Taiwan’s mobile market is fiercely competitive, driven by three major operators – Chunghwa Telecom, FarEasTone, and Taiwan Mobile, and two smaller ones, Asia Pacific Telecom (GT) and Taiwan Star (T Star). Earlier this year, two major mergers of telecom operators were approved, which is expected to alter the telecommunication competitive landscape of the country. In this article, we will examine the current state of 5G in Taiwan before the mergers take place and evaluate the potential impact these mergers will have on Taiwan’s telecommunications market.
Key Takeaways
- Recent mergers are set to alter Taiwan’s mobile market dynamics. The number of operators will be reduced from five to three major players, each with a comparable market share. Far EasTone and Taiwan Mobile will inherit additional spectrum bandwidth as a result of the mergers, enabling both operators to enhance customer experience, introduce new services, and compete more effectively with Chunghwa Telecom, the largest operator.
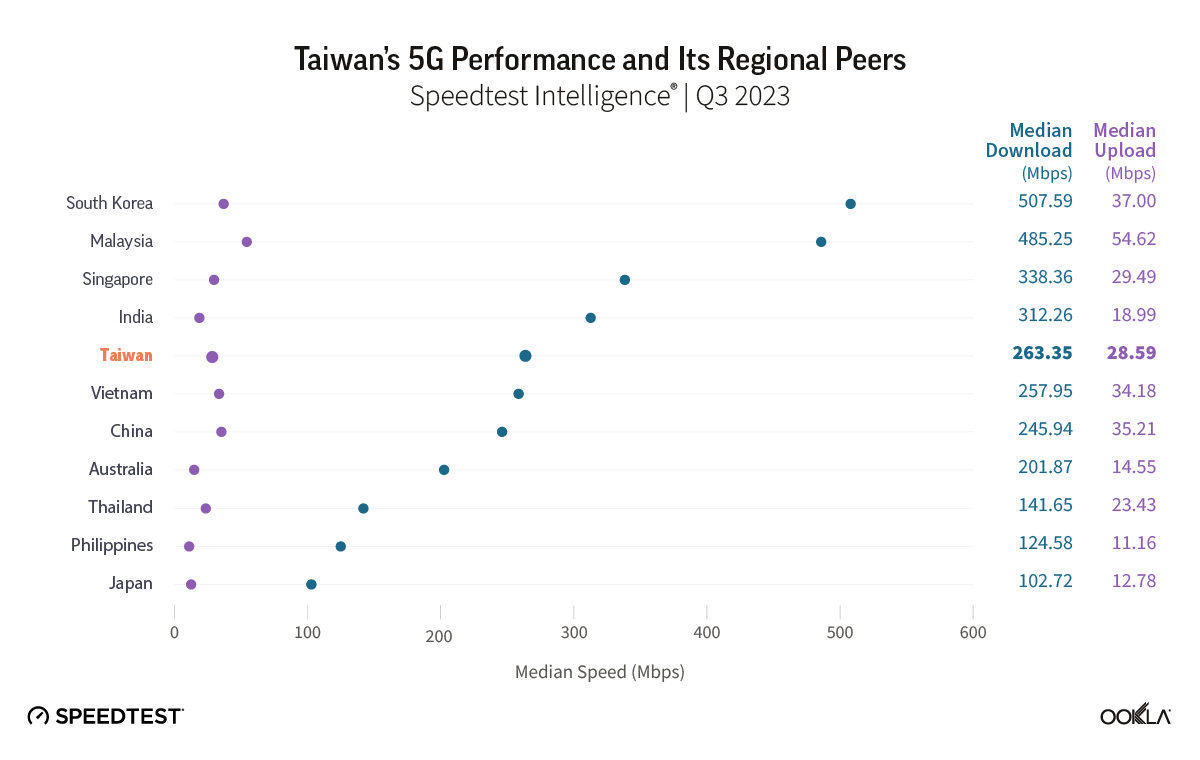
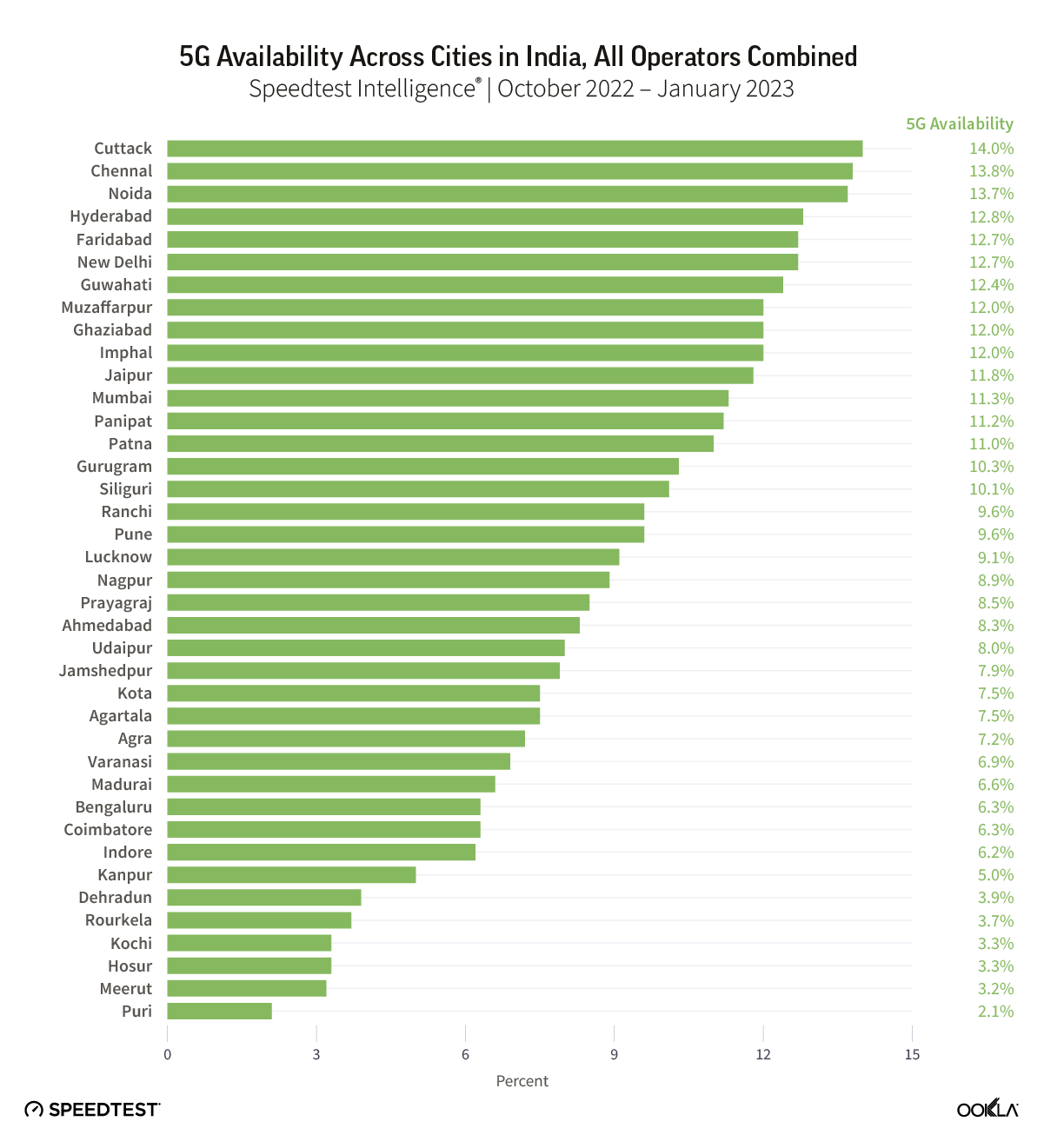
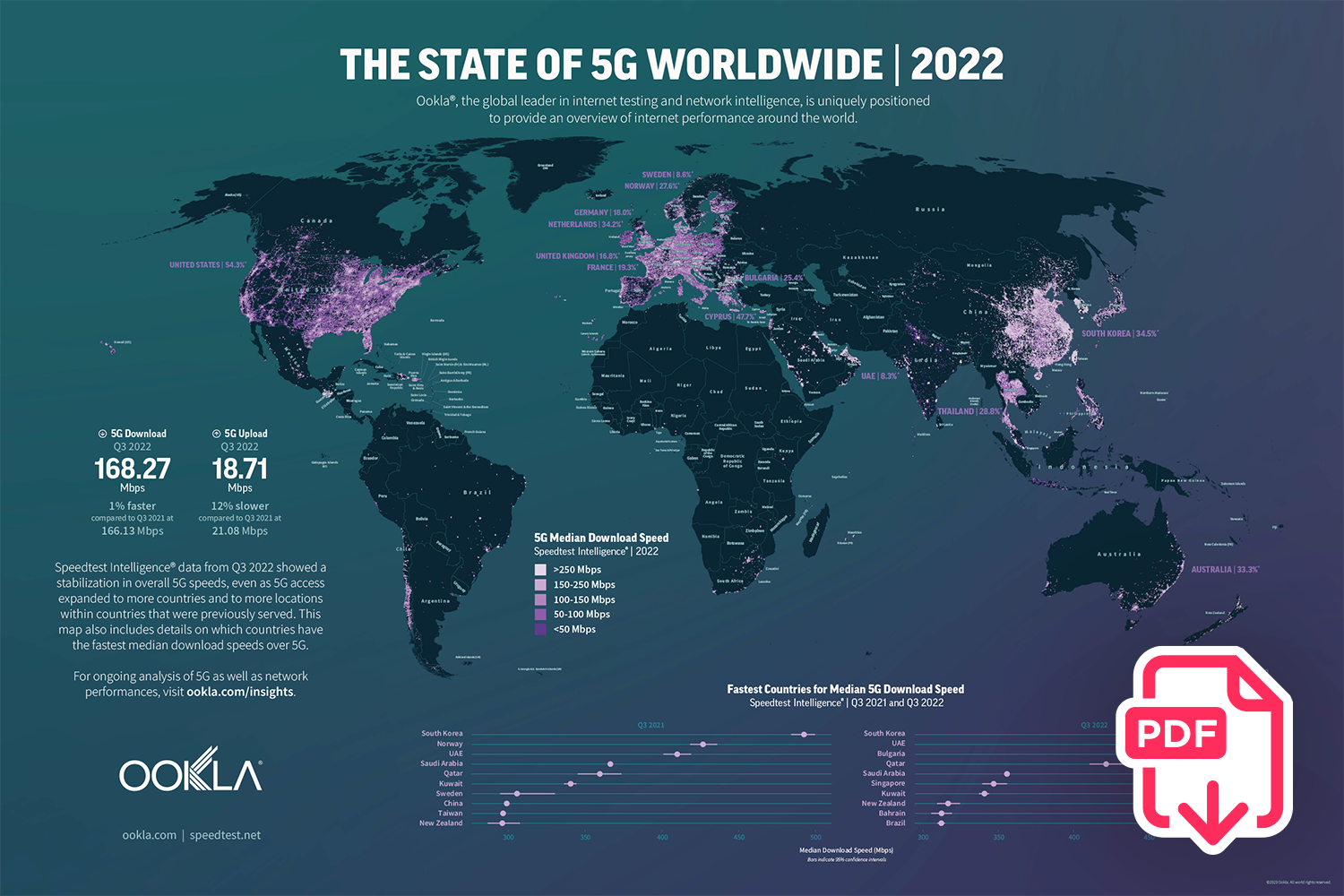
- Taiwan’s 5G network performs well compared to other countries in the region. In Q3 2023, Taiwan’s 5G network had a median download speed of 263.35 Mbps, outperforming other countries in the region, such as Vietnam, China, Hong Kong, the Philippines, and Japan.
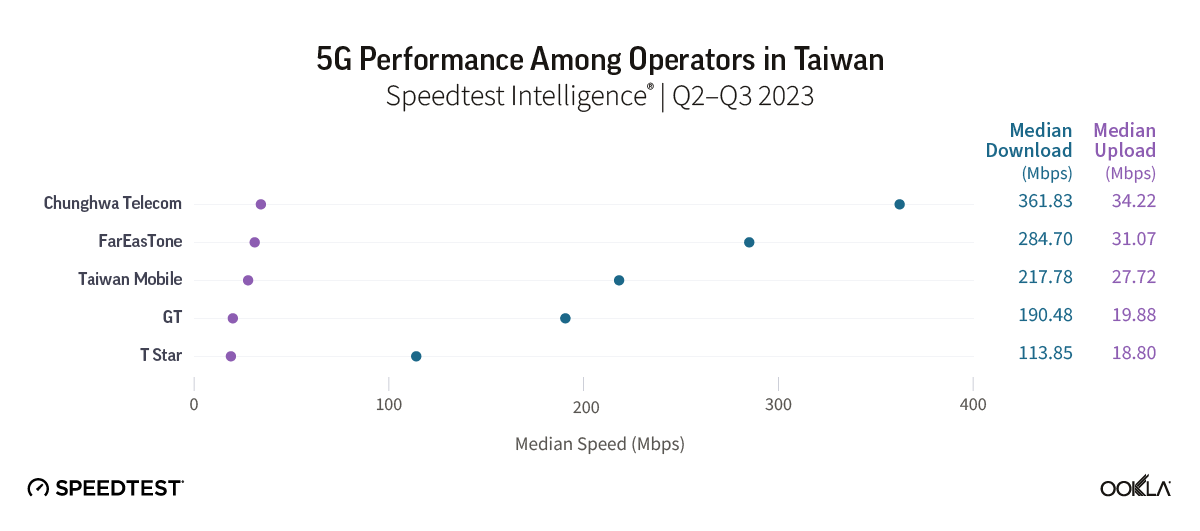
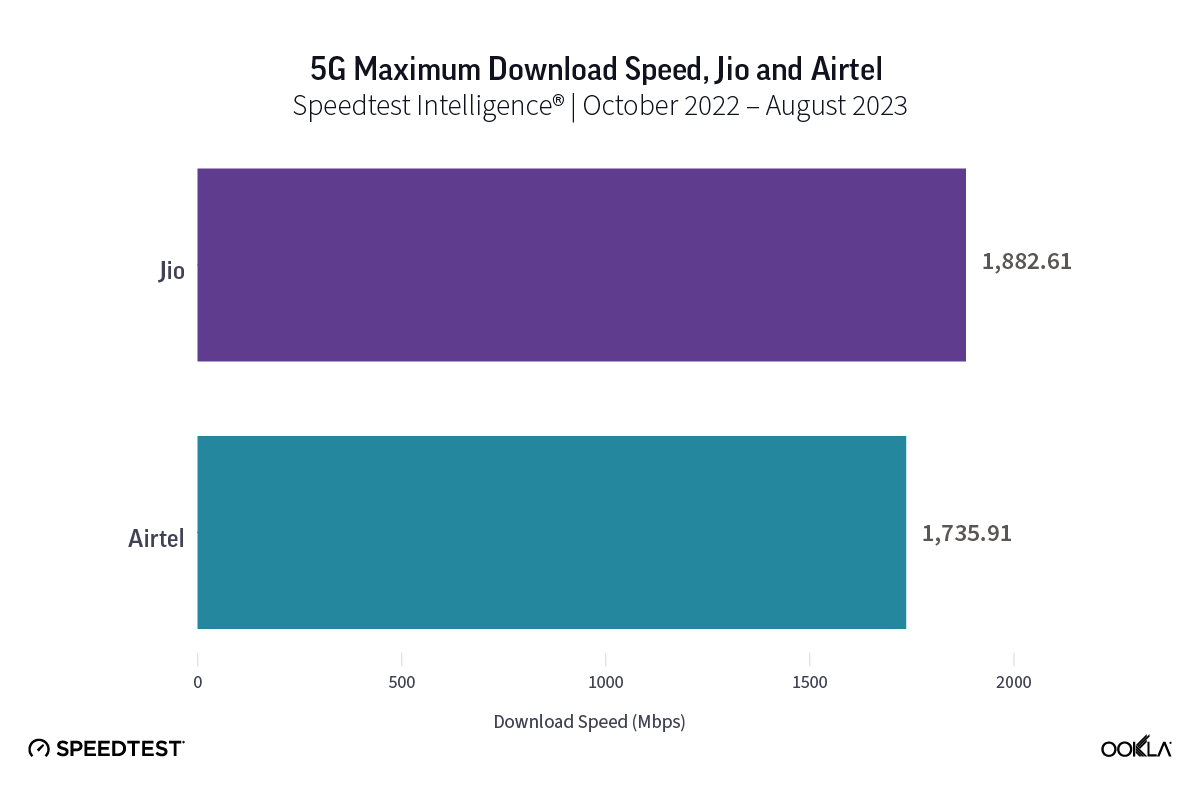
- Chunghwa Telecom leads the way in terms of 5G download speeds. Based on Speedtest Intelligence® data for Q2-Q3 2023, Chunghwa Telecom had the fastest median download speed with a reported speed of 361.83 Mbps. Far EasTone and Taiwan Mobile came in second and third place, respectively. GT and T Star ranked fourth and fifth, with median download speeds of 190.48 Mbps and 113.85 Mbps.
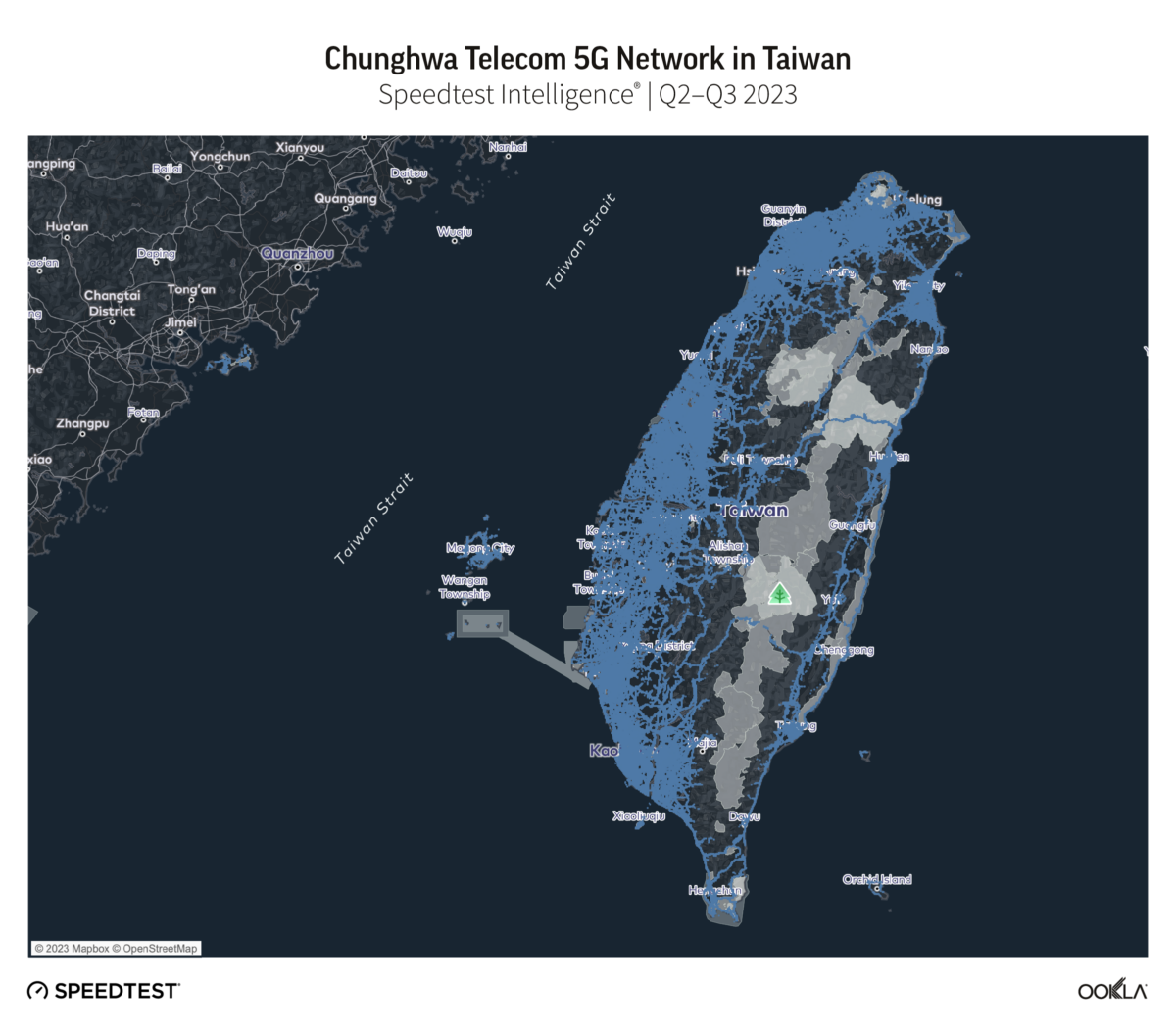
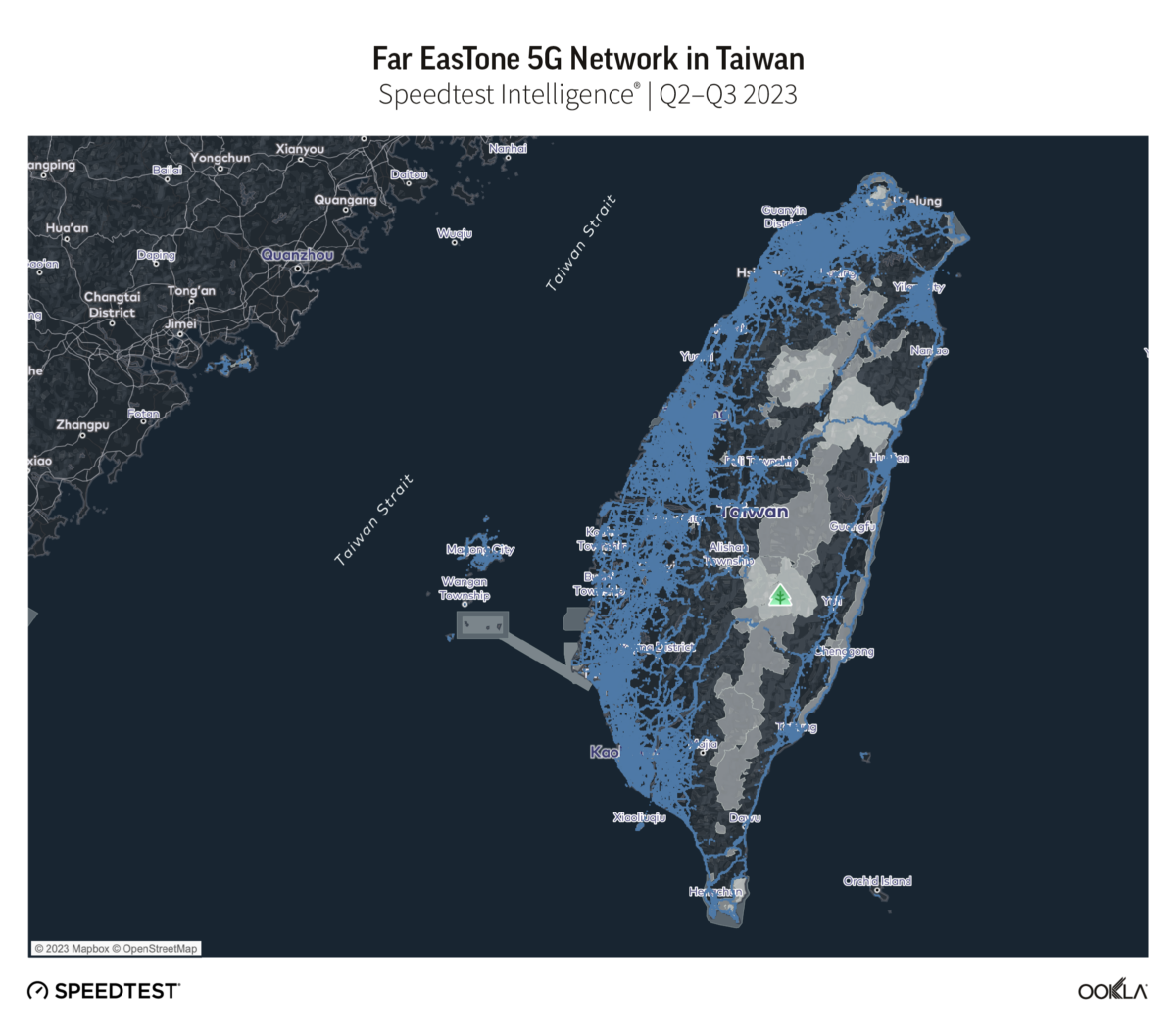
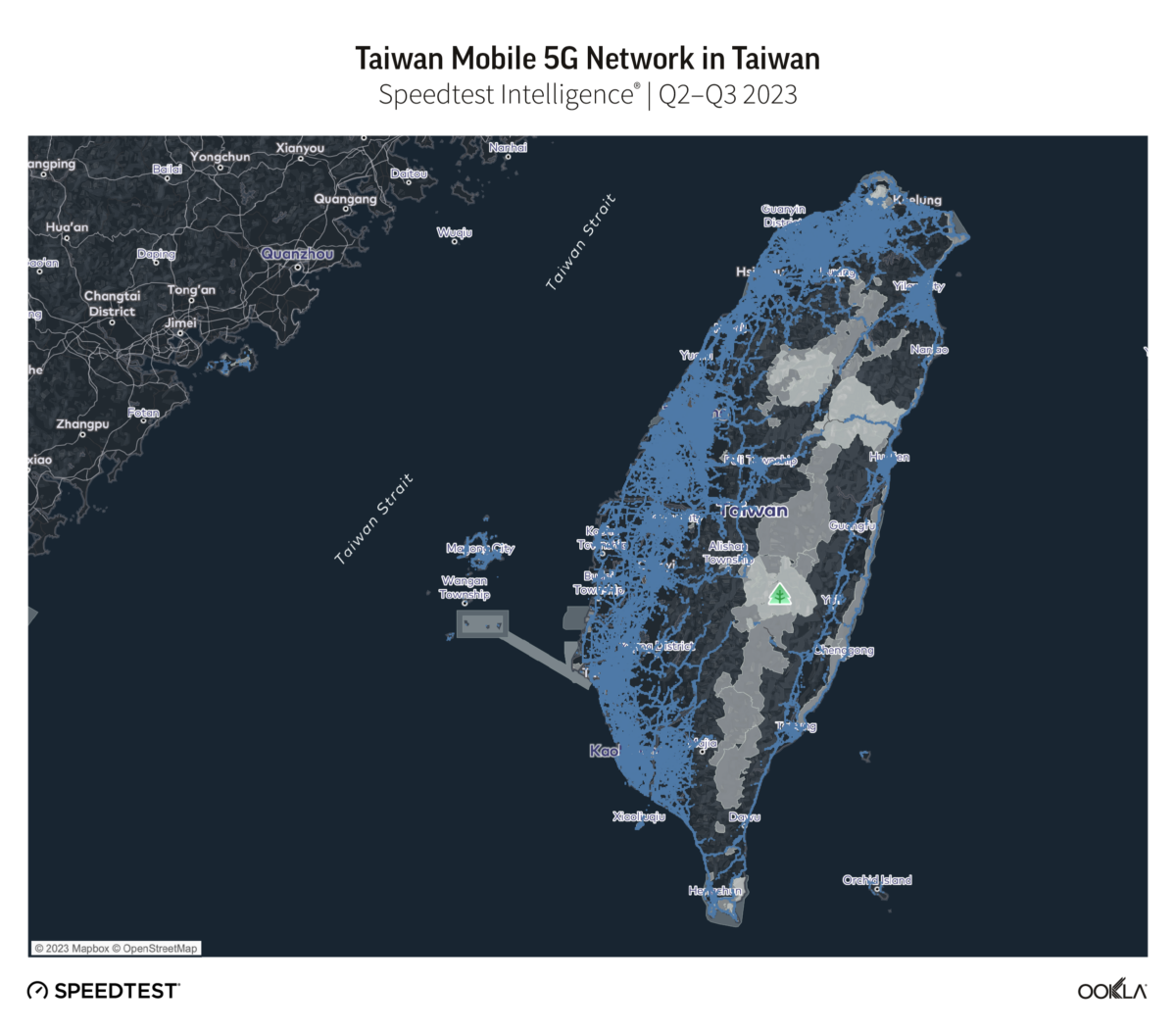
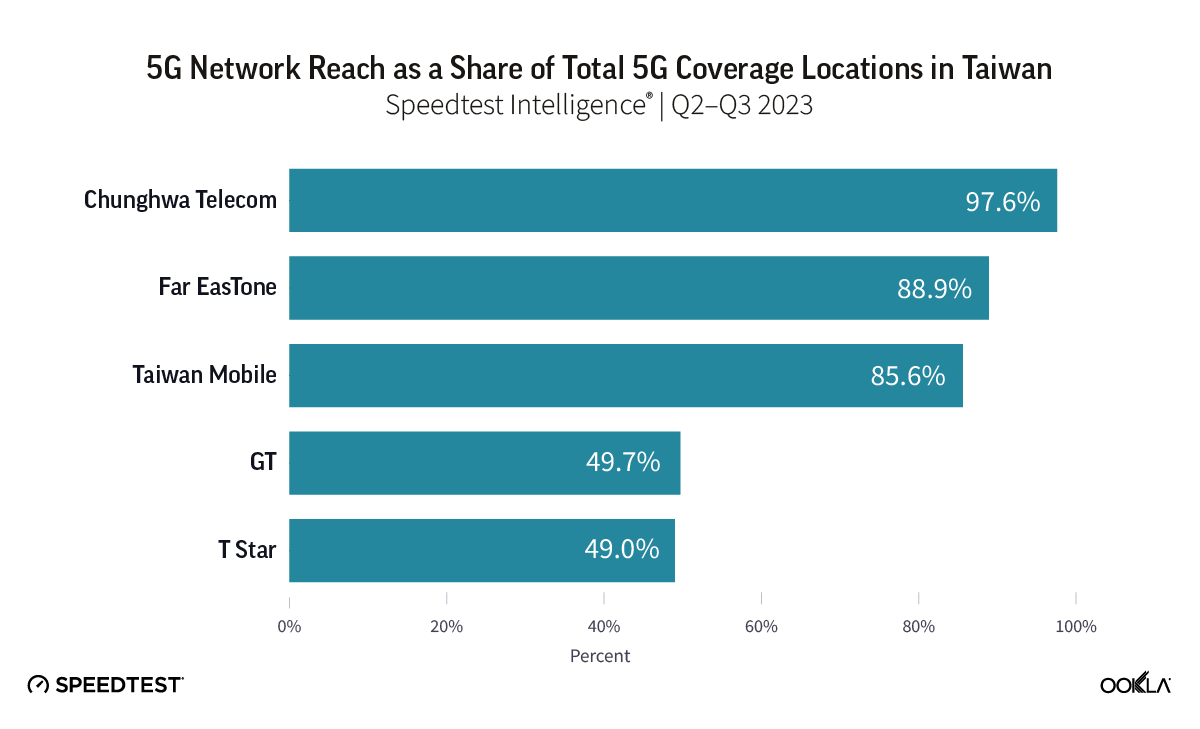
- Chunghwa Telecom’s 5G network extends to 97.6% of locations in Taiwan with 5G coverage. Chunghwa’s 5G network reached more locations across the island than its competitors, with next-placed Far EasTone following with 88.9%, and Taiwan Mobile with 85.6%.
Change in Taiwan’s Telecom Landscape
The Asia Pacific telecommunications markets have witnessed several notable mergers and acquisitions in recent years. This trend is primarily attributed to heavy investments in 5G technology, as companies strive to stay competitive in the market and sustain their growth in the face of economic challenges. Taiwan’s market is one such example, where the National Communications Commission (NCC) approved two mobile operator mergers earlier this year, which will significantly transform Taiwan’s telecommunications market landscape.
Mergers will increase market competition with three major players
The two mergers involve the consolidation of two major operators with minor operators. The first merger involves the integration of Taiwan Mobile and Taiwan Star Telecom (T Star), while the second merger sees Far EasTone partnering with GT’s parent company Asia Pacific Telecom (APT). As a result of the mergers, the number of operators will be reduced from five to three players with comparable market share. More importantly, this will give the new entities additional scale, allowing them to directly compete with Chunghwa Telecom, the current largest operator.
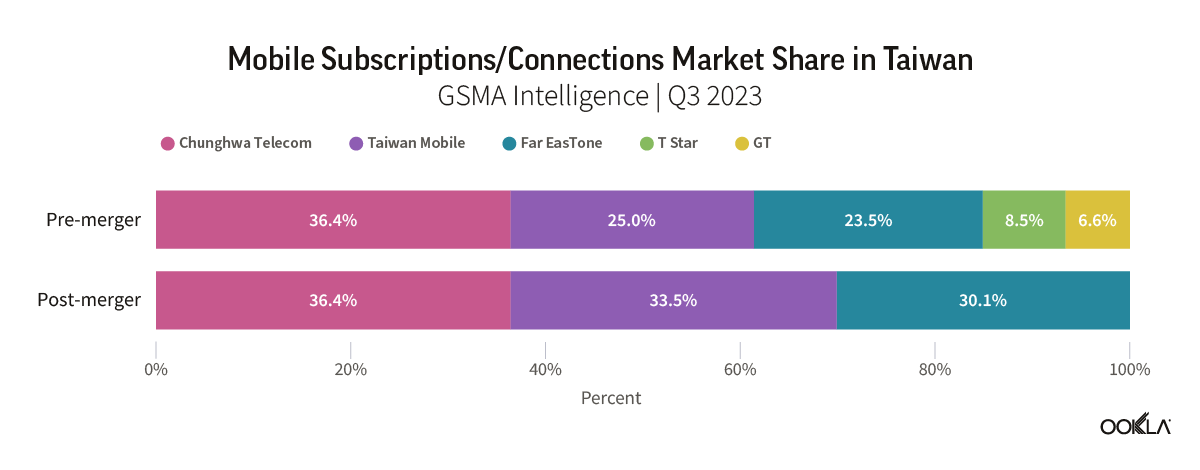
The merged operators could provide more competition to Chunghwa Telecom across all market segments, not only mobile. For instance, the newly merged entities could look at convergent offerings to compete with Chunghwa Telecom, which currently leads the fixed broadband market share and differentiates its services with value-added and bundling packages.
Additional spectrum for 5G use for merged entities
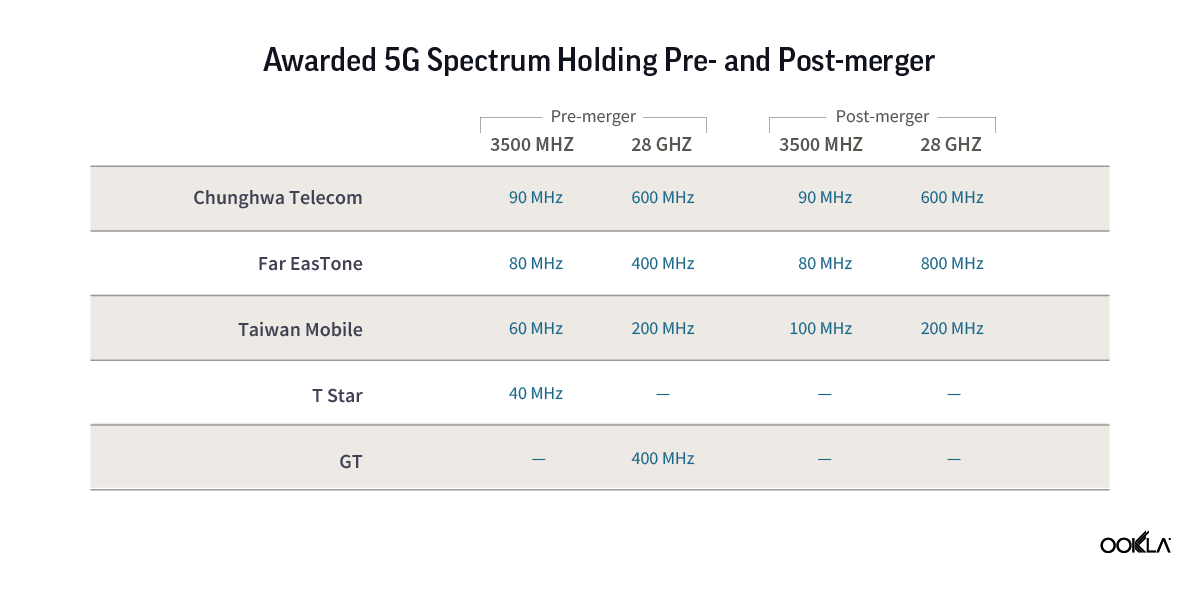
The merging of these operators will bring about significant benefits through synergies. Far EasTone and Taiwan Mobile will inherit the spectrum bandwidth previously held by the two dissolved entities, increasing their competitive edge in the market. The availability of increased resources will enable more efficient use of 5G spectrum, optimize network infrastructure, and reduce energy usage by decommissioning redundant base stations, resulting in a more cost-effective network.
After the consolidation, Far EasTone will see an increase of its 28 GHz spectrum holding from 400 MHz to 800 MHz, in addition to the 80 MHz of the 3.5 GHz band it initially acquired. Taiwan Mobile will now have a block of 100 MHz of the 3.5 GHz band, making it the operator with the most medium frequency bandwidth capacity in the market. When it comes to the high band of 28 GHz, Taiwan Mobile only holds 200 MHz, much less than Far EasTone’s 800 MHz, and Chunghwa Telecom, which holds 600 MHz. The additional spectrum bandwidths will come in very handy to enhance customer experience and introduce new enterprise offerings post-merger.
While the additional spectrum is welcome, in compliance with regulations, operators may only own up to one-third of the available spectrum. After merging with Taiwan Star, Taiwan Mobile will have 60MHz of sub-1GHz spectrum, exceeding one-third of the total available. They will need to divest 10MHz of their frequencies. Similarly, following its merger with GT, FET will be required to surrender any excess spectrum in bands below 3GHz, bands between 3GHz and 6GHz, and bands above 24GHz. How these operators will divest the excess spectrum remains to be seen.
Close scrutiny by the NCC on coverage and service enhancements
As the Taiwanese market undergoes a significant shift, it will naturally require thorough regulatory scrutiny to ensure a smooth transition. Apart from the disposal of excess bandwidth as mentioned earlier, the NCC also imposed additional conditions, including coverage targets, and ensuring uninterrupted subscriber services during the transition period.
Both Taiwan Mobile and Far EasTone will be required to increase 4G coverage across the island to 99% of the population, while 5G coverage must be at least 98% by 2027. The operators will also need to explore ways to reduce carbon emissions and implement effective energy-saving systems to achieve an annual energy saving of approximately 160 million kWh.
Taiwan’s 5G performs well compared to its regional counterparts
Taiwan rolled out its 5G network in 2020, with Chunghwa Telecom being the first operator to introduce 5G services in July of that year. Since then, Taiwan has experienced significant growth in mobile performance, particularly in 5G performance, compared to other countries across the globe.
In Q3 2023, Speedtest Intelligence® data revealed that Taiwan’s 5G network had achieved a median download speed of 263.35 Mbps, outperforming its regional counterparts, including Vietnam (257.95 Mbps) and China (245.94 Mbps). Furthermore, Taiwan’s 5G network was notably faster than those of Hong Kong (136.51 Mbps), the Philippines (124.58 Mbps), and Japan (102.72 Mbps).
Chunghwa Telecom tops 5G performance in Taiwan
Based on Speedtest Intelligence data, Chunghwa Telecom reported Taiwan’s fastest median 5G download speed during Q2-Q3 of 2023. It recorded a median download speed of 361.83 Mbps and a median upload speed of 34.22 Mbps. Far EasTone and Taiwan Mobile came second and third, respectively. The smaller operators, GT, and T Star, had median download speeds of 190.48 Mbps and 113.85 Mbps, placing them fourth and fifth in the rankings.
5G Coverage in Taiwan
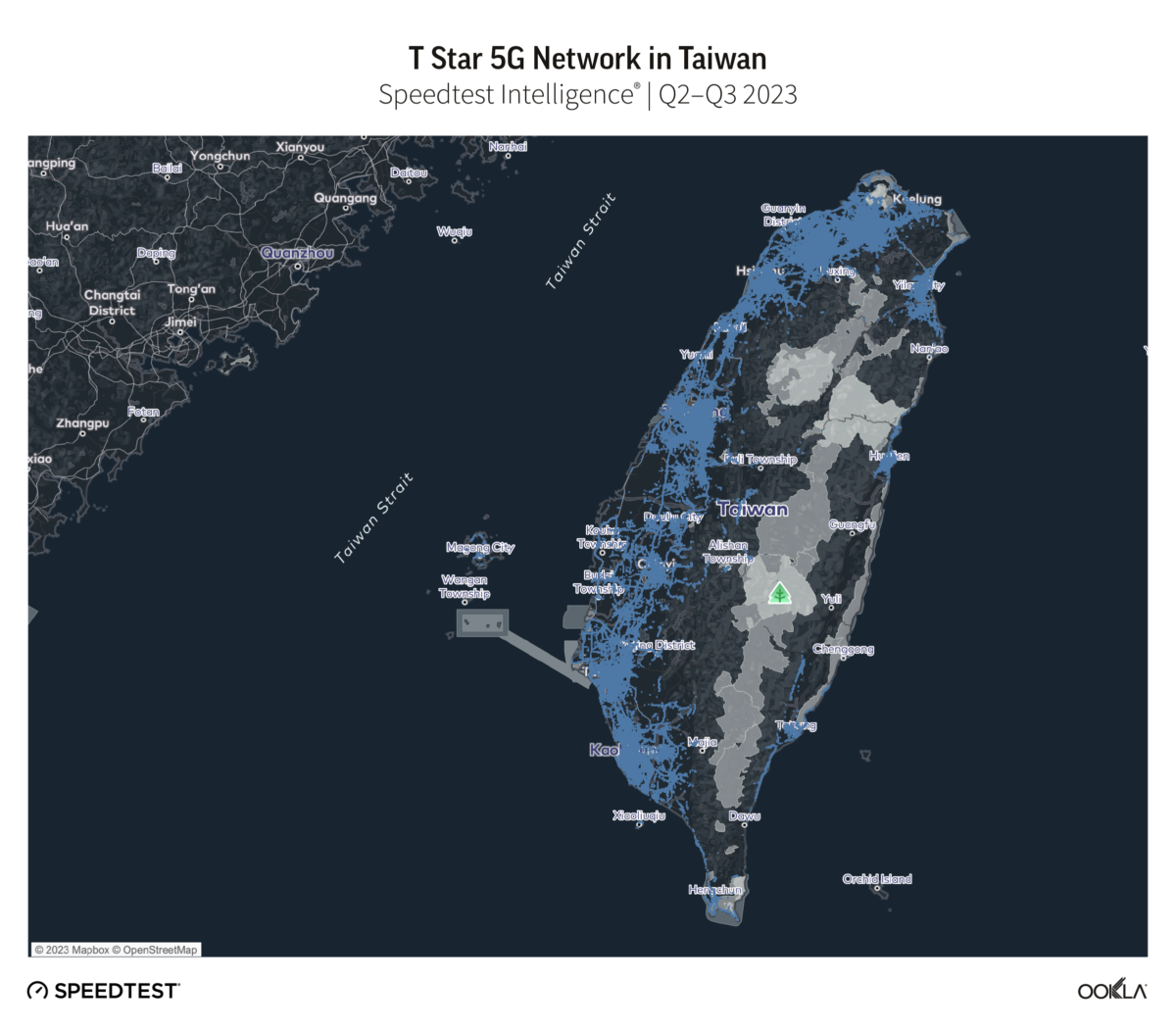
Taiwan’s terrain consists of rugged mountains dominating the length of the island, while the western part where most of the population lives is relatively flat. This contrast poses significant challenges in providing nationwide 5G coverage. In order to assess the reach of operator 5G networks, we examined Speedtest Intelligence data to plot locations with access to 5G across the island, with the results shown in the following maps.
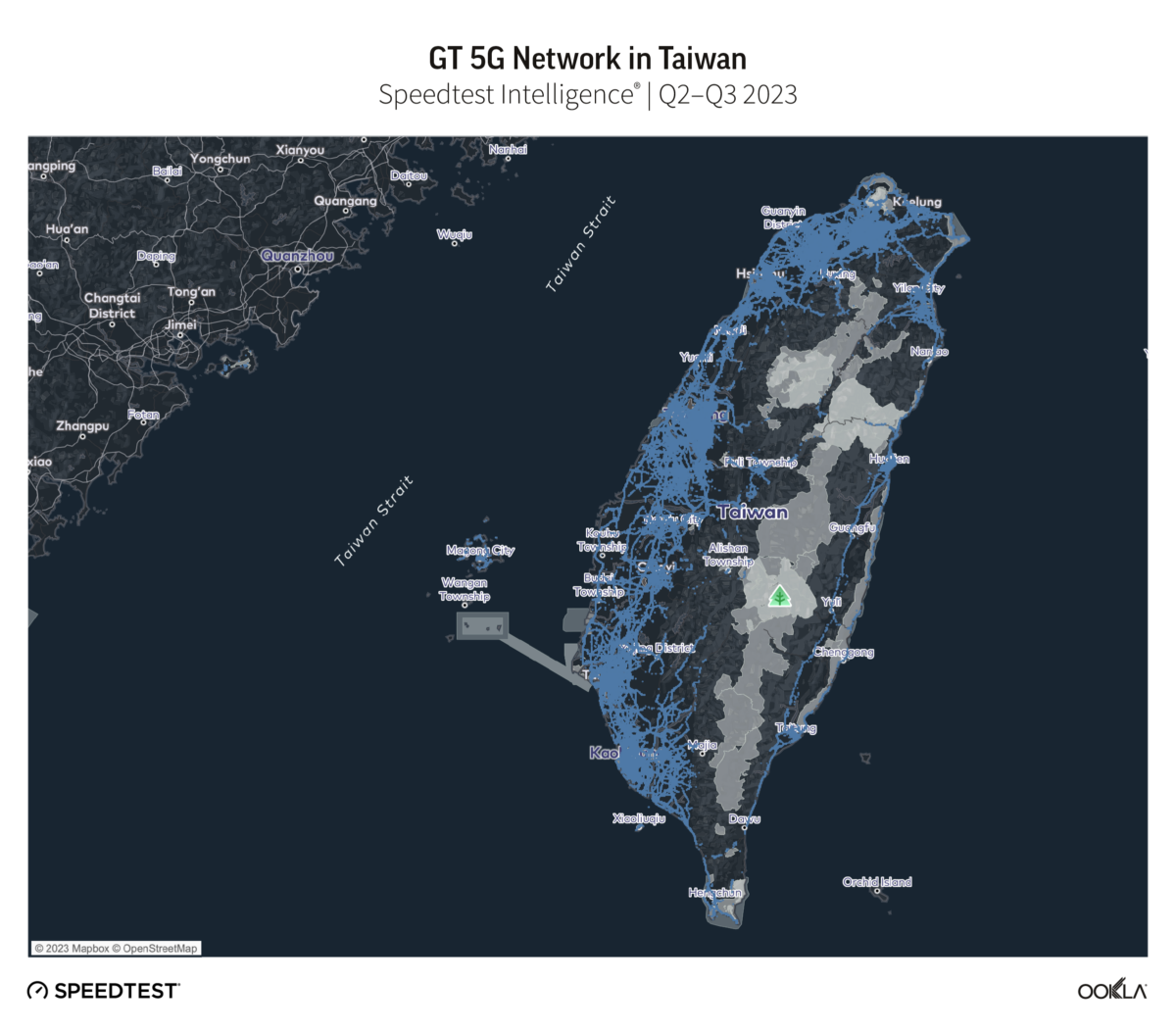
Chunghwa Telecom’s 5G network extended furthest across Taiwan, at 97.6% of locations with 5G coverage during Q2-Q3 2023. Far EasTone followed with 88.9%, and Taiwan Mobile with 85.6%. GT and T Star have an almost equal 5G footprint, reporting 49.7% and 49.0% respectively.
The full impact of the mergers will become apparent over time
It may take a while before we witness the effects of the two mergers. In fact, it may take years before consumers can benefit from the newly combined entities. However, one thing is sure – the market’s competitive landscape will change due to the reduction of major operators from five to three in Taiwan. We will continue to keep a close eye on the progress of these mergers and how they affect mobile performance in Taiwan. If you are interested in benchmarking your performance or want to learn more about internet speeds and performance in other markets around the world, visit the Speedtest Global Index™.
Ookla retains ownership of this article including all of the intellectual property rights, data, content graphs and analysis. This article may not be quoted, reproduced, distributed or published for any commercial purpose without prior consent. Members of the press and others using the findings in this article for non-commercial purposes are welcome to publicly share and link to report information with attribution to Ookla.