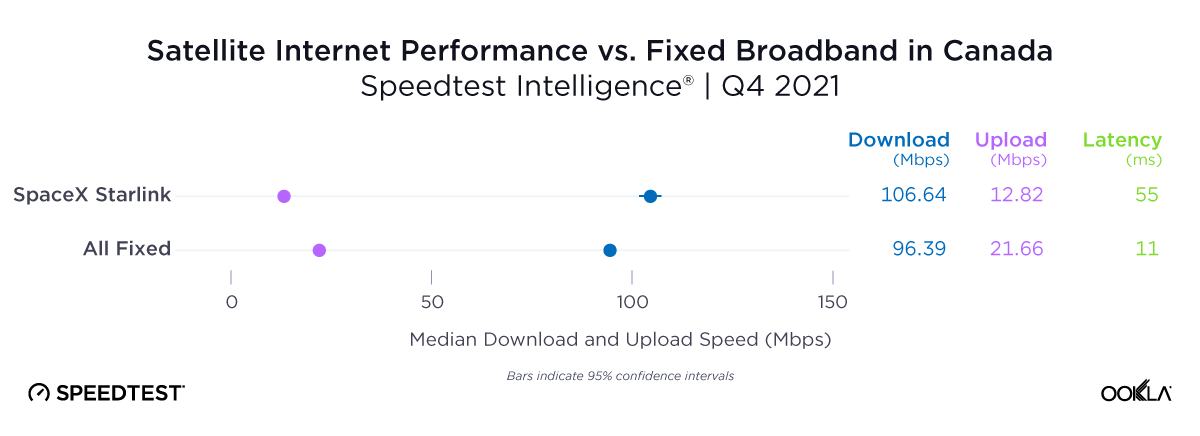
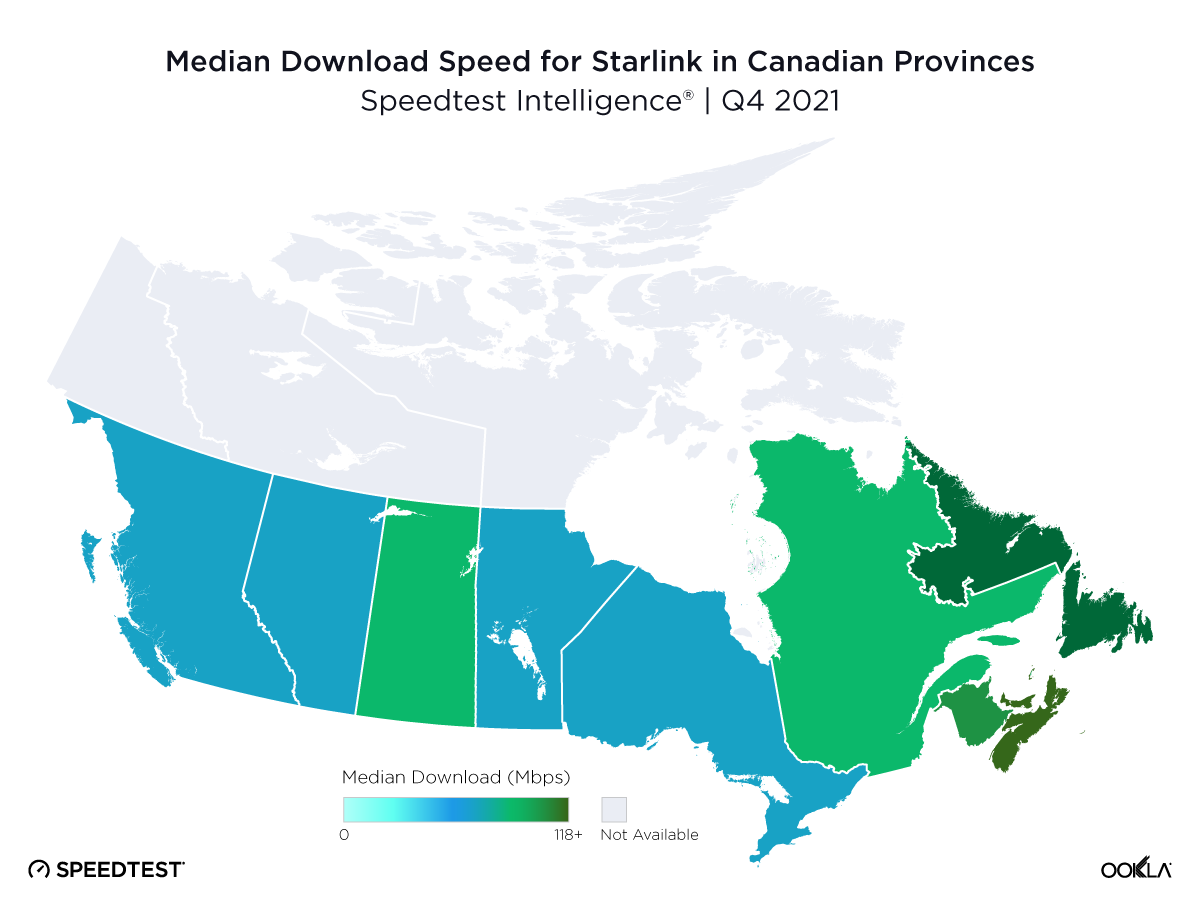
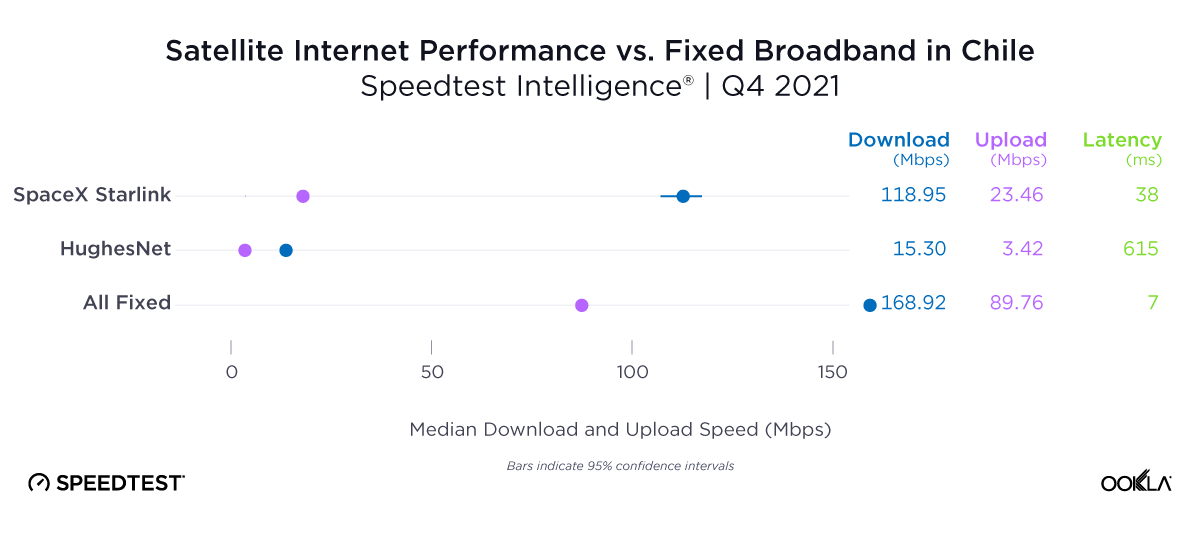
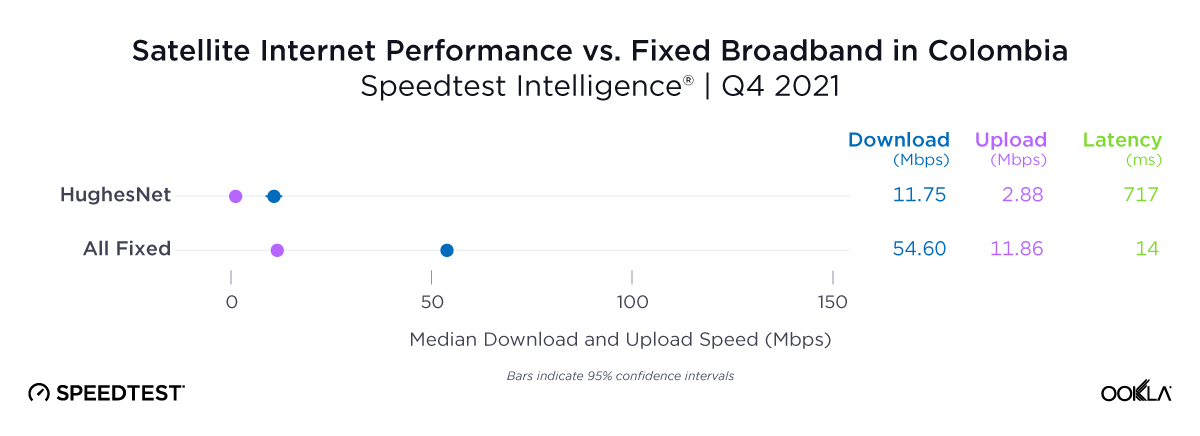
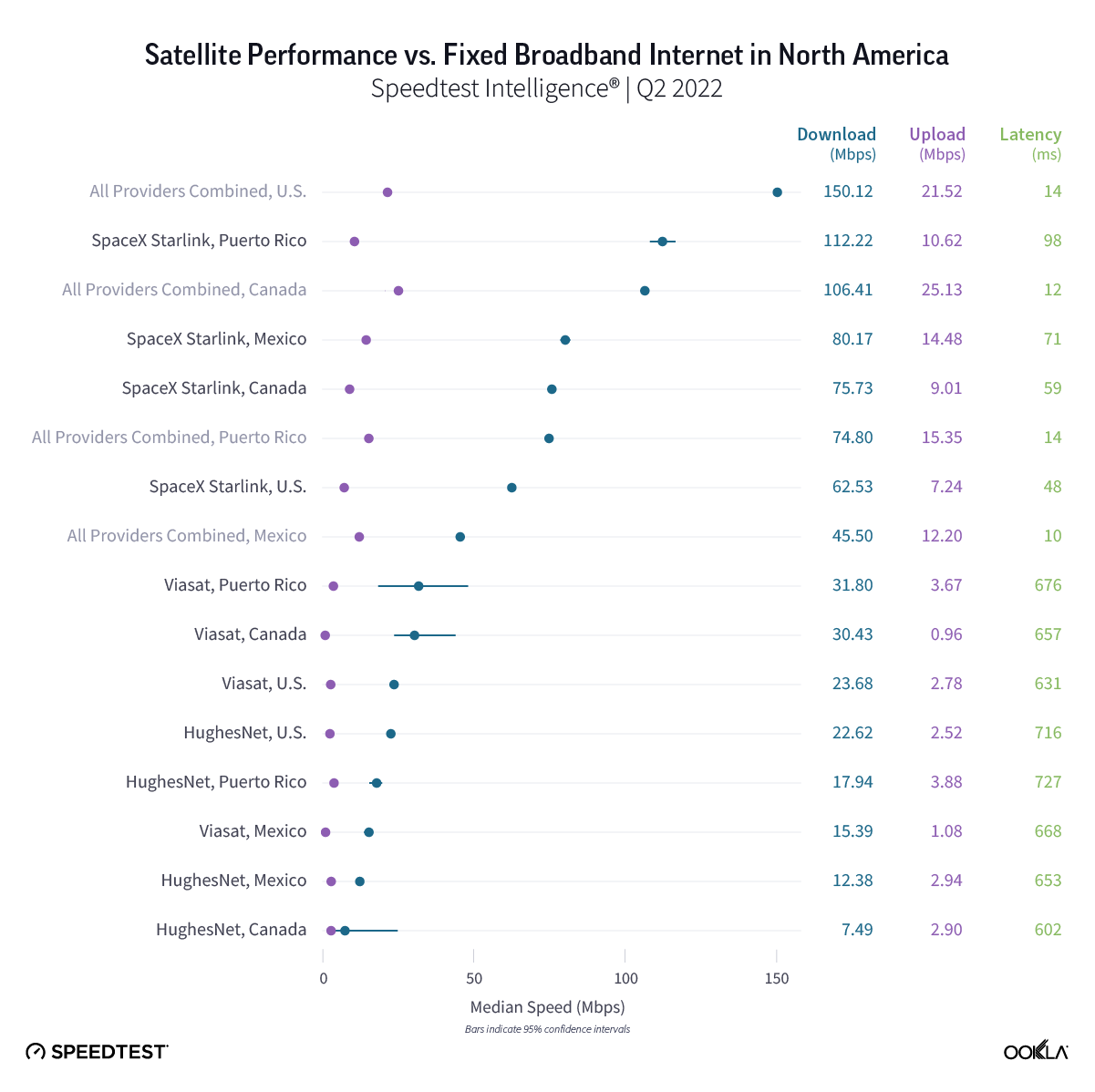
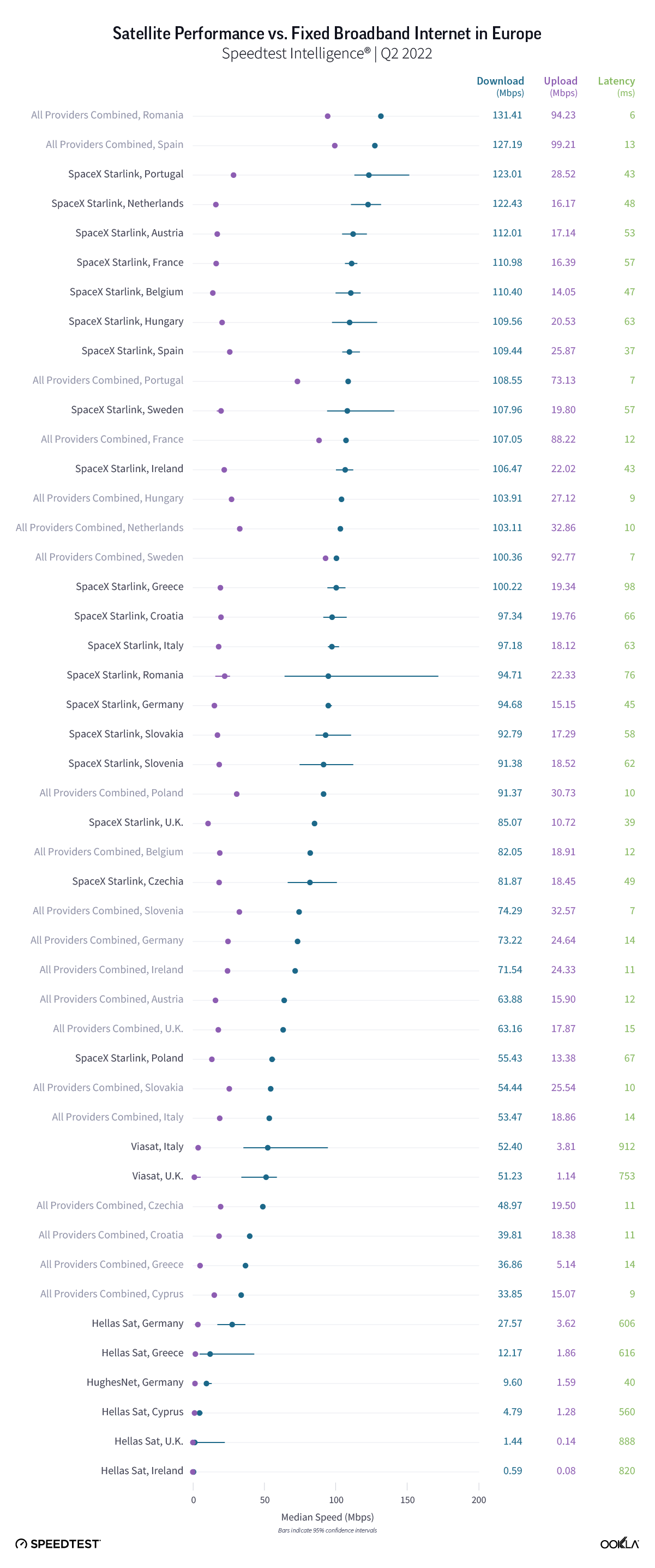
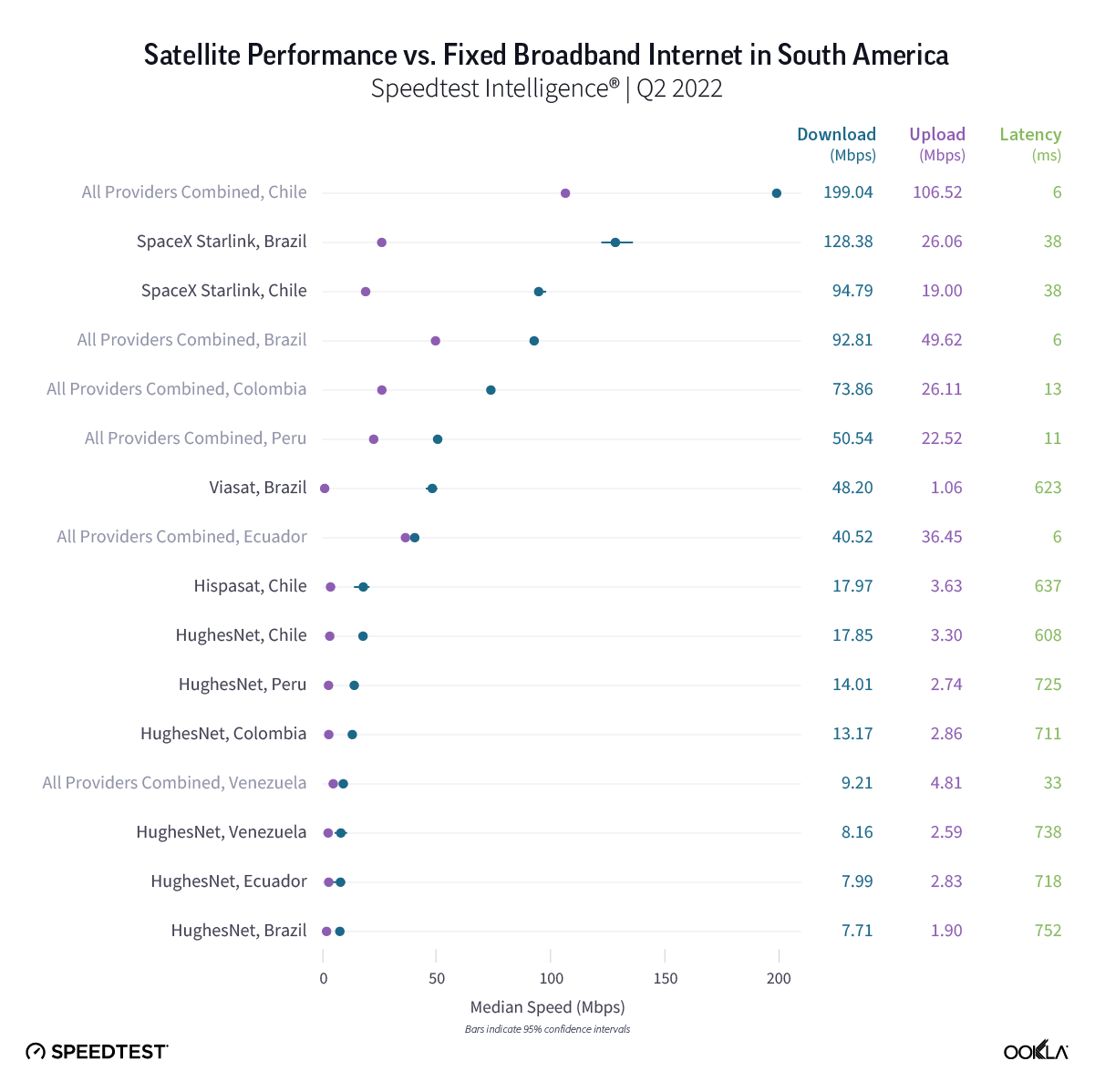
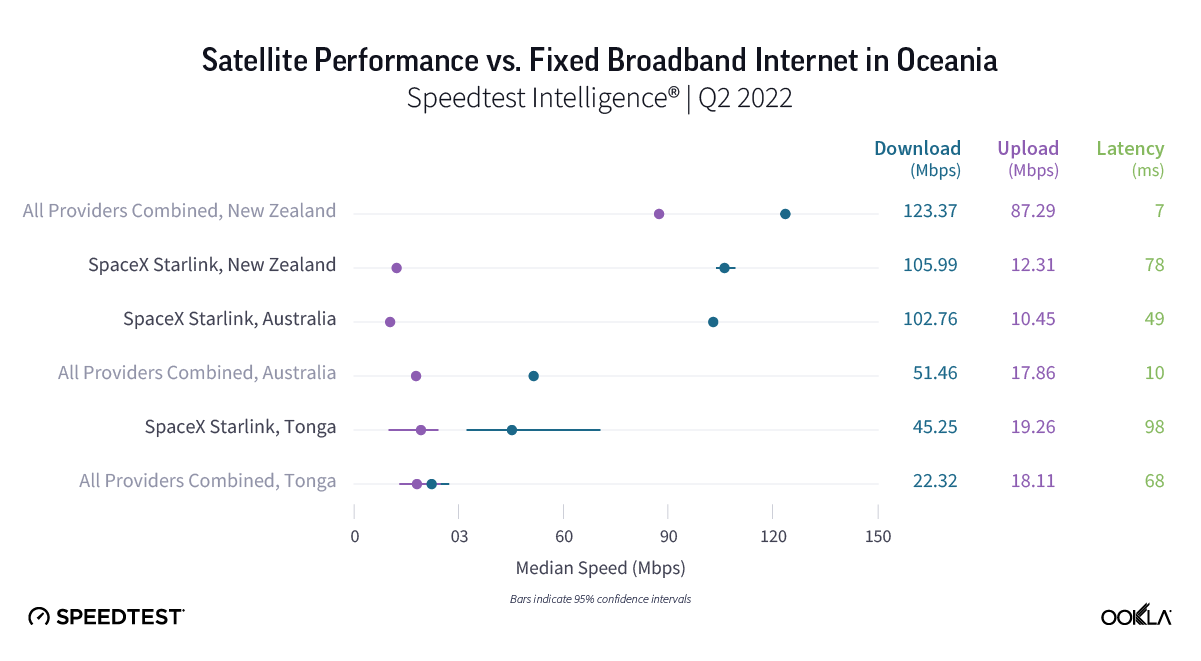
Consumers around the world eagerly awaited Samsung’s release of the latest line of its flagship Galaxy S series of smartphones on February 1, 2024. Was the wait worth it? In this article, we analyze how the Samsung Galaxy S24 family measures up against its predecessors in terms of 5G speed and latency during its first several weeks on the market (February 1 – March 24, 2024).
With new chipsets and technologies alongside plenty of other cool new features in Galaxy S24 devices, we examined early results from Speedtest® users in 15 select countries around the world to see whether the Galaxy S24 lineup — comprising the S24, S24+, and S24 Ultra models — outpaced Samsung’s earlier S22 and S23 families for 5G performance. Additionally, we’ve compared the 5G speeds and latency of Apple’s iPhone 15 family — including the iPhone 15, 15 Pro, and 15 Pro Max — against Samsung’s offerings.
It’s important to note that device performance metrics can vary significantly from one country to another. Factors such as government and mobile operator investments in 5G infrastructure, spectrum allocations, and the extent of 5G network deployment all contribute to these variations.
Key takeaways:
- The Samsung Galaxy S24 family showed a statistically significant lead for median 5G download speeds in seven out of 15 countries in this study. On the other hand, the Apple iPhone 15 family posted the fastest 5G speeds in only one country. It’s worth noting, however, that speed differences between Galaxy S24 devices and iPhone 15’s were relatively minor in some of the countries analyzed (see the charts below for details).
- The S24 family recorded the lowest median 5G multi-server latency in 10 of 15 countries, whereas iPhone 15 devices offered the highest median 5G latency in 10 markets.
- Samsung Galaxy S22 models unsurprisingly offered the slowest median 5G download speeds in eight countries, while the Galaxy S23 family was slowest in four countries.
- Devices in the Galaxy S24 family experienced the fastest median 5G upload speed in 13 of the 15 countries examined for this analysis. However, upload speeds were much slower than 5G download speeds, ranging from 11.83 Mbps to Mbps to 66.52 Mbps, with median 5G upload speeds of 50 Mbps or better found in only three countries (South Korea, Qatar, and the U.A.E.).
To learn more about what speeds mean in real-world terms, check out our article looking at how much speed users need for a variety of daily mobile activities.
Take me straight to the data!
Asia Pacific | Middle East & Africa | Europe | North America
New chipsets and modems in the Galaxy S24 family
Everyone wants to know if the newest technology is worth the upgrade when they’re investing in an expensive new smartphone. Each device within the Galaxy S24 family has various upgrades (including new AI features), but when it comes to features that impact speed and latency performance, here’s a look at the chipsets and modems for each line of smarthpones in our study:
- Samsung Galaxy S24 Ultra models use Qualcomm’s Snapdragon 8 Gen 3 chipset globally, while the S24 and S24+ use it only in Canada, China, Hong Kong, Taiwan, and the United States. The Samsung Exynos 2400 is used elsewhere for the S24 & S24+.
- The Galaxy S23 series uses Qualcomm’s Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 worldwide, while Samsung S22 models use an Exynos 2200 chipset in Europe and the Snapdragon 8 Gen 1 elsewhere.
- Galaxy S24 devices utilize the Snapdragon X75 5G modem, S23 models have a Qualcomm Snapdragon X70 modem, while S22 models have a Qualcomm Snapdragon X65 modem.
- Apple iPhone 15 models use Apple’s A16 Bionic chipset, while iPhone 15 Pro and Pro Max models use the A 17 Pro chip. All devices in the Apple iPhone 15 family utilize Qualcomm’s Snapdragon X70 5G modem.
Do you own one of these devices? See how your speeds compare by taking a quick Speedtest. And to learn more about mobile and fixed broadband performance in cities and regions across the world, visit the Speedtest Performance Directory™, where you’ll find ISP recommendations, insights on mobile and fixed broadband performance, and more.
Digging into the Data: Where does the Samsung Galaxy S24 Family Lead its S22, S23, and iPhone 15 Counterparts Around the Globe?
Early findings from Speedtest Intelligence® reveal that the latest Galaxy S24 family outperformed its predecessors — especially S22 models — in terms of 5G speed across several of the countries we analyzed. While differences in speed between devices were minimal in some countries, S24 models showed significant speed advantages over previous generation Samsung devices in markets like Qatar, the United Arab Emirates, and others.
Does that mean users in those locations should upgrade immediately? Not necessarily. The decision to upgrade depends on various factors, from price to features to performance and more. However, if speed is your primary concern, the Galaxy S24 series is a compelling option, especially for consumers currently utilizing devices from the Galaxy S22 lineup, which is now over two years old.
Read on to see our complete analysis of all 15 countries in this study or select a region below to dig into more localized results.
Asia Pacific | Middle East & Africa | Europe | North America
Asia Pacific
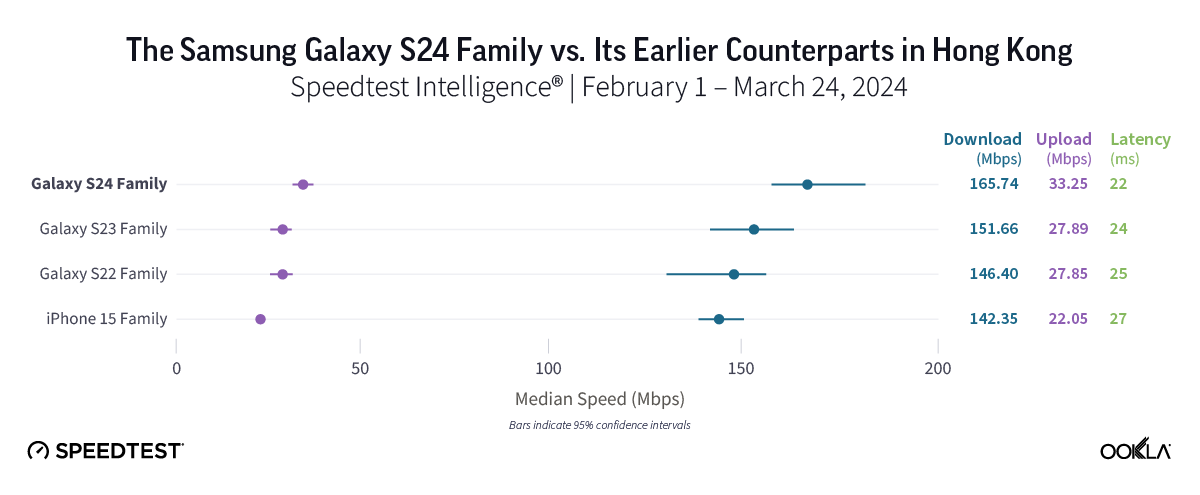
Consumers in Hong Kong who want new features might want to upgrade
Speedtest Intelligence data revealed strong performance for all device families in Hong Kong, with the new Galaxy S24 family performing particularly well, boasting a median 5G download speed of 165.74 Mbps and the lowest median 5G multi-server latency in the market at 21.74 ms. However, the S24’s median 5G download speed was statistically comparable to that of its older Samsung and iPhone 15 peers, making the choice to upgrade currently more about new features than about performance.
Bottom line: With strong — and similar — 5G download speeds across all device families in Japan, upgrading to a new Galaxy device isn’t a must just yet, unless you want to enjoy the S24 family’s new features.
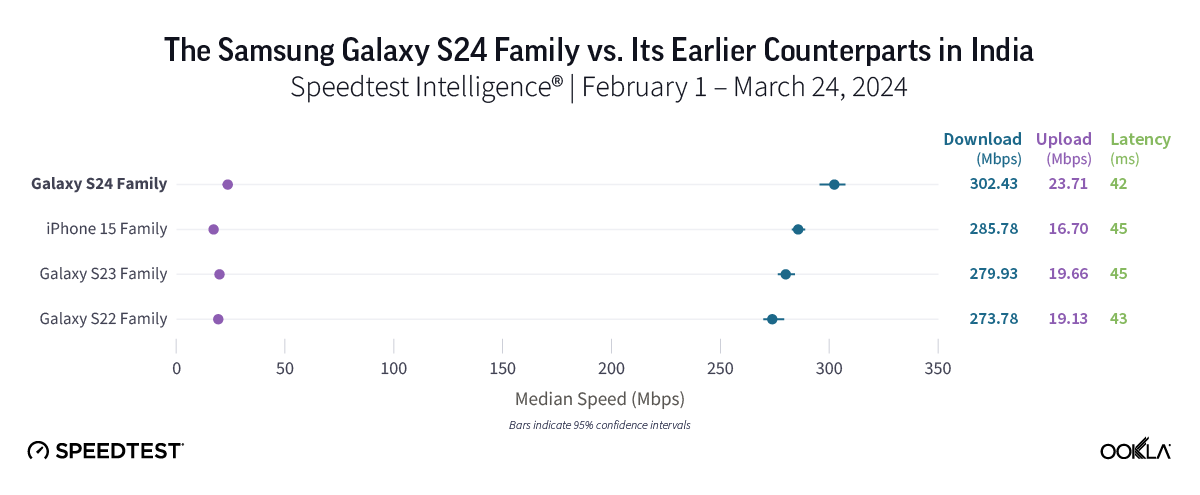
5G speeds were fast across the board in India, where the Samsung Galaxy 24 family held a slight edge
In the early days following the release of the Galaxy S24 series in India, the latest Samsung models led for both 5G download speeds and 5G multi-server latency. While 5G speeds impressed across all device families in India — all notched speeds of at least 273.78 Mbps — Galaxy S24 models posted the top median 5G download speed at 302.43 Mbps and the lowest median 5G multi-server latency at 41.56 ms. On the other hand, Galaxy S22 devices showed the slowest — but still impressive — speeds in India at 273.78 Mbps, while the Samsung Galaxy S23 was just a tick behind at 279.93 Mbps. The iPhone 15 family, meanwhile, clocked in with a median 5G download speed of 285.78 Mbps.
Bottom line: Consumers in India currently using S22 devices might want to upgrade to an S24 model, given the nearly 30 Mbps speed advantage the new devices provided in this study. However, with excellent 5G speeds across all device families and similar speeds for devices in the S22, S23, and iPhone 15 families, users might not feel a huge difference in their 5G experience from one device to another.
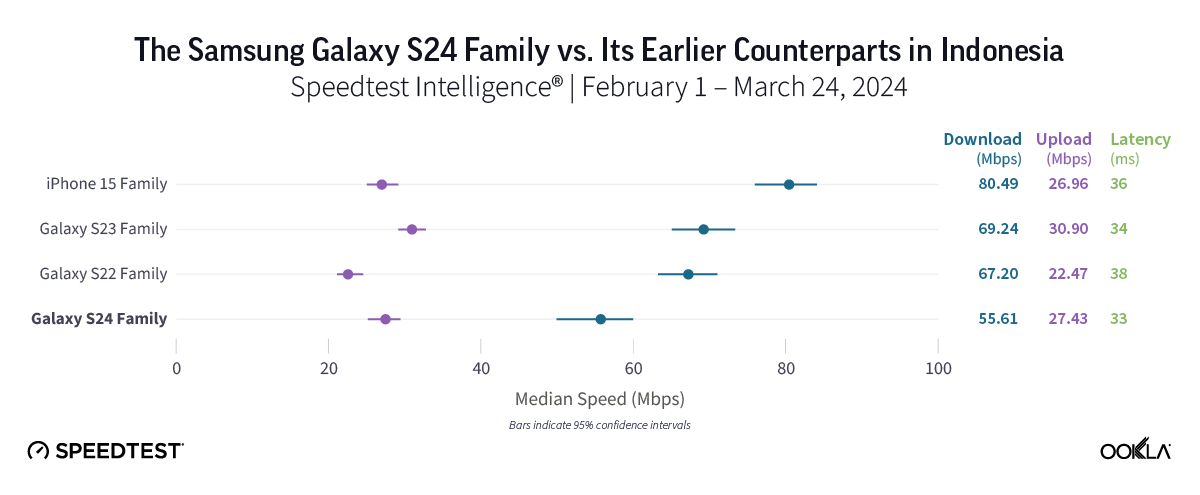
Samsung Galaxy enthusiasts in Indonesia needn’t rush to upgrade to an S24 device — yet
In contrast with what our results showed in most countries, the iPhone 15 family emerged as the leader in Indonesia with a median 5G download speed of 80.49 Mbps. All three Samsung Galaxy families trailed with speeds ranging from 55.61 Mbps for the S24 family to 69.24 Mbps for S23 models. While the iPhone 15 family’s 5G speed was nearly 25 Mbps faster than that of S24 devices, it’s worth noting that the difference among all three Samsung Galaxy models was only about 14 Mbps, and our results revealed no statistical difference in median 5G download speeds between the S22 and S23 families.
Bottom line: Despite the iPhone 15 providing the top speeds in the market, the Galaxy S24 could hold greater long-term potential for consumers in Indonesia, especially when compared to older Samsung models. Equipped with a newer processor and modem, the S24 could see quicker speeds over time as Indonesia’s 5G networks evolve. In the meantime, users shouldn’t experience notable disparities in speed or latency among all three Samsung device families analyzed.
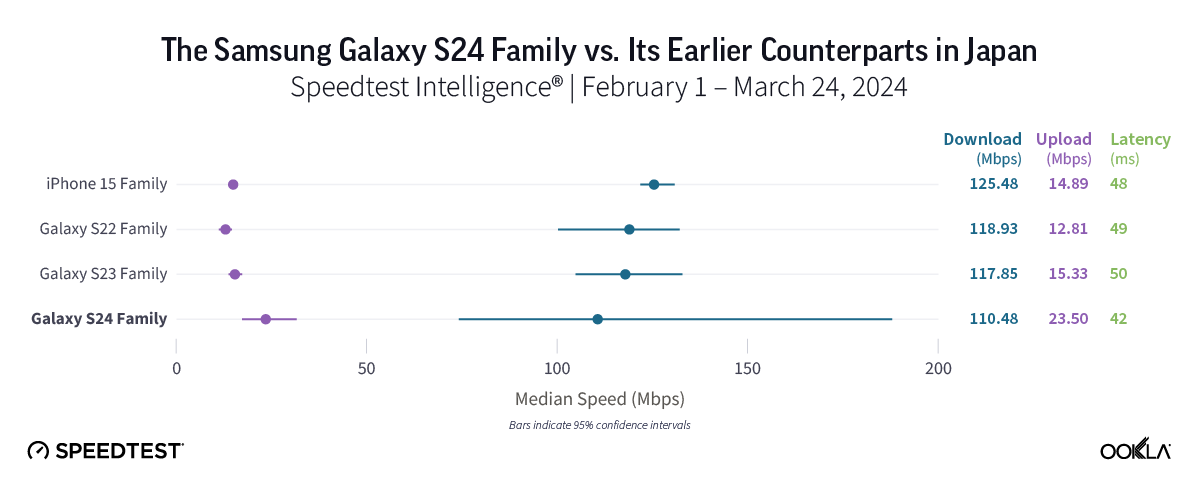
No clear advantage to upgrading to a new Galaxy S24 in Japan
People in Japan who upgraded to a Galaxy S24 device likely haven’t seen a performance boost just yet. While all four device families performed similarly well in Japan, there was no statistical difference in the median 5G download speeds offered by all three Galaxy families, with speeds ranging from 110.48 Mbps to 118.93 Mbps across all three Galaxy devices. The iPhone 15 lineup also had a strong speed at 125.48 Mbps.
Bottom line: With generally similar median 5G download speeds across all device families in Japan, users who are considering upgrading to a new Galaxy smartphone might want to wait. While we anticipate the S24’s speeds to surpass those of its predecessors over time, 5G speeds in the market were quite close across all three Galaxy device families in the early days of the S24’s release.
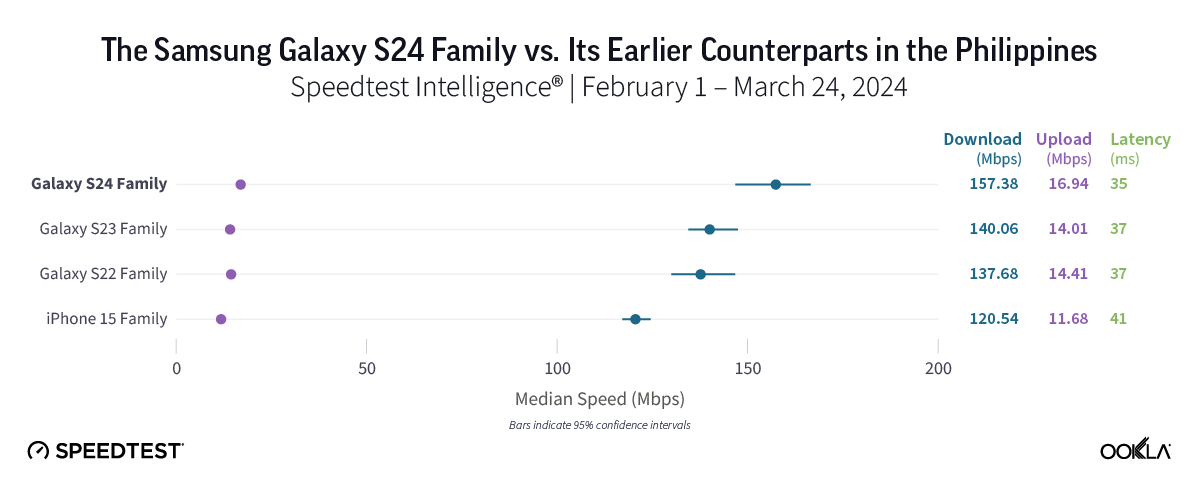
For users in the Philippines who want the fastest 5G, Galaxy S22 users may want to upgrade.
Samsung Galaxy S24 users in the Philippines might have noticed a modest improvement to their 5G speeds compared to those on older S23 and S22 models since they upgraded, as the Galaxy S24 family’s median 5G download speed of 157.38 Mbps was about 20 Mbps faster than that of Galaxy S22’s (137.68 Mbps) and a little over 15 Mbps faster than the Galaxy S23 family (140.06 Mbps). Meanwhile, the iPhone 15 family’s median 5G download speed of 120.04 Mbps trailed all three Samsung Galaxy families in the market.
Bottom line: For users in the Philippines seeking the fastest possible 5G experience, upgrading to an S24 device is worth considering. However, it’s worth noting that the differences in speed between devices wasn’t as stark as that in some other countries, and upgrading likely isn’t for everyone just yet.
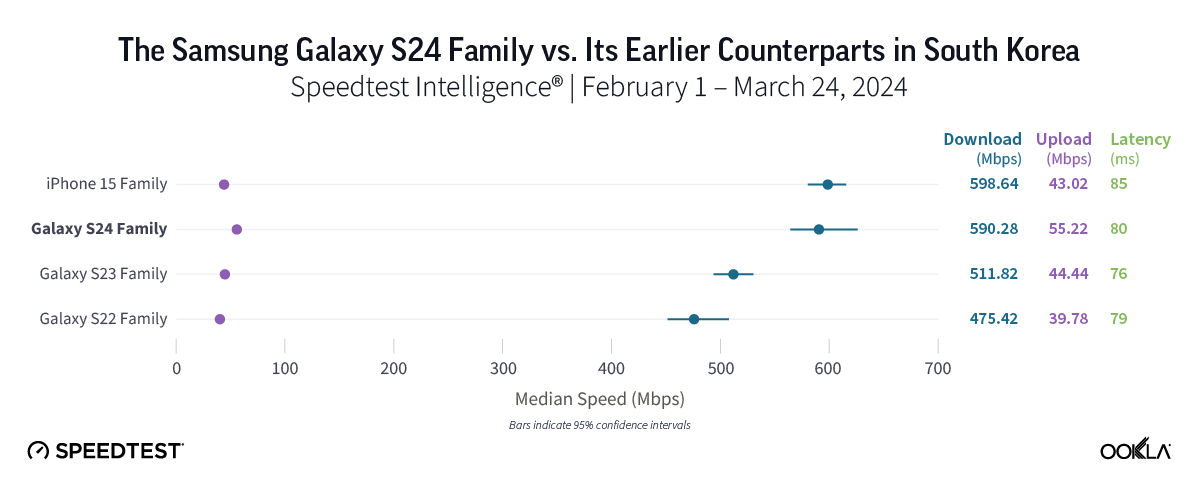
Samsung Galaxy S24 and iPhone 15 much faster on 5G in South Korea than S22 devices
In South Korea, home to the first widespread 5G launch in the world, our results reflected outstanding 5G speeds, with the iPhone 15 and Samsung Galaxy S24 families posting similar median 5G download speeds of 598.64 Mbps and 590.28 Mbps, respectively. The S22 family, meanwhile, offered the “slowest” 5G speeds in South Korea, posting an excellent median 5G download speed of 475.42 Mbps, while Galaxy S23 devices came in at 511.82 Mbps.
Bottom line: 5G users in South Korea can expect remarkable 5G speeds across the board, regardless of their device. However, Samsung Galaxy loyalists who currently use S22 models might want to consider moving to an S24 model, given that the S24 family was over 100 Mbps faster than Galaxy S22’s, while also offering the top median 5G upload speed in the market at 55.22 Mbps. For users who prioritize the fastest 5G experience, Galaxy S24’s and iPhone 15’s are both worth a look.
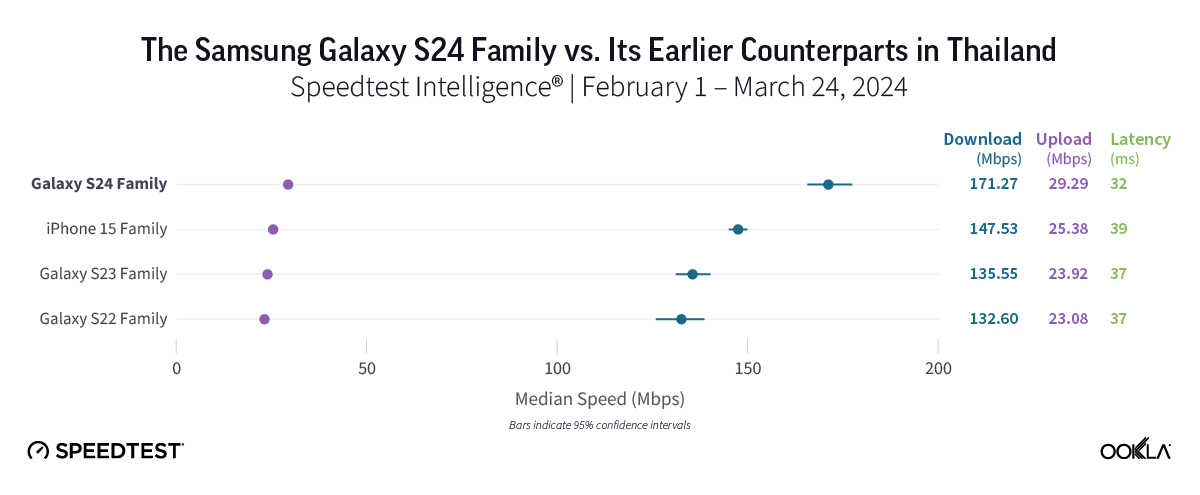
Samsung Galaxy S24 family provides top 5G download speeds in Thailand
In Thailand, Speedtest Intelligence showed that the Galaxy S24 family delivered the fastest median 5G download speed in the market at 171.27 Mbps. That speed marks a notable improvement of roughly 35 Mbps over the S22’s 132.60 Mbps and the S23’s 135.55 Mbps. The Galaxy S24 family also offered the lowest median 5G multi-server latency in Thailand at 32.46 ms. The iPhone 15 family provided the second-fastest median 5G download speed in the market at 147.53 Mbps.
Bottom line: If you’re thinking of upgrading from an S22 or S23 device, our findings suggest that the Galaxy S24 might be the right choice. With faster 5G speeds compared to previous generations, coupled with low latency, smartphones in the Galaxy S24 family should allow for quick content downloads and smooth connectivity overall.
Middle East and Africa
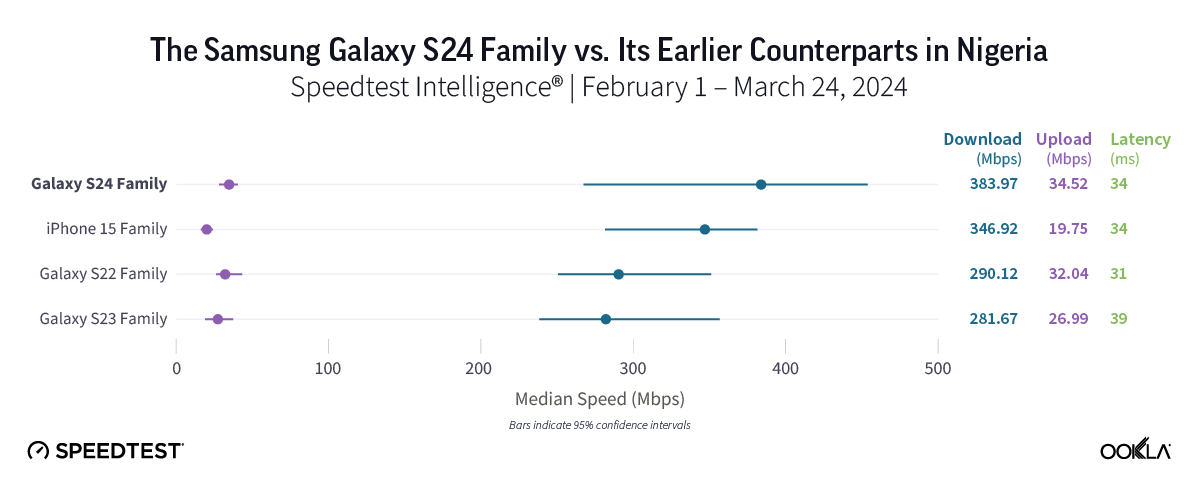
Excellent 5G speeds in Nigeria, but too soon to tell if you should upgrade for performance
In Nigeria, 5G speeds were impressive overall, from the Galaxy S23 family’s median 5G download speed of 281.67 Mbps to the new Galaxy S24’s speed of 383.97 Mbps. However, in these early days of the S24 lineup’s release, we are still waiting to see how things stabilize in the market before we can make a firm recommendation on whether to upgrade.
Bottom line: For users who like to have the latest gear and/or want the new features offered by the S24 lineup, upgrading is certainly worth considering. But with fast 5G speeds in general, users on any of the device families we looked at should see a quick download experience in general.
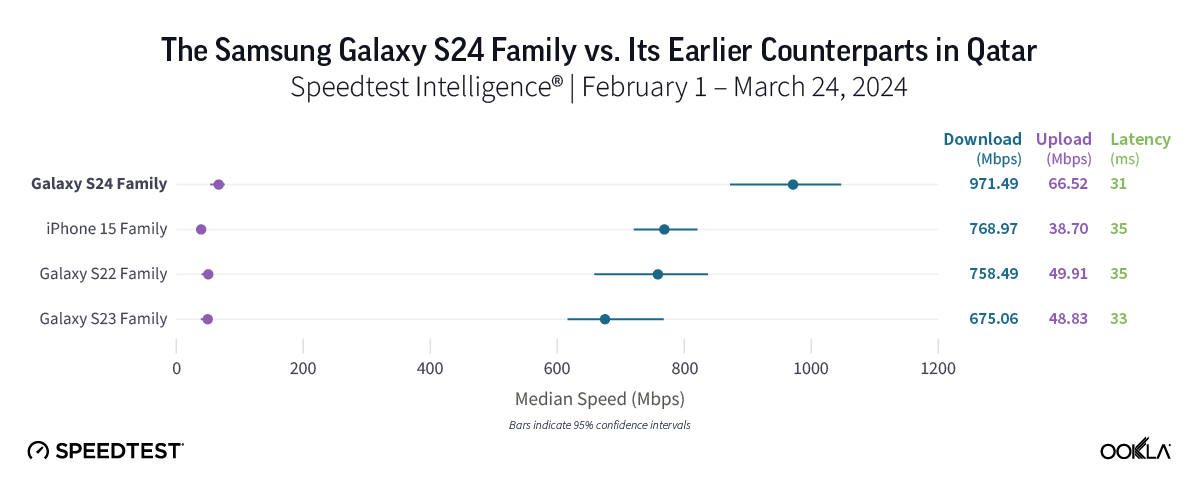
Samsung Galaxy S24 by far the fastest 5G in Qatar
Home to some of the fastest 5G speeds in the world, Qatar showcased impressive median 5G download speeds across all three device families analyzed. The Galaxy S24 family led the pack with a jaw-dropping median 5G download speed of 971.49 Mbps and the top median 5G upload speed in the market at 66.52 Mbps. The Galaxy S22 and S23 families trailed, albeit with great median 5G download speeds of 675.06 Mbps and 758.49 Mbps, respectively. The iPhone 15 family also had a strong showing in Qatar, posting a median 5G download speed of 788.97 Mbps.
Bottom line: Consumers in Qatar with older Galaxy S22 or S23 devices might want to make the switch, given that the S24 family’s remarkable median 5G download speed of nearly 1 Gbps was much faster than those of either the Galaxy S23 or especially S22 families.
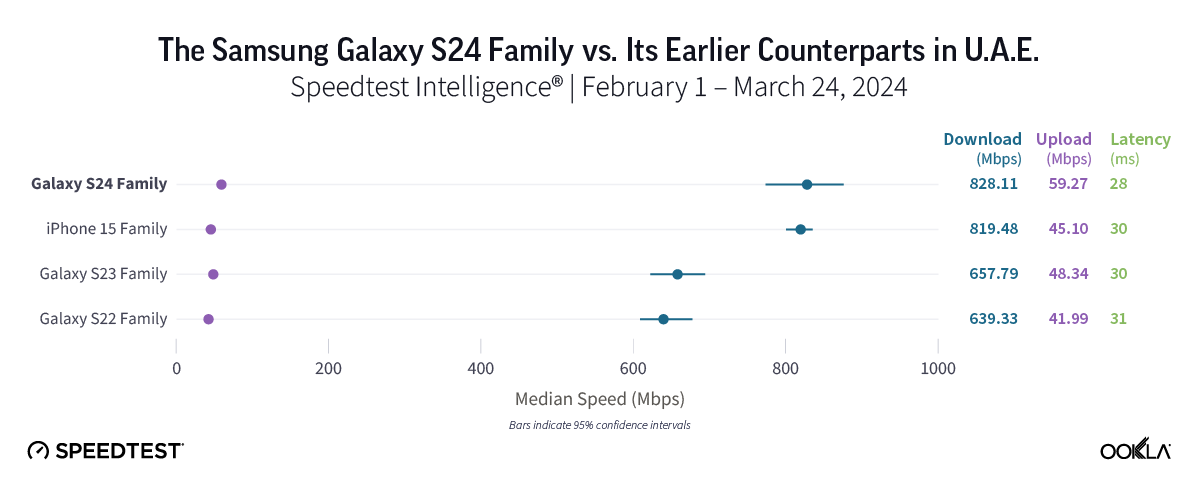
Galaxy S24 a good option for Samsung fans in the U.A.E.
In the U.A.E., which is home to outstanding 5G speeds in general, the Samsung Galaxy S24 and iPhone 15 families delivered the top median 5G download speeds in the market at 828.11 Mbps and 819.48 Mbps, respectively. When compared to its earlier generation Samsung predecessors, the S24 family held a commanding speed advantage, boasting speeds that were at least 170 Mbps higher than those of either the S22 (639.33 Mbps) or S23 (657.79 Mbps) families.
Bottom line: With median 5G download speeds ranging from 639.33 Mbps to 828.11 Mbps, consumers in the U.A.E. will likely enjoy fantastic speeds regardless of device model. However, for current S22 or S23 users hoping to boost their speeds, the Galaxy S24 family stands out as a good choice.
Europe
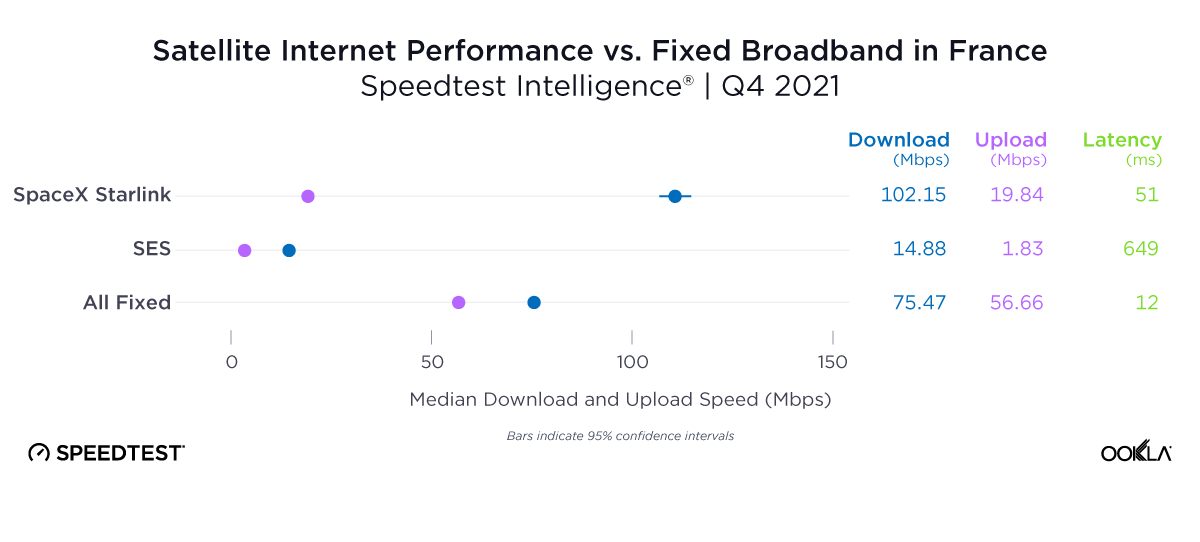
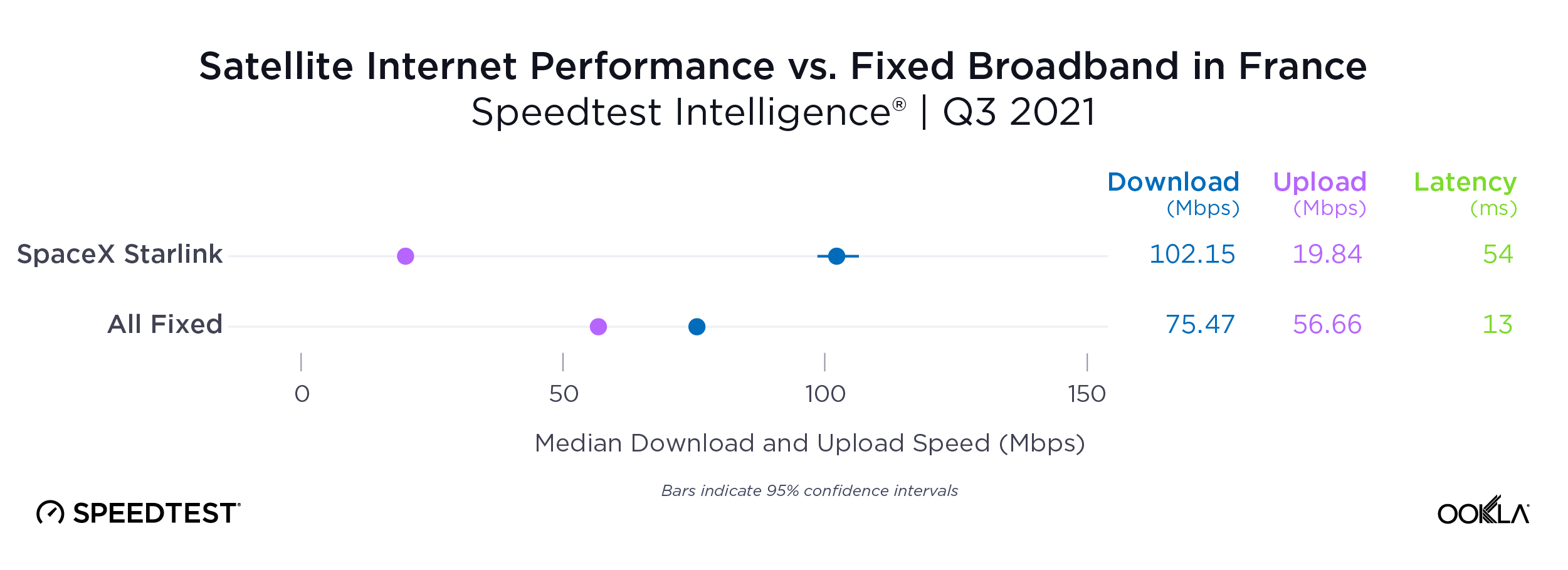
Galaxy 24 family clocked 5G speeds over 80 Mbps faster than those on S22 devices in France
In France, the Galaxy S24 family was the frontrunner, delivering the fastest median 5G download speed among all device families in the market at 292.15 Mbps. That marks a significant improvement of over 80 Mbps compared to the S22 family’s speed of 211.32 Mbps, along with a jump of more than 60 Mbps compared to the S23’s speed of 229.78 Mbps. Meanwhile, iPhone 15 users experienced the second-fastest median 5G download speed in the market at 257.15 Mbps, with 5G latency nearly identical to that of the S22 and S23 families.
Bottom line: For consumers currently using an S23 or especially an S22 model, upgrading to an S24 device is worth considering. Our results in France showed that the latest Samsung lineup delivered a superior 5G speed experience over older Galaxy models, especially those in the Galaxy S22 family.
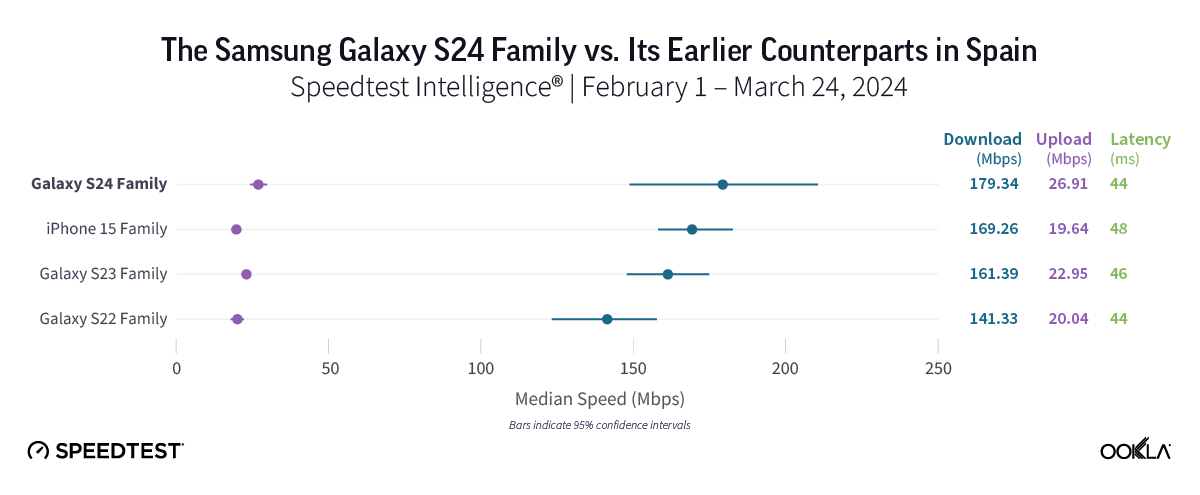
Galaxy S24’s a good choice over S22 models in Spain
All four device families in Spain provided good 5G speeds, ranging from the S22’s median 5G download speed of 141.33 Mbps to the S24 family’s speed of 179.34 Mbps. While speeds recorded on S24, S23, and iPhone 15 devices were statistically similar, the difference in speed between the S24 and S22 was much starker, with the S24 nearly 40 Mbps faster than the S22.
Bottom line: The decision to upgrade should be more straightforward for S22 users in Spain compared to those with S23 or iPhone 15 models, as the S24’s median 5G download speed of 179.34 Mbps was almost 40 Mbps faster than that of the S22 family.
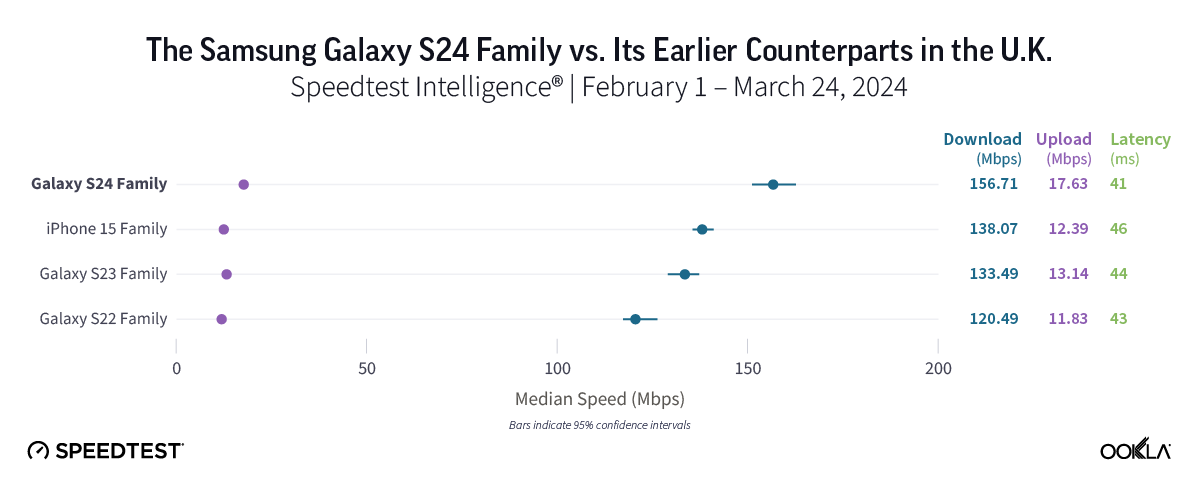
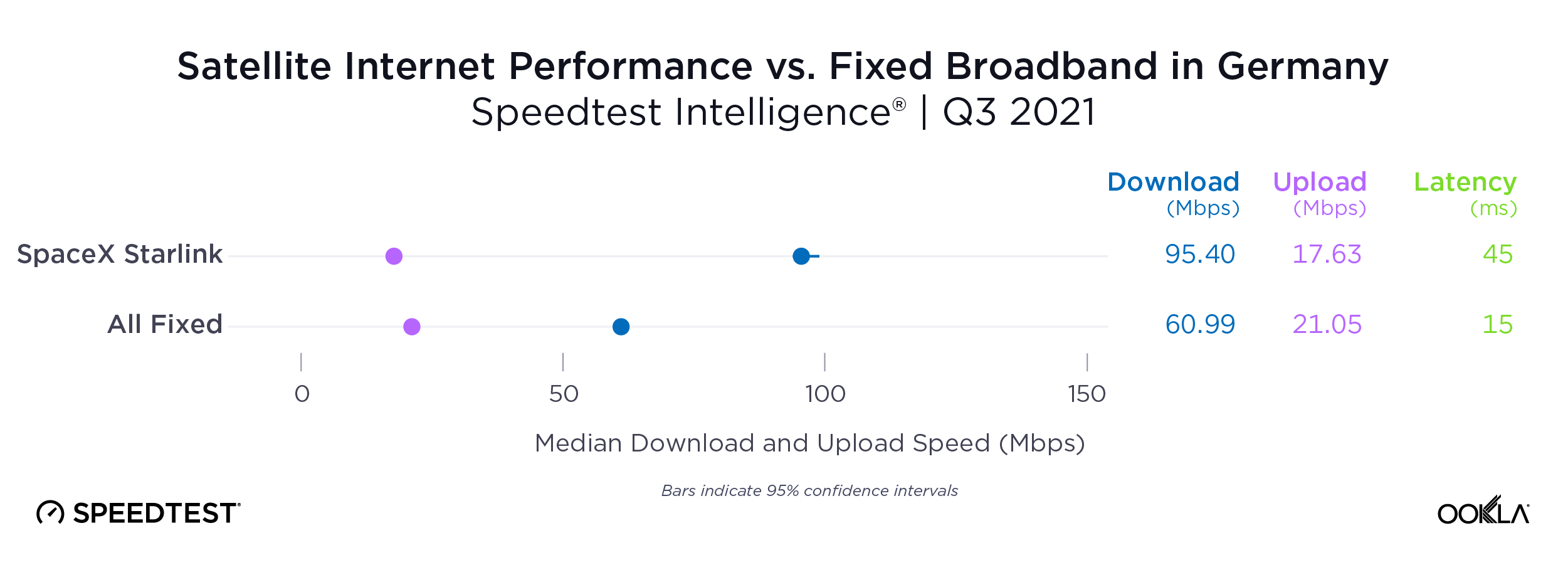
Samsung Galaxy S24 likely worth an upgrade from S22 in the U.K.
In the U.K., Samsung Galaxy S24 models were the fastest in the market, with the S24’s median 5G download speed of 156.71 Mbps offering a speed gain of nearly 40 Mbps compared to the Galaxy S22 family. Galaxy S24 models also posted faster speeds than both the Galaxy S23 and iPhone 15 families, but the difference was less stark than it was with the S22 family, with Galaxy S22 models clocking in at 120.49 Mbps, Galaxy S23’s at 133.49 Mbps, and iPhone 15’s at 138.07 Mbps.
Bottom line: U.K. consumers using either S22 or S23 models may want to look into upgrading to the S24 to enjoy faster speeds. That’s especially true for S22 users, given that the S24’s median 5G download speed was nearly 40 Mbps faster than that of S22 devices.
North America
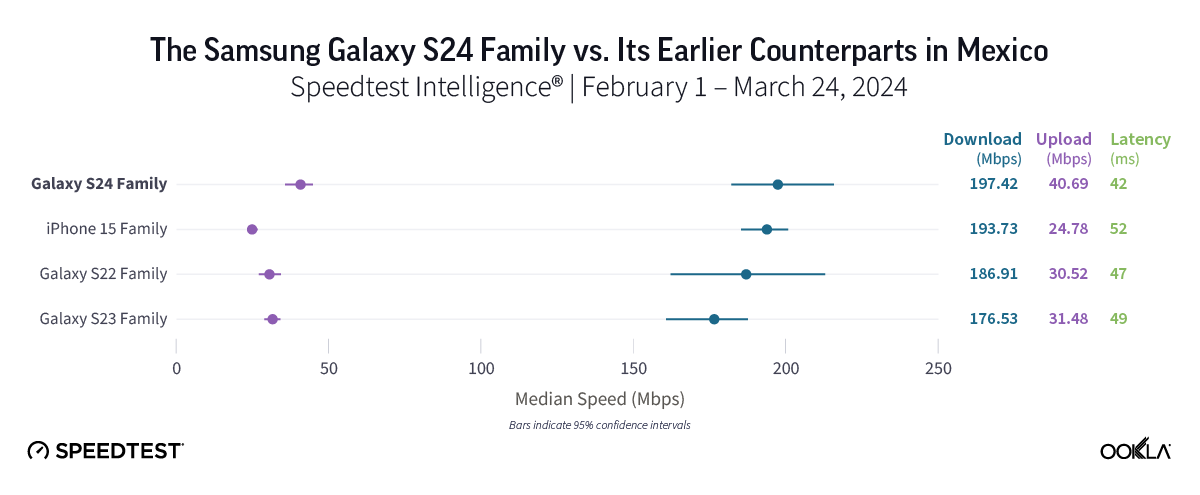
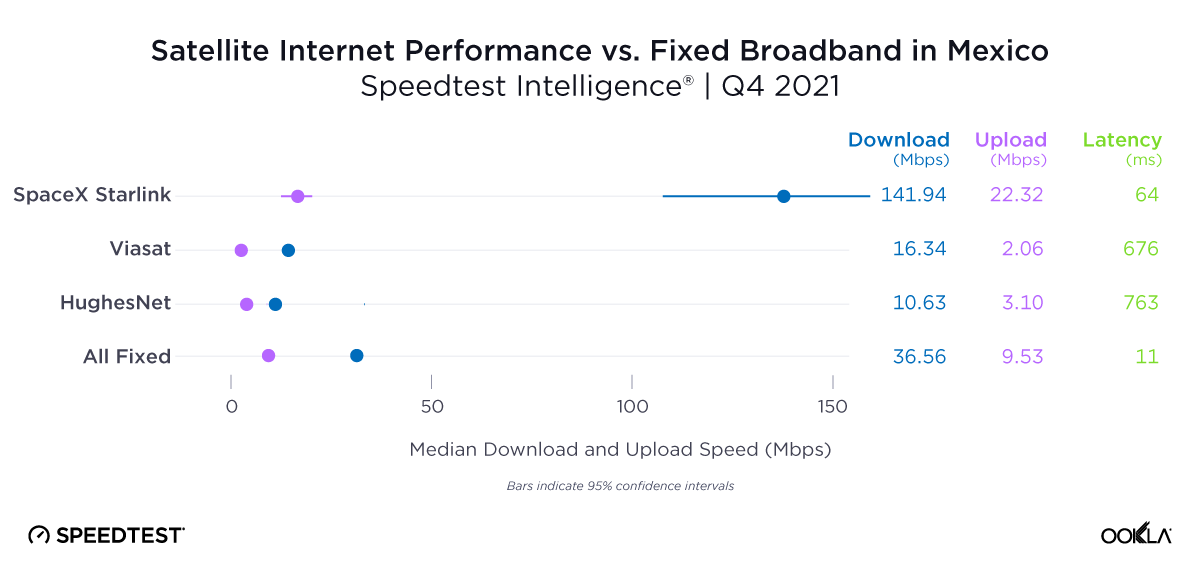
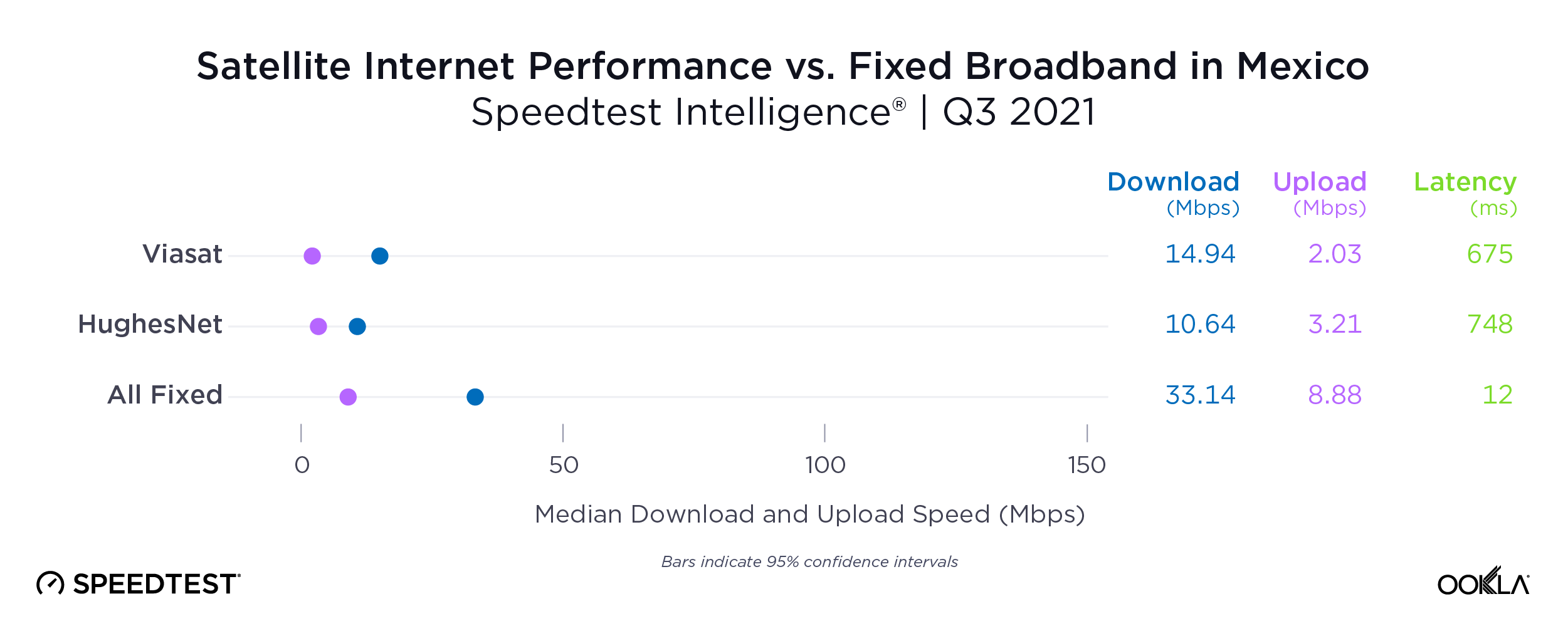
No major 5G speed boost for users in Mexico who upgraded to a Galaxy S24
5G speeds in Mexico were impressive, with all device families posting median 5G download speeds of 176.53 Mbps or better. While Speedtest users of the Galaxy S24 family experienced the fastest median 5G download speed in the market at 197.42 Mbps, that speed marked only a modest improvement compared to Galaxy S22 devices (186.51 Mbps) and iPhone 15 models (193.73 Mbps). The Galaxy S23 family showed the slowest 5G speed in the market at 176.53 Mbps, coming in about 20 Mbps slower than Galaxy S24 models
Bottom line: For users eager to embrace the new features offered by Galaxy S24 devices or move on from S23 devices, an upgrade might be worthwhile. However, with fast 5G speeds across all device families in Mexico and only about 20 Mbps separating all four device families in our study, users likely won’t see a major change in their 5G experience by upgrading.
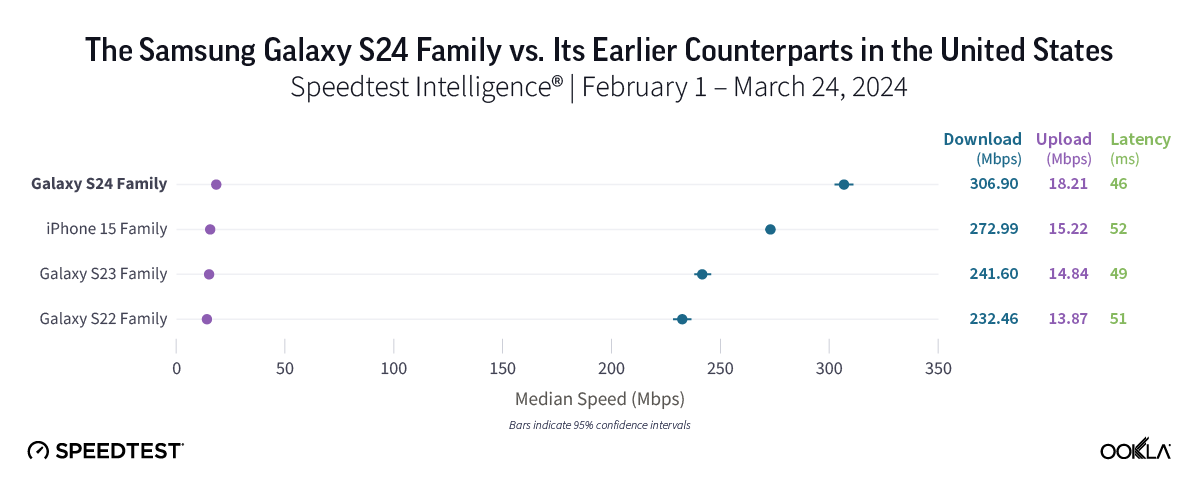
Galaxy S22 users in the U.S. could get faster 5G with the S24 family.
5G speeds in the U.S. had an impressive showing across the board, with median 5G download speeds of at least 232.46 Mbps across all device families. The Samsung Galaxy S24 family led the way with an excellent median 5G download speed of 306.90 Mbps and the lowest median 5G multi-server latency at 45.71 ms. Users of the Galaxy S24 family enjoyed speeds roughly 75 Mbps faster than those on S22 models (232.46 Mbps) and approximately 65 Mbps faster than those on S23 devices (241.60 Mbps). Meanwhile, the iPhone 15 family also offered a strong performance, with a median 5G download speed of 272.99 Mbps.
Bottom line: Users of older Samsung device models in the United States may want to switch to one of the newer models to capitalize on the faster 5G speeds offered by S24 devices, though speeds were strong for all device families in this study.
Ookla will continue monitoring how devices are performing
We’ll continue to check in on device performance as new models enter the market, so stay tuned for further insights into mobile and fixed broadband performance in countries around the world.
If you’ve recently made the switch to an S24 device, make sure you’re getting the speeds you need by downloading the iOS or Android Speedtest® app.