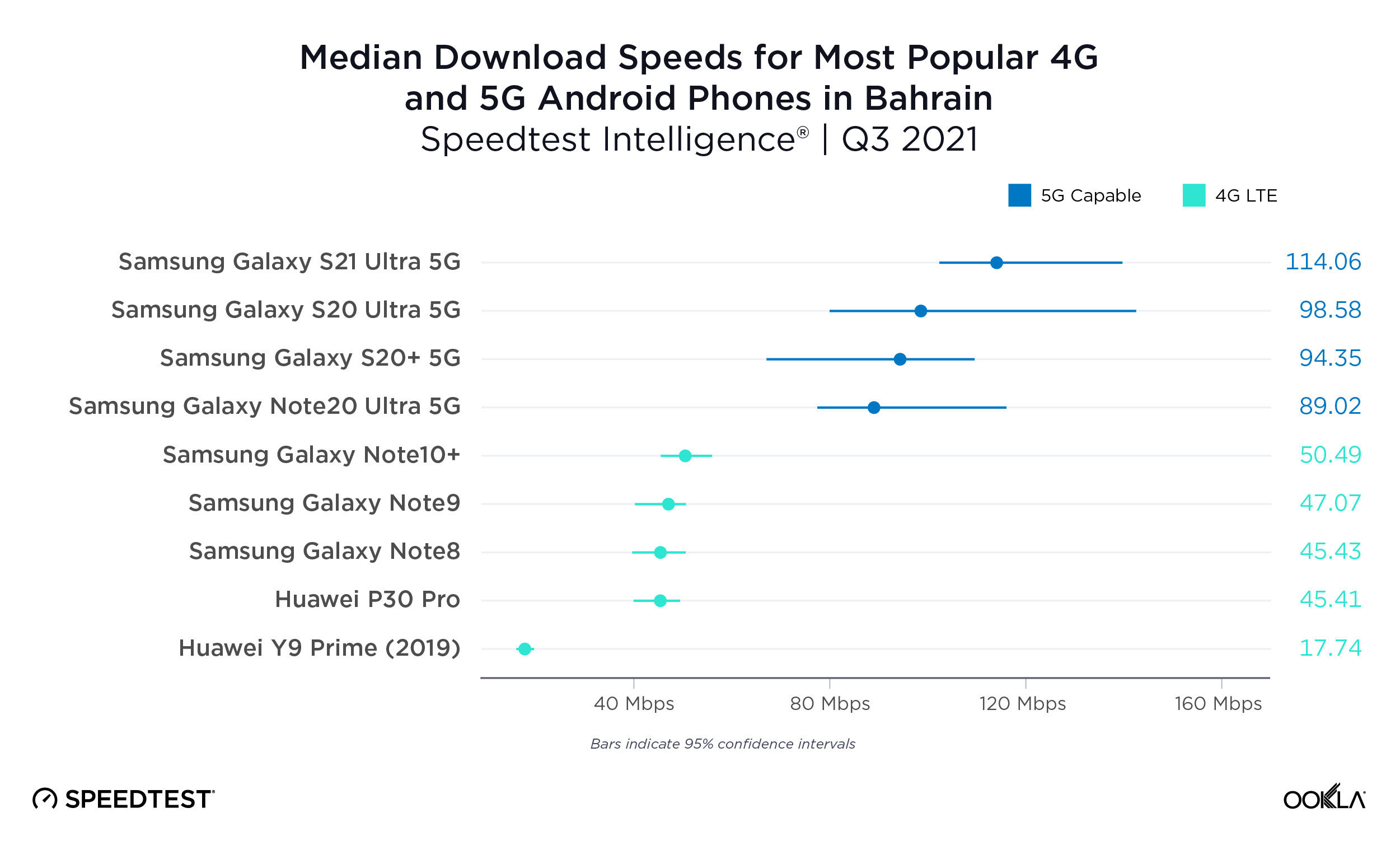
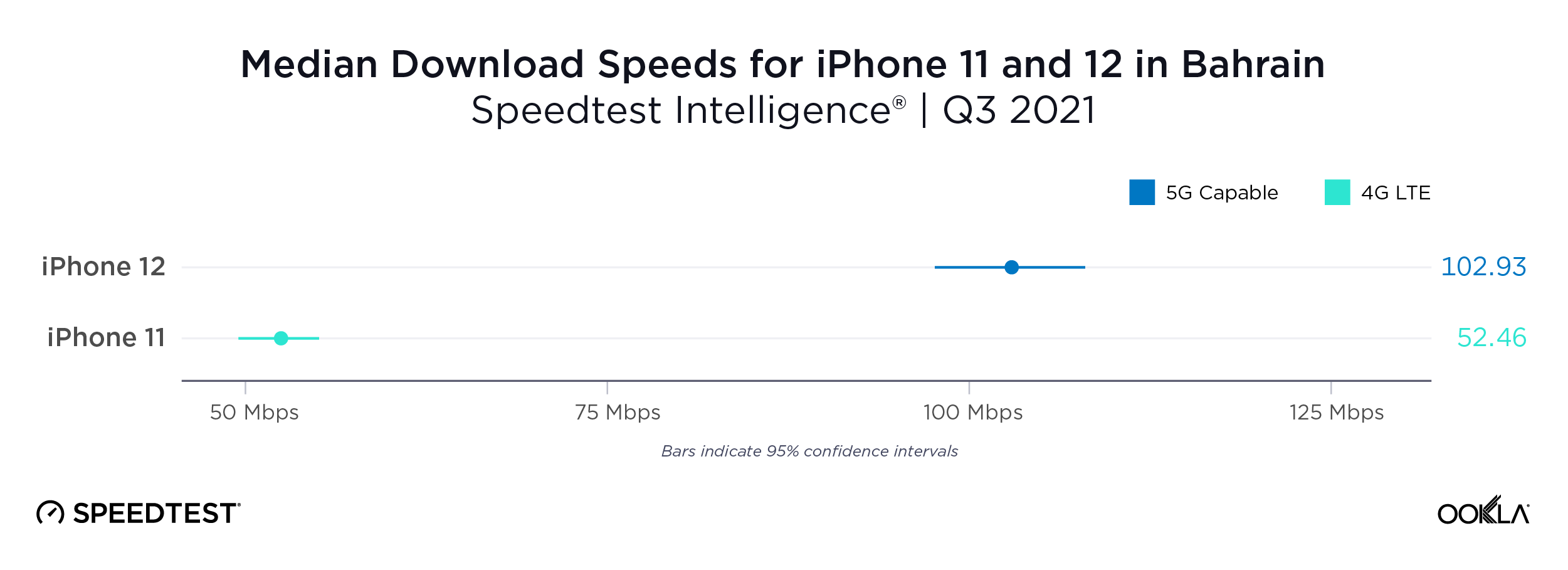
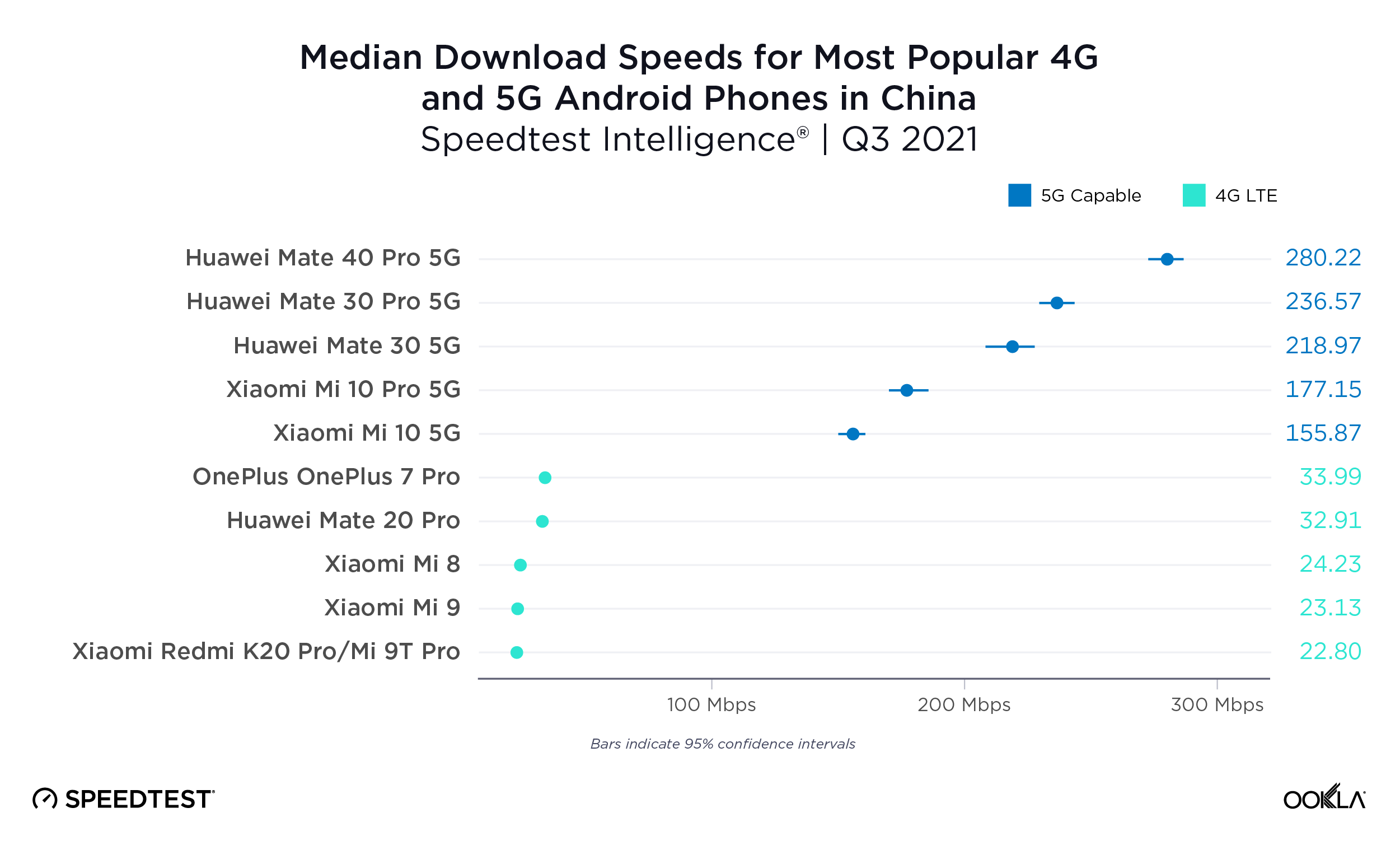
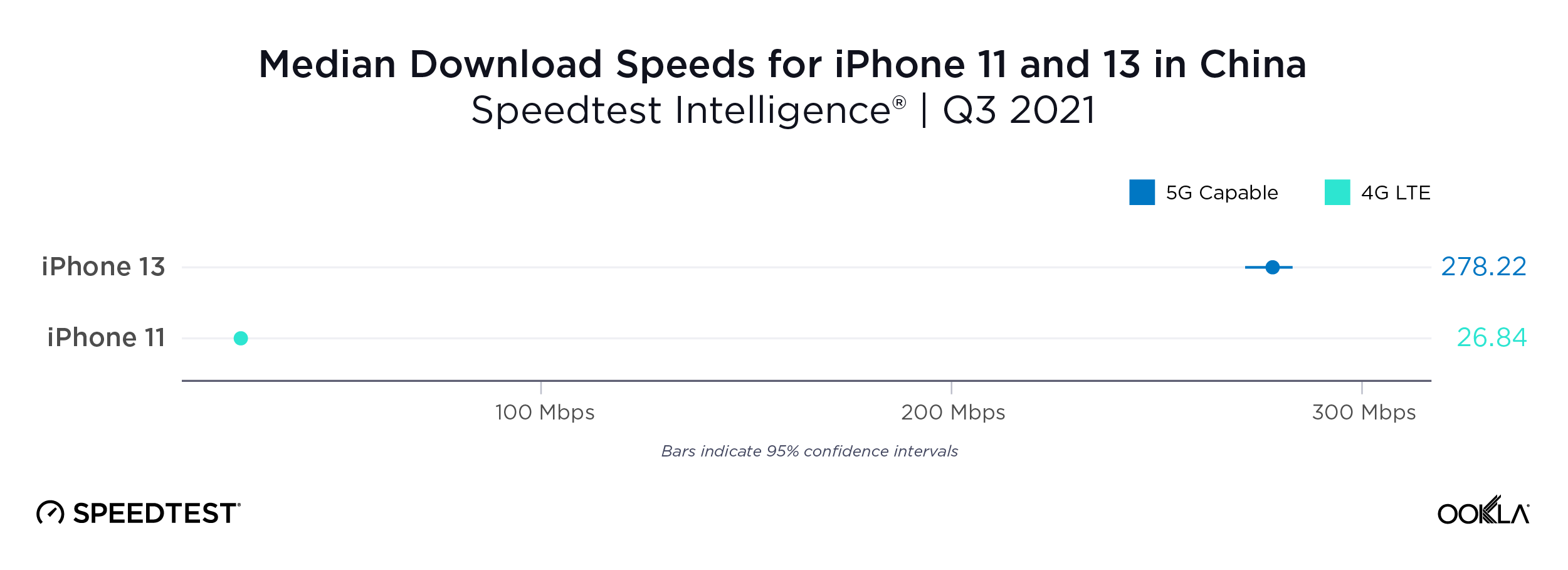
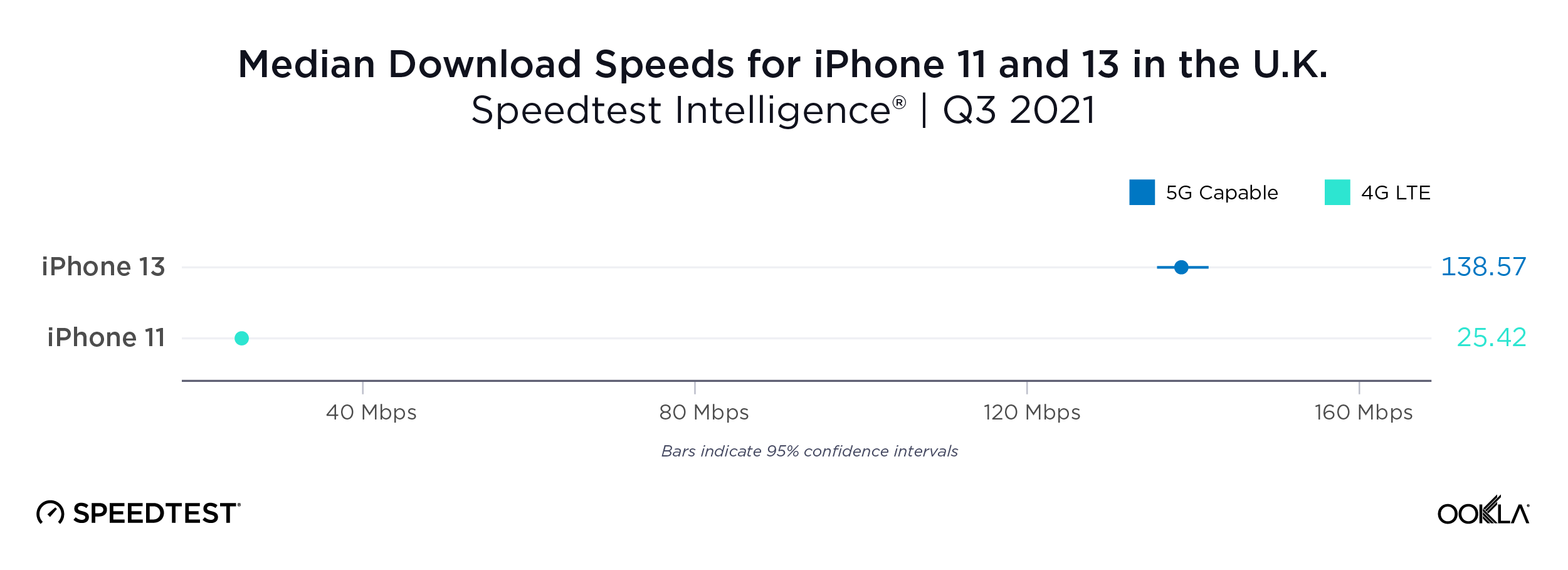
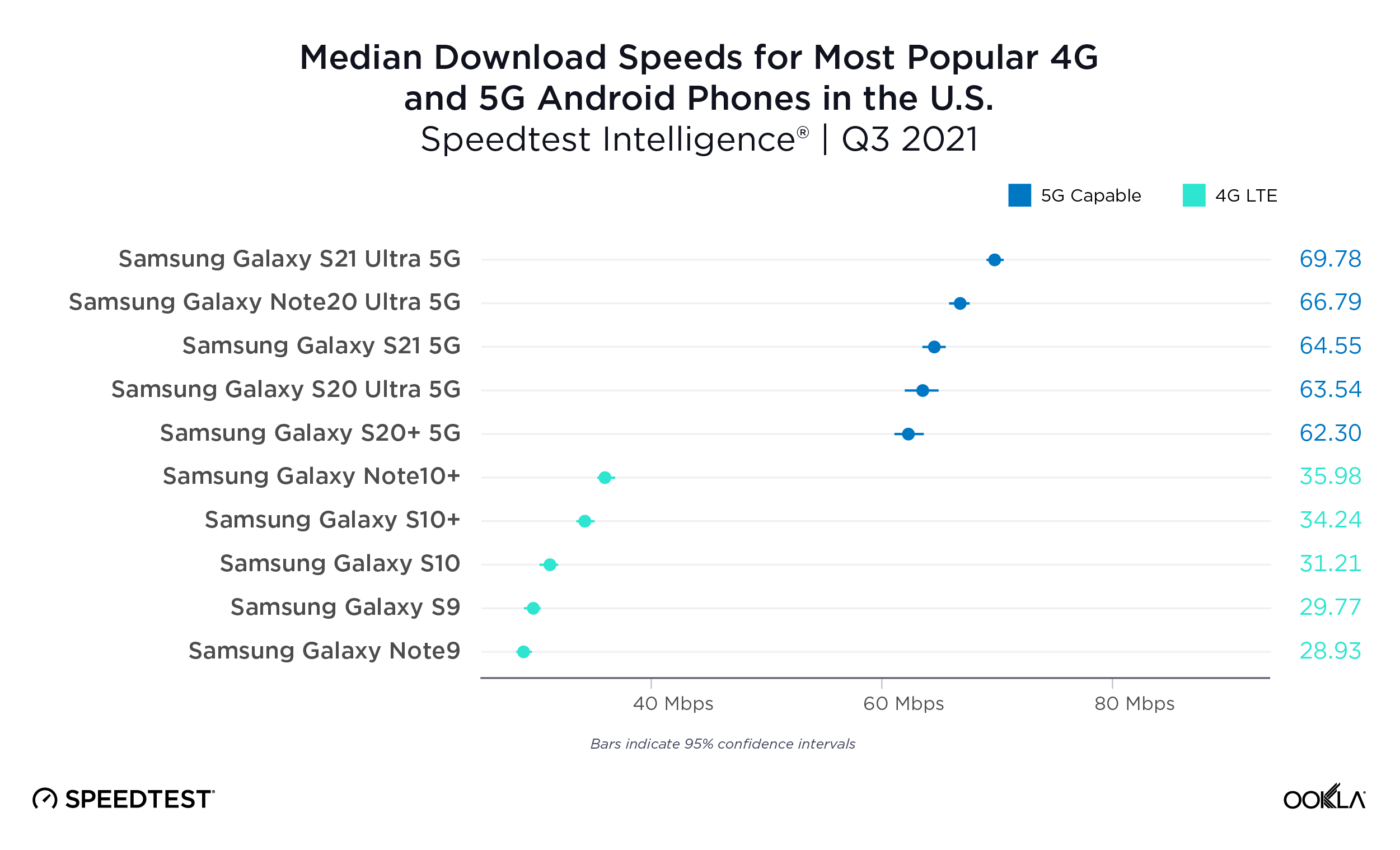
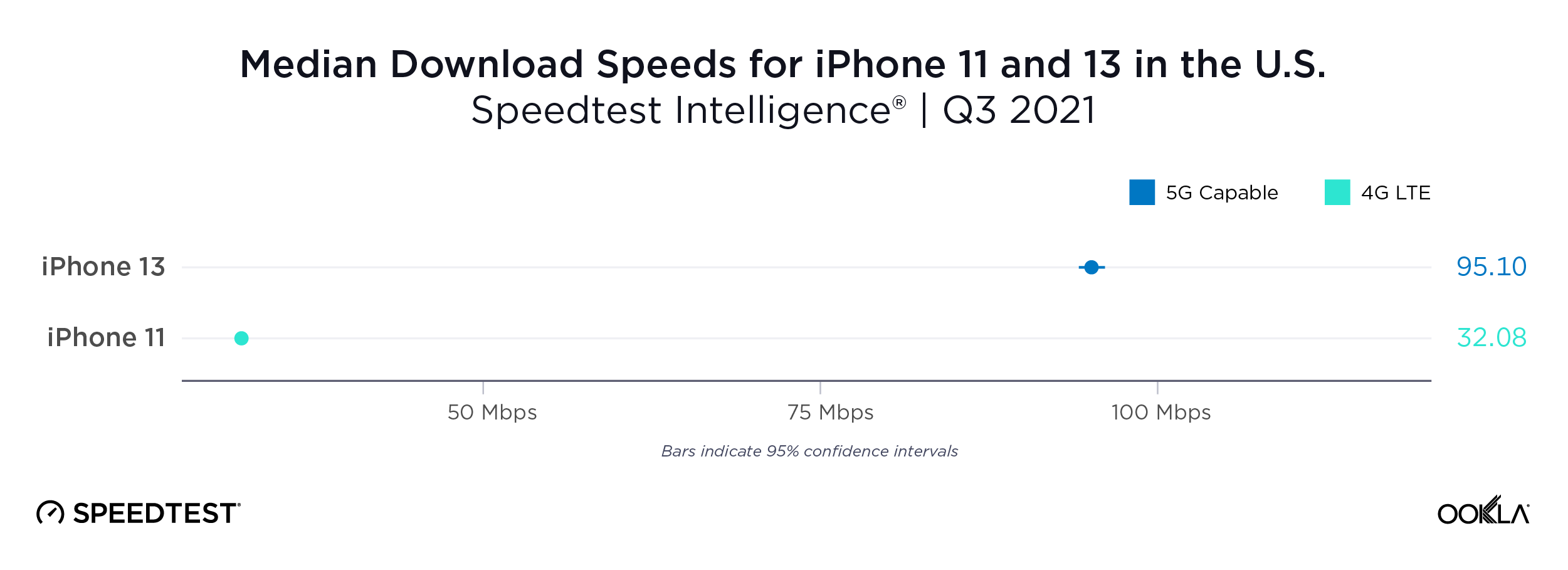
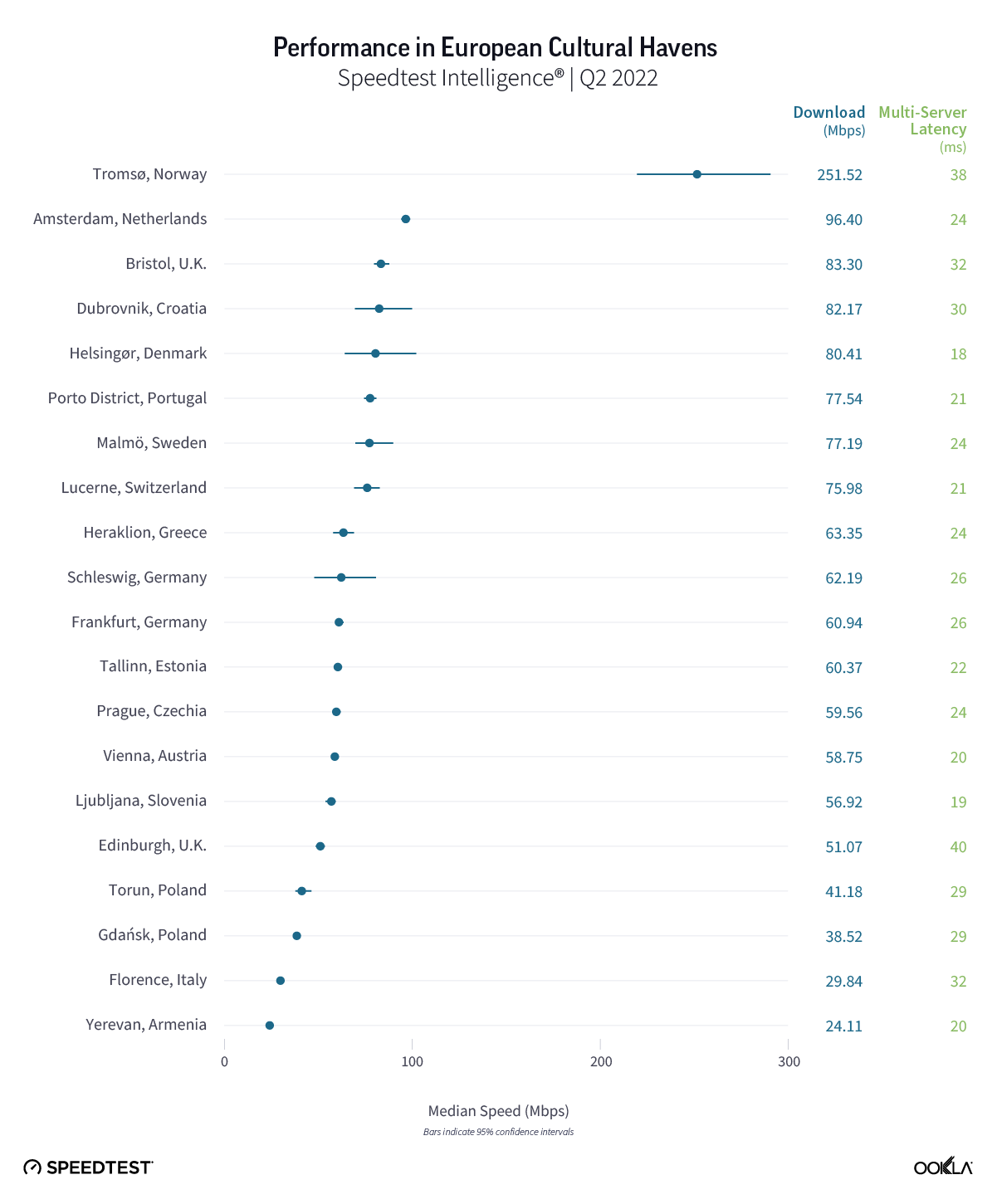
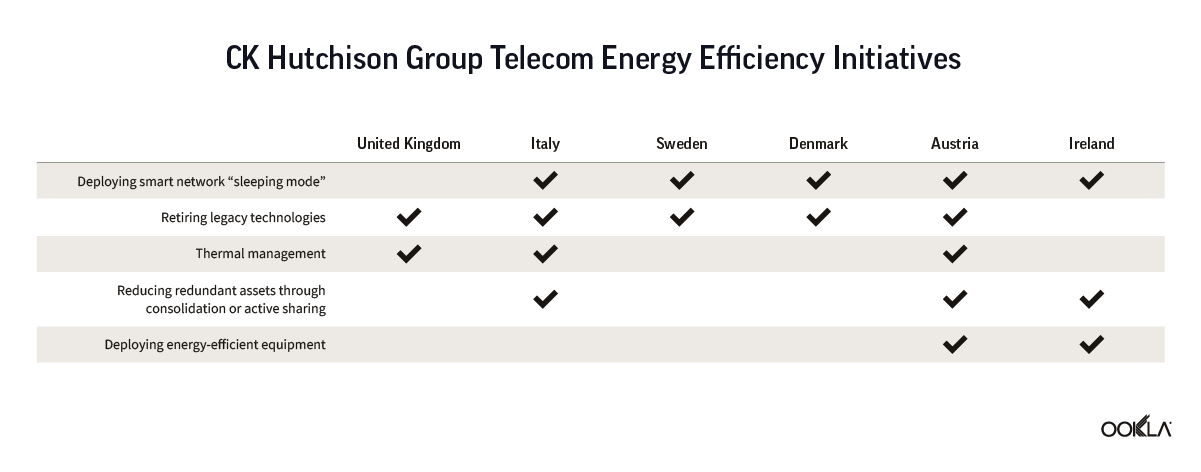
Fixed broadband internet reached 86% of households at the end of 2021 in the U.K., and most customers have access to speeds of at least 30 Mbps. While seven large internet service providers (ISPs) dominate the United Kingdom fixed broadband market, the competitive landscape is vibrant, hosting dozens of alternative providers (AltNets). The U.K. fibre market also attracts new funding, which allows alternative providers to expand their fibre footprint. In fact, Ookla Speedtest Intelligence® data reveals smaller providers are sometimes the fastest across a few cities and counties.
Key Takeaways:
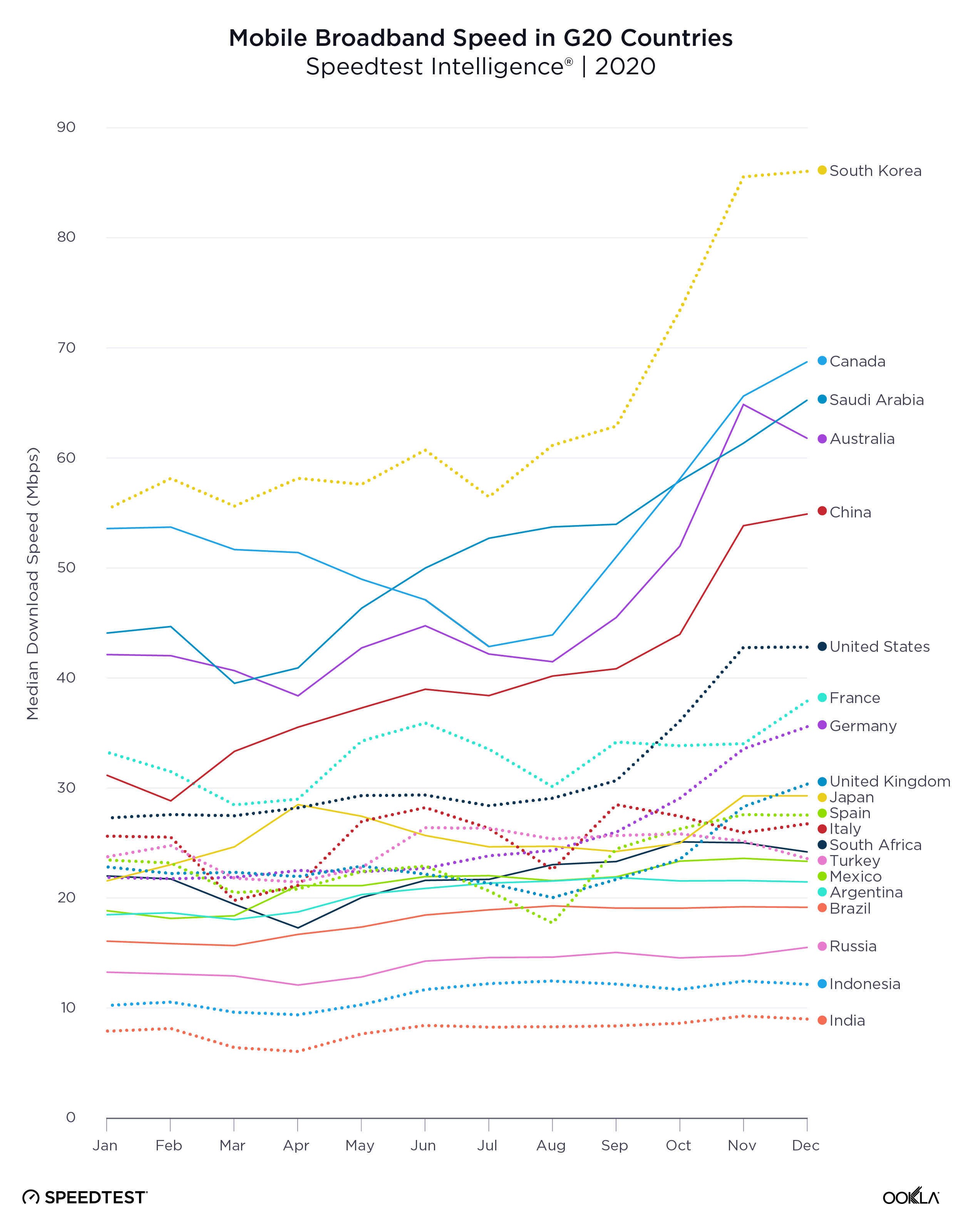
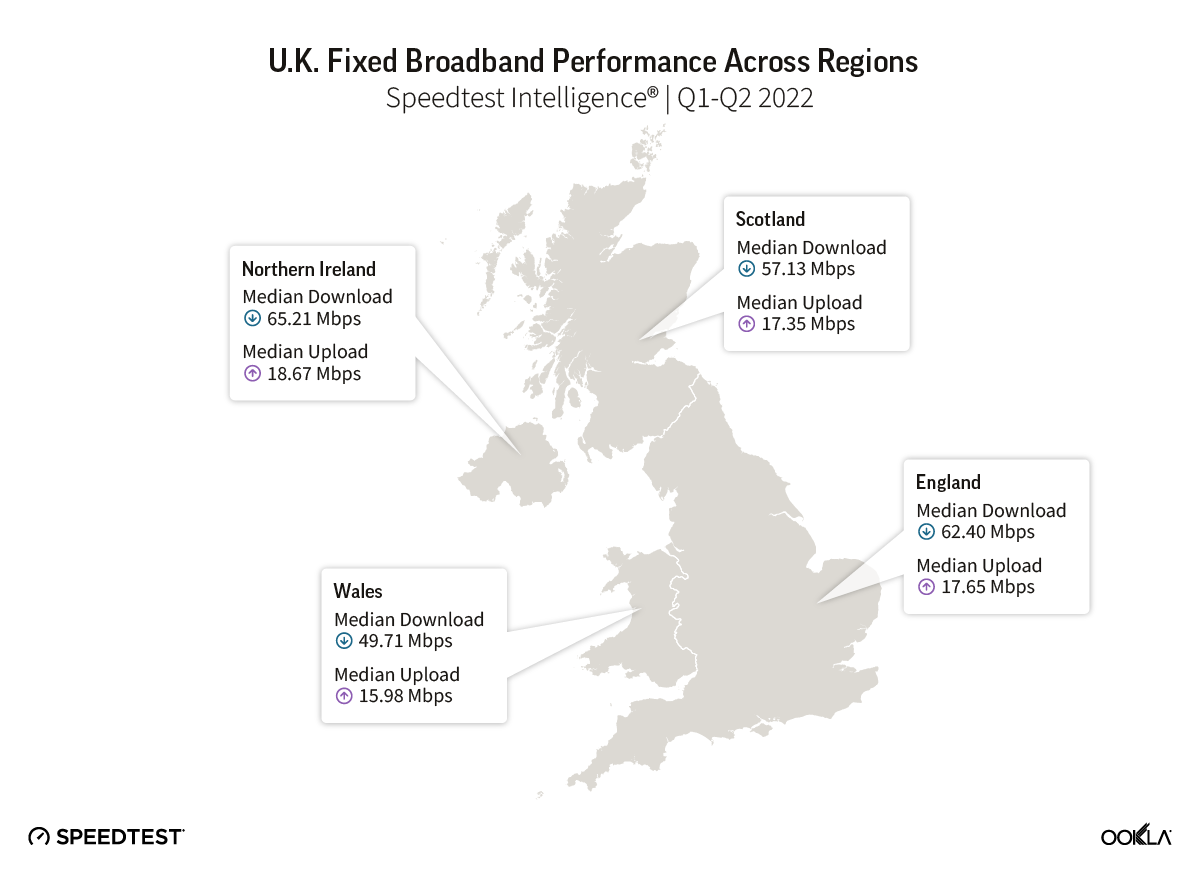
- Speedtest Intelligence® data shows that across the United Kingdom in the first half of 2022, the median broadband download speed was 61.69 Mbps, with a median upload speed of 17.63 Mbps. Northern Ireland ranked first for median download speed at 65.21 Mbps, followed by England (62.40 Mbps), Scotland (57.13 Mbps), and Wales (49.71 Mbps).
- Virgin Media O2 was the U.K.’s fastest fixed broadband provider, achieving a median download speed of 116.44 Mbps and an upload speed of 20.86 Mbps during Q1-Q2 2022. Across the 146 British counties we looked at, Speedtest Intelligence data showed that in Q1-Q2 2022 Virgin Media O2 was the clear speed leader, clocking the top download speeds in a whopping 71% of those counties. Virgin Media O2, having already upgraded its network to DOCSIS 3.1 plans to migrate to fibre to the premises (FTTP) over the next few years. The company is also planning to challenge Openreach in the wholesale market thanks to a new joint venture.
- AltNets had the top speeds in London, Glasgow, Liverpool, and Manchester, as well as across a number of counties. Public funding has helped facilitate the emergence of fibre ISPs in rural areas where fibre deployment is not commercially viable. Other AltNets like Hyperoptic are already well established, deploying and operating an FTTP network in areas with high density, which connects existing and new multi-dwelling buildings.
On the road to Gigabit connectivity
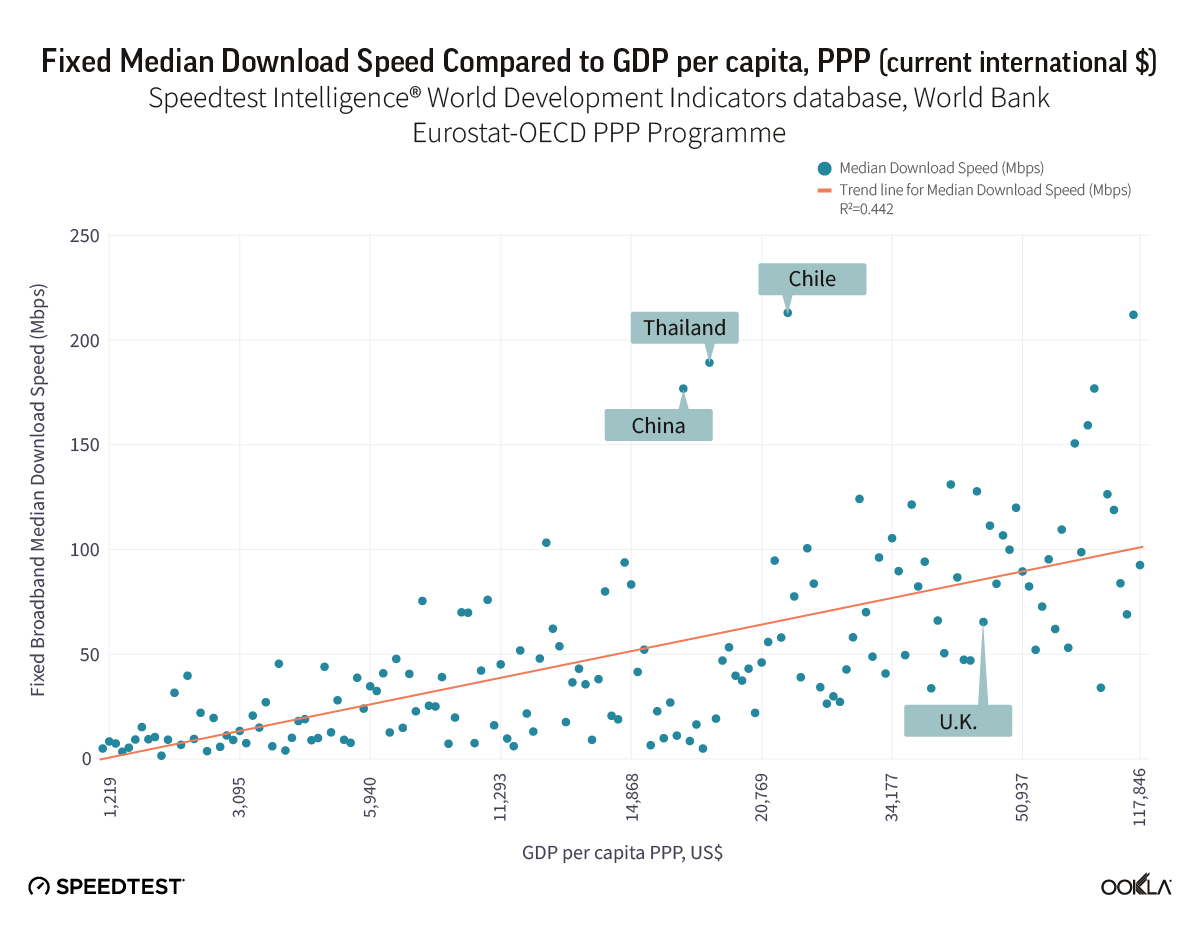
We looked at GDP and PPP in 2021 across 160 markets to see if there’s a correlation between wealth and internet speeds. While the correlation between fixed broadband speed and wealth was weak, many factors can determine a country’s internet performance like consumer demand, market competition, and regulatory stimulus. There are, however, some market exceptions like Chile, China, and Thailand, which outperform their economic peers. We discussed how Thailand’s supportive regulatory environment resulted in an increased fibre adoption in this article from 2021.
On the other hand, we would have expected some markets to transition to fibre more swiftly and provide users with faster median download speeds — but haven’t yet done so. The U.K. is one of those markets; according to Speedtest Global Index™ in August 2022, it ranked 55th, with a median fixed broadband download speed of 66.22 Mbps and 18.25 Mbps upload.
Northern Ireland was the speediest across the U.K.
Speedtest Intelligence® data shows the median fixed broadband download speed across the U.K. was 61.69 Mbps and the median upload speed was 17.63 Mbps in the first half of 2022. Looking at fixed speeds across the four British nations, Northern Ireland ranked first for fastest median download speed at 65.21 Mbps, followed by England (62.40 Mbps), Scotland (57.13 Mbps), and Wales (49.71 Mbps).
The number of homes that are gigabit-capable fixed broadband reached 19.3 million (66% of all U.K. homes) in January 2022, up from 13.7 million (47%) in September 2021. Most homes in the U.K. (97%) have access to “superfast broadband connection,” defined as download speeds of at least 30 Mbps. Yet, only a third can order a fibre-to-the-premise (FTTP) service. However, much faster speeds are on the horizon with the government targeting 85% gigabit-capable coverage by 2025, and nationwide fixed broadband speeds of 1 Gbps or better by 2030.
To help realise this, the British government created the U.K. Gigabit Programme, investing a total of £5 billion, of which at least £1.2 billion will be available by 2025 to provide connectivity for areas currently difficult to reach. This in turn has made the fibre market attractive for investors to provide funding for smaller network providers that want to take advantage of this market opportunity. There are about 100 smaller, alternative providers (AltNets) offer FTTP broadband across the U.K. These AltNets come in various sizes, stages of maturity, and have different business models. With the upcoming changes to regulation, which will allow pension funds to invest into venture capital to back high-growth tech startups, even more funding could be poured into the sector.
Virgin Media O2 leads for fastest download speed at 116.44 Mbps
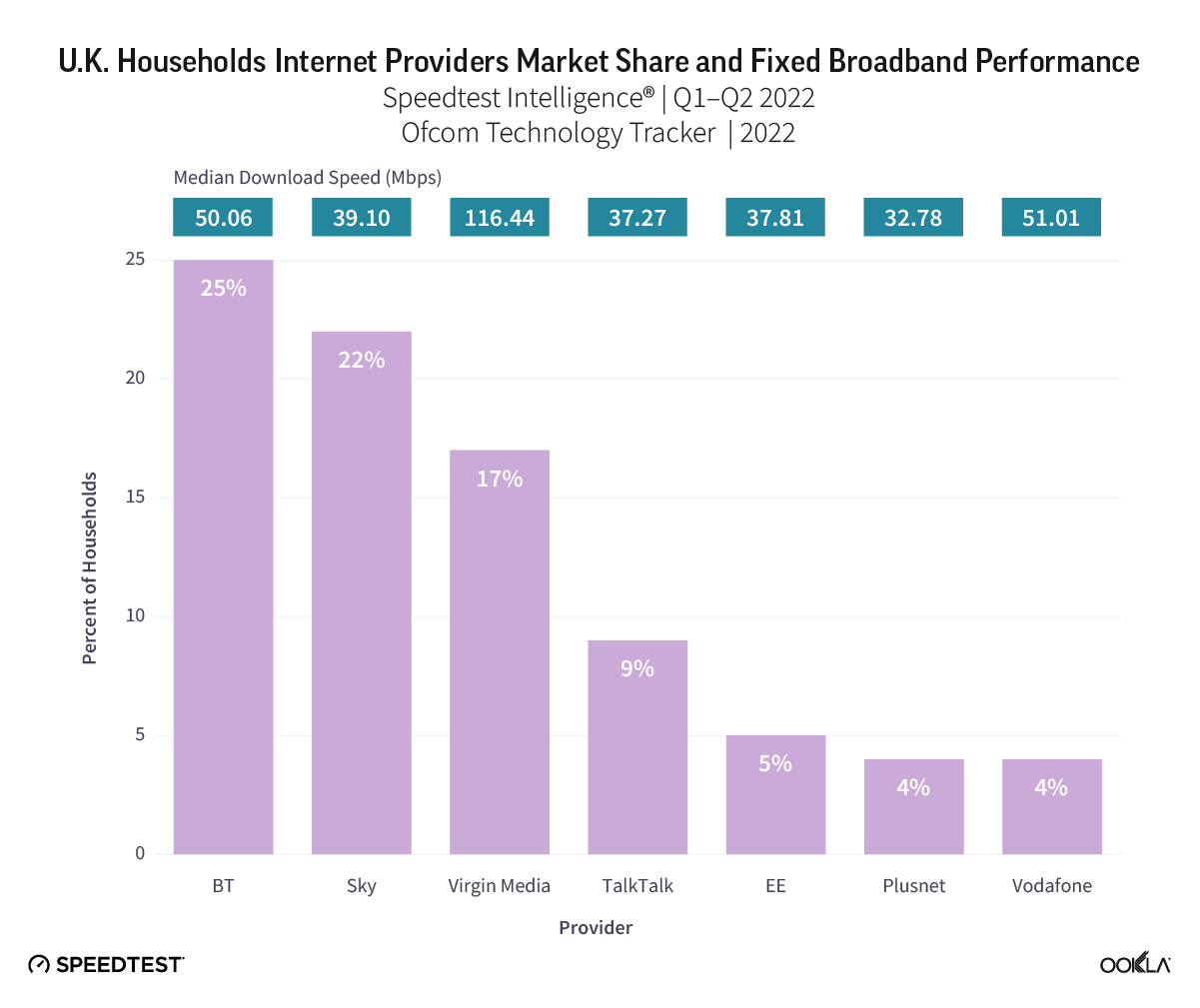
The U.K. market landscape is dynamic, with around 300 ISPs serving the market, but only a few offering nationwide coverage. The median fixed broadband speed in the U.K. is heavily influenced by the network technology provided by leading providers, which predominantly rely on copper-based network infrastructure supplied by Openreach. BT, Sky, Talk Talk, EE, Plusnet, and Vodafone all use Openreach, which itself is a wholly owned subsidiary of the BT Group but legally separated. Openreach has allocated £12 billion to upgrade its copper network to fibre. In August 2022, Openreach reported that its FTTP network passed over 8 million premises and is on target to provide fibre service to 25 million premises by the end of 2026.
The U.K.’s fastest broadband provider, Virgin Media O2, announced in December 2021 that it had completed its upgrade of its Hybrid Fibre Coax (HFC) network to a gigabit-capable DOCSIS 3.1 technology. Not to be outdone in the fibre race, the operator is upgrading that network to XGS-PON technology, which it aims to complete by 2028. In its Q2 2022 earning release, Virgin Media O2 stated that Project Lightning, a £3 billion network expansion programme, has been accelerating and “the cumulative Lightning footprint is now 2.9 million, [and] the company is on-track to add over 500,000 Lightning premises in 2022.”
Virgin Media O2’s shareholders, Liberty Global and Telefónica, alongside investment firm, InfraVia Capital Partners, announced a new fibre joint venture with a war chest of £4.5 billion. The initial goal is to roll out fibre to new greenfield areas, expanding to 5 million homes outside of Virgin Media O2’s network by 2026, with the opportunity to expand to an additional 2 million homes by 2027. Virgin Media O2 will be the anchor tenant of the network, but the network will be available to other ISPs on a wholesale basis.
Alternative players making headway in the wholesale market
Although Openreach and Virgin Media O2 dominate the fibre landscape in terms of homes passed, roll-out plans, and scale of investment, CityFibre has emerged as the largest alternative wholesale fibre network provider. CityFiber recently secured a £4.9 billion debt package that will fund a network covering a third of the U.K. market (8 million homes) by 2025. CityFibre is backed by Goldman Sachs, Antin Infrastructure Partners, Mubadala Investment Company, and Interogo Holding.
The reason the provider attracts such large-scale capital investment is because its fibre expansion plans are based on a long-term purchasing commitment from multiple wholesale customers, including TalkTalk, Vodafone, Zen, and 30 other ISPs. Thanks to this business model, CityFibre, established in 2011, scaled from a small start up aimed at rescuing failed fibre projects in small U.K. cities, to becoming a network that has just passed 2 million premises.
Another wholesale fibre provider, Netomnia, was founded in 2019 by the former CEO of Community Fibre and has ambitious plans to reach 1 million premises by 2023. To date, Netomnia has already passed 210,000 premises and it expects to extend across 48 towns and cities by the end of this year. Along with ISP YouFibre, Netomnia has secured £418 million in funding since 2020: £123 million in funding in November 2021, followed by £295 new funding led by DigitalBridge Investment Management in April 2022. The provider is a registered supplier in the Scottish Broadband Voucher Scheme (SBVS), which subsidises the cost of connecting a rural premise to a fibre network up to £1,500 per household and up to £3,500 for businesses.
AltNets had the top speeds in London, Glasgow, Liverpool, and Manchester
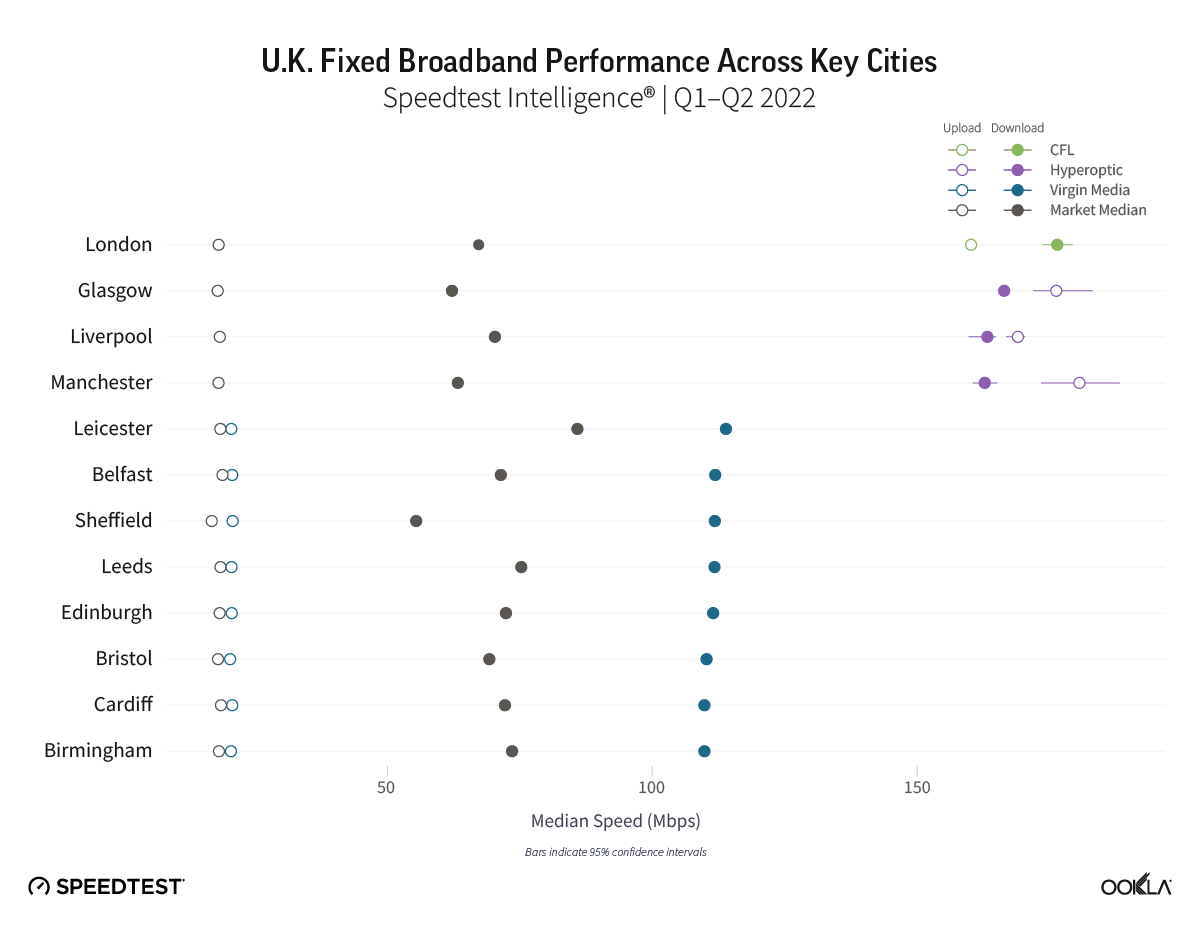
Using Speedtest Intelligence data, we looked at the median fixed broadband speeds across key British cities during Q1-Q2 2022. Virgin Media O2 led for speed in eight of the 12 cities we looked at.
However, in three cities – Glasgow, Liverpool, and Manchester – Hyperoptic had the fastest fixed broadband speeds, achieving download and upload speeds in excess of 150 Mbps during Q1-Q2 2022.
Hyperoptic, which is backed by private equity house KKR, currently reaches 1 million homes and is planning to exceed 2 million by the end of the year. The ISP committed to invest £200 million in 2022 to expand its network by laying more than 1,500 kilometres of fibre to connect an additional 400,000 homes and businesses. Hyperopitc’s strategy is to deploy and operate an FTTP network in buildings and areas with high customer acquisition potential, targeting areas with high density and connecting existing homes and new multi-dwelling buildings. Hyperoptic has a particularly strong position in social housing and works with social housing providers and councils to provide some residents with free or reduced priced fibre broadband. Hyperoptic also targets new building developments as these properties will soon have to be connected per proposed changes in the Building Regulation 2010. Hyperoptic also has partnerships with over 250 developers across the country, providing them an opportunity to deliver service to new homes as they’re built. The provider also has working relationships with 16 of the 20 largest building development companies, including Barratt Developments.
AltNets and their various business models
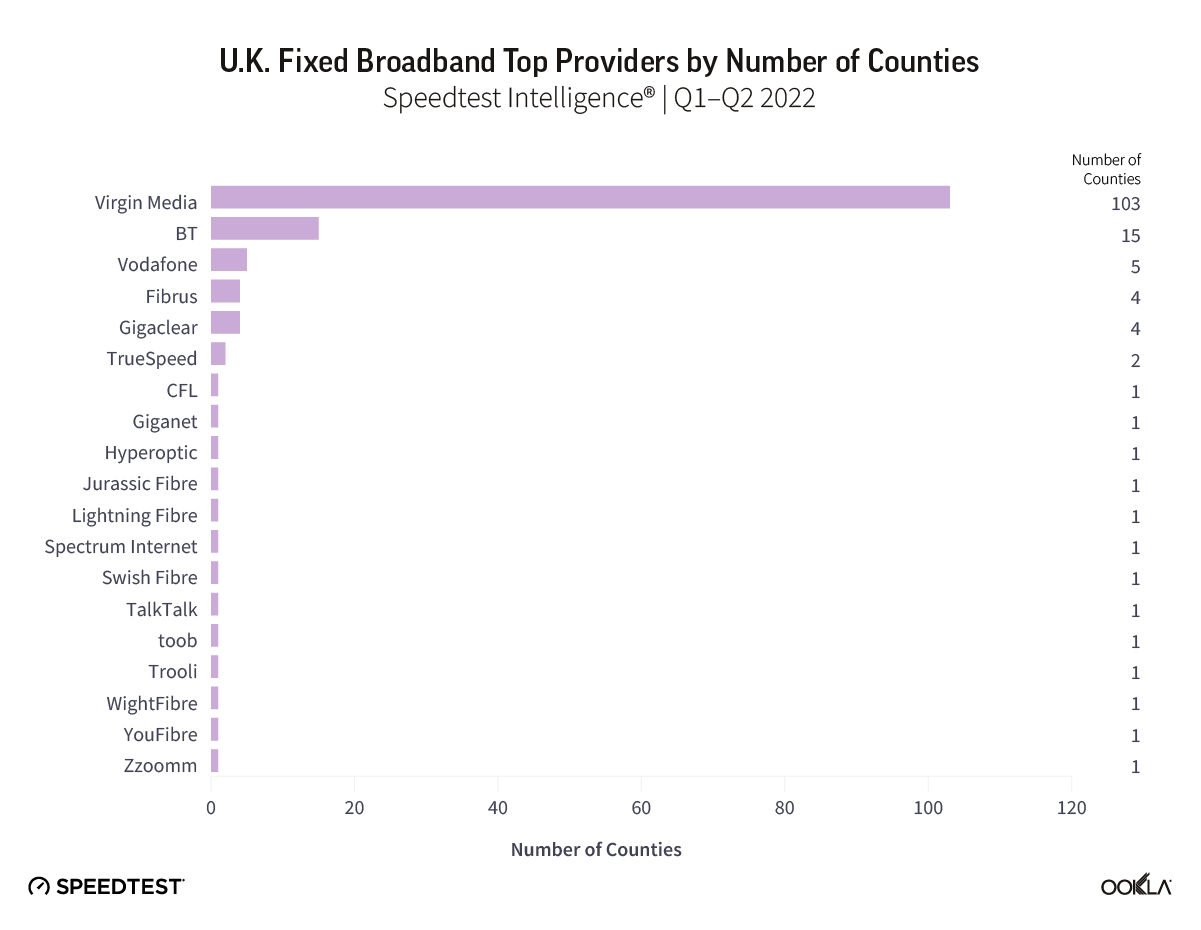
Across the 146 British counties we looked at, Speedtest Intelligence data shows that Virgin Media O2 had the fastest median download speeds in a whopping 71% of those counties. BT ranked a distant second, posting the top speeds in about 10% of counties, while Vodafone led in five counties. Fibrus and Gigaclear registered the top speeds in four counties each, with TrueSpeed leading in two counties. Various other providers led in one county.
Vodafone is CityFibre’s anchor customer nationwide, and the two providers have a strategic partnership. In November 2021, Vodafone expanded on the partnership, increasing its long-term volume commitment from 12 to 285 cities, towns, and villages across 8 million homes CityFibre is targeting. Vodafone initially signed a partnership with CityFibre in November 2017, which allowed it to offer fibre to Vodafone’s customers starting in Milton Keynes. In fact, Vodafone was the fastest provider in Milton Keynes, offering a median download speed of 159.64 Mbps, along with a median upload speed of 125.24 Mbps.
Fibrus had the fastest median download speed in four counties in Northern Ireland. Fibrus was selected to deliver Project Stratum, under which Fibrus will receive £165 million to bring full fibre connectivity to 76,000 premises across Northern Ireland. An additional £32 million was awarded to bring another 8,500 harder to reach premises into the project’s scope. By the end of 2021, Fibrus passed over 100,000 premises with Project Stratum accounting for 20% of these connections. The rapid growth, network expansion, and customer acquisition resulted in an operating loss of £15.5 million for Fibrus, and £92 million invested into network build. Fibrus secured £220 million from a consortium of banks consisting of NatWest, ABN Amro, ING, Sabadell, LBBW, and the U.K. Infrastructure Bank to fund its roll out.
The vast amount of public funding facilitated the emergence of fibre ISPs focusing on rural areas where fibre deployment is not commercially viable. For instance, Fibrus was chosen to deliver fibre in Northern Ireland, where Project Stratum funds fibre broadband deployments in rural communities.
Gigaclear had the fastest download speed in four counties: Buckinghamshire, Northamptonshire, Oxfordshire, and Rutland. Gigaclear passed 300,000 premises across 22 English counties in May, 60% of its target of 500,000 premises by the end of 2023. The provider secured £525 million worth of debt financing in 2020 with Lloyds, NatWest, Santander, and ABN AMRO, and in 2021, received a £190 million investment boost partially co-financed by the new U.K. Infrastructure bank. It has been reported that Gigaclear is working with Rothschild bankers to raise £200-300 million of additional capital to fund its network deployment. In some communities, the provider holds contracts with local authorities to build fibre networks through the Building Digital U.K. (BDUK) programme. In these communities, Gigaclear invested £9 of its capital for every £1 of subsidy it received.
Giganet, which was the fastest in Portsmouth, was the single-fastest provider at the county-level at 305 Mbps, about three times faster than England’s national average. The provider focuses on underserved rural areas, including some connected premises that are part of the BDUK programme.
WightFibre operates only in the Isle of Wight, and it aims to create the U.K.’s first “Gigabit Island.” The company has completed the migration of legacy cable network customers to a new full fibre network in 2021, and it switched off its copper network in August 2022. WightFibre’s fibre network is available to over 40,000 premises, with a target of 60,000 premises by end of 2022; 75,000 by 2024; and ultimately covering 96% of the island’s premises (80,000).
Broadband for the Rural North (B4RN) is a registered Community Benefits society. It is building a fibre network in isolated or socially deprived rural communities and also helping similar community-driven network deployments in other areas. The community is directly involved in bringing the network to residents and those in surrounding premises, installing it and passing on the skills to the next community. The fibre network was initially deployed in the rural northwest of England and has gradually expanded from there. Any profits were reinvested, with 5% of profits being paid to members. BR4N was the fastest provider in Cumbria with a median download speed of 113.74 Mbps and 127.98 Mbps upload.
Although Voneus does not have the fastest download speed in any county, its business model is worth noting. Voneus begins by rolling out its Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) solution, which has relatively low Capex and Opex, bringing communities quickly online, and then deploys FTTP. This allows the company to mitigate the risk associated with higher costs of fibre delivery in three ways:
- Thanks to FWA Voneus already has an established base of customers that recognise the benefits of faster broadband.
- Voneus takes advantage of the rural gigabit voucher scheme, securing a cost contribution toward every home connected.
- This reduces cost and build time. Voneus has code power and PIA accreditation that allows it to utilise existing pole and duct infrastructure.
Over £30 billion investment into fibre
According to the Independent Networks Cooperative Association (INCA) report, alternative providers connected over 1 million FTTP premises, having passed 5.5 million premises with fibre at the end of 2021. Virgin Media O2 passed 16.8 million households with its gigabit-capable (but not yet FTTP) network, while Openreach reported 8 million premises within reach of its fibre network. Looking ahead, the report predicts that alternative providers will pass 30 million premises by 2025. It also notes that Virgin Media O2 plans to extend its network to 22 million premises, and Openreach has a target of 26 million by 2026. All of these ambitious plans exceed 31 million premises in the U.K. This means there will be some level of overbuild, especially in more densely populated areas. To deploy fibre networks, AltNets will spend £12 billion on fibre networks, in addition to £12 billion announced by BT Group, £2 billion planned by Virgin Media O2, and £5 billion coming from the government.
Challenges are few, labour force shortage is the most pressing
Translating the fibre investment into ROI will remain a challenge, particularly for some smaller, regional players, while increasing interest rates will put pressure on others. Industry consolidation is already in place with CityFiber buying Fiber Nation, Swish Fiber acquiring People’s Fiber, and Community Fiber buying Box Broadband. There is even more on the horizon, as fibre roll out requires significant capital investment and most players, apart from Hyperoptic, aren’t turning a profit.
Another challenge is the consumer take-up, meaning the proportion of subscriptions and homes passed. This is most efficiently done in areas that are greenfield, but where customer acquisition can be tricky. Hyperoptic recently introduced its Switch Now campaign, offering free broadband for up to nine months if a customer switches providers to Hyperoptic.
BT reported it has 26% take-up equivalent to 1.3 million FTTP customers, while CityFibre reported that in Milton Keynes, fibre take-up of 25% with other locations growing on a similar trajectory.
Access to sufficient physical and human resources to upgrade to full fibre is another challenge. To alleviate these hurdles, the U.K. government proposed that it could fast-track entry for thousands of foreign workers to help with the roll-out of gigabit broadband. We will continue to follow the fibre race in the U.K. and we will monitor what impact it will have on fixed broadband speeds. If you’d like to learn more about internet speeds and performance in other markets around the world, visit the Speedtest Global Index.