This article examines the mobile performance of select MTN subsidiaries and joint-venture (hereafter referred to as “opcos”) across five of its nine markets in West and Central Africa (WCA). We look at how these opcos’ performance compares with each other and how it evolved between Q2 2022 and Q2 2024, analyze the factors that impacted their performance, and discuss their 5G plans.
Key Takeaways:
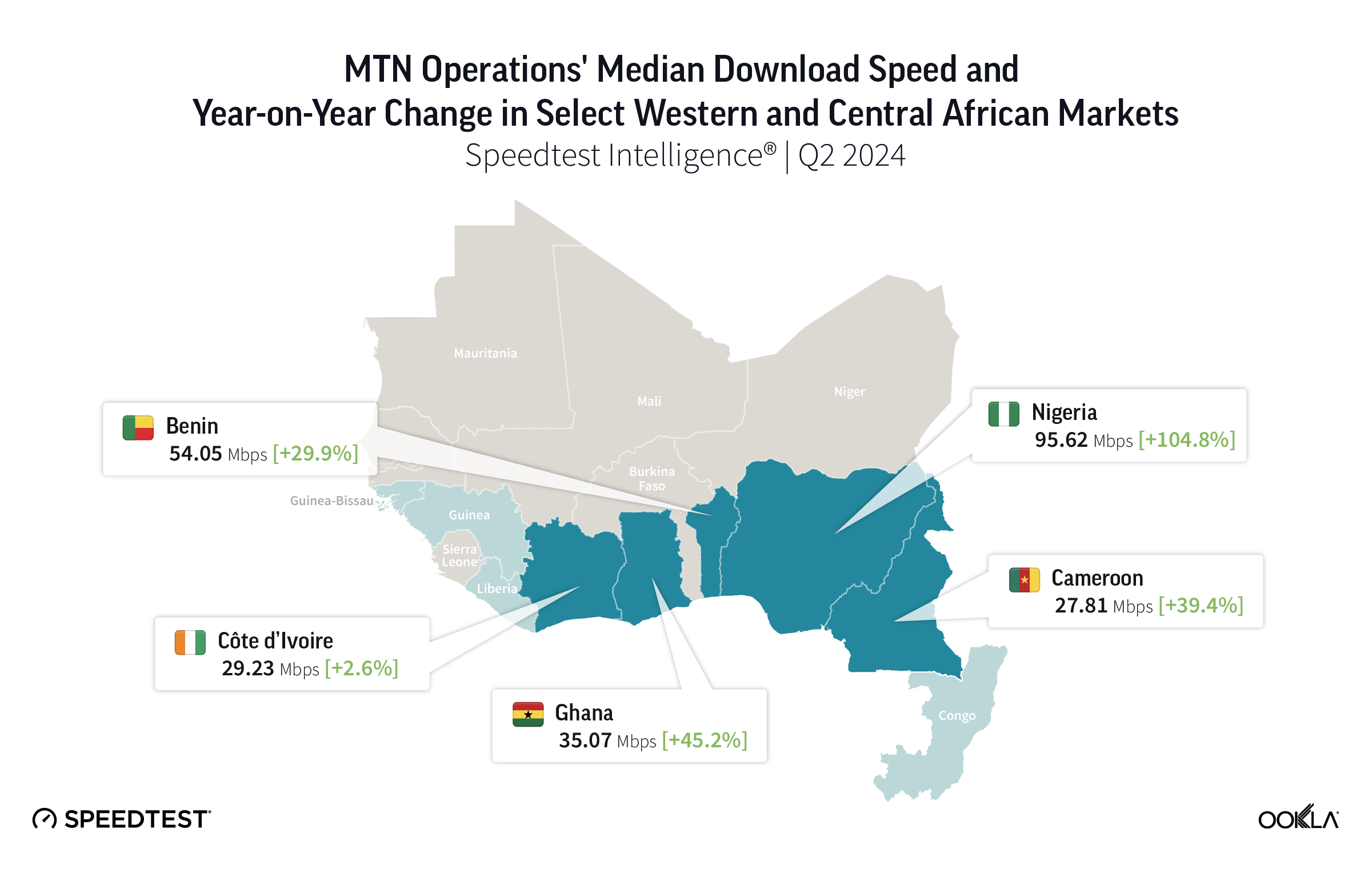
- Nigeria leads MTN opcos in West and Central Africa (WCA) in mobile download speed for handsets with modern chipsets, according to Speedtest Intelligence®. In Q2 2024, MTN Nigeria significantly widened its lead over the other opcos in WCA in terms of download speeds, reaching 95.62 Mbps. MTN Nigeria also excelled in median upload speed at 17.01 Mbps, closely followed by MTN Ghana at 16.74 Mbps.
- Despite challenging macroeconomic and operational conditions, MTN opcos in WCA improved their network performance. While all reviewed MTN opcos rose in performance since Q2 2022, Nigeria and Ghana stood out by moving up the most in download and upload speed rankings over the last 2 years. The two opcos were also the front runners for median multi-server latency, with Ghana achieving this without launching 5G.
- 5G service availability in Nigeria has significantly improved over the last 18 months. Speedtest Intelligence shows that 5G Service —a geospatial measure of the percentage of an operator’s known locations with 5G service— in Nigeria increased from 17.2% in Q1 2023 to 35.70% in Q2 2024, surpassing South Africa’s 31.6%.
MTN aims to continue investing in new network technologies and bridging the broadband coverage divide to remain competitive
MTN is the largest operator group in Africa operating in 15 markets, offering voice, data, fintech, digital, enterprise, and wholesale services to nearly 300 million fixed and mobile subscribers. MTN Group’s service revenue grew by 13.5% to ZAR210 billion ($11.1 billion), driven by data revenue of ZAR 84 billion ($4.5 billion) and voice revenue of ZAR 83 billion ($4.4 billion).
African countries in the MTN footprint face economic and political challenges, including slowing growth, high inflation, currency devaluation, and political instability in neighboring countries. These conditions dampen investment appetite and increase the cost of doing business. However, the large, fast-growing, and youthful population combined with low levels of data and digital adoption offer significant growth opportunities for telecom operators like MTN.
In 2023, service revenue from West and Central Africa (WCA) accounted for 63.6% of the Group’s revenue. Data revenue surged by 51.3% (excluding Nigeria) and by 38.6% in Nigeria, driven by increased data users and traffic and supported by network investments.
At the beginning of 2021, MTN announced its Ambition 2025 strategy to provide ‘leading digital solutions for Africa’s progress’. This growth strategy’s objective is to double the number of consumer mobile data users to 200 million and home broadband customers to 10 million by 2025, achieve 95% broadband population coverage, and ensure data contributes to half of the Group’s total revenue. This strategy is supported by network expansion, modernization, and improved service affordability.
In the following sections, we analyze MTN opcos’ performance in WCA and review their network deployment plans, including 5G.
Nigeria delivered the fastest median download speed in Q2 2024 across MTN opcos in WCA
In a previous article, we found that MTN performed best among other operator groups in Sub-Saharan Africa during Q2 2022. For the current analysis, we use Speedtest Intelligence data to compare mobile performance between Q2 2022 and Q2 2024 on modern chipsets across select five (out of nine) MTN opcos in WCA.
Our results show that Nigeria led MTN’s opcos in WCA in median download speeds, achieving 95.62 Mbps in Q2 2024. Nigeria along with Ghana, more than tripled their median download speeds within two years. Benin, Cameroon, and Nigeria saw greater jumps in download speeds between 2023 and 2024 compared to the previous year.
Generally, all opcos saw more modest improvements in upload speed compared to download speeds. MTN Nigeria led the group with a median upload speed of 17.01 Mbps in Q2 2024, closely followed by MTN Ghana at 16.74 Mbps. Both countries significantly increased their upload speeds between Q2 2022 and Q2 2024.
Cellular Network Performance, Select MTN Operators in West and Central Africa
Source: Speedtest Intelligence® | Q2 2022 – Q2 2024
Cellular Network Performance, Select MTN Operators in West and Central Africa
MTN Nigeria outperformed the other opcos in the region with a substantial margin in median download speed. Its upload speed also saw a remarkable recovery with an impressive 17.01 Mbps in Q2 2024.
MTN Benin’s download speed significantly increased between Q2 2022 and Q2 2023, plateauing around 56 Mbps. It then slightly declined during H1 2024, maintaining its position as the second-fastest opco in WCA.
MTN Ghana made an impressive turnaround, climbing from the bottom to among the top three operators in download and upload speeds. Its download speed increased more than 3x (similar to Nigeria’s improvement rate), and its upload speed more than doubled over the two years to Q2 2024. This improvement was partly due to MTN’s investments in network infrastructure and high smartphone penetration among its subscribers (63.8%) in 2023.
MTN Côte d’Ivoire, the second-largest mobile operator in the country, saw modest performance improvements until the end of 2023. Then download speeds peaked at 39.49 Mbps in Q1 2024, around the start of the African Football Championship (CAN), but fell to 29.23 Mbps in Q2 2024. Upload speeds also improved, but not as significantly as download speeds. MTN Cameroon showed the smallest network performance improvement over the two years, ending at the bottom of the pack.
MTN Ghana and Nigeria were the front runners for median latency, maintaining a tight range of approximately 42 ms to 54 ms between Q2 2022 and Q2 2024. Opco latency in Benin and Côte d’Ivoire fluctuated between a low of around 38 ms and a high of 143 ms. MTN Cameroon consistently had higher latency, over 230 ms, throughout the period.
MTN Nigeria could further solidify its leadership in Africa by expanding 5G coverage and boosting adoption rates
Nigeria, the continent’s most populous country, boasts the largest mobile market, with 217.5 million subscribers in 2023. Following regulatory impacts from the two SIM campaigns in 2017 and 2021, market growth resumed and is projected to continue into 2024. The country presents significant growth opportunities for data services, with internet penetration reaching 45.4% in 2023
However, Nigeria faces economic challenges, including currency depreciation, high inflation, and a shortage of hard currency. Operational challenges such as fuel shortages, infrastructure vandalism, and regional unrest also impede infrastructure expansion and maintenance. Despite these hurdles, MTN Group announced in 2023 its ambition to invest $3.5 billion in Nigeria over the next five years.
MTN was the first operator to launch 5G in Nigeria, followed by Airtel and ISP Mafab Communications in June and January 2023, respectively. By December 2023, MTN Nigeria’s 5G network covered 11.3% of the population. However, according to the Nigerian Communications Commission (NCC), Nigeria had 2.3 million 5G subscribers by the end of 2023, representing just 1.04% of the total 224.7 million active mobile subscribers.5G coverage has improved over the last 18 months. Speedtest Intelligence shows that 5G Service —a geospatial measure of the percentage of an operator’s known locations with 5G service— in Nigeria increased from 17.2% in Q1 2023 to 35.70% in Q2 2024, surpassing South Africa’s 31.6%. MTN invested $120 million to raise 5G network coverage from 3% to 11%, extending service to key cities in all six regions, but further expansion is needed.
Speedtest Intelligence’s 5G Availability data, which measures the percentage of users with 5G-capable devices who spend most of their time on a 4G or 5G network, indicates an upward trend in Nigeria to reach 13.9% in Q2 2024, reflecting increased service activation and adoption. However, the level remains low compared to South Africa, which reached 31.3% in Q2 2024. Customers may hesitate to activate 5G due to data usage and battery life concerns. MTN can address these concerns by offering affordable data plans and financing options to facilitate the acquisition of newer, more energy-efficient devices.
5G Service and 5G Availability, Nigeria
Source: Speedtest Intelligence® | Q1 2023 – Q2 2024
5G Service and 5G Availability, Nigeria
Apart from Nigeria, MTN’s 5G rollout plans in West and Central Africa are progressing slowly
Côte d’Ivoire is the only other country in the region where MTN launched 5G services. The rollout coincided with the African Football Championship (CAN) in January 2024, covering Abidjan and several major cities. Despite network rollout delays and logistics bottlenecks in 2023, MTN also upgraded its 4G networks in late 2023 in preparation for the football competition. The local telecom regulator, ARTCI (Autorite de Regulation des Telecommunications de Côte d’Ivoire), considered introducing network sharing to expedite 5G deployment, similar to the model adopted in Malaysia, but there have been no updates on this plan so far in 2024.
In the rest of the WCA region, MTN has conducted 5G pilot projects, such as in the Republic of Congo (Congo-Brazzaville) but remains committed to investing in 4G infrastructure to enhance accessibility. In Cameroon, MTN has been expanding its network capabilities and testing 5G since 2021. In 2023, it committed $200 million over three years towards network services. MTN has also pledged to invest $215 million over the next three years in Benin to develop its 5G infrastructure following successful trials.
In Ghana, MTN initially announced its readiness to roll out 5G in 2022, but the National Communications Authority (NCA) did not grant it the license, considering a shared infrastructure approach. Macroeconomic challenges, including slowed-down economic growth, high inflation (averaging 40.3% in 2023), and currency devaluation (down 34.5% against the US dollar), have also delayed the 5G rollout. In May 2024, the Ghanaian government partnered with seven industry players (excluding MTN) to establish the Next-Gen Infrastructure Company (NGIC) to deploy the infrastructure and launch 5G services within six months. However, concerns have been raised over the lack of transparency around this partnership. NGIC eventually launched 5G on the first of November, 2024. Finally, MTN confirmed its plan to exit Guinea-Bissau and Guinea-Conakry due to high risk and limited growth.
This analysis shows that mobile network performance has improved significantly in some key West and Central African markets. The impact of 5G has so far been limited to Nigeria as it is still in its early stages in most of the region. MTN is keen to expand 5G coverage to the rest of its footprint, following the examples of Nigeria and Côte d’Ivoire, while continuing to invest in its 4G network infrastructure. Despite ongoing political and macroeconomic challenges, MTN and other operators in the region are well-positioned to meet the growing demand for high-speed broadband.
We will continue to monitor mobile networks’ performance across Africa, benchmark countries, and operators, and explore how various factors affect it. For more information about Speedtest Intelligence data and insights, please contact us.
Ookla retains ownership of this article including all of the intellectual property rights, data, content graphs and analysis. This article may not be quoted, reproduced, distributed or published for any commercial purpose without prior consent. Members of the press and others using the findings in this article for non-commercial purposes are welcome to publicly share and link to report information with attribution to Ookla.