The National Telecom Regulatory Authority (NTRA) and Ookla hosted the MEA Regulatory Summit in Cairo, Egypt, from 6–8 May 2025. The theme was “Harnessing Data and Technology for Superior QoS: Strategies for Measuring and Optimizing Network Performance.” Regulators from the Middle East and Africa, along with representatives from the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), the World Broadband Association (WBBA), and various industry experts gathered at the Summit to share strategies for collecting, using, and sharing data to promote transparency, track policy impacts, and make smarter investment decisions for better network performance.
Key Takeaways:
- Importance of crowdsourced data in telecom regulation. The summit highlighted the growing significance of crowdsourced data in informing telecom regulatory decisions. By utilizing this data, regulators can identify service gaps, promote digital inclusion, and drive innovation. Crowdsourced insights complement traditional data sources, enabling smarter regulatory frameworks that adapt to market needs and foster competition.
- High-speed connectivity as a catalyst for economic growth. High-speed internet connectivity is crucial for driving socio-economic development in MEA. Studies indicate that improvements in broadband speeds can significantly boost GDP and labor productivity. Investments in fixed broadband infrastructure, particularly fiber-optic networks, are essential for enhancing service quality and expanding access, ultimately bridging the digital divide and attracting foreign investment.
- There is a need for a comprehensive network assessment and regulatory oversight. As telecom services evolve, regulators should adopt a more holistic approach to network assessment. This includes extending oversight to emerging critical services and ensuring consistent performance across various environments, including indoors. By leveraging advanced data collection methods, regulators can better understand user experiences and address the complexities of modern digital services, ensuring that all users receive reliable connectivity.
Regulators’ survey confirmed the importance of data in regulatory decision-making, and the growing role of crowdsourcing
A major takeaway from the summit was the importance of crowdsourced data in telecom regulation. Discussions highlighted how data can drive innovation and market growth by informing policy changes that encourage fair competition and enable new technologies. Data also helps promote digital inclusion by pinpointing service gaps and guiding interventions in underserved areas. Speakers shared examples of how network data can lead to smarter regulatory decisions, foster efficient telecom environments, and support broader economic growth.
A survey of attendees confirmed that most regulators are collecting more data on telecom networks, including QoS, coverage, and QoE. It also highlighted that crowdsourced data is playing a bigger role in the MEA region, complementing traditional field testing and operator data.
Martin Adolph from ITU confirmed this trend during the panel discussion, noting the development of two ITU standards by ITU-T Study Group 12 experts: E.806 (measurement campaigns, monitoring systems, and sampling methodologies) and E.812 (a crowdsourcing approach for assessing end-to-end QoS).
The survey also revealed a number of challenges in collecting and using data for connectivity assessments. The most frequently cited challenges include:
- Integrating data from multiple sources, validating its accuracy, and selecting the methodology
- A lack of data analysis skills and infrastructure
- Dealing with inconsistent and inaccurate reporting from the operators
Most surveyed regulators said they publish the data they collect, typically monthly. They prefer to share this information through reports, charts/dashboards, and interactive maps.
The critical role of high-speed connectivity in driving economic growth in MEA
Discussions emphasized the critical role of high-speed connectivity in driving digital transformation and socio-economic growth in the MEA region, helping to attract foreign direct investment and helping to bridge the digital divide. Studies mentioned in one presentation suggest that doubling download speeds (above 40 Mbit/s) can increase GDP by 0.73%, and a 10% increase in mobile broadband speed is linked to a 0.2% increase in labor productivity in non-OECD and low-income countries.
Giulia Rancati from WBBA stressed that developing fixed broadband infrastructure is essential for economic and social progress in Africa. Increased data usage through broadband can improve healthcare, education, business, and overall economic growth. That is why there have been increased investments in Africa to boost subscriber penetration rates and improve connection quality and speeds. The presentation noted that the business case for fiber-to-the-premises (FTTP) rollout in Africa can be viable, but efforts are needed to further reduce infrastructure rollout costs. In this context, WBBA, in partnership with Ookla, recently published an Africa-specific Broadband Investment Strategy that leverages existing best practices and toolkits.
In the Middle East, the fixed broadband market is growing rapidly due to the expansion of fiber-optic networks. Telcos are investing heavily in fiber to offer ultra-fast broadband services (10 Gbps and higher). This investment is crucial for meeting consumer and business demand, leading to significant revenue growth in the market. Governments in the Middle East are prioritizing digital transformation, resulting in supportive regulatory frameworks that encourage investment in high-speed broadband infrastructure. These frameworks include initiatives to streamline fiber network deployment and incentivize operators to expand coverage in underserved areas.
A call for a more comprehensive network assessment approach and broader regulatory oversight
As services evolve, the demand for faster networks and better experiences grows. However, the growing network complexity demands an extended approach to measuring customer experience. Modern applications depend on the internet, a shared resource with unpredictable performance, which means there’s a need for visibility across the entire digital service delivery chain.
During the summit, it was argued that the definition of ‘critical’ services should include over-the-top (OTT) services, such as mobile banking, telemedicine, educational, and communications platforms. Regulatory bodies, which historically focused on infrastructure, licensed spectrum, and core communication services, could consider extending their oversight to emerging critical services and networks using unlicensed spectrum standards like Wi-Fi.
Furthermore, users expect the same level of performance and experience everywhere, including indoors, where most of their time is spent and most data traffic is generated. In fact, the indoor experience can be a key differentiator in sectors like education and hospitality. Wi-Fi networks also support hospitals, airports, and large public venues, which could be considered part of the ‘critical layer’ as they support government and commercial services. These types of settings often lack standards for network resilience, reliability, and emergency response readiness, despite having comprehensive standards for physical infrastructure aspects like structural integrity and fire safety.
Regulators shared use cases on the role of crowdsourced data in performance benchmarking and network improvement
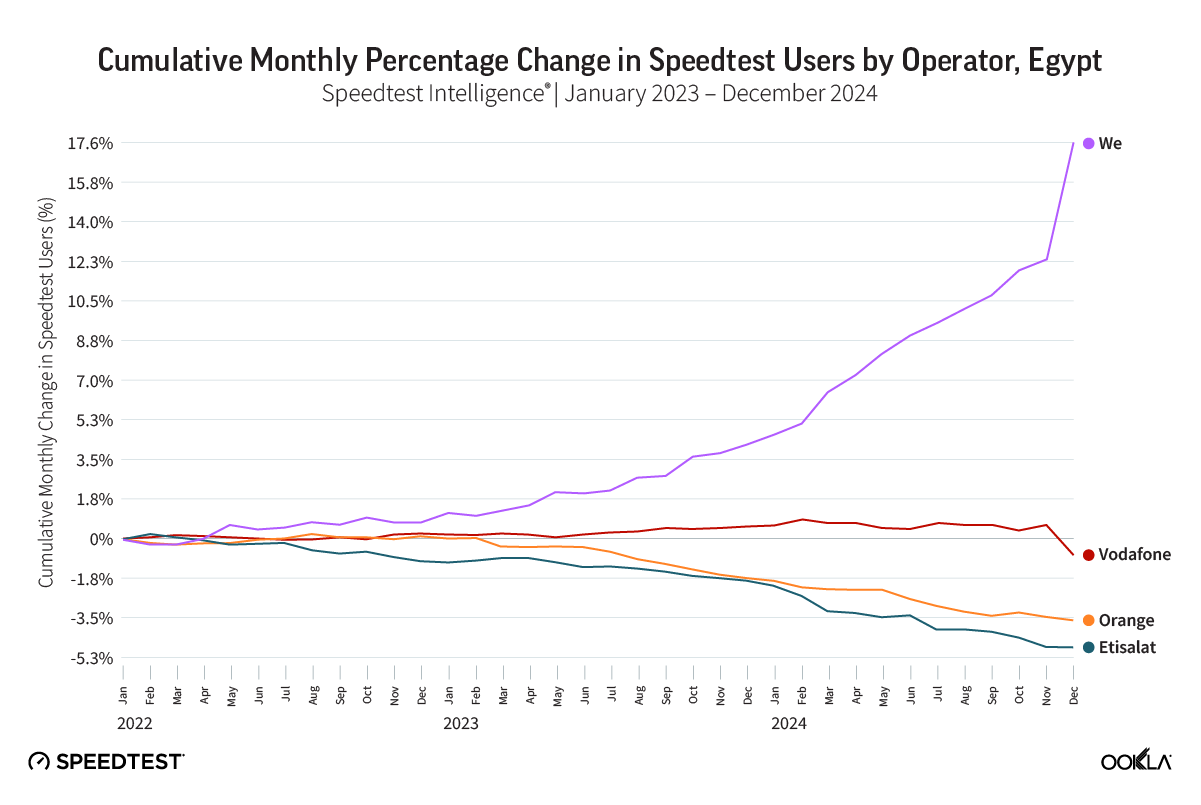
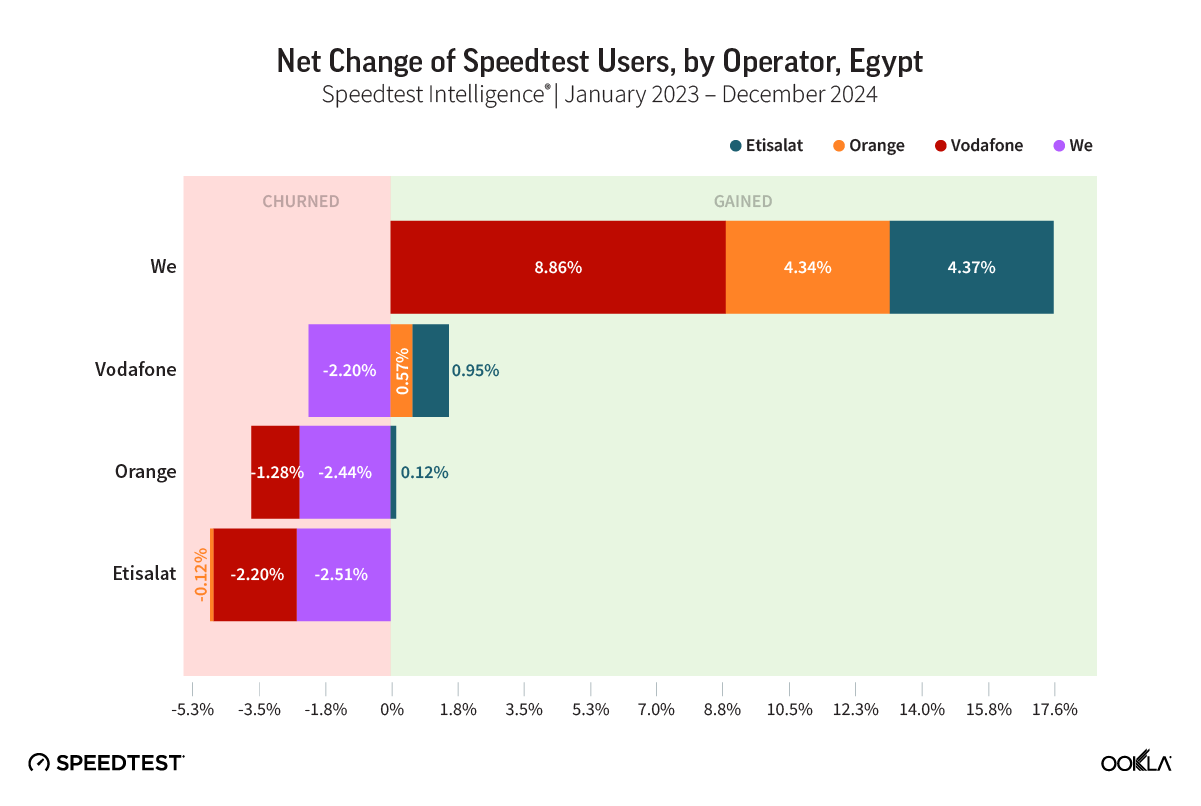
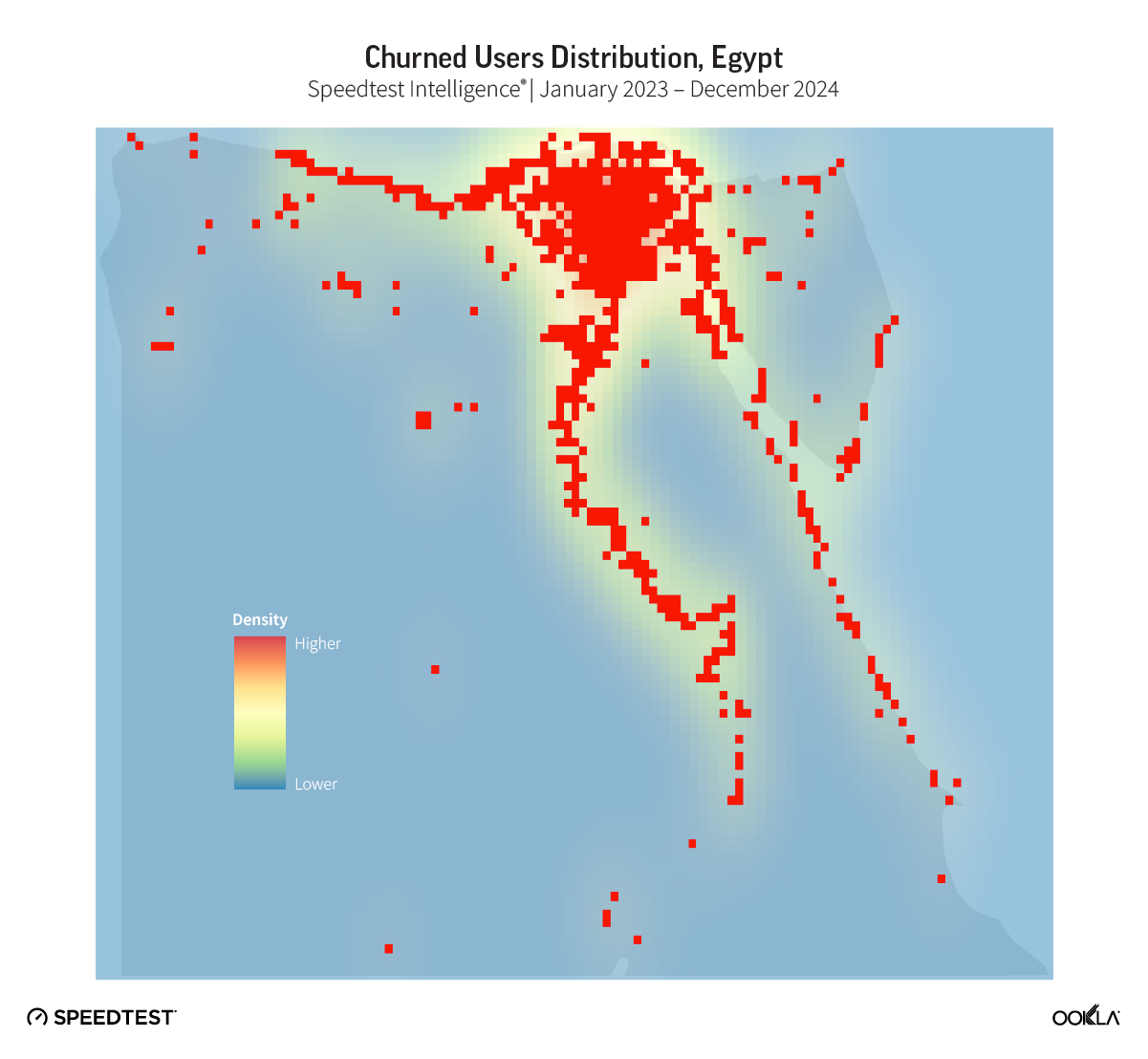
Representatives from the NTRA offered insights into Egypt’s telecommunications market development, regulatory approaches, and strategic initiatives. For example, the authority used crowdsourced data to assess and benchmark performance across different regions and direct investments, which resulted in a significant improvement in download speed, placing Egypt first in Africa.
The NTRA also discussed how it leveraged crowdsourced data to develop and apply a more adaptive, incentive-based regulatory framework. Mobile network operators (MNOs) can now reduce penalties for QoS violations if they meet performance targets based on crowdsourced data. The NTRA also gives MNOs the option to build new mobile sites to improve coverage instead of paying fines for QoS issues.
The “Decent Life” Initiative in Egypt was also presented, which aims to extend broadband access to rural populations by installing fiber optics and mobile towers. In the first phase, the NTRA partnered with licensed mobile operators, funding 593 new mobile stations through the Universal Service Fund, while operators funded 503 stations and upgraded 576 existing ones using 4G technology. The second and third phases involve establishing 1,585 new coverage stations, with the NTRA funding 885 stations and operators funding 700, and upgrading 717 existing stations. Crowdsourced data will be used to monitor the progress of fixed and mobile deployments in targeted areas and quantify the impact of the initiative on service reach and performance.
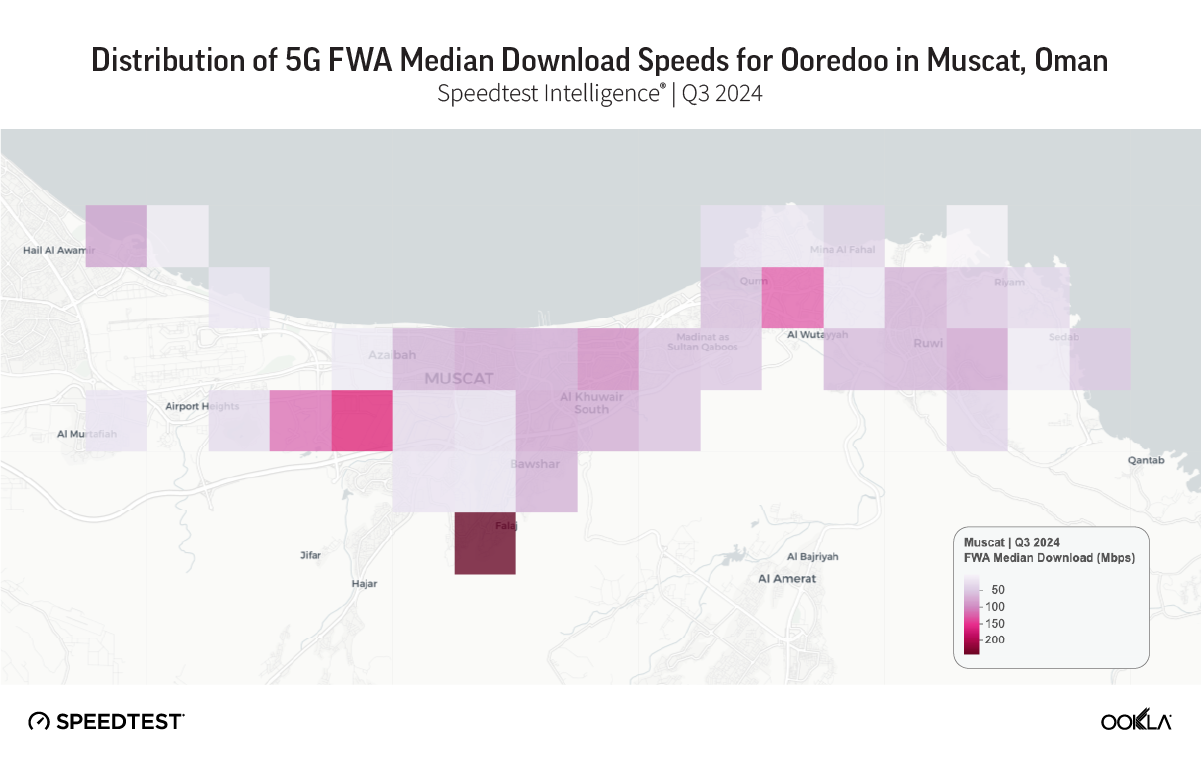
Similarly, Fatma Salim Nasser Al Mamar from TRA Oman presented use cases showing how they use Ookla’s QoS and QoE data to track fixed and mobile broadband performance across different regions, identify areas with weak coverage, and quantify indoor mobile data usage.
Early insights into 5G performance in Egypt and Tunisia, and Starlink’s performance in Sub-Saharan Africa
Several presentations showed how crowdsourced data can help regulators monitor 5G rollout, enforce license conditions, and benchmark operators. For example, in Jordan, the TRC used Ookla data to track 5G rollout progress, validate 5G NSA coverage (aiming for 50% population coverage by 2026), and identify coverage gaps to guide infrastructure investment.
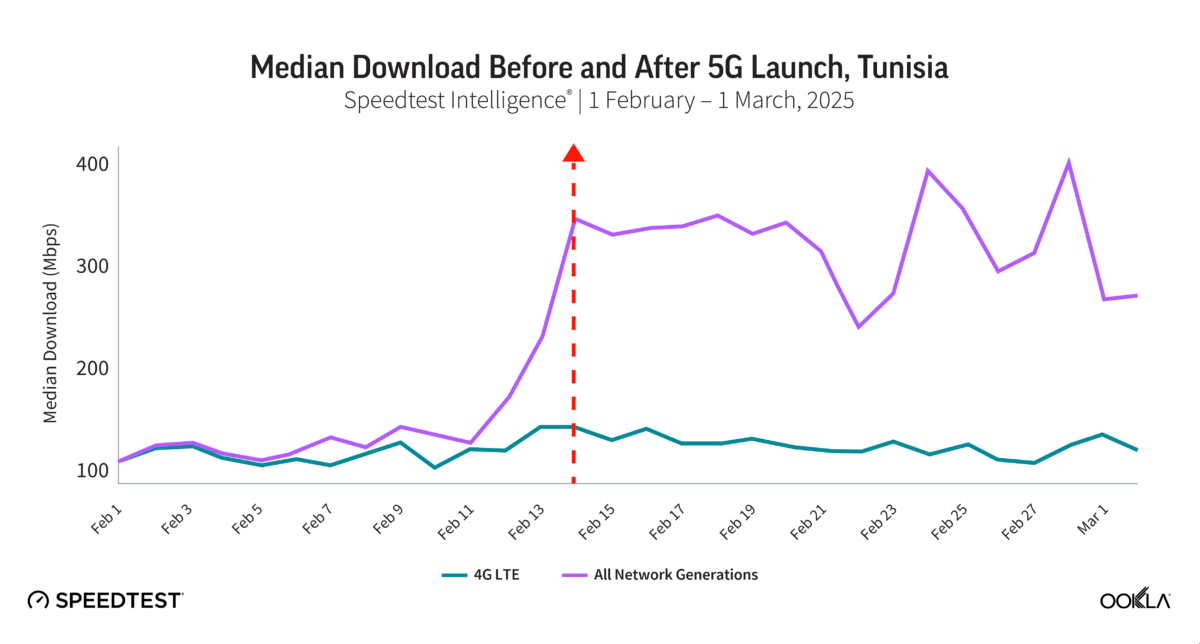
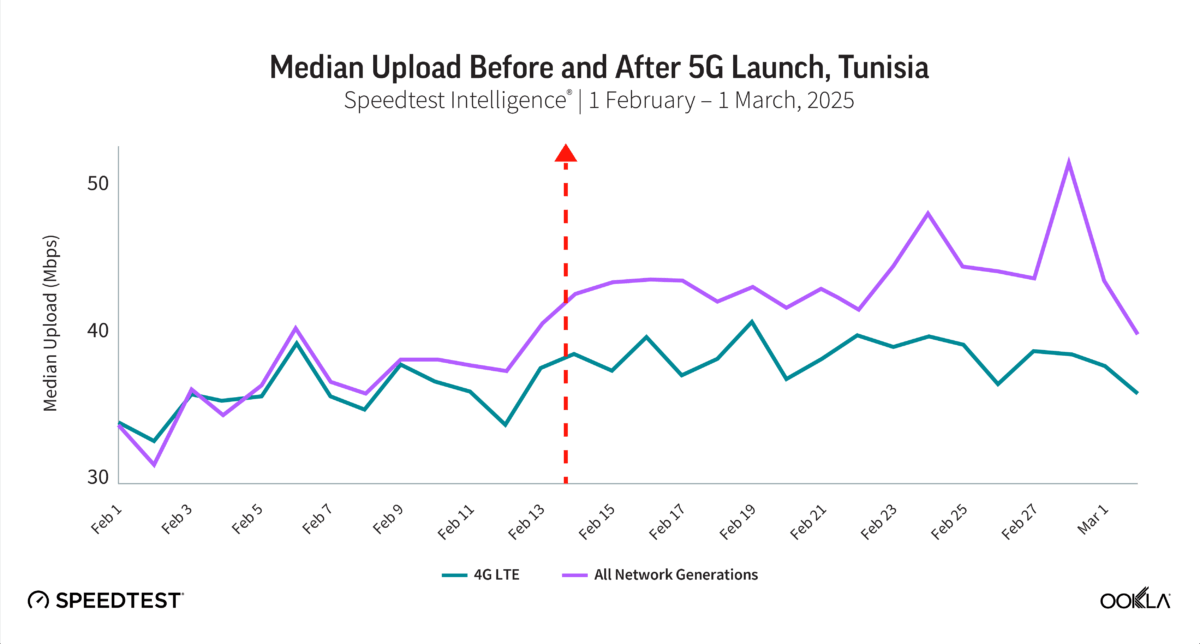
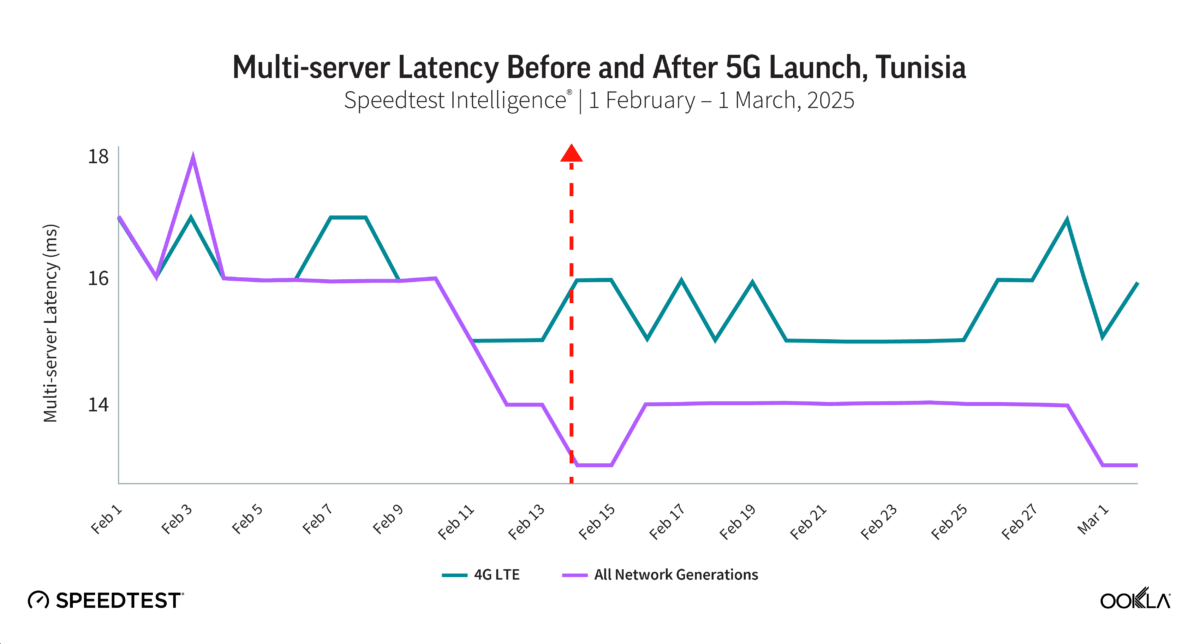
Ahmed Nabawy, Director, Client Services at Ookla, also shared early insights into 5G coverage and performance in Egypt and Tunisia. Ookla data helped identify high-impact rollout areas by using 5G-capable device density data to prioritize urban zones like Greater Cairo. This data also helps align spectrum strategy with demand and encourages investment where user readiness is strong. In Tunisia, where 5G services were launched in February 2025, the regulator can use Ookla data to focus spectrum awards and infrastructure build-out where user demand was most concentrated. Since launch, 5G test sample volumes have surged, and mobile download speeds have noticeably improved, reflecting expanding coverage and great market adoption.
Members of Ookla’s analyst team presented on Starlink services, their rapid expansion in Sub-Saharan Africa, and their performance compared to terrestrial options. Ookla data shows that median download speeds vary considerably, from under 50 Mbps in Nigeria, Zimbabwe, and Kenya, to over 85 Mbps in Botswana, Eswatini, and Rwanda, consistently outperforming existing ISPs. Starlink also offers relatively low latency in many African countries, although it still lags behind terrestrial ISPs for now.
Ookla presented its product portfolio strategy, which aims to empower smarter decisions and enable the next generation of connected experiences through data and actionable insights. The evolving strategy is centered around a unified data platform designed to unlock greater value from various data sources. This approach aims to move beyond QoS measurements to provide more comprehensive insights into network performance and user experience and to enable AI-based actionable insights and recommendations.
Empowering regulatory excellence in MEA through data-driven insights
Ookla recognizes the vital role regulatory bodies play in shaping the telecommunications landscape. This summit provided a valuable opportunity to exchange knowledge, discuss regulatory best practices, and explore potential collaborations that align with global industry trends. The summit underscored that data serves as a compass for regulators, providing an empirical foundation for decisions and enabling an informed approach to align policies with the evolving telecommunications landscape. Leveraging data enhances transparency and accountability, reinforcing the integrity and credibility of regulatory actions. The discussions highlighted the importance of moving beyond traditional network metrics to encompass customer experience (QoE) and address the complexities of modern digital services, including critical in-building connectivity and the impact of new players like Starlink, all supported by advanced data collection and analysis tools.
Ookla retains ownership of this article including all of the intellectual property rights, data, content graphs and analysis. This article may not be quoted, reproduced, distributed or published for any commercial purpose without prior consent. Members of the press and others using the findings in this article for non-commercial purposes are welcome to publicly share and link to report information with attribution to Ookla.