Airports in the United States have seen record-breaking numbers of travelers this year, and the always-busy Thanksgiving weekend could put even more stress on airport services. Including free Wi-Fi. We took a careful look at recent performance at the 50 largest airports by passenger volume in the U.S. as part of our ongoing series to help you plan ahead. Speeds have slipped at some of the top airports, but two more airports have free Wi-Fi download speeds over 150 Mbps than last year. Read on for details.
10 airports have free fixed broadband Wi-Fi over 150 Mbps
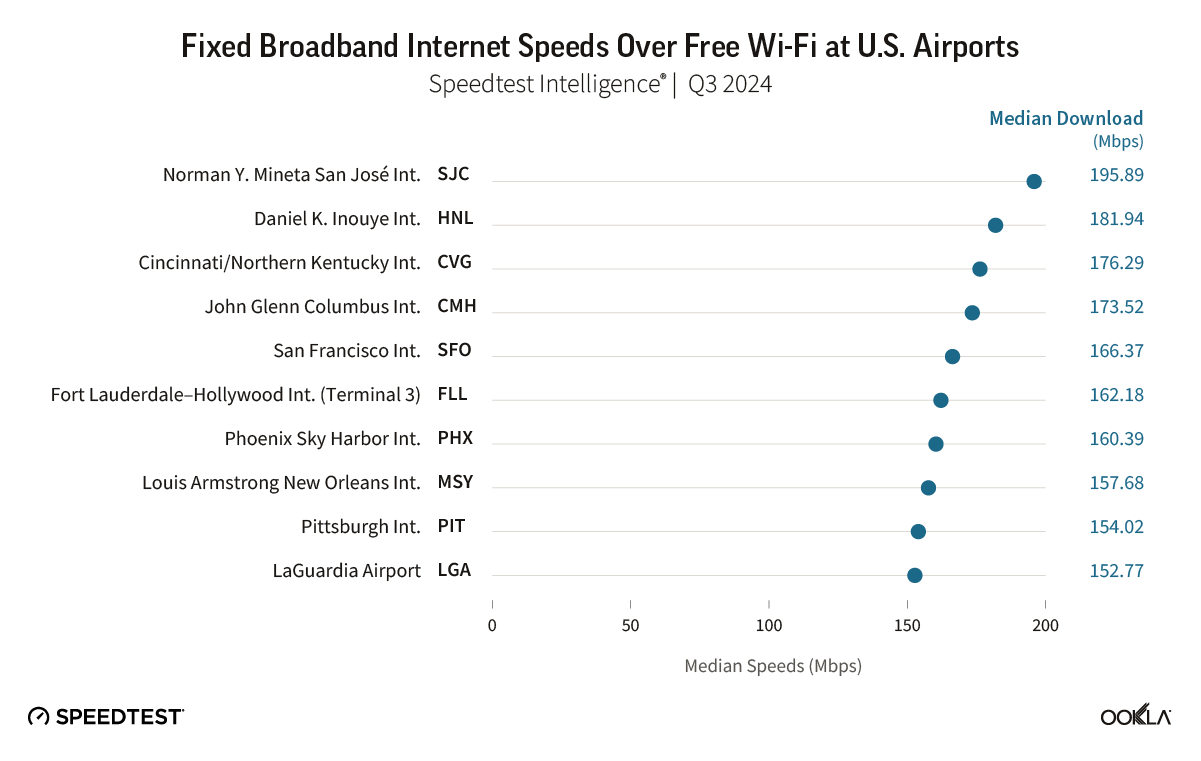
Fixed Broadband Internet Download Speeds Over Free Wi-Fi at U.S. Airports
Speedtest Intelligence® | Q3 2024
A map showing fixed broadband speeds in selected airports in the United States.
Speedtest Intelligence® shows Norman Y. Mineta San José International Airport, Daniel K. Inouye International Airport, and Cincinnati/Northern Kentucky International Airport were once again home to some of the fastest free airport Wi-Fi among the country’s busiest airports, with median download speeds of 195.89 Mbps (down from 259.37 Mbps last year), 181.94 Mbps (down from 187.58 Mbps), and 176.29 Mbps (down from 210.09 Mbps), respectively, during Q3 2024.
Rounding out the top 10 were:
- John Glenn Columbus International Airport (173.52 Mbps),
- San Francisco International Airport (166.37 Mbps),
- Fort Lauderdale–Hollywood International Airport (162.18 Mbps in Terminal 3),
- Phoenix Sky Harbor International Airport (160.39 Mbps),
- Fort Lauderdale–Hollywood International Airport (158.38 Mbps),
- Louis Armstrong New Orleans International Airport (157.68 Mbps),
- Pittsburgh International Airport (154.02 Mbps), and LaGuardia Airport (152.77 Mbps).
Keep in mind that 150 Mbps is more than fast enough for 4K streaming and multi-player gaming.
Ekahau®, our Wi-Fi solution, helps airports and other large-scale businesses ensure the networks you depend on are meeting your needs. Unfortunately, some airports are still not meeting the Wi-Fi optimization challenge. Specifically, two airports (William P. Hobby Airport and George Bush Intercontinental Airport) showed median download speeds over Wi-Fi of less than 25 Mbps. However, we are heartened that this is down from five last year with Raleigh-Durham International Airport, Philadelphia International Airport (Free PHL Airport WiFi-24), and Logan International Airport graduating by improving their speeds.
There was one change to our airport list this year, which is based on passenger volume: Kahului Airport was removed and John Glenn Columbus International Airport added. We have not included Kansas City International Airport, San Francisco Bay Oakland International Airport, San Antonio International Airport, or San Diego International Airport because there were insufficient samples.
Fort Lauderdale-Hollywood International Airport splits their free airport Wi-Fi among four separate SSIDs for different terminals, which we have listed separately in these results. While terminals 2 and 3 have a slight edge, the performance does not vary widely enough between them to intentionally hang out in the wrong terminal just to get a minor bump in speed, but if you’re in Philadelphia you definitely want to choose “Free PHL Airport WiFi” when possible, rather than “Free PHL Airport WiFi-24” if your device supports 5 GHz.
Mobile performance at 24 airports beats 150 Mbps
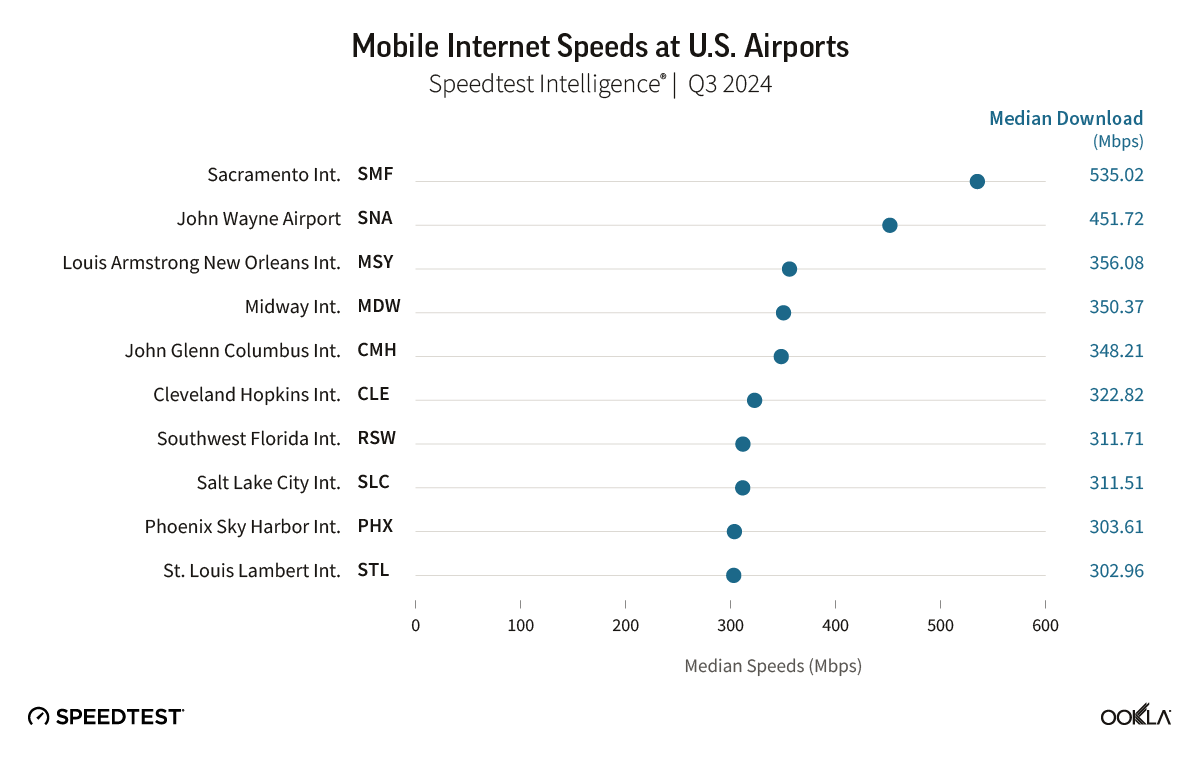
Mobile Internet Download Speeds at U.S. Airports
Speedtest Intelligence® | Q3 2024
Speedtest Intelligence® shows Sacramento International Airport and John Wayne Airport were the fastest airports on our list for mobile download speed during Q4 2024 at 535.02 Mbps and 451.72 Mbps, respectively. In all, 24 airports in our study had median download speeds over 150 Mbps, up from 18 in 2023. Fifteen of the airports showed median download speeds over 200 Mbps in 2024.
We’re happy to report that no airport on our list showed median mobile download speeds of less than 25 Mbps.
Wi-Fi or mobile? The airports where it makes a difference
Where Wi-Fi wins
Wi-Fi is the fastest choice at 10 airports where download speed over mobile network service is significantly slower than the free airport Wi-Fi. Details on how much faster the Wi-Fi is than mobile are as follows:
- 102% at Hartsfield–Jackson Atlanta International Airport,
- 90% at Orlando International Airport,
- 82% at San Francisco International Airport,
- 77% at Dallas/Fort Worth International Airport,
- 70% at Seattle-Tacoma International Airport,
- 42% at Baltimore/Washington International Airport,
- 28% at John F. Kennedy International Airport,
- 25% at Harry Reid International Airport, and
- 10% at Daniel K. Inouye International Airport.
It’s important to note that many of these differences are smaller than last year as mobile speeds are catching up to Wi-Fi capabilities.
Places to choose mobile service instead
Twenty-nine airports had faster download speeds over mobile than over free airport Wi-Fi during Q3 2024. Special mention goes to the following airports with massive improvements:
- Southwest Florida International Airport showed mobile service 635% faster than airport Wi-Fi,
- Mobile at Tampa International Airport was 528% faster than Wi-Fi, and
- Mobile was 341% faster than airport Wi-Fi at Sacramento International Airport.
Mobile service was 4X faster than airport Wi-Fi at:
- Salt Lake City International Airport, Logan International Airport, and
- Cleveland Hopkins International Airport.
Mobile was 3X faster than airport Wi-Fi at:
- Philadelphia International Airport,
- Indianapolis International Airport,
- John Wayne Airport,
- Denver International Airport,
- Detroit Metropolitan Airport, and
- George Bush Intercontinental Airport.
Mobile service was 2X faster at:
- Raleigh-Durham International Airport,
- Midway International Airport,
- Portland International Airport,
- St. Louis Lambert International Airport,
- Austin–Bergstrom International Airport,
- William P. Hobby Airport,
- Minneapolis–Saint Paul International Airport,
- Los Angeles International Airport,
- Louis Armstrong New Orleans International Airport,
- Phoenix Sky Harbor International Airport,
- John Glenn Columbus International Airport,
- Ronald Reagan Washington National Airport, and
- Miami International Airport.
And mobile service was 1X faster than airport Wi-Fi at:
- Charlotte Douglas International Airport,
- Washington Dulles International Airport,
- LaGuardia Airport, and
- Nashville International Airport.
All in all, it looks like your airport internet will probably be faster than the security line, and in many airports, faster than your mobile service. Set yourself up for success by downloading a few of your favorite shows along with the Speedtest apps for Android and iOS before you leave the house. And while you’re waiting for that flight, help out travelers next year by taking a Speedtest at the airport to share your experience.
Ookla retains ownership of this article including all of the intellectual property rights, data, content graphs and analysis. This article may not be quoted, reproduced, distributed or published for any commercial purpose without prior consent. Members of the press and others using the findings in this article for non-commercial purposes are welcome to publicly share and link to report information with attribution to Ookla.