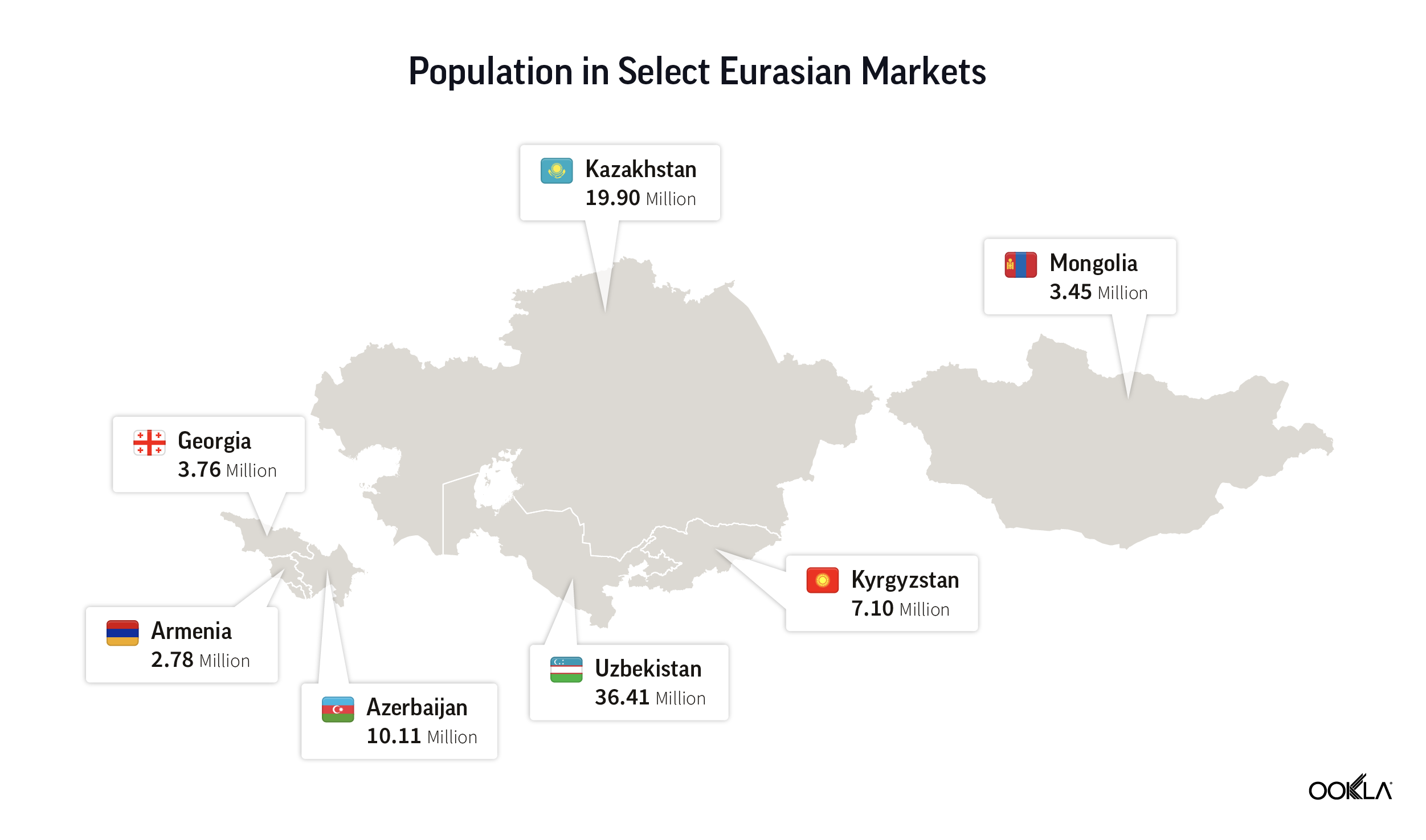
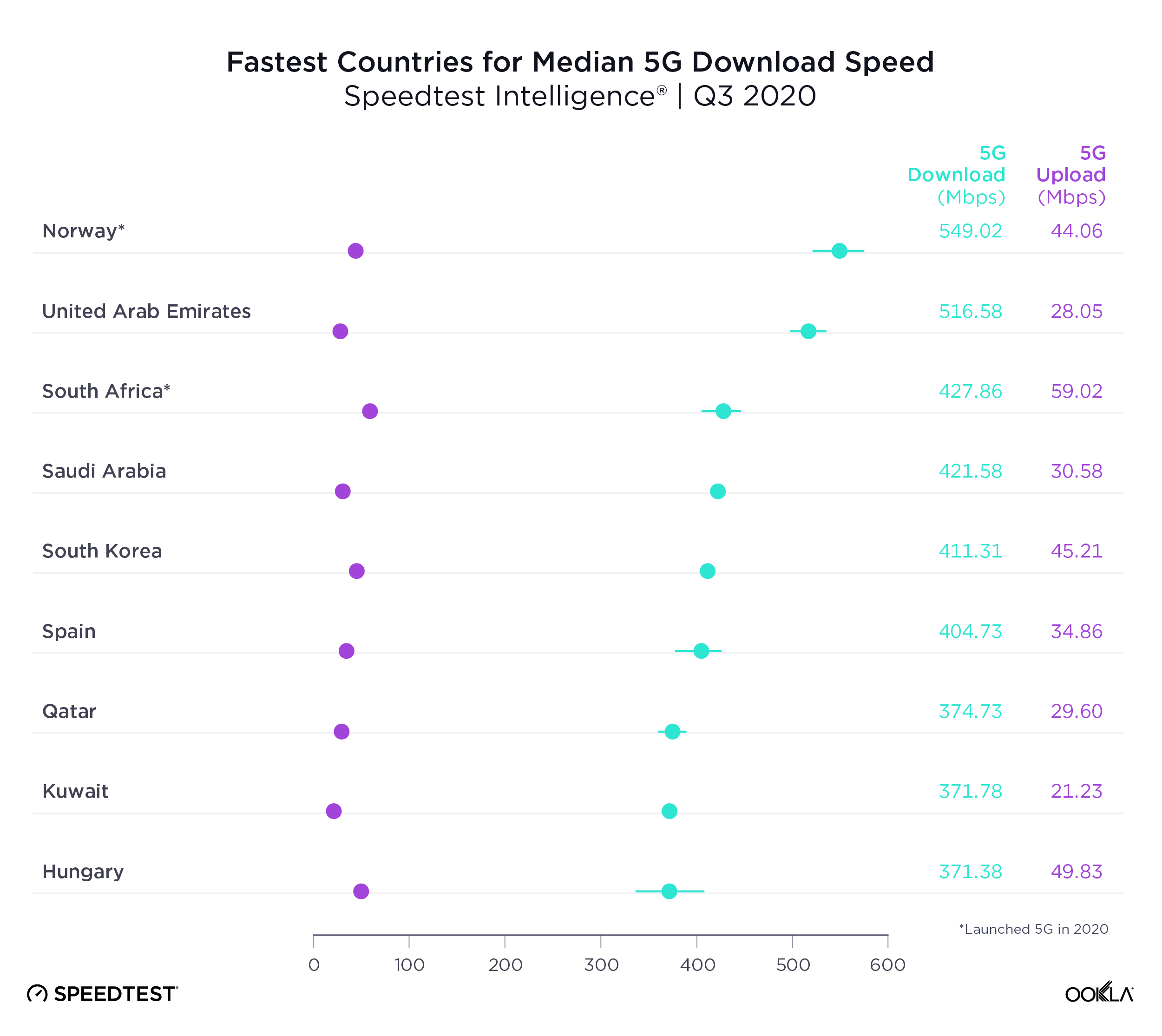
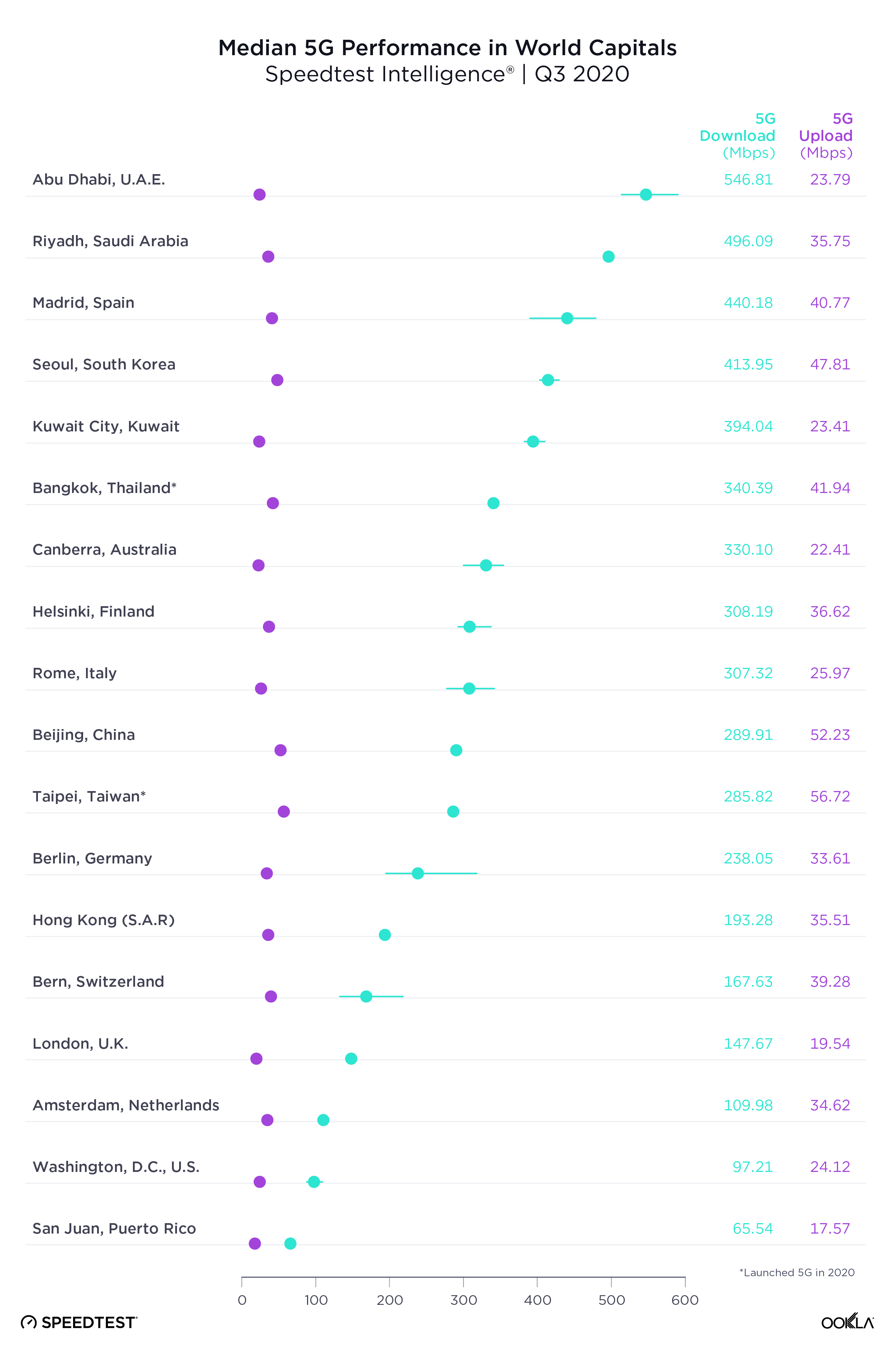
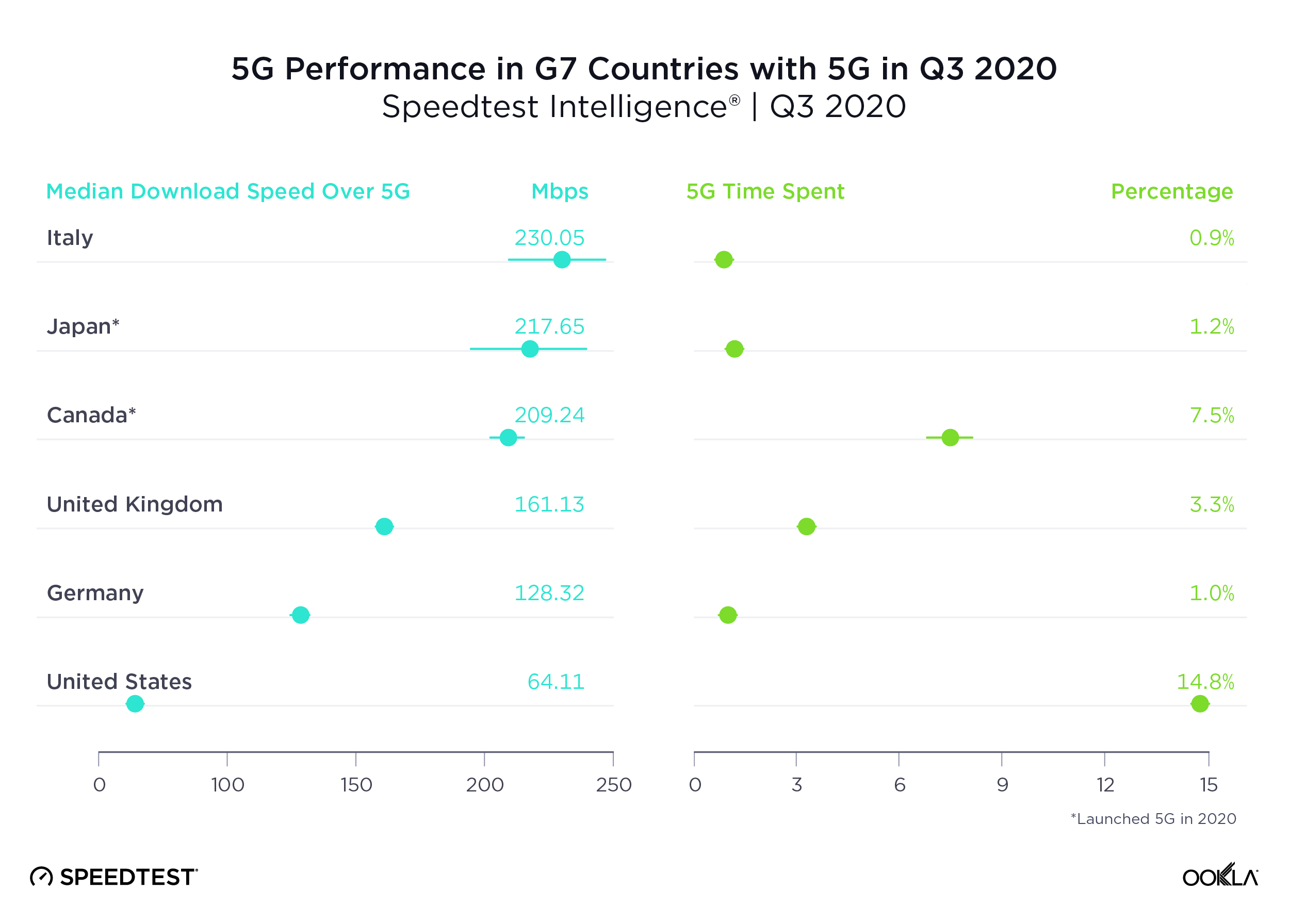
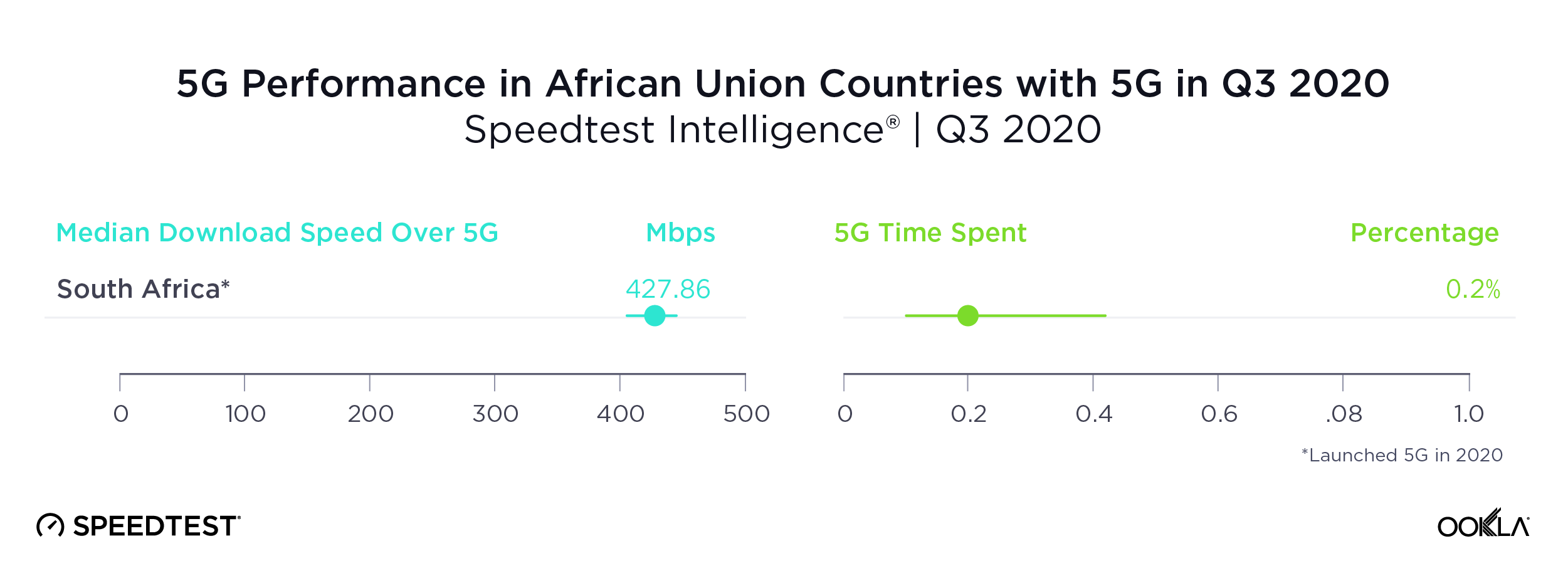
Eurasia’s mobile telecommunications landscape reflects a transition region, balancing urban-focused growth with efforts to extend connectivity into rural areas. While urban centers in these countries see high 4G coverage and improving data speeds, rural areas often need to catch up, a gap that mirrors challenges in other developing regions of Asia and Central Europe.
This report benchmarks the performance of top mobile providers—those with a sample share of 3% or more—in seven neighboring markets. It compares the median download and upload speeds and latency across all technologies, focusing on national-level performance and results in the two major cities within each selected country.
1. Armenia2. Azerbaijan
3. Georgia
4. Kazakhstan
5. Kyrgyzstan
6. Mongolia
7. Uzbekistan
Video start time measures the seconds a user waits for a video to begin during the adaptive bitrate stage. Adaptive start failure rate shows the percentage of video samples that fail to start playback due to timeouts or other issues in this stage. Together, these metrics provide insights into the video streaming experience for users across different operators in each market.
With video content making up a large portion of global network traffic, it’s essential to understand the actual experience of customers when they watch videos over mobile connections. This report assesses video performance using Speedtest Intelligence video metrics, focusing on two key indicators: video start time and adaptive start failure rate.
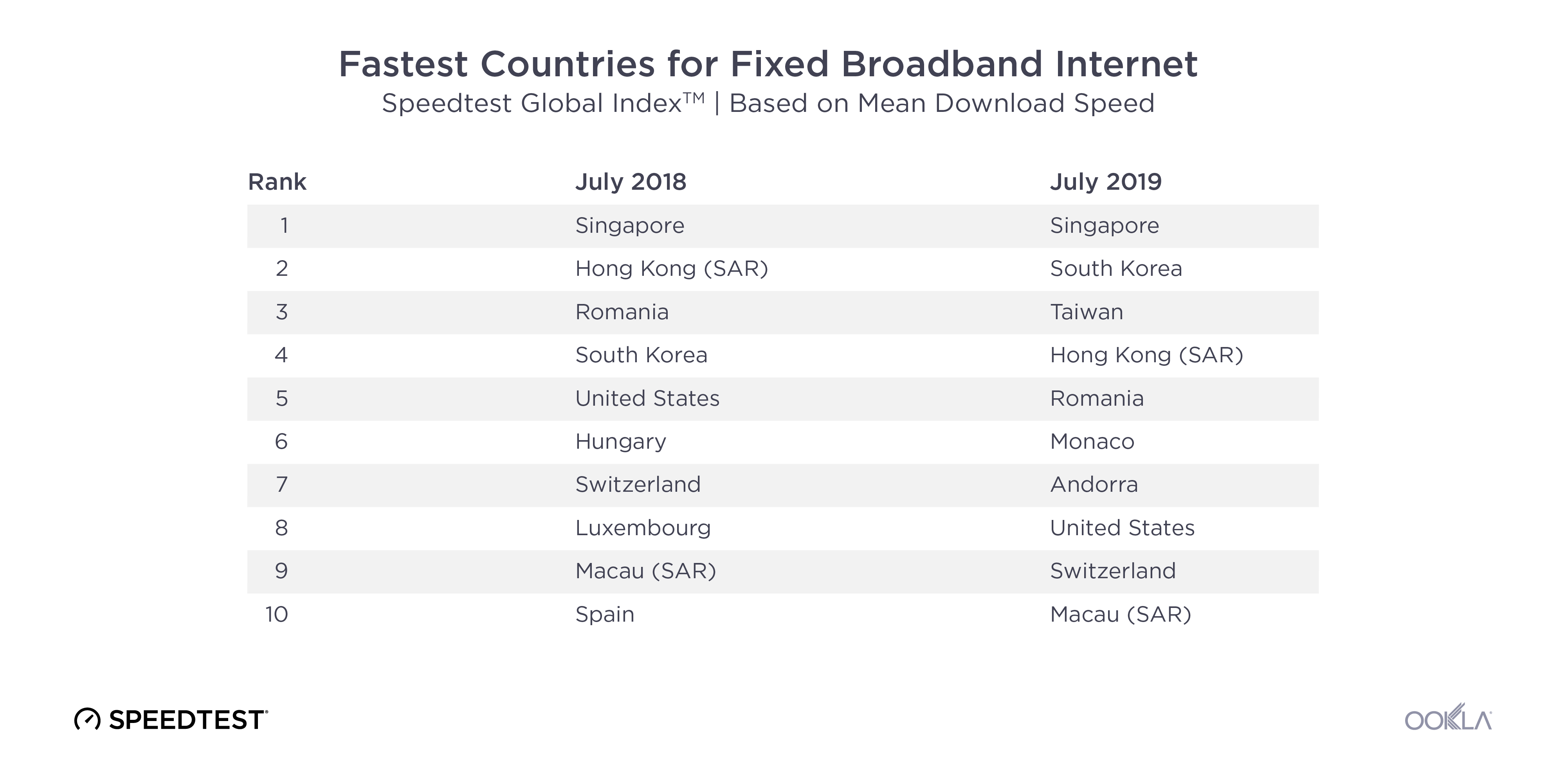
Markets in Eurasia showing continued performance improvements
Speedtest Intelligence® quarterly data shows that the mobile median download and upload speeds for all technologies across all the selected markets, apart from Mongolia, have gradually improved between the period of Q4 2022 and Q3 2024.
Quarterly Performance Trend for Selected Eurasia Markets
Source: Speedtest Intelligence® | Q3 2022 – Q3 2024
Quarterly Network Performance, Select Eurasian Markets
Markets that have introduced 5G saw or are in the early stages of 5G deployment saw overall improvements in both median download and upload speeds. Azerbaijan tops median download speed in Q3 2024, increasing from 34.82 Mbps in Q4 2022 to 55.62 Mbps in Q3 2024, driven by consistent network upgrades. Kazakhstan also demonstrates strong improvement, rising from 22.44 Mbps to 46.63 Mbps during the same period, maintaining steady growth in urban and rural connectivity, and the expansion of 5G services. Kazakhstan became one of the first countries in Central Asia to commercially launch 5G, with Kcell and Tele2 leading the deployment of 5G base stations. After securing 100 MHz blocks in the 3.6–3.7 GHz and 3.7–3.8 GHz spectrum bands, both operators have actively expanded their networks across the country’s major cities. By June 2024, they had installed 1,144 base stations across 20 cities, with ongoing efforts to extend 5G coverage further.
Uzbekistan also showed notable progress, starting at 14.67 Mbps in Q4 2022 and reaching 38.96 Mbps by Q3 2024, reflecting increased investments in mobile infrastructure and early-stage 5G deployment by the operators. In Uzbekistan, the government and operators have made significant strides in enhancing mobile network performance. The Republican Telecommunications Management Center of Uzbekistan (RTMC), through its “Digital Uzbekistan 2030” initiative, has focused on improving digital connectivity nationwide. Alongside these efforts, operators have begun rolling out 5G networks, collectively driving progress in the country’s telecom sector and boosting overall network performance.
In contrast, Mongolia showed limited improvement in network performance, with median download speeds remaining around 17 Mbps over the same period. Despite a steady rise in 4G connections, increasing from 35.4% in Q4 2022 to 54.1% in Q3 2024 (GSMA Intelligence), the market continues to face challenges. As the least densely populated country in the world, with a significant portion of the population living a nomadic lifestyle, challenges include limited infrastructure investment and high network congestion in the main cities, which have hindered its growth compared to other countries in the region.
Overall, the improvement in performance across the region reflects ongoing investments in mobile networks, driven by rising consumer demand for faster internet and government efforts to expand connectivity. As operators deploy advanced technologies, including 5G rollouts in some markets, mobile performance is expected to continue improving, narrowing the performance gap with more developed regions.
Armenia
In Armenia, the primary mobile operators are Viva-MTS, Beeline, and Ucom. All three operators offer 4G coverage across major cities, with efforts underway through Armenia’s Public Services Regulatory Commission (PSRC) to expand 4G coverage of the three existing operators in 80% of the settlements within the next two years. Viva-MTS, the market leader, has made investments in network upgrades, focusing on increasing capacity in urban regions to address data traffic demand. Ucom has prioritized the modernization of its network to improve end-user performance and service availability, while at the same time introducing 5G services in selected cities.
Based on data from Speedtest Intelligence® during the first half of 2024, Viva-MTS and Ucom both recorded median download speeds that are nearly identical, each just above 34 Mbps. Viva-MTS also outpaced its rivals in upload speeds, achieving 14.77 Mbps, followed by Ucom at 12.14 Mbps and Telecom Armenia at 11.95 Mbps.
When it comes to video quality of experience, Speedtest Intelligence reveals that Ucom had the fastest median adaptive start time for all mobile technologies combined in Armenia, at 1.38 seconds during 1H 2024, followed by Telecom Armenia CJSC at 1.55 seconds. Furthermore, Ucom reported a video start failure rate of just 2.9%, while Telecom Armenia CJSC and Viva-MTS experienced higher failure rates of 5.8% and 7.7%, respectively.
In Armenia’s main cities, Yerevan and Gyumri, Ucom leads in download speed, achieving the highest median download speed of 52.13 Mbps in Gyumri and 38.18 Mbps in the capital, Yerevan. Viva-MTS follows closely with 44.87 Mbps in Gyumri and 35.5 Mbps in Yerevan, while Telecom Armenia CJSC significantly lags behind in both cities, recording 25.74 Mbps in Gyumri and 21.11 Mbps in Yerevan.
For upload speeds, Viva-MTS leads in both cities, reaching 15.87 Mbps in Gyumri and 15.82 Mbps in Yerevan. Ucom performs slightly lower, with 12.63 Mbps in Gyumri and 14.65 Mbps in Yerevan, while Telecom.
All Technologies Mobile Operator's Performance In Major Cities, Armenia
Speedtest Intelligence® | 1H 2024
Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan’s mobile market is primarily served by three operators: Azercell, Bakcell, and Nar. Azercell, the largest operator, has actively expanded its 4G network, achieving a population coverage of 98.35% in urban and suburban areas. All three operators have initiated 5G services, with Azercell launching a 5G pilot zone in Baku’s Fountain Square, Bakcell introducing 5G trials in select locations, and Nar deploying 5G technology in Sumgait, marking the first 5G launch outside the capital.
Bakcell leads in both median download and upload speeds during the first half of 2024, achieving 55.36 Mbps for downloads and 18.68 Mbps for uploads. Azercell follows with a download speed of 50.65 Mbps and an upload speed of 11.46 Mbps, while Nar lagged behind at 42.23 Mbps for downloads but performs comparatively better in uploads with 13.96 Mbps.
When it comes to video quality of experience, Speedtest Intelligence reveals that Bakcell provided the most reliable and fastest video streaming experience among the three operators. In terms of video adaptive start performance, Bakcell and Azercell show relatively similar adaptive start times, with 1.26 and 1.27 seconds, respectively, while Nar has a slightly slower start time at 1.35 seconds.
Bakcell had the lowest video adaptive start failure rate at 3.7%, followed by Nar at 4.0%. Azercell showed the highest failure rate at 7.0%, suggesting that videos failed to start more often for its users compared to its competitors.
In the capital city of Baku, Bakcell leads with a median download speed of 66.62 Mbps, outperforming Azercell’s download speed of 59.51 Mbps. In Ganja, Azercell slightly outperforms Bakcell in download speed at 53.24 Mbps compared to Bakcell’s 50.16 Mbps.
All Technologies Mobile Operator's Performance In Major Cities, Azerbaijan
Speedtest Intelligence® | 1H 2024
Georgia
In Georgia, Magti, Geocell (Silknet), and Cellfie (formerly Beeline) are the primary mobile network operators, driving competition in the telecom market. The market has been shaped by ongoing investments in network upgrades and a push towards next-generation connectivity. Data from Speedtest Intelligence® for the first half of 2024 highlights Geocell as the leader in median download speed, achieving a download speed of 50.20 Mbps. Magti followed with a median download speed of 40.50 Mbps and upload speed of 15.12 Mbps, maintaining a competitive position. Geocell also outperformed other operators in latency, recording the lowest median multi-server latency of 38 milliseconds, compared to Magti’s 40 ms.
Cellfie, formerly Beeline, lagged in both speed and latency metrics. However, its focus on network modernization and the targeted 5G rollouts may provide opportunities for improvement. The company has emphasized plans to enhance its infrastructure and leverage the benefits of 5G, which could help bridge the gap with its competitors.
Magti reported the fastest video adaptive start time at 1.50 seconds, followed by Geocell at 1.75 seconds and Cellfie (formerly Beeline) at 2.02 seconds. Geocell achieved better reliability with the lowest video start failure rate of 3.1%, while Magti and Cellfie experienced higher failure rates of 5.1% and 6.1%, respectively.
With 5G rollouts advancing in 2024, operators will look at leveraging higher bandwidth and lower latency to enhance user experiences and support the increasing use of video services in Georgia.
In the capital city of Tbilisi, Geocell achieved a median download speed of 57.5 Mbps, surpassing Magti’s 37.92 Mbps and Cellfie’s 25.11 Mbps. Both Geocell and Magti recorded almost similar upload speeds in the capital, at around 19 Mbps. In Batumi, Magti led with a median download speed of 33.08 Mbps, while Geocell followed at 23.31 Mbps.
All Technologies Mobile Operator's Performance In Major Cities, Georgia
Speedtest Intelligence® | 1H 2024
Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan’s mobile market is highly competitive, with the three main operators, Beeline, Kcell, and Tele2, driving much of the country’s telecommunications development, providing widespread mobile network coverage and achieving high penetration rates. The country was one of the first in Central Asia to commercially launch 5G, with Kcell and Tele2-Altel having been the primary drivers in the rollout of 5G technology within the market.
Tele2 was the fastest mobile provider in Kazakhstan, based on Speedtest Intelligence® data for all technologies combined during 1H2024, with a median download speed of 55.12 Mbps. Kcell followed with 48.70 Mbps, while Beeline lagged at 27.94 Mbps. Tele2 recorded a median upload speed of 17.16 Mbps and a latency of 39 ms.
When it comes to video quality of experience, Speedtest Intelligence reveals that Tele2 had the fastest median adaptive start time for all mobile technologies combined in Kazakhstan, at 2.03 seconds during 1H 2024. Kcell was close behind at 2.09 seconds.
In Astana, Tele2 demonstrated strong overall performance, leading in all three key metrics: a median download speed of 78.55 Mbps, upload speed of 24.89 Mbps, and multi-server latency of 31 ms. In Almaty, KCell had a slight edge in median download speed at 104.38 Mbps, closely followed by Tele2 at 102.99 Mbps, highlighting competitive performance between the two operators in the city. Beeline, which currently lacks 5G services, reported lower download speeds of 26.57 Mbps in Astana and 38.26 Mbps in Almaty.
All Technologies Mobile Operator's Performance In Major Cities, Kazakhstan
Speedtest Intelligence® | 1H 2024
Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan’s mobile telecommunications market is served by three main operators: MEGA, O!, and Beeline. The country’s mobile landscape reflects its geographic challenges, with mountainous terrain making rural connectivity a significant hurdle. Despite this, government support has enabled gradual progress. The State Communications Agency, which regulates the telecom sector, has actively worked on policies to encourage network investment and bridging the urban-rural connectivity gap. The National Development Strategy of the Kyrgyz Republic 2018-2040 is one initiative that facilitates digital transformation to hasten the country’s economic development. Overall, Kyrgyzstan’s mobile network landscape shows steady growth, with operators competing on both speed and coverage.
Beeline edged the other operators in median download speed in Kyrgyzstan during the first half of 2024, achieving a median download speed of 34.99 Mbps, slightly ahead of O! 33.18 Mbps, and MEGA at 30.29 Mbps.
O! provided the best video experience in 1H 2024 among all the operators in the market, with median adaptive start time for all mobile technologies combined at 2.17 seconds and lowest adaptive start failure rate of 2.5%. O! was followed by Beeline with an adaptive start time of 2.48 seconds and MEGA with 2.64 seconds.
In Kyrgyzstan’s main cities of Bishkek and Osh, Beeline reported a median download speed of 44.44 Mbps in Bishkek and 31.49 Mbps in Osh, a slight edge over both MEGA and O!. MEGA, however, led in upload speeds in Osh, with a speed of 18.3 Mbps.
All Technologies Mobile Operator's Performance In Major Cities, Kyrgyzstan
Speedtest Intelligence® | 1H 2024
Mongolia
There are five top operators in Mongolia; MobiCom, GMobile, Supernet, Unitel and Skytel, each aiming to expand 4G LTE coverage to meet the growing demand for mobile internet. The country’s challenging geography and low population density create barriers for network expansion, especially in rural areas, making urban-focused network performance crucial for operators.
Based on Speedtest Intelligence® data for all technologies combined during 1H2024, MobiCom leads with a median download speed at 17.92 Mbps, followed by GMobile at 15.33 Mbps, and SuperNet closely behind at 15.07 Mbps. MobiCom also led upload speeds, with 11.81 Mbps, ahead of Unitel and GMobile. When it comes to latency, GMobile and Skytel provide the lowest median latency at 42 ms and 43 ms.
MobiCom reported the fastest video adaptive start time at 1.74 seconds, followed by Unitel at 1.87 seconds and SuperNet) at 2.28 seconds. gmobile achieved better reliability with the lowest video start failure rate of 2.2%, followed by Unitel and Skytel, with failure rates of 4.5% and 7.7%, respectively.
In the city of Erdenet, SuperNet leads with a substantial margin, achieving a median download speed of 35.69 Mbps. MobiCom follows with 16.24 Mbps, while other operators like GMobile (10.99 Mbps), Unitel (10.86 Mbps), and Skytel (13.26 Mbps) lag behind, indicating a considerable disparity in download performance across providers in this city.
In Ulaanbaatar, the capital and most populous city, MobiCom shows the highest median download speed at 18.78 Mbps, followed by Unitel at 15.03 Mbps and GMobile at 13.87 Mbps. Skytel records the lowest performance in Ulaanbaatar with just 8.12 Mbps.
All Technologies Mobile Operator's Performance In Major Cities, Mongolia
Speedtest Intelligence® | 1H 2024
Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan has increased investments in mobile network infrastructure, supported by government incentives and growing competition among operators. In 2020, the country introduced the “Digital Uzbekistan 2030” strategy to accelerate digital transformation across industries. The Republican Telecommunications Management Center (RTMC), which oversees this initiative, has worked closely with operators to expand telecommunications infrastructure, improve service quality, and reduce the urban-rural connectivity gap.
Uzbekistan’s mobile market is served by four major operators; Ucell, Uztelecom, Beeline Uzbekistan, and Mobiuz, with Ucell being the largest operator. Based on data from Speedtest Intelligence® during the first half of 2024, Ucell achieved the fastest median mobile download speed across all of the operators with a speed of 43.91 Mbps, followed by Uztelecom at 27.30 Mbps. Mobiuz followed closely with a reported speed of 26.79 Mbps.
When it comes to video quality of experience, Speedtest Intelligence reveals that Beeline had the fastest median adaptive start time for all mobile technologies combined in Uzbekistan, at 1.8 seconds during 1H 2024, followed by Uztelecom at 1.99 seconds, and UCell at 2.12 seconds. Furthermore, Beeline reported a video start failure rate of 3.5%, while Uztelecom and Mobiuz experienced higher failure rates of 4.6% and 4.8%, respectively.
In Uzbekistan’s two main cities, Samarkand and Tashkent, UCell led in median download speeds, achieving 83.12 Mbps in Samarkand and 83.36 Mbps in Tashkent. Uztelecom leads upload speed in Samarkand at 20.14 Mbps, while UCell ranks highest in Tashkent at 19.61 Mbps. UCell has the lowest latency in both cities, with 36 ms in Samarkand and 22 ms in Tashkent.
All Technologies Mobile Operator's Performance In Major Cities, Uzbekistan
Speedtest Intelligence® | 1H 2024
The mobile telecommunications landscape across Eurasia, particularly in Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Mongolia, and Uzbekistan, reveals varied network performance driven by differing levels of infrastructure investment, urban density, and regulatory initiatives.
Many operators in these countries face challenges, especially in rural and high-density urban areas where network congestion and limited infrastructure investment impact user experience. To address these gaps, several Eurasian governments are introducing policies to support 5G deployment, rural network expansion, and spectrum allocation, aiming to bridge connectivity disparities and support a growing digital economy. As these markets move towards 5G, continued regulatory support and investment in network infrastructure will be crucial to elevate service quality across the region, meeting the rising demand for fast and reliable mobile connectivity.
As operators in this region continue to modernize their networks, we are keeping a close eye on how the network deployments are progressing and the network performance end users experience. For more information about Speedtest Intelligence data and insights, please contact us.
Ookla retains ownership of this article including all of the intellectual property rights, data, content graphs and analysis. This article may not be quoted, reproduced, distributed or published for any commercial purpose without prior consent. Members of the press and others using the findings in this article for non-commercial purposes are welcome to publicly share and link to report information with attribution to Ookla.