This city-level mobile performance benchmark, comparing ten of the largest Mexican cities with a selection of other major cities across Latin America, highlights the challenges facing the Mexican mobile market, with city-level performance lagging, and at risk of falling further behind regional peers.
Key Takeaways
- 5G continues to underwhelm within Mexican cities. A lack of 5G momentum and a concentrated mobile market structure have negatively weighed on the Mexican mobile user experience. Mexican cities lag their more advanced Latin American counterparts across key metrics like median download speed, with the fastest Mexican city, Monterrey, recording 55.17 Mbps in Q1 2025, a far cry from the 250.71 Mbps recorded in Rio de Janeiro.
- Year-on-year data indicates the market’s digital competitiveness is eroding. The trajectory for most Mexican cities appears to be one of marginal performance gains, which indicates other regional peers are likely to continue to leapfrog Mexico as attractive inward investment destinations, particularly in cases where mobile digital infrastructure forms a key enterprise requirement.
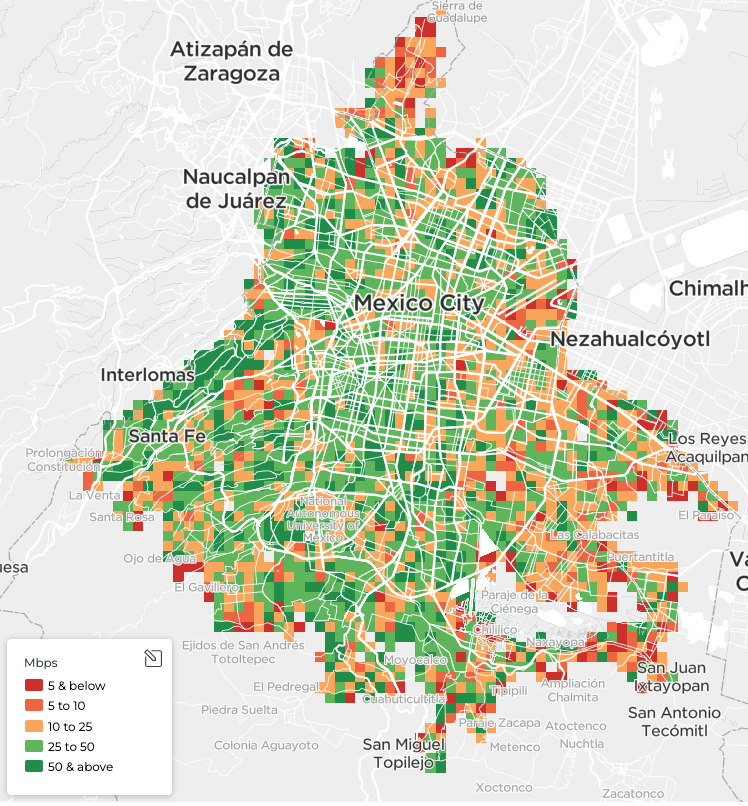
- Mexico City and its satellite cities underperform within Mexico. There is wide variation in mobile network performance outcomes between Mexican cities. Mexico City, and surrounding satellite cities including Ciudad Nezahualcóyotl, Ecatepec de Morelos, as well as Puebla, all perform relatively poorly compared to their peers, with median speeds of approximately 30 Mbps and lower. This is compounded for users experiencing the worst 10% of network performance, where recorded speeds were 3 Mbps and lower.
- Poor performance drags down web load times. User experienced web page load times exceeded a median of 2.4 seconds in three of the ten Mexican cities included in this analysis, well behind regional leader Buenos Aires, which clocked just 1.44 seconds. The varied outcomes across web page and video streaming performance highlight the challenges operators in the market face in ensuring consistent performance.
Mexican cities lag behind leading Latin American counterparts
Ookla’s Speedtest data recently played a key role in a World Bank study that exposed significant disparities in internet access across Brazilian cities. The research found that wealthier neighborhoods consistently experienced superior internet speeds, particularly on fixed networks. While mobile users across Brazil’s cities have benefited from 5G rollout, with the market placing 6th globally in the Speedtest Global Index based on median download speeds as of April 2025, Mexico, the second largest market by population in Latin America, languishes in 78th place. In this article, we benchmark mobile network performance outcomes across the ten largest Mexican cities, comparing them to a selection of other Latin American cities.
A majority of the population across Latin America resides in urban locations, which comprise 81.8% of the total population across Latin America and the Caribbean, according to World Bank data for 2023. Mexico marginally lags this regional average, at 81.6%, ahead of the EU at 75.7%, but behind other key competitors such as Argentina, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, and Uruguay.
Mexican cities ranked in the middle of the pack compared to regional rivals on median download speed, lagging far behind leading cities in Brazil, Uruguay and Argentina. The leading Mexican city, Monterrey, recorded a median of 55.17 Mbps in Q1 2025, compared to 250.71 Mbps in Rio de Janeiro. There was a wide variety of outcomes across Mexican cities, ranging from Monterrey’s high, to a low of 26.11 Mbps in Ecatepec. This is reinforced by performance for those users experiencing the lowest 10% of samples (the 10th percentile), with Mexico City and its satellite cities – Ecatepec, Ciudad Nezahualcoyotl, as well as Puebla seeing outcomes for these users of 3 Mbps and lower, and with only users in Santa Cruz de la Sierra in Bolivia faring worse.
It’s clear that users across Latin American cities value mobile network performance, as evidenced by the clear relationship between Q1 2025 download speeds and Net Promoter Score (NPS) data for Q1 2025. Among Mexican cities, this placed Monterrey first, with an NPS of +19.5, followed by Tijuana and Zapopan, and Guadalajara.
Maps are the best way to clearly illustrate performance differences within cities. Our recent study with Dublin City Council, which aimed to pinpoint areas of poor performance across that city, highlighted how crucial it is for urban leaders to understand the spread of mobile internet outcomes throughout their jurisdictions. This understanding allows them to combine this data with other information, such as the locations of city-owned infrastructure, as they seek to drive improvement.
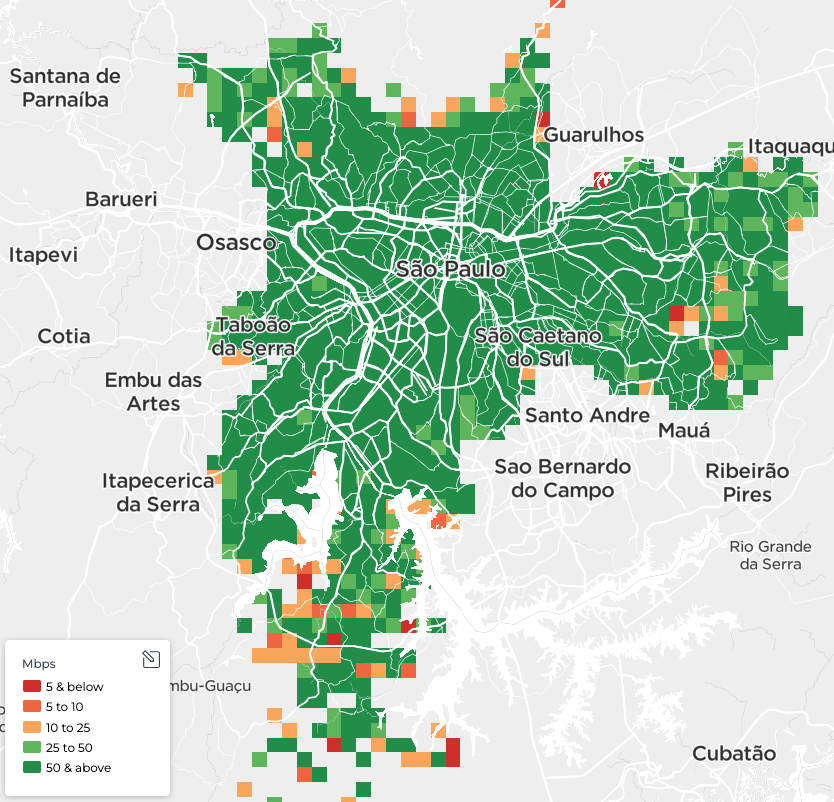
Comparing Mexico City to São Paulo visually demonstrates these performance differences. In São Paulo, based on Speedtest data for Q4 2024 – Q1 2025, a majority of locations have median download speeds exceeding 50 Mbps (colored dark green). Conversely, a significant portion of locations within Mexico City display median download speeds of 25 Mbps or less, as evidenced by the prevalence of orange and red tiles, especially along its eastern border with the State of Mexico.
Variation in mobile user experience highlights the impact of performance disparities
Key quality of experience (QoE) metrics such as web page load time, video start time, and the share of full HD samples, again show mixed outcomes for Mexican users across the nation’s cities.
The Mexican cities of Puebla, Zapopan, and Guadalajara had the worst web page load times, alongside Panama City, with median load times exceeding 2.4 seconds. In contrast, Mexico City and its satellite cities performed much better, recording median page load times of 1.75 seconds or less.
Regarding video streaming, only Guatemala City achieved a majority of users recording a fast video start time (where over 50% of samples played in under 2 seconds). Notably, five of the ten Mexican cities in this study recorded 40% or lower for this metric.
5G is yet to deliver on its potential for Mexican cities
Mexican cities underperform based on mobile network speeds compared to other major cities in Latin America, especially given their relatively high adoption of 5G. As of Q4 2024, Mexico ranks third in Latin America for the share of 5G connections per market (9.4%), according to GSMA Intelligence, trailing only Chile (18.6%) and Brazil (25.7%).
However, our data reveals significant disparities in 5G Service within Mexican cities. 5G Service refers to the percentage of locations where an operator provides service and 5G users can access the network. This variation suggests an uneven 5G rollout across the country. Specifically, Mexican cities with the lowest median download speeds consistently show lower 5G Service percentages. For example, Ecatepec recorded only 4.5% 5G Service, while Mexico City stood at 18.5%. In contrast, leading cities like Monterrey achieved nearly 40% 5G Service, highlighting the stark differences in network coverage across the market.
Mexican cities are disproportionately represented within the benchmark group of cities, among those with the smallest year-on-year improvements in median download speeds, comparing Q1 2024 to Q1 2025. Out of 24 cities included in our study, only Monterrey and Tijuana ranked in the top ten for the largest improvements. In contrast, six Mexican cities appeared in the bottom ten for performance gains.
Mexican cities face significant challenges in driving improved mobile network outcomes, despite 5G launching in the market in early 2022. High spectrum licence fees, which have led to a lack of operator interest, and even the handing back of allocated spectrum, highlight one of the key issues facing the development of 5G in the market. This continues to manifest through strong regional disparities in mobile performance between Mexican cities, in 5G Service across the market, and in the fact that Telcel continues to maintain a market share in excess of 50%. Couple this with the disbanding of the independent telecoms regulator, the IFT, by the government late last year, and it’s clear Mexico faces significant challenges in fostering the development of its mobile networks.
Ookla is attending the GSMA’s M360 Latin America, in Mexico City from 28-29th May. If you’re attending and would like to connect, please reach out to us.
Ookla retains ownership of this article including all of the intellectual property rights, data, content graphs and analysis. This article may not be quoted, reproduced, distributed or published for any commercial purpose without prior consent. Members of the press and others using the findings in this article for non-commercial purposes are welcome to publicly share and link to report information with attribution to Ookla.