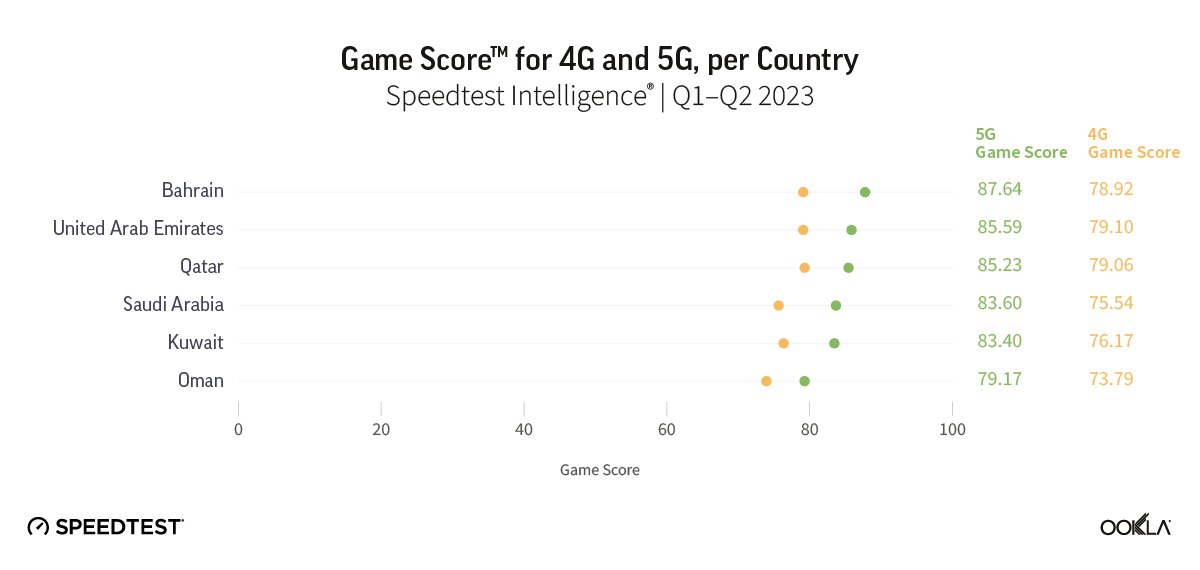
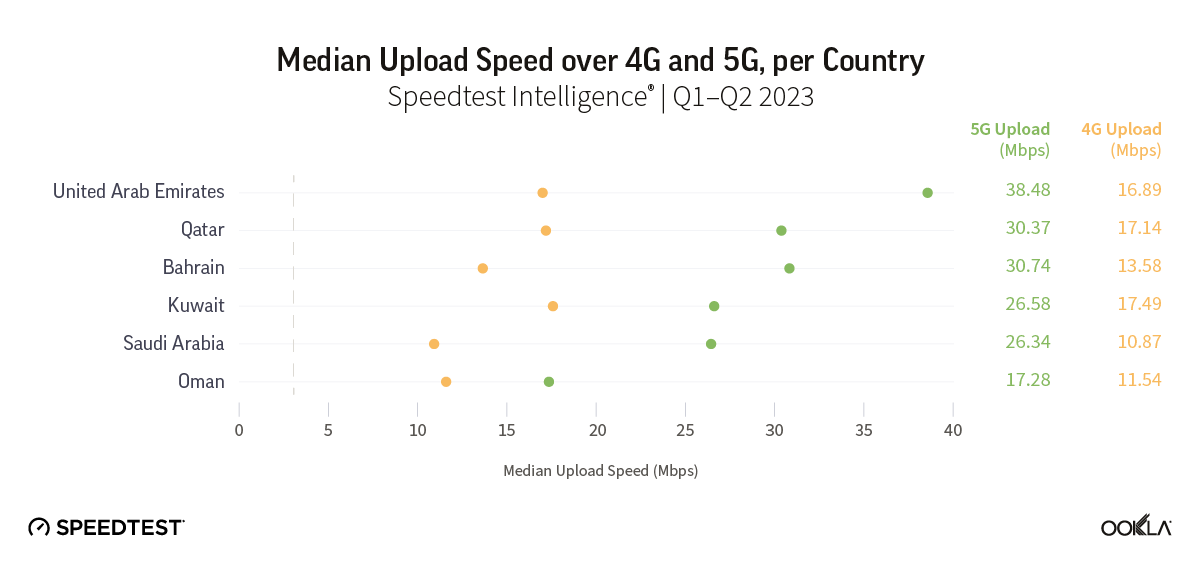
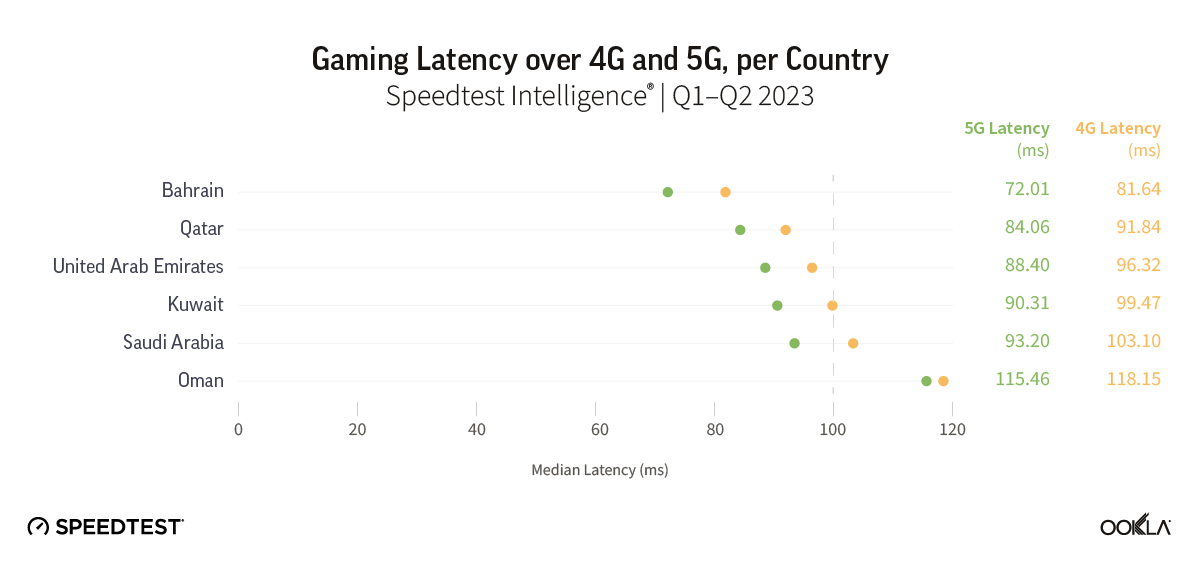
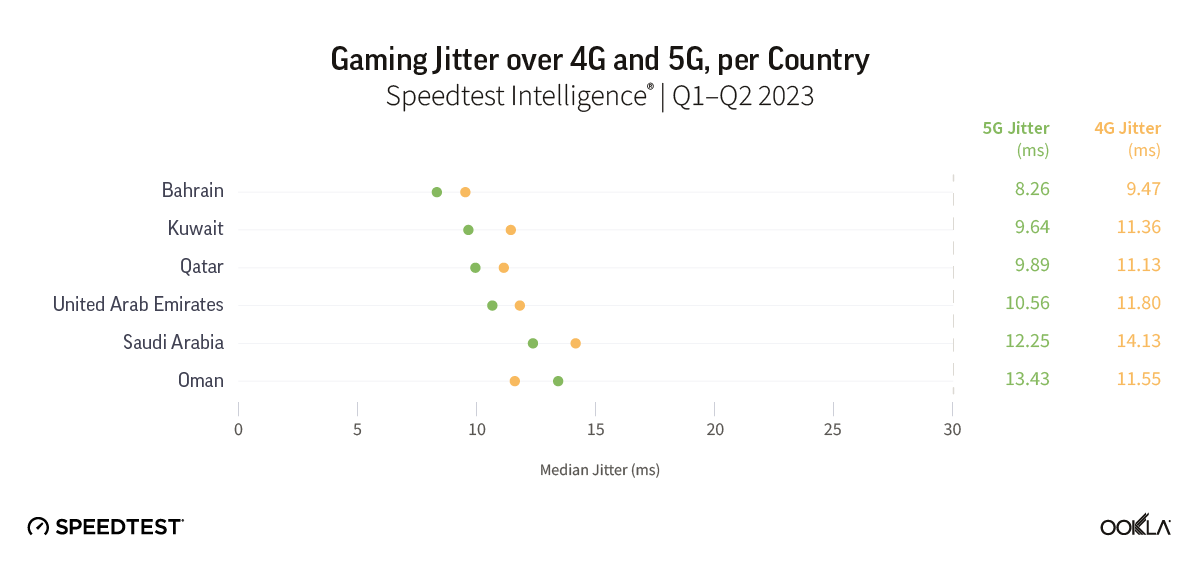
Belgium’s new entrant jolts the market with aggressive pricing, eyes Wi-Fi 7 in bid for QoE advantage
Romania’s DIGI has taken another bold step in its ambitious multi-country expansion strategy—the largest in Europe in over a decade—by launching fixed and mobile services in Belgium. It is replicating its signature disruptor strategy to swiftly capture market share, introducing a cut-price mobile tariff priced at €5 per month for 15 GB of data, alongside a fixed broadband offering at €10 per month for a 500 Mbps full-fibre connection.
The long-anticipated commercial launch is founded on a rebranded joint venture between Citymesh (51%), a subsidiary of IT services group Cegeka specialising in the B2B segment, and RCS & RDS, a subsidiary of the DIGI group. A five-year national roaming agreement with Proximus, Belgium’s largest mobile operator, has enabled DIGI’s market entry while it works to deploy its own greenfield radio infrastructure. DIGI aims to achieve 30% 5G population coverage by the end of 2025 and establish a network of 4,500 sites by the end of this decade.
As part of this roaming agreement, Proximus proposed to decommission and transfer around 400 of its own mobile sites to InSky, the company responsible for deploying the infrastructure for DIGI and Citymesh. With extensive spectrum holdings, including assets in the 700, 900, 1800 and 2100 MHz bands, along with a valuable 50 MHz of unpaired 3.6 GHz spectrum and 2.6 GHz frequencies it secured from neutral host operator Dense Air, it is fully equipped to execute its mobile network rollout.
DIGI subscribers rely on Proximus’ 4G network as it races to deploy its own 5G Standalone (SA) infrastructure
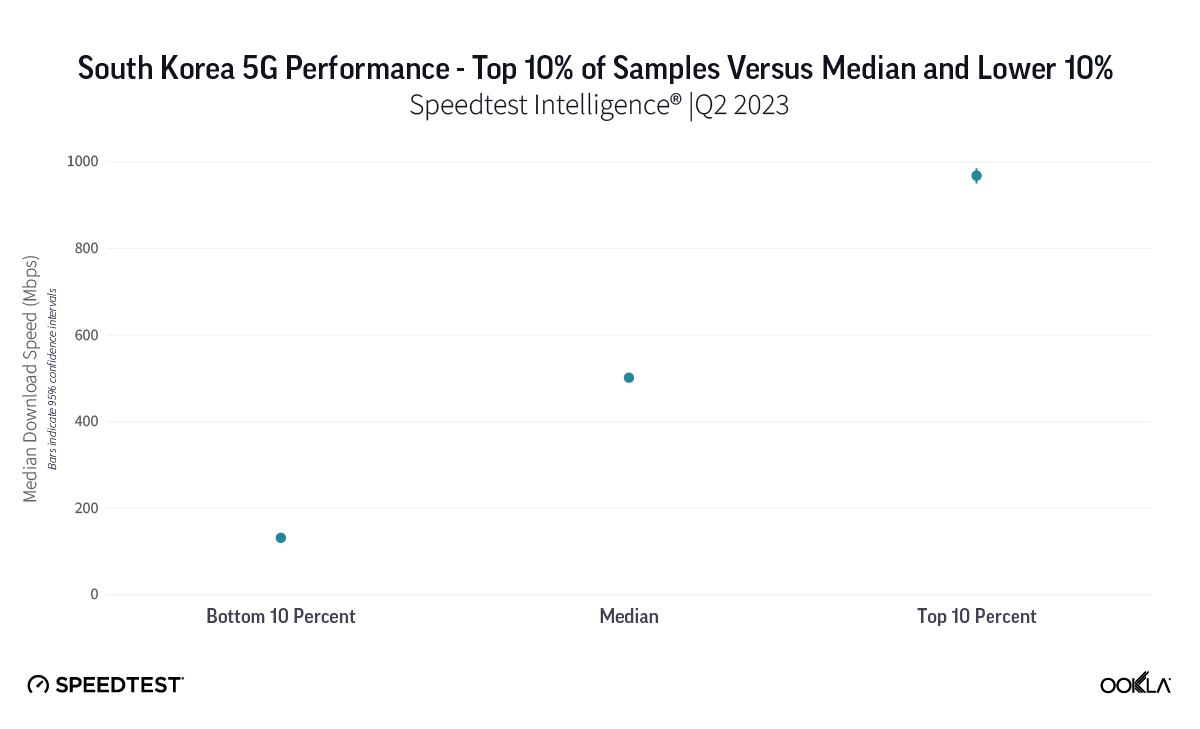
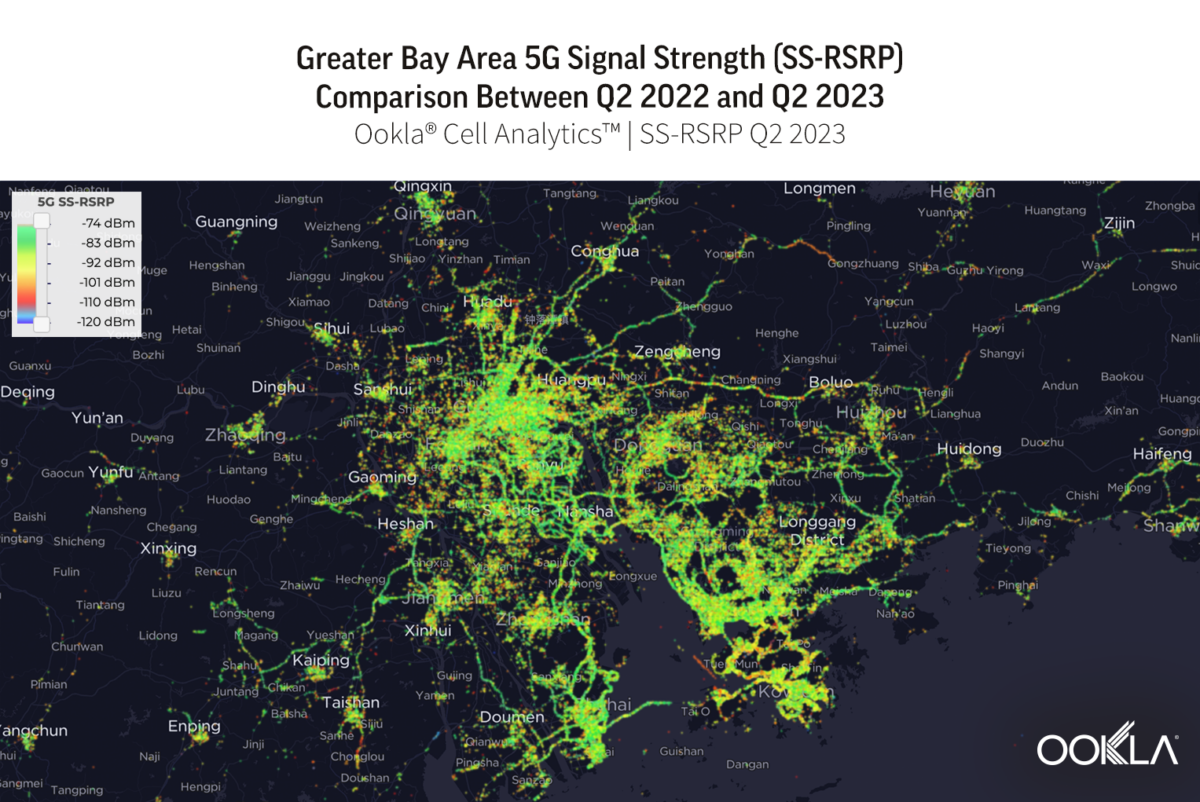
Subscribers to the new operator may initially be surprised by the limited availability of 5G services. DIGI’s roaming agreement with Proximus is restricted to its 4G network, with 5G access reliant on the progress of DIGI’s own greenfield site deployment. Whether this rollout will enhance Belgium’s international standing in 5G coverage remains to be seen, as the country continues to lag behind most of its developed peers due to delays in network deployment caused by conflicts between regional governments at the start of the 5G cycle.
Belgium continues to lag its neighbours in 5G Availability
Speedtest Intelligence® | Q3 2023 – Q3 2024
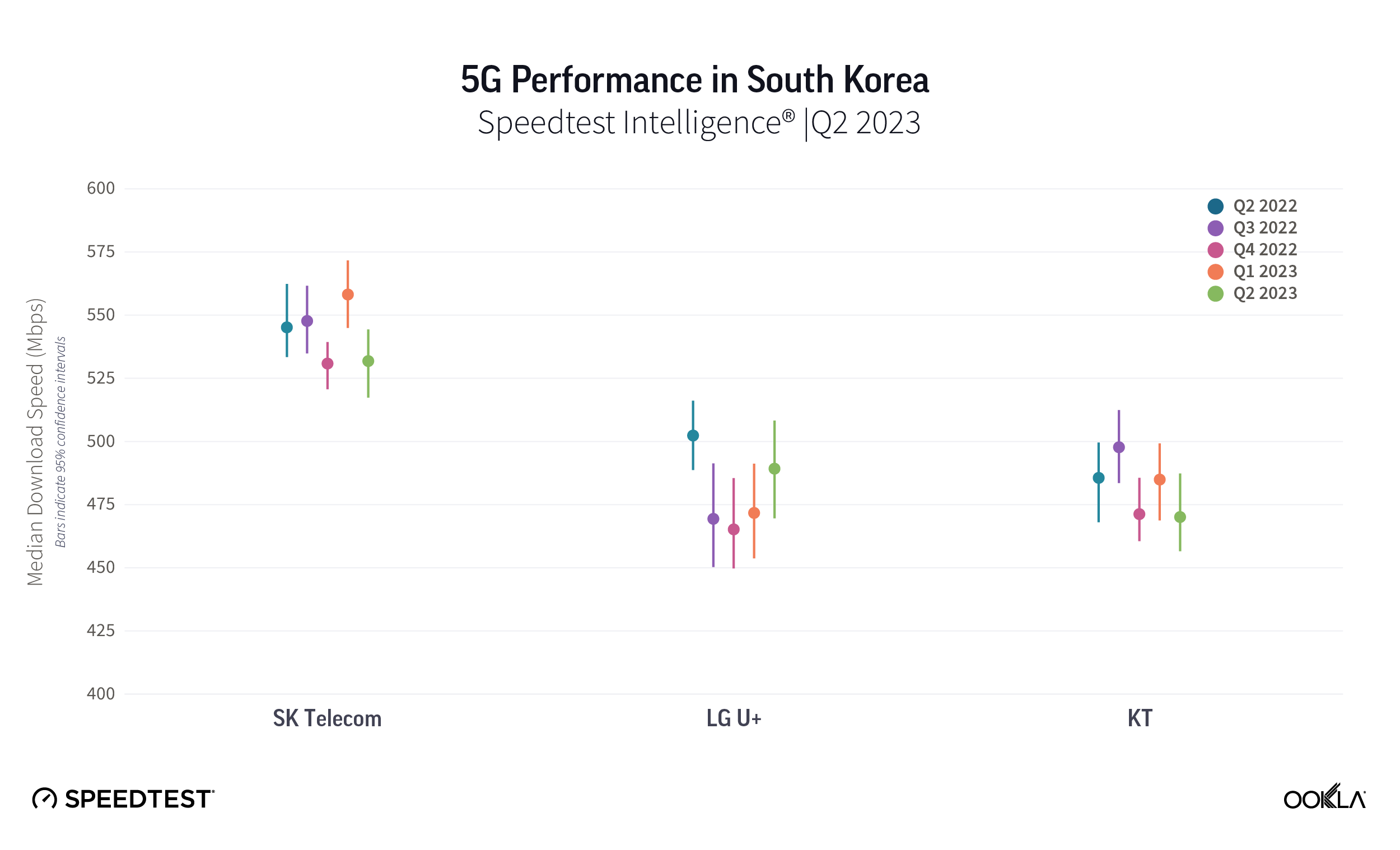
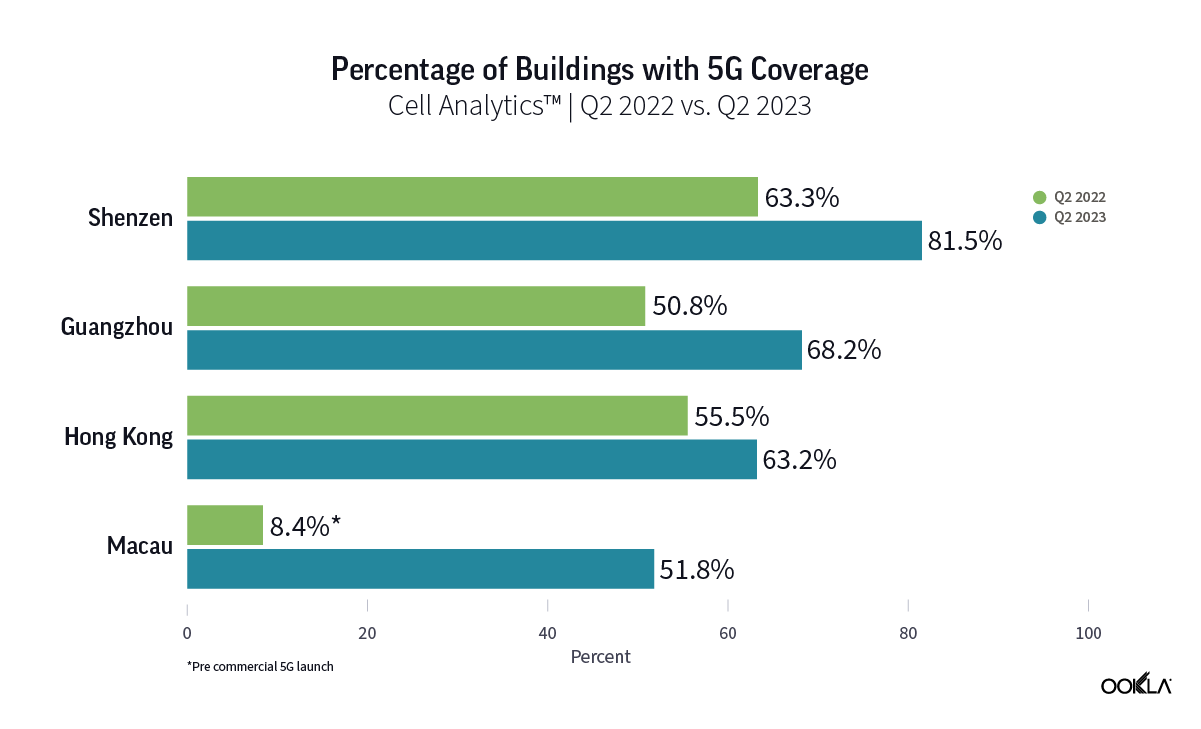
Analysis of Speedtest Intelligence® data from Q3 2024 reveals that Proximus, DIGI’s roaming partner, led the market in 4G download speed performance. Proximus’ subscribers enjoyed median 4G download speeds of 55.68 Mbps in the period, outperforming Telenet (47.91 Mbps) and Orange (36.22 Mbps).
DIGI subscribers will roam on Proximus' 4G network, which leads the Belgian market in 4G download speed performance
Speedtest Intelligence® | Q3 2023 – Q3 2024
However, this performance advantage does not extend to network reach. In Q3 2024, Proximus lagged behind its competitors in 4G Availability. Telenet led the market with 93.74% 4G Availability, followed by Orange at 86.02% and Proximus at 81.07%. Proximus’ comparatively lower 4G Availability has also contributed to its subscribers spending more time on 3G than those of other operators. On Proximus’ network, 11.21% of devices spent the majority of their time on 3G, compared to 7.92% on Orange’s network and just 3.41% on Telenet’s network.
Fibre ambitions put convergence and Wi-Fi 7 in the spotlight
DIGI’s ambitions in Belgium extend beyond disrupting the mobile market—it is taking aim at fixed broadband too. The operator has introduced ‘DIGI Fiber’, bringing its signature aggressive pricing to the FTTH market. Launching with a limited footprint in select Brussels suburbs, DIGI Fiber offers download speeds of up to 10 Gbps for as little as €20 per month. It plans to scale this fibre footprint rapidly, as it has done in Spain, targeting 2 million households within two years.
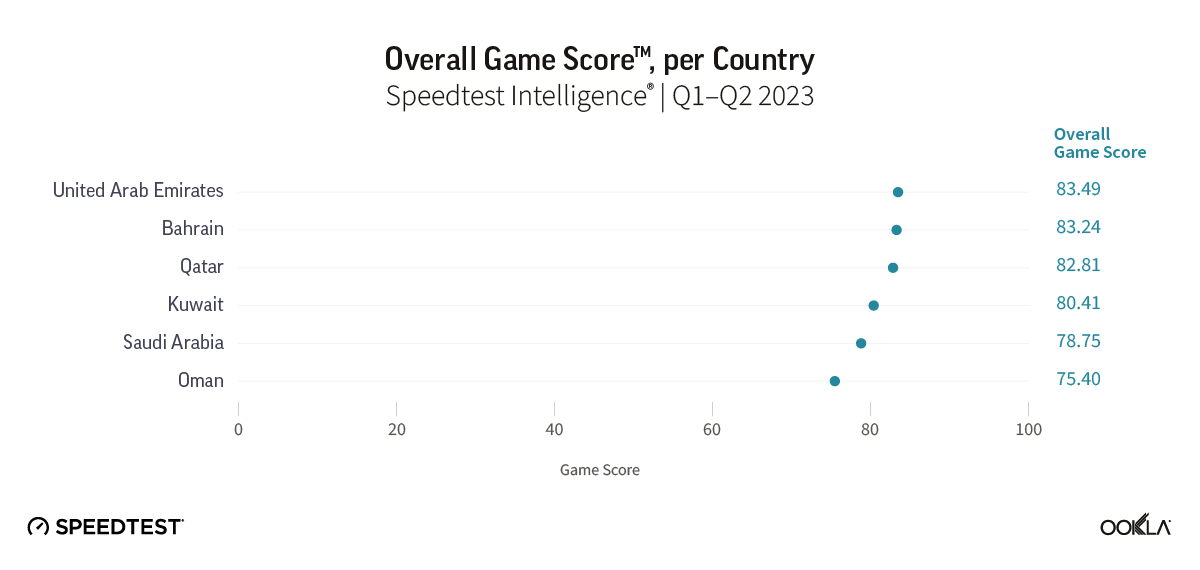
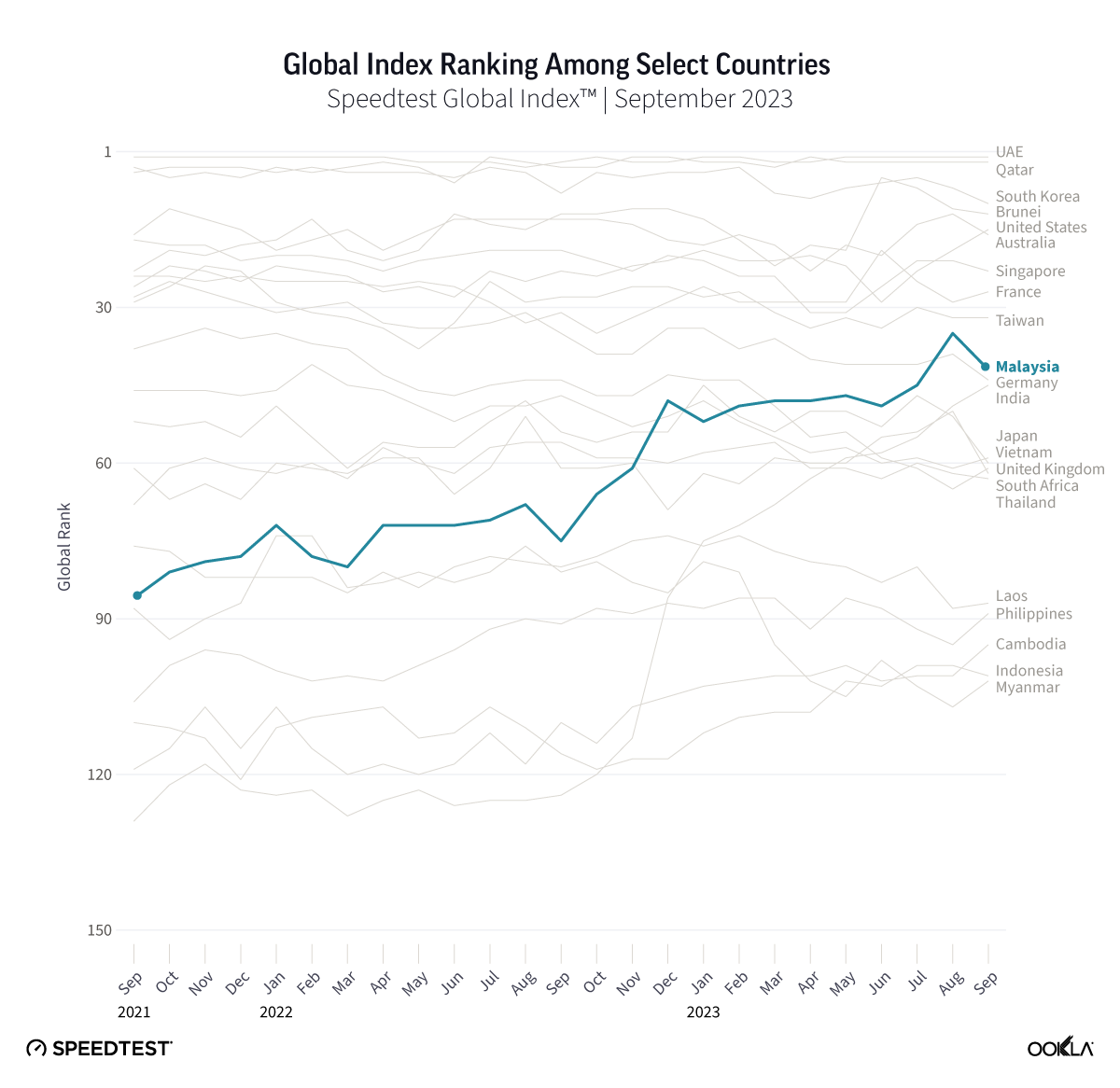
DIGI’s fibre offering is highly competitive in the Belgian market context, promising speeds that are many multiples of the country-wide median of 101.97 Mbps observed across fixed networks in Belgium in Q3 2024. While Proximus’ fibre service led the market during this period with median download speeds of 303.25 Mbps, DIGI’s entry may disrupt the market order.
Proximus Fiber leads in fixed download speed performance across Belgium's largest cities
Speedtest Intelligence® | Q3 2024
The operator is placing significant emphasis on Wi-Fi performance as part of its foray into the home, providing Wi-Fi 6-capable CPE as standard and preparing to introduce Wi-Fi 7 solutions “soon” for customers subscribing to its 10 Gbps service. This follows the playbook of other leading fixed operators seeking to differentiate fibre services through an enhanced focus on quality of experience (QoE) in the home, with BT’s EE in the UK and Iliad’s Free in France also debuting Wi-Fi 7 solutions in a bid to sell premium fibre experiences.
DIGI aims to leverage converged bundling of fixed and mobile tariffs to maximise customer retention and minimise churn, as it seeks to position itself as a leader in both price and network quality in Belgium. However, this convergence strategy is far from novel in the Belgian market, where competitors have successfully offered triple- and quad-play bundles for years. Notably, DIGI has yet to introduce a TV service in Belgium, leaving a gap in its bundling proposition at launch.
Has DIGI precipitated a race to the bottom in Belgium?
DIGI’s arrival disrupts a market long known for generating some of the highest average revenue per user (ARPU) levels in Western and Central Europe, coupled with a higher degree of market concentration compared to other countries in the region, based on analysis of GSMA Intelligence data. In Q3 2024, Belgian operators reported a monthly ARPU of €18.26, significantly outpacing neighbouring markets such as the Netherlands (€13.15) and Germany (€11.03).
Market incumbents have been bracing for an intense price war for some time. Earlier this year, Proximus cut its dividend, increased debt and struck agreements with alt-nets to accelerate its fibre rollout in Flanders. In a strategic counter move, Orange responded to DIGI’s aggressive mobile pricing by launching an equivalently priced tariff through its budget-focused ‘Hey!’ sub-brand, setting the stage for a race to the bottom in Belgium’s telecoms market.
This development shifts the Belgian market from a three- to four-player structure, marking a notable countertrend at a time when regulators in Brussels are signalling a softer stance on merger reviews and competition policy. It also follows closely on the heels of the Vodafone-Three merger approval in the UK, highlighting the increasingly diverse regulatory dynamics at play across Europe.
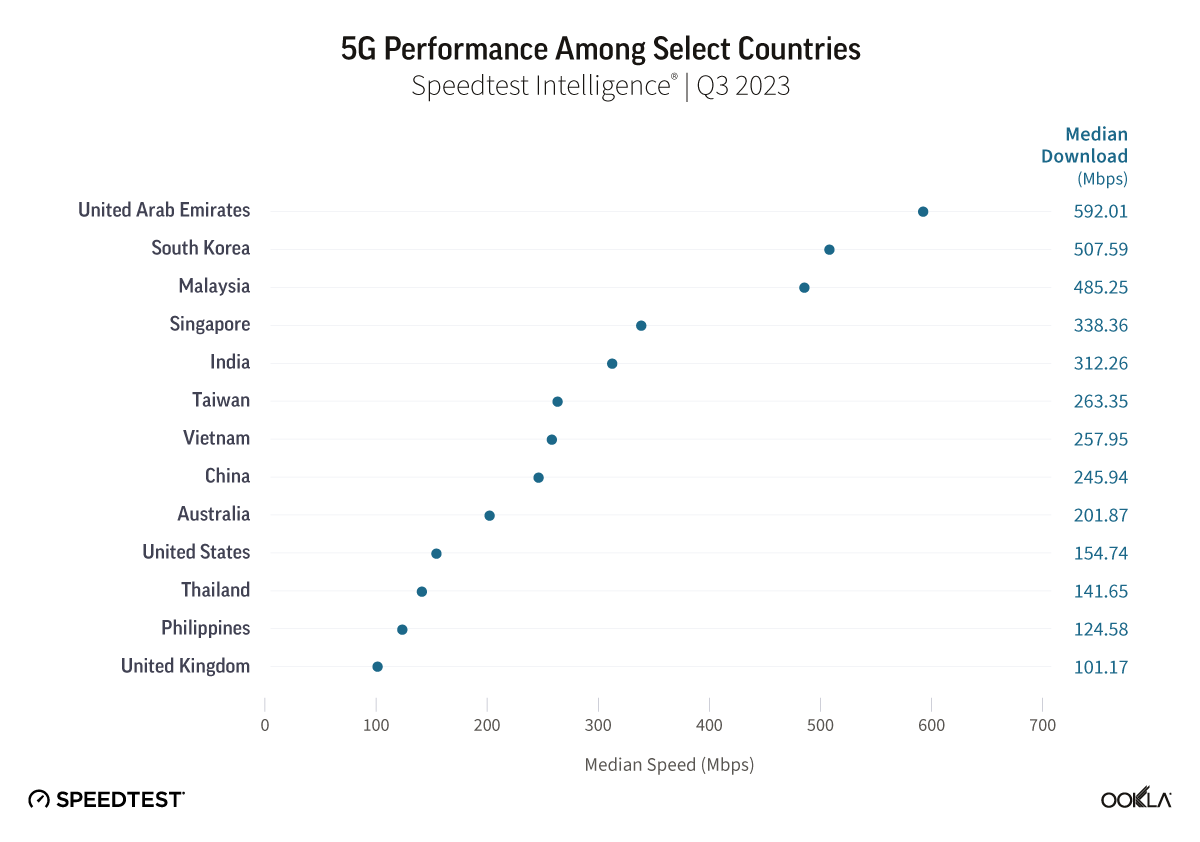
DIGI's success in Spain has been a cornerstone of its revenue growth, fueling its expansion ambitions in Belgium
Analysis of DIGI Group financial accounts | 2018 – 2024
Regardless of the outcome in the Belgian market, this marks a critical litmus test for DIGI’s growth ambition in Western Europe. Over the past decade, the Bucharest-based group has nearly tripled its annual revenues, growing from €624 million in 2013 to over €1.69 billion in 2023. It continues to distinguish itself through an obsessive strategic focus on operational efficiency—a model that has been similarly instrumental to Iliad’s success in Europe and its ability to achieve economies of scale.
This emphasis on a lean organisational structure has not dampened its long-term investment commitments. Last year alone, DIGI splurged €729.7 million on network spending and sold part of its fixed network in Spain to unlock additional funds for reinvestment, as it navigates a period of record capital intensity across its markets.
Ookla retains ownership of this article including all of the intellectual property rights, data, content graphs and analysis. This article may not be quoted, reproduced, distributed or published for any commercial purpose without prior consent. Members of the press and others using the findings in this article for non-commercial purposes are welcome to publicly share and link to report information with attribution to Ookla.