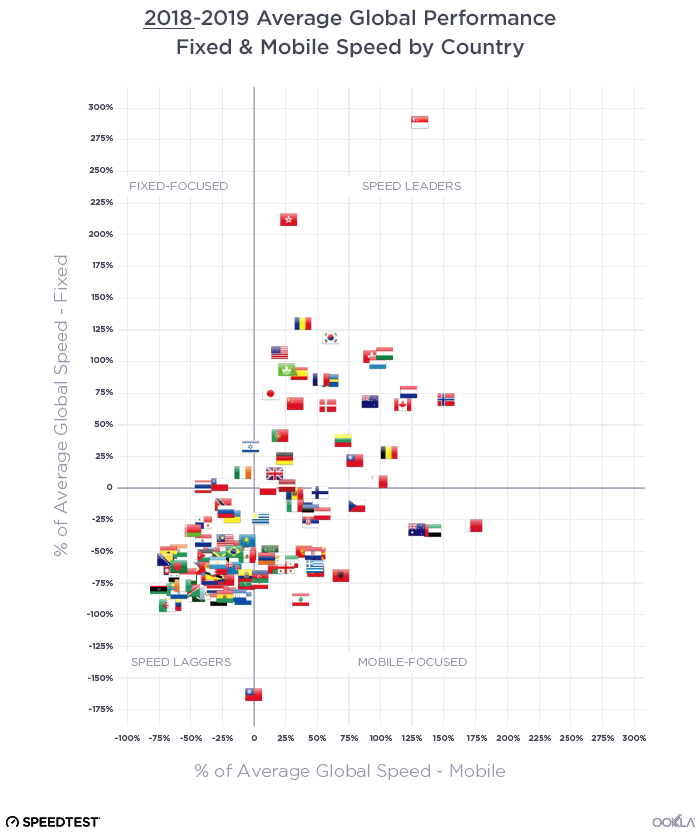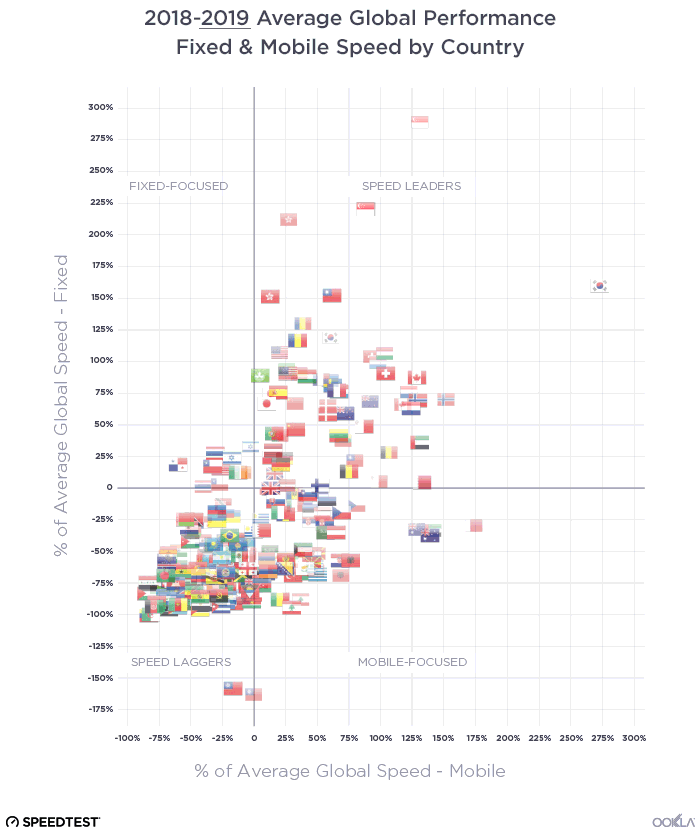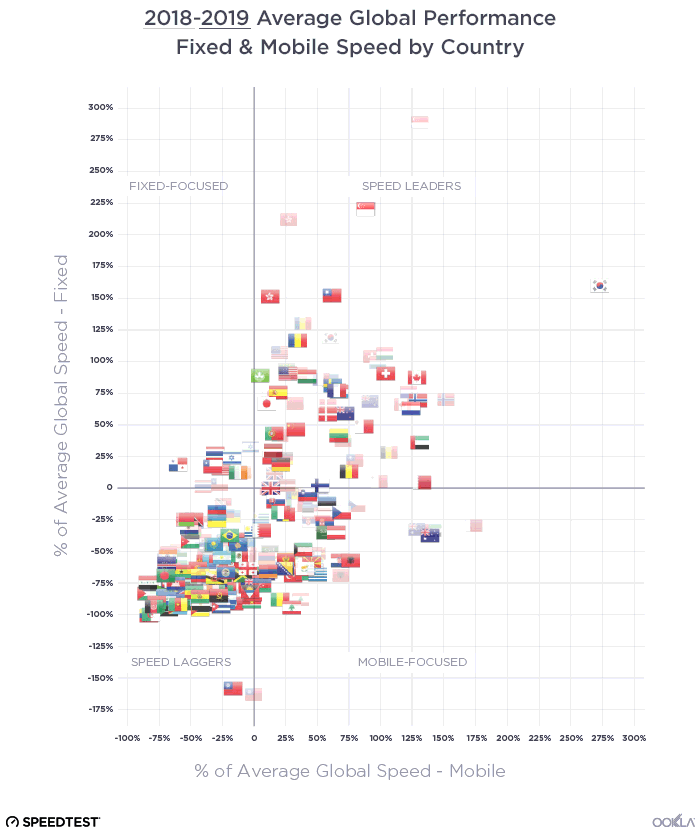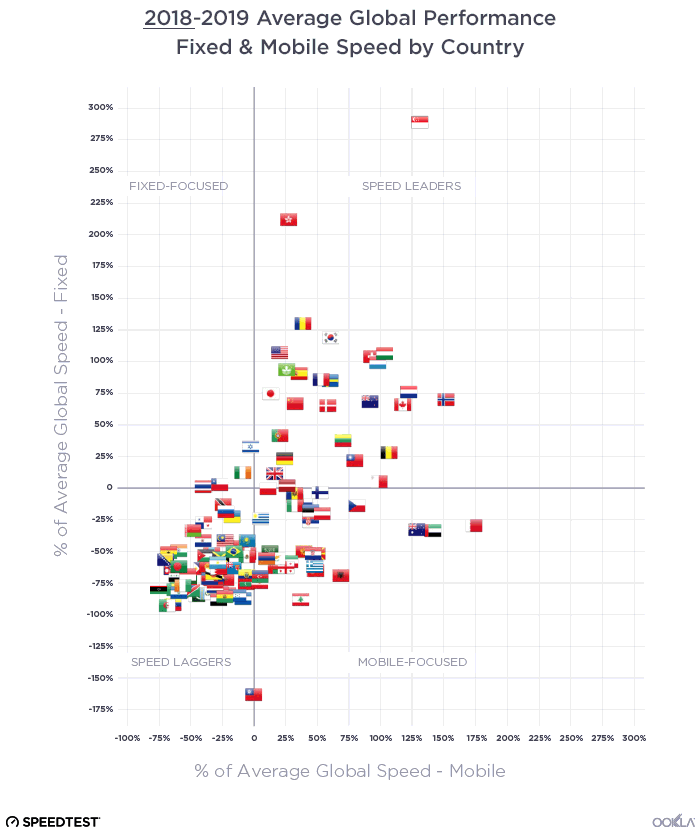
In this article, we analyze select African countries that have consistently improved their ranking in Ookla’s Speedtest Global Index™ between June 2020 and June 2023 and discuss the drivers that contributed to this rise. These countries can provide lessons and best practices that other operators and regulators can apply to bridge the 4G performance gap.
Key takeaways
- Government and policy intervention is critical in supporting the rollout of 4G networks in Africa. Operators need more than ever support amid the challenging macroeconomic, operating conditions, and shrinking consumer disposable income. For example, the government intervened in Nigeria to cancel excise tax to reduce operators’ financial burden, promoted infrastructure sharing in Cote d’Ivoire and Zimbabwe to speed up network deployment, and led the expansion of 4G infrastructure in Libya.
- Spectrum availability is crucial to improving network performance and coverage to meet growing data demand. For example, public authorities encouraged the efficient spectrum usage by freeing up legacy bands and refarming existing ones in Mauritius, Namibia, and Tanzania, and by adopting technology-neutral spectrum licensing in Zimbabwe.
- Non-punitive network QoS compliance policies can help drive investments and promote fair competition. Policymakers and regulators in Africa are increasingly adopting alternatives to financial sanctions to encourage operators to meet coverage and QoS obligations. For example, the regulator in Tanzania mandated network investments instead of issuing non-compliance penalties.
Some African countries show a marked improvement in 4G download and upload speeds as well as coverage
Cellular networks are critical to connect individuals and businesses as internet access in Africa is predominantly mobile. In addition, the adoption of digital services, spurred by the COVID-19 pandemic, has rapidly increased the demand for data services. As a result, consumer needs and economic growth will increasingly depend on a fast, reliable mobile network.
We used Ookla’s Speedtest Global Index™ to identify African countries that have consistently improved their mobile speed ranking between June 2020 and June 2023. We then used Speedtest Intelligence® data to compare 4G mobile performance on modern chipsets between Q2 2020 and Q2 2023.
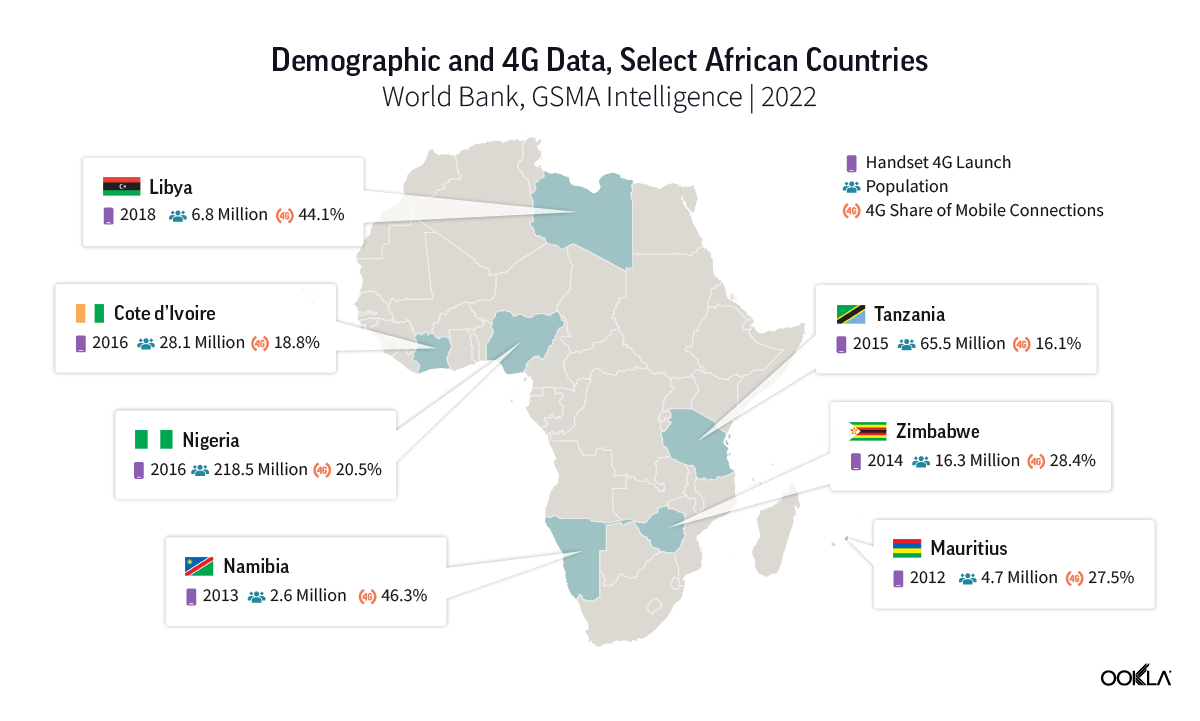
We focused on markets that offer strong growth potential for 4G, so we selected countries whose 4G share of connections was lower than 50% at the end of 2022 (based on data from GSMA Intelligence). The shortlisted countries represent different sub-regions and have different demographical and geographical characteristics, as shown on the map below.
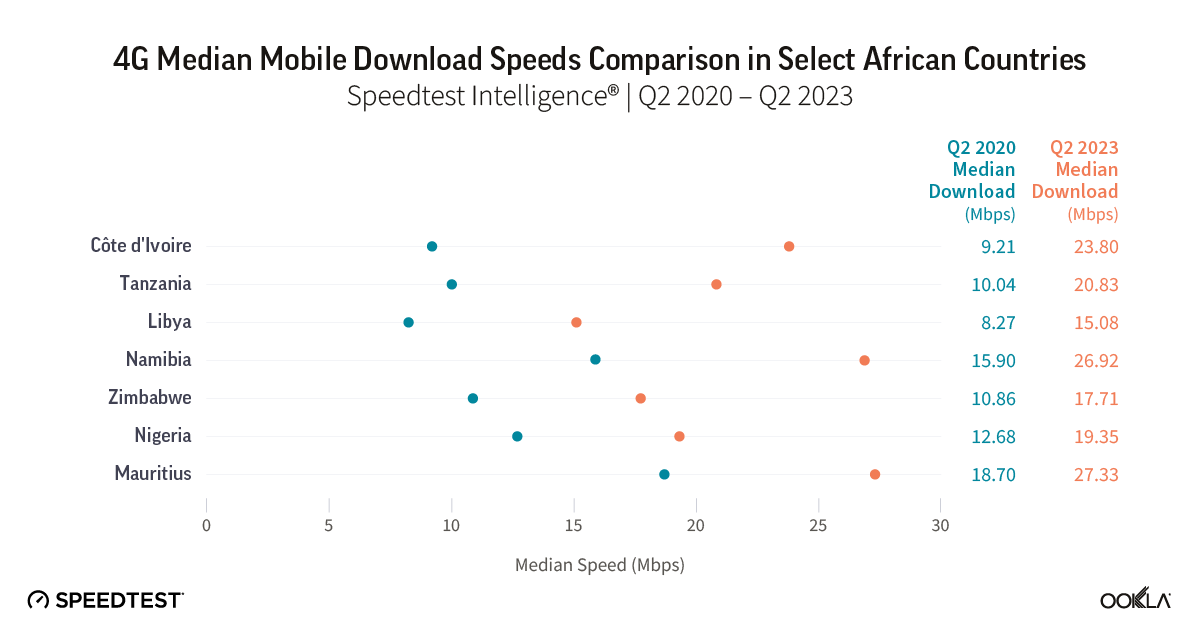
According to Speedtest Intelligence data, Cote d’Ivoire showed impressive improvement in 4G network performance since Q2 2020, reaching a median download speed of 23.8 Mbps in Q2 2023, the third highest speed behind only Mauritius with 27.33 Mbps and Namibia with 26.92 Mbps. Tanzania doubled its 4G download speeds to 20.83 Mbps while Libya, Nigeria, and Zimbabwe had download speeds between 15 Mbps and 20 Mbps in Q2 2023.
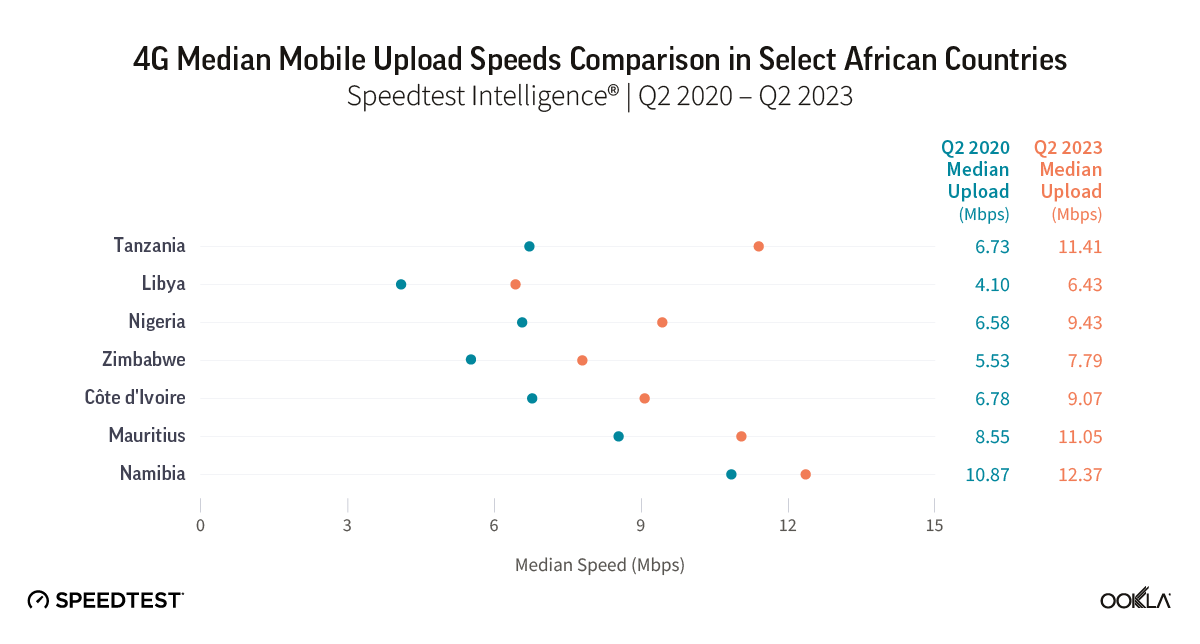
Improvements in upload speeds over the same period and the differences between the countries were less pronounced than download speed results. With a jump of 1.6 times in 4G upload speed between Q2 2020 and Q2 2023, Tanzania moved from fourth to second place, ahead of Cote d’Ivoire and Mauritius and just behind Namibia. Notably, Libya lagged behind other countries in download and upload speeds but improved markedly over three years, despite being the last one to launch 4G in 2018, and arguably, where operators had the most challenging environment.
In the following sections, we analyze market dynamics in each country, review operators’ 4G investments, and discuss the factors that drove (or inhibited, at times) 4G market development.
Cote d’Ivoire has plenty of room to increase 4G adoption
Mobile penetration of the population in Cote d’Ivoire increased rapidly since 2020 to reach 142.4% in Q1 2023 (according to Autorité de Régulation des Télécommunications (ARTCI)).
Orange is the largest mobile operator in Côte d’Ivoire in terms of subscribers (45.6% in Q1 2023) and 4G network population coverage (90.6% in December 2022). It launched 4G services in March 2016 over 1800 MHz. It expanded its subscriber base rapidly thanks, in part, to a $312 million investment in network deployment and upgrades in 2019 and 2020. It also set a plan to invest a further USD120 million between 2020 and 2025 to upgrade the fiber-optic backbone of its 4G network.
MTN captured just over a third of mobile subscribers in March 2023. It launched 4G shortly after Orange, followed by LTE-A in Abidjan in December 2020, the only operator to offer this service to date in the country. In October 2022, it signed a $75 million five-year contract with Canadian infrastructure supplier NuRAN Wireless to expand its network coverage in rural areas. However, we understood that this only concerns 2G and 3G services. MTN’s 4G coverage reached 57.4% of the population at the end of 2022, way behind Orange.
Moov had been capturing an increasing share of mobile connections until 2018. Since then, its market share has remained mostly stable at around 20%. It launched 4G services in Q3 2016 over 900 MHz. Moov has extensive network coverage in remote areas, which has helped it to grow its subscriber base. Coverage reached just over half of the population at the end of 2022, lagging behind Orange and MTN.
The three operators managed to rapidly expand 4G coverage after launch. According to Speedtest Intelligence®, 4G service availability, which represents the proportion of an operator’s known locations where a device has access to 4G LTE service, already reached 83.5% in 2018 and increased to 94.3% during Q1-Q3 2023. Despite this, 4G share of mobile connections remains low at 18.8% in 2022 (according to GSMA Intelligence). The unaffordability of smartphones, combined with the limited coverage in rural areas and poor network QoS remain obstacles to mobile data adoption.
To address these challenges, Orange and MTN launched financing schemes and introduced affordable handset models. Further, ARTCI initiated discussions with the operators in 2022 on how to implement improvements in their network and was given additional powers to improve service quality levels. ARTCI also awarded the three operators 2×20 MHz in the 2600 MHz band for LTE to improve network data capacity and is looking for infrastructure sharing as an option to speed up 5G deployment, in time for the African Cup, which will take place at the beginning of 2024.
Government support was pivotal in Libya to accelerate 4G rollout amidst challenging conditions
Libya experienced prolonged political unrest and violence since 2011, leading to the destruction of communication networks, equipment theft, and power shortage. The progressive return to stability since 2021 has somewhat enabled the restoration and extension of existing network infrastructure.
Despite these challenges, Libya has one of the highest mobile penetration in Africa (178.5% in June 2023, according to GSMA Intelligence), and it is one of the few North African countries with an MVNO (albeit capturing less than 1% of the market). The market is a duopoly with two subsidies of Libyan Post, Telecommunication and Information Technology Company (LPTIC): Al Madar Aljaded and Libyana. Both operators introduced 4G over 1800 MHz in 2018, initially covering only a few cities.
Libyana took the lead by launching LTE in January 2018 and covering 30 major towns and cities by the end of that year. It subsequently expanded coverage to more than 49 towns and cities by April 2022.
Almadar Aljaded launched LTE and LTE-A in October 2018 in Greater Tripoli Benghazi and Misrata before expanding nationwide, claiming coverage for more than 80% of the population in 2022.
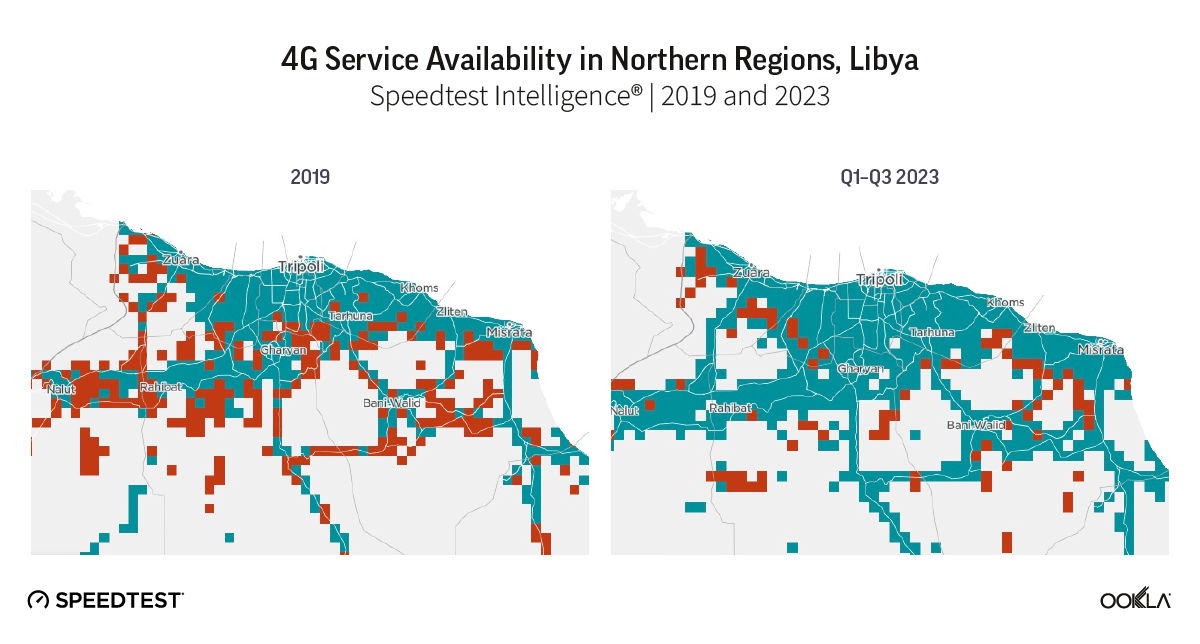
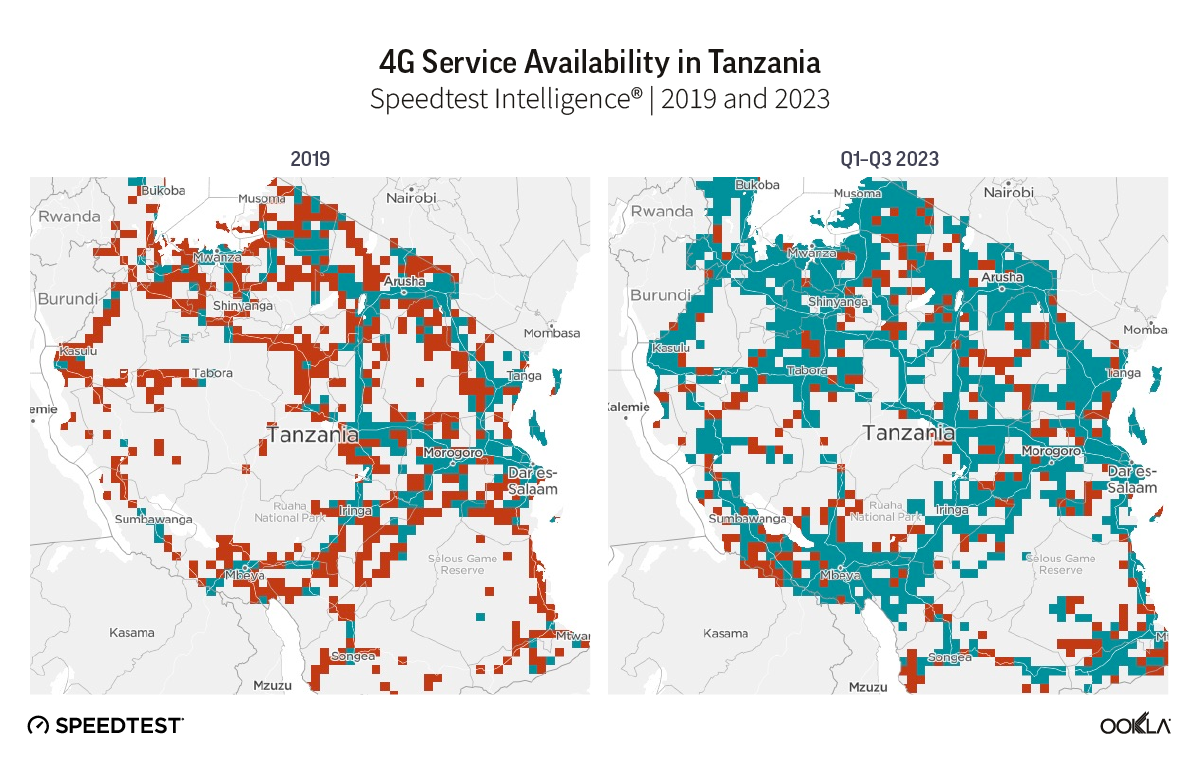
4G deployment gained momentum and the restoration of the telecoms infrastructure resumed thanks to LPTIC’s program launched in 2021 to extend LTE coverage to underserved areas thanks to cooperation agreements with foreign governments and telecoms groups. According to Speedtest Intelligence®, access to 4G service increased from 11.8% in 2019 to 76.8% during Q1-Q3 2023. Northern regions had particularly benefited from network coverage enhancements as shown in the map below where green squares show locations where 4G service is available and red squares where 4G service is unavailable.
This coverage expansion was accompanied by a boost to median download and upload speeds reaching 15.08 Mbps and 6.43 Mbps in Q2 2023, respectively. However, 4G network throughput is low compared to the performance of other countries featured in this article, suggesting that there is room to improve capacity.
Unfortunately, the deadly floods that struck the eastern part of the country in September 2023 are a significant setback. We expect network expansion and upgrade efforts will be delayed as funding will be directed toward relief efforts and the restoration of basic mobile services.
The allocation of additional spectrum in Mauritius helped to improve 4G coverage and speed
Mauritius is an early adopter of 4G with a saturated mobile market (population penetration reached 160.0% in Q3 2023). The market has three active mobile network operators: incumbent operator Cellplus Mobile Communications (under my.t mobile), Emtel, and Mahanagar Telephone Mauritius Limited (MTML) (operating under the CHiLi brand).
Cellplus Mobile launched 4G in 2012 over the 1800 MHz band. It initiated a major network modernization project in 2017, which resulted in a 50% increase in data traffic in 2018 enabling 4G traffic to overtake 3G traffic for the first time. It achieved quasi-nationwide 4G coverage by mid-2019.
The second operator Emtel also launched 4G in 2012 and claimed its 4G network covered the whole island by end-2022. Lastly, MTML (CHiLi), introduced LTE services in 2015 and progressively expanded coverage until it reached 90% of the population by end-2022. This led to a 7% increase in monthly data traffic year-on-year in FY2022/2021.
Operators continued to improve 4G coverage and speed as they prepared to launch 5G. According to Speedtest Intelligence®, access to 4G service increased from 64.40% in 2019 to 96.3% during Q1-Q3 2023. During that period, Mauritius pulled further ahead than the other countries with 27.33 Mbps median 4G download speed in Q2 2023, overtaking Namibia which, until then, had the fastest download speed among the countries analyzed.
These achievements were partly driven by initiatives led by the Information and Communication Technologies Authority (ICTA) which continually encouraged the refarm and release of additional spectrum. For example, the 2100 MHz spectrum (1920‐1980 MHz paired with 2110‐2170 MHz) was reused for LTE and LTE-A services since 2018, after being used exclusively for 3G. ICTA also assigned 2×10 MHz of spectrum in the range 832MHz-862MHz and 791MHz-821MHz for LTE services in 2021, which helped to increase 4G coverage.
Access to additional spectrum and operators’ investment in Namibia helped to boost 4G coverage and performance
Mobile population penetration reached 110.7% in Q3 2023, behind other African markets with similar GDP. Similar to Libya, the market is a duopoly with two mobile operators controlled by a state company, Namibia Post and Telecommunications Holdings (NPTH): MTC, with an 86% market share, and Telecom Namibia (TN Mobile).
Market leader MTC launched a 4G LTE network over 1800 MHz in May 2012, initially for mobile broadband only. MTC then activated LTE-A in April 2016 contributing to boosting download speed, despite limited service availability in selected urban areas. MTC refarmed 2100 MHz for LTE in 2018 and was awarded 2x5MHz lots in the 900 MHz spectrum band in August 2021, but that was deemed insufficient to serve its large subscriber base. It initiated the ‘081EVERY1’ project to build additional base stations and upgrade 4G infrastructure in towns to provide 100% population coverage by the end of 2023. However, we understand that this objective has not been attained as of October 2023 (LTE coverage expanded to more than 68% of the population in 2022).
TN Mobile launched 4G in November 2013 and LTE-A in late 2019, using only 1800 MHz. In July 2022, the operator outlined a plan to invest more than $124 million over five years to modernize its network, starting with its national backbone, core network, and access technologies to boost population coverage and network QoS. Before that, TN Mobile had been deploying or upgrading mobile sites in selected rural and urban areas since 2019 to achieve 100% population 4G coverage by end-2023. However, the cost of competing with the dominating incumbent operator will likely make it difficult to achieve it.
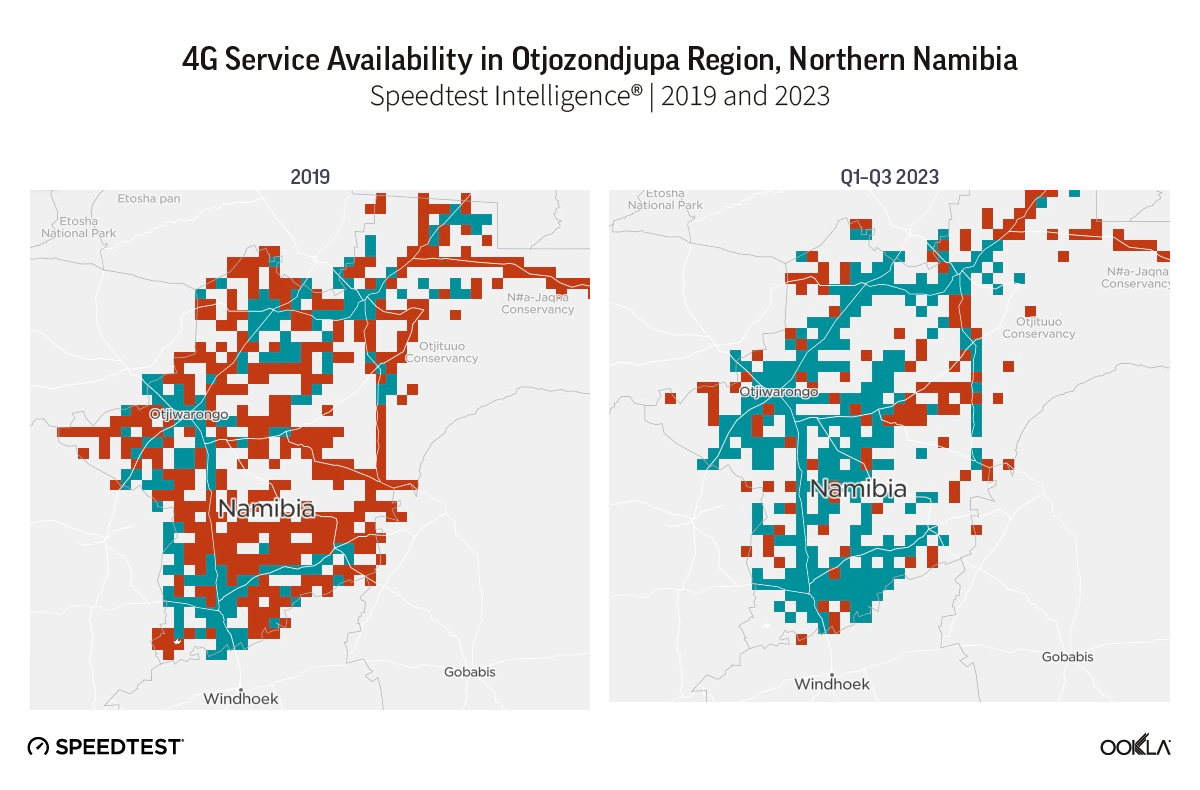
According to Speedtest Intelligence, 4G service availability in Nambia increased from 24.7% in 2019 to 76.6% over January-October 2023, with the Otjozondjupa region showing substantial improvement (see map below). However, according to the Communications Regulatory Authority of Namibia (CRAN), only seven out of fourteen regions were covered by 4G, calling for more private-sector investment to increase 4G footprint. To support these efforts, the CRNA kicked off the auction process for 700 MHz (703-788 MHz) and 800 MHz (790-862 MHz) frequency bands in February 2023. The spectrum was awarded in October 2023 to the two mobile operators and local ISP Loc8 Mobile for 4G and 5G services.
The three licensees should provide 4G and 5G services with at least 20 Mbps download speed and have to extend 4G coverage to at least 80% of the population in six out of the 14 regions. This suggests that operators will need substantial investments in network infrastructure to satisfy these coverage and speed requirements.
Access to multiple spectrum bands helped operators in Nigeria to rapidly expand 4G network coverage
Nigeria is the largest market in Africa in terms of mobile connections with over 220 million mobile subscribers. The market peaked in 2020 and then contracted due to the implementation of the SIM registration policy. The market started recovering more in the second half of 2021 as previously-restricted subscribers obtained a new SIM through ID verification. Mobile penetration reached 90.3% in Q3 2023.
The market is highly competitive with three main players: MTN (38.7% share of subscribers in July 2023), Glo (Globacom) (27.82%), and Airtel (27.24%). 4G coverage increased rapidly to reach 80.9% at the end of 2022 though adoption peaked at around 25% before starting to fall as some customers migrate to 5G.
Glo was the first main operator to introduce 4G services in 2016 over 700 MHz, which it then combined with 1800 MHz spectrum in 2019. It launched LTE-A in 2023 by combining 700 MHz, 1800 MHz, and 2600 MHz (which it acquired recently), and plans to deploy 4,000 LTE-A mobile sites in major towns and cities.
MTN launched 4G the same year using 1800 MHz and 2600 MHz bands. It then launched LTE-A by combining 2600 MHz and 1800 MHz in 2019. MTN then acquired 800 MHz spectrum to improve coverage 4G coverage which reached 83% in 2023. Its CAPEX (excluding right-of-use assets) increased by 18.1% in 2022 to around $470 million to accelerate 4G and 5G network expansion. In September 2023, it acquired an additional 10 MHz of spectrum in the 2600 MHz band to improve the capacity of its LTE network.
Airtel was the last to launch LTE over 1800 MHz, before incorporating 2600 MHz in 2019 and 900 MHz in 2022, which helped to expand coverage to more than 463 locations in the country.
Operators faced several technical and operational challenges that impacted the quality of 4G connectivity in Nigeria. This was the result of the network infrastructure not being able to keep up with pent-up demand for mobile device services. Other factors also contributed to the deterioration of network quality including the limited access to continuous power supply, vandalism, and multiple taxes and levies.
Furthermore, the Nigerian Communications Commission (NCC) and the government took a tough stand against operators for failing to meet QoS obligations or delaying tax payments, resulting in significant fines between 2012 and 2016.
The NCC started adopting less punitive measures against operators recently and being more actively engaged with them on QoS issues, following the South African model. The government also reversed its decision to impose a 5% excise duty on telecom services in 2023. These measures should help somewhat operators weather the current challenging macroeconomic climate.
The regulator’s efforts helped improve 4G coverage in Tanzania but data services remain unaffordable to most of the population
Tanzania has a crowded mobile market with seven operators and fierce price competition. The introduction of biometric SIM identification slowed market growth in 2020 (the market contracted by 9.5 million) before recovering in 2021. Mobile penetration reached 93.9% in June 2023.
Three operators dominate the market: Vodacom (30% of subscribers in June 2023), Airtel (27%), and third-placed Tigo (27%), which was acquired by a consortium led by Axian Telecom in April 2022.
Vodacom launched 4G commercially in 2016. It uses 700 MHz and 1800 MHz spectrum bands. It reported having deployed 2315 4G sites by the end of 2022 (up from 1814 in September 2021) and that broadband coverage reached 93% of the population.
Airtel launched LTE services over 1800 MHz in the capital Dodoma in November 2019 then expanded to other cities in 2020. It announced the deployment of its ‘Supa 4G’ LTE-A network in 2021 which uses 700 MHz and 2100 MHz in 500 cities and villages. It claims to have rolled out LTE-A in 80% of its mobile sites by April 2022. Airtel was also allocated an additional spectrum in the 1800 MHz band in 2019.
Tigo launched LTE services in Dar es Salaam in April 2015 over 800 MHz. It progressively expanded its network to reach 26 regions by February 2022. It launched LTE-A in September 2018 over 800/1800 MHz in a limited number of cities. In May 2022, Axian Telecom announced plans to invest $500 million in infrastructure over the next five years to improve 4G coverage and QoS, especially in rural areas, and to support the country’s digital transformation and bridge the digital divide.
The Tanzania Communications Regulatory Authority (TCRA) has been less punitive than before. For example, in 2019, it fined the six operators $2.6 million for failing to meet QoS standards. However, in 2021, the TCRA ordered the operators to invest $16.4 million to address network issues rather than issue a new fine
The government also freed up the 700 MHz band and auctioned it off in 2018 to enable operators to provide 4G data services to more communities. Four years later, another auction was completed for 2300 MHz, 2600 MHz, and 3500 MHz bands to be used for 4G and 5G. More recently, the government launched the ‘Digital Tanzania’ project in May 2023 in partnership with mobile operators and with support from the World Bank to reach 80% broadband population penetration by 2025. Operators will use the universal access fund to deploy 758 mobile towers to provide data services to 1407 villages and over 8.5 million potential users.
While 4G coverage reached 65%, Tanzania has the lowest 4G share of connections among the countries reviewed in this article, at 17.8% in Q2 2023. Furthermore, according to TCRA, only 27% of Tanzanians owned smartphones and mobile internet-enabled devices in 2022.
This suggests that many consumers still can not afford data-enabled handsets and that data tariffs remain out of reach for most Tanzanians, given low income levels, since most of them live in rural areas and work in the agriculture sector.
The government plays a crucial role in progressing the national broadband connectivity agenda in Zimbabwe
According to the Postal and Telecommunications Regulatory Authority (POTRAZ), mobile penetration reached 91.9% at the end of Q2 2023. Mobile data connectivity is the most common way to access internet services. 3G and 4G services represented more than 98% of data connections in the country, and the main driver for internet penetration.
The market is dominated by Econet which controls 72.3% of subscriptions as of June 2023. It launched 4G over 1800 MHz in August 2013, but adoption was muted because of limited coverage, and expensive tariffs. Fast forward to October 2022, and 4G network reached 39% of the population. Econet has the highest number of LTE base stations in the country, 54.3% of the 1962 stations in June 2023. In September 2023, it announced the deployment of 30 new 4G sites by March 2024 and an upgrade of all existing 2G sites to 4G in the eastern provinces.
NetOne is a state-owned operator and the second-largest player with a 25.5% market share in June 2023. It launched 4G in November 2014, using 1800 MHz before adding 700 MHz in 2016. It resumed deployment of LTE base stations in rural areas in 2021, which helped it to control more than 44.5% of total 4G towers in the country (867 base stations) and grow its data subscribers.
Telecel has been struggling to maintain its market share over the past few years. It initially opted not to launch LTE along with competitors because it believed that the market was not ready. It eventually introduced LTE in late 2017 but had just 17 LTE base stations according to the regulator by mid-2022.
The government announced its plan to raise internet penetration to above 75.0% by 2025, up from 65.2% in Q2 2023. It announced the national broadband program covering 2023–2030 to reduce the cost of broadband access to 2% of the average monthly income from 10.1%. The government is committed to raising the funds for this plan which includes the deployment of fibre infrastructure for broadband access and backhaul. It also plans to deploy 300 base stations across the country to be shared by the operators to support mobile services in rural areas using the universal services fund.
This is a vital initiative as operators are struggling to finance their network deployment and upgrade their networks due to currency depreciation, and limited access to foreign currency to pay for equipment. Their revenues are also down due to the reduction in consumer spending as a result of inflation and reduced disposable income, which is impacting their ability to finance their infrastructure development plan.
It is clear, from the examples discussed above, that the role of governments and regulatory authorities is crucial to making mobile data services accessible in Africa. Operators need sufficient spectrum, favorable policies and regulations, and the support they need to expand 4G infrastructure. In light of the current macroeconomic and operational challenges hindering the adoption of 4G, such as spectrum availability, coverage requirements, and handset affordability, overcoming these challenges will help with the next phase of 5G development.
Connectivity is crucial to economic development, competitiveness, and innovation in the Middle East and Africa region. Ookla’s crowdsourced insights and data help policymakers make informed decisions on how to use spectrum efficiently and improve network performance and user experience. Ookla also regularly hosts events in the region to help regulators share knowledge and experiences on how to close the digital divide. Regulatory officials from Jordan, Palestine, Iraq, Qatar, Bahrain, and Libya attended the last regulatory summit in June 2023 in Jordan.
Ookla retains ownership of this article including all of the intellectual property rights, data, content graphs and analysis. This article may not be quoted, reproduced, distributed or published for any commercial purpose without prior consent. Members of the press and others using the findings in this article for non-commercial purposes are welcome to publicly share and link to report information with attribution to Ookla.