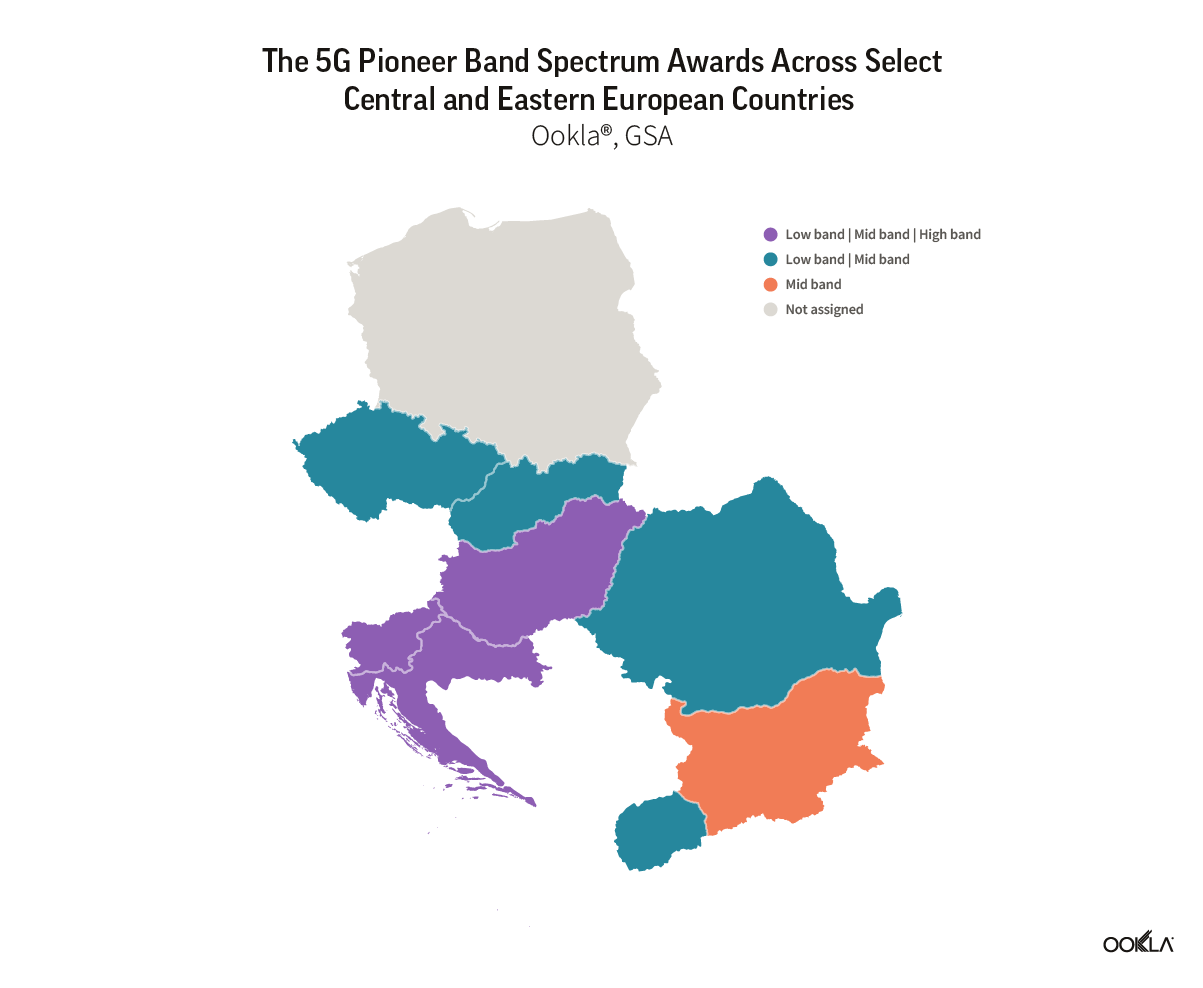
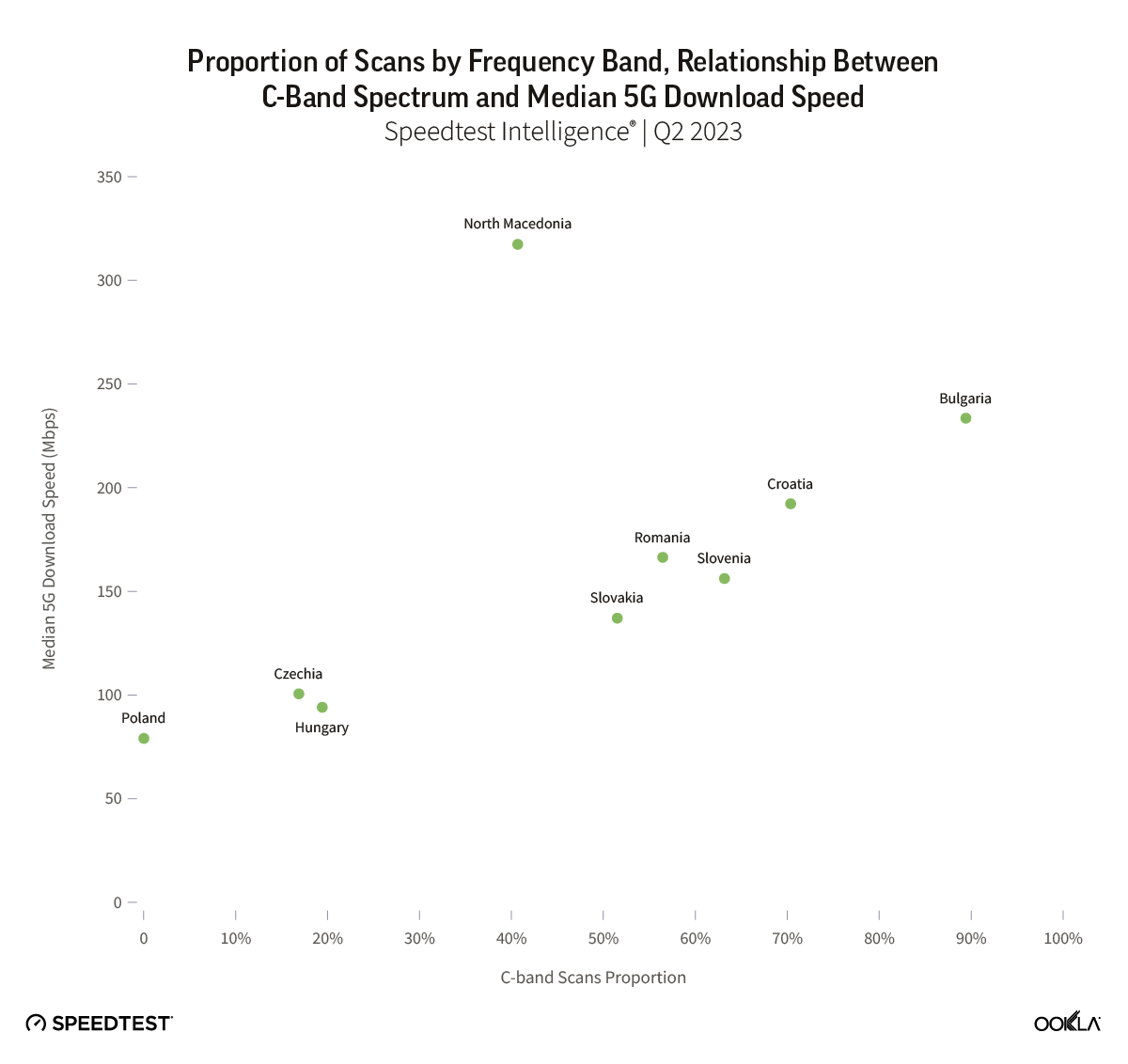
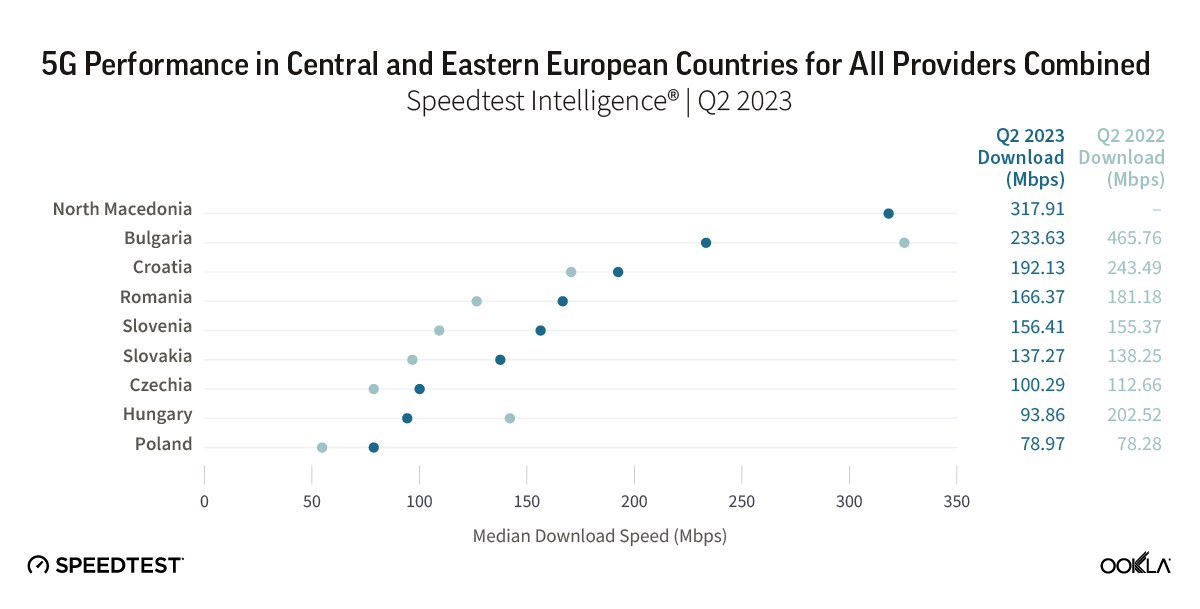
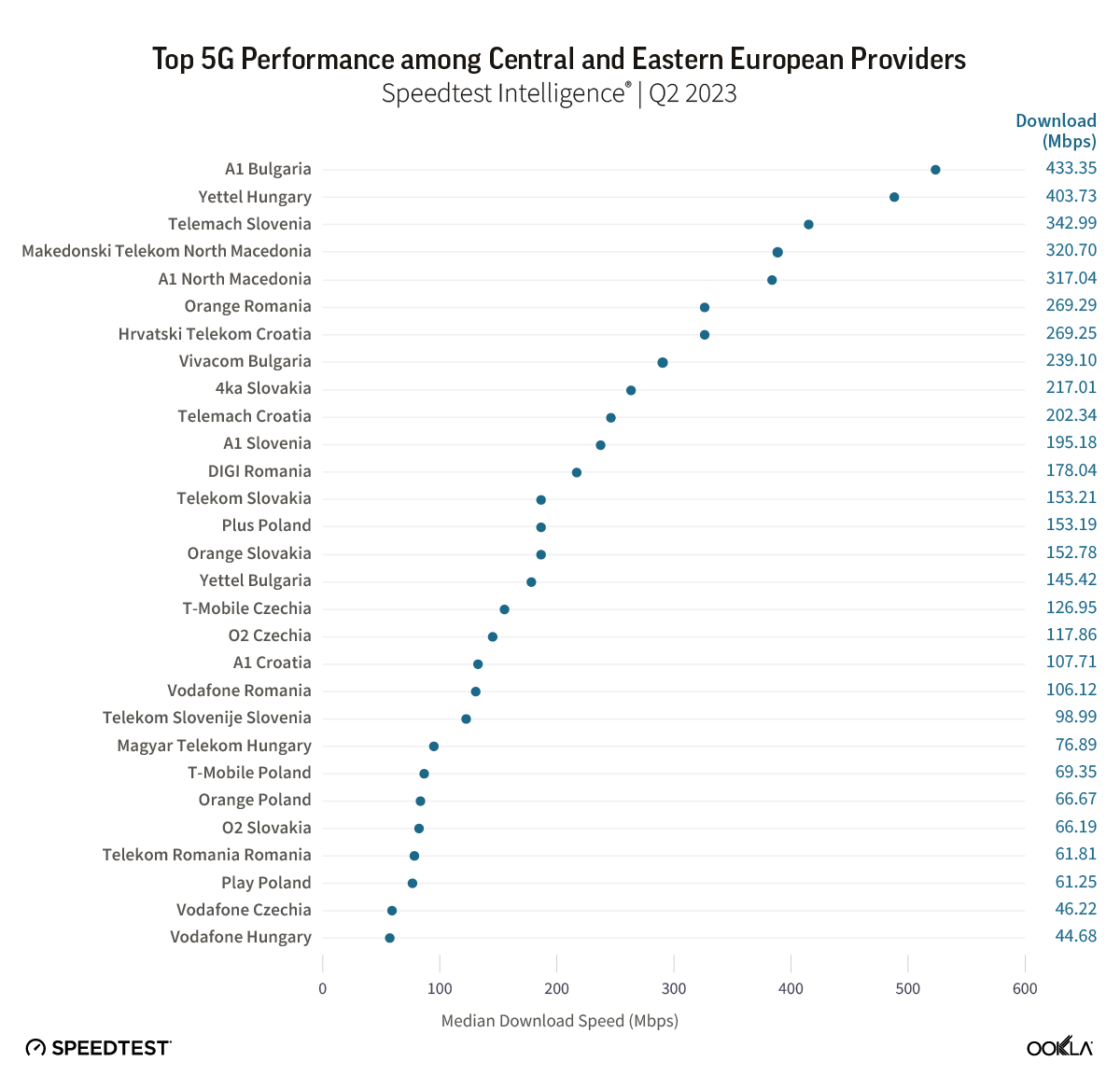
Mobile operators in the Czech Republic have made progress in expanding 5G coverage and improving network performance. In this article, we review the 5G performance of O2, T-Mobile, and Vodafone at the national level between Q2 2022 and Q2 2024 and highlight their achievements in three regions.
Key Takeaways:
-
- O2 and T-Mobile have steadily increased their download and upload speeds since Q2 2022. O2 saw its median download speed more than double in 2 years to reach 92.78 Mbps in Q2 2024 while T-Mobile achieved a median download speed of 95.48 Mbps. The median upload speed is more highly contested by the two operators, with O2 taking pole position with 23.85 Mbps in Q2 2024. O2 also steadily improved its multi-server latency, leading the market with 33.34 ms in Q2 2024.
- All operators have considerably improved their 5G coverage since Q1 2023. The percentage of operators’ known locations where a device has access to 5G service has increased from 40.7% in Q1 2023 to 66.2% in Q2 2024. Operators’ efforts to deploy new base stations and use sub-1Ghz frequency bands have driven these coverage improvements.
- O2 leads in the capital region in 5G download speeds. O2 significantly outperforms its competitors in Prague in download speed at 241.86 Mbps compared to 167.85 Mbps for T-Mobile and 90.2 Mbps for Vodafone.
- T-Mobile provides faster 5G download speeds in some other regions. T-Mobile notably outperformed O2 in the Central Bohemian and South Moravian regions. T-Mobile download speeds in the two territories were 129.36 Mbps and 165.54 Mbps, respectively, compared to O2’s 93.02 Mbps and 136.68 Mbps.
O2 and T-Mobile consolidated their lead in 5G performance over the last year while Vodafone outperformed in 5G coverage
The Czech mobile market is very competitive with three key operators: O2, T-Mobile, and Vodafone. The country made a relatively early foray into 5G. O2 introduced 5G services first in July 2020, initially covering parts of Prague and Koline, after acquiring 700 MHz and 3400–3600 spectrum bands. Vodafone followed suit with its 5G network launch in October 2020 and T-Mobile the following month. In November 2023, O2 completed the rollout of 5G across Prague’s metro network, making it the first underground system in Europe with full 5G coverage.
The market remains dominated by the three operators despite the regulator’s efforts to encourage the entry of new players by auctioning the 700 MHz and 3.4-3.6 GHz spectrum bands in 2020. The silver lining is that access to the new spectrum, combined with the refarming of the sunset 3G spectrum, helped incumbent operators expand 5G coverage.
After T-Mobile and O2 began sharing their mobile infrastructure in 2012, their combined networks covered 85% of the population. Following the settlement of an antitrust dispute with the European Commission, they amended the network-sharing agreement in 2022 and extended it through October 2033 to support nationwide 5G deployment. Both operators committed to making their base stations 5G-ready and continue investing in the infrastructure. The network sharing agreement excluded the capital, Prague, and Brno for up to 10 years.
The network performance of both operators improved significantly since Q2 2022 according to Ookla® Speedtest Intelligence® data. O2 more than doubled its download speed over 2 years to reach 92.78 Mbps in Q2 2024, while T-Mobile pulled slightly ahead of O2 with a peak of 95.48 Mbps. The upload speeds of both operators remained relatively stable before Q3 2023 in the range of 15 Mbps to 20 Mbps before increasing, with O2 taking pole position with a speed of 23.85 Mbps in Q2 2024 and T-Mobile following closely behind at 21.28 Mbps. Vodafone’s download and upload speeds remained relatively flat over the same period before increasing rapidly from Q3 2023, in tandem with the other two operators, to reach 15.77 Mbps in Q2 2024.
O2 has maintained a relatively stable latency with a slight improvement observed since Q4 2023 resulting in the lowest latency in the market at 33.34 ms. T-Mobile exhibited a reduction in latency from Q3 2022 through Q1 2023, followed by an increase, bringing it closer to Vodafone’s performance by Q2 2024 at 35.4 ms. Vodafone gradually decreased its latency over the same period, almost converging with T-Mobile and O2 by Q2 2024.
All Technologies’ Network Performance, Czechia
Source: Speedtest Intelligence® | Q2 2022 — Q2 2024
All Technologies’ Network Performance, Czechia
Due to the growing adoption of 5G service, median 5G download and upload speeds have been declining since launch until 2023. This suggests a growing network usage while capacity was not increased sufficiently to cater to the growing demand. However, 5G network performance started recovering after 3Q 2023. T-Mobile leads the market with a 5G download speed of 153.12 Mbps in Q2 2024, after lagging behind O2 across most quarters since Q2 2022.
Vodafone’s 5G download speed has been declining until Q3 2023, when it reversed the trend rapidly to catch up with the other two operators, reaching 93.12 Mbps in Q2 2024. T-Mobile’s lead is more evident for 5G upload as the median speed reached 39.11 Mbps in Q2 2024, while O2 achieved a speed of 31.61 Mbps. Since Q3 2023, Vodafone’s upload speed gained nearly 10Mbps, reaching 20.52 Mbps.
Vodafone had the lowest download and upload speeds among the three operators throughout the period. The use of Dynamic Spectrum Sharing (DSS), which allows it to share spectrum between 4G and 5G, could explain Vodafone’s underperformance. While this approach enables Vodafone to offer 5G services without physically upgrading its radios, it also weighs on performance since both networks share the same radio spectrum. Furthermore, Vodafone demonstrated significant improvement since Q3 2023, suggesting a strategic focus on enhancing network capabilities to remain competitive.
O2 had the lowest 5G latency compared to T-Mobile and Vodafone during most quarters since Q2 2022, though it peaked around Q3 2023 at 32.9 ms before dropping to 31.3 ms in Q2 2024. T-Mobile exhibited the most significant fluctuation, with latency spiking in Q3 2022 but showing a general decline afterward, reaching comparable levels with Vodafone by Q2 2024. Vodafone also displayed a downward trend but remained above O2 throughout the period.
5G Network Performance, Czechia
Source: Speedtest Intelligence® | Q2 2022 — Q2 2024
5G Network Performance, Czechia
Operators have been using the 700MHz and 3500MHz spectrum bands acquired in 2020 to increase 5G coverage. According to Speedtest Intelligence, 5G Service, a geospatial measure of the percentage of an operator’s known locations where a device has access to 5G service (including roaming), has increased from 40.7% in Q1 2023 to 66.2% in Q2 2024. This significant improvement in coverage is driven mainly by Vodafone’s 5G coverage, with 5G Service value boosted from 59.3% to 78.5% during that period. Vodafone reported 70% coverage of the population within less than two years after launching 5G in 2020. O2 and T-Mobile also improved their 5G coverage during the same period to reach 65.8% and 60.0%, respectively, in Q2 2024, according to Speedtest Intelligence.
More users with 5G-enabled SIMs and handsets were connected to 5G networks in Czechia than before, indicating greater popularity and adoption. According to Speedtest Intelligence, 5G Availability, which represents the percentage of users with 5G-enabled devices and 5G-activated services that spend most of their time connected to 4G and 5G, has been increasing for all operators. Vodafone saw the fastest jump since Q1 2023 reaching 64.9% in Q2 2024. O2 and T-Mobile are also trending upwards and at a similar pace, reaching 35.2% and 40.2%, respectively.
O2 tops 5G performance in Prague but T-Mobile leads in other regions
O2 and T-Mobile have been competing for the top spot for 5G network performance. The tightening of the gap between the two operators in download speeds suggests that subscribers on either network can expect similar performance. However, this similarity in median download speed at the national level hides some disparities at the regional level. For example, O2 excels in Prague, the region with the most samples but lags behind T-Mobile in two parts of the country which are Central Bohemian and South Moravian regions.
O2 and T-Mobile 5G Network Performance, Select Regions, Czechia
Source: Speedtest Intelligence® | Q2 2022 — Q2 2024
O2 and T-Mobile 5G Network Performance, Select Regions, Czechia
Prague
The capital city and its surroundings have the largest population in Czechia with over 2 million people. It is no surprise then that the operators prioritized this region when launching 5G and when upgrading network equipment. We also note that this region has been excluded from the network-sharing agreement signed between O2 and T-Mobile, allowing the two operators to offer distinctively different performances.
In Prague, O2 significantly outperforms T-Mobile in 5G download speeds, with O2 reaching 241.86 Mbps compared to T-Mobile’s 167.85 Mbps. It is also the region where O2 has a large advantage compared to T-Mobile (compared to the other three regions). However, the median 5G upload speeds between the two providers are much closer, with O2 at 47.04 Mbps and T-Mobile at 46.18 Mbps.
Central Bohemian and South Moravian regions
These two regions show a clear trend where T-Mobile outperformed O2 in both 5G download and upload speeds, varying from the pattern observed in Prague, where O2 had a strong lead in download speed. In the Central Bohemian Region, T-Mobile’s download speed is 129.36 Mbps, notably higher than O2’s 93.02 Mbps. Similarly, T-Mobile’s upload speed of 29.47 Mbps is higher than O2’s.
In the South Moravian Region, T-Mobile is also leading with a speed of 165.54 Mbps compared to O2’s 136.68 Mbps. However, the gap between the two is narrower here than in the Central Bohemian Region. Its lead in 5G upload speeds is less pronounced at 38.39 Mbps compared to O2’s 26.29 Mbps. T-Mobile also outperformed O2 in both metrics in six other regions, while there is no clear winner in the remaining five regions.
The Czech Republic is on track to reach EU 5G coverage targets ahead of schedule and has opportunities to improve network speed
According to a European Union (EU) report published in September 2023, 5G deployment is accelerating in Czechia with population coverage increasing from 49% in 2021 to 83% in 2022, ahead of the European average of 81%. This puts the country in a very good position to reach the EU’s target of 100% 5G coverage of the population way before the deadline of 2030.
As 5G coverage issues have been largely addressed, operators turned their attention to improving throughput, especially since Q3 2023. They can optimize their usage of the allocated spectrum in the 700 MHz and 3400–3600 MHz bands, while waiting for the release of the 26 Ghz which promises to offer much higher download speed. The extensive use of dynamic spectrum sharing also poses a bottleneck to unlocking 5G’s full potential. According to the EU’s Observatory Report published in June 2024, nearly half of the 13,870 5G base stations deployed in Czechia use that technology. While operators relied on DSS to expand their 5G footprint, they should now consider moving 5G services to dedicated spectrum channels, just like AT&T and Verizon in the U.S., to accelerate speed improvements.
We will continue to monitor fixed and mobile networks’ performance across Europe. For more information about Speedtest Intelligence data and insights, please contact us.
Ookla retains ownership of this article including all of the intellectual property rights, data, content graphs and analysis. This article may not be quoted, reproduced, distributed or published for any commercial purpose without prior consent. Members of the press and others using the findings in this article for non-commercial purposes are welcome to publicly share and link to report information with attribution to Ookla.