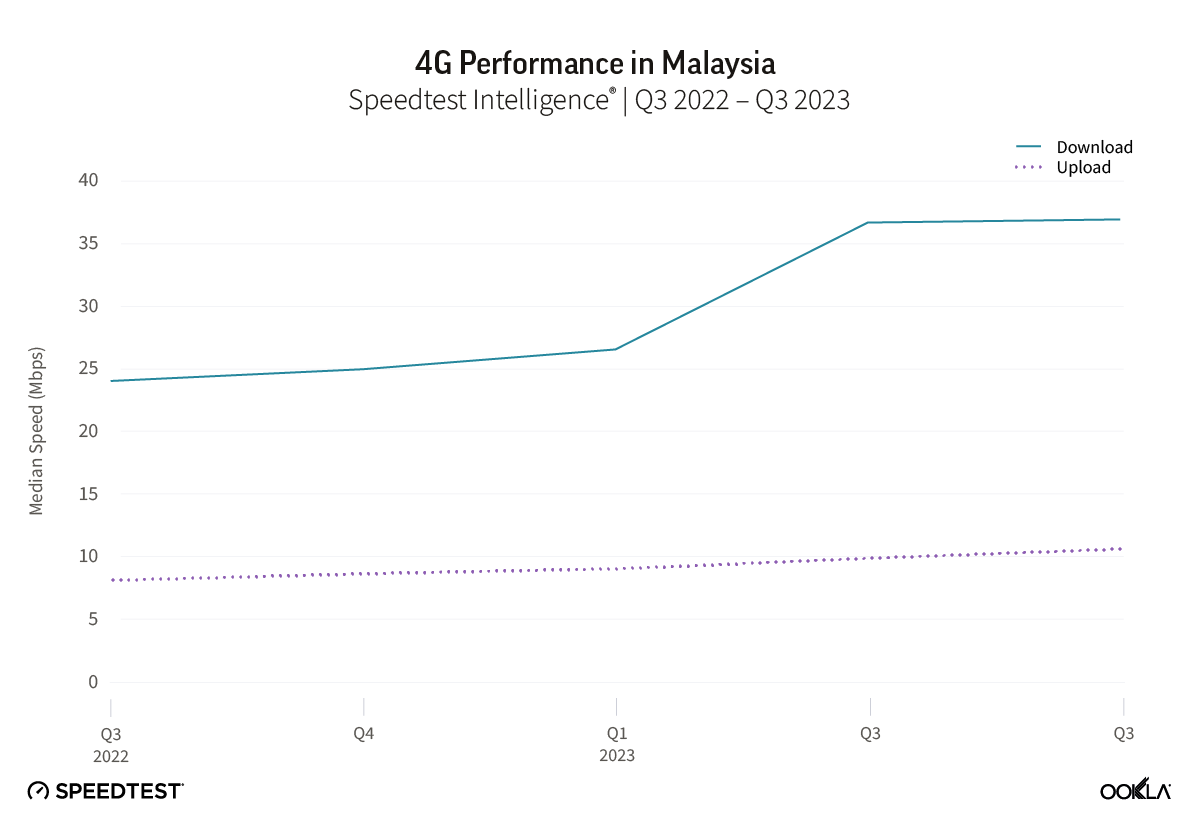Ookla® Market Reports™ identify key data about internet performance in countries across the world. This quarter we’ve provided updated analyses for 52 markets using Speedtest Intelligence® and summarized the top takeaways below. Click through to the market report to see more details and charts about the countries you’re interested in, including the fastest fixed broadband providers and mobile operators, who had the most consistent service, as well as 5G and device performance in select countries during Q4 2023. Jump forward to a continent using these links:
Africa | Americas | Asia | Europe | Oceania
Africa
- Côte d’Ivoire: Orange recorded the fastest median mobile and fixed download speeds during Q4 2023, at 30.13 Mbps and 65.90 Mbps, respectively. Moov Africa recorded the lowest mobile median multi-server latency at 83 ms, while CANALBOX recorded the lowest latency over fixed broadband at 70 ms. Of Côte d’Ivoire most populous cities, Abidjan had the fastest median fixed download speed of 58.88 Mbps.
- Mozambique: Tmcel recorded the fastest mobile median download speed of 27.80 Mbps in Q4 2023, and also the highest mobile Consistency at 91.6%. Of Mozambique’s most populous cities, Maputo had the fastest median mobile and fixed download speeds at 26.33 Mbps and 14.65 Mbps, respectively. SpaceX’s Starlink recorded the fastest fixed broadband median download speed in Q4 2023 at 36.13 Mbps, along with the highest Consistency at 49.7%. Meanwhile, TVCABO recorded the lowest latency over fixed broadband at 16 ms.
- Senegal: There was no winner of fastest median mobile performance in Senegal during Q4 2023, with Free and Orange both tied. Orange led the market for median fixed broadband download performance, with 21.46 Mbps in Q4 2023. Orange also had the lowest latency at 90 ms and highest Consistency of 45.4%. Of Senegal’s most populous cities, Dakar had the fastest median fixed download speed of 27.11 Mbps.
Americas
- Argentina: Personal had the fastest median download speed over mobile at 36.59 Mbps, while also registering the lowest latency of 39 ms during Q4 2023. In the fixed broadband market, there was no statistically fastest network, with Movistar and Telecentro delivering median download speeds of 106.41 Mbps and 105.98 Mbps, respectively. Movistar recorded the lowest latency of 9 ms. Among Argentina’s most populous cities, Mendoza recorded the fastest mobile median download speed of 37.75 Mbps, while Buenos Aires recorded the fastest fixed download speed of 109.79 Mbps.
- Belize: Digi had the fastest median mobile download and upload speeds of 17.50 Mbps and 9.28 Mbps, respectively during Q4 2023. Digi also recorded the highest Consistency of 80.3%, while smart! recorded the lowest median latency of 56 ms. There was no statistically fastest fixed network in the market based on download speed, however NEXGEN recorded the fastest median upload speed at 47.47 Mbps.
- Canada: Bell was the fastest mobile operator in Canada with a median download speed of 121.33 Mbps in Q4 2023. Bell also had the fastest median 5G download speed at 194.23 Mbps. Rogers had the fastest median mobile upload speed of 15.10 Mbps, and the highest Consistency of 88.2%. Bell pure fibre was fastest for fixed broadband, recording a median download speed of 307.77 Mbps and a median upload speed of 264.97 Mbps. Bell pure fibre also recorded the highest Video Score, of 87.90. Of Canada’s most populous cities, St. John’s recorded the fastest median mobile download speed at 171.76 Mbps, while Fredericton recorded the fastest median fixed broadband download speed of 247.89 Mbps.
- Colombia: Movistar was fastest for fixed broadband with a median download speed of 210.46 Mbps in Q4 2023. ETB had the lowest latency over fixed broadband at 7 ms. Of Colombia’s most populous cities, Cartagena recorded the fastest median fixed download speed of 146.74 Mbps.
- Costa Rica: Claro had the fastest median download speed among mobile operators at 40.56 Mbps during Q4 2023. Liberty recorded the fastest median upload speed at 10.73 Mbps, the lowest mobile latency at 33 ms, and the highest Consistency at 78.6%. Metrocom was fastest for fixed broadband download and upload performance, at 225.94 Mbps and 179.66 Mbps, respectively. Metrocom also recorded the lowest latency, at 6 ms.
- Dominican Republic: Claro had the fastest median download and upload speeds among mobile operators at 34.27 Mbps and 9.84 Mbps, respectively. Claro also recorded the highest Consistency, at 77.0%. Viva had the lowest mobile latency at 43 ms. SpaceX’s Starlink was fastest for fixed broadband download performance at 48.08 Mbps, while Claro recorded the fastest median upload speed at 25.38 Mbps, and the lowest latency at 41 ms. Altice recorded the highest fixed broadband Consistency, at 66.6%.
- Ecuador: CNT recorded the fastest median mobile download speed during Q4 2023, at 26.22 Mbps, while Movistar recorded the lowest mobile multi-server latency at 41 ms. Netlife was fastest for fixed broadband, with a median download speed of 91.56 Mbps. Netlife also recorded the lowest latency over fixed broadband at 8 ms. Xtrim recorded the highest fixed broadband Consistency at 84.8%. Of Ecuador’s most populous cities, Santo Domingo recorded the fastest median mobile download speed of 31.58 Mbps, while Guayaquil recorded the fastest median fixed download speed of 88.59 Mbps.
- El Salvador: Claro had the fastest median download speed among mobile operators in El Salvador, at 40.97 Mbps, along with the highest Consistency of 90.4%. Movistar registered the fastest median mobile upload speed of 13.35 Mbps and lowest latency at 73 ms. Cable Color recorded the fastest median fixed download speed at 55.57 Mbps, the top median upload speed at 57.04 Mbps, and the lowest median latency of 51 ms. Of El Salvador’s most populous cities, Santa Tecla showed the fastest median mobile and fixed download speeds during Q4 2023 at 39.27 Mbps and 54.98 Mbps respectively.
- Guatemala: Claro was the fastest mobile operator in Guatemala during Q4 2023 with a median download speed of 41.63 Mbps and a median upload speed of 19.61 Mbps. Claro also had the highest Consistency at 87.9%, while also leading the market for 5G performance, with a median 5G download speed of 388.34 Mbps. Tigo recorded the lowest median mobile latency at 79 ms. SpaceX’s Starlink was fastest for median fixed download performance at 54.32 Mbps, while Cable Color was fastest for fixed upload performance at 33.45 Mbps. Cable Color also had the lowest median latency on fixed broadband at 27 ms. Claro recorded the highest fixed broadband Consistency at 73.1%. Of Guatemala’s most populous cities, Escuintla showed the fastest median mobile download speed during Q4 2023 at 44.16 Mbps, while Villa Nueva recorded the fastest median fixed download speed, at 60.83 Mbps.
- Guyana: There was no winner of fastest median mobile performance in Guyana during Q4 2023, with ENet and Digicel posting median download speeds of 24.64 Mbps and 23.53 Mbps, respectively. ENet recorded the fastest median mobile upload speed at 18.49 Mbps and offered the lowest median latency at 143 ms. In the fixed broadband market, ENet recorded the fastest median download and upload speeds, of 70.20 Mbps and 52.25 Mbps, respectively, while also recording the lowest median latency of 130 ms. GTT recorded the highest fixed broadband Consistency during Q4 2023, at 69.2%.
- Haiti: Digicel was the fastest mobile operator in Haiti with a median mobile download speed of 14.26 Mbps, a median upload speed of 10.52 Mbps, and Consistency of 67.2%. Natcom recorded the lowest mobile latency, of 62 ms. SpaceX Starlink had the fastest median fixed download speed at 41.73 Mbps. Natcom had the fastest median fixed upload speed at 31.89 Mbps, the lowest median fixed latency at 47 ms, and the highest fixed broadband Consistency of 64.0%.
- Honduras: Claro recorded the fastest median mobile download and upload speeds during Q4 2023, of 53.06 Mbps and 16.22 Mbps, respectively, while also recording the highest Consistency at 87.2%. Tigo recorded the lowest median mobile latency at 93 ms. Claro had the fastest median fixed download speed at 47.26 Mbps during Q4 2023, and the highest fixed broadband Consistency at 80.2%. TEVISAT recorded the fastest median upload speed, of 22.36 Mbps, and the lowest median fixed latency at 20 ms. Of Honduras’ most populous cities, El Progreso recorded the fastest median mobile download speed during Q4 2023, of 41.69 Mbps, while Tegucigalpa showed the fastest median fixed download speed at 41.97 Mbps.
- Jamaica: There was no winner of fastest median mobile download performance in Jamaica during Q4 2023, with Flow and Digicel tied. Digicel recorded the fastest median upload speed of 8.37 Mbps and highest Consistency of 81.9%. Flow had the lowest mobile median latency at 38 ms. SpaceX Starlink had the fastest median download speed over fixed broadband at 84.10 Mbps, and the highest fixed broadband Consistency at 77.8%. Digicel+ recorded the fastest median upload speed of 46.14 Mbps, while Flow recorded the lowest median fixed latency at 25 ms.
- Mexico: Telcel had the fastest median download and upload speeds over mobile at 52.06 Mbps and 13.50 Mbps, respectively, and the operator also delivered the fastest median 5G download speed at 233.82 Mbps. Telcel also had the lowest mobile median latency at 62 ms and highest Consistency at 87.2%. Totalplay was fastest for fixed broadband with a median download speed of 88.87 Mbps and a median upload speed of 30.50 Mbps. Totalplay also had the lowest median fixed broadband latency at 28 ms and the highest Consistency at 84.0%. Among Mexico’s most populous cities, Monterrey recorded the fastest median mobile download speed of 38.36 Mbps, while Guadalajara recorded the fastest median fixed broadband speed of 80.32 Mbps.
- Panama: MasMovil was the fastest mobile operator with median download and upload speeds of 27.24 Mbps and 15.18 Mbps, respectively, as well as the highest Consistency of 79.3%. Digicel recorded the lowest median mobile latency, at 34 ms. There was no winner of the fastest median fixed download performance, with both Tigo and MasMovil tied. MasMovil recorded the fastest median upload speed of 33.38 Mbps and the lowest median latency at 16ms. Among Panama’s most populous cities, David recorded the fastest median mobile download speed of 21.57 Mbps, while La Chorrera recorded the fastest median fixed broadband speed of 156.71 Mbps.
- Peru: Claro was the fastest mobile operator in Peru with a median download speed of 23.30 Mbps during Q4 2023, and also had the highest mobile Consistency in the market with 80.6%.
- Trinidad and Tobago: Digicel had the fastest median download speed over mobile at 33.29 Mbps and the highest Video Score in the market at 74.86. bmobile recorded the fastest median mobile upload speed of 12.17 Mbps, and the lowest median latency at 32 ms. Digicel+ had the fastest median fixed broadband download and upload speeds at 118.53 Mbps and 107.24 Mbps, respectively. Digicel+ also had the lowest median latency at 7 ms.
- United States: T-Mobile was the fastest mobile operator with median download and upload speeds of 188.96 Mbps and 12.19 Mbps, respectively. T-Mobile also recorded the highest mobile Consistency at 87.3%, and the lowest median mobile latency of 50 ms. T-Mobile also led the market with the fastest median 5G download speed at 238.87 Mbps, as well as the lowest 5G latency of 48 ms. T-Mobile secured the highest Video Score across all technologies with 78.21, and for 5G, with a Video Score of 81.54. Cox led the market as the fastest fixed broadband provider with a median download speed of 261.27 Mbps, while AT&T Internet recorded the fastest median fixed upload speed of 195.64 Mbps, and Verizon had the lowest median latency over fixed broadband at 15 ms.
- Uruguay: Antel was the fastest mobile operator in Uruguay during Q4 2023 with a median download speed of 117.79 Mbps, and recorded the lowest median latency of 44 ms.
- Venezuela: Digitel was the fastest mobile operator with a median download speed of 14.37 Mbps and a median upload speed of 6.97 Mbps during Q4 2023. Digitel also recorded the highest Consistency in the market, with 68.0%, and the lowest median latency of 97 ms. Airtek Solutions had the fastest median fixed download and upload speeds of 94.76 Mbps and 94.89 Mbps, respectively. Airtek Solutions also recorded the highest fixed broadband Consistency of 86.0%, and the lowest median latency at 7 ms. Among Venezuela’s most populous cities, Maracaibo recorded the fastest median mobile and fixed download speeds of 17.17 Mbps and 82.35 Mbps, respectively.
Asia
- Afghanistan: The fastest mobile operator in Afghanistan was Afghan Wireless with a median download speed of 6.68 Mbps in Q4 2023. The operator also had the lowest median latency at 77 ms and the highest Consistency of 51.0%.
- Bangladesh: Banglalink was the fastest mobile operator in Bangladesh with a median download speed of 26.74 Mbps in Q4 2023. Banglalink also recorded the highest Consistency of 89.0% and the lowest median latency of 33 ms. DOT Internet was the fastest fixed broadband provider with a median download speed of 91.35 Mbps, while also recording the highest Consistency at 87.5% and the lowest median latency at 5 ms.
- Bhutan: There was no statistical winner for fastest mobile download performance during Q4 2023 in Bhutan, with TashiCell and BT both tied with speeds of 31.52 Mbps and 28.15 Mbps, respectively. TashiCell recorded the lowest median mobile latency of 52 ms.
- Brunei: There was no statistical winner for fastest mobile download performance during Q4 2023 in Brunei, with DST and Imagine both tied with speeds of 97.34 Mbps and 91.53 Mbps, respectively.
- Cambodia: Cellcard recorded the fastest median mobile download speed at 33.74 Mbps during Q4 2023, while Metfone recorded the highest Consistency at 80.8% and the lowest median latency at 38 ms. MekongNet was the fastest fixed broadband provider, with a median fixed download speed of 48.29 Mbps. MekongNet also recorded the highest Consistency at 71.1%. OpenNet recorded the lowest median latency over fixed broadband, at 7ms.
- China: China Broadnet was the fastest mobile operator in China during Q4 2023, with a median download speed of 248.77 Mbps, and median 5G download speed of 305.61 Mbps. China Mobile recorded the lowest median mobile latency, at 42 ms. There was no statistical winner for fastest fixed download performance, with China Unicom and China Mobile both tied with speeds of 246.93 Mbps and 245.59 Mbps, respectively. China Mobile recorded the highest fixed broadband Consistency, of 93.4%, while China Telecom recorded the lowest median fixed broadband latency at 22 ms. Among China’s most populous cities, Beijing recorded the fastest median mobile download speed of 232.41 Mbps, while Tianjin recorded the fastest median fixed download speed of 326.07 Mbps.
- Georgia: Geocell recorded the fastest mobile download performance during Q4 2023 in Georgia, at 50.52 Mbps, and the lowest mobile latency at 37 ms. MagtiCom had the fastest median fixed download speed at 27.81 Mbps and the highest Consistency of 66.5%. Among Georgia’s most populous cities, Tbilisi recorded the fastest median mobile download speed of 36.17 Mbps, while Rustavi recorded the fastest median fixed download speed of 27.38 Mbps.
- Hong Kong (SAR): China Mobile Hong Kong was the fastest mobile operator in Hong Kong (SAR) during Q4 2023, with a median download speed across all technologies of 98.94 Mbps, and a median download speed over 5G of 177.96 Mbps. csl recorded the fastest median mobile upload speed, at 16.89 Mbps.
- Indonesia: Telkomsel was the fastest Indonesian mobile operator with a median download speed of 31.14 Mbps. Telkomsel also had the lowest median mobile latency at 45 ms.
- Japan: Rakuten Mobile recorded the fastest mobile download and upload speeds during Q4 2023 in Japan, at 51.16 Mbps and 20.21 Mbps, respectively. Rakuten Mobile also recorded the highest Consistency in the market at 90.6%, while SoftBank recorded the lowest median latency at 43 ms. So-net had the fastest fixed download and upload speeds, at 296.29 Mbps and 219.53 Mbps, respectively, as well as the lowest median latency over fixed broadband at 9 ms. SpaceX Starlink recorded the highest fixed broadband Consistency in the market at 96.4%.
- Kazakhstan: Tele2 recorded the highest mobile Consistency in Kazakhstan during Q4 2023 with 85.3% and the lowest median mobile latency at 39 ms.
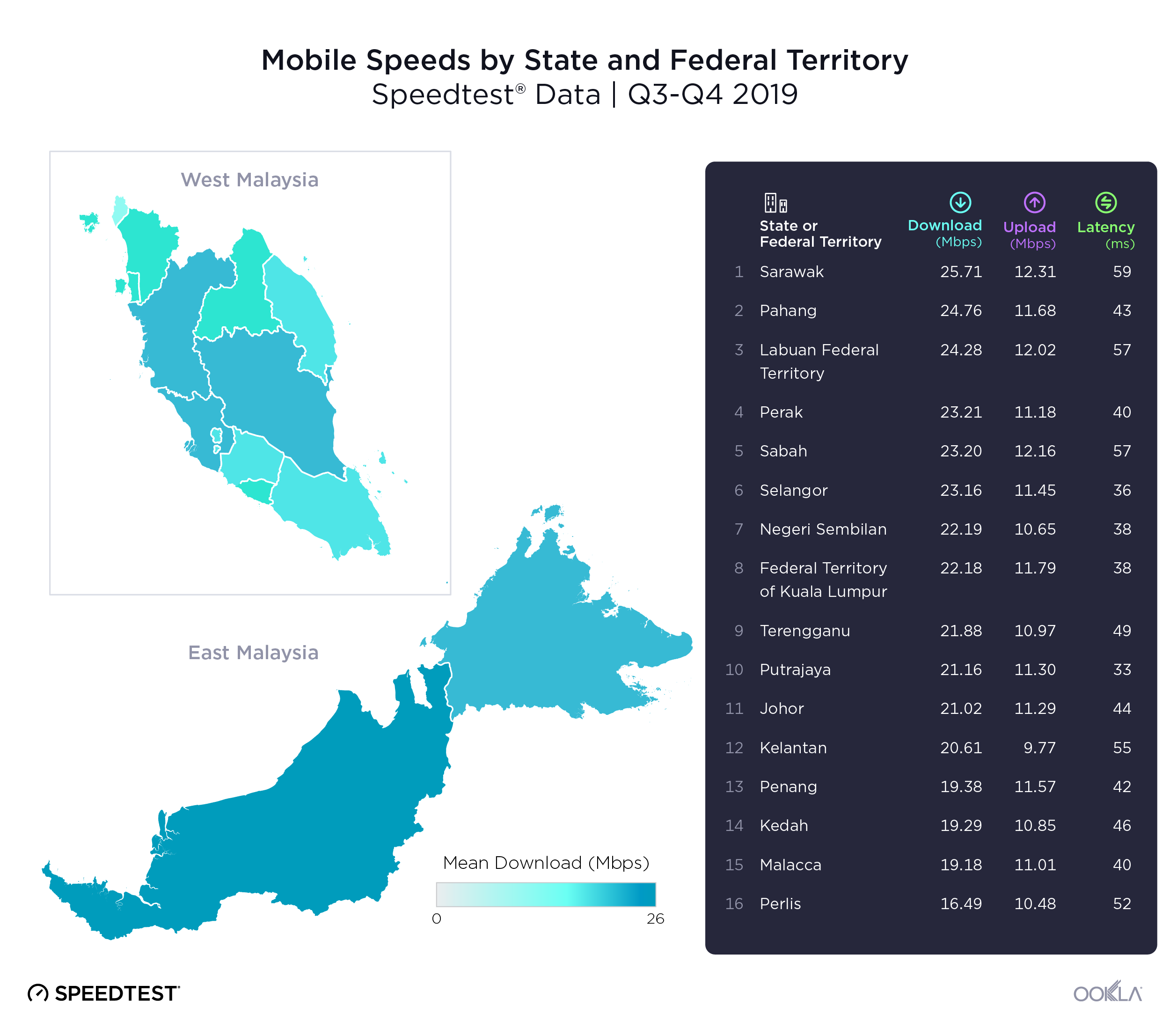
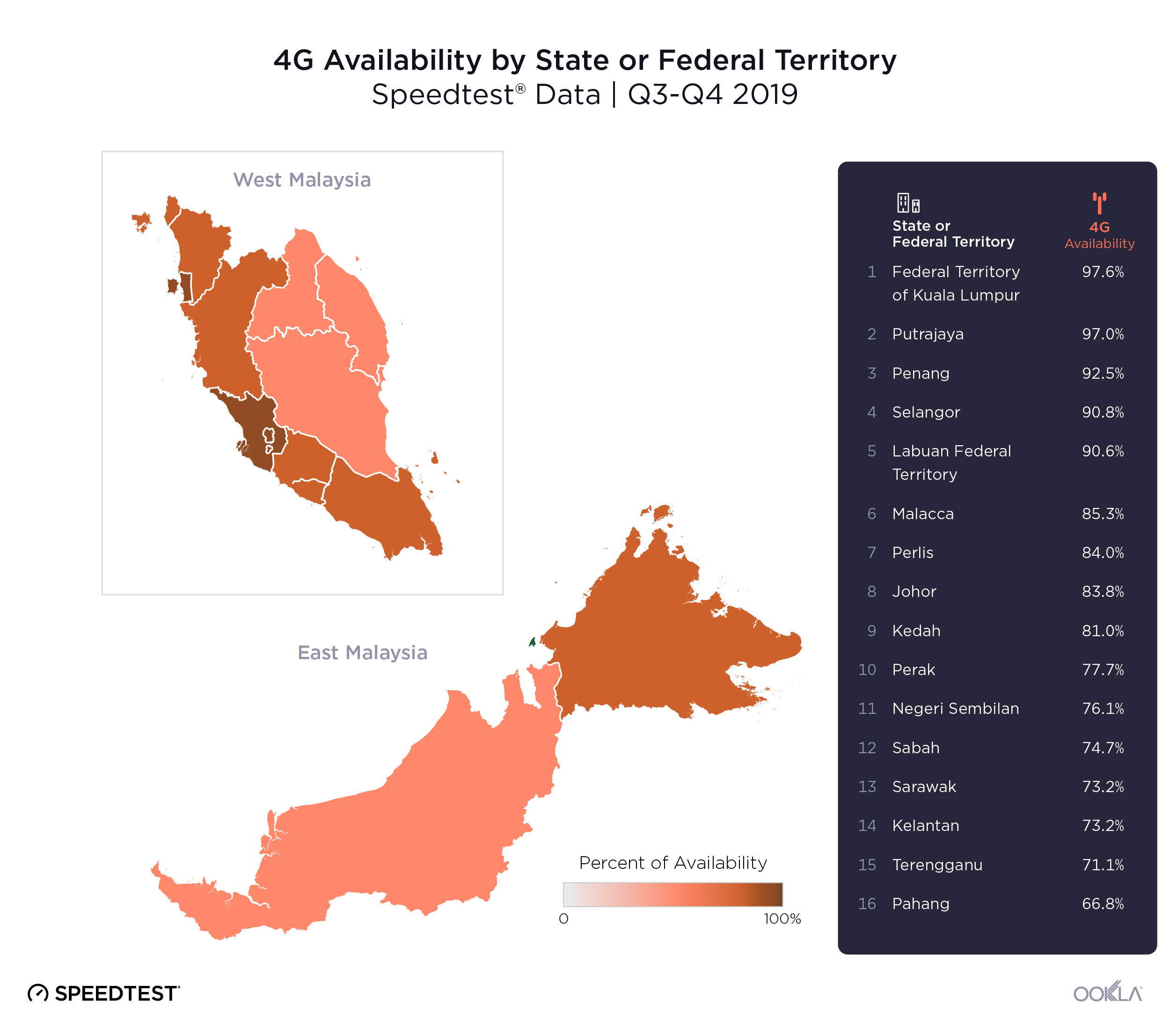
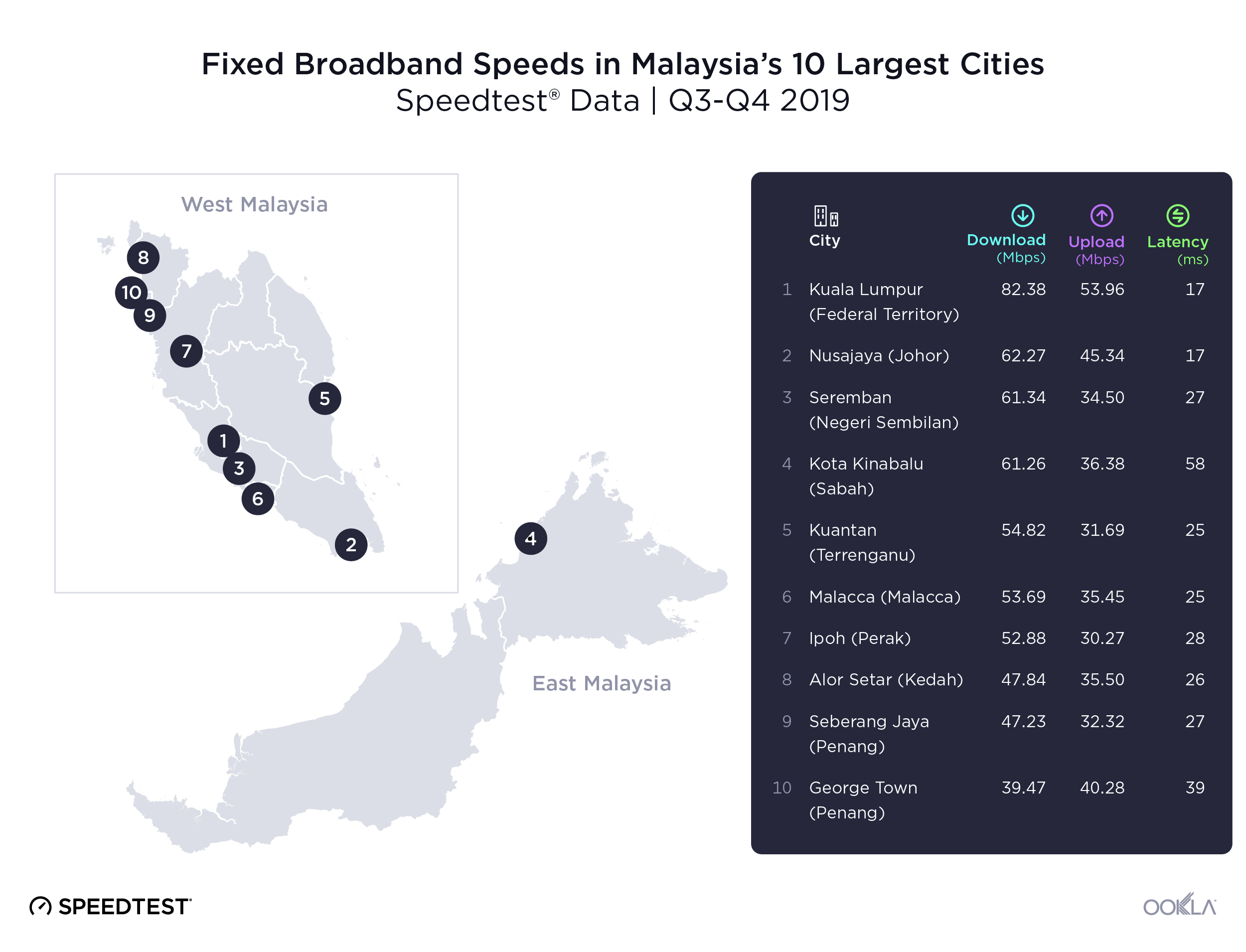
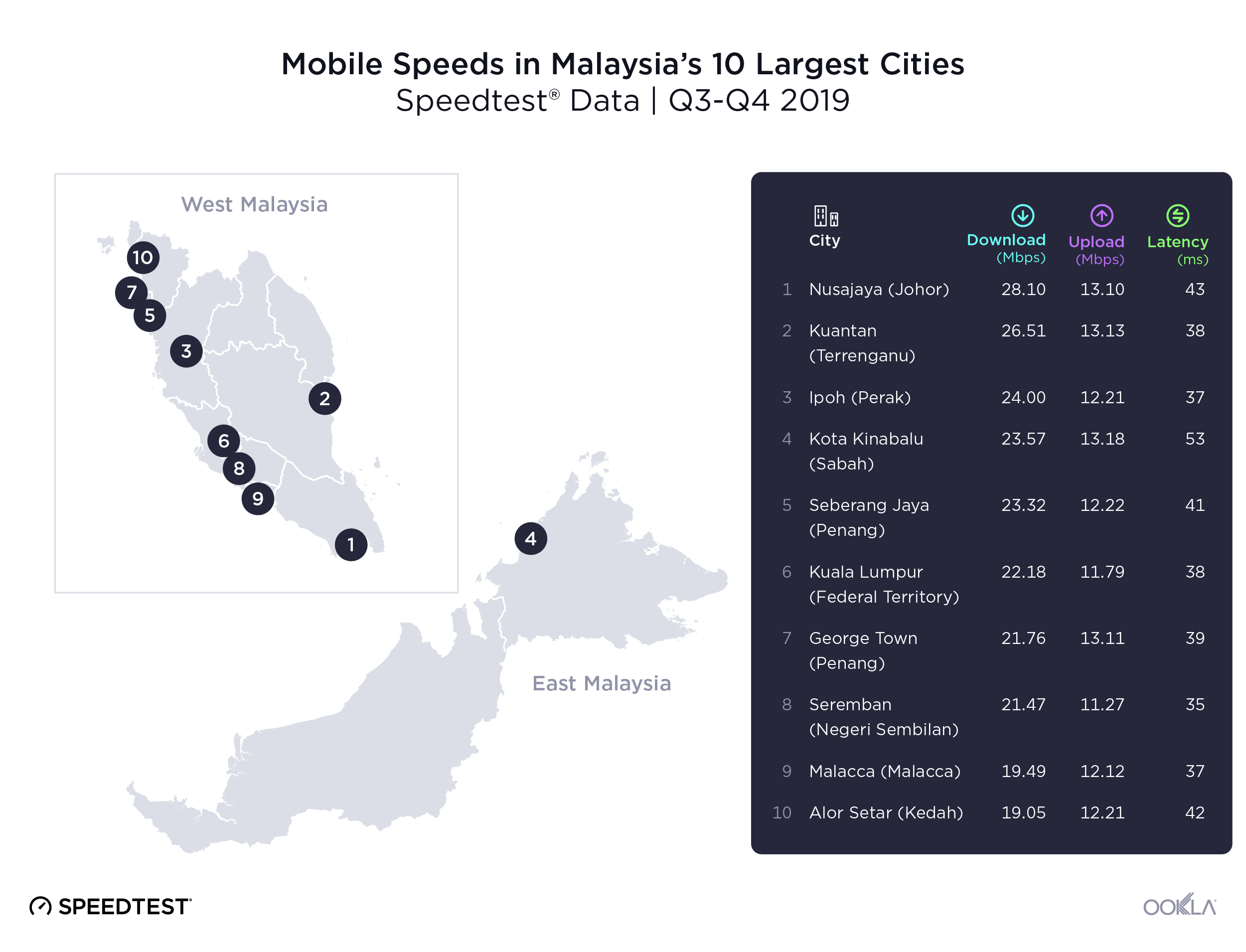
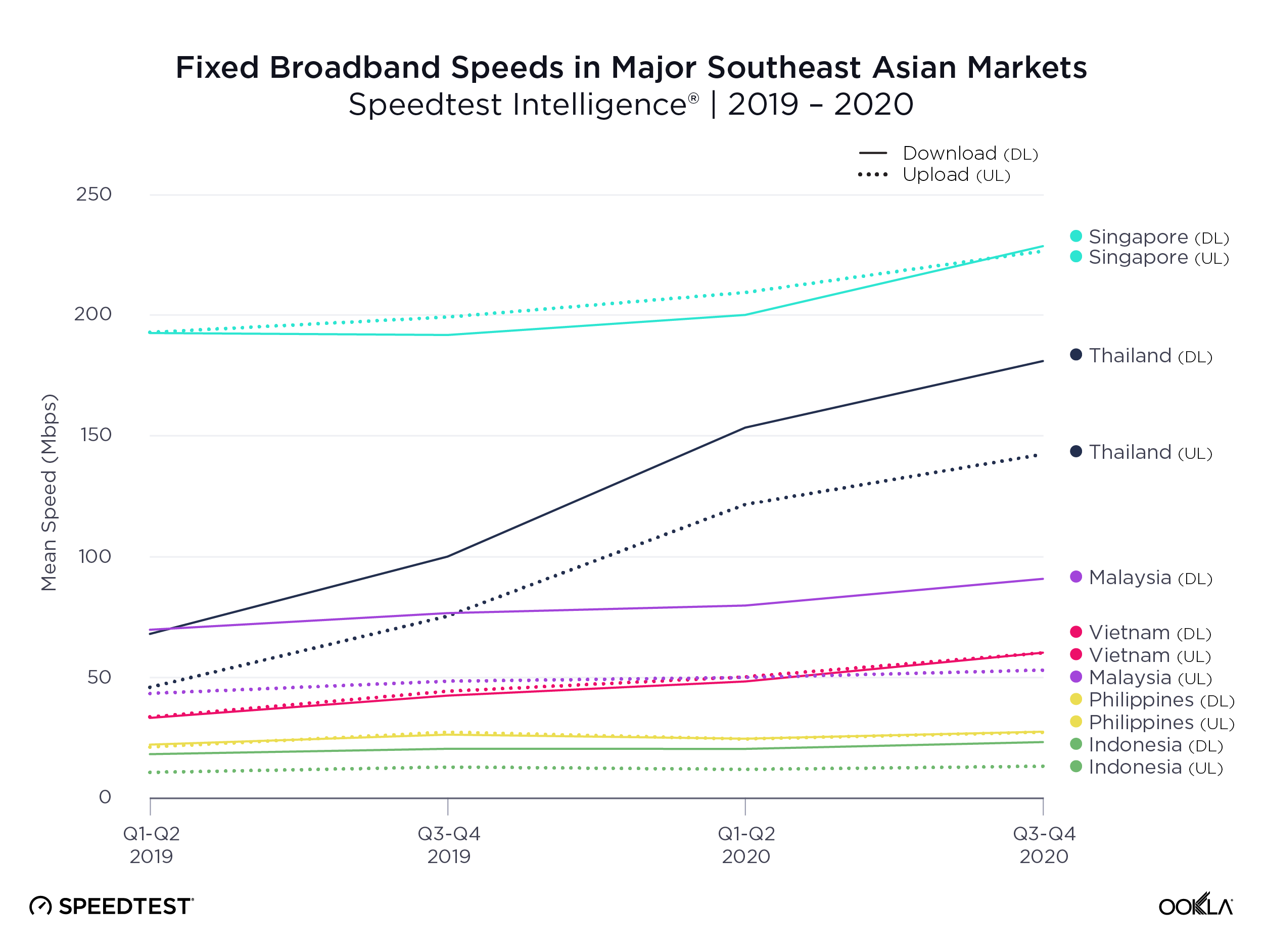
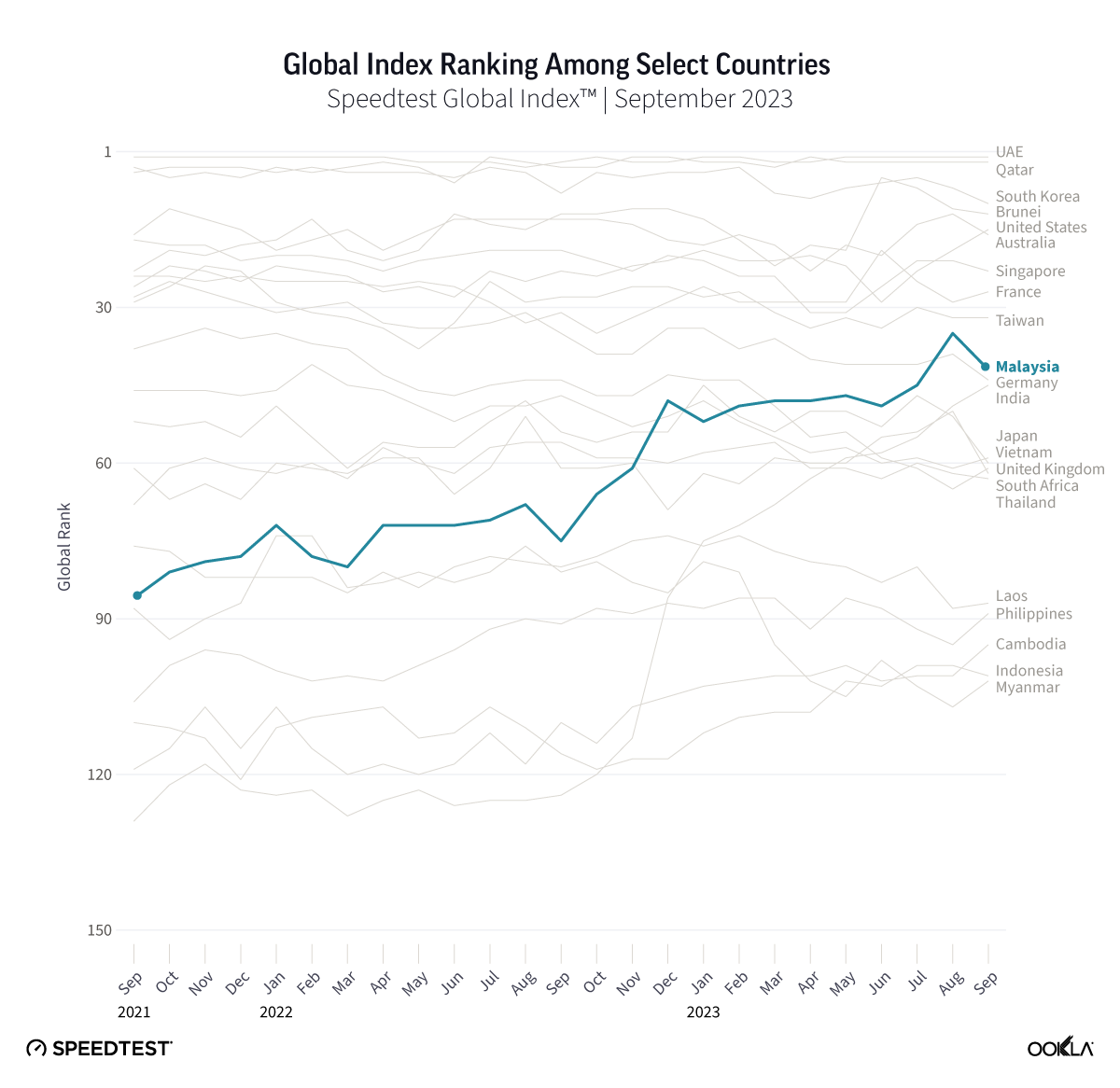
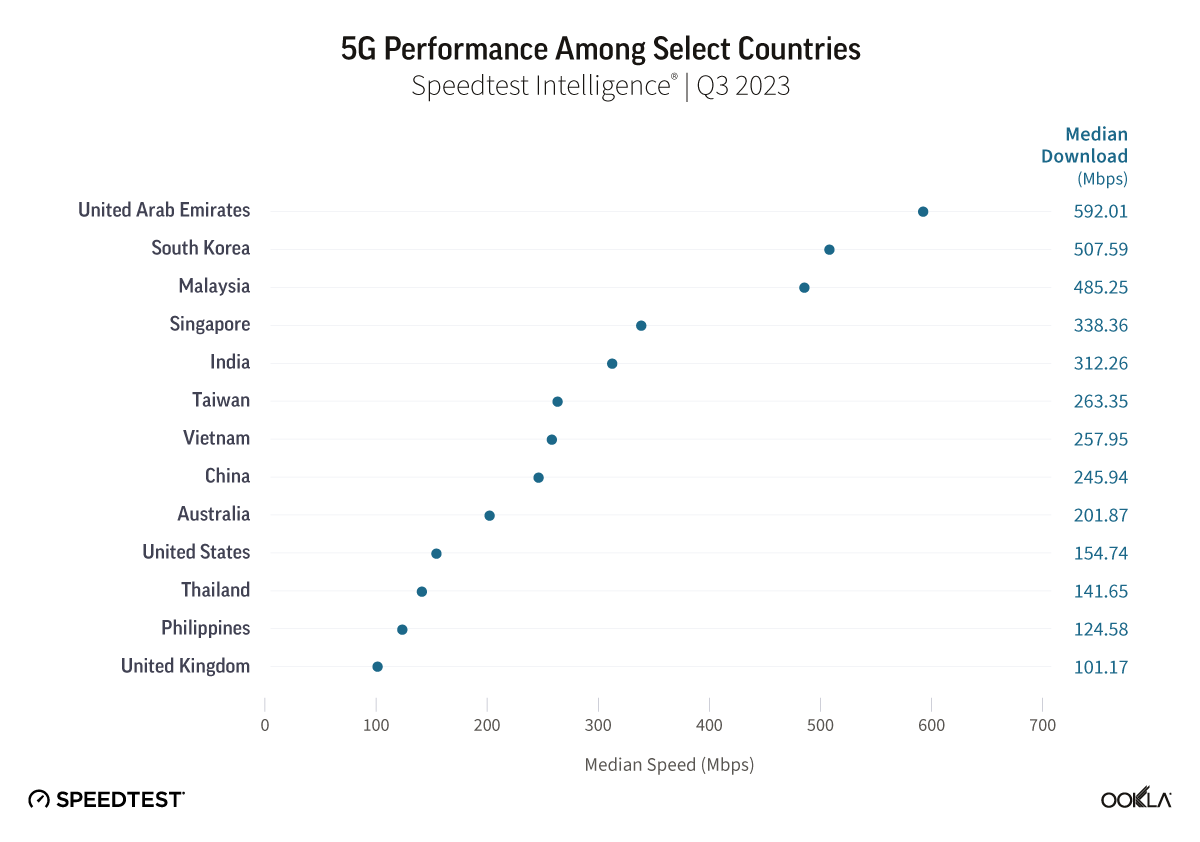
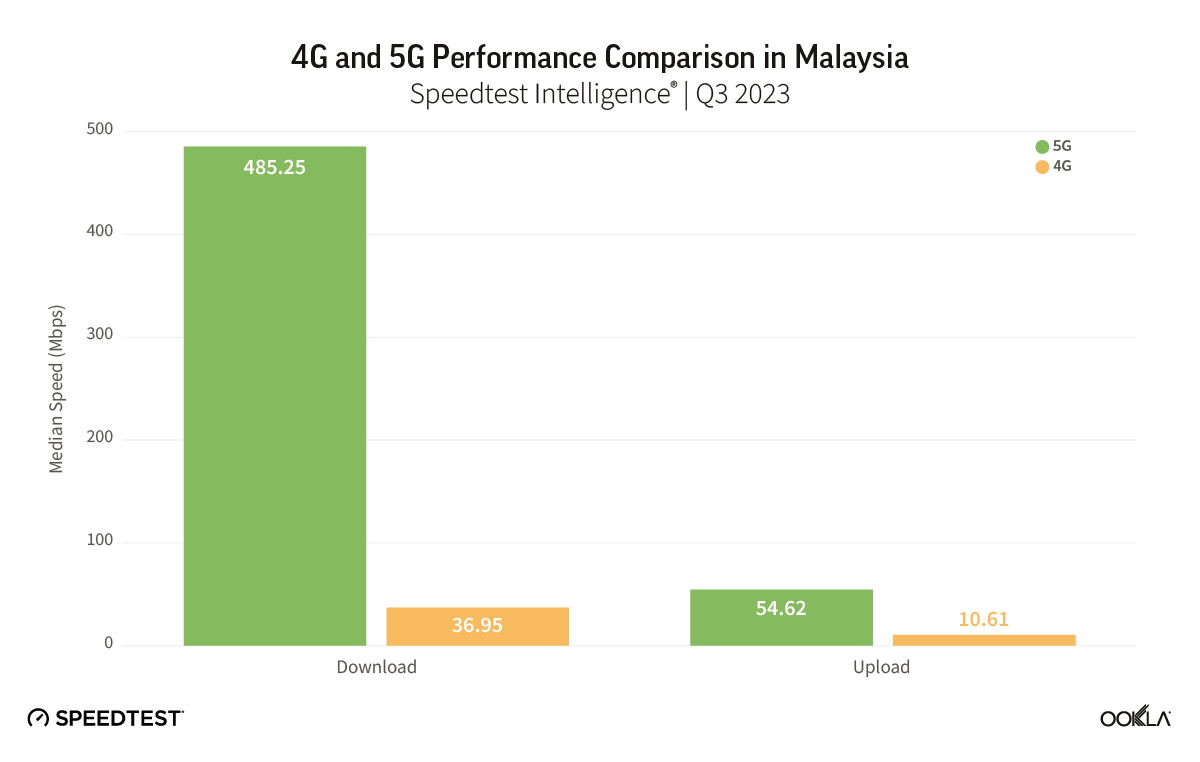
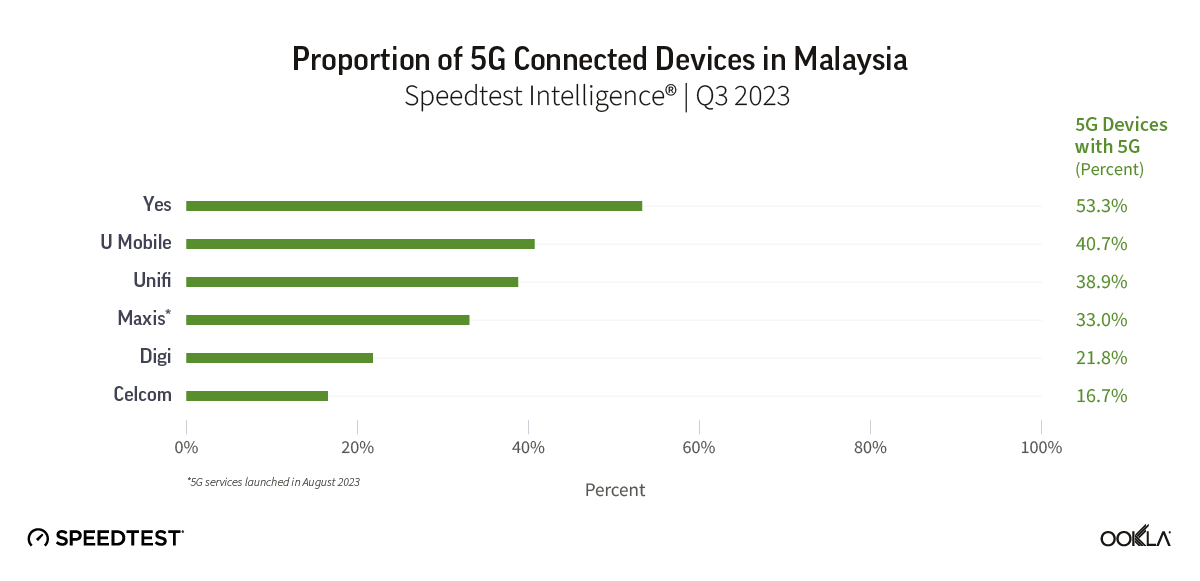
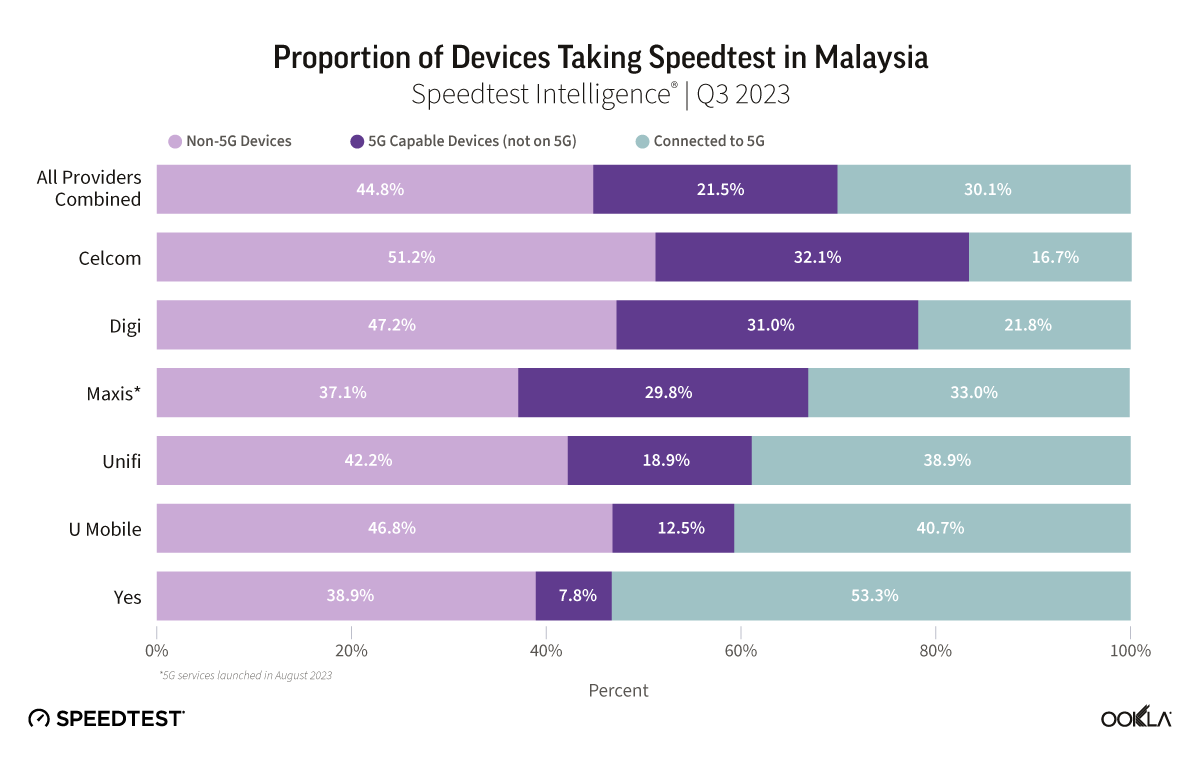
- Malaysia: TM was the fastest fixed broadband provider in Malaysia with a median download speed of 112.00 Mbps in Q4 2023. TIME recorded the lowest fixed broadband latency at 9 ms.
- Pakistan: Jazz delivered the fastest median mobile download speed in Pakistan at 21.38 Mbps in Q4 2023. Zong recorded the highest mobile Consistency, at 83.2%, and the lowest median mobile latency of 45 ms. Transworld recorded the fastest median fixed broadband download speed at 22.08 Mbps and the highest Consistency at 46.1%, while Connect Communications recorded the lowest median fixed broadband latency at 12 ms.
- Philippines: Smart delivered the fastest median mobile download speed in the Philippines at 37.64 Mbps in Q4 2023.
- South Korea: SK Telecom recorded the fastest median mobile download speed at 192.67 Mbps, while also recording the highest Consistency in the market at 89.1%. LG U+ had the lowest median mobile latency in the market at 76 ms. In South Korea’s fixed broadband market, LG U+ delivered the fastest median download speed at 146.20 Mbps, and the lowest median latency of 57 ms.
- Sri Lanka: There was no statistical winner for fastest mobile download performance during Q4 2023 in Sri Lanka, with Dialog and SLT-Mobitel both tied with speeds of 23.98 Mbps and 23.89 Mbps, respectively. Dialog delivered the lowest median mobile latency of 36 ms. SLT-Mobitel recorded the fastest fixed download speed of 37.46 Mbps, as well as the highest fixed broadband Consistency of 57.9% and the lowest fixed broadband latency at 13 ms.
- Vietnam: Viettel was the fastest fixed provider in Vietnam during Q4 2023, with a median download speed of 107.40 Mbps. Viettel also recorded the highest fixed broadband Consistency at 94.8% and the lowest median fixed broadband latency of 4 ms.
Europe
- Albania: Vodafone recorded the fastest median mobile download speed in Albania during Q4 2023, of 53.36 Mbps. One Albania recorded the highest mobile Consistency of 86.1%. Digicom was the fastest fixed broadband provider with a median download speed of 94.74 Mbps. Abissnet recorded the lowest fixed broadband latency, at 7 ms. Among Albania’s most populous cities, Vlorë recorded the fastest median mobile download speed of 75.34 Mbps, while Shkodër recorded the fastest median fixed download speed of 69.91 Mbps.
- Belgium: Proximus recorded the fastest median mobile download speed in Belgium during Q4 2023, at 89.67 Mbps. Proximus also recorded the highest mobile Consistency in the market at 89.8%. There was no statistical winner for fastest fixed download performance, with Telenet and VOO both tied with speeds of 158.08 Mbps and 156.00 Mbps, respectively. VOO recorded the highest Consistency at 89.8%. Among Belgium’s most populous cities, Ghent recorded the fastest median mobile and fixed download speeds, of 168.89 Mbps and 90.14 Mbps, respectively.
- Denmark: Telia was the fastest mobile operator in Denmark during Q4 2023, with a median download speed of 163.41 Mbps. Hiper was fastest for fixed broadband, with a median download speed of 277.56 Mbps.
- Estonia: The fastest mobile operator in Estonia was Telia with a median download speed of 92.39 Mbps in Q4 2023. Elisa recorded the highest mobile Consistency of 91.9%. Elisa was the fastest fixed broadband provider, with a median download speed of 100.13 Mbps. Elisa also recorded the highest fixed broadband Consistency, of 86.3%. Infonet recorded the lowest median fixed broadband latency of 5 ms.
- Finland: DNA had the fastest median mobile download speed at 113.57 Mbps in Q4 2023, and the highest Consistency of 95.4%. DNA also recorded the fastest median 5G download performance, at 247.54 Mbps. Telia recorded the lowest median mobile latency of 31 ms. Lounea was fastest for fixed broadband with a median download speed of 171.31 Mbps. Lounea also recorded the highest fixed broadband Consistency in the market at 91.5%, as well as the lowest median fixed broadband latency at 13 ms.
- Germany: Telekom was the fastest mobile operator in Germany during Q4 2023, with a median download speed of 90.26 Mbps, as well as the top median download speed over 5G at 179.25 Mbps. Telekom also recorded the highest mobile Consistency in the market at 92.1% and the lowest median mobile latency of 38 ms. Deutsche Glasfaser recorded the fastest fixed broadband performance, with a median download speed at 201.43 Mbps. Deutsche Glasfaser also recorded the highest fixed broadband Consistency in the market at 90.5% and the lowest latency of 14 ms.
- Latvia: There was no statistical winner for fastest mobile download performance in Latvia during Q4 2023, with BITĖ and LMT both tied with speeds of 81.56 Mbps and 81.11 Mbps, respectively. BITĖ recorded the highest mobile Consistency in the market of 91.3%, while LMT recorded the lowest mobile latency at 27 ms. Balticom was fastest for fixed broadband with a median download speed of 275.19 Mbps, while also leading with the highest fixed broadband Consistency of 93.7%, and the lowest median latency at 4 ms. Among Latvia’s most populous cities, Olaine recorded the fastest median mobile download speed, of 170.18 Mbps, while Salaspils recorded the fastest median fixed broadband download speed of 94.64 Mbps.
- Lithuania: Telia was the fastest mobile operator in Lithuania during Q4 2023, with a median download speed of 116.58 Mbps in Q4 2023. Telia also recorded the highest Consistency in the market at 94.7%, and the lowest median mobile latency at 32 ms. Cgates was fastest for fixed broadband with a median download speed of 177.14 Mbps. Cgates also recorded the highest Consistency over fixed broadband in the market at 90.9%, while Penki recorded the lowest fixed broadband latency, at 4ms. Among Lithuania’s most populous cities, Panevėžys recorded the fastest median mobile download speed, of 106.34 Mbps, while Klaipėda recorded the fastest median fixed broadband download speed of 138.34 Mbps.
- Poland: T-Mobile was the fastest mobile operator in Poland during Q4 2023, with a median download speed of 49.10 Mbps. T-Mobile also recorded the highest Consistency in the market at 88.4%. Plus recorded the fastest 5G performance in the market, with a median 5G download speed of 133.34 Mbps. Plus also recorded the lowest median mobile latency, at 43 ms. UPC was the fastest provider for fixed broadband with a median download speed of 232.36 Mbps, while Netia recorded the lowest fixed broadband latency, at 16 ms. Among Poland’s most populous cities, Łódź recorded the fastest median mobile download speed of 46.53 Mbps, while Wrocław recorded the fastest median fixed download speed of 172.86 Mbps.
- Turkey: Turkcell was the fastest mobile operator in Turkey with a median download speed of 56.73 Mbps in Q4 2023, and Turkcell also recorded the highest Consistency of 91.3%. Türk Telekom had the lowest median mobile latency at 39 ms. TurkNet was fastest for fixed broadband, with a median download speed of 66.57 Mbps. TurkNet also recorded the lowest median fixed latency at 13 ms, and the highest Consistency at 81.5%. Among Turkey’s most populous cities, Istanbul recorded the fastest median download speeds across mobile and fixed, at 38.50 Mbps and 47.81 Mbps, respectively.
Oceania
- New Zealand: There was no statistical winner for fastest mobile download performance during Q4 2023 in New Zealand, with One NZ and Spark both tied with speeds of 73.52 Mbps and 70.23 Mbps, respectively. 2degrees led the market with the highest Consistency of 91.0% and the lowest median mobile multi-server latency at 40 ms.
The Speedtest Global Index is your resource to understand how internet connectivity compares around the world and how it’s changing. Check back next month for updated data on country and city rankings, and look for updated Ookla Market Reports with 1H 2024 data in July.
Ookla retains ownership of this article including all of the intellectual property rights, data, content graphs and analysis. This article may not be quoted, reproduced, distributed or published for any commercial purpose without prior consent. Members of the press and others using the findings in this article for non-commercial purposes are welcome to publicly share and link to report information with attribution to Ookla.