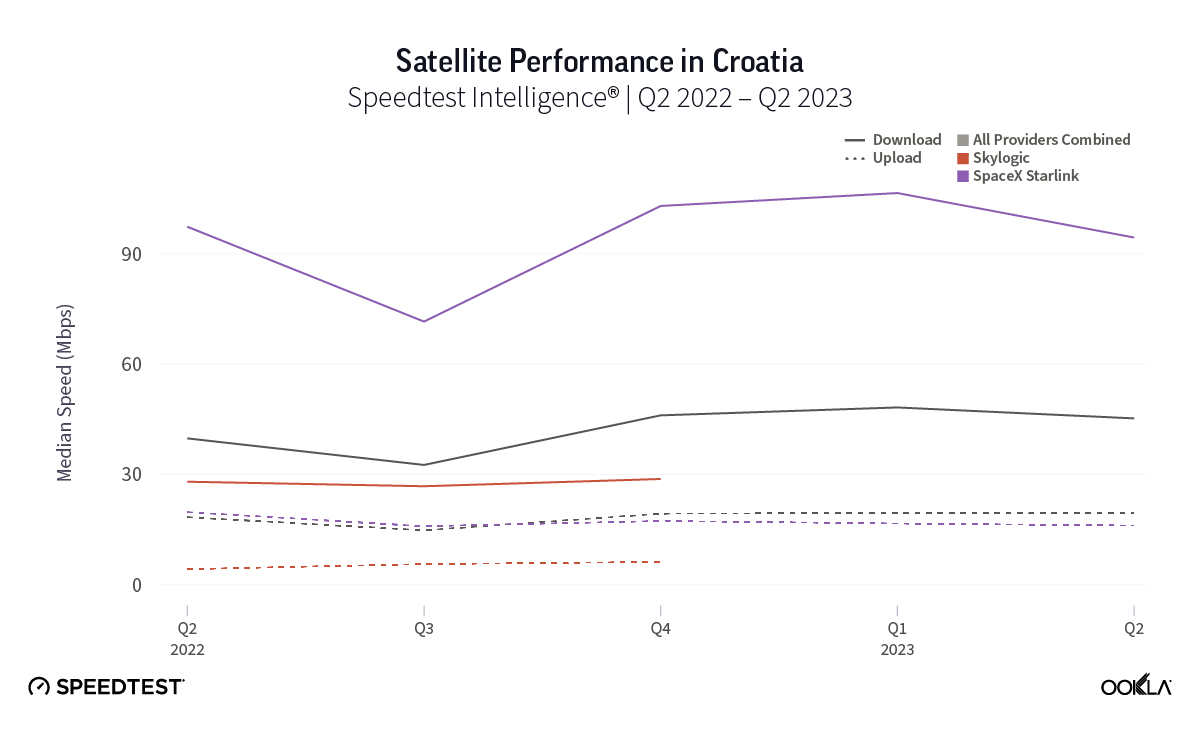
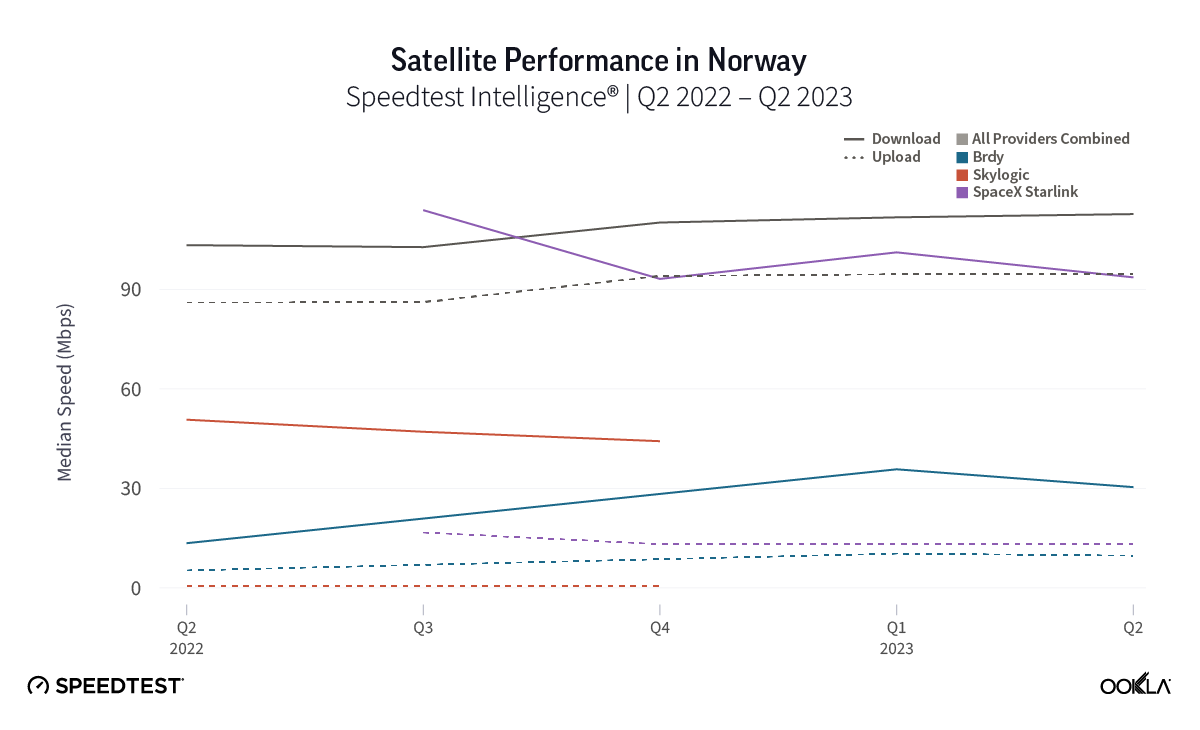
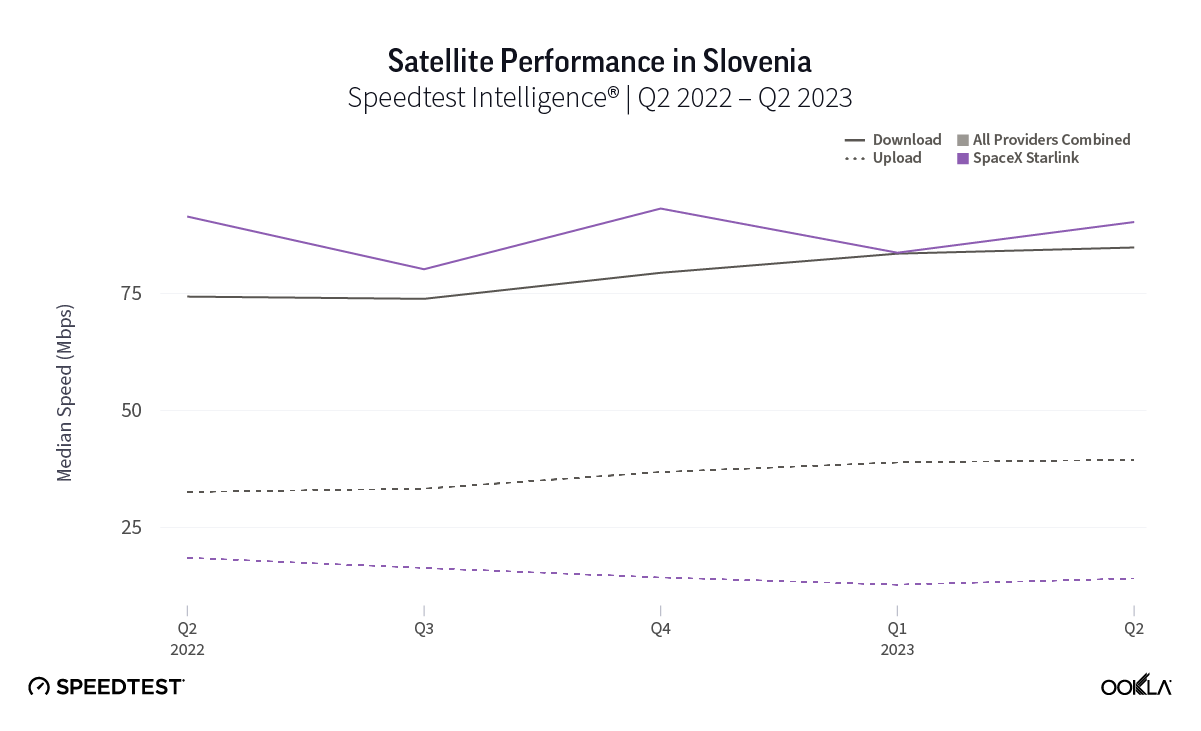
We recently examined operators’ plans for sunsetting 2G and 3G networks in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) and highlighted the benefits and challenges of phasing out legacy networks. In contrast, Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA) is just beginning this journey, with South Africa leading the way compared to other large markets like Nigeria, as it aims to shut down 2G and 3G by 2027. This article examines the factors contributing to slower progress in SSA and suggests how operators might expedite the transition.
Key Takeaways:
- Sunsetting is not yet a priority for most African operators. The shift from 2G/3G to more advanced technologies will be slower in Africa due to economic, social, and infrastructural factors as well as the strong dependence on existing legacy ecosystems. A gradual approach is recommended to maintain digital inclusiveness in Africa.
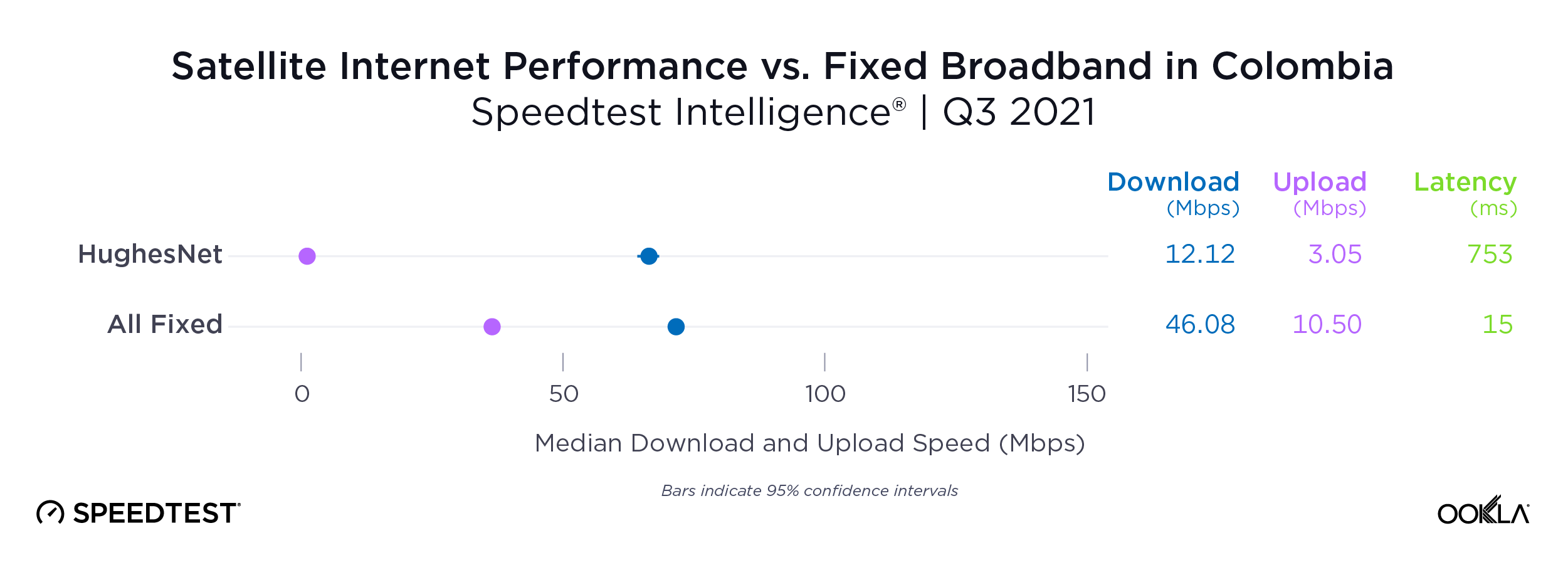
- South Africa is the only country in SSA with an established plan to sunset 2G and 3G networks. Cell Analytics® data shows a large concentration of 2G and 3G users in suburban and rural areas as well as along transportation routes. South Africa plans to decommission these networks by 2027, but most countries, including Nigeria, have not yet set a date. We expect network sunsetting to be in full swing from 2030 onwards.
- Operators should strike a balance between driving progress and maintaining the inclusivity of their services. African operators should continue to support and potentially expand their legacy networks to ensure continued access to critical communication services for most of the population while investing in the roll-out of 4G and 5G networks.
Network sunsetting could play a key role in addressing the growing demand for data and spectrum in Africa
More operators are contemplating turning off their 2G and/or 3G networks to refarm their existing spectrum and combine it with other bands to enhance 4G and 5G services, promising faster data speeds, lower latency, and enhanced connectivity. At the same time, operators seek to optimize spectrum utilization as it is a scarce and expensive resource.
Our previous article delved into how decommissioning 2G or 3G networks can boost efficiency, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction. We also emphasized the importance of careful planning to minimize service disruption and potential financial and reputational damage.
2G and 3G network sunsetting across Africa is evolving very slowly, with no country on the continent having completed the transition yet. This delay in transitioning to newer network technologies has significant implications on the ability of the population to access high-speed internet which is vital for socio-economic development. It is important to explore the reasons behind the slow progress and identify potential strategies to overcome the challenges associated with sunsetting old networks.
3G remains the most prevalent network technology in SSA, but 4G will overtake it by 2027. The GSMA predicts that 3G’s share of connections will fall below 50% in 2025, while 2G adoption will decline under 10%. 4G connections will almost double between 2022 and 2030 to represent nearly half of the total, overtaking 3G by the end of 2027. Continued network upgrades and better device affordability will drive this surge. While 5G adoption will initially be slow, it is anticipated to gain momentum during the second half of the decade, reaching 17% by 2030. This shift will lead to a fourfold increase in mobile data traffic per smartphone by 2028, a higher rate than any other region, to 19 GB per month.
Network sunsetting is more important in SSA because of limited spectrum availability and the rapid growth in demand for faster-speed data services. As regulators released only a small quantity of spectrum, operators resorted to refarming existing spectrum bands to deploy 4G and 5G services. The low-frequency bands occupied by earlier network technologies are valuable due to their excellent propagation characteristics, making them ideal for fulfilling coverage obligations with 4G and 5G.
Network sunsetting in Africa is hampered by the prevalence of legacy infrastructure and the high cost of migrating customers
Many parts of the continent still heavily rely on legacy technology and will continue to do so in the short-to-medium term. This reliance makes the transition to newer generation networks more challenging and costly. In 2023, 3G represented 55% of mobile connections in SSA and is expected to represent a third of total connections by 2030.
This shows that many revenue-generating customers are still on legacy networks. Operators are understandably hesitant to risk service disruptions and incur the significant investment and planning required to upgrade the infrastructure, which will make the transition more challenging and lengthier. Besides, 3G was launched less than a decade ago in several countries. In Burundi, Cameroon, Ethiopia, and Liberia, some operators have only introduced 3G services since 2019 or later, meaning the network costs have not yet been fully amortized.
In the enterprise sector, Africa hosts millions of machine-to-machine (M2M) devices, some of them in difficult-to-reach geographies or embedded in cars and equipment, making replacement or upgrades challenging. For example, South Africa had 11.5 million M2M connections in Q3 2022, according to the Independent Communications Authority of South Africa (ICASA), while Kenya recorded more than 1.5 million M2M connections in Q3 2023.
Despite the expansion of mobile networks in many African countries, coverage gaps persist, posing a connectivity challenge. If operators decide to rush the decommissioning of older networks, they could leave many people losing mobile access, thus widening the digital divide. 2G is particularly suitable for the region’s large rural population because 2G base stations can provide good coverage across large distances. That is why in many African countries, 2G coverage of the population has reached or exceeded 90% while that of 3G and 4G lag behind.
The prevalence of basic and feature phones across the continent is another barrier. Handset compatibility issues with newer technologies and the higher costs of smartphones and data plans represent significant hurdles for low-income populations, complicating the transition process.
Finally, operators may face regulatory challenges when retiring old technologies. Spectrum freed from legacy networks may not be readily available for new networks after the switch-off if it is tied to a specific technology. Repurposing it for modern networks can also be a bureaucratic and time-consuming process.
African operators can adopt different strategies to address challenges that hinder the sunsetting process
The challenges outlined above contribute to the slower rate of network sunsetting in Africa compared to other regions. However, operators can employ various strategies to facilitate the decommissioning process while mitigating the negative impact on revenue and brand.
The decision to sunset one network before another should be informed by market conditions, including the number of customers that use legacy networks, the cost of maintaining their operations, and the dependency of enterprise services on these networks. In either case, it is important to adopt a phased approach to sunsetting, prioritizing areas with higher 4G coverage first, before moving to rural and remote regions. This approach will help to minimize disruption and allow users more time to prepare for the transition.
Operators could encourage subscribers to upgrade to newer devices that support 4G and 5G networks through incentives such as handset trade-in programs or subsidies for low-income individuals. They should couple it with awareness campaigns to educate subscribers about the benefits of newer networks and the steps they need to take to ensure a smooth migration.
Operators should also communicate early about potential service disruptions and the timeline for the switch-off to make the necessary adjustments to their M2M systems. For example, they could offer incentives or subsidies to upgrade to 4G-grade M2M technologies, such as LTE-M, which offer longer usable life, larger operating range, and higher data rates. Offering assistance to enterprises to address any network compatibility and reliability issues during and after the migration is also essential. The regulator should be involved in the discussions around sunset plans as it may require operators to maintain some capacity and coverage for critical IoT infrastructure.
For spectrum reuse, operators should lobby the regulators for technology-neutral licenses, enabling them to use the old spectrum once released. Reducing regulatory constraints and requirements will help to improve network coverage and reduce capital expenditure. A recent GSMA report highlights that countries in Africa that adopted technology-neutral licensing have seen a 30% rise in mobile internet penetration, and a 74% improvement in 4G coverage, in contrast to 24% and 57%, respectively, for countries without such licensing.
Network sunsetting is not yet a priority in Africa given the prevalence of 2G and 3G connections
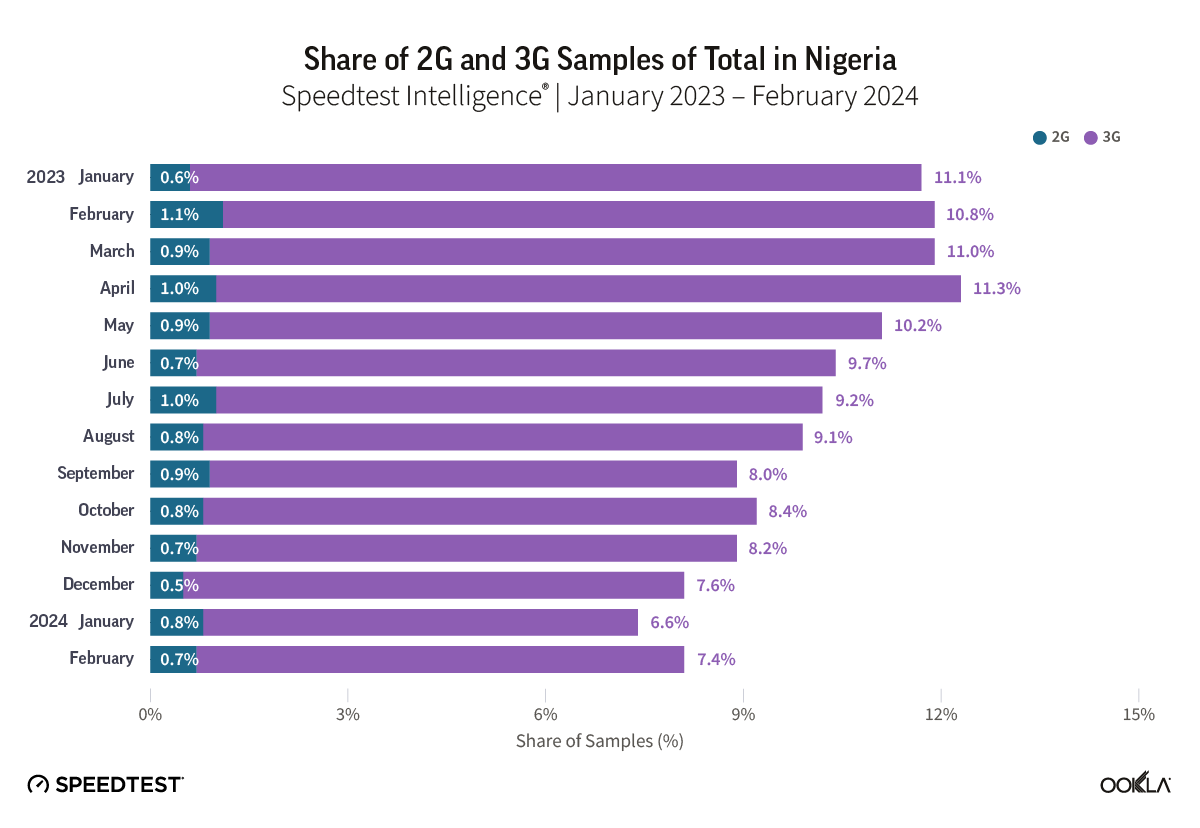
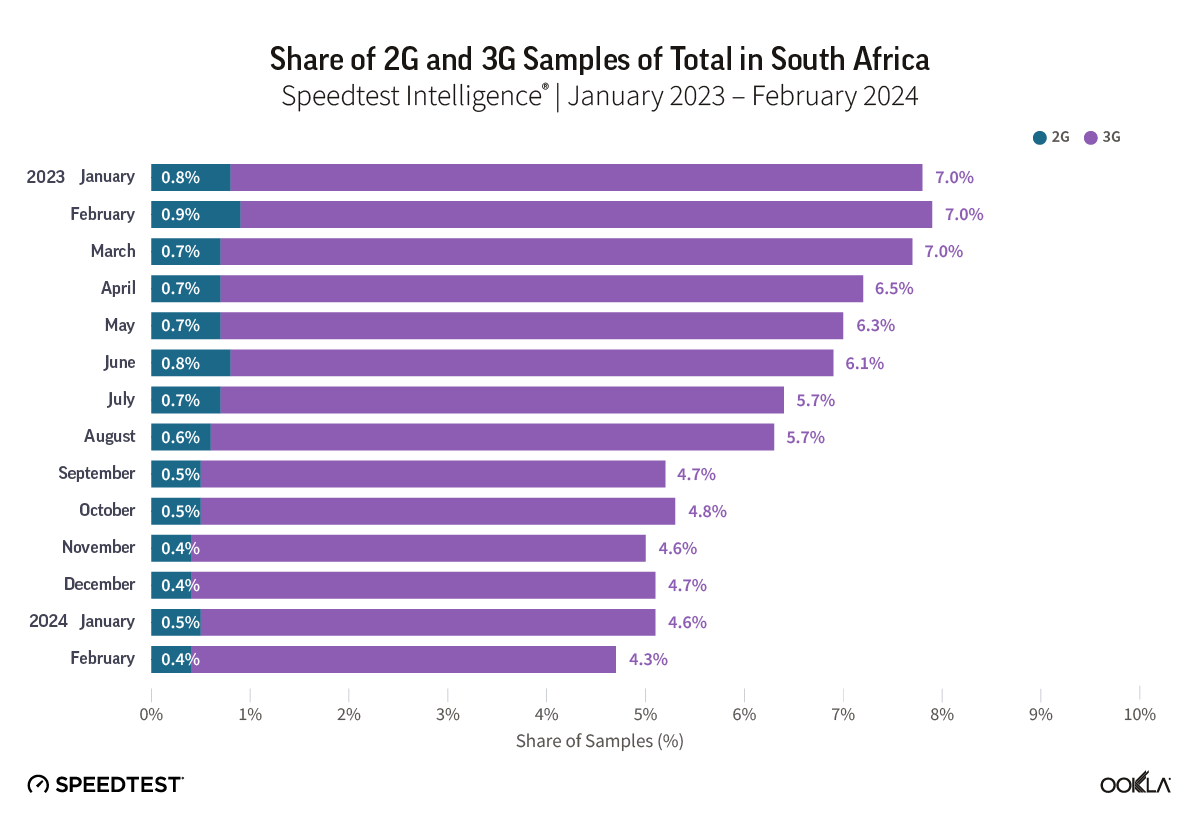
2G will likely remain important during the rollout of 4G and 5G for years to come because it supports essential consumer services in Africa, including voice, basic information, and mobile money transactions. As 4G provides a much better data experience than 3G, operators will likely consider sunsetting 3G before 2G. We used Speedtest Intelligence’s “Availability” data to get the percentage of users with a service-active device who spend the majority of their time connected to 2G and 3G in Nigeria and South Africa, the two largest markets in Sub-Saharan Africa by revenue. This data is a proxy for the relative penetration of 2G and 3G in these markets. Since customer-initiated Speedtest® measurements require a relatively modern phone, samples reported as 2G or 3G indicate the unavailability of 4G and 5G coverage rather than actual 2G and 3G usage. As such, we rely on this data solely to gauge the relative penetration of 2G and 3G in these markets.
Speedtest Intelligence® data showed that the 2G/3G share of connections has been trending down in Nigeria and South Africa throughout 2023. By February 2024, 3G penetration in Nigeria was at 7.4% and in South Africa at 4.3%, with 2G penetration significantly lower at 0.7% and 0.4%, respectively. This suggests that more subscribers in Nigeria than in South Africa spend the majority of their time on 2G/3G.
According to the Nigerian Communications Commission (NCC), 67.6% of subscribers used 2G or 3G as of December 2023. ICASA in South Africa does not publish detailed mobile connection technology data. However, we can estimate that 2G/3G subscribers accounted for around 35-40% of total connections in South Africa at the end of 2023 based on Speedtest Intelligence and NCC data. Since South Africa is the most developed mobile market in SSA, the penetration of legacy networks is expected to be much higher in less developed markets.
Network sunsetting is not yet on the table for Nigerian operators
Nigeria’s journey with 5G began in December 2022 with the auctions for 5G licenses using the 3500 MHz spectrum band. MTN and ISP Mafab Communications emerged as winners. Airtel acquired its 5G license about a year later. MTN launched 5G in September 2022, initially in seven cities, expanding to 300 cities by the end of 2023. Despite this, 5G adoption has been limited, with 4G capturing a growing market share and 5G representing just 1.0% of mobile subscribers by the end of 2023.
This is mainly due to limited 5G coverage, device affordability, and customer demand. ITU’s report shows that while 94% and 87% of the population had access to 2G and 3G coverage, respectively, only 6% could access 5G at the end of 2022. Furthermore, 58% of the urban population had a smartphone at the end of 2022, compared to only 32% in rural areas, according to the GSMA.
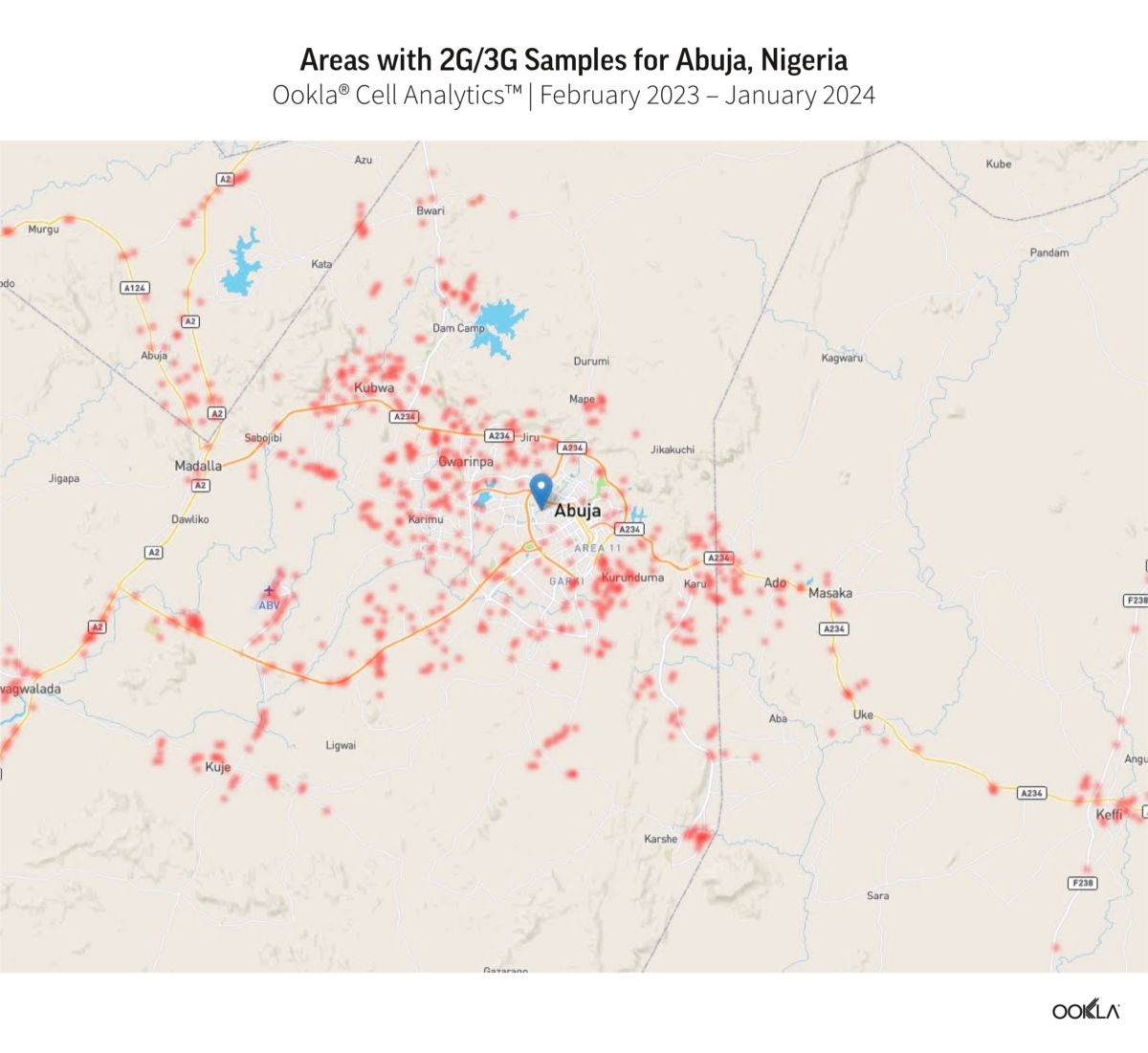
Call Analytics® identified areas with 2G and 3G concentration between February 2023 and January 2024 in high-population centers, Abuja, Ibadan, and Lagos. The red dots on the map pinpoint customers connected to 2G and 3G because they have SIM cards not provisioned for LTE (including roamers), lack 4G coverage, or use devices incompatible with 4G.
Data shows that mobile operators still heavily rely on 2G and 3G networks to provide connectivity across city centers, suburban regions, rural areas, and along transport routes. With the rising cost of living, people are expected to reduce their data usage and continue using 2G and 3G devices due to budget constraints and increasing mobile phone prices. Notably, Nigeria’s annual inflation rate reached a nearly 30-year high of 28.9% in December 2023 due to currency devaluation, reduction of subsidies, and foreign exchange liberalization.
The combination of high living expenses and Nigeria’s extensive geography suggests the full transition to modern networks will be slow and gradual while 2G and 3G networks remain in operation for the foreseeable future. This is evidenced by MTN and Airtel’s renewal of their 2100MHz spectrum license in 2022, primarily for 3G uses while progressing with 5G deployment. An operator can choose to repurpose that spectrum for 4G and 5G in the future or use dynamic spectrum sharing to share it between different technologies.
South Africa plans to turn off 2G and 3G by the end of 2027
Local operators have long awaited the release of new spectrum to enhance 4G services and launch 5G. Faced with this delay, Vodacom and MTN introduced 5G services in May and June 2020 using the emergency spectrum granted by ICASA during COVID-19 and refarming some of their existing spectrum assets on 2G and 3G.
The much-anticipated spectrum auction was finally completed in March 2022 with spectrum bands across 700 MHz, 800 MHz, 2.6 GHz, and 3.5 GHz bands awarded to six operators Cell C, Liquid Intelligent Technologies, MTN, Rain, Telkom, and Vodacom.
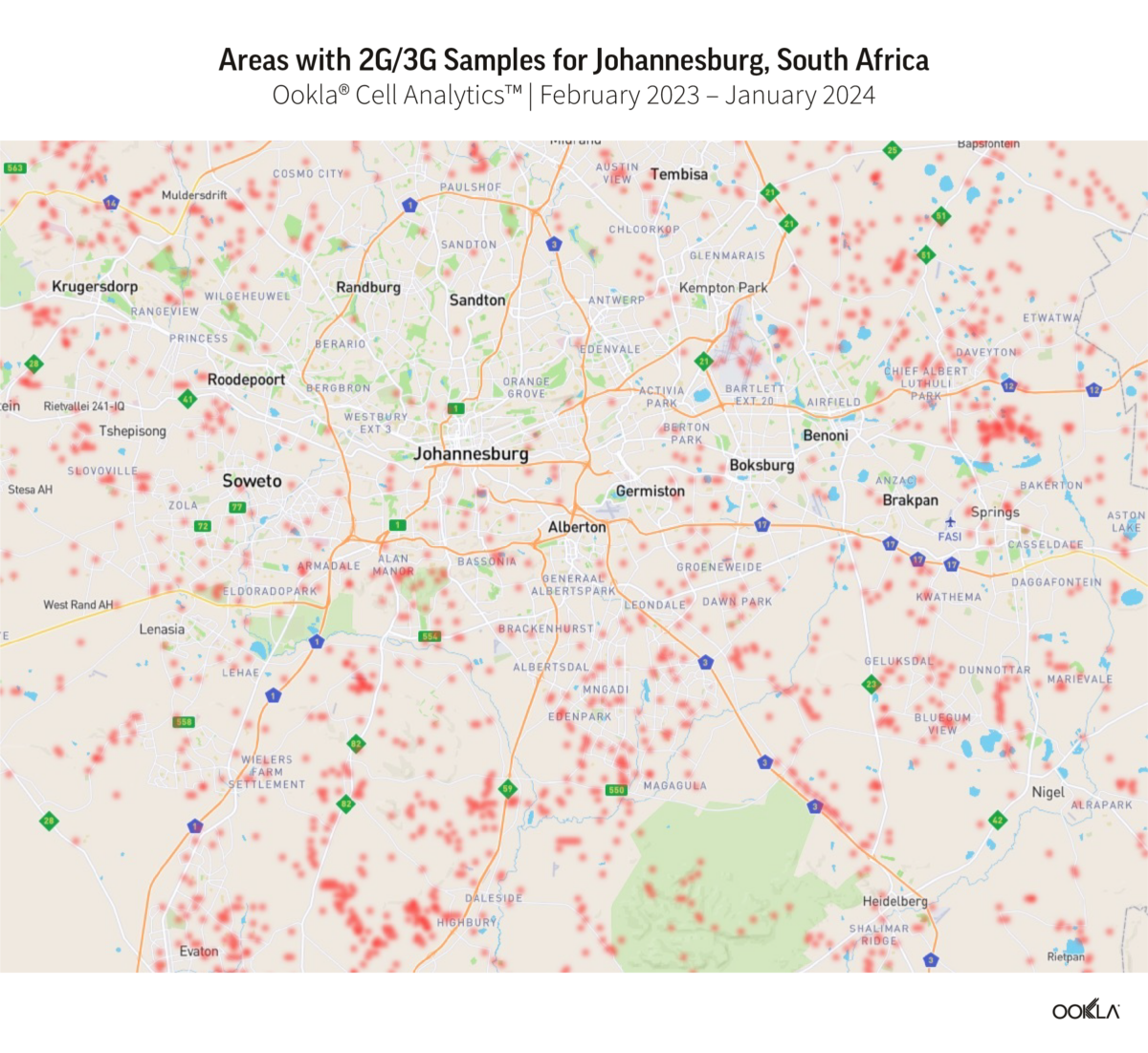
Cell Analytics’ Service Availability maps show that 2G and 3G remain prevalent in suburban and rural areas of major cities like Cape Town, Johannesburg, and Pretoria. While South Africa leads SSA in 4G and 5G penetration, 3G is still widespread and offers a satisfactory experience for basic use cases like checking the news. 2G is less relevant since it supports mainly voice services but occupies a valuable sub-1Ghz spectrum which could be repurposed for more efficient technologies.
In light of this, the Department of Communications and Digital Technologies (DCDT) proposed a plan in 2022 to sunset 2G and 3G networks to free up spectrum for 5G and future technologies. Initially, the plan aimed to shut down 2G and 3G networks by the end of June 2024 and March 2025, respectively. The DCDT subsequently extended the deadlines twice to give more time for the operators to prepare for the transition. The most recent amendment was in February 2024, scheduling the phase-out to begin in June 2025 and conclude by the end of 2027. It will also include new spectrum auctions, likely to take place in 2024
The revised deadline seems to be more practical, but it still needs to be discussed with all the stakeholders to make sure that the end-users and businesses don’t face any challenges during this transition. The DCDT will allow operators to choose which network to switch off first. Based on operators’ current positions on network retirement, 3G will likely be the first to go:
- Vodacom’s initial plan was to end 3G services before 2G, but their latest stance is less definitive. Their decision will significantly impact Cell C, whose contract customers use Vodacom’s network.
- Telkom has already shut down most 2G services as they account for less than 1% of its traffic.
- MTN suggested that 3G should be shut down before 2G, as migrating 2G devices to 4G will take longer than moving from 3G. This presents a challenge as MTN has the highest proportion of 3G samples in South Africa, (according to Speedtest data) at 6.35% in January 2024 compared to 3.4% for Vodacom and 3.3% for Telkom.
A phased approach to retiring networks, with consideration for affordability and coverage, is essential to maintain digital inclusiveness
The sunsetting of 2G and 3G networks is a global trend, led by developed countries. It promises to bring benefits like faster data speeds, improved connectivity, and more efficient spectrum usage. Yet, Sub-Saharan Africa trails in this transition because of the heavy reliance on legacy networks, the cost barrier to the operators and consumers, and the unequal distribution of new network infrastructure, especially in poorer regions.
2G and 3G networks form the backbone of mobile communications for a large proportion of the population, enabling vital services such as voice and mobile money transactions. Operators thus face the challenge of investing in advanced network rollouts while maintaining and even expanding their legacy networks to ensure everyone has access to communication services.
Using network analytical tools such as Ookla’s Speedtest Intelligence and Cell Analytics can provide valuable insights to help prepare for network decommissioning. These tools can track the progress of the switch off, and monitor its impact on network and spectrum usage as well as gauge consumer sentiment, ensuring that the transition to 4G and 5G is as smooth and beneficial.
Ookla retains ownership of this article including all of the intellectual property rights, data, content graphs and analysis. This article may not be quoted, reproduced, distributed or published for any commercial purpose without prior consent. Members of the press and others using the findings in this article for non-commercial purposes are welcome to publicly share and link to report information with attribution to Ookla.