Français
Since 2020, fixed broadband speeds in North Africa have improved substantially. However, there is still potential for further enhancement and adoption. This article explores the performance drivers of fixed wired internet performance (excluding fixed wireless access (FWA)) in Algeria, Egypt, Morocco, and Tunisia between Q3 2020 and Q3 2023 and discusses the market prospects.
Key takeaways
- Egypt leads North Africa in the Ookla Speedtest Global Index™ for fixed broadband in Q3 2023. Egypt widened its lead in North Africa, achieving a median download speed of 56.61 Mbps and an upload speed of 25.07 Mbps. Meanwhile, Algeria saw a significant improvement in median fixed broadband download speed, with a 4.5-fold increase to 11.34 Mbps between Q3 2020 and Q3 2023. Morocco’s upload speed has also significantly improved, rising more than 22-fold to 19.09 Mbps during that period.
- North African countries adopted different DSL migration strategies. Egypt upgraded most of its ADSL to VDSL and concentrated FTTH/B in greenfield areas. On the other hand, Algeria focused on replacing copper lines with FTTH/B, while Morocco and Tunisia deployed VDSL in tandem with FTTH/B rollout.
- Fiber upgrades and revised broadband packages help to boost speed. The deployment and adoption of FTTH/B do not necessarily lead to increased broadband speed. ISPs should consider increasing headline speeds of entry-level packages and offering discounts on higher-speed tiers to incentivize customers to upgrade.
Egypt tops North Africa in download and upload speeds for fixed broadband
In our June 2021 report on internet speed in North Africa, Egypt ranked first in North Africa for fixed broadband, followed by Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia. All countries, except Tunisia, saw more than a 25% improvement in median broadband speeds from Q2 2020 to Q1 2021, with Algeria more than doubling its median broadband download speed.
This upward trend continued through Q3 2023, with most North African countries improving their median download and upload speeds over fixed broadband. This has resulted in a boost in their ranking in the Ookla Speedtest Global Index. Notably, Egypt extended its lead within North Africa, achieving a median download speed of 56.61 Mbps and a median upload speed of 25.07 Mbps.
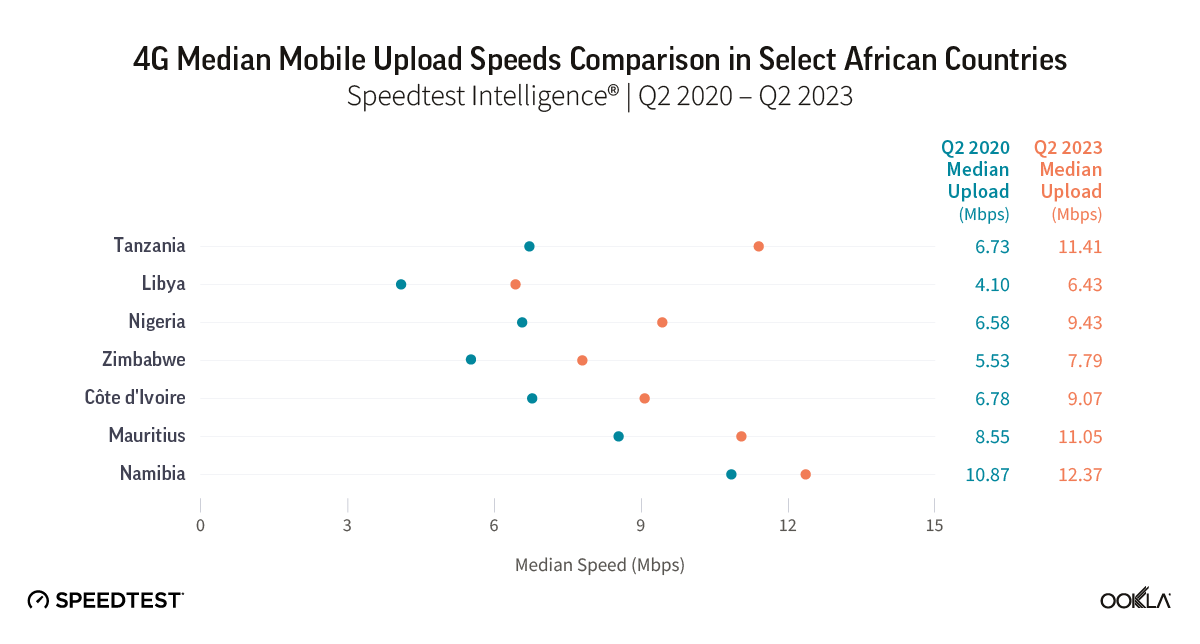
Algeria showed a substantial improvement in median fixed broadband download speed between Q3 2020 and Q3 2023, increasing 4.5-fold to 11.34 Mbps. Other countries, except Tunisia, saw their median fixed broadband download speeds more than double over the same period.
Median Download Speed for Wired Fixed Broadband, Select African Countries
Speedtest Intelligence, Q3 2020 and Q3 2023
Morocco saw a significant rise in median upload speed, with a more than 22-fold increase to 19.09 Mbps in Q3 2023. Despite this, it still lags behind South Africa, the African leader, which boasts more than double the upload speed at 38.53 Mbps. The other North African countries saw more modest improvements in upload speeds, ranging from a 1.5-fold increase in Algeria to a 2.5-fold increase in Tunisia.
Median Upload Speed for Wired Fixed Broadband, Select African Countries
Speedtest Intelligence, Q3 2020 and Q3 2023
DSL and wireless access are the most common technologies used for fixed broadband services in North Africa
Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) is the leading technology for fixed broadband services in North Africa, as they use existing phone lines for internet connectivity. The two main types of DSL are Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL) with speeds of up to 24 Mbps and Very high-speed Digital Subscriber Line (VDSL) offering speeds of up to 52 Mbps for VDSL1 and 200 Mbps for VDSL2. The latter can be further enhanced with G.Fast technology.
VDSL employs fiber that terminates at a nearby cabinet, a configuration often referred to as Fiber-to-the-Cabinet (FTTC). The ‘last mile’ connection to users’ premises then uses existing copper lines. FTTC typically serves as a transitional step towards Fiber-to-the-Home/Building (FTTH/B), where the fiber extends directly to the user’s location premises.
In countries like Algeria and Tunisia, mobile broadband and FWA services that use 3G and 4G technologies account for almost 30% of all fixed broadband connections. However, these cellular connections are less prevalent in Morocco and Egypt. 4G offers download speeds comparable to ADSL and VDSL1 but falls short of VDSL2 and FTTH/B.
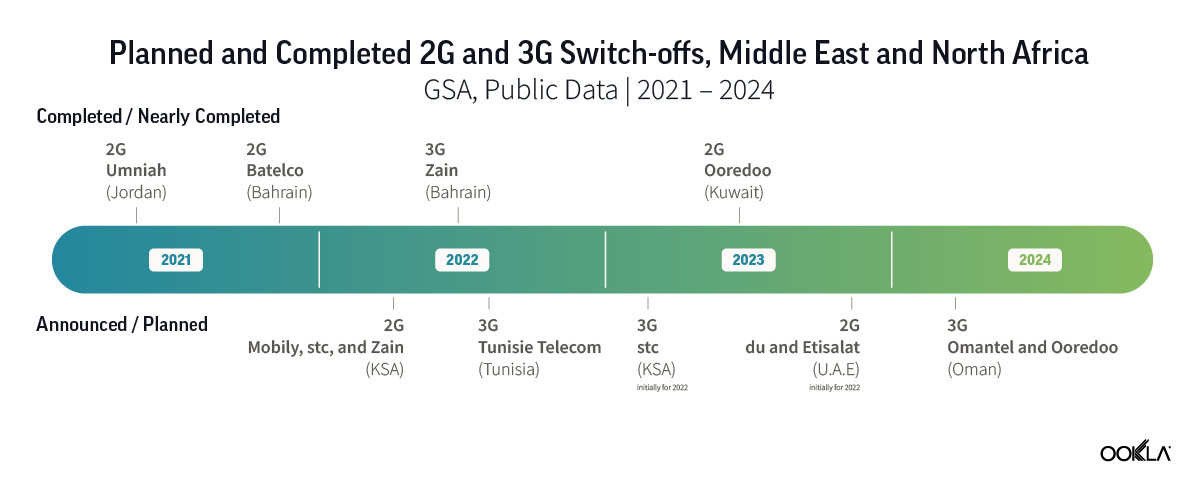
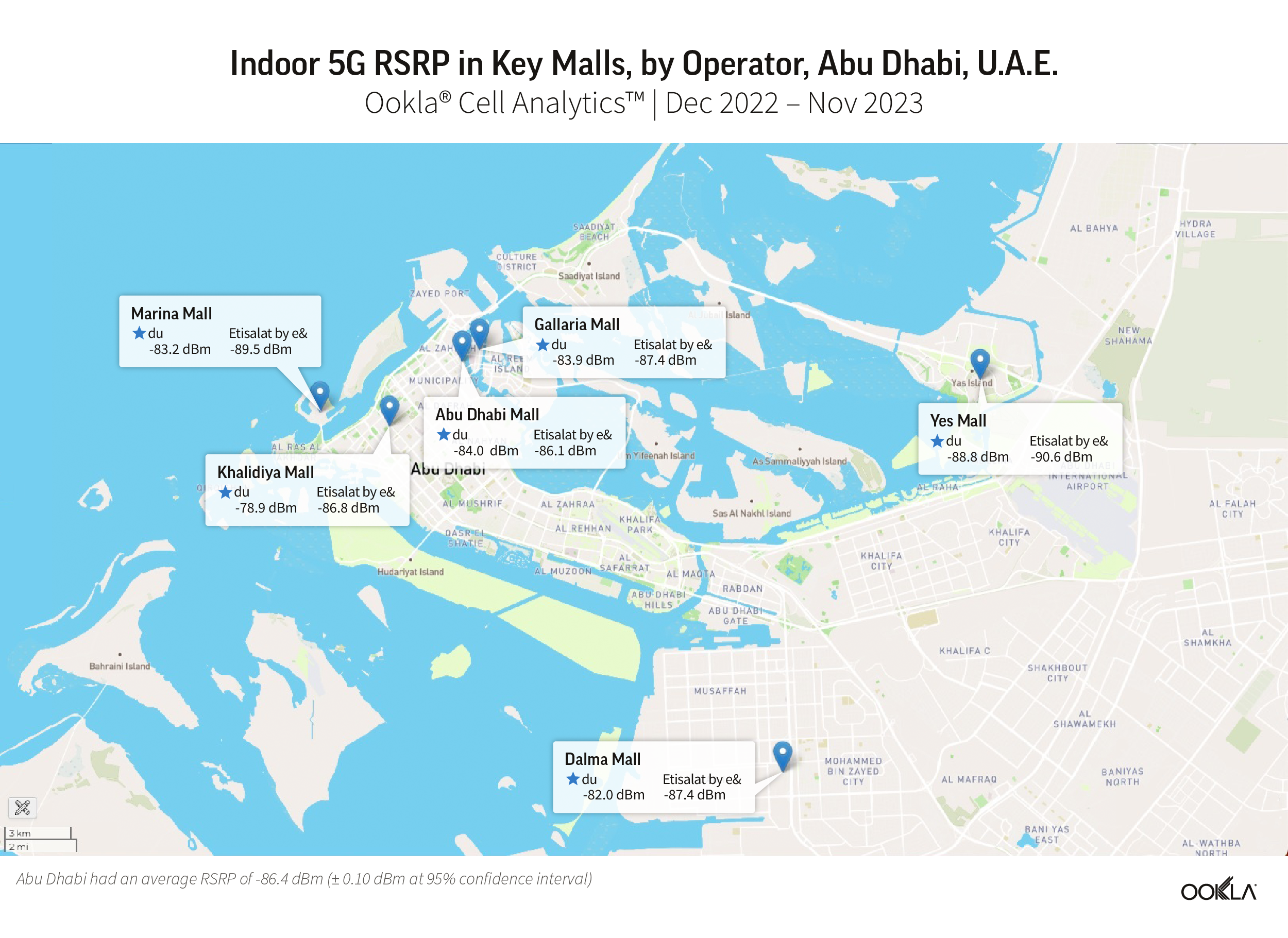
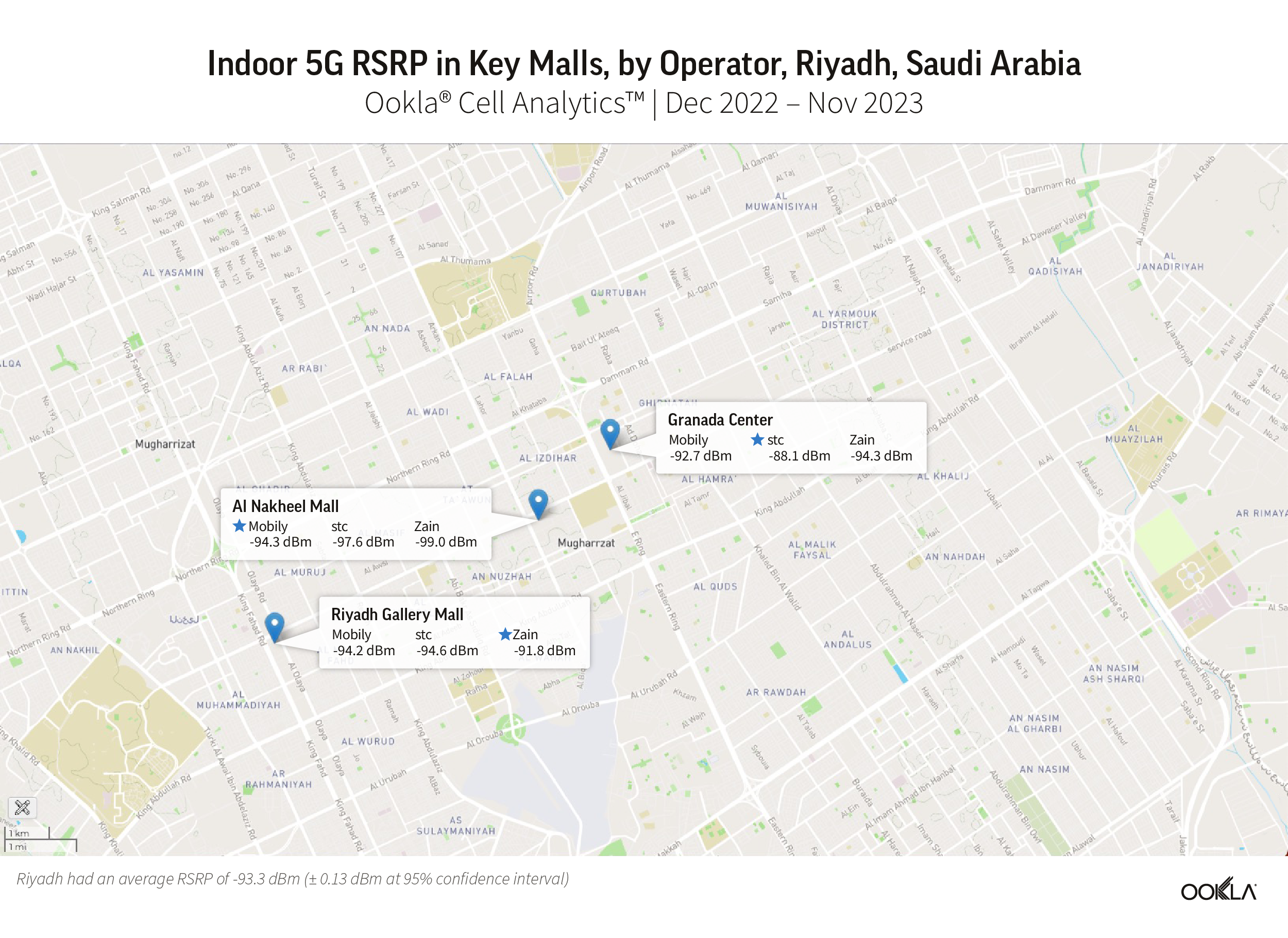
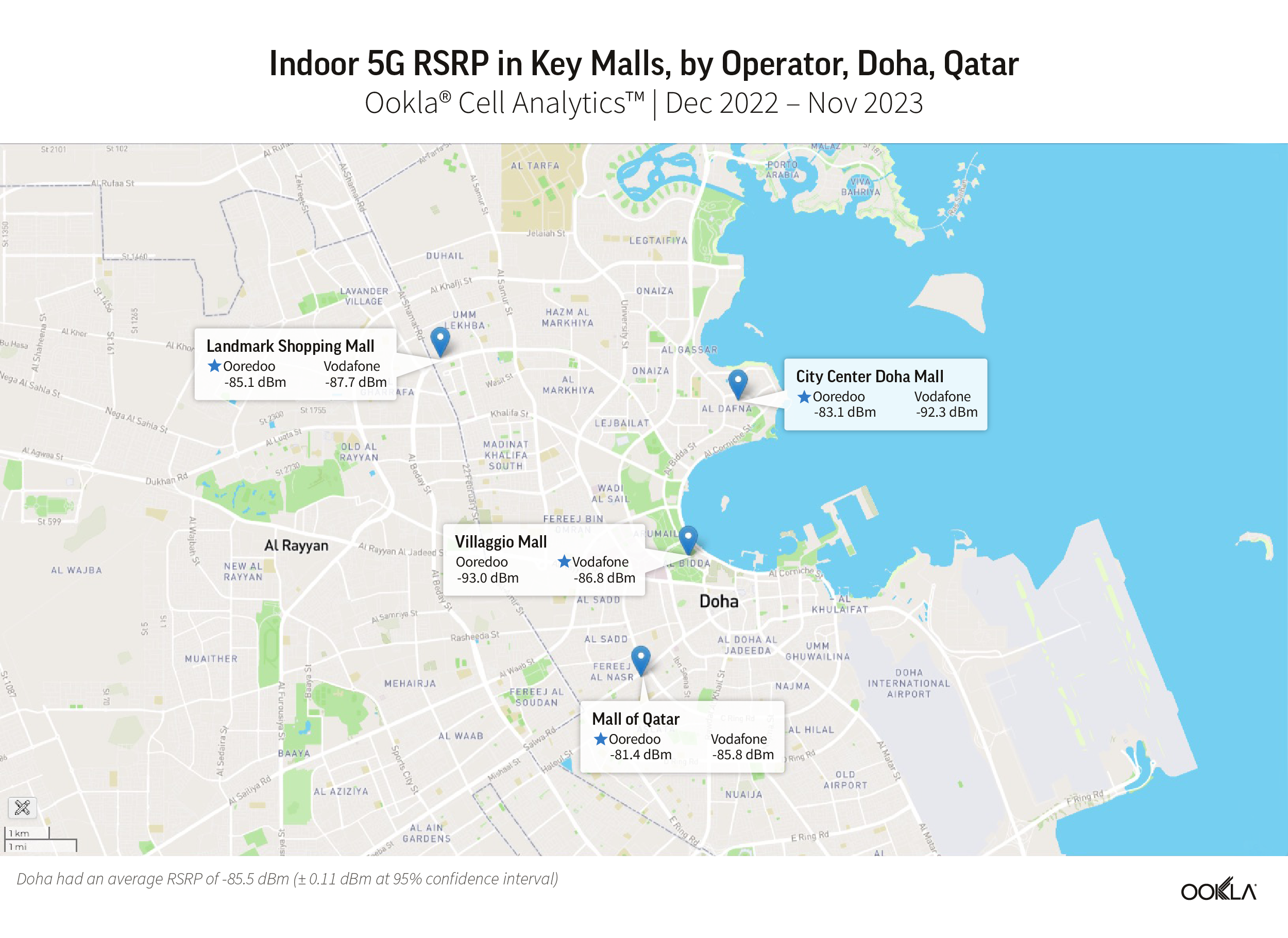
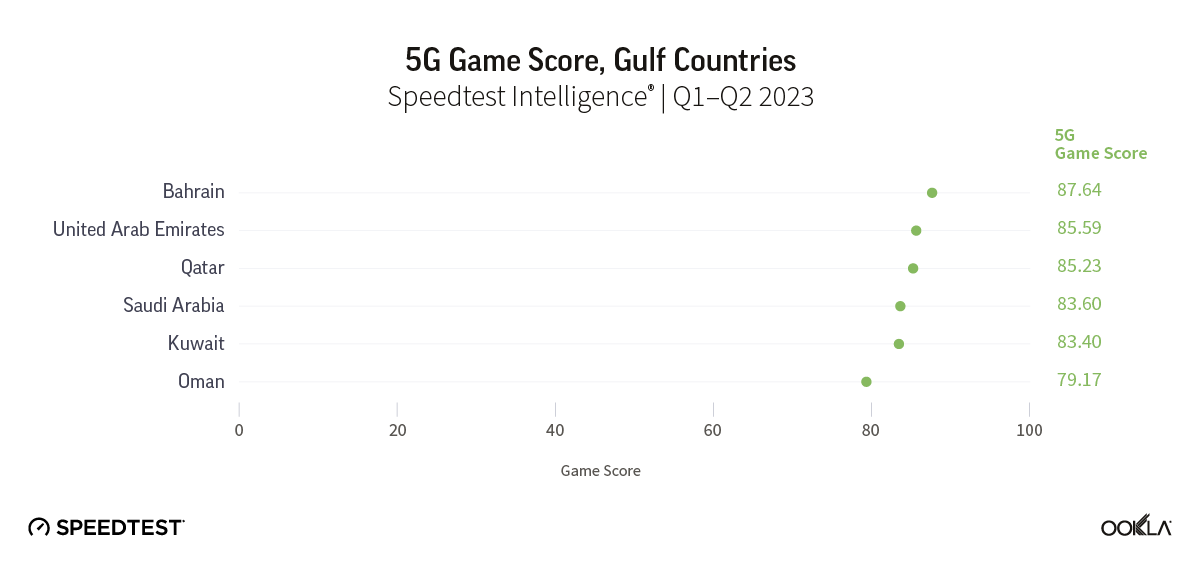
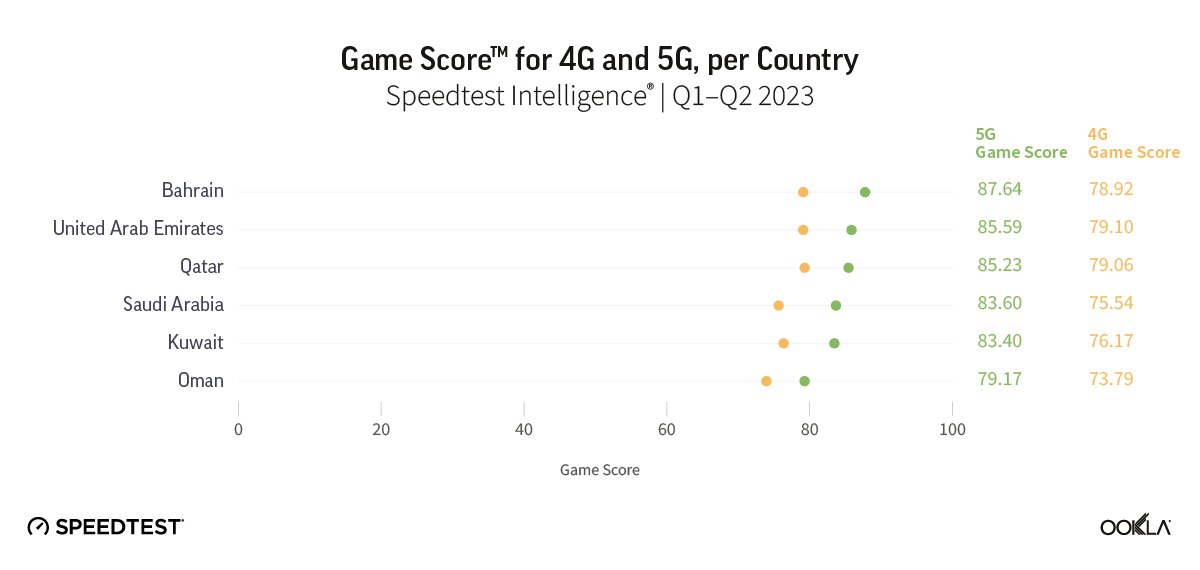
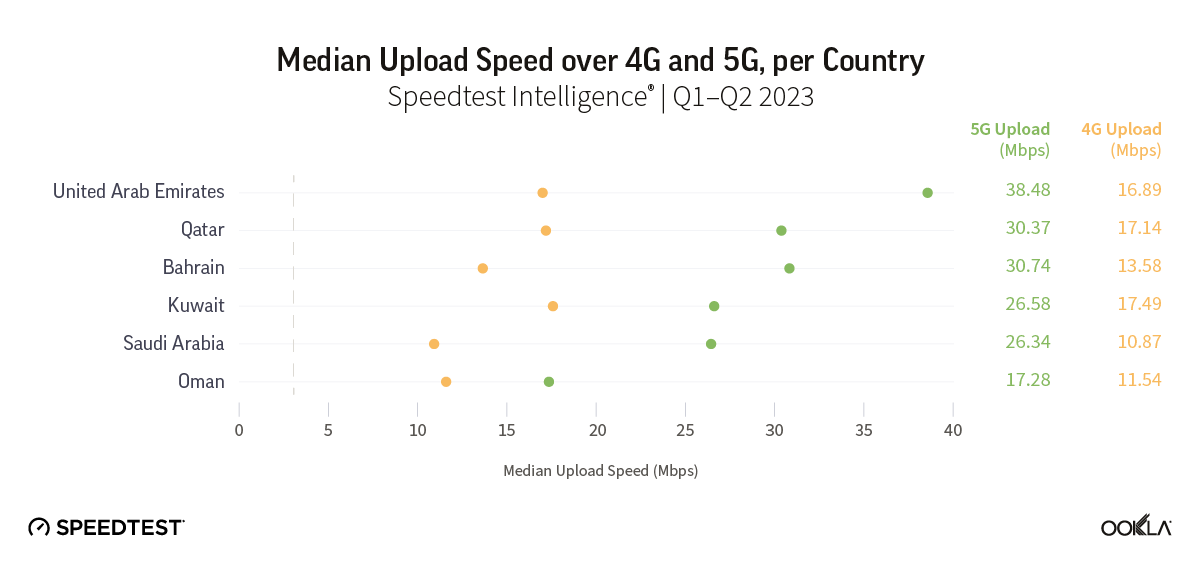
North Africa lags behind the Gulf region in fiber coverage, adoption, and internet speed. Ambitious fiber development plans placed Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, and the U.A.E. high on the global speed leaderboard. For example, in Q3 2023, the U.A.E. ranked fourth on the Speedtest Global Index™ with a median download speed of 231.98 Mbps. Kuwait ranked twenty-second, and Qatar twenty-third. Other Gulf countries trailed the U.A.E. but were ahead of all markets in North Africa.
Fixed internet speeds are still relatively low in North Africa despite significant improvements in FTTH/B access
The slow pace of fiber deployment compared to the Gulf countries can be attributed to factors such as limited public funding, restrictive telecom regulations, scant private investments, as well as geographical and urbanization challenges. Most North African countries also have a larger land mass, more varied geology, and a lower level of urbanization, making fiber deployment more complex and costly.
The market’s competitive landscape is also a factor, with incumbents controlling over 80% of fixed internet subscriptions. Even in Tunisia, which boasts more alternative ISPs, Tunisie Telecom holds the majority of DSL and fiber subscriptions. By contrast, alternative network providers play a key role in accelerating fiber adoption in Europe. Furthermore, North Africans have a lower income than Gulf residents, and most cannot afford high-speed broadband services because of their high costs.
Market challenges delayed fiber deployment and limited service adoption and innovation. However, local ISPs have made significant progress since 2020 in upgrading the fixed infrastructure and making their services more affordable. Egypt has primarily upgraded its ADSL to VDSL and focused FTTH/B deployments in greenfield areas. Algeria concentrated on replacing copper lines with FTTH/B while Morocco and Tunisia deployed VDSL while also progressing with FTTH/B rollout.
As of June 2023, Algeria has the highest number of FTTH/B connections in North Africa, totaling 800,000. Morocco follows closely with 730,000 connections and boasts the largest fiber share of the wired broadband market (see chart below). Egypt has the highest number of VDSL connections in the region, and an estimated few hundred thousand active FTTH/B customers as of September 2023. Tunisia is in fourth position with 55,000 FTTH/B connections and 176,000 VDSL connections.
In the following sections, we provide an overview of the fixed broadband market in Algeria, Egypt, Morocco, and Tunisia. We highlight the status of fiber rollout, and its impact on network performance, and discuss ISPs’ future deployment plans.
FTTH/B Connections, Algeria, Morocco and Tunisia
Telecoms Regulators, ISPs | 2019-Q2 2023
FTTH/B Connections and Share of Fixed Wired Connections, Algeria, Morocco and Tunisia
Telecoms Regulators, ISPs | 2019-Q2 2023
Significant progress achieved in fiber coverage in Algeria but room to drive adoption and boost speed
As of March 2023, Algeria boasted over 3.4 million fixed wired connections, according to the Autorité de Régulation de la Poste et des Communications Electroniques (ARPCE). The state-owned Algerie Telecom (AT) is the sole provider of wired broadband services. With an additional 1.5 million 4G FWA connections, Algeria is among Africa’s largest fixed broadband markets.
AT prioritized the replacement of copper lines with fiber in major cities while maintaining its ADSL services. It also used 4G FWA technology to service areas where wired infrastructure is unavailable or costly to deploy. AT was late to the game but it rapidly expanded FTTH/B services since their introduction in 2018. It also increased maximum speeds on fiber from 100 Mbps to 300 Mbps for consumers in 2023. AT introduced regular promotions, such as free speed doubling for new customers. It has also reduced tariffs every year since 2020, with a 100 Mbps fiber line costing $22/month in 2023. These actions contributed to the surge in the number of fiber subscribers by nearly 14-fold between 2020 and November 2023, reaching the 1 million milestone, making Algeria one of the largest FTTH/B markets in Africa.
Fixed Broadband Connections by Technology, Algeria
ARPCE | 2019-Q1 2023
The migration from ADSL to FTTH has undoubtedly improved the quality of service for consumers. However, it has yet to boost the speed that most households experience. While the download speed of the fastest 10% samples increased from 8.01 Mbps in Q3 2020 to 45.71 Mbps in Q3 2023, the median download speed only reached 11.34 Mbps during that period, according to Ookla Speedtest Intelligence® data.
According to the ARPCE, more than 85% of connections had a download speed of 10 Mbps in March 2023. To improve the country’s median download speed, AT should increase the speed of its entry-level fiber package from the current 10-15 Mbps. It should also work towards lowering the price of its higher-speed packages. The government proposed to exempt fixed broadband services from VAT in 2024, which should help make it more affordable for customers to upgrade to higher-speed packages.
AT has set ambitious goals to expand its fiber coverage substantially. The number of households passed by fiber (i.e. premises that can connect to the fiber network) is expected to increase from 3.5 million in 2022 to 6 million by 2024 (out of an estimated 7.4 million households). This is part of the government’s broader strategy to provide two-thirds of households with fixed broadband service by 2024, potentially adding 2 million new subscribers to the market.
Rapid network performance improvement in Egypt thanks to the incumbent’s ambitious FTTC strategy
With nearly 11 million subscribers at the end of 2022, Egypt is North Africa’s biggest fixed broadband telecoms market. State-owned Telecom Egypt (TE) dominates the sector, controlling over 80.1% of the market with over 8.7 million fixed broadband subscribers.
Other operators such as Vodafone, Orange, and Etisalat by e&, offer broadband services through wholesale access to TE’s network. This allows them to provide comparable broadband speeds. Notably, the combined market share of these alternative ISPs has been on an upward trend year-on-year since 2019.
TE’s strategic focus has been to develop its core and transmission networks, upgrade ADSL to VDSL, and expand fiber to the street cabinets. As of September 2023, TE connected 95% of households to the next-generation FTTC network (up from 85% in 2019).
The introduction of VDSL services in Egypt in 2018 marked a significant shift in broadband speeds, raising the maximum from 16 Mbps to 100 Mbps. TE took this opportunity to increase the speed of its entry-level plan from 5 Mbps to 30 Mbps, with a modest price increase of 9%. Infrastructure upgrades also positively impacted alternative ISPs that boosted their broadband packages’ speeds.
These improvements in VDSL coverage, speeds, and affordability significantly accelerated the adoption of broadband services. The number of fixed broadband subscribers surged by 55% from the end of 2019 to June 2023. Raising the minimum broadband speed to 30 Mbps led to a substantial increase in the country’s median download speed to 56.61 Mbps in Q3 2023, up from 25.07 Mbps in Q3 2020, according to Ookla Speedtest Intelligence. Given that TE currently offers speeds of up to 150 Mbps, there’s ample opportunity to enhance download speeds further.
Fixed Broadband Connections by ISP, Egypt
Telecom Egypt | 2019-Q2 2023
TE launched FTTH/B services in 2009, making Egypt among the early adopters of fiber in the region. It prioritized FTTH/B deployments in greenfield areas such as new developments, gated communities, and residential compounds. TE aims to eventually migrate existing VDSL customers to FTTH/B.
The government allocated a $360 million budget in 2021 to extend Fiber-To-The-Home (FTTH) to a million households to improve fiber accessibility. The development of ‘New Cairo,’ a new mega-city located 35 km east of the Capital, is also expected to spur demand for fiber services.
The competitive fiber market in Morocco drove broadband adoption and speed improvements
Maroc Telecom (MT) dominates the fixed broadband market in Morocco. The operator’s control over the copper infrastructure has spurred other ISPs, inwi and Orange, to develop their own fiber infrastructure and lease capacity from local utility and transport companies.
The fixed wired broadband market has been expanding rapidly in Morocco, increasing from just over 1.6 million in 2019 to over 2.2 million connections in June 2023 (out of around 8 million households). This growth is mainly due to a shift from DSL to FTTH/B since 2020, as observed in the chart below.
Fixed Broadband Connections by Technology, Morocco
ANRT | 2019-Q2 2023
Consumers have been leaning toward faster and more reliable services, with demand for DSL connections falling since 2020 and FWA adoption decreasing since 2022. MT launched fiber in 2014 as a premium service with speeds of 100 Mbps and 200 Mbps. In 2022, MT accelerated the deployment of its FTTH/B network and increased network capacity by 40% year-on-year in June 2023, helping to expand its fiber customer base by 43%.
inwi and Orange introduced their fiber services in 2018, offering a broader range of speeds starting from 20 Mbps and lower price points than MT at the high end. These services are available in big cities like Casablanca, Rabat, and Fez. They accounted collectively for 52.69% of the fiber market in June 2023 which shows that the segment is quite competitive in Morocco.
This has resulted in a boost to user-end speeds. As of Q3 2023, the median download speed of fixed internet services had increased to 21.68 Mbps, up from 9.07 Mbps in Q3 2020, according to Ookla Speedtest Intelligence data. There has been a marked shift to higher-speed broadband packages, as evidenced by the fact that 17.3% of fixed broadband subscribers had speeds of at least 20 Mbps in June 2023, a dramatic increase from only 0.6% in 2019 who had a minimum speed of 16 Mbps, according to the Agence Nationale de Réglementation des Télécommunications (ANRT)
As only around one-third of wired broadband subscribers in Morocco use FTTH/B, there is still an ample opportunity to migrate more DSL customers to fiber and encourage existing fiber users to upgrade to higher-speed packages. This is especially relevant for inwi and Orange as they offer more affordable fiber packages starting at 20 Mbps, compared to MT’s 100 Mbps fiber package which costs around $50/month.
Looking ahead, the Moroccan government has ambitious plans to connect more households to high-speed broadband services under the “Maroc Digital 2030” program. The government aims to connect 5 million households with fiber by 2026, potentially making Morocco one of the largest FTTH/B markets in Africa.
Limited infrastructure sharing and investments in Tunisia constrained speed improvement
Tunisia has the lowest fixed download speeds in North Africa at 8.61 Mbps in Q3 2023, according to Ookla Speedtest Intelligence. This is despite having eight ISPs – compared to one in Algeria, three in Morocco, and five in Egypt. The poor network performance is due to the limited coverage of high-speed broadband services and their unaffordability for many households. For example, a 50 Mbps VDSL line costs more than $26/month. Furthermore, it was not until 2022 that the ISPs lifted the speed of basic DSL packages from 4 Mbps to 10 Mbps
The wired broadband sector has consistently grown, reaching over 1.2 million subscribers by June 2023. This represents a 50% increase from 2019 levels. Interestingly, this growth rate outpaced that of the 4G fixed wireless access segment, which only saw a 27.4% increase, reaching just over 470,000 connections during the same period. On the other hand, fiber service remains a niche offering due to its limited coverage and high cost. Fiber share of the fixed wired broadband market saw a minor increase, rising from 3.0% in 2019 to a modest 4.5% in June 2023.
Fixed Broadband Connections by Technology, Tunisia
INT | 2019-Q2 2023
Tunisie Telecom (TT), a state-owned entity, holds the majority stake in the fixed broadband sector. TT controls the national copper infrastructure, operates the nationwide fiber-optic backbone, and competes both directly and indirectly in the retail market via its subsidiary, Topnet. Ownership of TT is divided between the Tunisian state (at 65%) and Emirates International Telecommunications (EIT, at 35%).
TT maintains a strong position within this sector, controlling 72.9% of all fiber connections in Tunisia by June 2023. This figure includes direct customers (39.1%) and those provided through Topnet (33.8%). Fiber services, which were launched in 2012, are only available in Greater Tunis and Sfax. Additionally, TT dominates the VDSL market with a substantial 92.4% market share, mostly through Topnet.
Regulatory pressure from the telecom authority INT (Instance Nationale des Telecommunications) has urged TT to reduce its network access charges and expedite line activation to help other ISPs. Despite these efforts, various challenges persist, prompting operators such as Ooredoo and Orange to supplement their wired offerings with mobile broadband services based on 3G and 4G, in addition to TD-LTE-based FWA.
Ooredoo, which introduced fiber services in 2013, saw its share of the fiber market rise to 16.8% by June 2023. Its fiber network covers Greater Tunis and Sfax. Orange, however, lacks consumer fiber offerings. Other ISPs, including Bee, GlobalNet, and HexaByte, use a mix of ADSL, VDSL, and FTTH/B by accessing TT’s infrastructure.
In the short term, TT plans to upgrade most DSL ports to VDSL and promote higher-speed packages. This strategy aims to increase the average fixed speed from 10 Mbps in 2022 to 50 Mbps in 2024. Over the medium term, TT aims to expand its FTTH coverage and capacity from 100,000 connections in 2022 to 500,000 by 2025. These initiatives are expected to enhance fiber service accessibility and improve the country’s median download and upload speeds.
Furthermore, the INT initiated a consultation in August 2023 to set the conditions required to share facilities to avoid infrastructure duplication and ensure efficient fiber investments. The proposal is to have all ISPs and infrastructure operators provide shared access to their telecom facilities after 12 months of commercial operations. This initiative should help expand fiber coverage, reduce access costs, and support the development of 5G.
Fiber can further unlock the connectivity potential in North Africa
As discussed above, North African ISPs have adopted various strategies to roll out fiber and promote its take-up. They have made considerable strides in enhancing fiber accessibility and fixed broadband speed since 2020. However, a significant gap remains when compared to more advanced markets in the Middle East and Africa.
To bridge this gap, it is essential to facilitate fiber investment through public-private partnerships, promote infrastructure sharing, encourage competition, provide robust regulatory frameworks, and increase international bandwidth. Such initiatives will make high-speed broadband services more affordable and accessible, which is integral to advancing national digital transformation and boosting economic growth.
Ookla has been working with ISPs, such as Bahrain Network (BNET) and telecoms regulators, to support their national broadband plans, track improvements to fiber connectivity and coverage, and promote their networks to consumers. If you are interested in Ookla’s solutions and services for network intelligence and management, get in touch.
La Vitesse de l’Internet Fixe s’Améliore en Afrique du Nord, et la Fibre Pourrait l’Augmenter Encore d’Avantage
English
Depuis 2020, les débits du haut débit fixe en Afrique du Nord se sont considérablement améliorés. Cependant, il existe encore un potentiel d’amélioration et d’adoption. Cet article s’intéresse aux facteurs de performance de l’Internet fixe filaire (hors accès fixe sans fil (FWA)) en Algérie, en Égypte, au Maroc et en Tunisie, entre le troisième trimestre 2020 et le troisième trimestre 2023 et discute des perspectives du marché.
À retenir
- L’Égypte est en tête de l’Afrique du Nord dans le Speedtest Global Index™ pour le haut débit fixe au troisième trimestre 2023. L’Égypte a élargi son avance en Afrique du Nord, atteignant une valeur médiane du débit descendant de 56,61 Mbps et celle du débit ascendant de 25,07 Mbps. Parallèlement, l’Algérie a connu une amélioration significative du débit descendant sur le fixe, avec une multiplication par 4,5 pour atteindre 11,34 Mbps entre le troisième trimestre 2020 et le troisième trimestre 2023. Le débit ascendant au Maroc s’est également considérablement amélioré, multiplié par plus de 22 pour atteindre 19,09 Mbps au cours de cette période.
- Les pays d’Afrique du Nord ont adopté différentes stratégies de migration DSL. L’Égypte a mis à niveau la plupart de son ADSL vers le VDSL et a concentré le FTTH/B pour le déploiement .dans de nouvelles zones. D’autre part, l’Algérie s’est concentrée sur le remplacement des lignes de cuivre par du FTTH/B, tandis que le Maroc et la Tunisie ont déployé le VDSL parallèlement au déploiement du FTTH/B.
- Les mises à niveau de la fibre optique et les forfaits haut débit révisés contribuent à augmenter la vitesse. Le déploiement du FTTH/B et son adoption ne conduisent pas nécessairement à une augmentation de la vitesse de haut débit. Les FAI devraient envisager d’augmenter les vitesses de pointe des forfaits d’entrée de gamme et d’offrir des réductions sur les niveaux de vitesse plus élevés pour inciter les clients à améliorer leur forfait.
L’Égypte est en tête de l’Afrique du Nord en termes de débit descendant et ascendant pour le haut débit fixe
Dans notre rapport de juin 2021 sur le débit Internet en Afrique du Nord, l’Égypte se classe au premier rang en Afrique du Nord pour le haut débit fixe, suivie du Maroc, de l’Algérie et de la Tunisie. Tous les pays, à l’exception de la Tunisie, ont connu une amélioration de plus de 25 % des valeurs médianes du débit descendant entre le deuxième trimestre 2020 et le premier trimestre 2021, l’Algérie ayant plus que doublé sa valeur médiane du débit descendant.
Cette tendance à la hausse s’est poursuivie jusqu’au troisième trimestre 2023, la plupart des pays d’Afrique du Nord améliorant leurs valeurs médianes médianes du débit descendant et ascendant sur le haut débit fixe. Cela a permis d’améliorer leur classement dans l’Ookla Speedtest Global Index™. L’Égypte a notamment accru son avance en Afrique du Nord, atteignant une valeur médiane du débit descendant de 56,61 Mbps et une valeur médiane du débit ascendant de 25,07 Mbps.
L’Algérie a enregistré une amélioration substantielle de la valeur médiane du débit descendant sur le fixe entre le troisième trimestre 2020 et le troisième trimestre 2023, augmentant de 4,5 fois à 11,34 Mbps. D’autres pays, à l’exception de la Tunisie, ont vu leurs valeurs médianes du débit descendant sur le fixe plus que doubler au cours de la même période.
Valeur Médiane du Débit Descendant sur le Fixe Filaire dans Certains Pays Africains
Speedtest Intelligence, T3 2020 and T3 2023
Le Maroc a connu une augmentation significative de la valeur médiane du débit ascendant, avec une multiplication par plus de 22 pour atteindre 19,09 Mbps au troisième trimestre 2023. Malgré cela, il reste à la traîne de l’Afrique du Sud, le leader africain, qui affiche plus du double du débit ascendant, à 38,53 Mbps. Les autres pays d’Afrique du Nord ont connu des améliorations plus modestes du débit ascendant, allant d’une multiplication par 1,5 en Algérie à une multiplication par 2,5 en Tunisie.
Valeur Médiane du Débit Ascendant sur le Fixe Filaire dans Certains Pays Africains
Speedtest Intelligence, T3 2020 et T3 2023
L’accès DSL et sans fil sont les technologies les plus couramment utilisées pour les services de haut débit fixe en Afrique du Nord.
La ligne d’abonné numérique (DSL) est la principale technologie pour les services fixes à haut débit en Afrique du Nord, exploitant les lignes téléphoniques existantes pour la connectivité Internet. Les deux principaux types de DSL sont la ligne d’abonné numérique asymétrique (ADSL) avec des vitesses allant jusqu’à 24 Mbps et la ligne d’abonné numérique à très haut débit (VDSL) offrant des vitesses allant jusqu’à 52 Mbps pour le VDSL1 et 200 Mbps pour le VDSL2. Cette dernière peut être encore améliorée grâce à la technologie G.Fast.
Le VDSL utilise une fibre optique qui se termine à une armoire à proximité, une configuration souvent appelée Fiber-to-the-Cabinet (FTTC). La connexion du « dernier mile » vers les locaux des utilisateurs utilise ensuite les lignes de cuivre existantes. Le FTTC sert généralement d’étape de transition vers la fibre jusqu’au domicile/bâtiment (FTTH/B), où la fibre s’étend directement jusqu’aux locaux de l’utilisateur.
En Algérie et la Tunisie, les services haut débit mobile et FWA qui utilisent les technologies 3G et 4G représentent près de 30 % de toutes les connexions haut débit fixes. Toutefois, ces connexions cellulaires sont moins répandues au Maroc et en Égypte. La 4G offre des débits descendants comparables à l’ADSL et au VDSL1 mais inférieures au VDSL2 et au FTTH/B.
L’Afrique du Nord est à la traîne par rapport à la région du Golfe en termes de couverture, d’adoption et de vitesse Internet de la fibre optique. Des plans ambitieux de développement de la fibre optique ont placé le Bahreïn, le Koweït, Oman, le Qatar, l’Arabie saoudite et les Émirats arabes unis en tête du classement mondial de vitesse. Par exemple, au troisième trimestre 2023, les Émirats arabes unis, classés quatrièmes dans le Speedtest Global Index™ avec une valeur médiane du débit descendant de 231,98 Mbps. Le Koweït s’est classé vingt-deuxième et le Qatar vingt-troisième. Les autres pays du Golfe sont à la traîne des Émirats arabes unis, mais étaient en avance sur tous les marchés d’Afrique du Nord.
Les débits Internet fixes restent relativement faibles en Afrique du Nord malgré des améliorations significatives de l’accès FTTH/B
La lenteur du déploiement de la fibre optique par rapport aux pays du Golfe peut être attribuée à des facteurs tels qu’un financement public limité, des réglementations restrictives en matière de télécommunications, des investissements privés limités, ainsi que des défis géographiques et d’urbanisation. La plupart des pays d’Afrique du Nord ont également une plus grande superficie terrestre, une géologie plus variée et un niveau d’urbanisation plus faible, ce qui rend le déploiement de la fibre optique plus complexe et plus coûteux.
Le paysage concurrentiel du marché joue également un rôle, les opérateurs historiques contrôlant plus de 80 % des abonnements Internet fixes. Même en Tunisie, qui compte davantage de FAI alternatifs, Tunisie Télécom détient la majorité des abonnements DSL et fibre. En revanche, les fournisseurs de réseaux alternatifs jouent un rôle clé dans l’accélération de l’adoption de la fibre optique en Europe. En outre, les Nord-Africains ont un revenu inférieur à celui des résidents du Golfe, et la plupart ne peuvent pas se permettre les services à haut débit en raison de leurs coûts élevés.
Les défis du marché ont retardé le déploiement de la fibre et limité l’adoption et l’innovation des services. Cependant, les FAI locaux ont réalisé des progrès significatifs depuis 2020 en modernisant l’infrastructure fixe et en rendant leurs services plus abordables. L’Égypte a principalement mis à niveau son ADSL vers le VDSL et concentré les déploiements FTTH/B dans les zones en friche. Pendant ce temps, l’Algérie s’est concentrée sur le remplacement des lignes de cuivre par du FTTH/B. Le Maroc et la Tunisie ont déployé le VDSL tout en progressant dans le déploiement du FTTH/B.
En juin 2023, l’Algérie possède le plus grand nombre de connexions FTTH/B en Afrique du Nord, soit 800 000. Le Maroc suit de près avec 730 000 connexions et possède la plus grande part de fibre sur le marché du haut débit filaire (voir graphique ci-dessous). L’Égypte possède le plus grand nombre de connexions VDSL de la région et comptait quelques centaines de milliers de clients FTTH/B actifs en septembre 2023. La Tunisie occupe la quatrième position avec 55 000 connexions FTTH/B et 176 000 connexions VDSL.
Dans les sections suivantes, nous donnons un aperçu du marché du haut débit fixe en Algérie, en Égypte, au Maroc et en Tunisie. Nous mettons en évidence l’état du déploiement de la fibre optique et son impact sur les performances du réseau, et discutons des futurs plans de déploiement des FAI.
Connexions FTTH/B, Algérie, Maroc et Tunisie
Autorités de régulation des télécommunications, FAI | 2019-T2 2023
Connexions FTTH/B et part des connexions filaires fixes, Algérie, Maroc et Tunisie
Autorités de Régulation des Télécommunications, FAI | 2019-T2 2023
Des progrès significatifs réalisés dans la couverture de la fibre optique en Algérie, mais il reste encore de la marge pour stimuler l’adoption et augmenter la vitesse
En mars 2023, l’Algérie comptait plus de 3,4 millions de connexions filaires fixes, selon l’ Autorité de Régulation de la Poste et des Communications Electroniques (ARPCE). La société publique Algérie Télécom (AT) est l’unique fournisseur de services haut débit filaires. Avec 1,5 million de connexions 4G FWA supplémentaires, l’Algérie figure parmi les plus grands marchés du haut débit fixe d’Afrique.
AT a privilégié le remplacement des lignes de cuivre par de la fibre dans les grandes villes tout en conservant ses services ADSL. Il a également utilisé la technologie 4G FWA pour desservir les zones où l’infrastructure filaire n’est pas disponible ou est coûteuse à déployer. AT a tardé à adopter la technologie, mais a rapidement étendu ses services FTTH/B depuis leur introduction en 2018. Il a également augmenté les vitesses maximales sur la fibre de 100 Mbps à 300 Mbps pour les consommateurs en 2023. AT a introduit des promotions régulières, telles que le doublement de la vitesse gratuit pour les nouveaux clients. Il a également réduit ses tarifs chaque année depuis 2020, avec une ligne fibre 100 Mbps coûtant 22 dollars/mois en 2023. Ces actions ont contribué à multiplier par près de 14 le nombre d’abonnés fibre entre 2020 et novembre 2023, pour atteindre le jalon important d’un million, faisant de l’Algérie l’un des plus grands marchés FTTH/B en Afrique.
Connexions à Haut Débit Fixe par Technologie, Algérie
ARPCE | 2019-T1 2023
La migration de l’ADSL vers le FTTH a sans aucun doute amélioré la qualité de service pour les consommateurs. Cependant, il lui reste encore à augmenter la vitesse que connaissent la plupart des ménages. Alors que le débit descendant des 10 % d’échantillons les plus rapides est passée de 8,01 Mbps au troisième trimestre 2020 à 45,71 Mbps au troisième trimestre 2023, la valeur médiane n’a atteint que 11,34 Mbps au cours de cette période, selon les données d’Ookla Speedtest Intelligence®.
Selon l’ARPCE, plus de 85 % des connexions avaient un débit descendant de 10 Mbps en mars 2023. Pour améliorer le débit descendant du pays, AT devrait augmenter le débit descendant de son forfait fibre d’entrée de gamme, qui est entre 10 et 15 Mbps. Il devrait également s’efforcer de réduire le prix de ses forfaits à vitesse plus élevée. Le gouvernement a proposé d’exonérer de TVA les services à haut débit fixe en 2024, ce qui devrait permettre aux clients de passer à un forfait à vitesse plus élevée plus abordable.
AT s’est fixé des objectifs ambitieux pour étendre considérablement sa couverture fibre. Le nombre de foyers desservis par la fibre (c’est-à-dire de locaux pouvant se connecter au réseau fibre) devrait passer de 3,5 millions en 2022 à 6 millions d’ici 2024 (sur un nombre estimé de 7,4 millions de foyers). Cela fait partie de la stratégie plus large du gouvernement visant à fournir un service haut débit fixe à deux tiers des foyers d’ici 2024, ce qui pourrait ajouter 2 millions de nouveaux abonnés au marché.
Amélioration rapide des performances du réseau en Égypte grâce à la stratégie ambitieuse FTTC de l’opérateur historique
Avec près de 11 millions d’abonnés fin 2022, l’Égypte est le premier marché de télécommunications à haut débit fixe d’Afrique du Nord. La société d’État Telecom Egypt (TE) domine le secteur, contrôlant plus de 80,1 % du marché avec plus de 8,7 millions d’abonnés au haut débit fixe.
D’autres opérateurs tels que Vodafone, Orange et Etisalat by e&, offrent des services haut débit via un accès de gros au réseau de TE. Cela leur permet de fournir des vitesses haut débit comparables. Il convient de noter que la part de marché combinée de ces FAI alternatifs suit une tendance à la hausse d’année en année depuis 2019.
L’objectif stratégique de TE a été de développer ses réseaux centraux et de transmission, de mettre à niveau l’ADSL vers le VDSL et d’étendre la fibre jusqu’aux armoires de rue. En septembre 2023, TE a connecté 95 % des foyers au réseau FTTC de nouvelle génération (contre 85 % en 2019).
L’introduction des services VDSL en Égypte en 2018 a marqué un changement significatif dans les vitesses du haut débit, augmentant le maximum de 16 Mbps à 100 Mbps. TE a aussi augmenté la vitesse de son forfait d’entrée de gamme de 5 Mbps à 30 Mbps, avec une modeste augmentation de prix de 9%. Les mises à niveau des infrastructures ont également eu un impact positif sur les FAI alternatifs, qui ont augmenté les vitesses de leurs forfaits haut débit.
Ces améliorations de la couverture VDSL, des vitesses et du prix abordable ont considérablement accéléré l’adoption des services haut débit. Le nombre d’abonnés au haut débit fixe a bondi de 55% entre fin 2019 et juin 2023. L’augmentation de la vitesse minimale du haut débit à 30 Mbps a entraîné une augmentation substantielle de la valeur médiane du débit descendant du pays, à 56,61 Mbps au troisième trimestre 2023, contre 25,07 Mbps au troisième trimestre 2020, selon Ookla Speedtest Intelligence. Étant donné que TE offre actuellement des vitesses allant jusqu’à 150 Mbps, il existe de nombreuses possibilités d’améliorer encore le débit descendant.
Connexions à Haut Débit Fixe par FAI, Egypte
Telecom Egypt | 2019-T2 2023
TE a lancé les services FTTH/B en 2009, faisant de l’Égypte l’un des premiers utilisateurs de la fibre optique dans la région. Il a donné la priorité aux déploiements FTTH/B dans des zones vierges telles que les nouveaux développements et les complexes résidentiels. TE vise à terme à migrer les clients VDSL existants vers FTTH/B.
Le gouvernement a alloué un budget de 360 millions de dollars en 2021 pour étendre la fibre jusqu’au domicile (FTTH) à un million de foyers afin d’améliorer l’accessibilité à la fibre. Le développement du “Nouveau Caire”, une nouvelle mégapole située à 35 km à l’est de la capitale, devrait également stimuler la demande de services de fibre optique.
Le marché concurrentiel de la fibre optique au Maroc a favorisé l’adoption du haut débit et l’amélioration de la vitesse
Maroc Telecom (MT) domine le marché du haut débit fixe au Maroc. Le contrôle de l’opérateur sur l’infrastructure cuivre a incité d’autres FAI, inwi et Orange, à développer leur propre infrastructure fibre, et louer de la capacité auprès des sociétés de services publics et de transport locales.
Le marché du haut débit fixe filaire connaît une croissance rapide au Maroc, passant d’un peu plus de 1,6 million en 2019 à plus de 2,2 millions de connexions en juin 2023 (sur environ 8 millions de foyers). Cette croissance est principalement due au passage du DSL au FTTH/B depuis 2020, comme on l’observe dans le graphique ci-dessous.
Connexions à Haut Débit Fixe par Technologie, Maroc
ANRT | 2019-T2 2023
Les consommateurs se tournent vers des services plus rapides et plus fiables, avec une demande de connexions DSL en baisse depuis 2020 et une adoption FWA en baisse depuis 2022. MT a lancé la fibre en 2014, offrant un service premium à 100 Mbps et 200 Mbps. En 2022, MT a accéléré le déploiement de son réseau FTTH/B et a augmenté la capacité de son réseau de 40 % sur un an en juin 2023, contribuant ainsi à élargir sa base de clients fibre de 43 %.
inwi et Orange ont lancé leurs services fibre en 2018, offrant une gamme de vitesses plus large à partir de 20 Mbps et des prix inférieurs à ceux de MT pour le haut de gamme. Ces services sont disponibles dans les grandes villes comme Casablanca, Rabat et Fès. Ils représentaient collectivement 52,69 % du marché de la fibre en juin 2023, ce qui montre que le segment est assez compétitif au Maroc.
Cela a entraîné une augmentation des vitesses côté utilisateur. Au troisième trimestre 2023, la valeur médiane du débit descendant des services Internet fixes était passée à 21,68 Mbps, contre 9,07 Mbps au troisième trimestre 2020, selon les données d’Ookla Speedtest Intelligence. Il y a eu une évolution marquée vers les forfaits haut débit fixe de vitesse supérieure, comme en témoigne le fait qu’en juin 2023, 17,3 % des abonnés au haut débit fixe disposaient d’une vitesse d’au moins 20 Mbps, soit une augmentation spectaculaire par rapport à seulement 0,6 % en 2019 qui avaient des vitesses d’au moins 16 Mbps, selon l’Agence Nationale de Réglementation des Télécommunications (ANRT)
Étant donné qu’environ un tiers seulement des abonnés au haut débit filaire au Maroc utilisent le FTTH/B, il existe encore de nombreuses opportunités de migrer davantage de clients DSL vers la fibre et d’encourager les utilisateurs existants de la fibre à passer à des forfaits à plus haut débit. Ceci est particulièrement pertinent pour inwi et Orange, car ils proposent des forfaits fibre plus abordables à partir de 20 Mbps, par rapport au forfait fibre 100 Mbps de MT qui coûte environ 50 $/mois.
Pour l’avenir, le gouvernement marocain a des projets ambitieux pour connecter davantage de foyers aux services à haut débit dans le cadre du programme “Maroc Digital 2030”. Le gouvernement vise à connecter 5 millions de foyers à la fibre optique d’ici 2026, faisant potentiellement du Maroc l’un des plus grands marchés FTTH/B d’Afrique.
Le partage limité des infrastructures et des investissements en Tunisie ont restreint l’amélioration du débit descendant
La Tunisie offre les plus bas débits descendants sur le fixe en Afrique du Nord, soit 8,61 Mbps au troisième trimestre 2023, selon Ookla Speedtest Intelligence. Et ce, malgré le nombre de huit FAI, contre un en Algérie, trois au Maroc et cinq en Égypte. La faible performance du réseau est due à la couverture limitée des services de haut débit à grande vitesse et à leur coût inabordable pour de nombreux foyers. Par exemple, une ligne VDSL à 50 Mbps coûte plus de 26 $/mois. De plus, il a fallu attendre 2022 pour que les FAI augmentent le débit des forfaits DSL de base de 4 Mbps à 10 Mbps.
Le secteur du haut débit filaire n’a cessé de croître, atteignant plus de 1,2 million d’abonnés en juin 2023. Cela représente une augmentation de 50 % par rapport aux niveaux de 2019. Il est intéressant de noter que ce taux de croissance a dépassé celui du segment de l’accès fixe sans fil 4G, qui n’a connu qu’une augmentation de 27,4 %, atteignant un peu plus de 470 000 connexions au cours de la même période. En revanche, le service fibre reste une offre de niche en raison de sa couverture limitée et de son coût élevé. La part de la fibre sur le marché du haut débit filaire fixe a connu une légère augmentation, passant de 3,0 % en 2019 à un modeste 4,5 % en juin 2023.
Connexions à Haut Débit Fixe par Technologie, Tunisie
INT | 2019-T2 2023
Tunisie Telecom (TT), une entité publique, détient la majorité des parts dans le secteur du haut débit fixe. TT contrôle l’infrastructure nationale de cuivre, exploite le réseau dorsal de fibre optique à l’échelle nationale et est en concurrence directe et indirecte sur le marché de détail via sa filiale Topnet. La propriété de TT est répartie entre l’État tunisien (à 65 %) et Emirates International Telecommunications (EIT, à 35 %).
TT maintient une position forte dans ce secteur, contrôlant 72,9 % de toutes les connexions fibre en Tunisie en juin 2023. Ce chiffre comprend les clients directs (39,1 %) et ceux fournis via Topnet (33,8 %). Les services fibre, lancés en 2012, ne sont disponibles que dans le Grand Tunis et à Sfax. De plus, TT domine le marché VDSL avec une part de marché substantielle de 92,4 %, principalement via Topnet.
La pression réglementaire exercée par l’autorité des télécommunications INT (Instance Nationale des Télécommunicationss) a exhorté TT à réduire ses frais d’accès au réseau et accélérer l’activation de la ligne pour aider les autres fournisseurs d’accès Internet (FAI). Malgré ces efforts, divers défis persistent, incitant les opérateurs tels que Ooredoo et Orange à compléter leurs offres filaires avec des services de haut débit mobile basés sur la 3G et la 4G, en plus du FWA basé sur TD-LTE.
Ooredoo, qui a introduit les services fibre en 2013, a vu sa part de marché fibre s’élever à 16,8 % en juin 2023. Son réseau fibre couvre le Grand Tunis et Sfax. Orange manque cependant d’offres fibre grand public. D’autres FAI, notamment Bee, GlobalNet et HexaByte, utilisent un mélange d’ADSL, de VDSL et de FTTH/B en accédant à l’infrastructure de TT.
À court terme, TT prévoit de mettre à niveau la plupart des ports DSL vers le VDSL et de promouvoir des forfaits à plus haut débit. Cette stratégie vise à augmenter le débit fixe moyen de 10 Mbps en 2022 à 50 Mbps en 2024. À moyen terme, TT vise à étendre sa couverture et sa capacité FTTH de 100 000 connexions en 2022 à 500 000 d’ici 2025. Ces initiatives devraient améliorer l’accessibilité du service de fibre optique et améliorer les valeurs médianes des débits descendants et ascendants du pays.
En outre, l’INT a lancé une consultation en août 2023 pour définir les conditions requises pour partager les installations afin d’éviter la duplication des infrastructures et garantir des investissements efficaces dans la fibre. La proposition est que tous les FAI et opérateurs d’infrastructures fournissent un accès partagé à leurs installations de télécommunications après 12 mois d’opérations commerciales. Cette initiative devrait permettre d’étendre la couverture fibre, de réduire les coûts d’accès et de soutenir le développement de la 5G.
La fibre peut libérer davantage le potentiel de connectivité en Afrique du Nord
Comme indiqué ci-dessus, les FAI nord-africains ont adopté diverses stratégies pour déployer la fibre optique et promouvoir son adoption. Ils ont fait des progrès considérables dans l’amélioration de l’accessibilité à la fibre optique et de la vitesse du haut débit fixe depuis 2020. Cependant, un écart important demeure par rapport aux marchés plus avancés du Moyen-Orient et d’Afrique.
Pour combler cet écart, il est essentiel de faciliter les investissements dans la fibre optique par le biais de partenariats public-privé, de promouvoir le partage des infrastructures, d’accroître la concurrence, de fournir des cadres réglementaires solides et d’étendre la bande passante internationale. De telles initiatives rendront les services à haut débit plus abordables et accessibles, ce qui fait partie intégrante de la progression de la transformation numérique nationale et de la stimulation de la croissance économique.
Ookla a travaillé avec des FAI, tels que Bahrain Network (BNET) et les régulateurs de télécoms, pour soutenir leurs plans nationaux de haut débit, suivre les améliorations de la connectivité et de la couverture fibre et promouvoir leur réseaux auprès des consommateurs. Si vous êtes intéressé par les solutions et services d’Ookla en matière d’intelligence et de gestion des réseaux, contactez-nous.