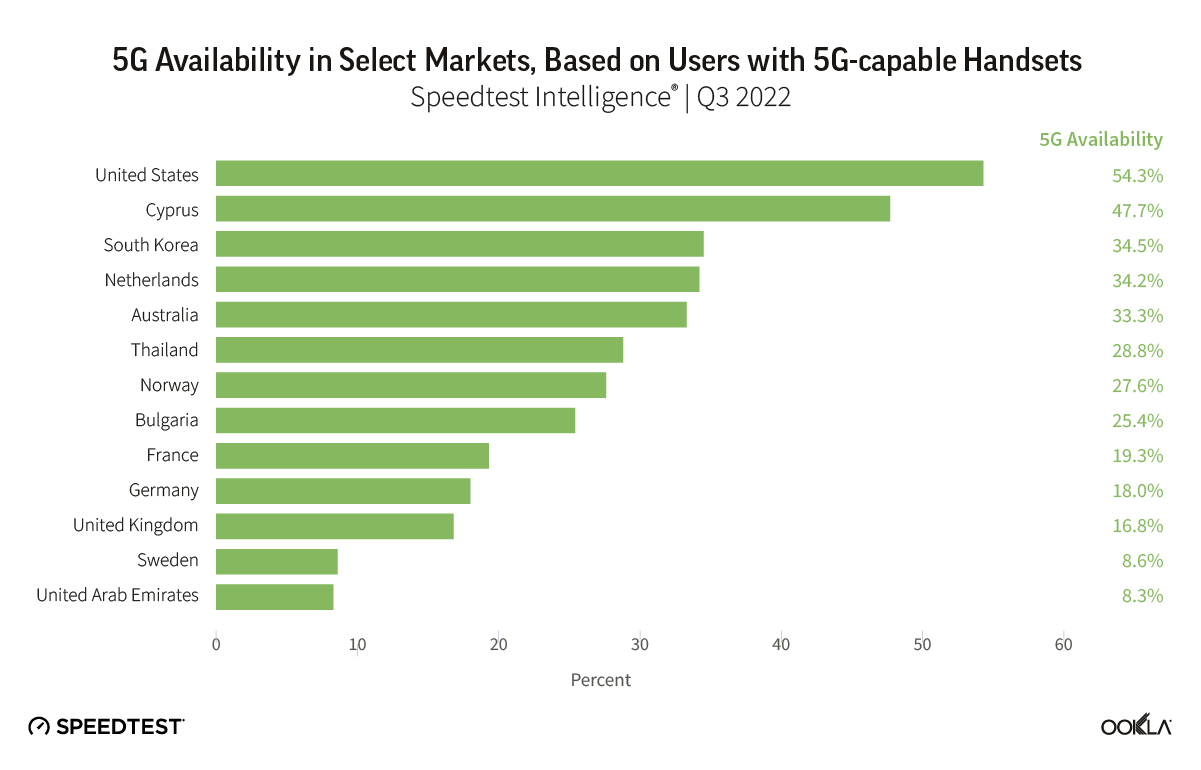
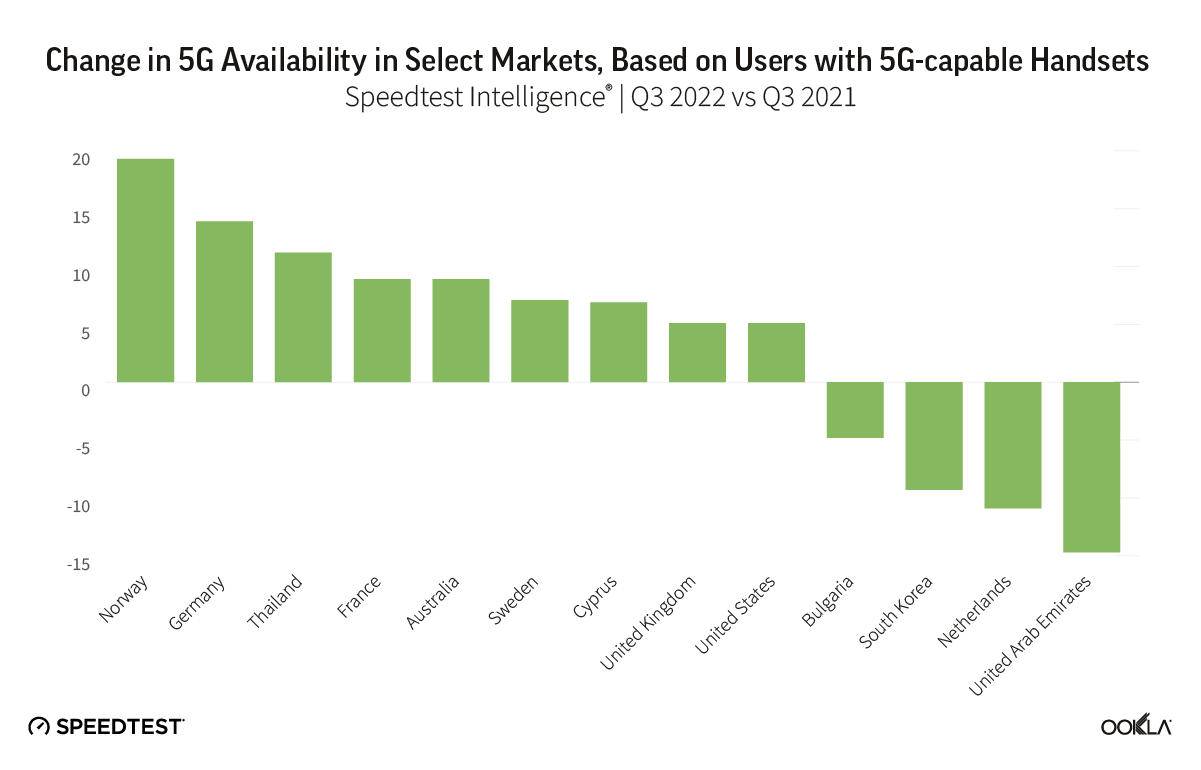
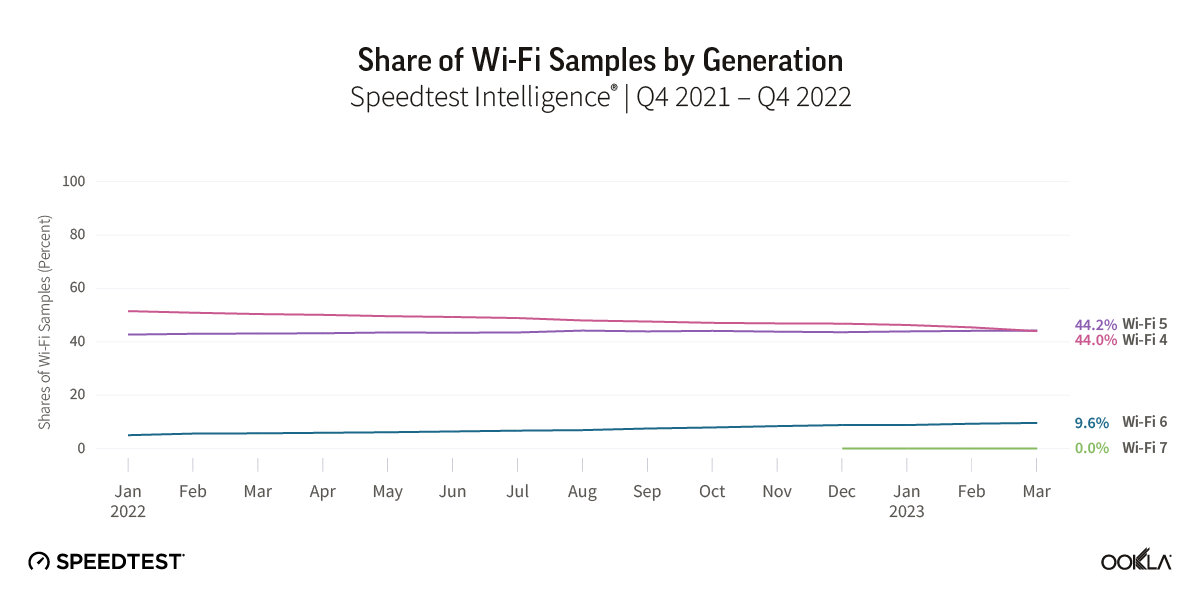
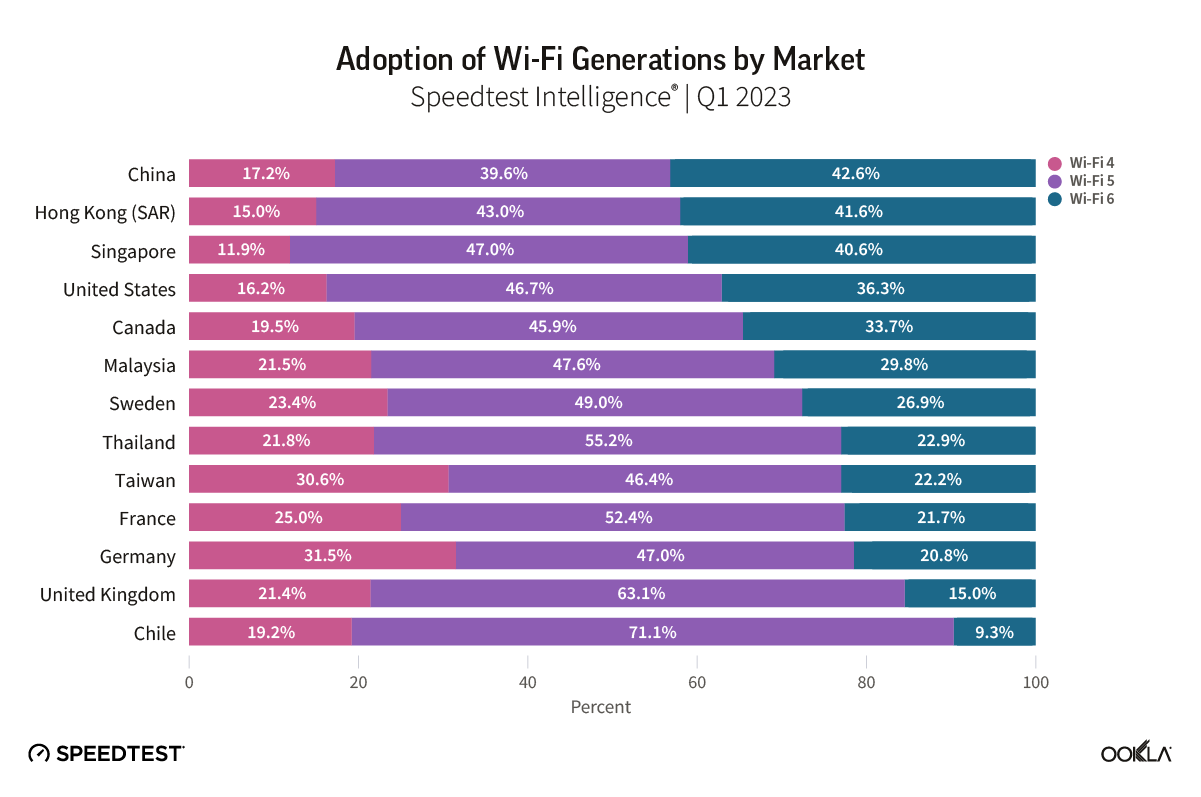
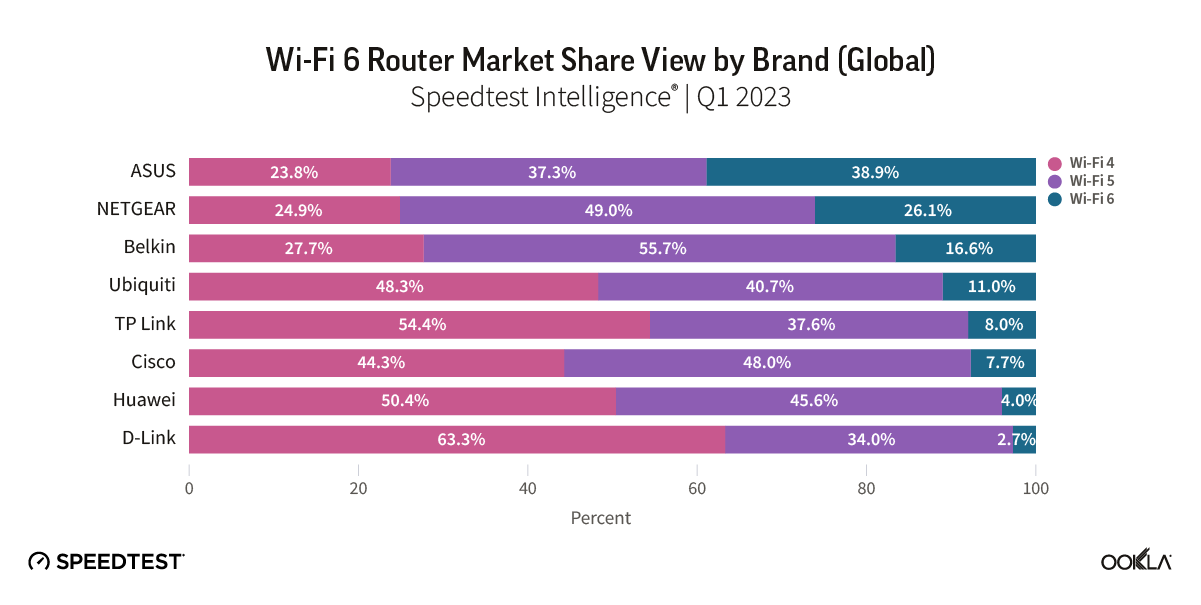
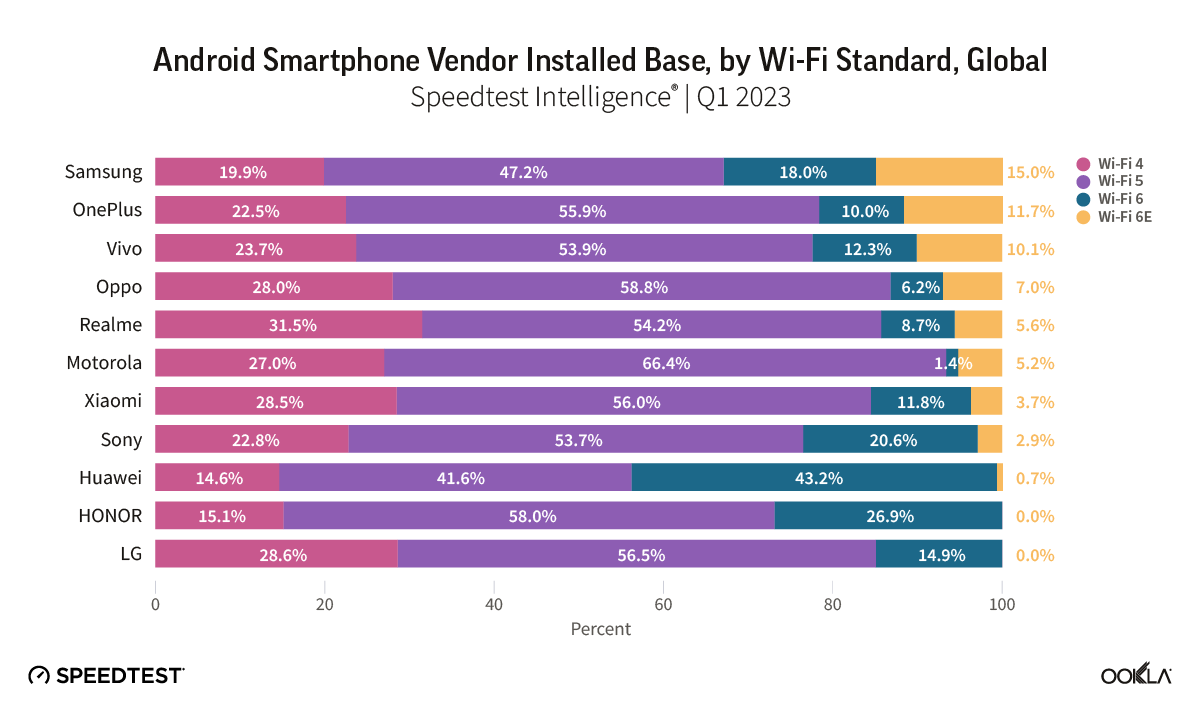
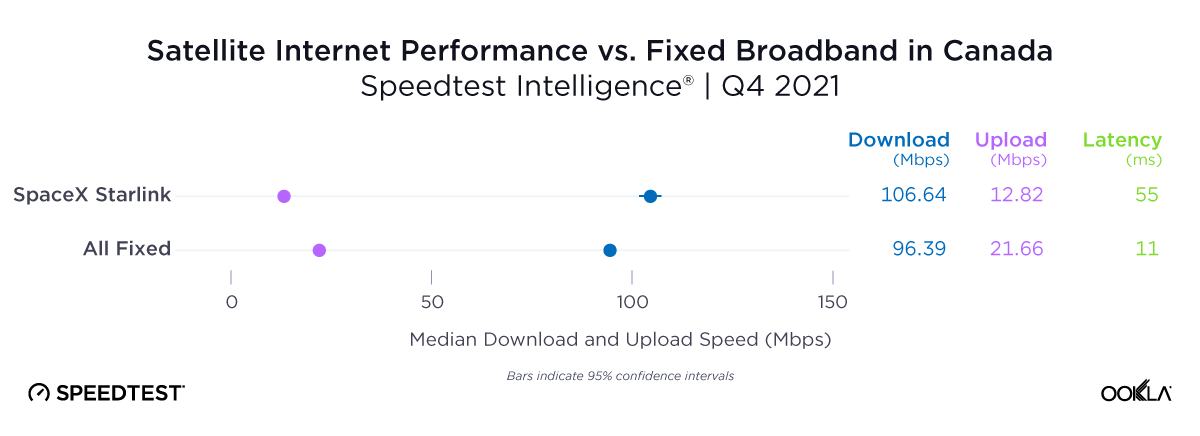
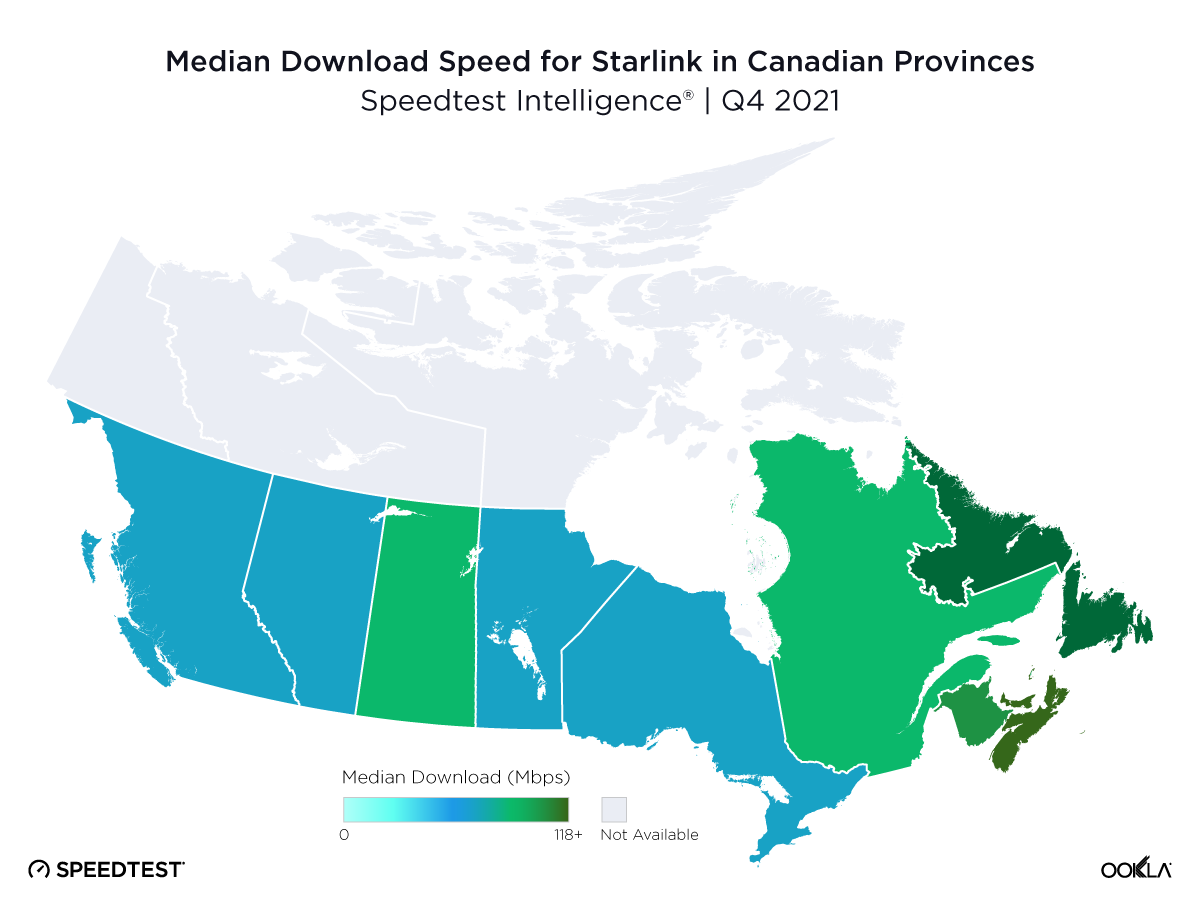
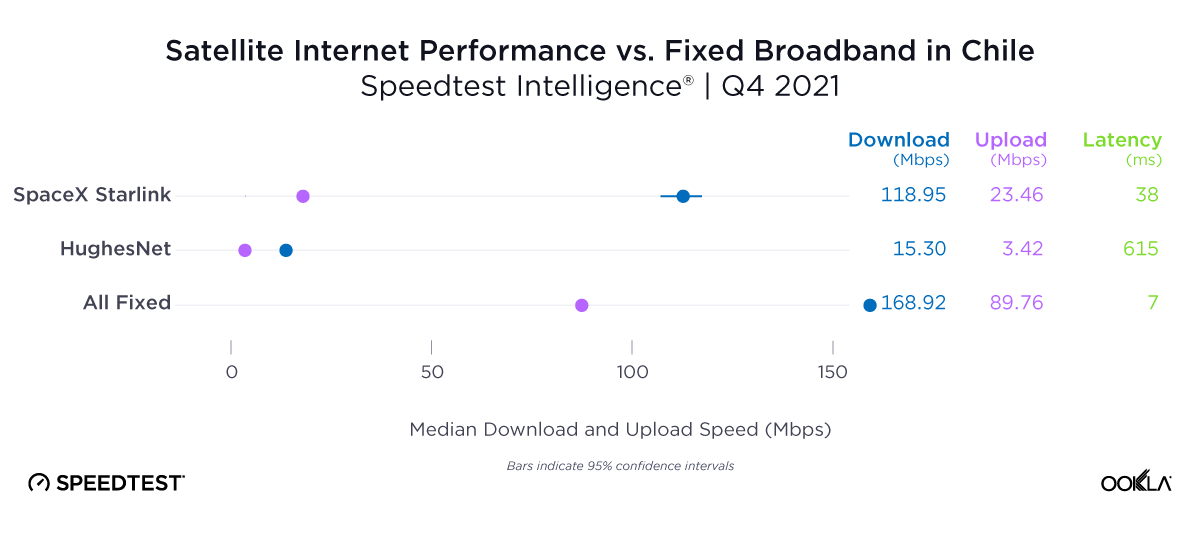
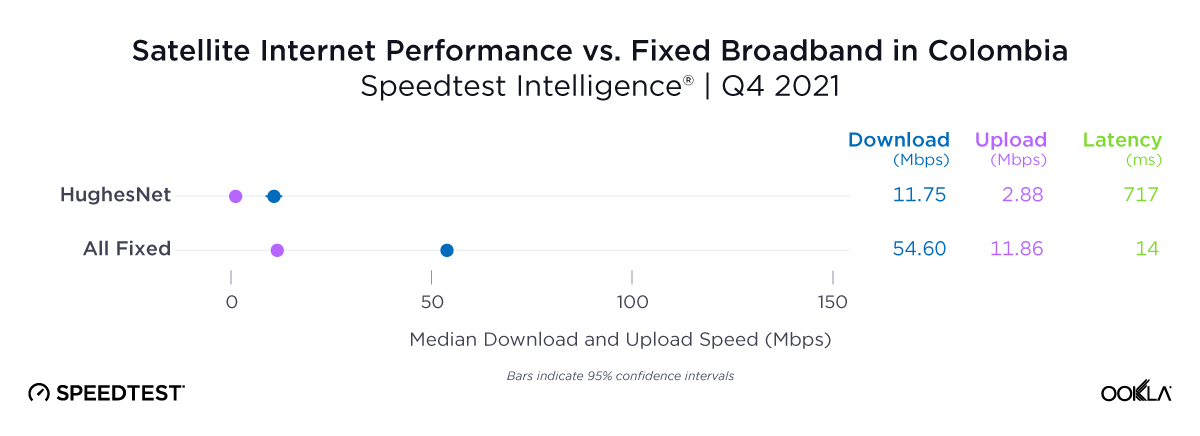
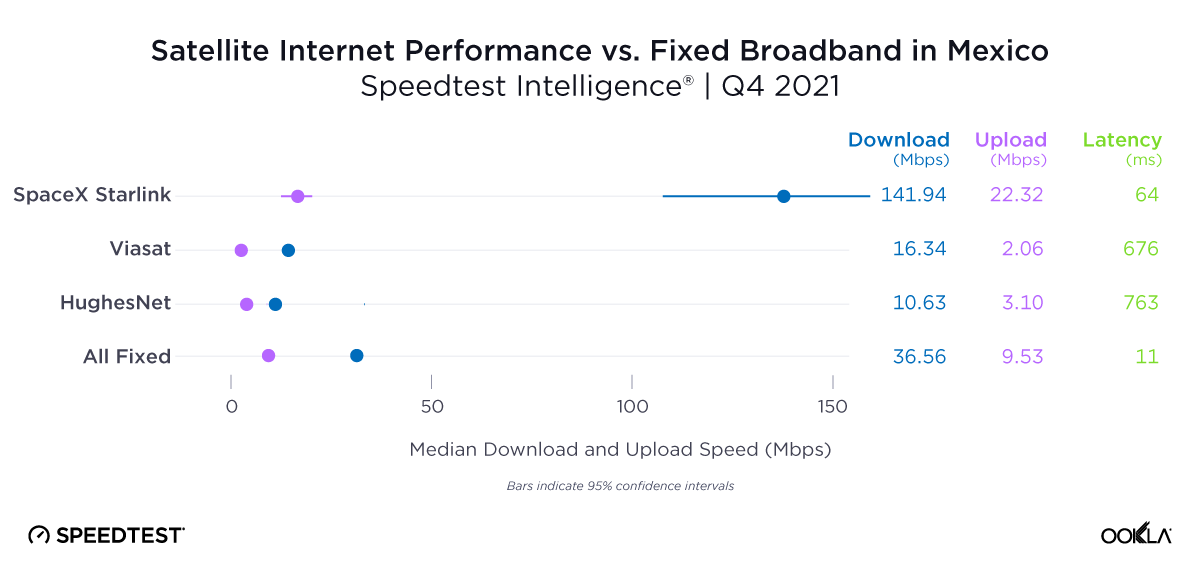
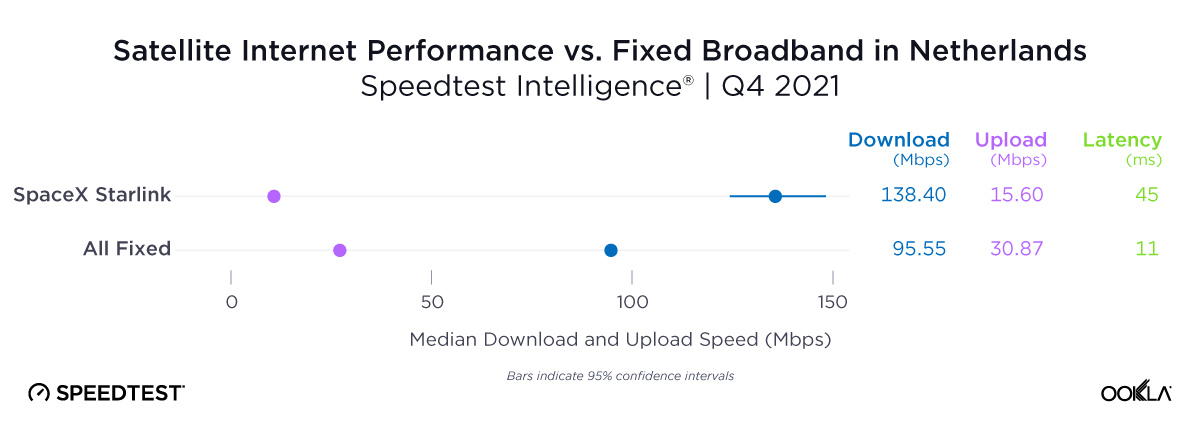
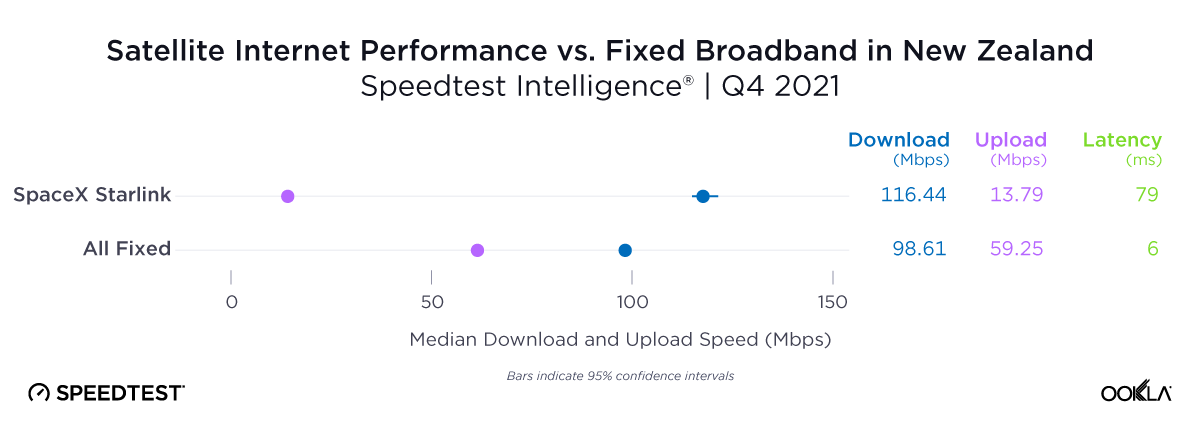
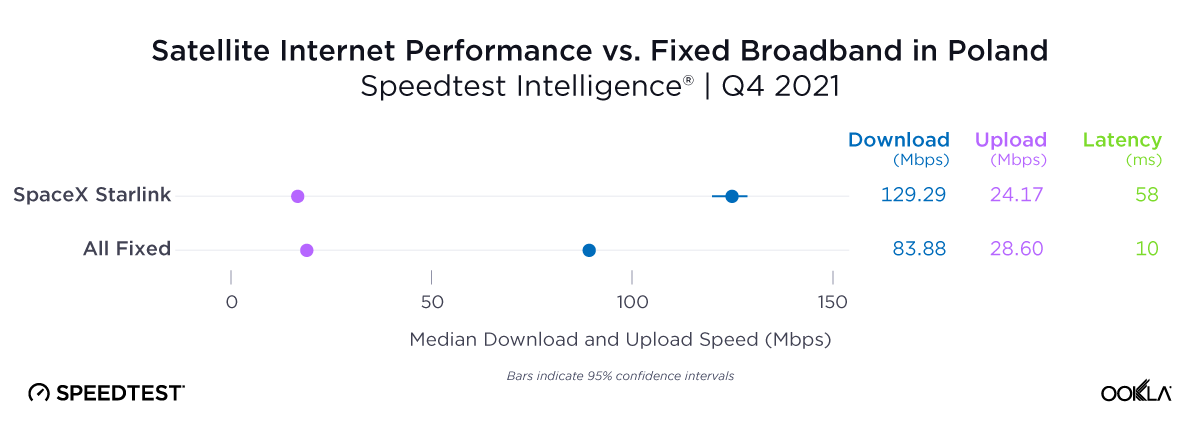
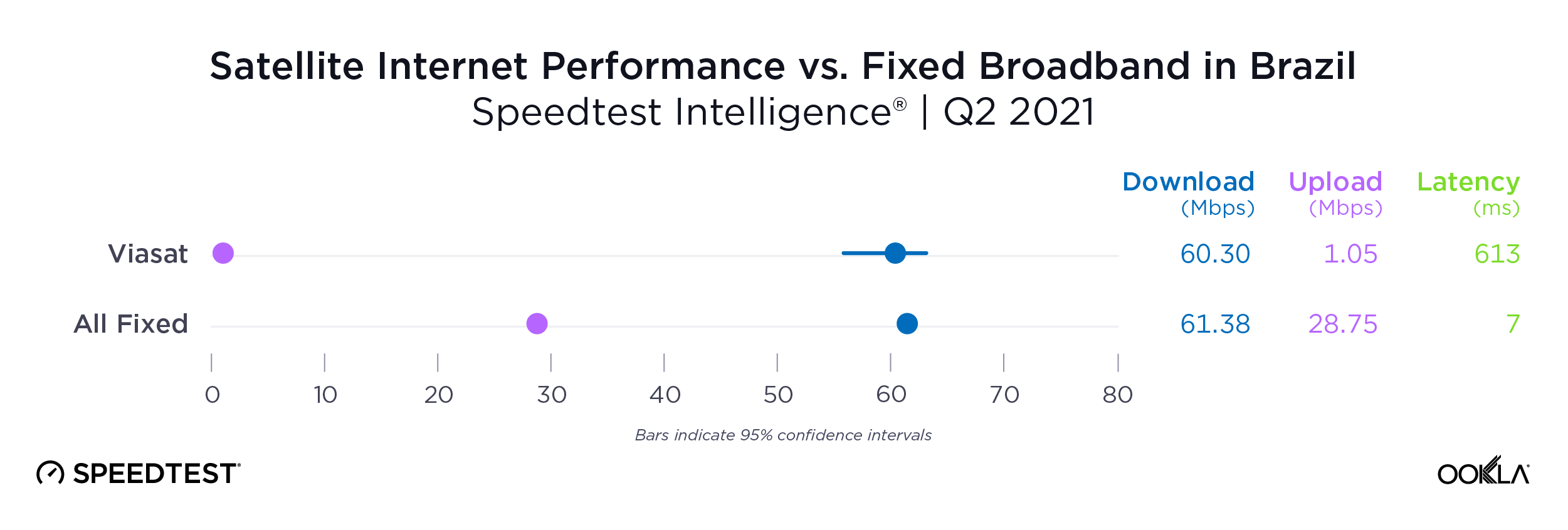
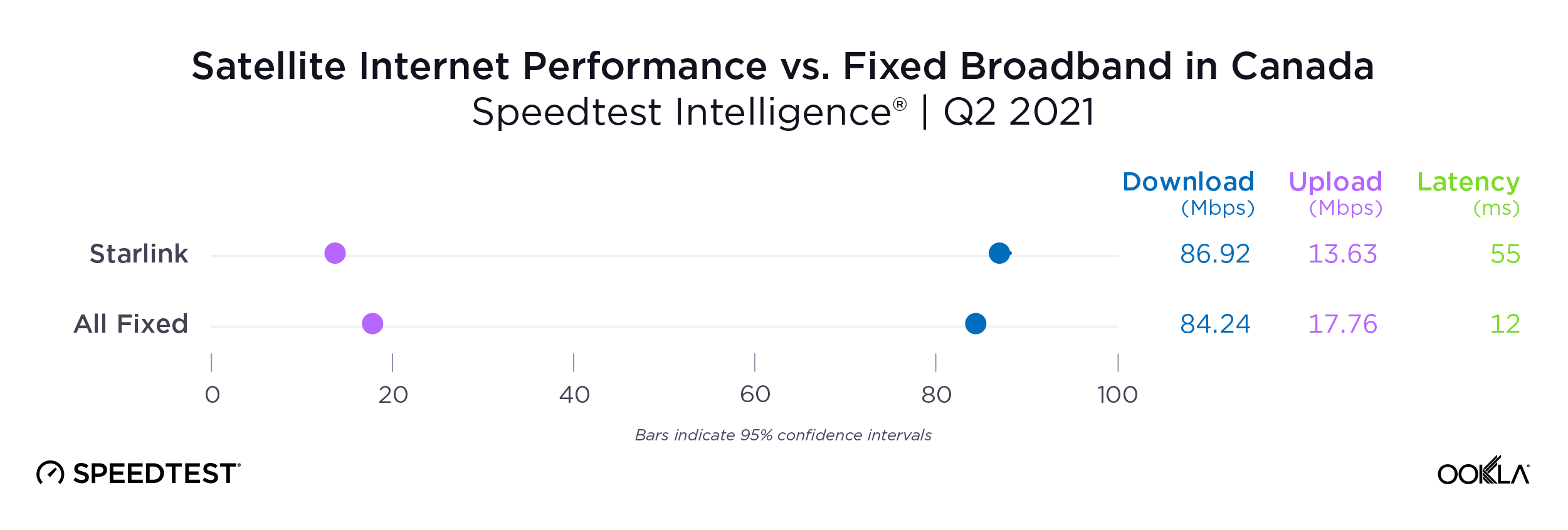
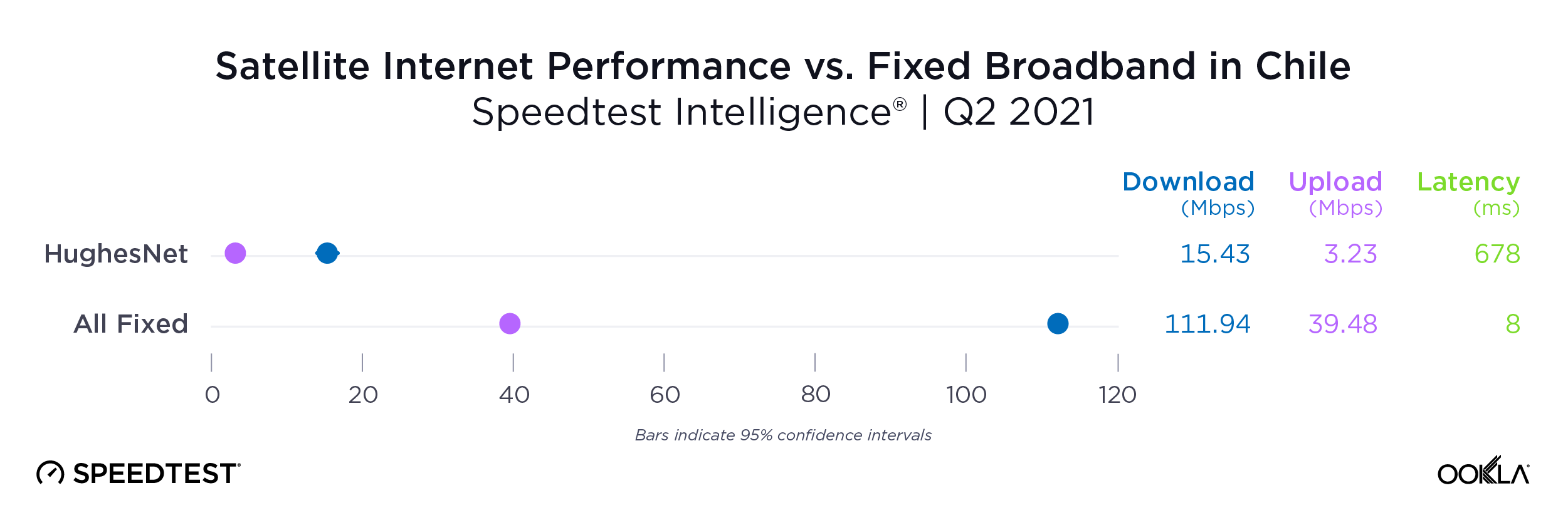
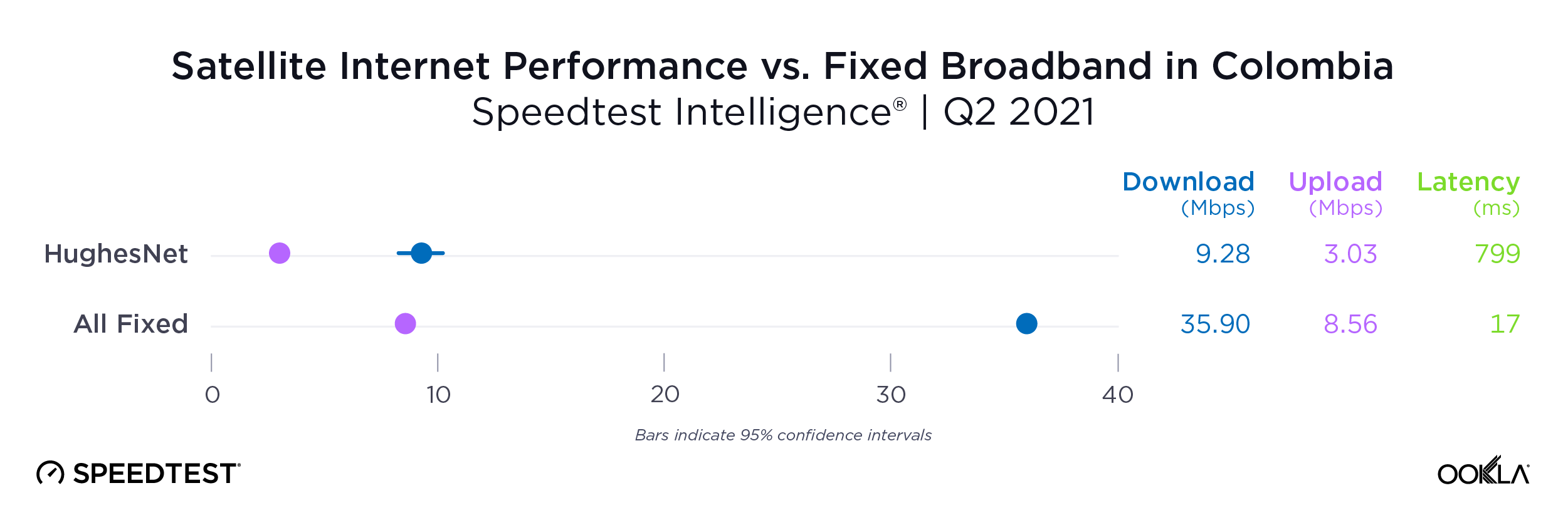
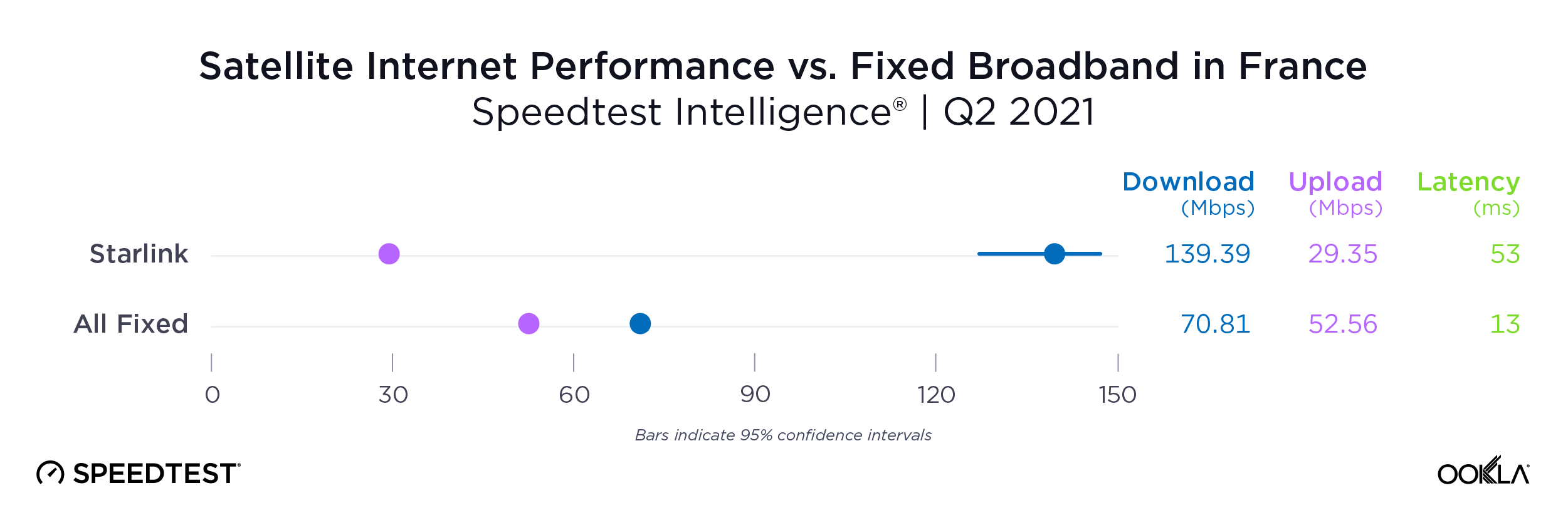
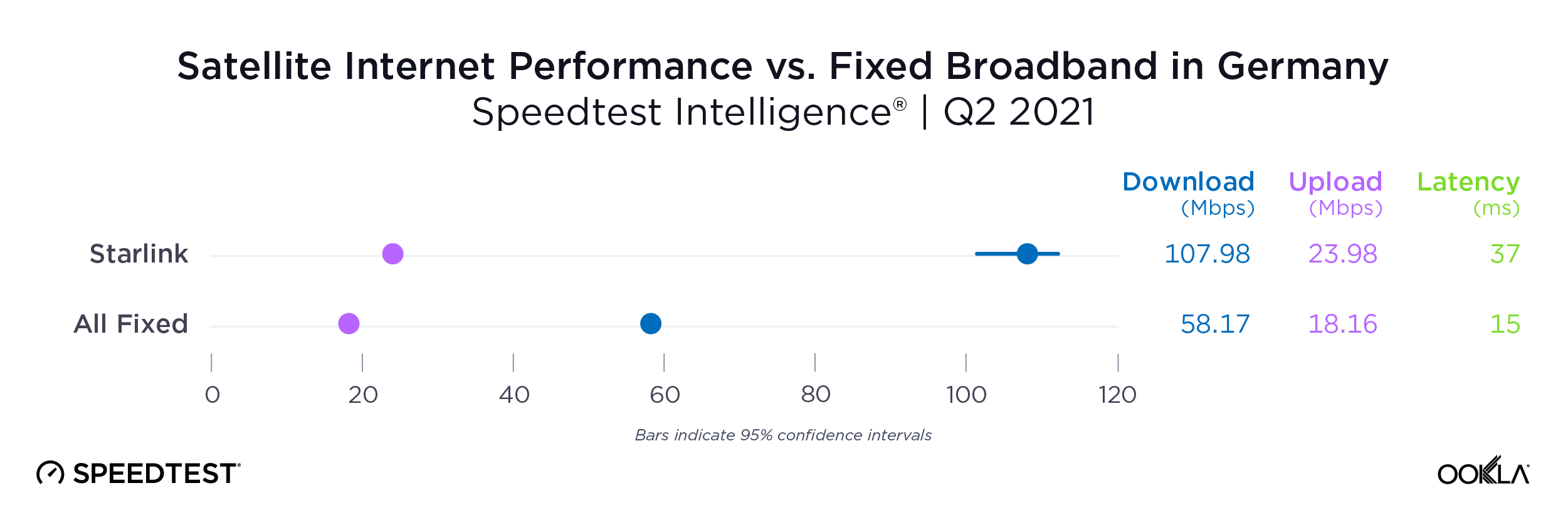
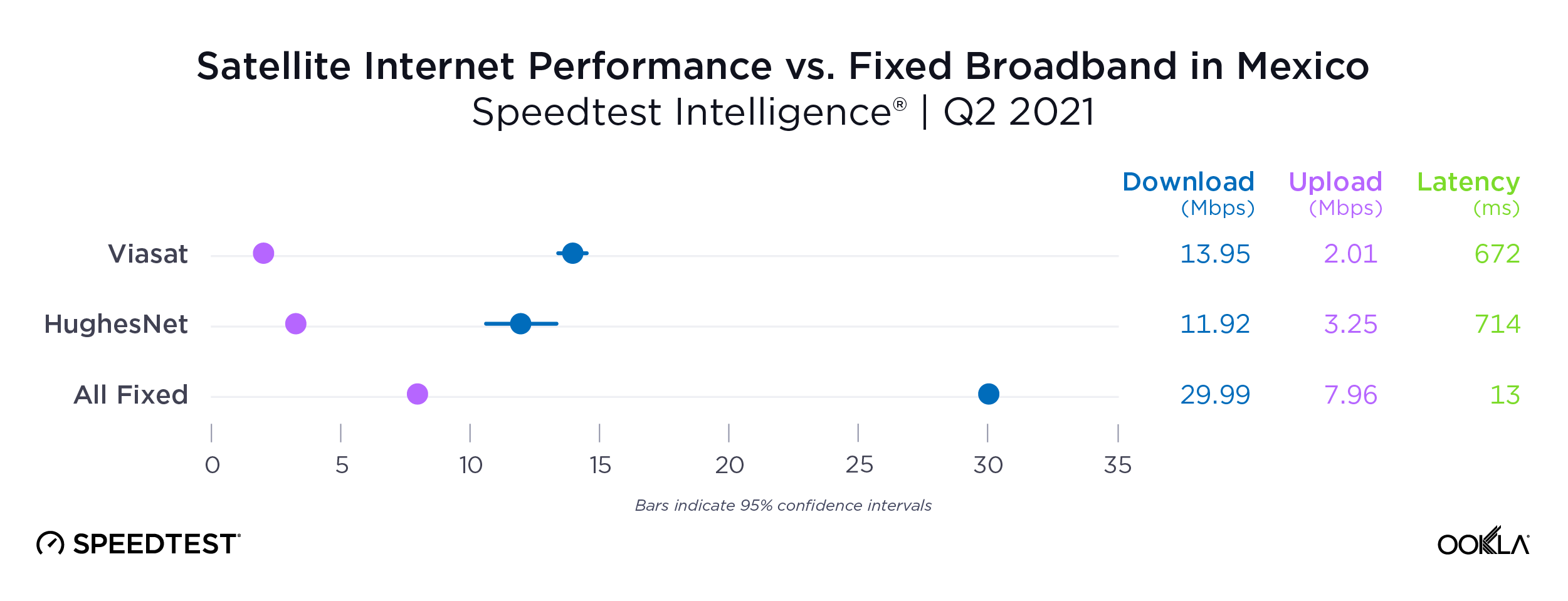
Satellite providers are playing no small part in the rapid expansion of global connectivity. Some experts predict there will be 58,000 satellites orbiting the earth by 2030 — a nearly 725% increase from 2023. Ookla® is back with our ongoing satellite internet series with compelling, fresh data for satellite providers in Africa, Europe, and Oceania during Q2 2023, including SpaceX’s Starlink, Viasat, and Skylogic.
This analysis includes Starlink Net Promoter Score (NPS) data for France, Germany, Italy, New Zealand, and the United Kingdom, year-over-year data for satellite providers in Europe and Oceania from Q2 2022 to Q2 2023, and new Q2 2023 data from Starlink in Africa.
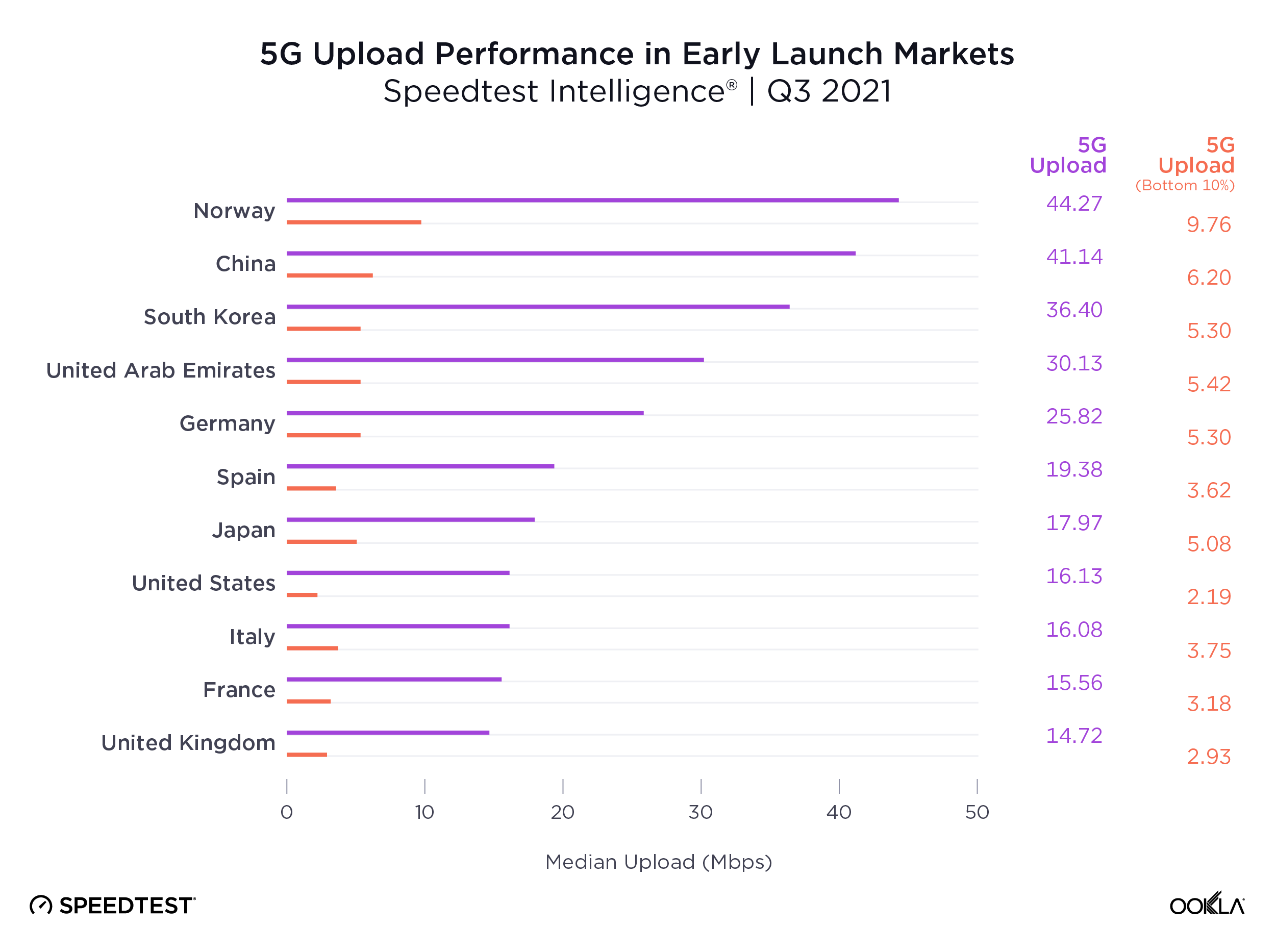
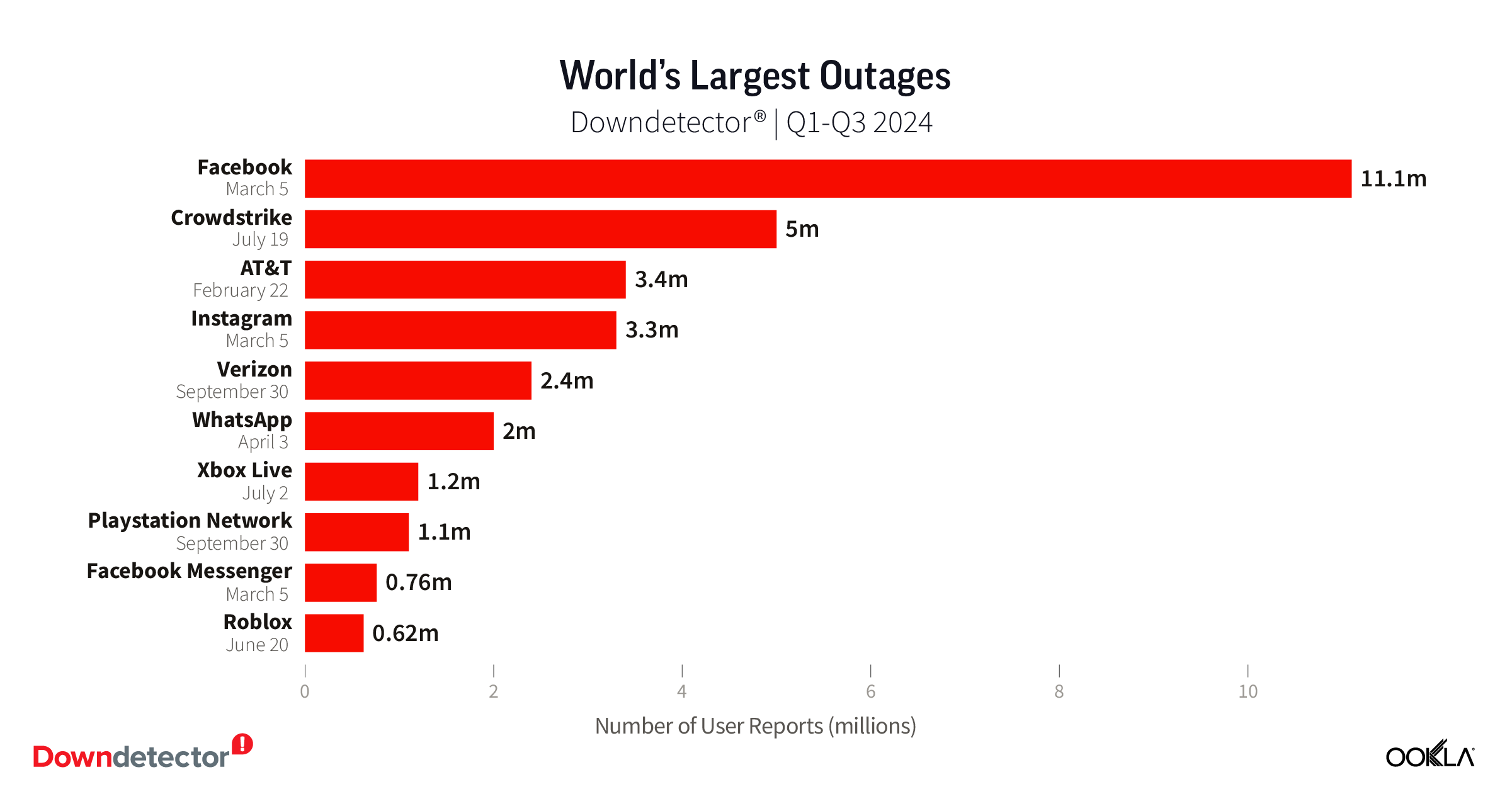
Starlink users across different continents continue to love the service
Using Speedtest Intelligence®, we examined NPS ratings data for Starlink users against an aggregate of all fixed broadband providers combined.
NPS is based on Speedtest® user responses after being asked how likely they are to recommend their provider to friends or family on a 0 to 10 scale. NPS ratings are categorized into Detractors (score 0-6), Passives (score 7-8), and Promoters (score 9-10), and is calculated as (% Promoters – % Detractors) x 100. Any NPS score above 0 indicates that a provider’s audience is more loyal than not.
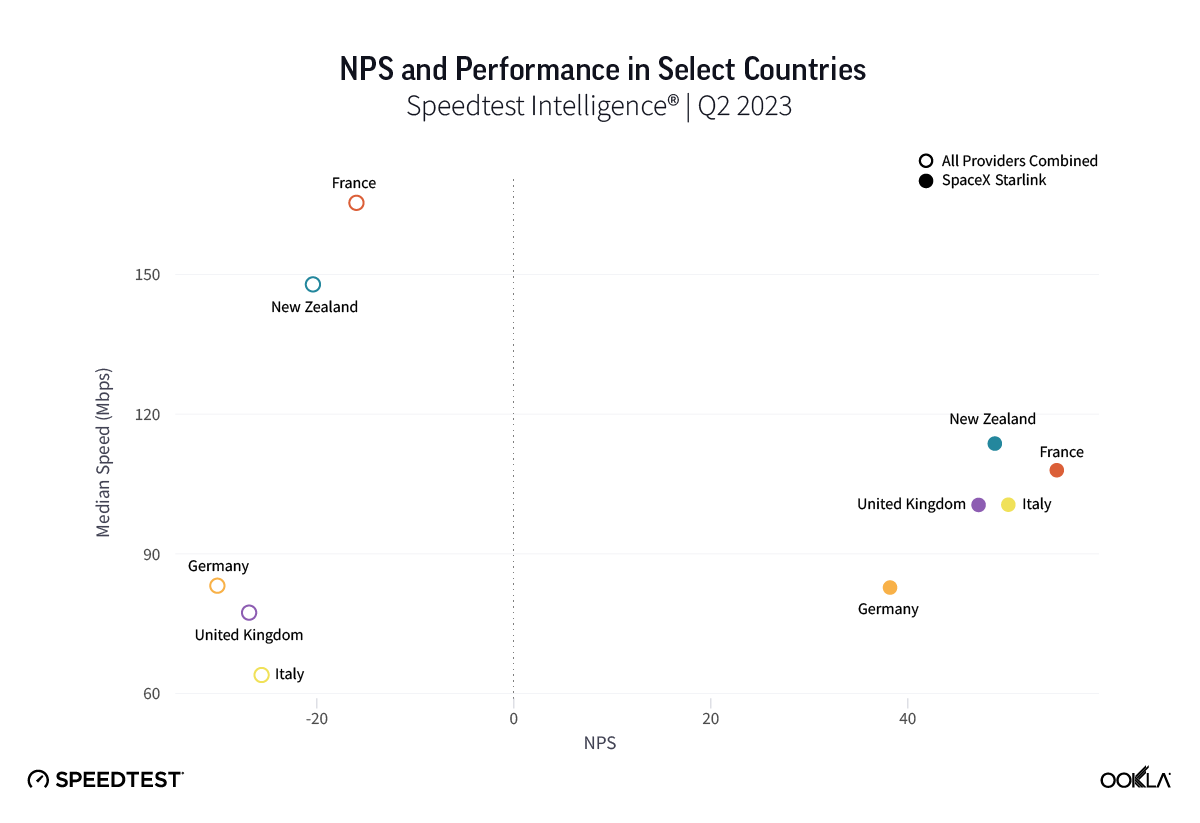
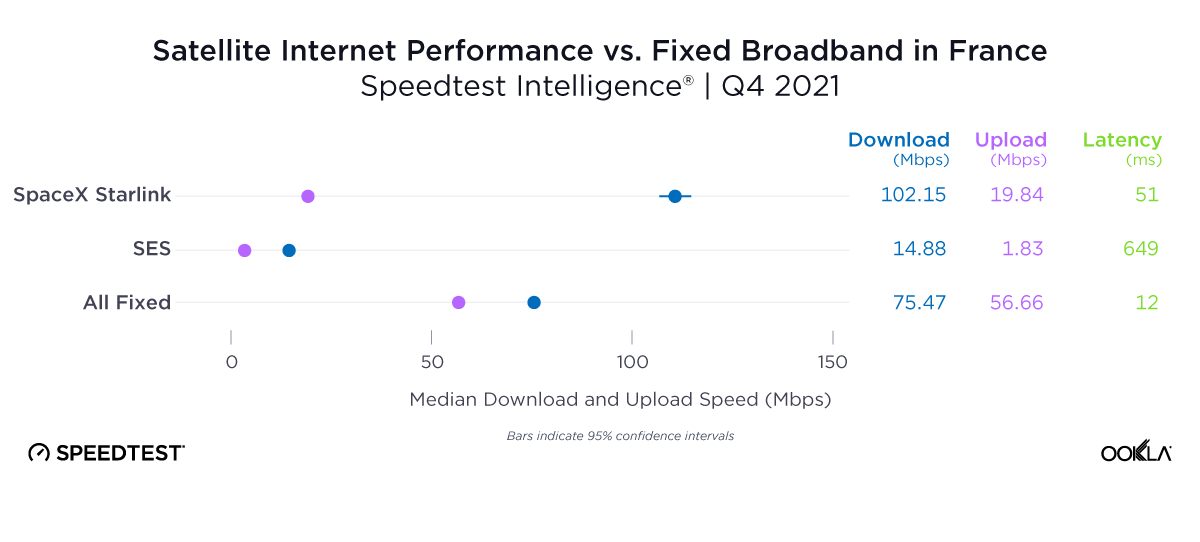
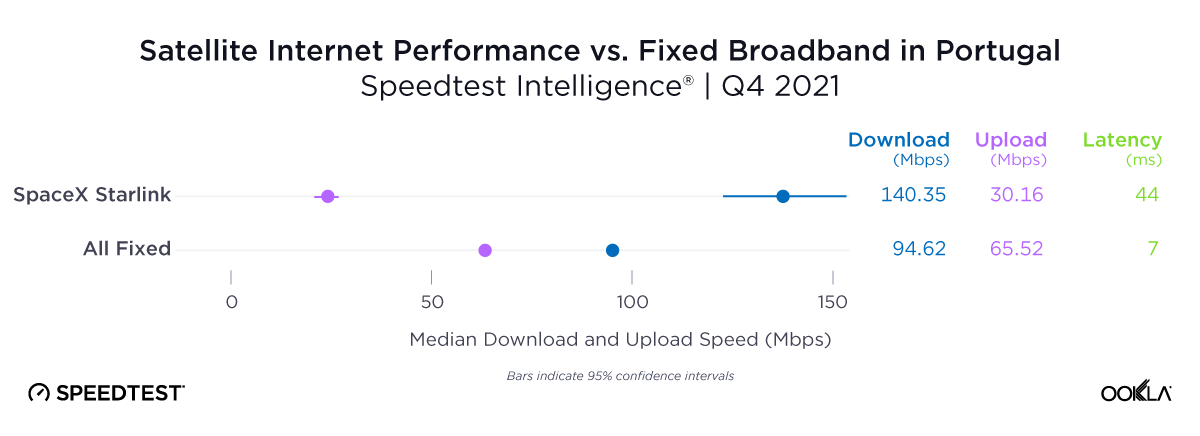
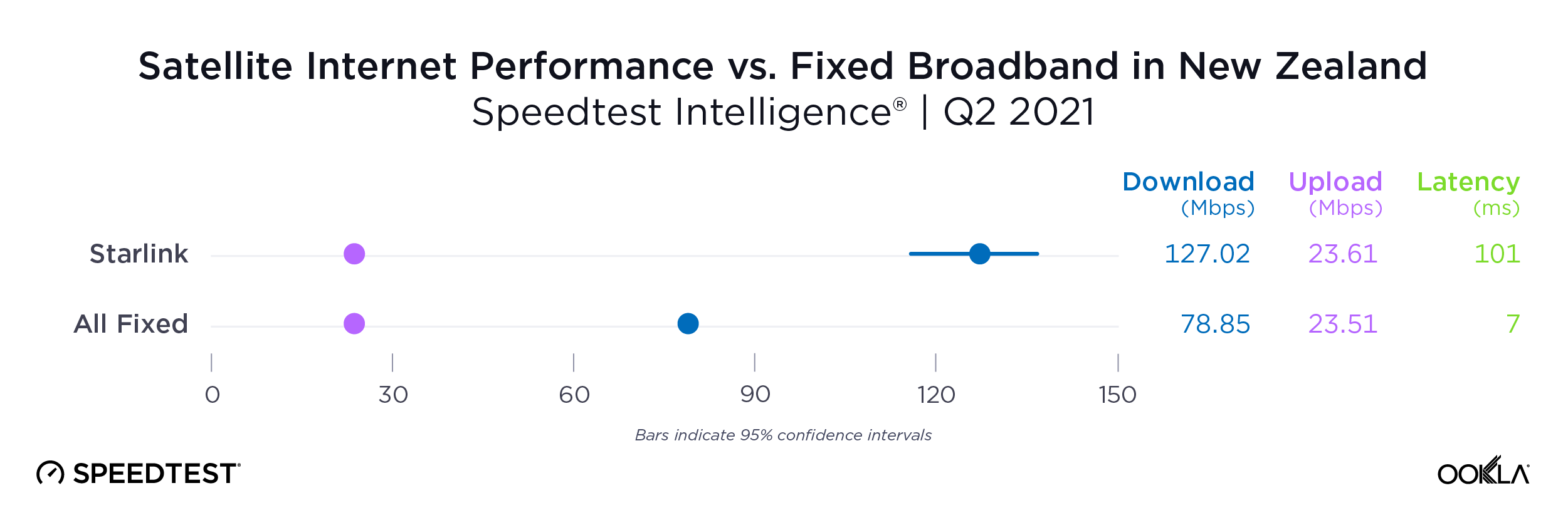
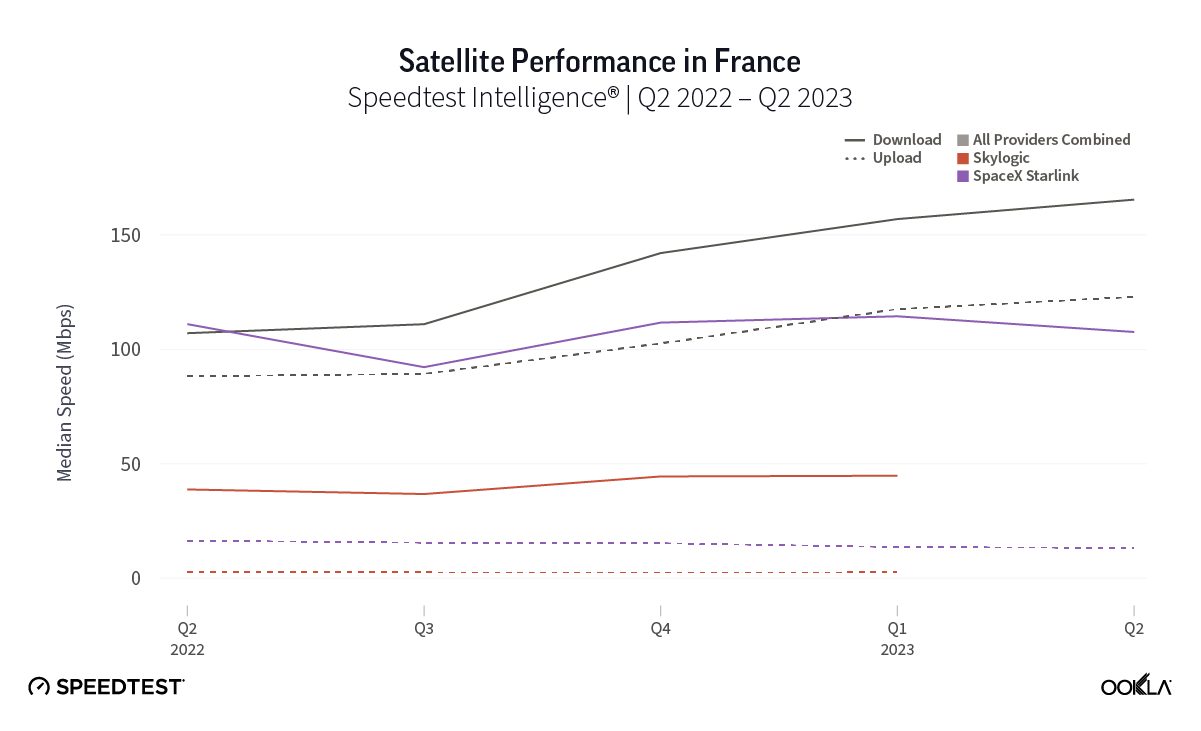
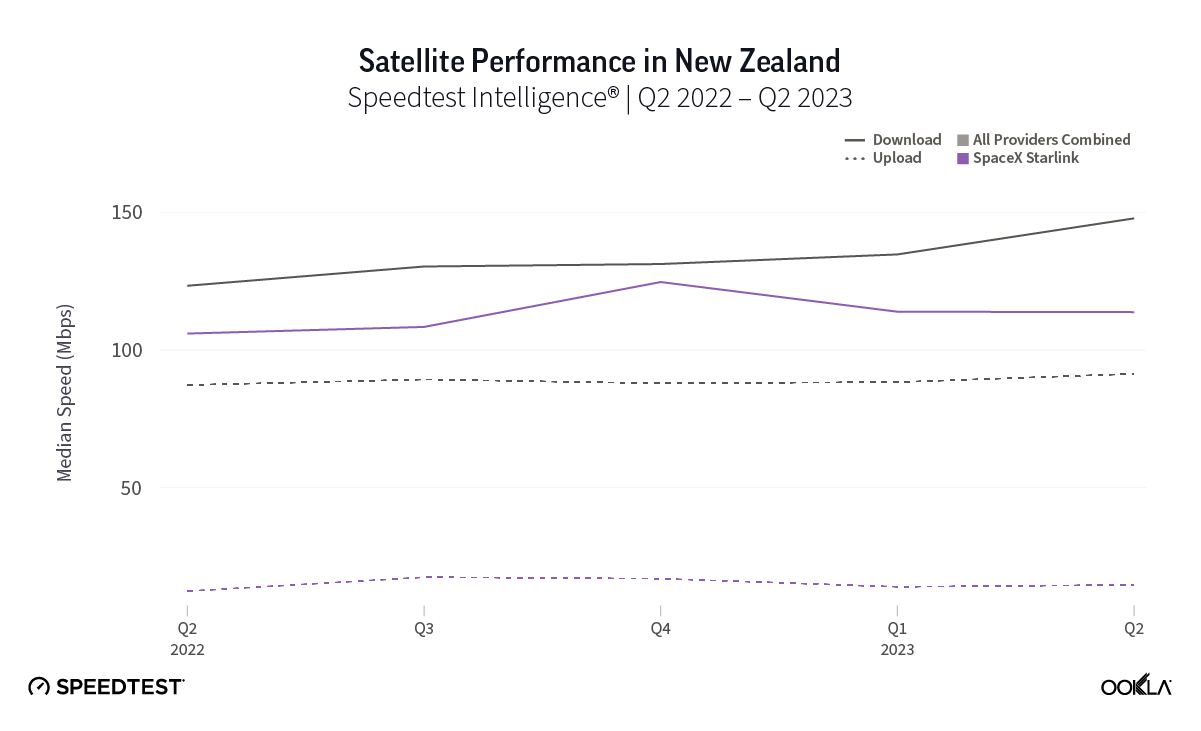
As you can see from the above image, Starlink users in France, Germany, Italy, New Zealand, and the U.K. had an NPS score much higher than the aggregate score for all fixed broadband providers combined during Q2 2023. France had the highest NPS among the aggregate of fixed broadband providers for the countries we surveyed at -15.98 and fixed broadband providers had a much faster median download speed at 165.37 Mbps to Starlink’s 107.56 Mbps. In New Zealand there was a similar story with the aggregate of fixed broadband providers having a -20.40 NPS to Starlink’s 48.83, while having a faster median download speed 147.86 Mbps to 113.78 Mbps during Q2 2023.
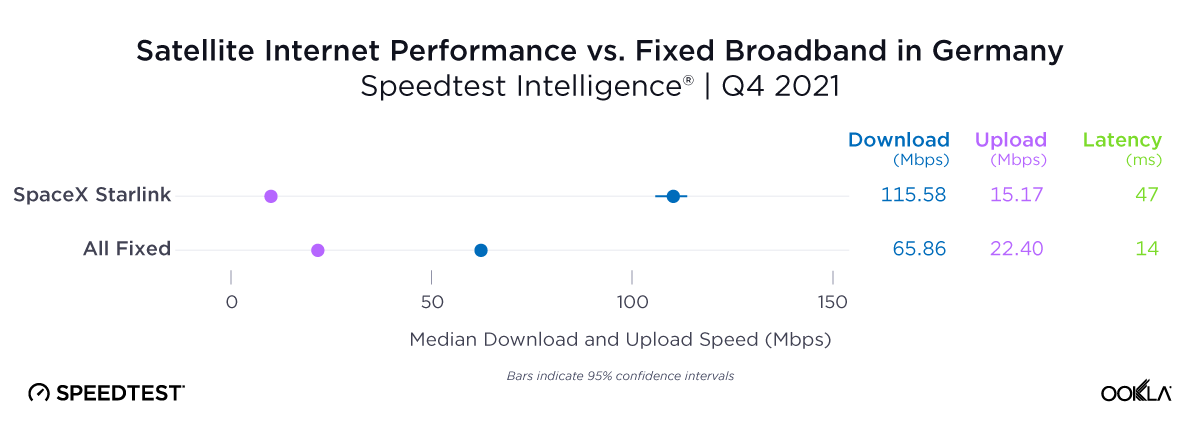
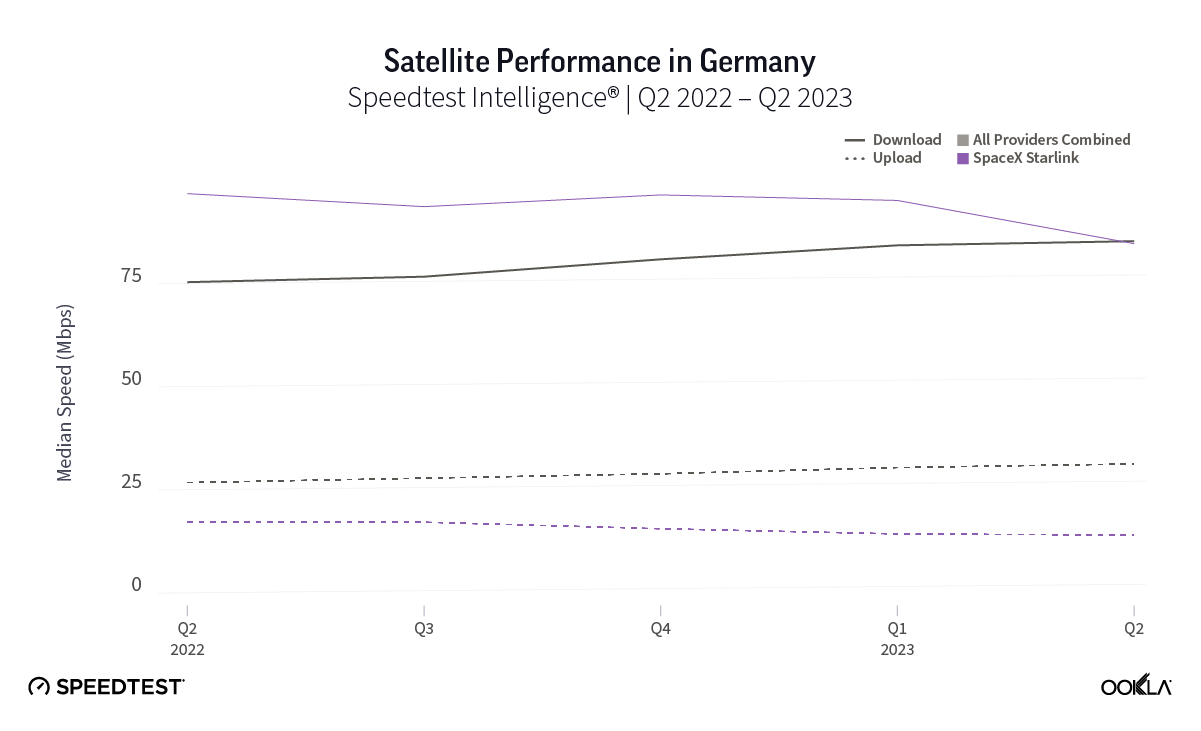
Germany, which had the lowest NPS rating of aggregate of fixed broadband providers in Europe at -30.10, also had the smallest difference in NPS with Starlink scoring 38.19. Interestingly, the aggregate of fixed broadband providers and Starlink both had similar median download speeds at 83.16 Mbps and 82.56 Mbps, respectively, during Q2 2023.
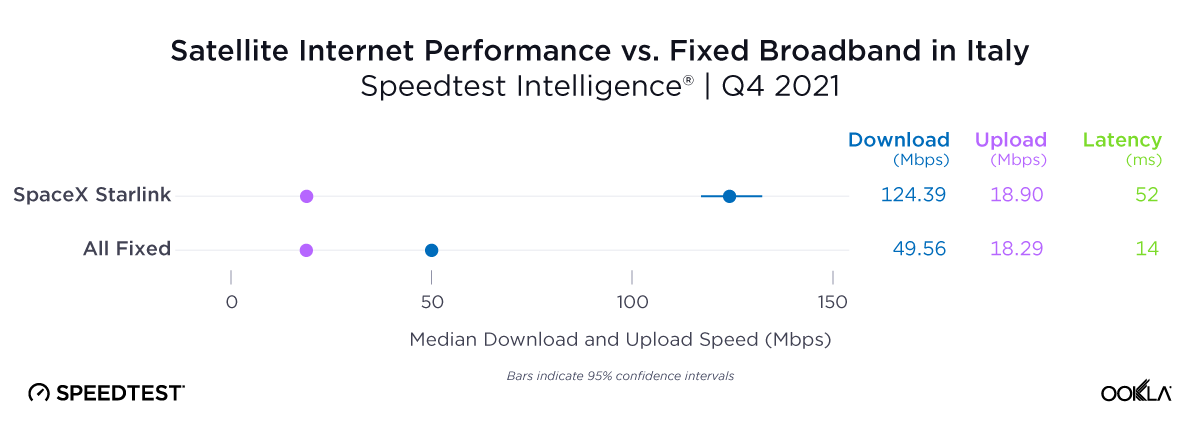
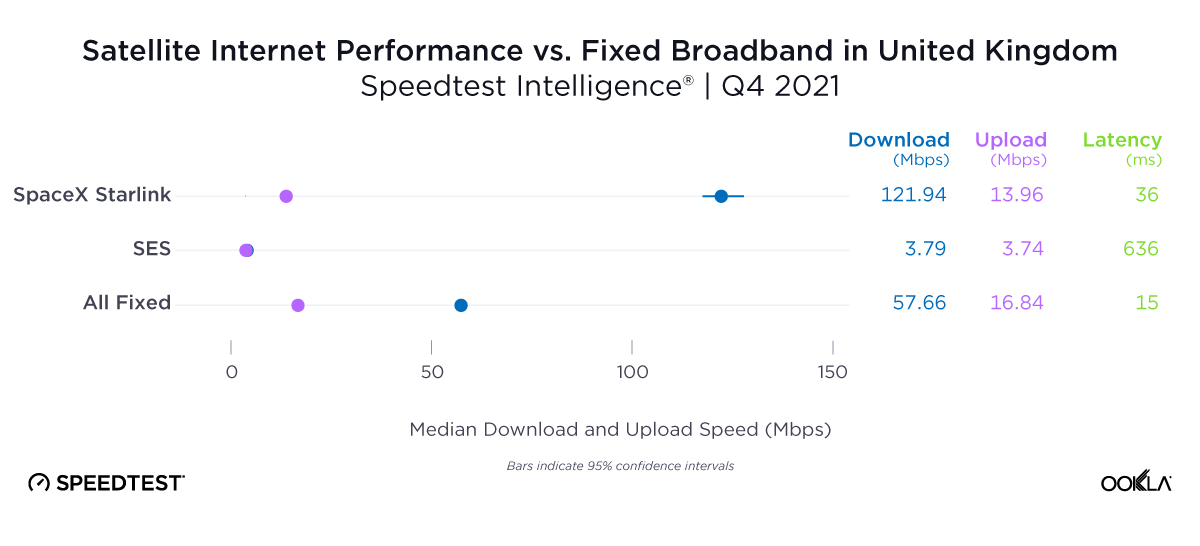
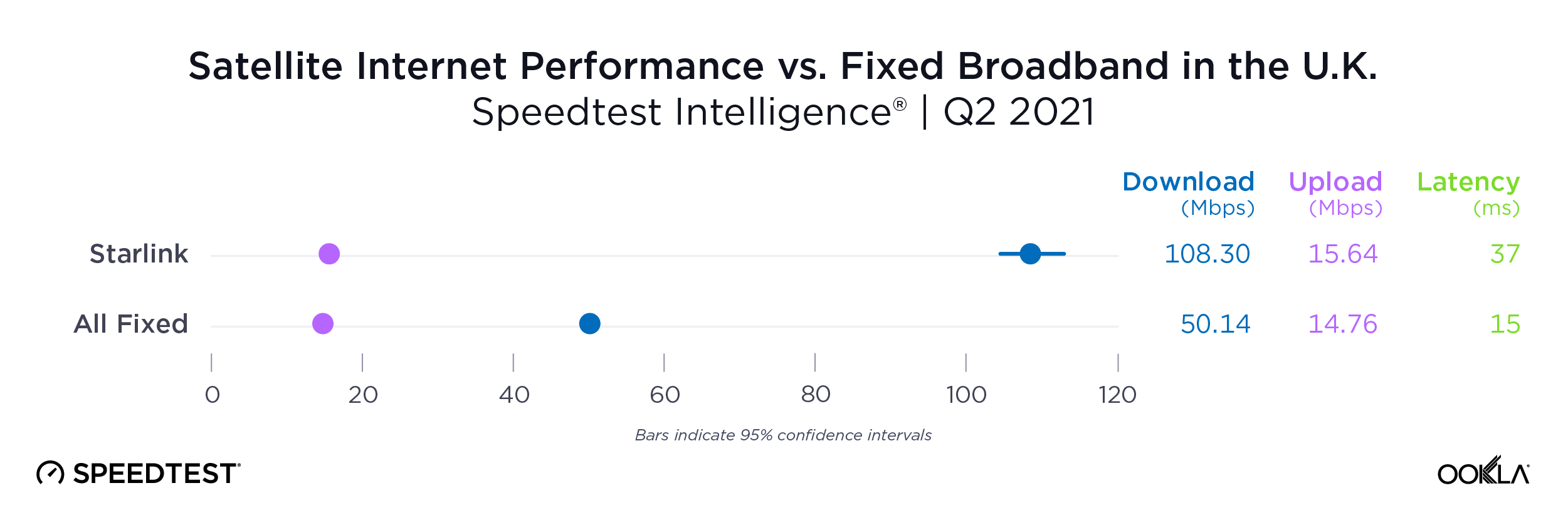
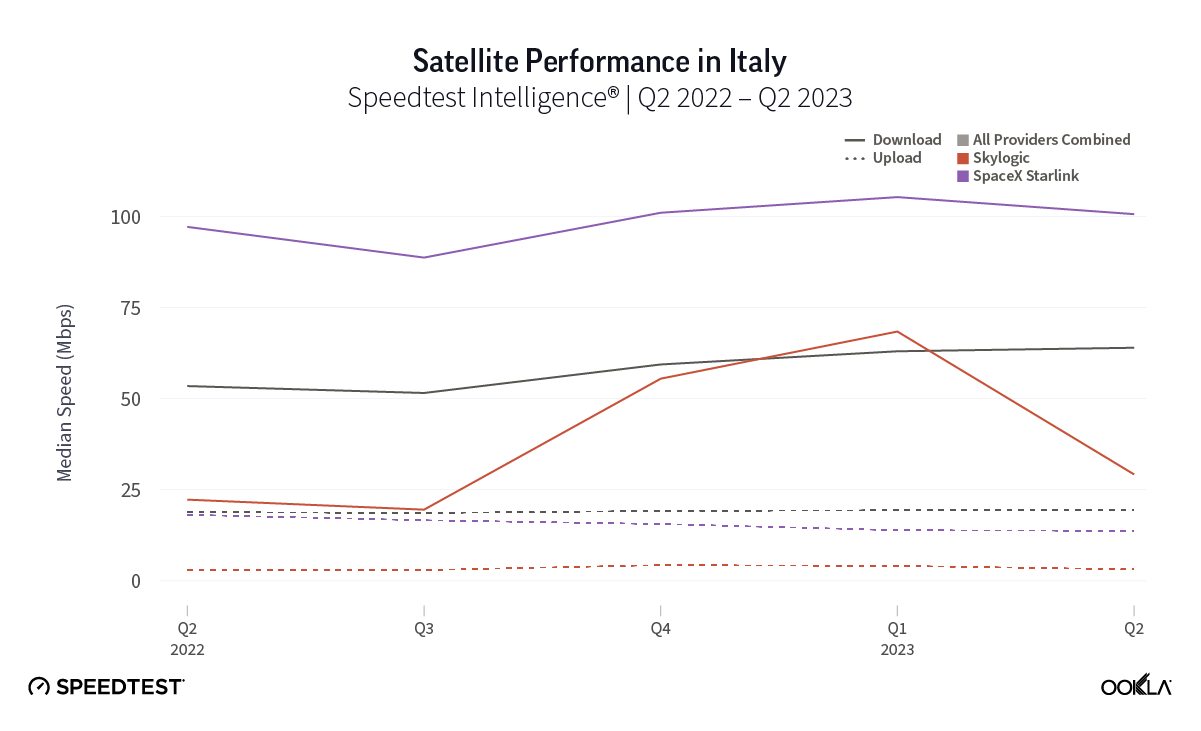
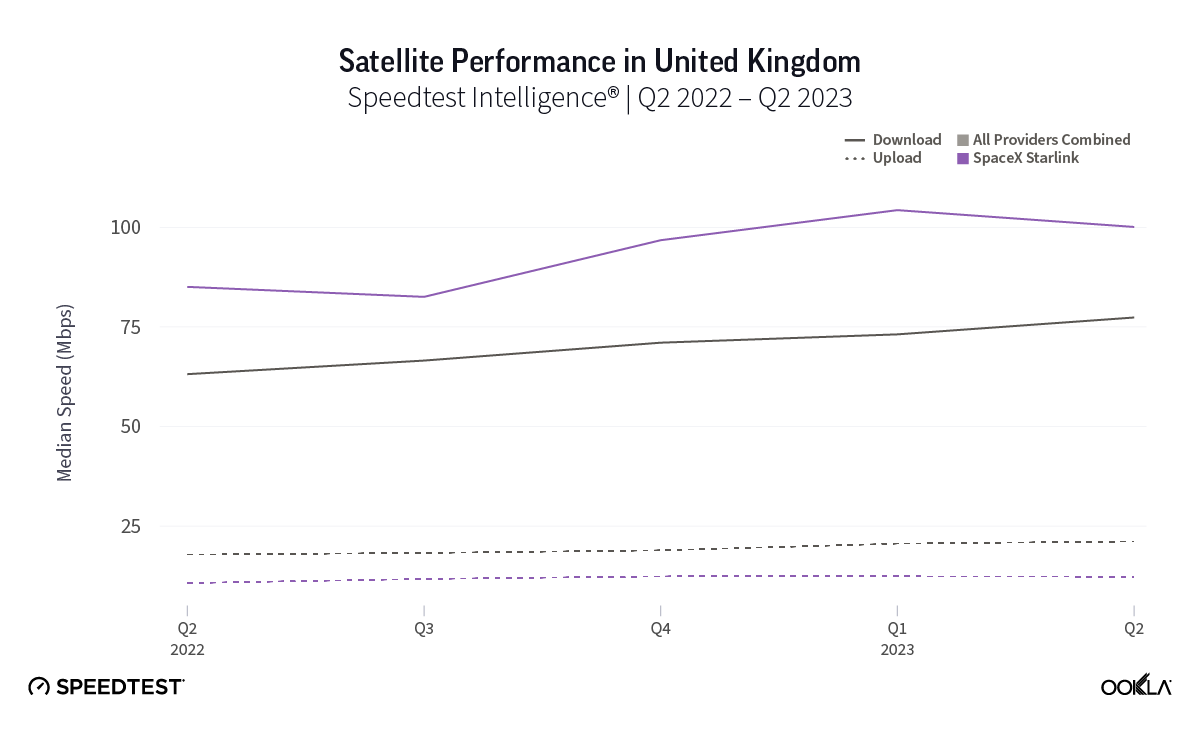
Of note, Starlink had much higher NPS ratings and median download speeds than the aggregate of all fixed providers combined in Italy and the U.K., respectively, during Q2 2023. Starlink’s NPS was 50.20 to -25.61 for the aggregate of all fixed broadband providers in Italy during Q2 2023, while the median download speeds were 100.68 Mbps to 63.99 Mbps. In the U.K., Starlink’s NPS was 47.18 to -26.88 for the aggregate of all fixed broadband providers combined, with the median download speeds a little closer, 100.11 Mbps to 77.38 Mbps, respectively.
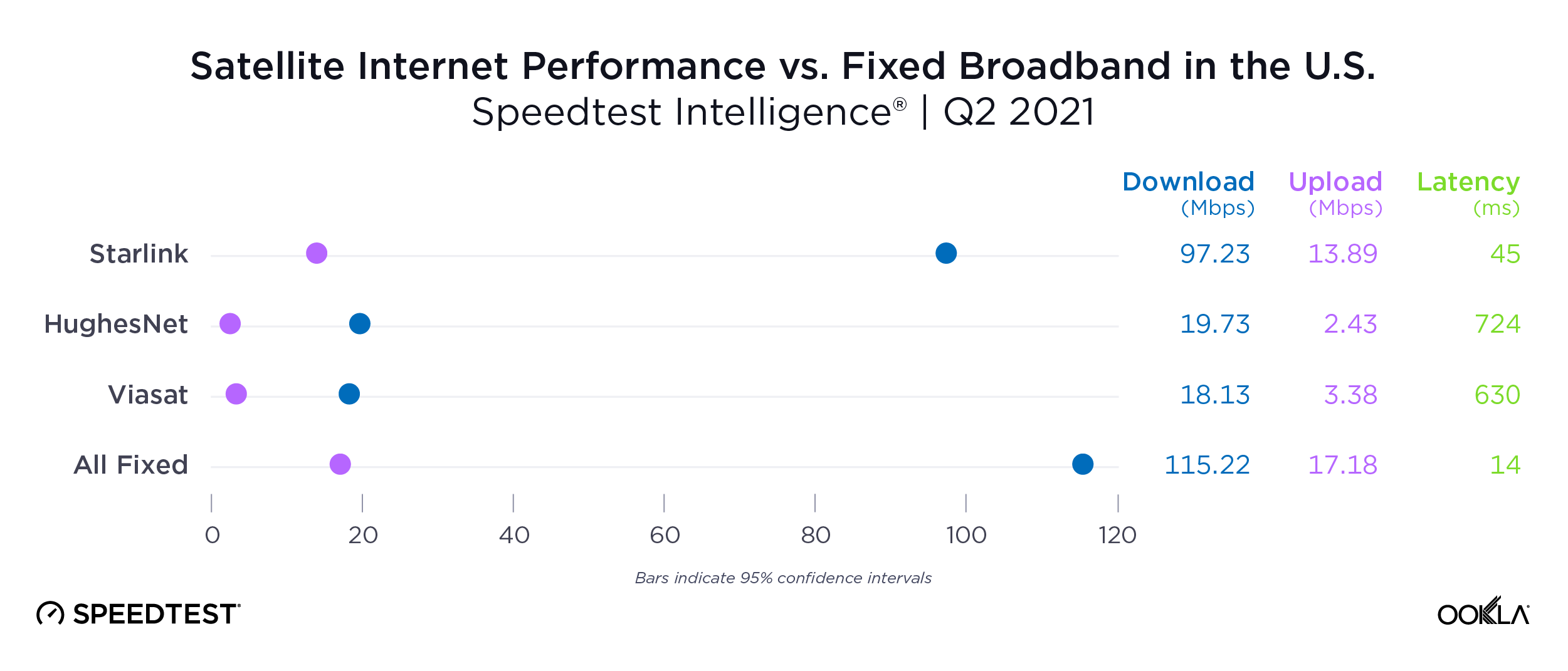
In our last report, we found a wide NPS gap between U.S. rural Starlink users — who often have fewer options for fixed broadband access — and the corresponding aggregate of fixed broadband providers. Given that all five of these countries have rural or remote regions that are underserved or not served by traditional broadband offerings, it may be no surprise that Starlink users who reside in those areas may feel positive about having access to fast broadband internet.
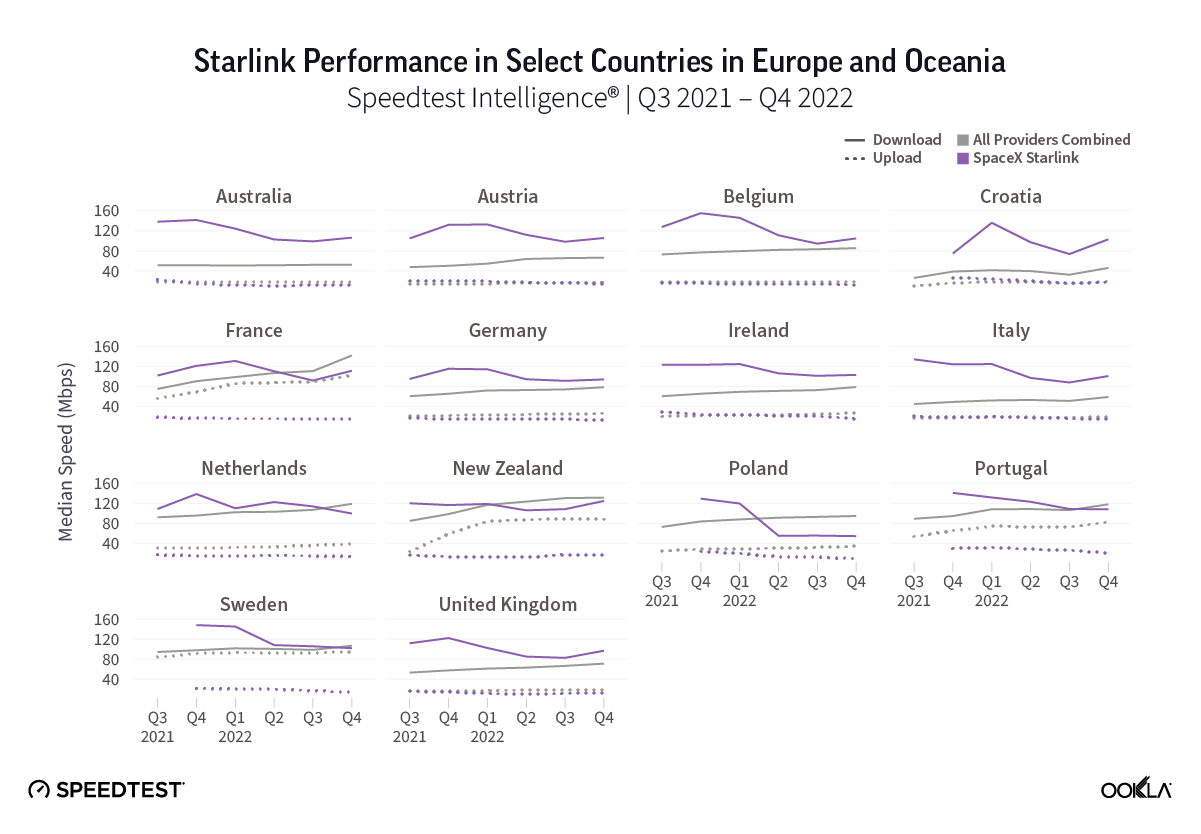
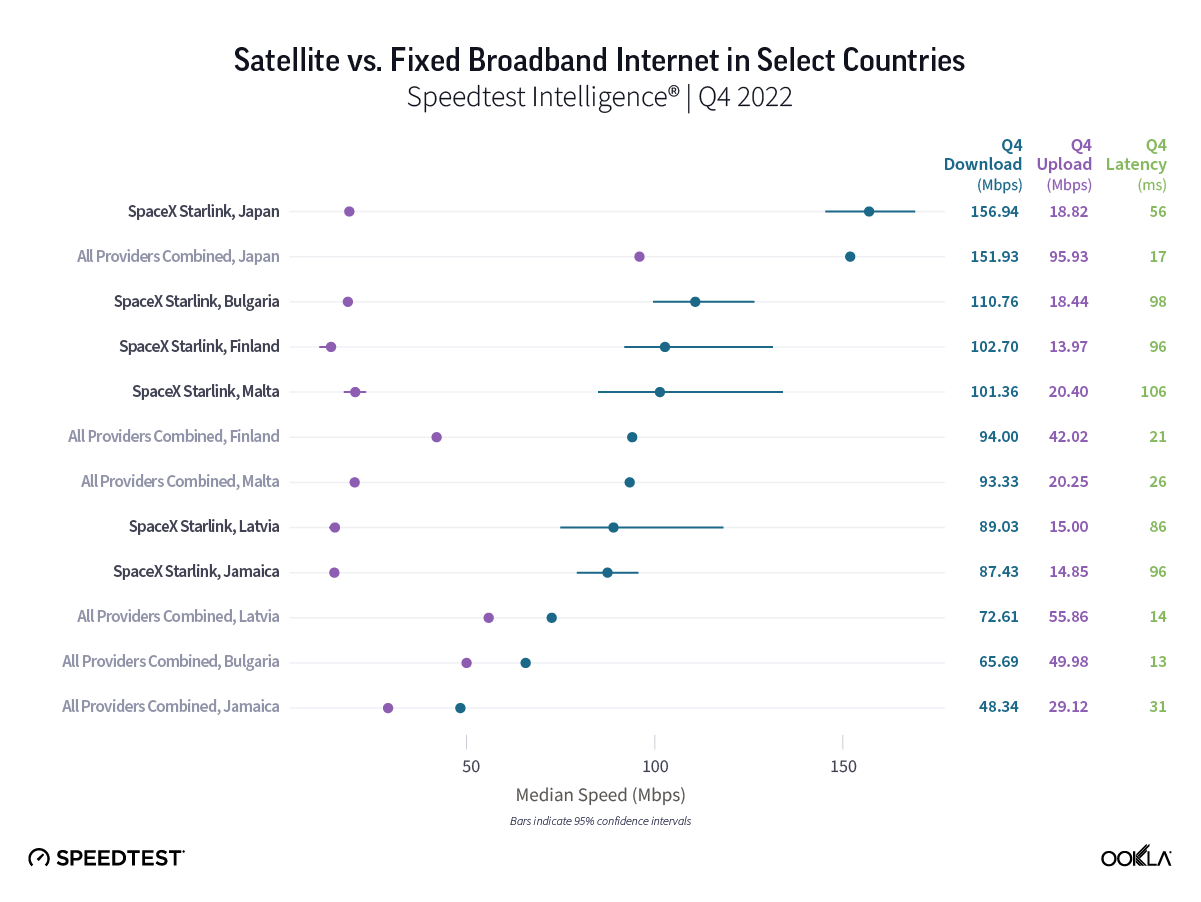
Starlink speeds over 100 Mbps in 14 European countries during Q2 2023, speeds stabilizing across Europe
Key takeaways:
- Starlink results were the fastest among satellite providers we surveyed.
- Starlink quarter-to-quarter speeds improved or remained about the same (between 5% and -5%) in 23 countries, while decreasing in 4 countries.
- Among the 27 European countries we surveyed, Starlink had median download speeds greater than 100 Mbps in 14 countries, greater than 90 Mbps in 20 countries, and greater than 80 in 24 countries, with only three countries failing to reach 70 Mbps.
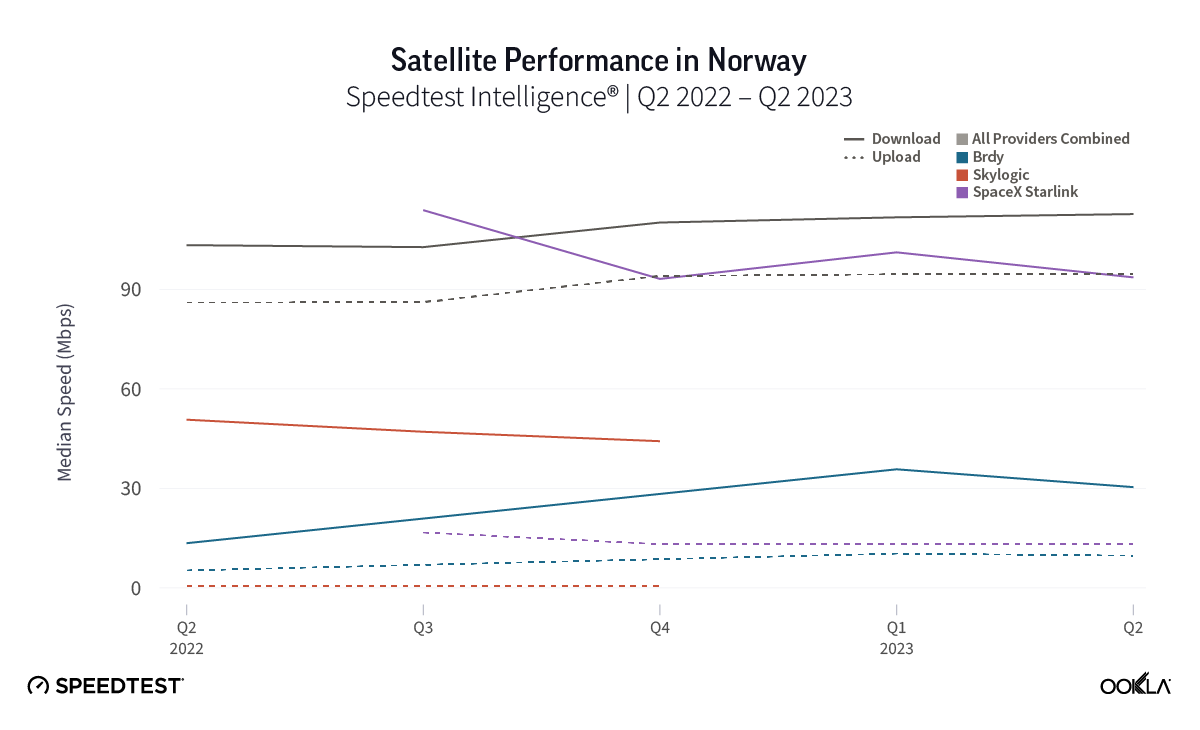
- Skylogic, while delivering speeds slower than Starlink, showed stabilized broadband speeds over the past year for those seeking a Starlink alternative.
Over the past year, we’ve seen huge developments in the global satellite market, Europe notwithstanding, with Amazon’s Project Kuiper moving forward, the EU creating its own satellite constellation, and OneWeb and Eutelsat merging. While Starlink continues to lead for performance among satellite providers we surveyed, Starlink has experienced some major hurdles over the past year as users flock to the service and speeds have subsequently dipped — but of note those concerns seem to have started allaying in most of Europe during Q2 2023.
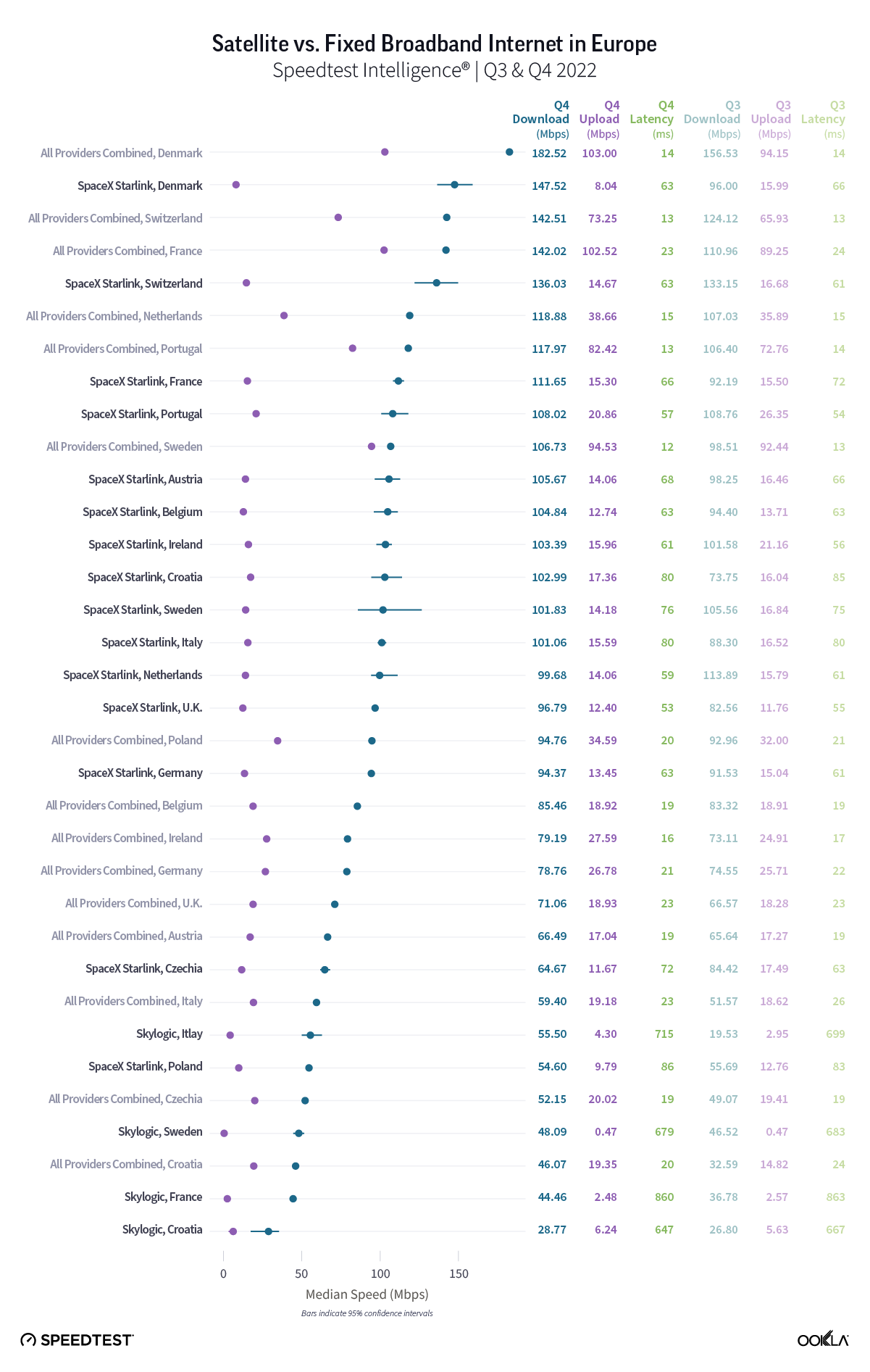
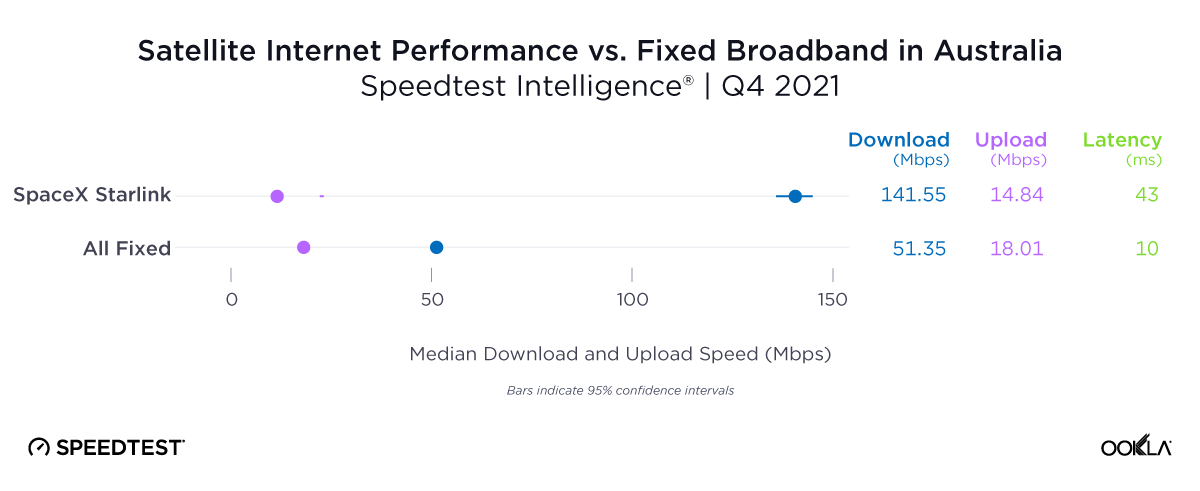
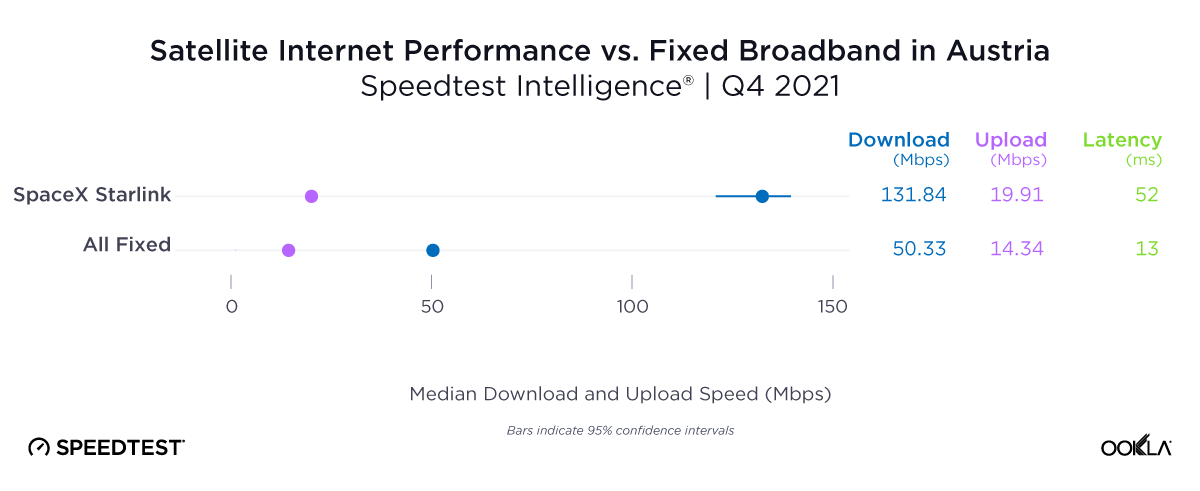
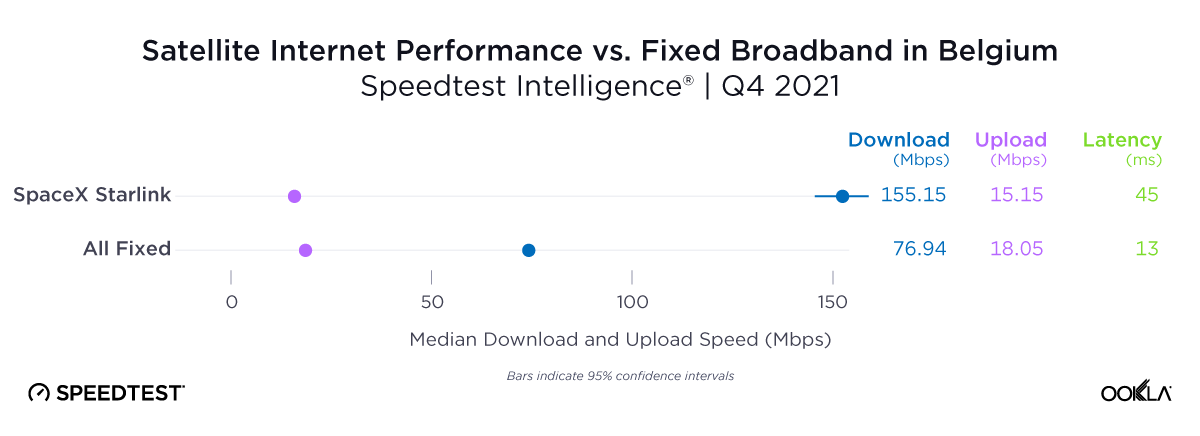
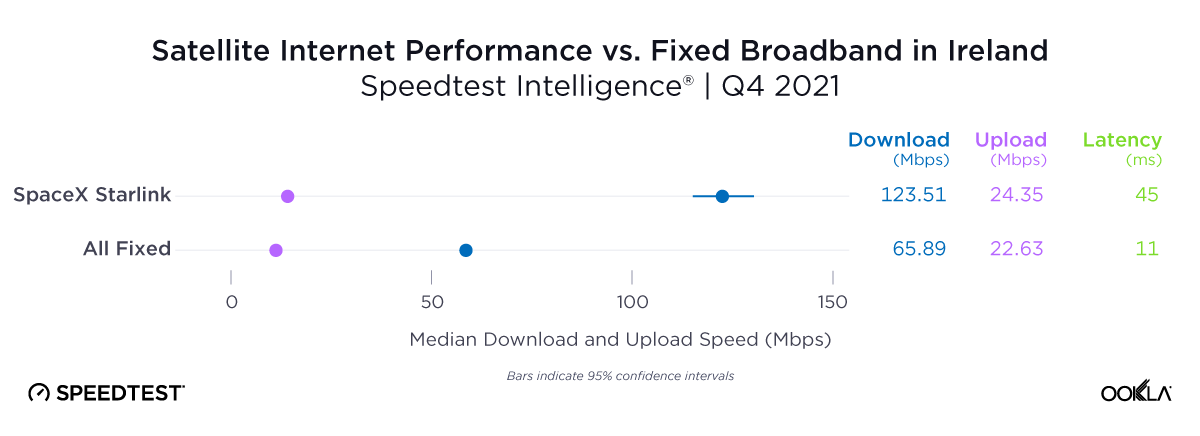
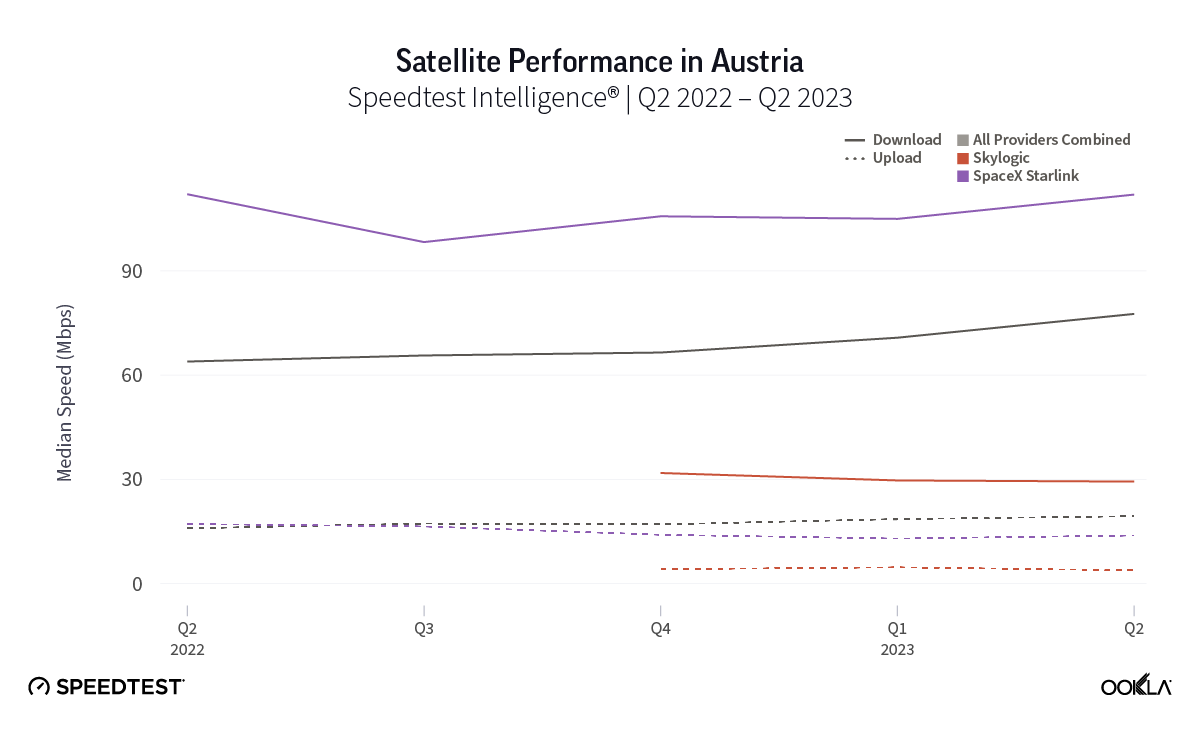
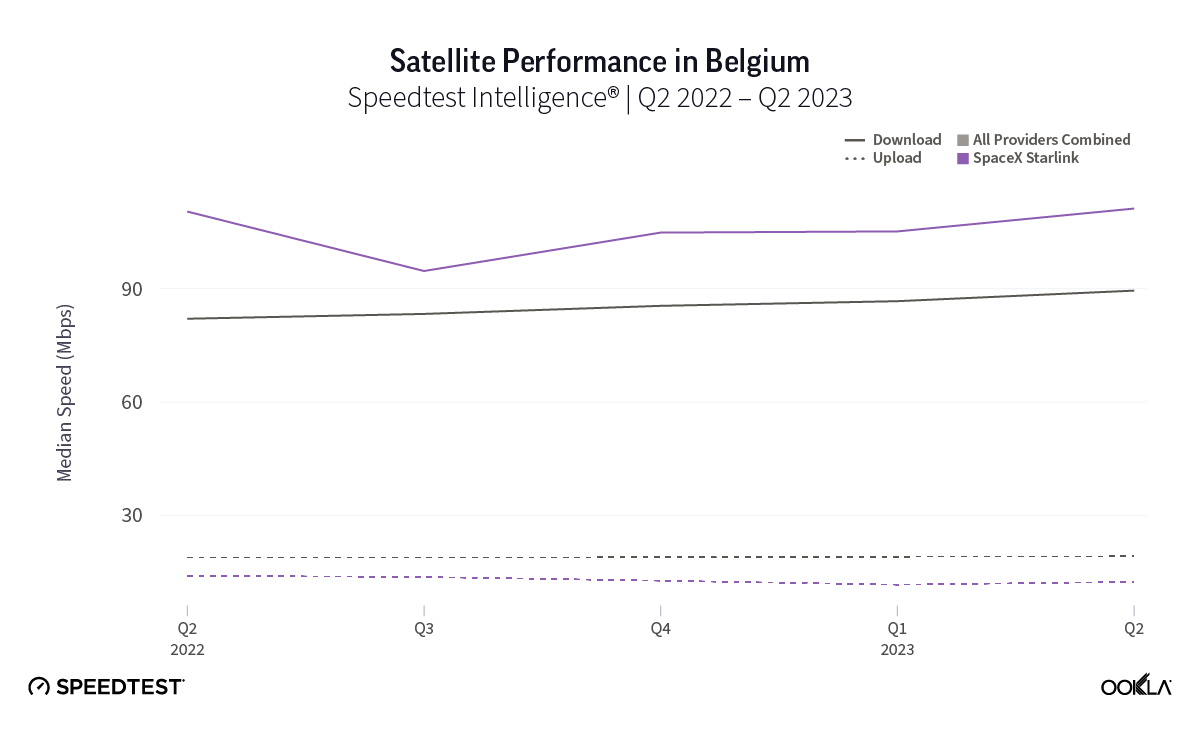
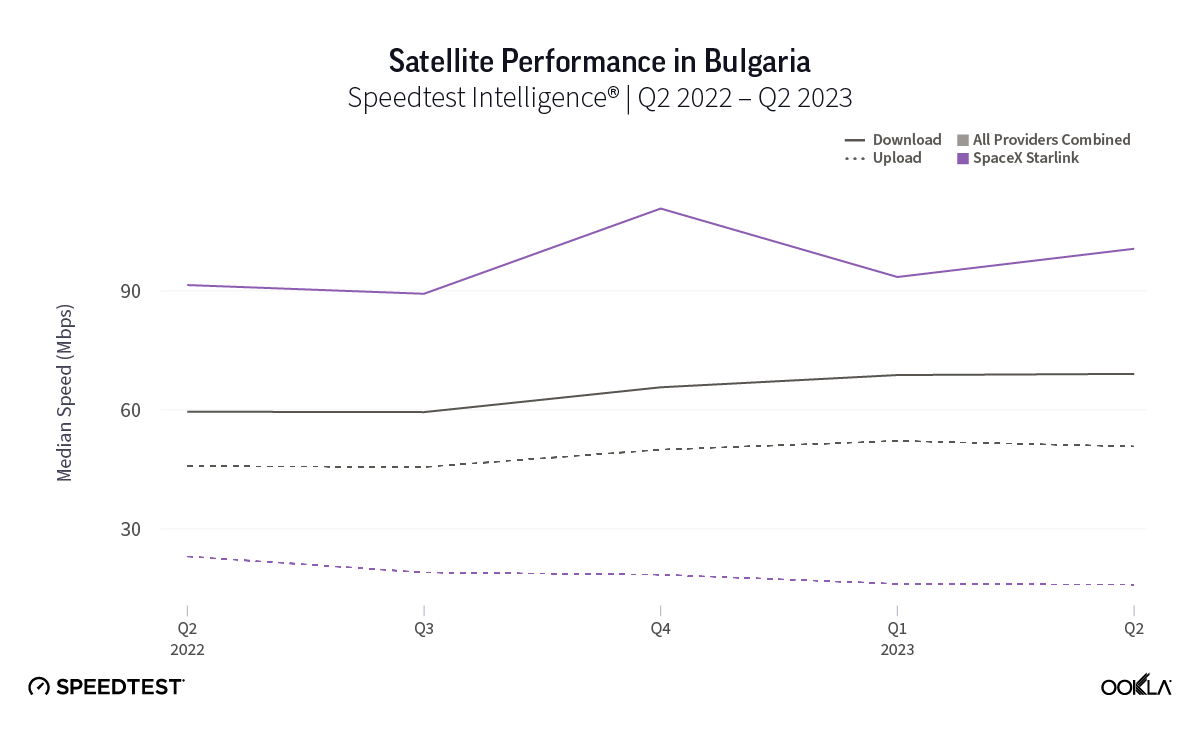
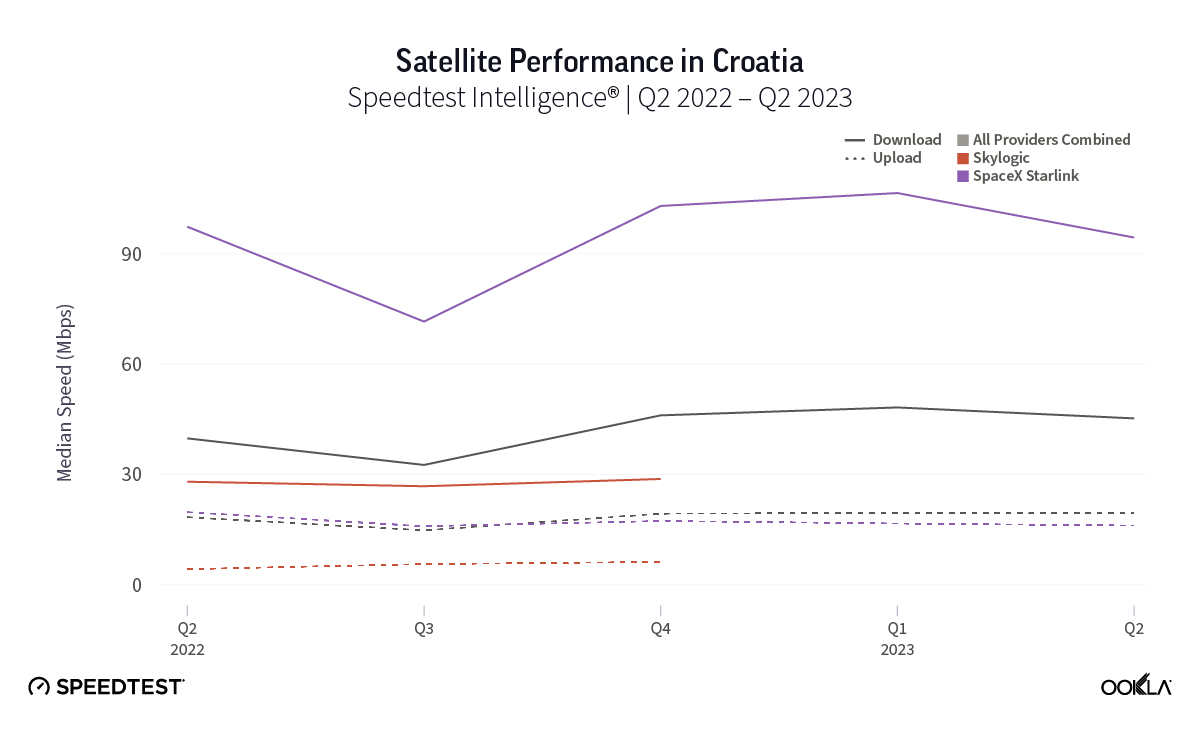
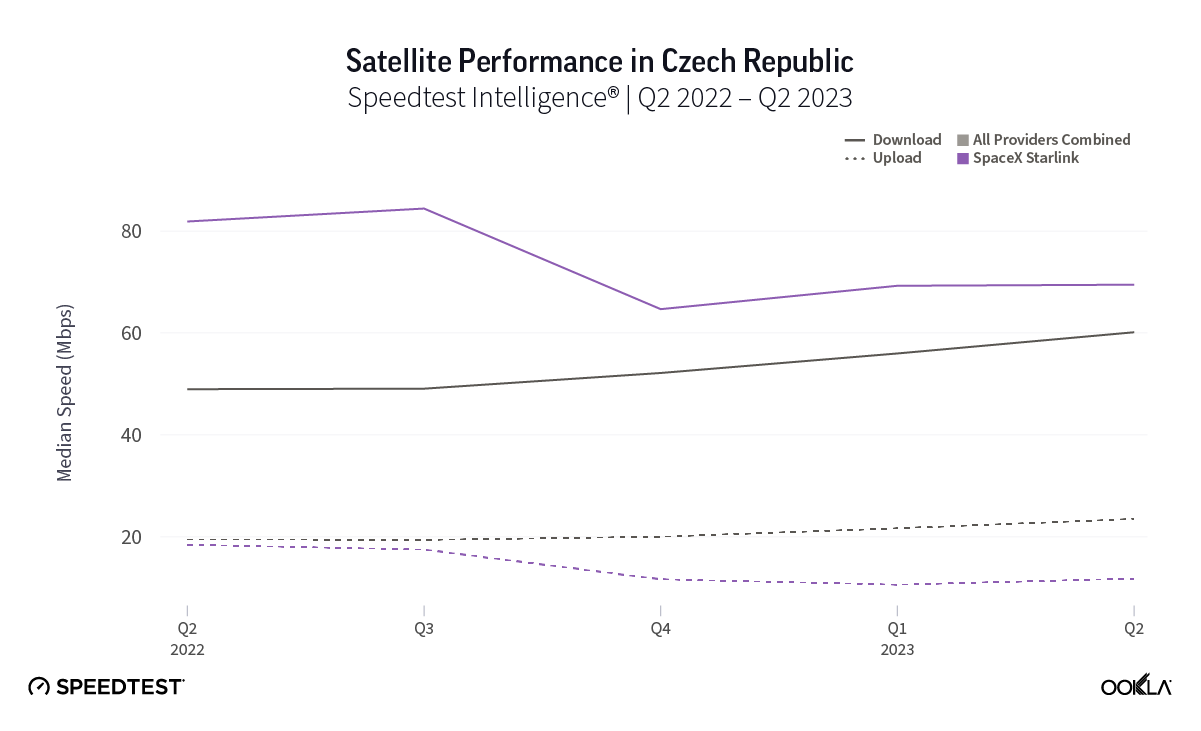
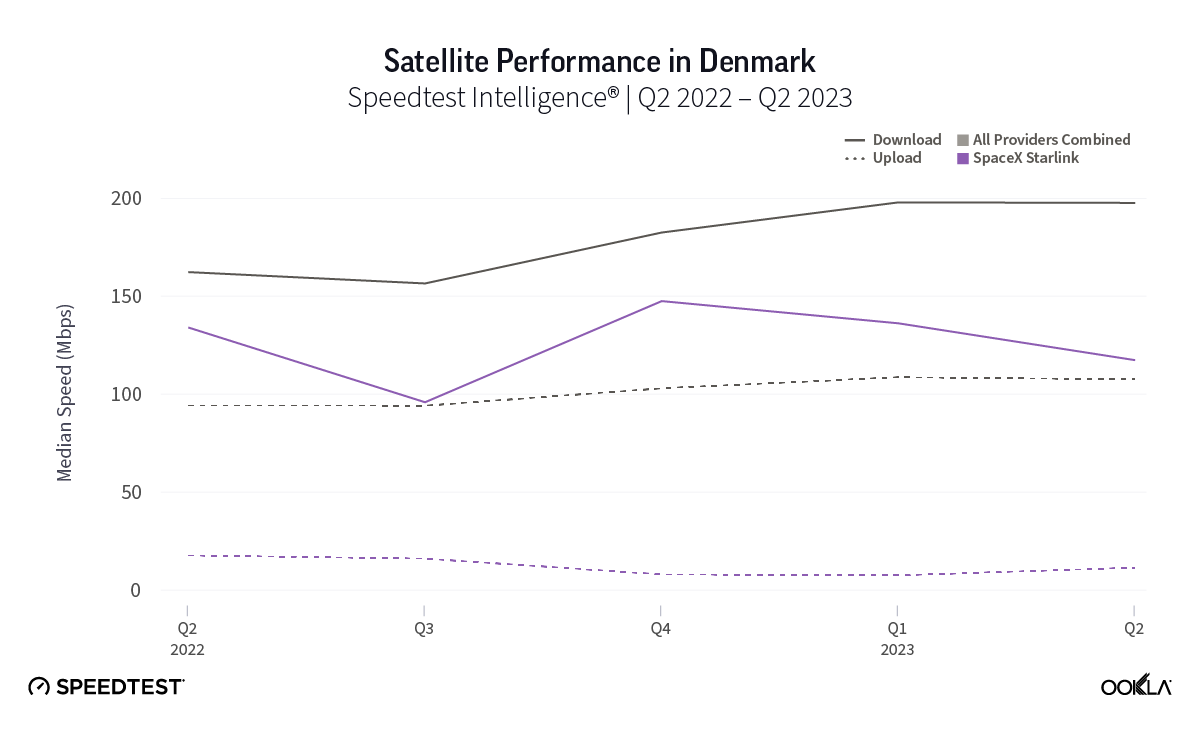
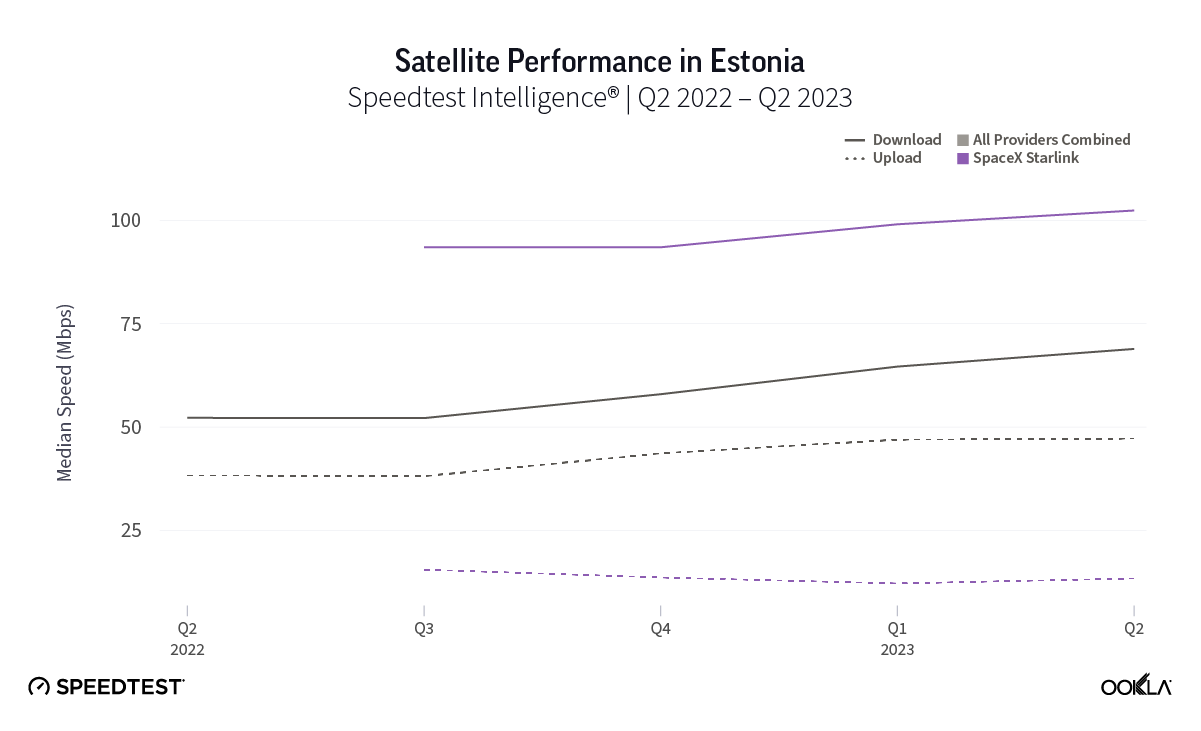
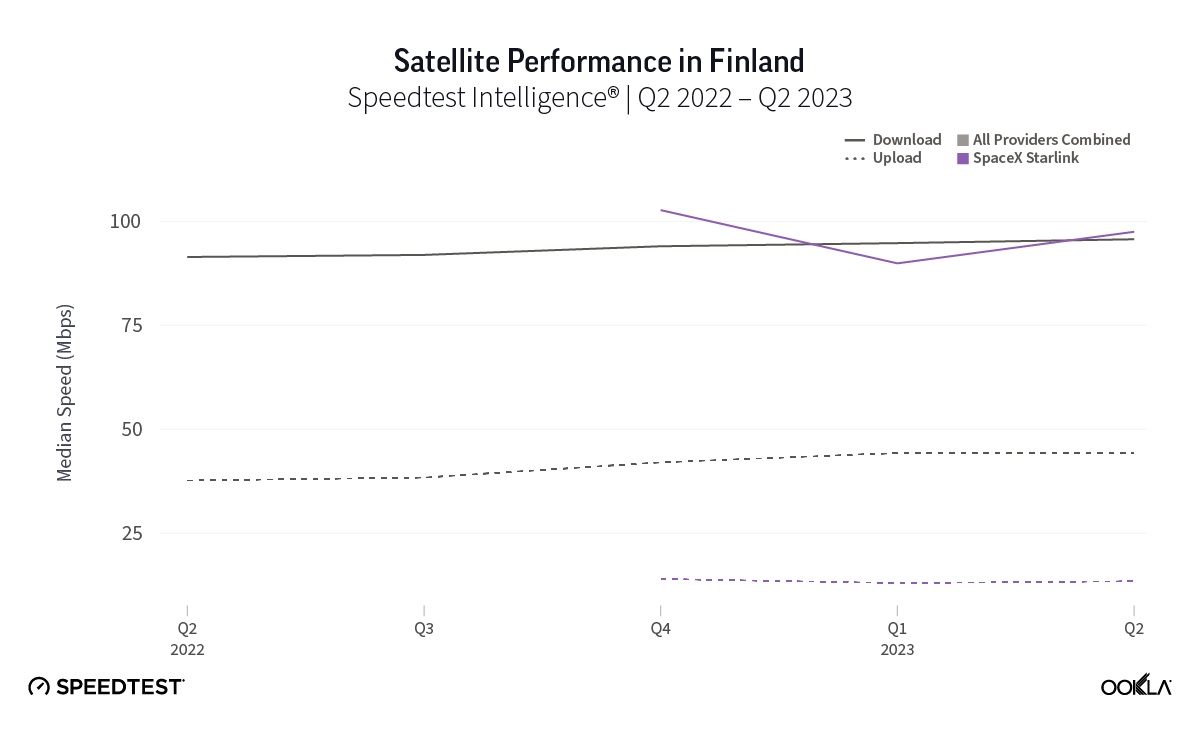
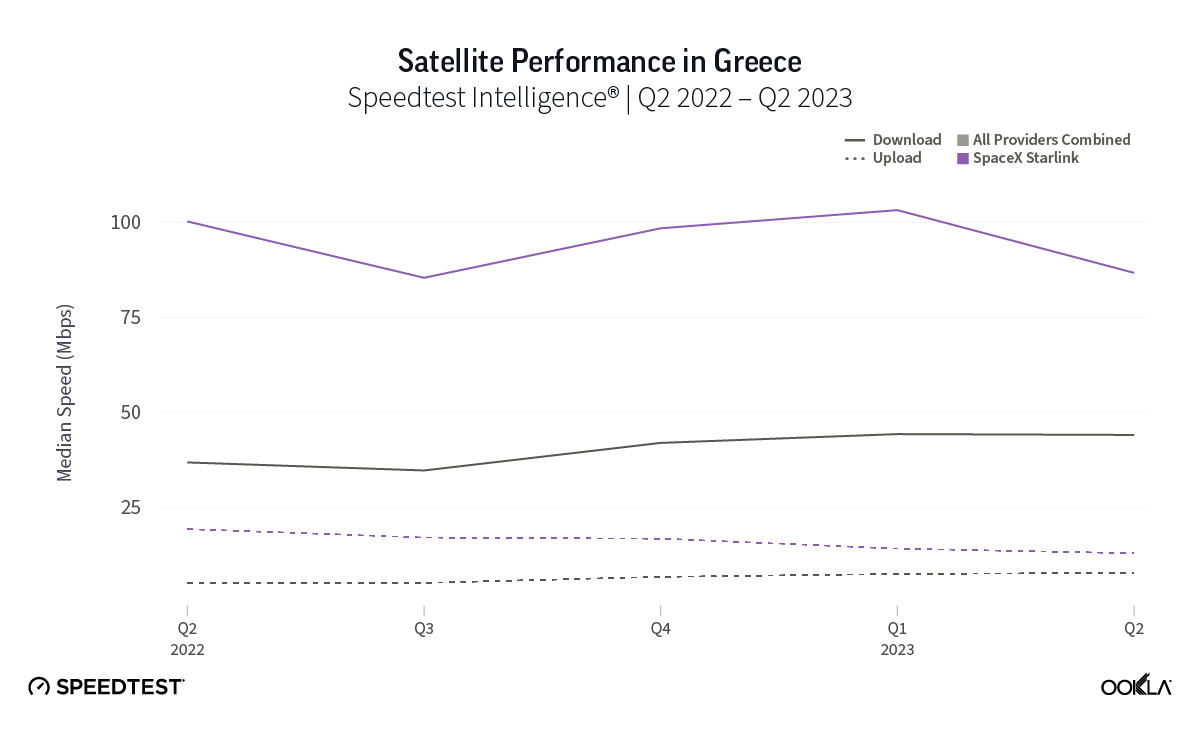
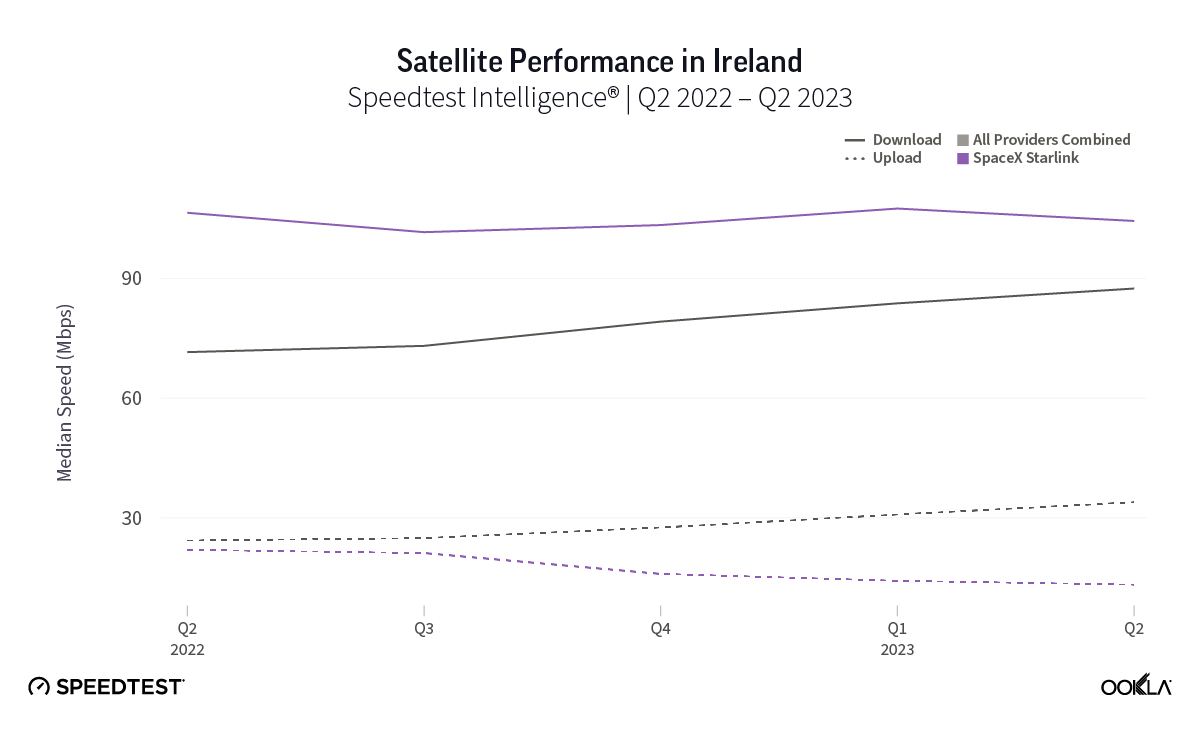
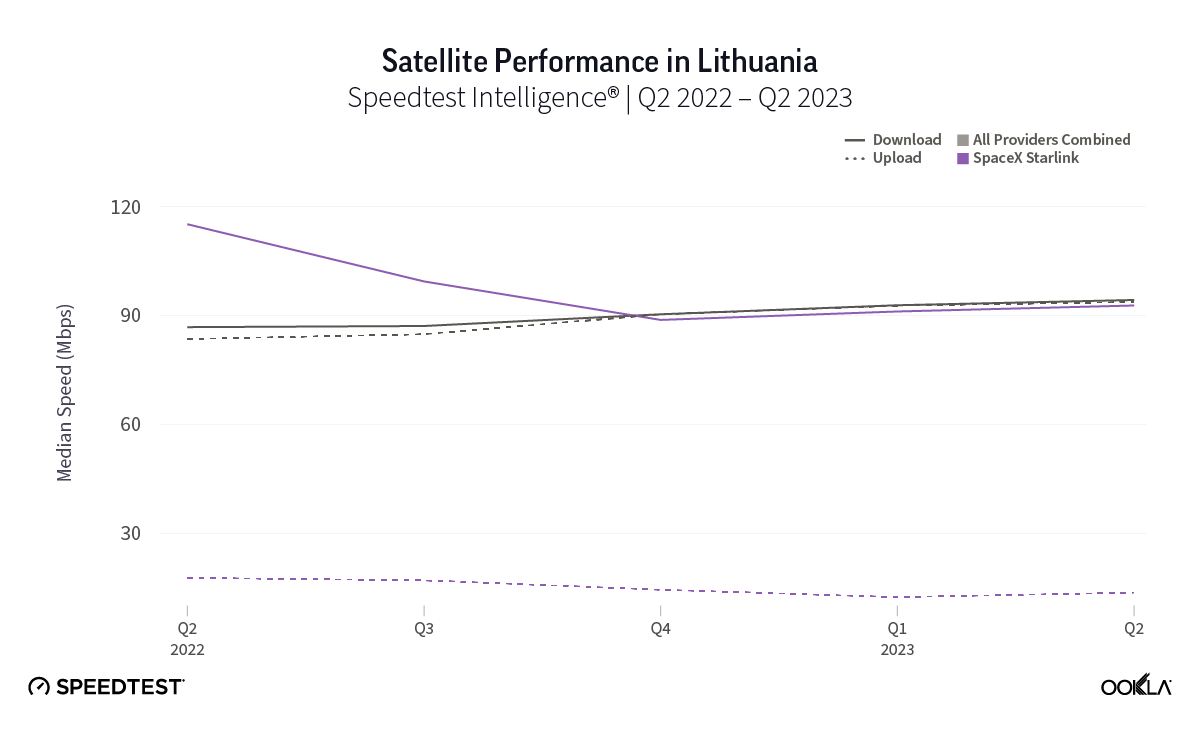
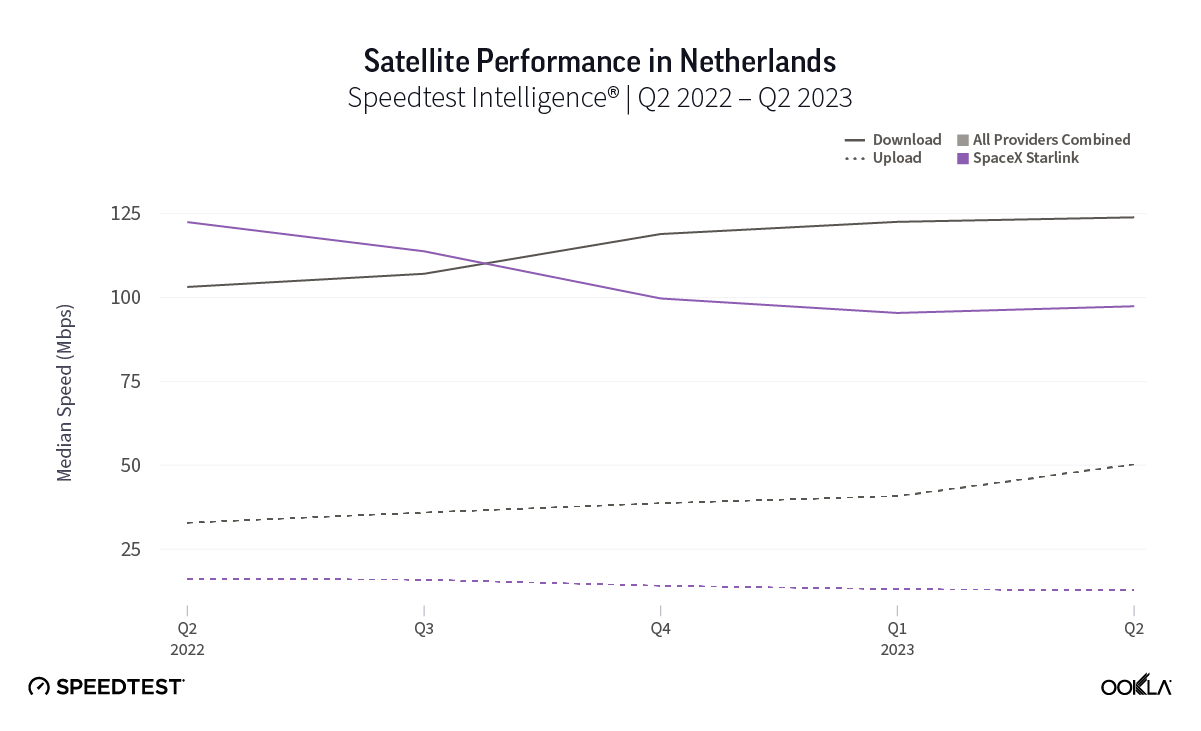
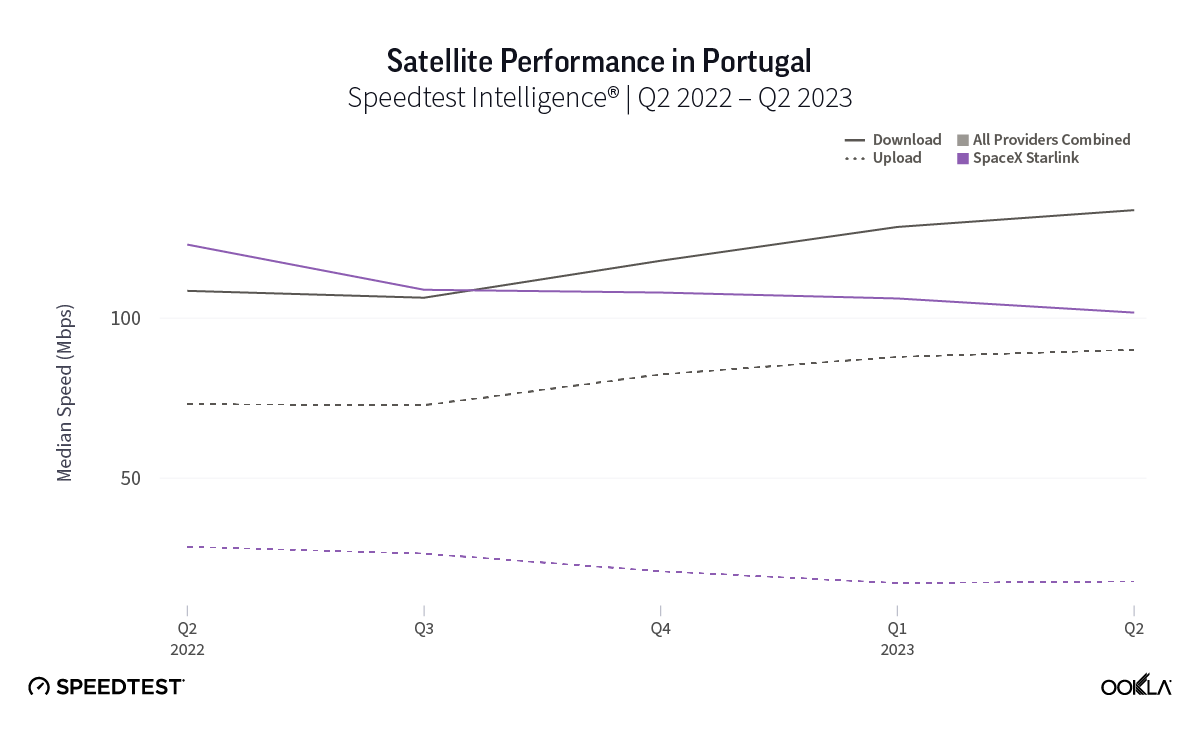
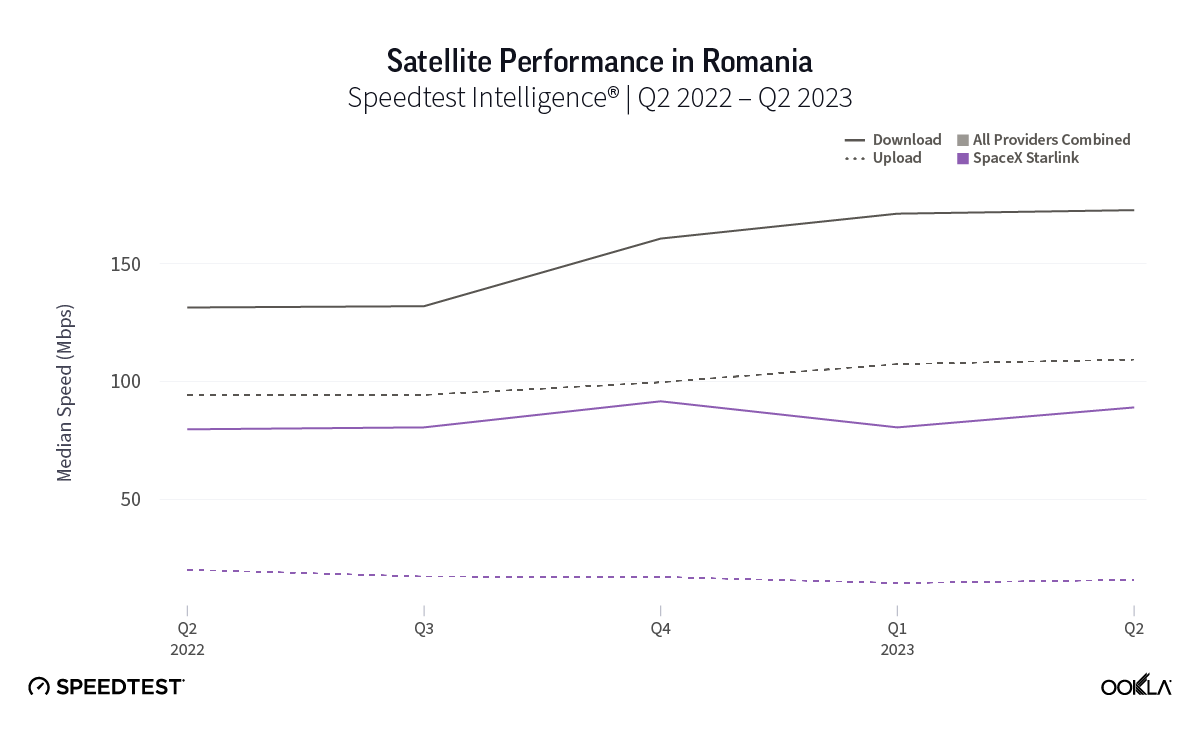
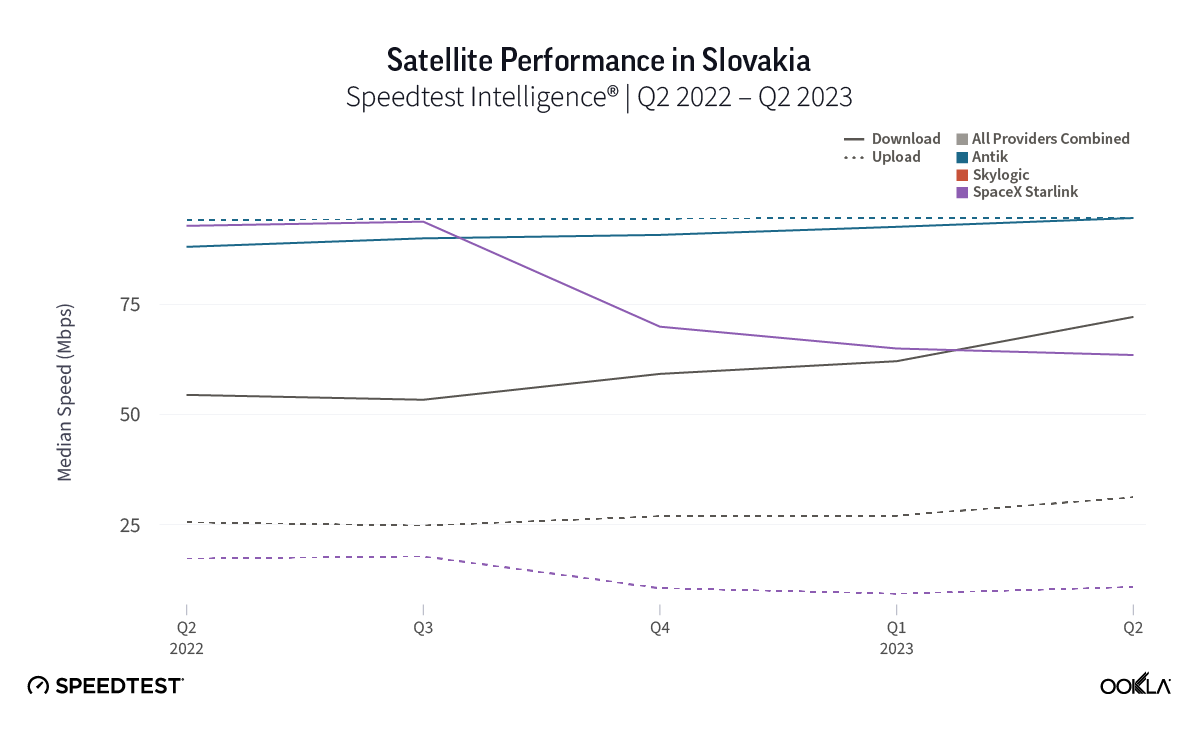
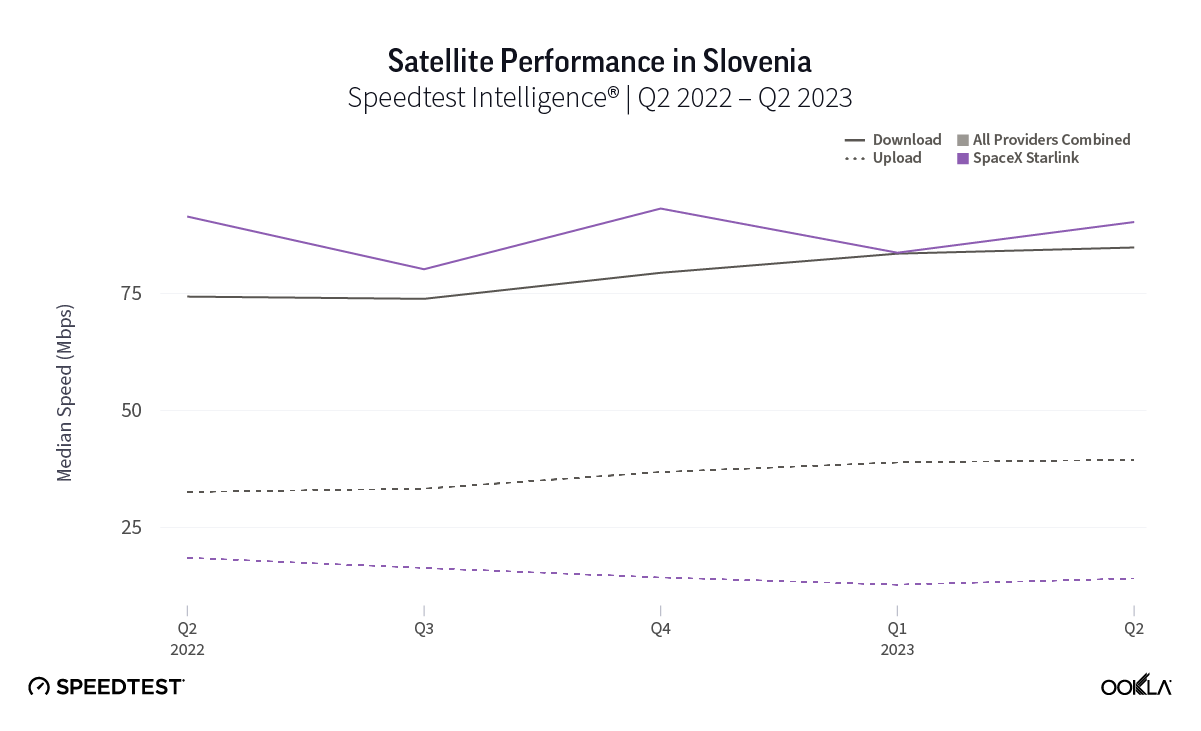
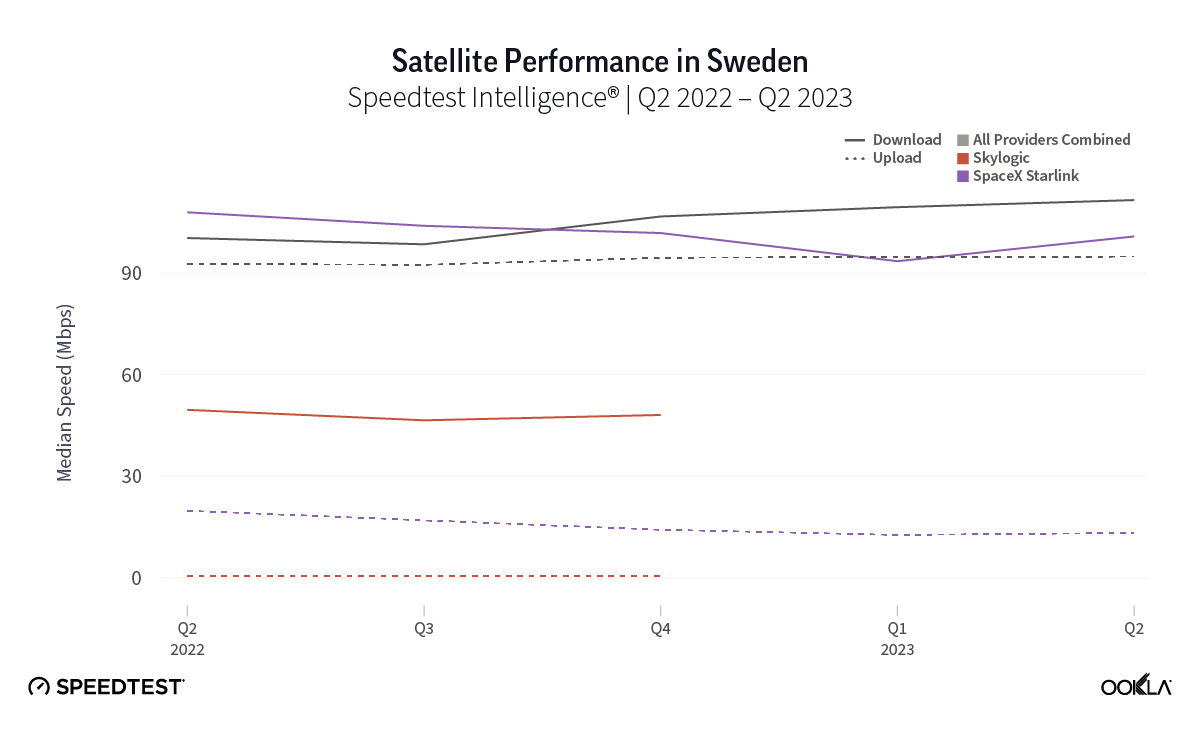
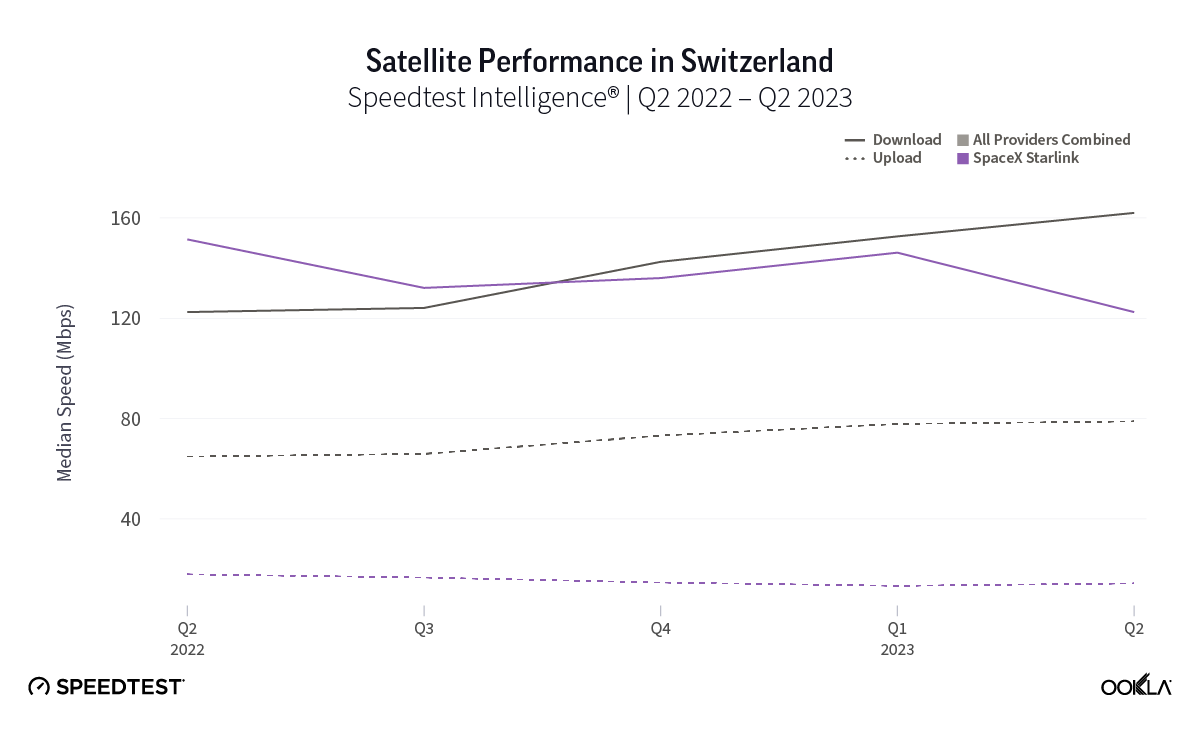
At first glance, year-over-year median download speeds for Starlink are about the same (-5% to 5%) or better (greater than 5%) from Q2 2022 to Q2 2023 in 15 countries and slower (decreasing more than 5%) in 8 countries. But among the 27 countries we surveyed during Q2 2023, Starlink had speeds faster than the aggregate of all fixed broadband providers combined in 11 countries (Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Croatia, Czechia, Estonia, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, and the U.K.) Those speeds were most notably faster in Croatia and Greece for Starlink at 94.41 Mbps to 45.24 Mbps and 108.97 to 44.09 Mbps, respectively, during Q2 2023. Speeds were about the same in four countries (Finland, Slovenia, Germany, and Lithuania), and speeds were slower than the aggregate of fixed broadband providers in 12 countries, most notably in Poland, Spain, Romania, Denmark, and France which saw between 50% and 105% faster aggregate fixed broadband speeds than Starlink.
Quarterly download speeds stabilizing or improving
Looking at results from Q1 2023 to Q2 2023, median download speeds for Starlink remained about the same (between 5% and -5%) in 23 countries, while decreasing in four countries. That’s a big deal, especially given Starlink had median download speeds greater than 100 Mbps in 14 countries, and greater than 90 Mbps in 20 countries, and greater than 80 in 24 countries — with only three countries failing to reach 70 Mbps.
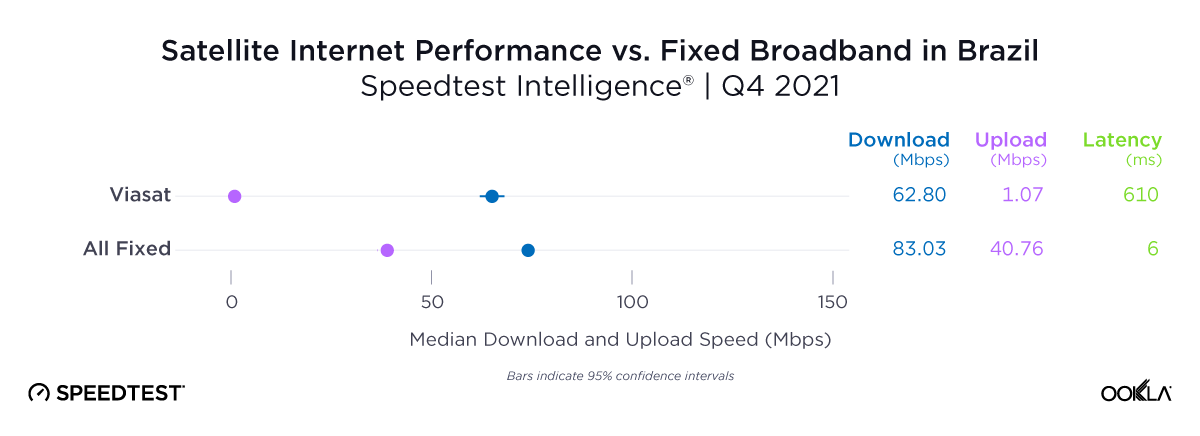
While trailing Starlink speeds, Skylogic recorded median download speeds in Italy at 29.21 Mbps during Q2 2023, a roughly 27% statistical increase year-over-year from 22.28 Mbps during Q2 2022. Notably, Skylogic recorded a median download speed of 68.44 Mbps in Italy during Q1 2023. Among the various countries we recorded Skylogic data for during the past year, the range of median download speeds varied between 19.53 Mbps and 68.44 Mbps, with most speeds between 28 and 50 Mbps, all fast enough to stream 4K video online. Viasat, had relatively similar download speeds in Germany and Italy at 17.22 Mbps and 17.45 Mbps, respectively, during Q2 2023.
Top 10 fastest Starlink download speeds in European countries
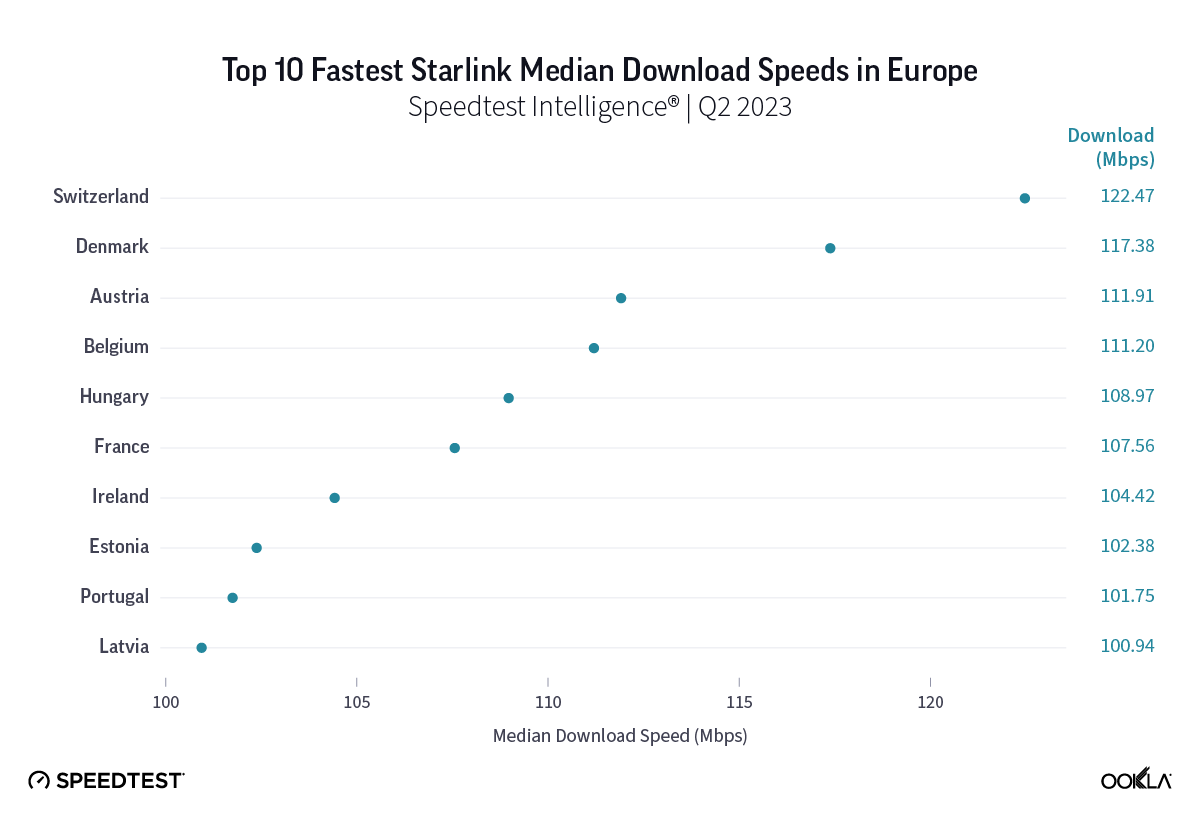
Starlink in Switzerland had one of the fastest median download speed among countries with Starlink during Q2 2023 at 122.47 Mbps, followed by Denmark (117.38 Mbps), Austria (111.91 Mbps), Belgium (111.20 Mbps), Hungary (108.97 Mbps), France (107.56 Mbps), Ireland (104.42 Mbps), Estonia (102.38 Mbps), Portugal (101.75 Mbps), and Latvia (100.94 Mbps). Sweden, Italy, Bulgaria, and the U.K. all followed but had speeds greater than 100 Mbps.
Upload speeds for Starlink are down year over year, but quarterly speeds almost all improved or were about the same
Upload speeds for Starlink mostly decreased notably year over year, with only the U.K. showing an improved median upload speed in Q2 2023 out of 27 countries surveyed. However, looking quarter to quarter, Q2 2023 upload speeds for Starlink stayed about the same or improved in 25 out of 27 countries, with only Greece and Ireland showing declines. For upload speeds, Starlink all 27 countries we surveyed had upload speeds between 10 Mbps and 15 Mbps except Portugal (17.70 Mbps), Hungary (16.91 Mbps), Croatia (16.12 Mbps), Bulgaria (15.93 Mbps), Romania (15.82 Mbps), Spain (15.79 Mbps), and Poland (9.11 Mbps). Starlink in Greece was the only instance of a satellite provider in Europe having an upload speed greater than the aggregate of all fixed providers combined, 12.97 Mbps for Starlink to 7.85 Mbps for the aggregate of fixed broadband providers combined. Skylogic showed upload speeds lower than 4 Mbps in both Austria and Italy during Q2 2023. Viasat had upload speeds of 3.51 Mbps in Germany and 4.69 Mbps in Italy during Q2 2023.
Multi-server latency is stabilizing for Starlink users across Europe
As an low-earth orbiting (LEO) satellite internet provider, Starlink has a leg up on some satellite competitors who rely on further away geosynchronous-earth orbit (GEO) and medium-earth orbit (MEO) satellite constellations. However, once again, all the aggregates of all fixed broadband providers in Europe had much lower multi-server latencies than Starlink, Viasat (which had latencies over 600 ms) and Skylogic (which had latencies over 700 ms). That being said, Starlink still saw multi-server latencies under 60 ms in the U.K. (51.26 ms), Spain (53.37 ms), Portugal (55.84 ms), and Belgium (59.34 ms). Starlink saw most countries’ multi-server latencies between 60 and 90 ms.
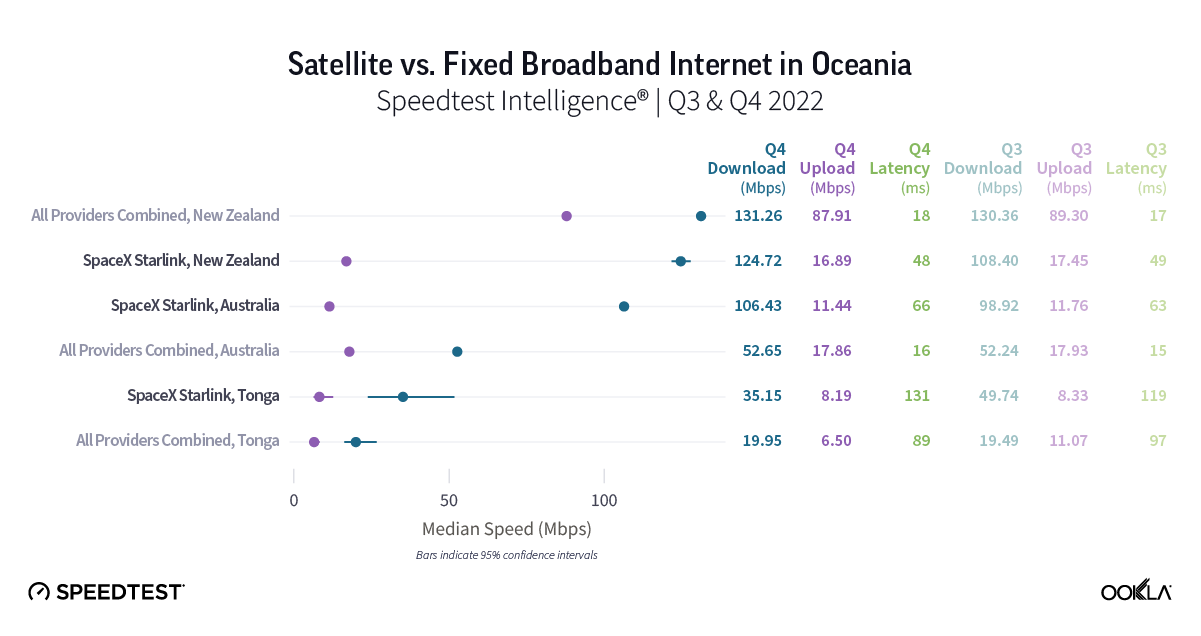
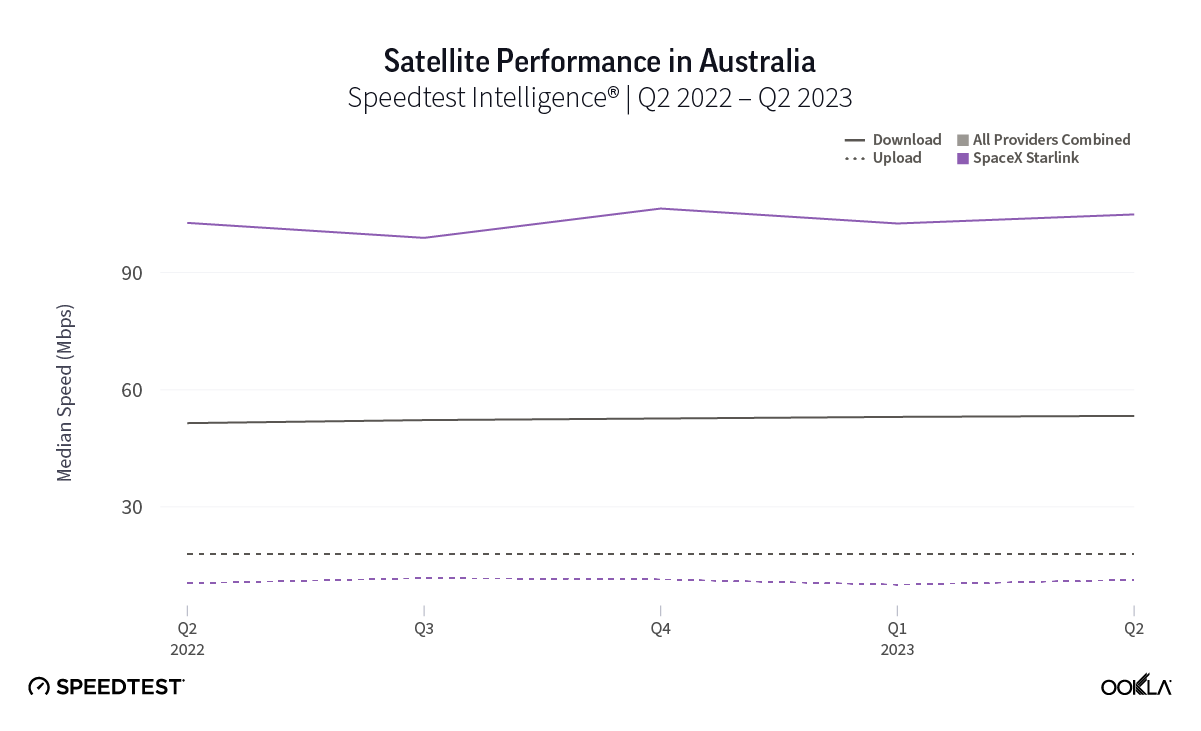
Starlink speeds stabilize in Oceania
Oceania, the second least densely populated continent in the world to Antarctica, has rural and remote populations that benefit from (and even rely on) satellite internet connections. Luckily for rural and remote Starlink users, they’ve probably seen a good amount of stability over the past year with Q2 2023 median download speeds in New Zealand at 113.78 Mbps (105.99 Mbps in Q2 2022) and Australia at 104.92 Mbps (102.76 Mbps in Q2 2022). Tonga, which is very remote, saw download speeds drop from 45.25 Mbps in Q2 2022 to 37.95 Mbps in Q2 2023.
Upload speeds also showed some stability with Australia going from 10.45 Mbps in Q2 2022 to 11.33 Mbps during Q2 2023 and New Zealand going from 12.31 Mbps to 14.62 during the same time period. Tonga saw a notable drop in speeds year over year from 19.26 Mbps in Q2 2022 to 6.66 Mbps Q2 2023.
Multi-server latency, which usually will be higher for satellite internet options, showed promising results for Starlink in Oceania during Q2 2023. Multi-server latency dropped noticeably in New Zealand year over year, going from 89.38 ms in Q2 2022 to 46.42 ms in Q2 2023. Australia saw a more modest drop with multi-server latency going from 63.04 ms to 59.78 ms from Q2 2022 to Q2 2023. Tonga saw an increase in multi-server latency from 125.24 ms to 137.16 ms during the same time period.
Starlink in Africa is off to a promising start
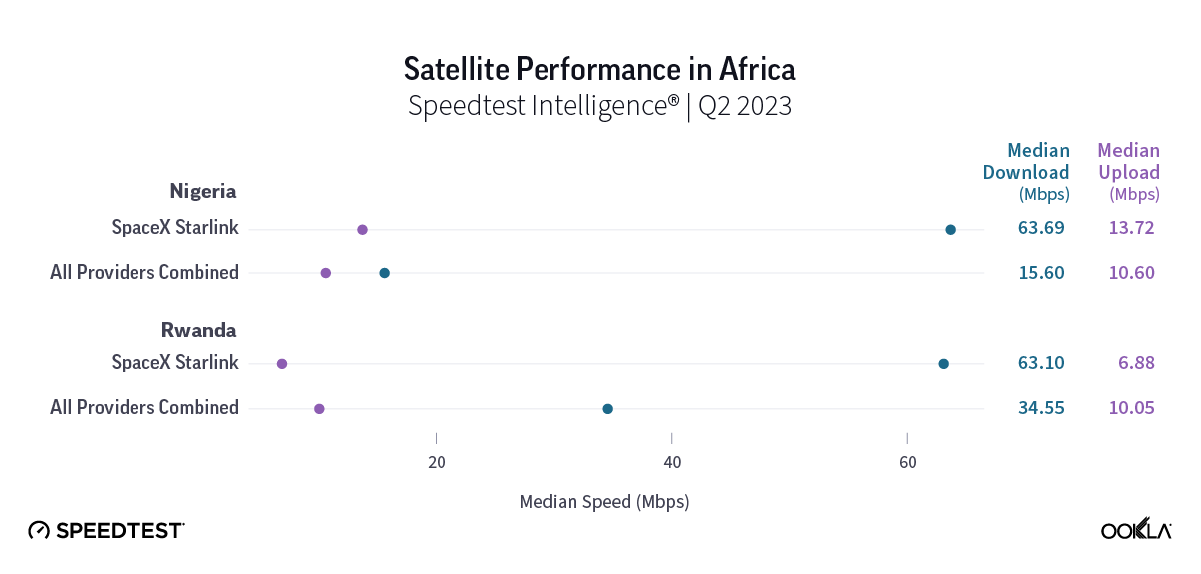
Starlink, which first launched on the African continent in Nigeria this past January, is showing intriguing early results. Speedtest Intelligence showed that Starlink in Nigeria had a faster median download speeds than all aggregate fixed broadband providers combined at 63.69 Mbps to 15.60 Mbps during Q2 2023. Upload speeds were more similar during the same time period with Starlink at 13.72 Mbps and the aggregate of all fixed broadband providers combined at 10.60 Mbps. Starlink did have a marginally higher multi-server latency at 55.88 ms to 50.26 ms during Q2 2023.
In Rwanda, median download speeds were a little closer with Starlink recording a median download speed at 63.10 Mbps in Q2 2023 compared to the aggregate of all fixed broadband providers combined at 34.55 Mbps. Starlink trailed behind for median upload speed at 6.88 Mbps to 10.05 Mbps for fixed broadband providers during Q2 2023. Multi-server latency for Starlink was much higher at 320.45 ms to 29.04 ms for fixed broadband providers during the same time period.
The 2023 space revolution is off to a huge start
Here are some major updates about what’s next for various different satellite competitors:
After delays, Amazon’s Project Kuiper aim to launch prototype satellites this fall
Facing a series of rocket-related delays, Amazon recently announced it could send its first two Project Kuiper prototypes into orbit in late September. That news follows a recently announced $120 million 100,000-square-foot satellite processing facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Planning on offering internet service in 2025, Amazon is slated to have half of its 3,236 LEO satellite constellation in space by 2026.
China’s grand ambitions to provide internet connectivity to over 362 million people
According to the Wall Street Journal, over 362 million people in China don’t have access to the internet — which is about 1 in every 4 people in China, a large portion of which live in rural or remote communities. In order to overcome that connectivity gap, China is looking to the sky to create its own satellite constellation with potentially over 12,000 satellites. China’s biggest gap seems to be with recreating the success of SpaceX’s reusable rockets — however, initial tests are far underway and a host of reusable rockets are slated for test launches in 2024.
SpaceX’s Starlink service offerings are about to rapidly expand
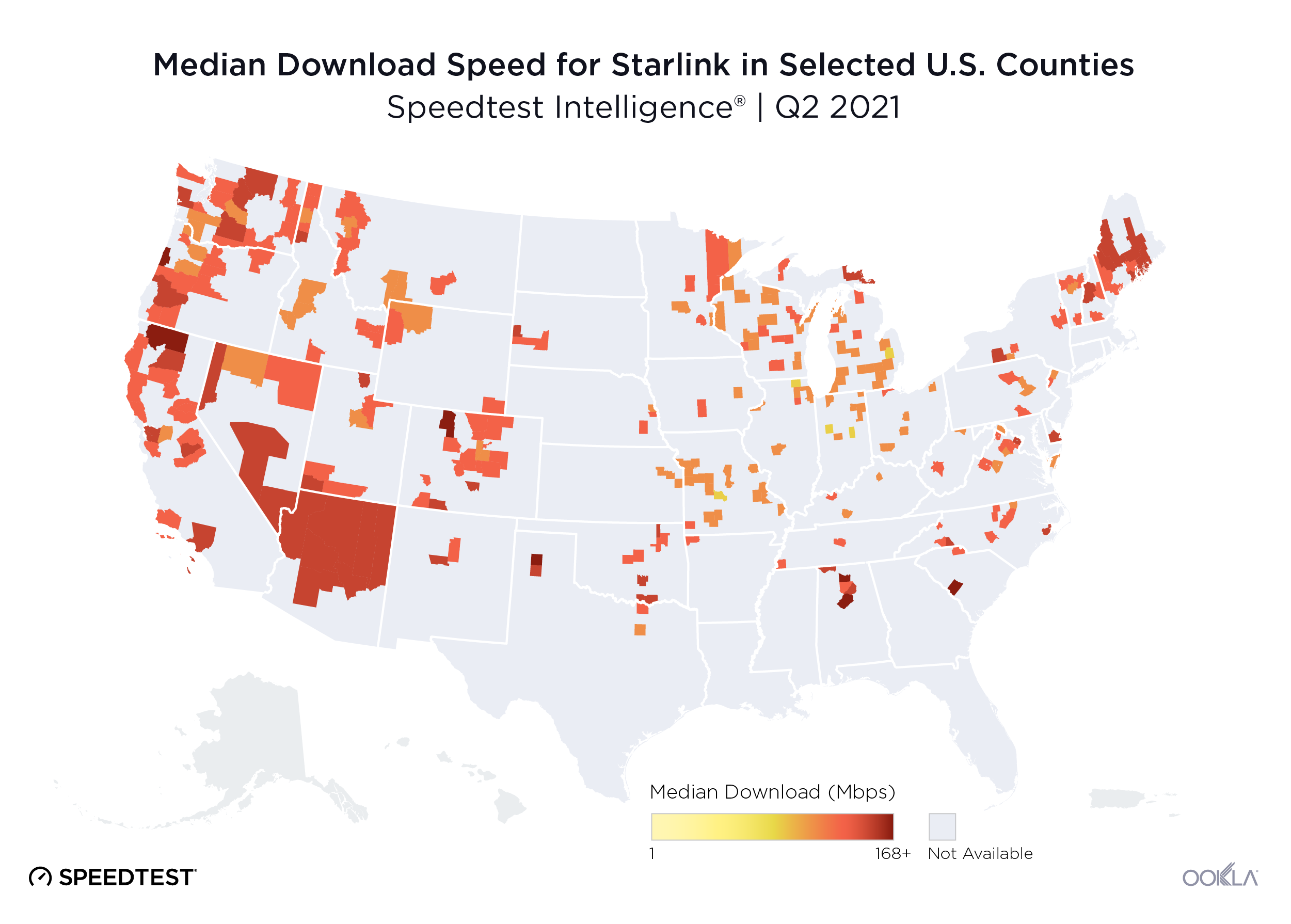
While Starlink continues to lead among satellite providers in most areas of the world, their expansion is only starting. Looking at the Starlink availability map, Starlink has an incredibly busy rest of 2023 and 2024 in Africa, Asia, and South America — and they’re marking their intent to expand into most of the world. That comes as Starlink marked launching over 5,000 satellites into space at the end of August. With some wiley entrepreneurs already renting out their Starlink “Dishy McFlatfaces” to vacationers and campers for $25-30 dollars a day, satellite connectivity is truly becoming a full-time gig.
Viasat’s bad luck might affect entire industry
Viasat launched the first of its three long-awaited Viasat-3 arrays — but then their first satellite suffered an antenna anomaly, which prevented a large reflector to deploy that affects whether or not the satellite can operate as intended. While Viasat is rushing to solve the issue, this could ultimately trigger a $420 million insure claim for the loss of the $700 million satellite. With such a high-value loss, this could send ripples through the satellite industry, causing insurance premiums to skyrocket for companies looking to mitigate potential losses through insurance. All of this comes on the heels of acquiring Inmarsat in May for $7.3 billion to expand its satellite arrays and spectrum holdings. We’ll be watching to see whether or not Viasat can find a solution.
Eutelsat and OneWeb merger imminent, big moves abound
The Eutelsat and OneWeb merger should make competitors take notice — combining satellite networks, expanding enterprise offerings, and competing in emerging markets has big revenue potential — with OneWeb having an already established LEO network of 630 satellites and Eutelsat offering 36 GEO satellites. Of note, OneWeb recently inked a deal with Telstra in Australia to provide satellite backhaul for locations “where satellite backhaul is a preferred or only viable option.” OneWeb is also partnering with the European Space Agency to develop a next-gen 5G beam-hopping satellite, which could quickly increase connectivity for people traveling or for disaster areas that need emergency connectivity. Shareholders are set to vote on approving the merger on Sept. 28.
European Union greenlights multi-orbit constellation
With grand ambitions to launch a multi-orbit, €6 billion constellation in 2024, the European Union is partnering with a consortium of industry players including Airbus, SES, Eutelsat, Hispasat, and Thales to develop the EU’s IRIS² project. The EU still expects to have the first of its satellites go live by the end of 2024 and have a fully operational constellation by 2027.
HughesNet aiming to launch Jupiter 3 array in Q2 2023
HughesNet successfully launched its Jupiter 3 array on July 29, which aims to provide U.S. and Latin America consumers with higher broadband download speeds. While the actual satellite will take some time to reach its geosynchronous orbit and deploy, this satellite adds 500 Gbps of Ka-band capacity for HughesNet, which could see consumers reaching download speeds between 50 Mbps and 100 Mbps. We’ll be eagerly awaiting Speedtest® results from HughesNet’s Jupiter 3 array.
Ookla will continue monitoring new satellite internet developments
2023 continues to be an important year for satellite internet providers. Satellite connectivity is something we’ll be watching closely and we’ll continue our series next quarter with Q3 2023 data from select continents including North America. In the meantime, be sure to download the Speedtest app for Windows and Mac computers or for iOS or Android for devices and see how your satellite internet stacks up to our results.