザーのために広大で地理的に困難な地域をカバーする必要があります。
日本政府は、MICを通じて、公平なサービスアクセスを確保するために5Gスペクトルライセンスに厳格な義務を課しています。これらの要件により、通信事業者は、すべての47都道府県にわたる義務的なカバレッジ義務を含め、主要な都市中心部を超えて大幅な投資を行うことを余儀なくされています。
Speedtest Intelligenceデータは、日本の都道府県全体で5G Availabilityに重大な格差があることを明らかにしています。この変動は、主に国の独自の人口分布と、ネットワーク構築に伴う経済的要因に起因しています。5G Availabilityのパーセンテージは、大阪の35.2%を最高に、山梨の9.1%を最低として、劇的に異なっています。この格差は、ユーザーが最も低いランクの都道府県(山梨)で最も高いランクの都道府県(大阪)と比較して、5G接続にアクセスできる可能性が約4分の1未満であることを意味します。
都道府県別 5G Availability (%)
Source: Speedtest Intelligence® | Q3 2025
5G Availabilityの結果が最も高い都道府県は、日本の最も人口が多く経済的に重要な地域に対応しており、大阪 (35.2%)、東京 (33.7%)、愛知 (30.6%)、神奈川 (29.1%) がリードしています。通信事業者は、より高度な技術の容量を最大化し、高価値の顧客を確保するために、これらの高密度地域での5G展開を戦略的に優先してきました。対照的に、山梨 (9.1%) や長野 (9.8%) のように、人口が散在している内陸または山岳部の多い都道府県では、最低の5G Availabilityが記録されました。この最小限の5Gの存在は、人口密度の低い地域や困難な地形での5G展開の重大な課題を浮き彫りにしており、通信事業者は既存の4Gネットワークに頼り続けることを余儀なくされています。
都道府県別 5G中央値ダウンロード速度(Mbps)
Source: Speedtest Intelligence® | Q3 2025
データは、最高のネットワークアクセスを持つ都道府県と最低のネットワークアクセスを持つ都道府県との間で、5G Availabilityに大きな格差がある地域的なデジタルデバイドを示しています。この不平等は、より地方の都道府県のユーザーが5Gネットワークに接続して過ごす時間が著しく少ないだけでなく、メディアン5Gダウンロード速度も低く、都市部と地方の格差を広げているという事実によってさらに悪化しています。
例えば、大阪では5G Availabilityが35.2%、メディアン5Gダウンロード速度が172 Mbpsを記録しましたが、東京では5G Availabilityが33.7%、メディアン5Gダウンロード速度が128 Mbpsでした。これらの中心地での高密度なサイト展開は、大規模なインフラ投資と、より堅牢なスペクトル戦略を裏付けています。この戦略的な大都市圏への集中は、記録されたより高い速度を直接的に支えています。
しかし、いくつかの都道府県はこの相関関係に反しています。例えば、山形県は、5G Availabilityが13.9%と低いにもかかわらず、国内最高の速度である181 Mbpsを記録しており、この傾向の明確な例外です。これは、通信事業者が規制上のカバレッジ義務を満たすために5Gインフラを展開したものの、ユーザー密度の低さがネットワークの競合を防いでいるシナリオを示唆しています。
通信事業者の10パーセンタイル5Gパフォーマンスが、都市と地方の品質格差を浮き彫りに
2025年第3四半期における日本の47都道府県全体での10パーセンタイル5Gダウンロード速度の分析は、最低限のパフォーマンス品質の重要な指標を提供し、全ユーザーの下位10%が経験する速度を表しています。
NTT DOCOMOは、一般的に10パーセンタイルでより高いダウンロード速度を記録し、最も広範な都道府県で最高(石川県で41 Mbpsをピーク)またはそれに近いスコアを確保しました。対照的に、SoftBankは、全都道府県の中で単一で最高の最低10パーセンタイルダウンロード速度を記録し、青森県で49 Mbpsに達しました。しかし、SoftBankの10パーセンタイルパフォーマンスは大きく変動し、長野県で4 Mbps、千葉県で6 Mbpsにまで落ち込みました。auとRakuten Mobileは、一般的に低く、より密接にグループ化された最低速度を示しており、通常、セルエッジや混雑時に見られる、より大きなパフォーマンスの脆弱性を示唆しています。
データは、10パーセンタイルダウンロード速度と都市化の間に明確な関連性があることを示しています。高度に都市化された都道府県、または地方の中心都市として機能する都道府県は、すべての通信事業者で一貫してより高い最低速度を示しています。これは、より高いサイト密度と、より大きなユーザーボリュームを管理するための集中的なミッドバンドスペクトル展開による可能性が高いです。例えば、大阪では、すべての通信事業者が10パーセンタイル速度でより狭い範囲を報告しており、それは18 Mbpsから28 Mbpsの間に及んでいます。
Speedtest dataはまた、日本の都道府県全体で、メディアン5Gダウンロード速度と5G Consistency Scoreの間に正の相関関係があることを示しています。Ooklaの5G Consistency metricは、4Kビデオストリーミングなどの高品質なユーザーエクスペリエンスを一貫して提供するネットワークの能力を測定します。具体的には、25 Mbpsのダウンロード速度と3 Mbpsのアップロード速度の性能閾値を満たす、または超えるユーザーサンプルの割合を定量化します。メディアンダウンロード速度が高い都道府県は、ユーザーが信頼性の高いサービスを経験する可能性が比例して高いことを一貫して示しています。
SoftBankは、すべての地域で多くの都道府県で最高の5G Consistencyを記録し、特に北海道と東北地方で優れたベースラインの信頼性を示しています。注目すべき例としては、東北の青森県と九州の長崎県があり、どちらも90.9%のconsistencyを記録し、岩手県(東北)は90.7%でした。NTT DOCOMOとauもまた、成熟した最適化されたインフラストラクチャの利点を反映して、強力で一貫したパフォーマンスを示しました。
地域間の大きな格差が依然として残っており、早急なインフラ改善が必要な特定の地域を浮き彫りにしています。最高の5G Consistency scoresは中国・四国地方に集中しており、複数の通信事業者が80%を超えています。逆に、最低のconsistency scoresは、主に北関東地方(茨城、群馬、栃木)のような地方や困難な環境の都道府県で見られます。
日本の5G展開は成功しており、積極的な規制政策と通信事業者からの多大な投資により、高い全国カバレッジを達成しました。ユニバーサルな人口カバレッジという主要な政策目標は明確に達成されています。しかし、5Gパフォーマンスの分析は、戦略的な通信事業者の展開決定と地理的な課題の影響を受けている可能性が高い、都市部と地方との間に測定可能な格差があることを示しています。2030年という目標までに、日本の47すべての都道府県でユニバーサルで高品質なデジタル接続を確保するためには、5Gインフラの拡張への継続的かつ的を絞った投資と、Non-Terrestrial Networks (NTN) のような革新的な技術の戦略的な統合が、デジタルデバイドを埋めるために不可欠です。
Ookla retains ownership of this article including all of the intellectual property rights, data, content graphs and analysis. This article may not be quoted, reproduced, distributed or published for any commercial purpose without prior consent. Members of the press and others using the findings in this article for non-commercial purposes are welcome to publicly share and link to report information with attribution to Ookla.