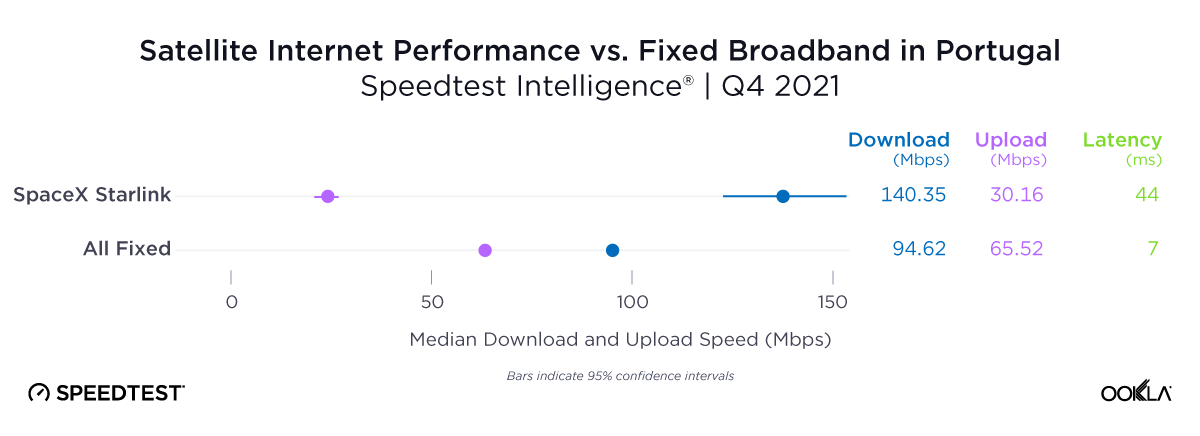
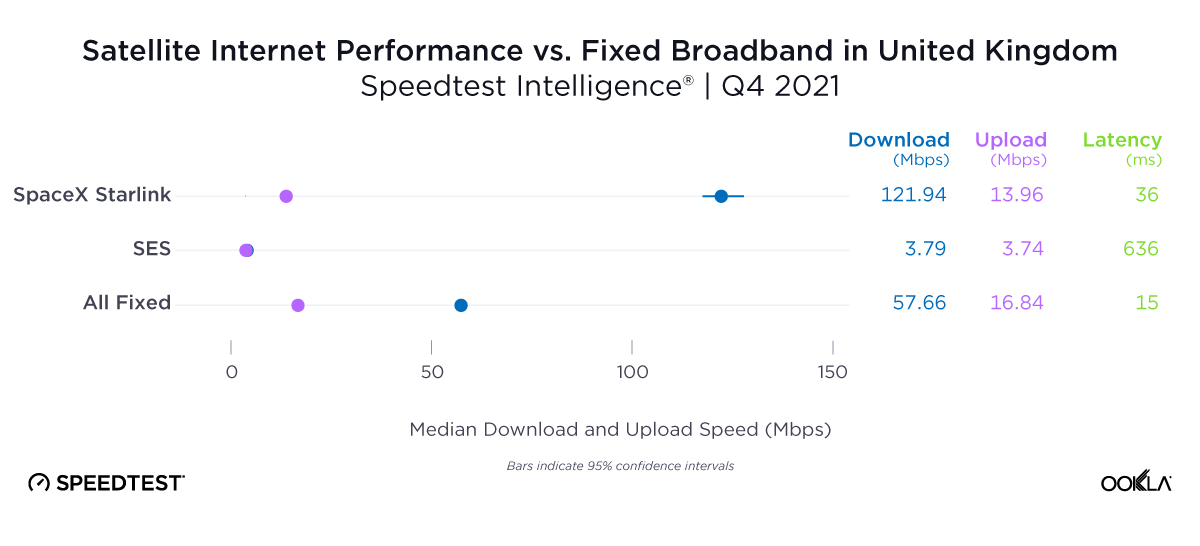
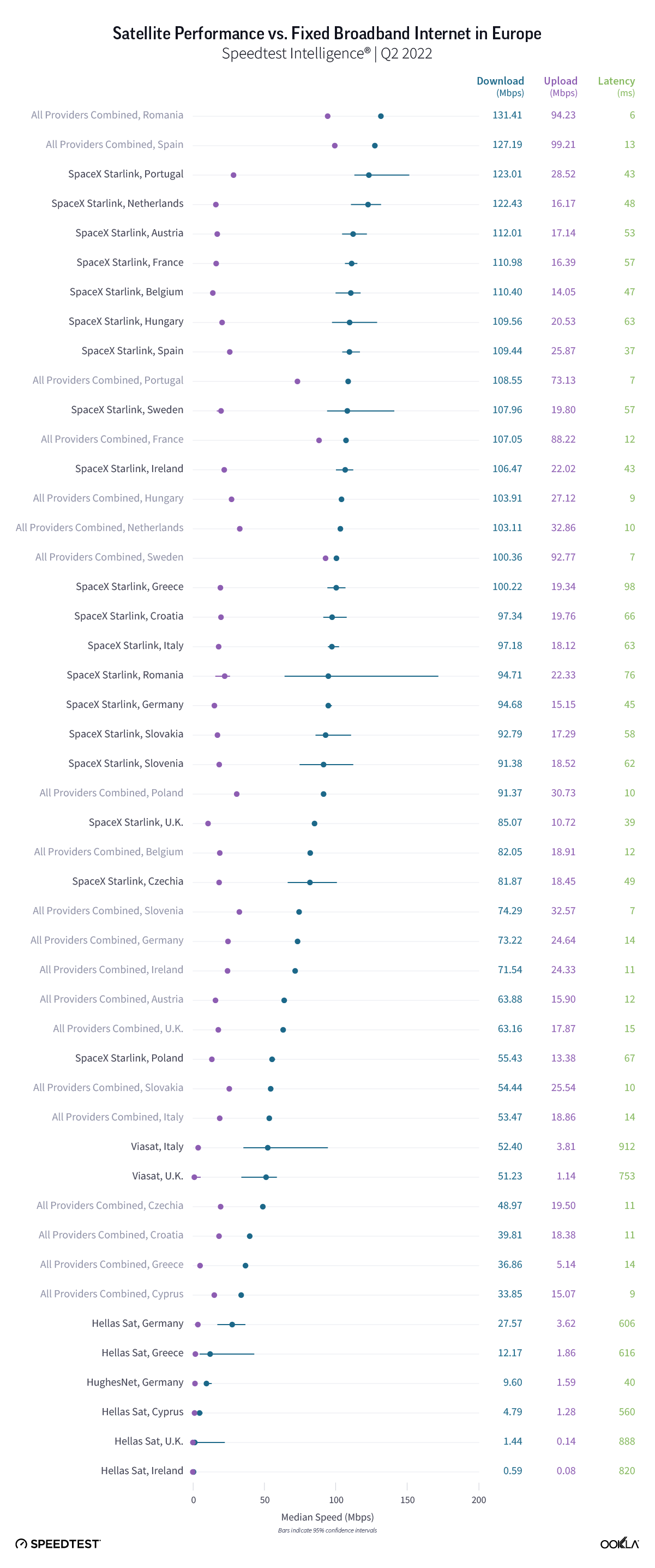
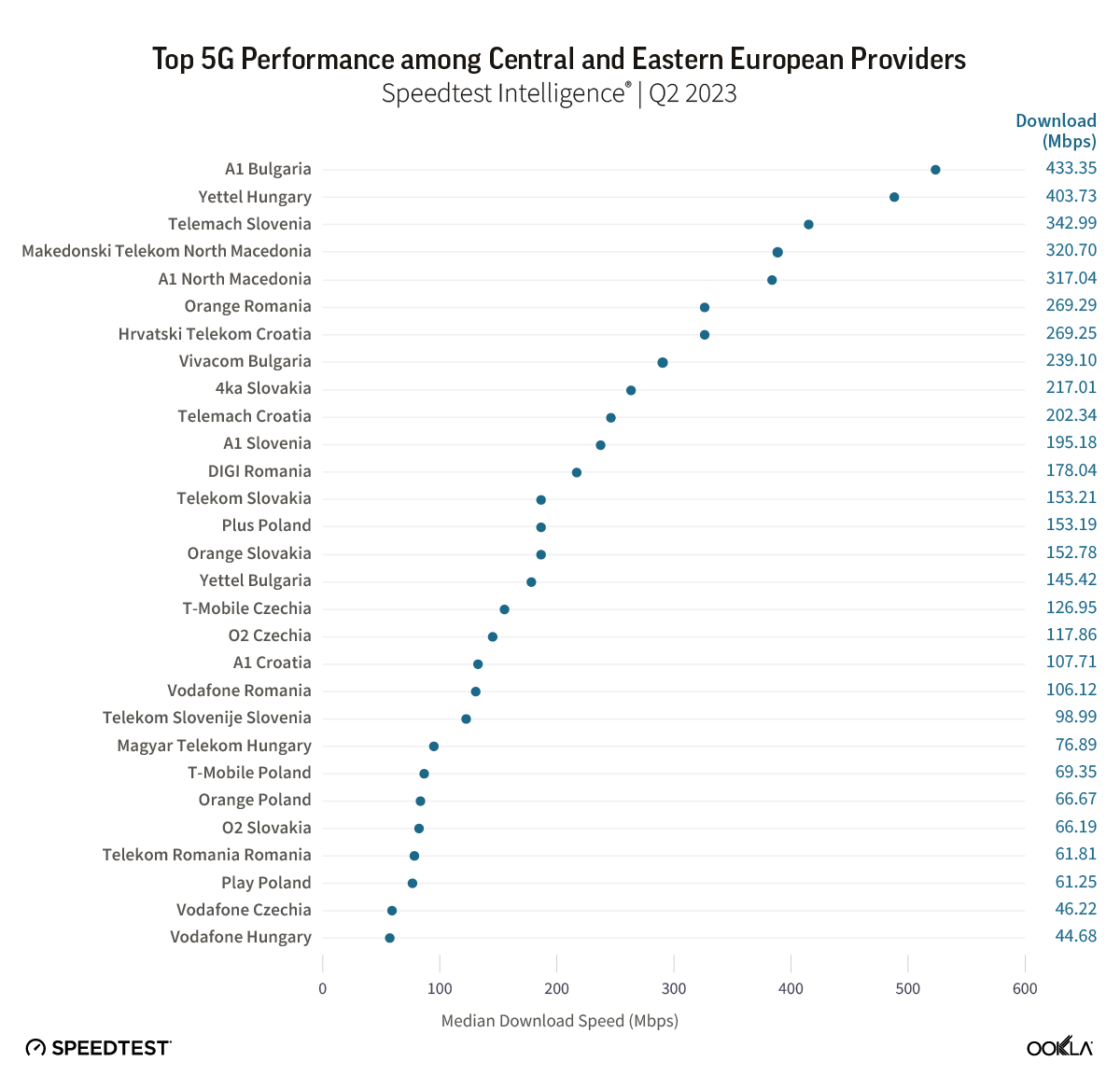
Poland’s operators are rapidly deploying mid-band 5G in an attempt to capture the growing premium market segment
Late to the game in staging a mid-band auction, Poland has lagged behind its European peers in 5G deployment in recent years. This delay has weighed on the country’s global competitiveness in mobile network performance and slowed its progress toward meeting the European Commission’s flagship 5G deployment targets, which require universal 5G coverage across every EU member state by the end of the decade.
This article examines the state of Poland’s mobile market and its broader regional 5G competitiveness in the context of ongoing mid-band deployments. A follow-up report will assess the longer-term impact of the commercialization of the recently awarded low-band spectrum and ongoing network sunsets on network coverage and availability.
Key Takeaways:
- Intensive capital spending on mid-band deployment drives substantial uplift in 5G performance across Polish operators from Q1 2024, pushing the country ahead of regional peers over the last year. Median 5G download speeds in Poland jumped by over 50% to 160.30 Mbps between Q1 2024 and Q1 2025, based on Speedtest Intelligence® data, propelling the country ahead of Czechia, Romania, and Slovakia for the first time in 5G performance. Despite this progress, Poland continues to trail its regional peers in 5G network Consistency, a measure of how reliably a mobile connection remains “fast enough” for normal use.
- T-Mobile and Orange surpass Play and Plus in speed and select Quality of Experience (QoE) measures. Differences in how quickly and extensively Polish operators have deployed their mid-band spectrum assets have led to a diverging market profile since Q1 2024, with T-Mobile and Orange significantly extending their speed lead over their rivals. Between Q1 2024 and Q1 2025, median 5G download speeds rose by as much as 72% on Play (to 122.64 Mbps), 86% on T-Mobile (to 201.76 Mbps), and 90% on Orange (to 222.10 Mbps)—while declining by over 10% on Plus (to 116.76 Mbps).
- Network investments have broadened 5G coverage in Poland, but significant regional disparities remain. Nationally, 5G availability rose from 28.5% in Q1 2024 to 43.1% in Q1 2025, driven by continued Dynamic Spectrum Sharing (DSS) rollouts and the activation of mid-band spectrum—placing the country ahead of regional peers Bulgaria, Romania, and Hungary in 5G availability. Nonetheless, by Q4 2024, a pronounced coverage gap persisted between the country’s best- and worst-served provinces, with 5G availability in the populous Masovian Voivodeship (47.2%) double that of the Lubusz Voivodeship (23.6%).
Over the last year, Polish operators have been locked in an intense four-way race to catch up with their regional peers in 5G deployment, driven by stringent coverage obligations imposed by the Polish telecoms regulator (UKE), a wave of funding support from Brussels, and a growing push to compete for a larger share of the country’s widening premium market segment, where network performance has emerged as a key competitive differentiator.
Poland’s mobile market is today awash with deployment activity, as operators ramp up capital spending to the highest levels in years to equip thousands of mobile sites with mid-band spectrum, accelerate the sunset of 3G networks, and lay the groundwork for launching 5G standalone (SA) in the coming years. This flurry of activity follows the completion of the 700/800 MHz auction at the end of March this year, where all Polish operators secured low-band 5G spectrum for the first time—paving the way for improved rural and deep in-building 5G coverage and rounding out the country’s 5G spectrum release plans.
While 5G capital spending has slowed across much of Europe, Poland sees different dynamics due to late spectrum auctions
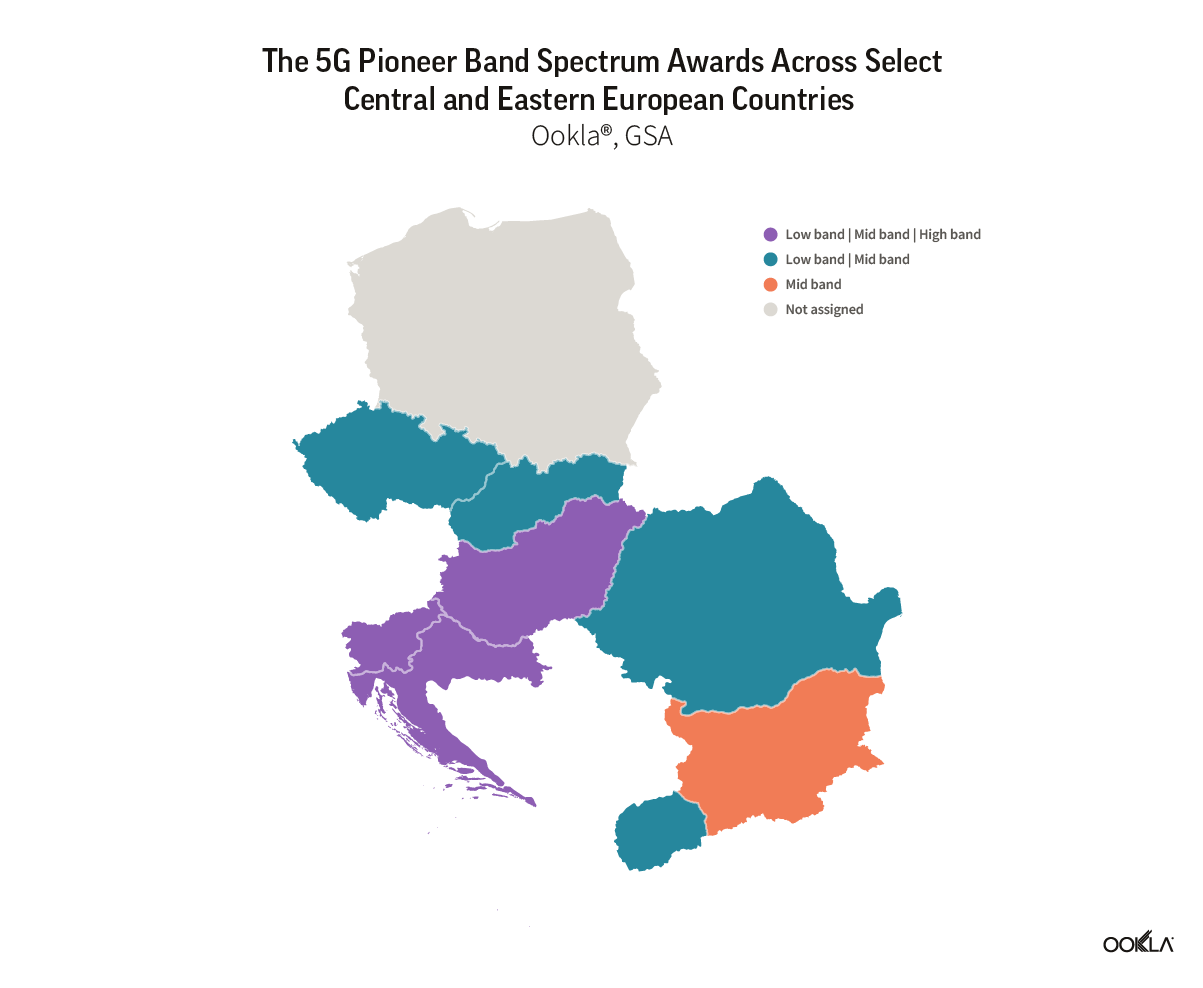
Poland was notably late in releasing dedicated 5G spectrum in the ‘pioneer bands’ identified by the European Commission as critical to the timely commercialization and rollout of 5G across EU member states. The country’s mid-band (3.6 GHz) auction, initially planned for mid-2020, was repeatedly delayed—by more than three years—due to the pandemic and a protracted security legislation process.
These delays in spectrum availability have contributed to Poland’s divergence from much of the rest of Europe in both the economic and technical dimensions of the 5G rollout. Until recently, Polish mobile operators exhibited lower capital intensity (they invested less of their revenue) compared to peers in other European countries. Most of their spending went into upgrading 4G sites and preparing for the 3G shutdown, instead of building a new 5G mid-band capacity layer or expanding 5G coverage using low-band (700 MHz) spectrum.
Orange's Rising Mobile Capex Reflects 5G Network Expansion
Analysis of Orange Poland accounts | 2020 – 2024
Analysis of financial data published by Orange, Poland’s largest mobile operator by subscriber count, confirms that the era of lower capital intensity (relative to elsewhere in Europe) is over. The recent spectrum auctions have triggered a new cycle of investment, with Orange doubling its mobile network spending in the past three years. Play has also rapidly increased its investment, as its French parent Iliad reported injecting record amounts into Play’s mobile infrastructure last year.
Play's Contribution to Capex in the Iliad Group Surges as 5G Buildout Ramps Up
Analysis of Iliad Group accounts | 2020 – 2024
On the technical side, meanwhile, Poland’s spectrum delay meant that three of the country’s four operators were forced to rely heavily on Dynamic Spectrum Sharing (DSS)—a technology that allows 4G and 5G to operate on the same band and adjust ‘dynamically’ to demand—in an effort to deliver early 5G coverage in the 2100 MHz band while awaiting spectrum auctions. This strategy resulted in Poland’s initial 5G performance more closely resembling those typical of 4G networks, as DSS deployments are typically based on a 10 MHz carrier where part of the capacity is still reserved for 4G signals, making 5G speeds with DSS around 15–25 % lower than if the band were dedicated solely to 5G.
The limitations of using DSS to deliver a “5G experience” were exemplified by the speed advantage maintained by Plus earlier in the 5G rollout. Importantly, Plus was the only Polish operator that did not rely on DSS and instead dedicated a full 40 MHz carrier in the 2600 MHz (TDD) band to 5G before mid-band spectrum became available at the start of last year. Prior to the 3.5 GHz band coming online, when the other operators were still wholly dependent on DSS for 5G coverage, Plus’s median 5G download speed of 133.34 Mbps was as much as 77 % higher than T-Mobile’s, 81 % higher than Orange’s, and 92 % higher than Play’s.
Intense Mid-Band Deployment lifts Poland’s Regional 5G Competitiveness and Reshapes Operator Dynamics
Polish operators move from mid-band spectrum acquisition to mass commercial deployment in record time
The pent-up demand for mid-band spectrum in Poland was evident when mobile operators like Orange, T-Mobile, and Play launched commercial services just three months after acquiring mid-band spectrum, moving quickly from the auction in October 2023 to commercial launches by January 2024. T-Mobile reported that its mid-band 5G network already covered more than 25% of the Polish population by April 2024, with more than 2,100 sites active, while Orange announced it had reached 40% coverage by mid-June.
This rollout pace is exceptional by European standards and indicative of the increased pace of deployment possible later in the 5G technology cycle. It took Spain’s Telefónica (Movistar) about six months to reach its first 1,000 mid-band sites by comparison, and Germany’s operators needed around nine months to achieve the same milestone.
Each operator secured a contiguous 100 MHz block of spectrum in the 3.5 GHz band, which is widely regarded as optimal due to the large channel bandwidth this configuration affords. However, Plus has been notably slower to commercialise this allocation at scale. Plus’s earlier strategy of deploying 5G in the dedicated 2600 MHz band (rather than relying on DSS), alongside later using the 2100 MHz band as well, gave it more flexibility to delay a broad mid-band rollout as it previously enjoyed a significant 5G speed advantage over competitors while they were still heavily dependent on DSS deployments.
Mid-band deployment shifts 5G performance rankings among Polish operators
Mass deployment of a new capacity layer by the other three operators has since decisively altered performance dynamics in the Polish market and eroded Plus’s lead. In the space of one year between Q1 2024 and Q1 2025, Plus has moved from market leader in median 5G download speed to laggard, becoming the only Polish operator to see a year-on-year decline in 5G speed, down 10%, indicating the increasing limitations of its 2600 MHz strategy.
Orange and T-Mobile Pull Ahead in 5G Performance with Mid-Band Deployment
Speedtest Intelligence® | Q1 2023 – Q1 2025
By contrast, mid-band deployment has boosted performance across the rest of the market, with median 5G speeds rising by as much as 72% on Play, 86% on T-Mobile, and 90% on Orange between Q1 2024 and Q1 2025. While Orange led the Polish market in Q1 with a median 5G download speed of 222.11 Mbps, the operator’s lead has narrowed significantly as T-Mobile’s mid-band buildout has progressed, with T-Mobile now recording median 5G download speeds of 201.76 Mbps, well ahead of third- and fourth-placed Play (122.64 Mbps) and Plus (116.76 Mbps), respectively.
Plus's Lead in 5G Consistency Narrows as 2600 MHz Advantage Recedes with Mid-Band Deployment
Speedtest Intelligence® | Q1 2023 – Q1 2025
Despite losing its lead in median 5G download speed, Plus continues to lead at the 10th percentile (29.44 Mbps in Q1 2025), meaning subscribers in its lowest-performing areas still enjoy comparatively better speeds than those on rival networks. This advantage is likely linked to Plus’s lower dependence on DSS. However, T-Mobile (24.48 Mbps) and Orange (21.88 Mbps) are quickly closing the gap, with their 10th percentile 5G speeds now converging toward Plus. Plus’s 5G network consistency, measured as the proportion of Speedtest samples meeting a minimum download and upload threshold of 25/3 Mbps, has also declined over the past year, although it remains the market leader.
On upload performance, meanwhile, Play’s 5G network led the market in Q1 2025, recording median speeds of 19.33 Mbps, followed by Orange (18.99 Mbps), T-Mobile (17.32 Mbps), and Plus (14.96 Mbps). Unlike the substantial gains seen in download speeds, there is limited evidence so far that the mid-band rollout has materially improved upload performance, with median upload speeds about 6% lower in Q1 2025 compared to the same quarter last year. This discrepancy arises primarily because all four operators continue to deploy 5G in non-standalone (NSA) mode, requiring devices to transmit uplink traffic via existing 4G anchor bands. Consequently, the newly available 3.5 GHz spectrum enhances downlink capacity but leaves the congested 4G uplink path unchanged.
Play Develops Lead in 5G Upload Performance
Speedtest Intelligence® | Q1 2023 – Q1 2025
The operators’ investments in deploying a new 5G capacity layer have coincided with a broader RAN refresh effort, translating into improved quality of experience for users in key use cases such as video streaming and web browsing. Median web page load times on T-Mobile’s network, for instance, improved by around 4% between Q3 2024 and Q1 2025. Orange led in video metrics such as start time, resolution, and uninterrupted playback in the last quarter.
5G Drives QoE Improvements in Use Cases like Web Browsing
Speedtest Intelligence® | Q1 2025
Capital investment expands 5G coverage, but Poland’s rural-urban digital divide persists
While investments in DSS and the mid-band rollout have enabled Polish operators to make significant strides in 5G availability, which increased nationally from 28.5% in Q1 2024 to 43.1% in Q1 2025, regional coverage disparities continue to be a feature of the mobile network experience in Poland. Operators have prioritized 5G deployments in the richest and densest parts of Poland where fiber is heavily deployed, including the Masovian (Warsaw) and Pomeranian (Tri-City) provinces. In these provinces, 5G availability reached more than 40% by the end of last year and contributed to driving materially higher median download speeds than the national average.
5G Availability Remains Highly Varied Across Poland Outside of Urbanized Areas
Speedtest Intelligence® | 5G Availability (%) in Q4 2024
By contrast, border provinces along the south and west of the country continue to experience much lower levels of 5G availability. Lubusz had the lowest availability (23.6% at the end of last year), where there is lower population density and lower subscriber spending, which reduces operators’ commercial incentives for widespread 5G investment. This trend has driven the development of a notable speed gap between provinces, with mobile subscribers in Lubusz also experiencing the lowest median download speeds (59.97 Mbps) in Poland, almost 33% below the leading Masovian province.
Mobile Download Speeds Are Lower in Less Urbanized Areas of Poland
Speedtest Intelligence® | Median Download Speed (Mbps) in Q4 2024
Mid-band deployment improves Poland’s mobile competitiveness, but 5G consistency continues to trail regional peers
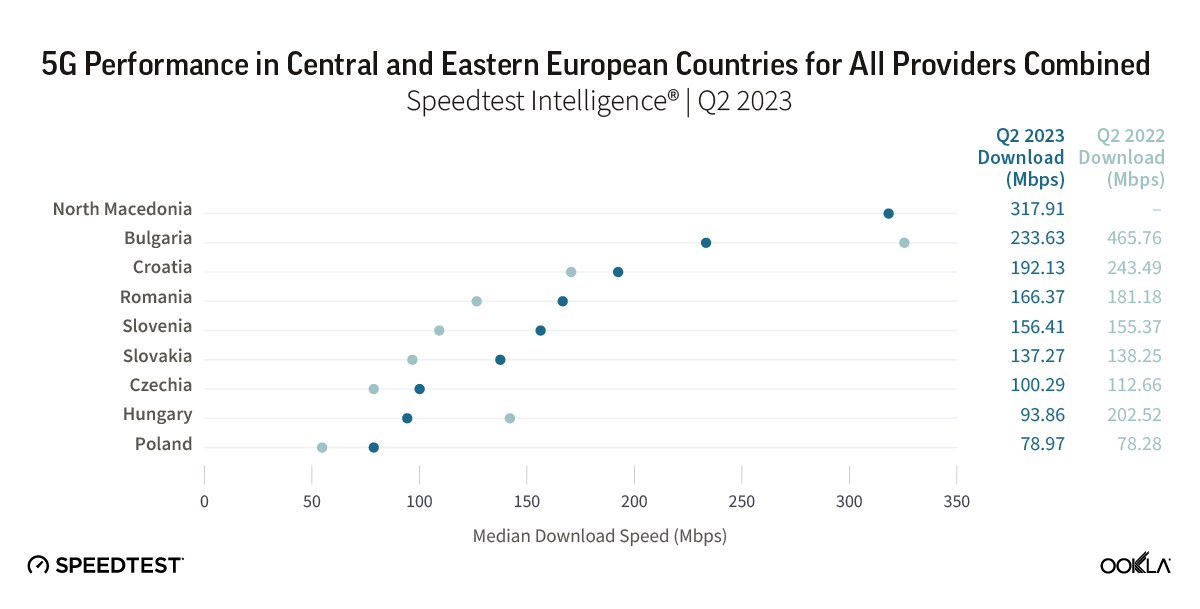
From a regional competitiveness lens, intensive mid-band deployments have been successful in breaking Poland’s cycle of mobile network underperformance, with median 5G download speeds rising by over 50% on average to 160.30 Mbps between Q1 2024 and Q1 2025. This has propelled the country ahead of Czechia, Romania, and Slovakia for the first time in terms of 5G download speed performance.
Mid-Band Deployments Propel Poland's Regional Competitiveness
Speedtest Intelligence® | 2020 – 2025
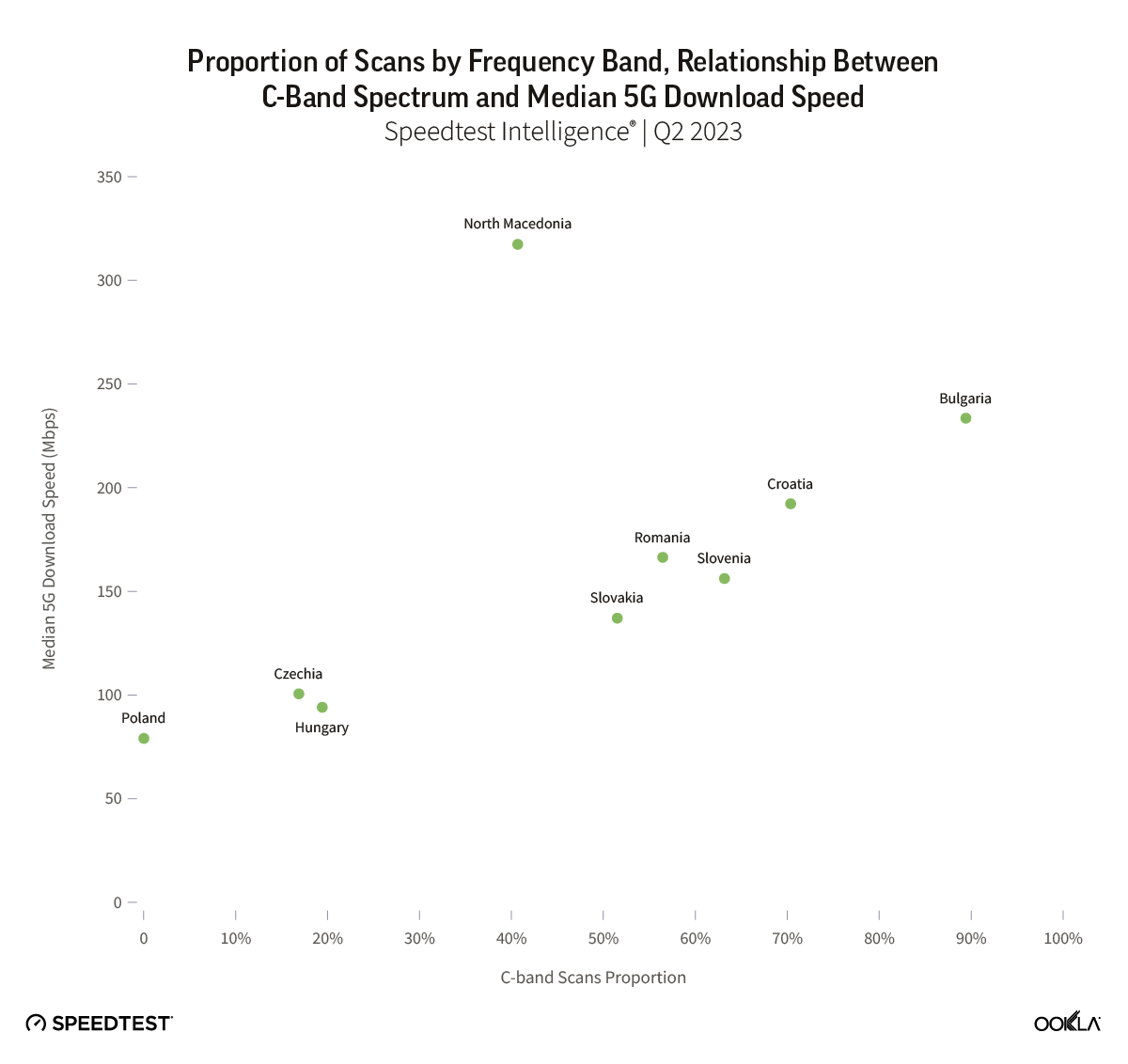
Despite Poland’s progress on its mid-band 5G rollout, the lingering effects of reliance on DSS and limited 5G spectrum diversity—up until the recent 700/800 MHz auction—mean that Poland continues to trail its regional peers in terms of 5G network consistency. In Q1 2025, 82% of Speedtest samples in Poland met the minimum 5G performance threshold for a consistent mobile experience, compared to 86% in Hungary, 89% in Romania, and 93% in Bulgaria.
Newfound spectrum diversity lends Polish operators potent tool to stimulate ARPU growth
Poland’s previous reliance on DSS, driven by limited 5G spectrum diversity, likely contributed to its slower average revenue per user (ARPU) growth compared to neighboring countries in recent years. Polish operators initially introduced tariffs with “5G at no extra cost” bolted onto existing 4G bundles, keeping prices flat to defend market share (and thereby maintaining depressed ARPU levels relative to regional peers). Combined with the external shock induced by markedly higher energy prices, stagnant ARPU levels created challenging operating conditions in the Polish market and weighed on operator profitability.
Intense Priced-Based Competition Precipitated Revenue Erosion in Poland During the First Half of the 5G Cycle
Analysis of GSMA Intelligence Data | % Change in Mobile ARPU (Q1 2020 vs Q1 2023)
In neighboring markets, by contrast, operators were able to leverage mid-band spectrum deployments as both technical and marketing levers, shifting their strategies from price competition toward service-based differentiation. This enabled them to more effectively upsell premium speed tiers or monetize specific use cases, such as fixed wireless access (FWA), which dedicated mid-band 5G deployments uniquely support.
T-Mobile and Play Outpaced Rivals in Subscription Share Growth in Recent Years
Analysis of UKE Market Data | 2019 – 2023
Similarly, the delayed timing of Poland’s mid-band 5G auction likely dampened supply-side factors key for driving growth in mobile data traffic. Between Q1 2020 and Q4 2024, traffic volumes in neighboring Bulgaria converged with that in Poland for the first time, increasing by 4.8x vs. Poland’s 2.6x. Meanwhile, Bulgarian operators capitalized early on mid-band spectrum availability to aggressively promote competitive FWA solutions (a major driver of mobile traffic in developed markets) and to introduce cheap unlimited data tariffs with fewer usage restrictions.
Poland Maintains Regional Lead in Mobile Data Volumes, but Bulgaria is Catching Up
Analysis of GSMA Intelligence data | 2020 – 2024
Polish operators have since sought to replicate Bulgaria’s success by debuting distinct marketing for their mid-band 5G deployments to differentiate the newer mid-band 5G rollouts from earlier DSS-based 5G networks in terms of performance and user experience. T-Mobile has leaned on ‘5G More’ branding, while Plus has used ‘5G Ultra’ to indicate the additional performance gains unlocked by their new 5G networks in locations where dedicated mid-band spectrum is deployed. This strategy has formed part of a broader shift in the market, with all operators moving away from a hyper-focus on price competition and toward ‘more for more’ pricing strategies, supporting improved profitability and renewed ARPU growth in the market with inflation-linked tariffs.
Poland Has Led Regional ARPU Growth Since Mid-Band 5G Deployments Started
Analysis of GSMA Intelligence Data | % Change in Mobile ARPU (Q1 2023 vs Q1 2025)
Low-band activation and network sunset progress set to reinforce mid-band 5G gains
With Poland’s telecom regulator, UKE, having set among Europe’s most ambitious coverage obligations for recent mid- and low-band spectrum auctions, operators are unlikely to delay commercial deployments in the newly acquired 700 and 800 MHz bands. These deployments are expected to start next month and will be crucial for establishing a national 5G coverage layer that, for the first time, extends deep indoors and into rural areas. This expanded coverage will also support wider rollout of voice over LTE (VoLTE) services, accelerating the 3G sunset and freeing up additional spectrum in the 900 MHz band.
We will revisit shortly to assess how Polish operators are progressing with deploying their new low-band spectrum and how effectively it is complementing the ongoing 3G sunset.
Polska galopuje do odzyskania konkurencyjności 5G w Europie dzięki wdrożeniu średniego pasma częstotliwości
Polscy operatorzy przyśpieszyli z wdrażaniem 5G w średnim paśmie, próbując przejąć rosnący segment rynku premium.
Polska, która spóźniła się z przeprowadzeniem aukcji na średnie pasmo, w ostatnich latach pozostawała w tyle za swoimi europejskimi rówieśnikami w zakresie wdrażania 5G. Opóźnienie to odbiło się na globalnej konkurencyjności kraju pod względem wydajności sieci mobilnych i spowolniło postępy w realizacji sztandarowych celów Komisji Europejskiej w zakresie wdrażania 5G, które wymagają powszechnego zasięgu 5G w każdym państwie członkowskim UE do końca dekady.
Niniejszy artykuł analizuje stan polskiego rynku telefonii komórkowej i jego szerszą regionalną konkurencyjność 5G w kontekście trwających wdrożeń średniego pasma. Kolejny raport oceni długoterminowy wpływ komercjalizacji niedawno przyznanego niskiego pasma na potrzeby pokryciowe 5G.
Kluczowe wnioski:
- Intensywne wydatki kapitałowe na wdrożenie średniego pasma napędzają znaczny wzrost wydajności 5G u polskich operatorów od pierwszego kwartału 2024 r., pozycjonując kraj przed regionalnych konkurentów w ciągu ostatniego roku. Mediana prędkości pobierania 5G w Polsce wzrosła o ponad 50% do 160,30 Mb/s w okresie od I kwartału 2024 r. do I kwartału 2025 r., w oparciu o dane Speedtest Intelligence®, dzięki czemu Polska po raz pierwszy wyprzedziła Czechy, Rumunię i Słowację pod względem wydajności 5G. Pomimo tego postępu, Polska nadal pozostaje w tyle za swoimi regionalnymi rówieśnikami pod względem spójności sieci 5G, która jest miarą tego, jak niezawodnie zestawione połączenie mobilne pozostaje “wystarczająco szybkie” do normalnego użytkowania.
- T-Mobile i Orange przewyższają Play i Plus pod względem prędkości i wybranych wskaźników jakości doświadczenia usług (QoE). Różnice w strategiach, jak szybko i szeroko polscy operatorzy wdrożyli swoje aktywa widma w średnim paśmie, doprowadziły do rozbieżnego profilu rynku od pierwszego kwartału 2024 r., przy czym T-Mobile i Orange znacznie zwiększyły swoją przewagę w zakresie prędkości nad rywalami. Pomiędzy I kwartałem 2024 r. a I kwartałem 2025 r. mediana prędkości pobierania 5G wzrosła aż o 72% w Play (do 122,64 Mb/s), 86% w T-Mobile (do 201,76 Mb/s) i 90% w Orange (do 222,10 Mb/s) – przy jednoczesnym spadku o ponad 10% w Plusie (do 116,76 Mb/s).
- Inwestycje sieciowe zwiększyły zasięg 5G w Polsce, ale nadal utrzymują się znaczne różnice regionalne. W ujęciu krajowym dostępność sieci 5G wzrosła z 28,5% w I kwartale 2024 r. do 43,1% w I kwartale 2025 r., co wynikało z dalszego wdrażania dynamicznego współdzielenia widma (DSS) i aktywacji widma w średnim paśmie, dzięki czemu Polska wyprzedziła pod względem dostępności sieci 5G regionalne kraje takie jak Bułgaria, Rumunia i Węgry. Niemniej jednak do IV kwartału 2024 r. utrzymywała się wyraźna luka w zasięgu między najlepiej i najgorzej obsługiwanymi województwami w kraju, przy czym dostępność 5G w zaludnionym województwie mazowieckim (47,2%) była dwukrotnie wyższa niż w województwie lubuskim (23,6%).
- Wyłączenia sieci 3G (ang. “3G sunset”) powodują gwałtowny spadek czasu spędzonego na 3G w 2024 r., ponieważ polscy operatorzy reorganizują widmo dla 4G (ang. “refarming”), ale ma to ogromny wpływ na dostępność usług w miejscach mniej zurbanizowanych. Podczas gdy T-Mobile pozostał jedynym polskim operatorem, który w pełni zakończył proces wygaszania sieci 3G do pierwszego kwartału 2025 r., zarówno Orange, jak i Play czynią obecnie znaczne postępy w zakresie refarmingu widma 3G 900 MHz i 2100 MHz na potrzeby 4G. Czas spędzony na 3G spadł poniżej 3% dla obu operatorów do końca 2024 roku. Natomiast abonenci Plusa nadal spędzali znacznie więcej czasu w sieci 3G – 13,41% na koniec 2024 roku.
W ciągu ostatniego roku polscy operatorzy byli jednak zamknięci w intensywnym wyścigu, aby dogonić swoich regionalnych kolegów we wdrażaniu 5G, napędzanym przez rygorystyczne obowiązki w zakresie zasięgu nałożone przez polskiego regulatora telekomunikacyjnego (UKE), falę wsparcia finansowego z Brukseli i rosnące dążenie do konkurowania o większy udział w poszerzającym się segmencie rynku premium w kraju, w którym wydajność sieci stała się kluczowym wyróżnikiem konkurencyjnym.
Polski rynek telefonii komórkowej jest dziś zdominowany aktywnością wdrożeniową, stąd operatorzy zwiększają wydatki kapitałowe do najwyższych poziomów od lat, aby wyposażyć tysiące stacji bazowych w widmo średniego pasma, przyspieszyć wyłączanie sieci 3G i położyć podwaliny pod uruchomienie samodzielnej sieci 5G (SA) w nadchodzących latach. Taką falę aktywności można zwłaszcza zauważyć po zakończeniu aukcji 700/800 MHz pod koniec marca tego roku, w której wszyscy polscy operatorzy po raz pierwszy zabezpieczyli widmo 5G w niskim paśmie – torując sobie drogę do poprawy zasięgu 5G na obszarach wiejskich i głęboko wewnątrz budynków (ang. “deep in-building”) w miastach oraz uzupełniając krajowe plany udostępniania widma 5G.
Podczas gdy wydatki kapitałowe na 5G spowolniły w dużej części Europy, Polska doświadcza inną dynamikę ze względu na późne aukcje na częstotliwości
Polska znacznie spóźniła się z udostępnieniem dedykowanych częstotliwości 5G w “pionierskich” pasmach zidentyfikowanych przez Komisję Europejską jako krytyczne dla terminowej komercjalizacji i wdrożenia 5G w państwach członkowskich UE. Krajowa aukcja częstotliwości pasma środkowego (3,6 GHz), początkowo planowana na połowę 2020 r., była wielokrotnie opóźniona – o ponad trzy lata – z powodu pandemii i przedłużającego się procesu legislacyjnego w zakresie bezpieczeństwa.
Te opóźnienia w dostępności częstotliwości przyczyniły się do tego, że Polska odbiega od reszty Europy zarówno w wymiarze ekonomicznym, jak i technicznym wdrażania 5G. Do niedawna polscy operatorzy komórkowi wykazywali niższą kapitałochłonność (inwestowali mniejszą część swoich przychodów) w porównaniu do innych europejskich operatorów. Większość ich wydatków przeznaczono na modernizację 4G i przygotowanie do wyłączenia 3G, zamiast budować nową warstwę pojemności 5G w średnim paśmie lub rozszerzać zasięg 5G przy użyciu niskich częstotliwości (700 MHz).
Rosnące nakłady Orange na sieć mobilną odzwierciedlają rozwój sieci 5G
Analiza rachunków Orange Polska | 2020–2024
Analiza danych finansowych opublikowanych przez Orange, największego operatora komórkowego w Polsce pod względem liczby abonentów, potwierdza, że era niższej kapitałochłonności (w porównaniu z innymi krajami w Europie) dobiegła końca. Niedawne aukcje częstotliwości wywołały nowy cykl inwestycyjny, a Orange podwoił wydatki na sieć mobilną w ciągu ostatnich trzech lat. Play również gwałtownie zwiększył swoje inwestycje, jego francuska spółka dominująca Iliad poinformowała w zeszłym roku o zainwestowaniu rekordowych kwot w infrastrukturę mobilną Play.
Udział Play w nakładach inwestycyjnych Grupy Iliad gwałtownie rośnie wraz z przyspieszeniem rozbudowy sieci 5G
Analiza rachunków Grupy Iliad | 2020–2024
Tymczasem od strony technicznej opóźnienie aukcji częstotliwości 5G w Polsce oznaczało, że trzech z czterech operatorów w kraju było zmuszonych w dużym stopniu polegać na dynamicznym współdzieleniu widma (ang. “Dynamic Spectrum Sharing” – DSS) – technologii, która pozwala 4G i 5G działać w tym samym paśmie i “dynamicznie” dostosowywać się do zapotrzebowania na pojemność danej technologii – w celu zapewnienia wczesnego zasięgu 5G w paśmie 2100 MHz w oczekiwaniu na aukcje częstotliwości. Strategia ta spowodowała, że początkowa wydajność 5G w Polsce bardziej przypominała typową dla sieci 4G, ponieważ wdrożenia DSS są zwykle oparte na nośnej 10 MHz, w której część pojemności jest nadal zarezerwowana dla sygnałów 4G, co powoduje, że prędkości 5G z DSS są o około 15-25% niższe niż gdyby pasmo było przeznaczone wyłącznie dla 5G.
Ograniczenia wykorzystania DSS do zapewnienia “doświadczenia 5G” zostały zilustrowane przewagą prędkości utrzymywaną przez Plusa na wcześniejszym etapie wdrażania 5G. Co ważne, Plus był jedynym polskim operatorem, który nie polegał na DSS i zamiast tego przeznaczył pełną nośną 40 MHz w paśmie 2600 MHz (TDD) na 5G, zanim na początku ubiegłego roku częstotliwości średniego pasma stały się dostępne. Przed uruchomieniem pasma 3,5 GHz, gdy pozostali operatorzy byli nadal w pełni zależni od DSS w zakresie zasięgu 5G, średnia prędkość pobierania 5G Plusa wynosząca 133,34 Mb/s była aż o 77% wyższa niż w T-Mobile, 81% wyższa niż w Orange i 92% wyższa niż w Play.
Intensywne wdrażanie średniego pasma podnosi regionalną konkurencyjność Polski w zakresie 5G i zmienia dynamikę operatorów
Polscy operatorzy w rekordowym czasie przechodzą od zakupu częstotliwości w średnim paśmie do masowego wdrożenia komercyjnego
Stłumiony popyt na częstotliwości średniego pasma w Polsce był widoczny, gdy operatorzy komórkowi, tacy jak Orange, T-Mobile i Play, uruchomili usługi komercyjne zaledwie trzy miesiące po nabyciu częstotliwości średniego pasma, szybko przechodząc od aukcji w październiku 2023 r. do komercyjnego uruchomienia do stycznia 2024 roku. T-Mobile poinformował, że jego średniopasmowa sieć 5G obejmowała już ponad 25% populacji Polski do kwietnia 2024 r., z ponad 2100 aktywnymi stacjami bazowymi, podczas gdy Orange ogłosił, że osiągnął 40% zasięgu do połowy czerwca.
To tempo wdrażania jest wyjątkowe jak na standardy europejskie i wskazuje na zwiększone tempo wdrażania możliwe w późniejszym okresie cyklu technologicznego 5G. Dla porównania, hiszpańska Telefónica (Movistar) potrzebowała około sześciu miesięcy, aby osiągnąć pierwsze 1000 stacji bazowych w średnim paśmie, a niemieccy operatorzy potrzebowali około dziewięciu miesięcy, aby osiągnąć ten sam kamień milowy.
Każdy z operatorów zabezpieczył ciągły blok częstotliwości o szerokości 100 MHz w paśmie 3,5 GHz, który jest powszechnie wykorzystywany. Jednak Plus był znacznie wolniejszy w komercjalizacji tej alokacji na dużą skalę. Wcześniejsza strategia Plusa polegająca na wdrażaniu 5G w dedykowanym paśmie 2600 MHz (zamiast polegać na DSS), a później także na wykorzystaniu pasma 2100 MHz, dała mu większą elastyczność w opóźnianiu szerokiego wdrożenia średniego pasma, ponieważ wcześniej cieszył się znaczną przewagą prędkości 5G nad konkurentami, podczas gdy byli oni nadal silnie uzależnieni od wdrożeń DSS.
Wdrożenie średniego pasma zmienia rankingi wydajności 5G wśród polskich operatorów
Masowe wdrożenie nowej warstwy pojemności przez pozostałych trzech operatorów zdecydowanie zmieniło dynamikę wydajności 5G na polskim rynku i zmniejszyło przewagę Plusa. W ciągu jednego roku, między pierwszym kwartałem 2024 r. a pierwszym kwartałem 2025 r., Plus przesunął się z lidera rynku pod względem mediany prędkości pobierania 5G do jednego z wolniejszych, stając się jedynym polskim operatorem, który odnotował spadek prędkości 5G rok do roku, o 10%, co wskazuje na rosnące ograniczenia jego strategii 2600 MHz.
Orange i T-Mobile zyskują przewagę w wydajności 5G dzięki wdrożeniu pasma średniego
Speedtest Intelligence® | I kwartał 2023 – I kwartał 2025
Z kolei wdrożenie średniego pasma zwiększyło wydajność na pozostałej części rynku, a mediana prędkości 5G wzrosła aż o 72% w Play, 86% w T-Mobile i 90% w Orange między 1. kwartałem 2024 r. a 1. kwartałem 2025 r. Podczas gdy Orange był liderem polskiego rynku w pierwszym kwartale ze średnią prędkością pobierania 5G wynoszącą 222,11 Mb/s, przewaga operatora znacznie się zmniejszyła wraz z postępem budowy średniego pasma T-Mobile, przy czym T-Mobile odnotowuje obecnie medianę prędkości pobierania 5G na poziomie 201,76 Mb/s, znacznie wyprzedzając odpowiednio trzeciego i czwartego Play (122,64 Mb/s) i Plusa (116,76 Mb/s).
Przewaga Plusa w spójności 5G maleje, gdy przewaga pasma 2600 MHz ustępuje wraz z wdrożeniem pasma średniego
Speedtest Intelligence® | I kwartał 2023 – I kwartał 2025
Pomimo utraty pozycji lidera pod względem mediany prędkości pobierania 5G, Plus nadal prowadzi w 10. percentylu (29,44 Mb/s w 1. kwartale 2025 r.), co oznacza, że abonenci w obszarach o najniższych wynikach nadal cieszą się stosunkowo lepszymi prędkościami niż abonenci konkurencyjnych sieci. Przewaga ta jest prawdopodobnie związana z mniejszą zależnością Plusa od DSS. Jednak T-Mobile (24,48 Mb/s) i Orange (21,88 Mb/s) szybko zmniejszają lukę, a ich 10-procentowe prędkości 5G zbliżają się teraz do Plusa. Spójność sieci 5G Plusa, mierzona jako odsetek próbek Speedtest spełniających minimalny próg pobierania i wysyłania 25/3 Mbps, również spadła w ciągu ostatniego roku, chociaż pozostaje liderem rynku.
Tymczasem pod względem wydajności wysyłania, sieć 5G Play była liderem na rynku w pierwszym kwartale 2025 r., odnotowując medianę prędkości 19,33 Mb/s, a następnie Orange (18,99 Mb/s), T-Mobile (17,32 Mb/s) i Plus (14,96 Mb/s).
W przeciwieństwie do znacznych wzrostów prędkości pobierania, jak dotąd istnieją ograniczone dowody na to, że wdrożenie średniego pasma znacznie poprawiło wydajność wysyłania, przy czym mediana prędkości wysyłania była o około 6% niższa w pierwszym kwartale 2025 r. w porównaniu z tym samym kwartałem ubiegłego roku. Rozbieżność ta wynika przede wszystkim z faktu, że wszyscy czterej operatorzy nadal wdrażają 5G w trybie non-standalone (NSA), nadal wymagają od urządzeń technologii 4G do obsługi ruchu wysyłania i warstwy sygnałowej. W związku z tym nowo dostępne widmo 3,5 GHz zwiększa przepustowość łącza w dół, ale pozostawia zatłoczoną ścieżkę łącza 4G w górę bez zmian.
Play zyskuje przewagę w wydajności wysyłania danych w sieci 5G
Speedtest Intelligence® | I kwartał 2023 – I kwartał 2025
Inwestycje operatorów we wdrażanie nowej warstwy przepustowości 5G zbiegły się w czasie z szerszymi działaniami w zakresie modernizacji sieci RAN, przekładając się na lepszą jakość usług doświadczanych przez użytkowników w kluczowych zastosowaniach, takich jak wideo streaming i przeglądanie stron internetowych. Na przykład mediana czasu ładowania strony internetowej w sieci T-Mobile poprawiła się o około 4% między 3. kwartałem 2024 r. a 1. kwartałem 2025 r., co stawia ją w czołówce pod tym względem. Tymczasem Orange był liderem pod względem wskaźników wideo, takich jak czas rozpoczęcia, rozdzielczość i nieprzerwane odtwarzanie w ostatnim kwartale.
5G napędza poprawę jakości doświadczeń (QoE) w zastosowaniach takich jak przeglądanie stron internetowych
Speedtest Intelligence® | I kwartał 2025
Inwestycje kapitałowe zwiększają zasięg 5G, ale przepaść cyfrowa między wsią a miastem w Polsce utrzymuje się
Podczas gdy inwestycje w DSS i wdrożenie średniego pasma umożliwiły polskim operatorom poczynienie znaczących postępów w zakresie dostępności 5G, która wzrosła w skali kraju z 28,5% w I kwartale 2024 r. do 43,1% w I kwartale 2025 r., regionalne różnice w zasięgu nadal są cechą charakterystyczną sieci mobilnej w Polsce.
Operatorzy nadali priorytet wdrożeniom 5G w najbogatszych i najbardziej zaludnionych częściach Polski, gdzie światłowody są mocno rozwinięte, w tym w województwach mazowieckim (Warszawa) i pomorskim (Trójmiasto). W tych województwach dostępność 5G osiągnęła ponad 40% pod koniec ubiegłego roku i przyczyniła się do osiągnięcia znacznie wyższych średnich prędkości pobierania niż średnia krajowa.
Dostępność 5G pozostaje wysoce zróżnicowana w Polsce poza obszarami zurbanizowanymi
Speedtest Intelligence® | Dostępność 5G (%) w IV kw. 2024
Natomiast województwa przygraniczne na południu i zachodzie kraju nadal doświadczają znacznie niższych poziomów dostępności 5G. Województwo lubuskie miało najniższą dostępność (23,6% na koniec ubiegłego roku), gdzie występuje mniejsza gęstość zaludnienia i niższe wydatki abonentów, co zmniejsza zachęty komercyjne operatorów do powszechnych inwestycji w 5G. Tendencja ta doprowadziła do powstania znacznej luki prędkości między województwami, a abonenci mobilni w Lubuskiem również doświadczają najniższej mediany prędkości pobierania (59,97 Mb/s) w Polsce, prawie 33% poniżej wiodącego województwa mazowieckiego.
Prędkości pobierania w sieciach mobilnych są niższe na mniej zurbanizowanych obszarach Polski
Speedtest Intelligence® | Mediana prędkości pobierania (Mbps) w IV kw. 2024
Wdrożenie średniego pasma poprawia konkurencyjność mobilną Polski, ale spójność 5G nadal ustępuje regionalnym konkurentom
Z punktu widzenia konkurencyjności regionalnej, intensywne wdrożenia średniego pasma skutecznie przełamały cykl słabej wydajności sieci mobilnej w Polsce, a mediana prędkości pobierania 5G wzrosła średnio o ponad 50% do 160,30 Mb/s między 1. kwartałem 2024 r. a 1. kwartałem 2025 r. Dzięki temu Polska po raz pierwszy wyprzedziła Czechy, Rumunię i Słowację pod względem prędkości pobierania 5G.
Wdrożenia pasma średniego napędzają regionalną konkurencyjność Polski
Speedtest Intelligence® | 2020–2025
Pomimo postępów Polski we wdrażaniu 5G w średnim paśmie, utrzymujące się skutki polegania na DSS i ograniczonej różnorodności widma 5G aż do niedawnej aukcji 700/800 MHz oznaczają, że Polska nadal pozostaje w tyle za swoimi regionalnymi rówieśnikami pod względem spójności sieci 5G. W pierwszym kwartale 2025 r. 82% próbek Speedtest w Polsce spełniło minimalny próg wydajności 5G dla spójnego doświadczenia mobilnego, w porównaniu do 86% na Węgrzech, 89% w Rumunii i 93% w Bułgarii.
Nowo pozyskana różnorodność częstotliwości 5G daje polskim operatorom potężne narzędzie do stymulowania wzrostu ARPU
Wcześniejsza zależność Polski od DSS, wynikająca z ograniczonej różnorodności widma 5G, prawdopodobnie przyczyniła się do wolniejszego wzrostu średniego przychodu na użytkownika (ARPU) w porównaniu z sąsiednimi krajami na przestrzeni ostatnich lat. Polscy operatorzy początkowo wprowadzili taryfy z “5G bez dodatkowych kosztów” dodane do istniejących pakietów 4G, utrzymując ceny na stałym poziomie w celu obrony udziału w rynku (a tym samym utrzymując obniżone poziomy ARPU w porównaniu do regionalnych konkurentów). W połączeniu z zewnętrznym szokiem makroekonomicznym wywołanym znacznie wyższymi cenami energii, stagnacja poziomów ARPU stworzyła trudne warunki operacyjne na polskim rynku i wpłynęła na rentowność operatorów.
Intensywna konkurencja cenowa spowodowała erozję przychodów w Polsce w pierwszej połowie cyklu 5G
Analiza danych GSMA Intelligence | Zmiana procentowa ARPU w usługach mobilnych (I kw. 2020 vs I kw. 2023)
Z kolei na sąsiednich rynkach operatorzy byli w stanie wykorzystać wdrożenie częstotliwości w średnim paśmie zarówno jako korzyści techniczne, jak i marketingowe, przenosząc swoje strategie z konkurencji cenowej na zróżnicowanie oparte na usługach. Pozwoliło im to skuteczniej sprzedawać wyższe poziomy prędkości lub zarabiać na konkretnych rozwiązaniach, takich jak stały dostęp bezprzewodowy (FWA), dla którego działania wdrożone 5G w średnim paśmie nadaje się idealnie.
T-Mobile i Play wyprzedziły konkurentów w tempie wzrostu udziału subskrypcji w ostatnich latach
Analiza danych rynkowych UKE | 2019–2023
Podobnie, opóźniony termin polskiej aukcji 5G dla średniego pasma prawdopodobnie osłabił czynniki po stronie podaży, będące kluczowymi dla napędzania wzrostu konsumpcji danych z sieci mobilnych. W okresie od I kwartału 2020 r. do IV kwartału 2024 r. wolumen ruchu w sąsiedniej Bułgarii po raz pierwszy zrównał się z wolumenem w Polsce, wzrastając 4,8-krotnie w porównaniu do 2,6-krotnego wzrostu w Polsce.
W międzyczasie bułgarscy operatorzy wcześnie wykorzystali dostępność widma w średnim paśmie, aby agresywnie promować konkurencyjne rozwiązania FWA (główny czynnik napędzający ruch mobilny na rynkach rozwiniętych) i wprowadzić tanie taryfy nieograniczonej transmisji danych z mniejszymi ograniczeniami użytkowania.
Polska utrzymuje regionalne prowadzenie w wolumenach danych mobilnych, ale Bułgaria szybko nadrabia
Analiza danych GSMA Intelligence | 2020–2024
Od tego czasu polscy operatorzy starali się powtórzyć sukces Bułgarii, wprowadzając odrębny marketing dla swoich wdrożeń 5G w średnim paśmie, aby odróżnić nowsze wdrożenia 5G w średnim paśmie od wcześniejszych. T-Mobile oparł się na marce “5G Bardziej”, podczas gdy Plus użył sloganu marketingowego “5G Ultra”, aby wskazać dodatkowy wzrost wydajności odblokowany przez ich nowe sieci 5G w lokalizacjach, w których wdrożono dedykowane częstotliwości średniego pasma. Strategia ta stała się częścią szerszej zmiany na rynku, w której wszyscy operatorzy odchodzą od hiper-koncentracji opierającej się na konkurencji cenowej w kierunku strategii cenowych “więcej za więcej”, wspierając poprawę rentowności i ponowny wzrost ARPU.
Polska przoduje w regionalnym wzroście ARPU od momentu rozpoczęcia wdrożeń średniego pasma 5G
Analiza danych GSMA Intelligence | Zmiana procentowa ARPU w usługach mobilnych (I kw. 2023 vs I kw. 2025)
Aktywacja niskiego pasma i postępy w budowie sieci mają na celu wzmocnienie zysków 5G w średnim paśmie
W związku z tym, że polski regulator telekomunikacyjny, UKE, ustanowił jeden z najbardziej ambitnych zobowiązań dotyczących zasięgu w Europie dla ostatnich aukcji częstotliwości średniego i niskiego pasma, operatorzy raczej nie opóźnią komercyjnych wdrożeń w nowo nabytych pasmach 700 i 800 MHz. Oczekuje się, że wdrożenia te rozpoczną się w przyszłym miesiącu i będą miały kluczowe znaczenie dla ustanowienia krajowej warstwy zasięgu 5G, która znacznie poprawi pokrycie ciężko dostępnych miejsc wewnątrz budynków w miastach i zdalnych obszarów wiejskich. Rozszerzony zasięg będzie również wspierał szersze wdrażanie usług głosowych przez LTE (VoLTE), przyspieszając schyłek 3G i uwalniając dodatkowe widmo w paśmie 900 MHz.
Wkrótce powrócimy do tego tematu, aby ocenić, jak polscy operatorzy radzą sobie z wdrażaniem nowych częstotliwości niskopasmowych i jak skutecznie uzupełniają trwający proces wygaszania 3G.
Ookla retains ownership of this article including all of the intellectual property rights, data, content graphs and analysis. This article may not be quoted, reproduced, distributed or published for any commercial purpose without prior consent. Members of the press and others using the findings in this article for non-commercial purposes are welcome to publicly share and link to report information with attribution to Ookla.