Middle Eastern countries — particularly within the oil-rich Gulf — have been investing heavily in expanding and upgrading their mobile networks over the past few years. That’s been paying off for consumers across the region, with United Arab Emirate (U.A.E.) operator Etisalat being awarded with the World’s fastest mobile network operator in 2020 and Gulf nations holding four of the top 10 spots on the Speedtest Global Index™ during September 2021. With Oman rising in the mobile rankings and Muscat placing in the top 10 world capitals for fastest 5G during Q1-Q2 2021, Oman’s rise as a potential mobile powerhouse merits further investigation.
This article examines the state of Oman’s mobile performance during Q3 2021, including which provider had the fastest mobile performance, Oman’s 5G evolution, a governorate-level mobile analysis and snapshot of provider performance in Muscat using Ookla® Cell Analytics™.
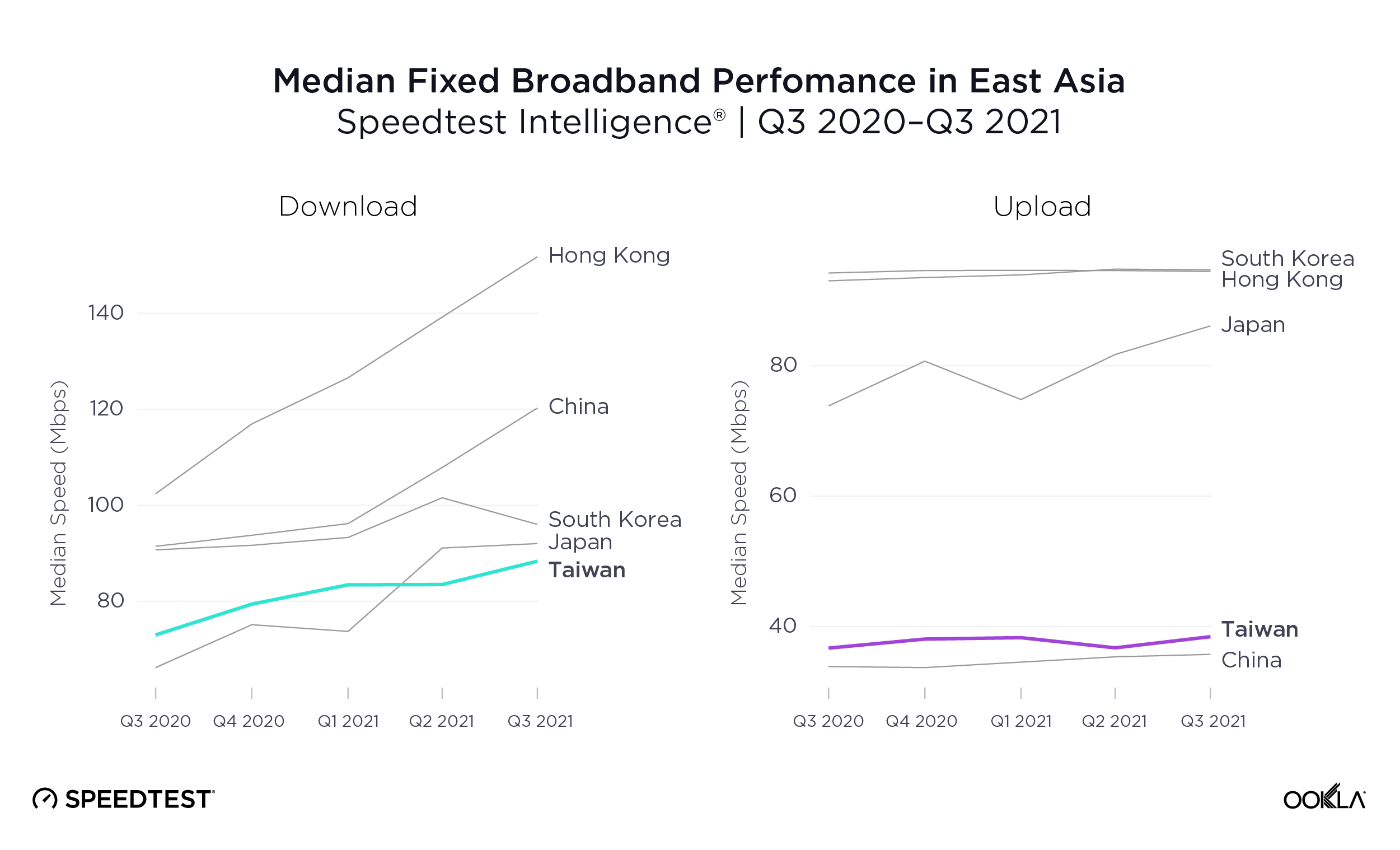
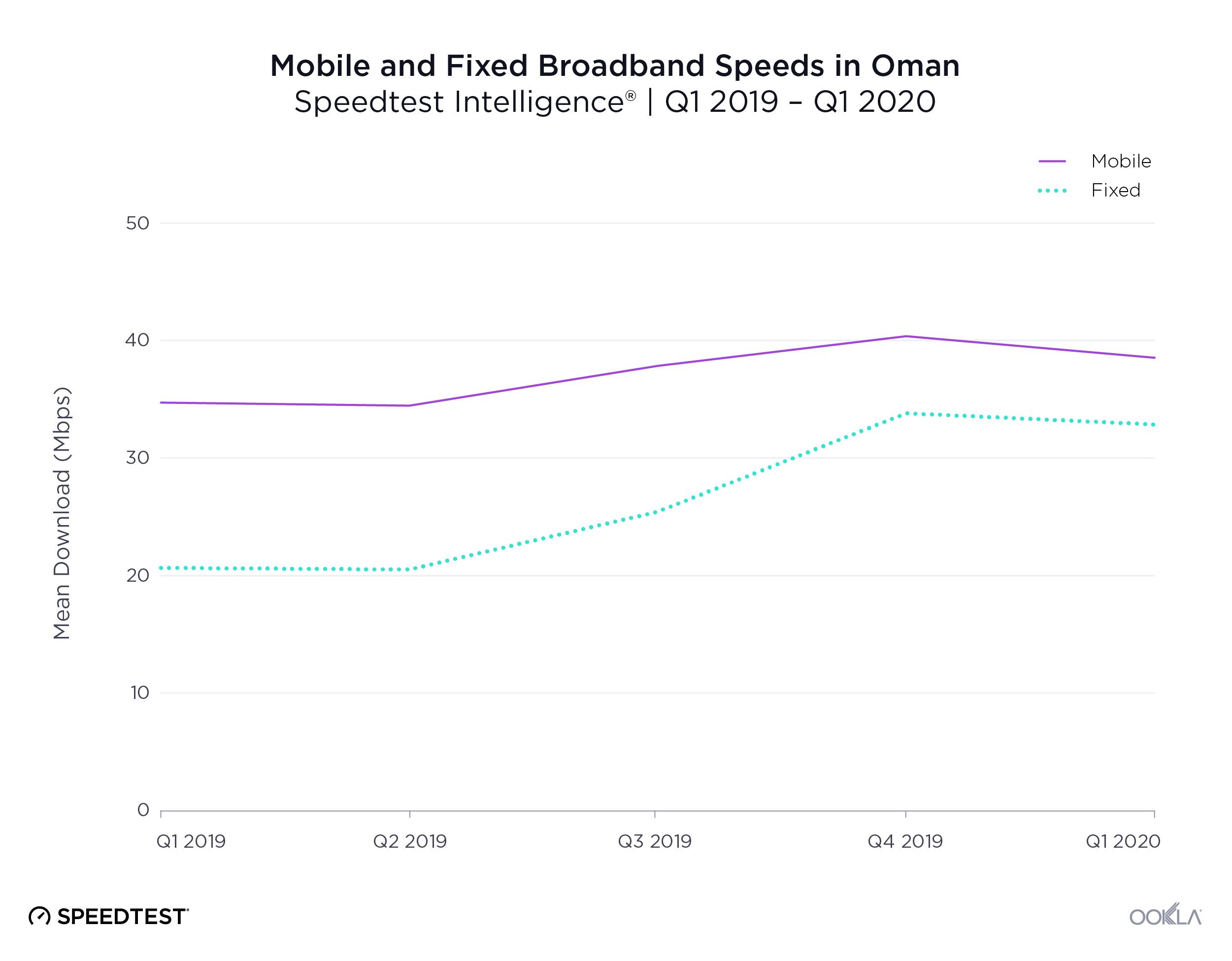
Oman is behind its regional partners for mobile performance during Q3 2021, but speeds are rapidly accelerating
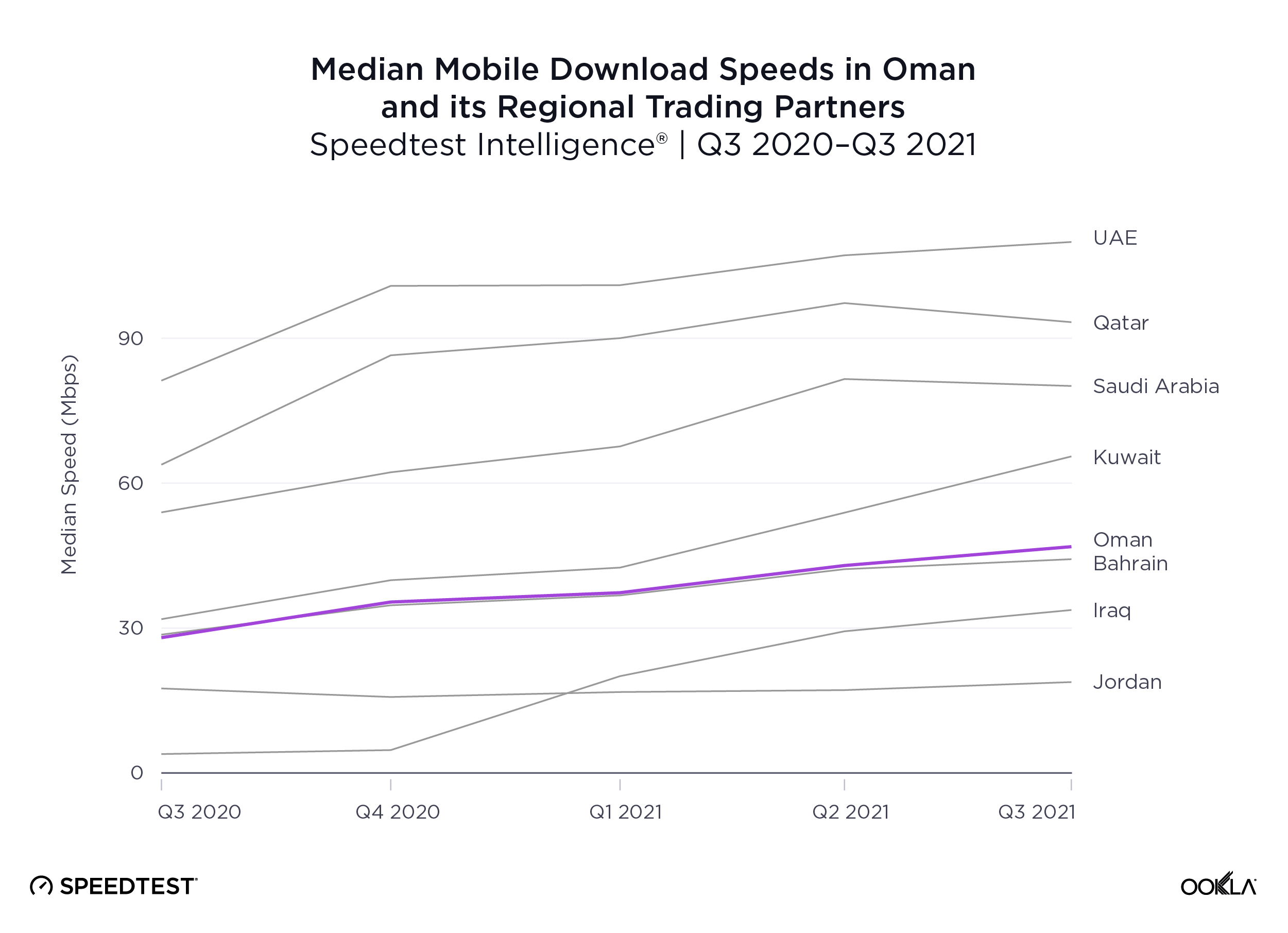
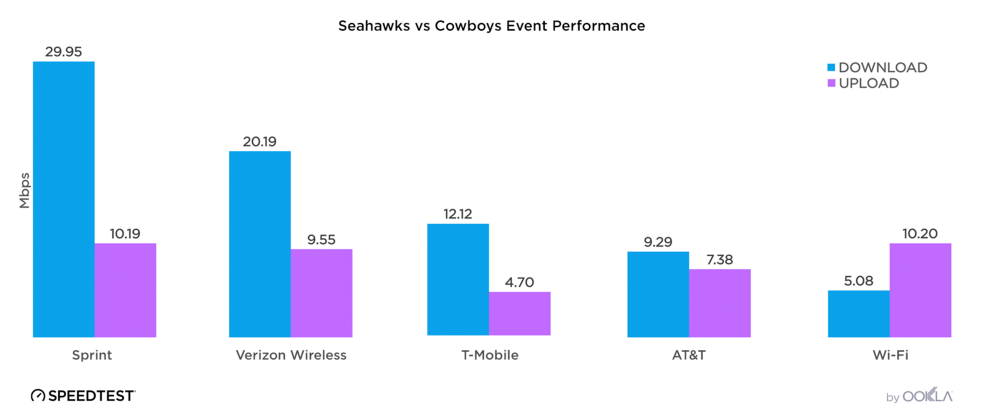
Speedtest Intelligence® revealed the U.A.E. had the fastest median mobile download speed among Oman’s regional trading partners at 109.92 Mbps during Q3 2021. Oman was a hair faster than Bahrain at 46.85 Mbps. Jordan and Iraq had the slowest median download speeds on this list at 18.82 Mbps and 33.74 Mbps, respectively.
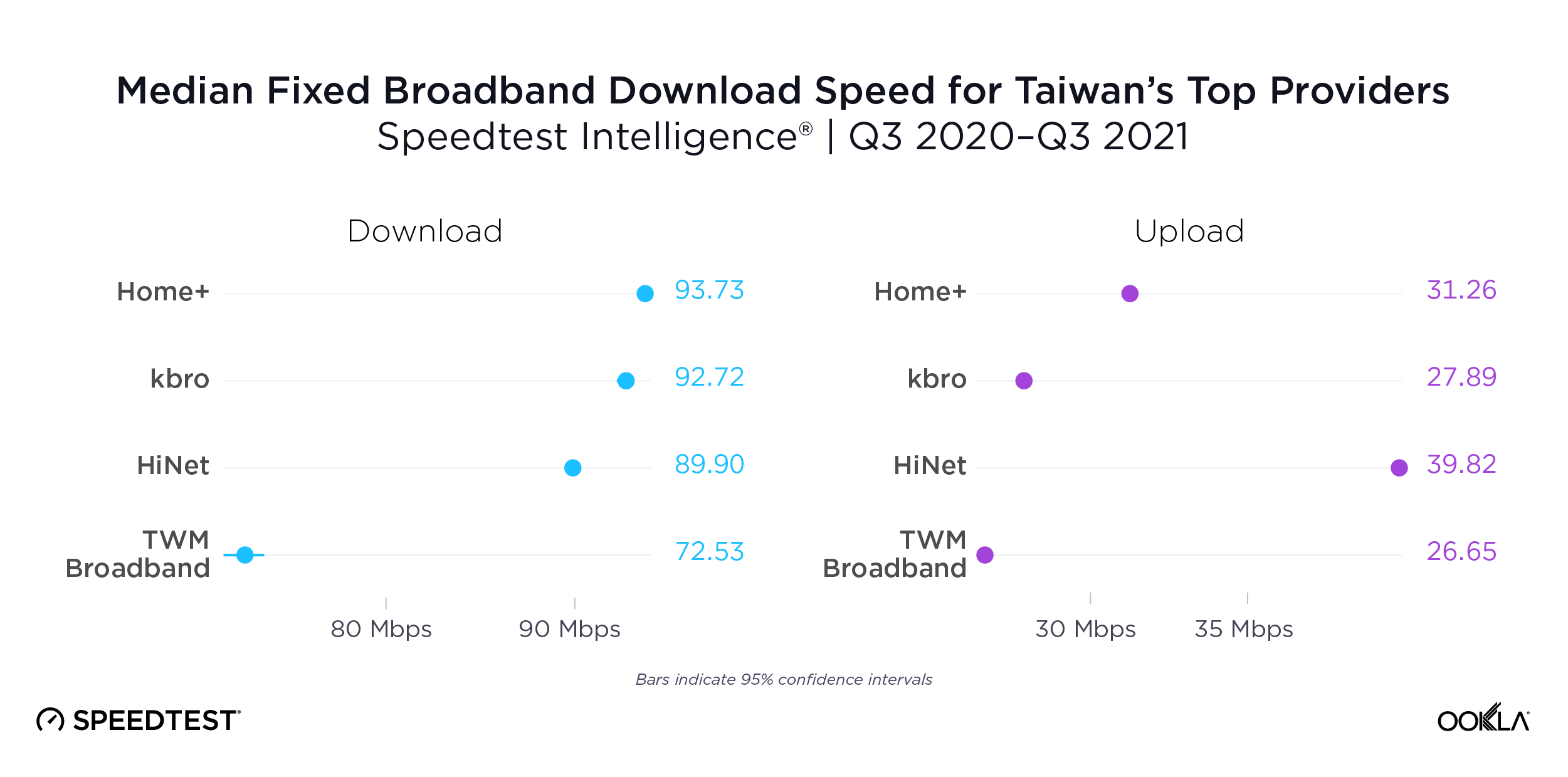
Ooredoo overtook Omantel as Oman’s fastest mobile operator
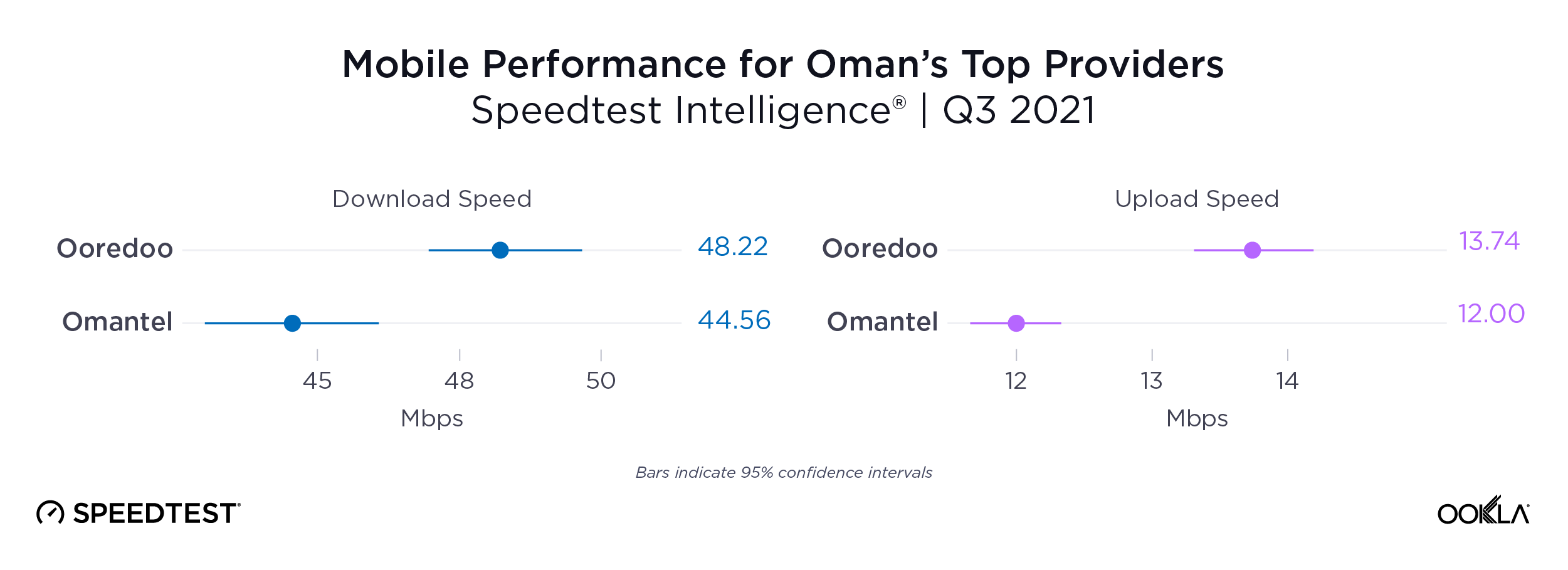
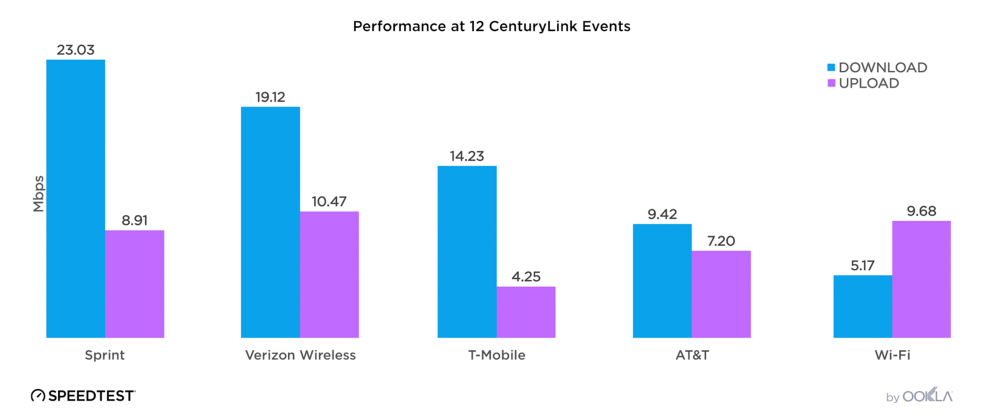
Competition between Oman’s top providers, Ooredoo and Omantel, has been fierce over the past year. However, Ooredoo pulled ahead of Omantel during Q3 2021, achieving a median mobile download speed of 48.22 Mbps to Omantel’s 44.56 Mbps. Ooredoo also had the fastest median mobile upload speed during Q3 2021 at 13.74 Mbps to Omantel’s 12.00 Mbps.
Ooredoo outpaced Omantel for fastest 5G download speed
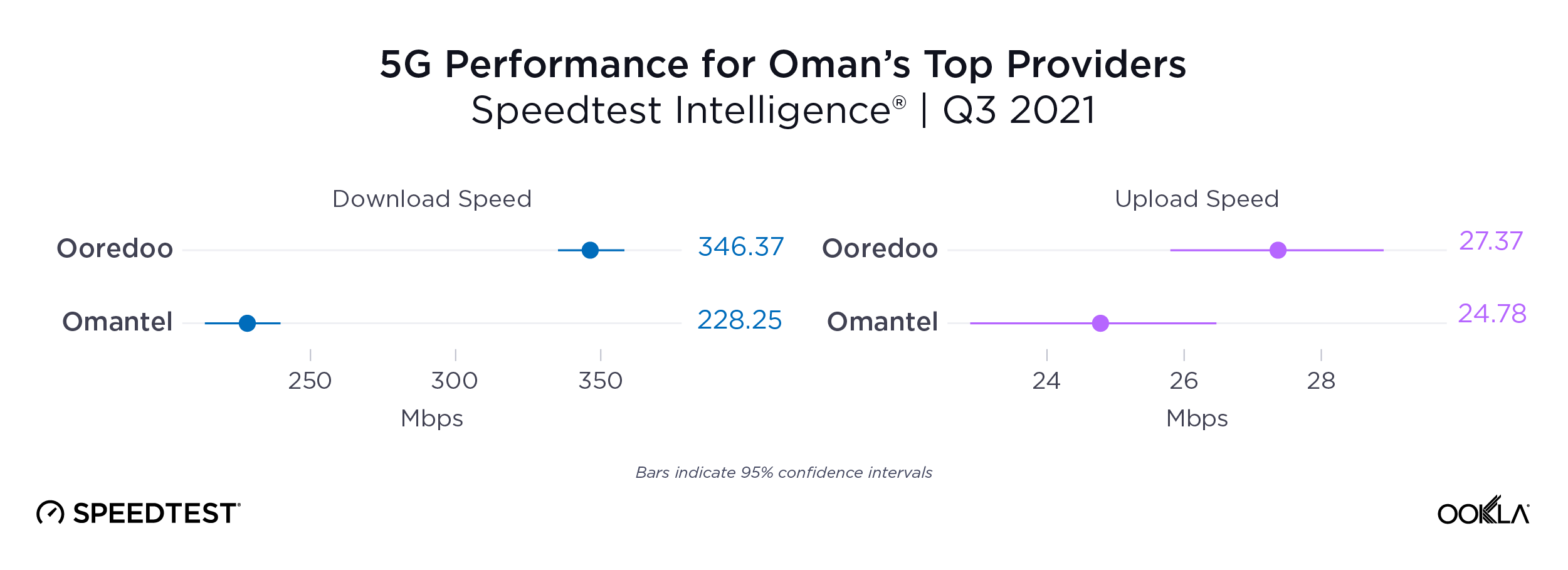
Ooredoo also achieved the fastest 5G in Oman during Q3 2021, achieving a median 5G download speed of 346.37 Mbps to Omantel’s 228.25 Mbps. The fastest median 5G upload speed during Q3 2021 was much closer with Ooredoo achieving a median upload speed of 27.37 Mbps to Omantel’s 24.78 Mbps.
Ooredoo beat Omantel for 4G Availability, Omantel pulled ahead for 5G Availability
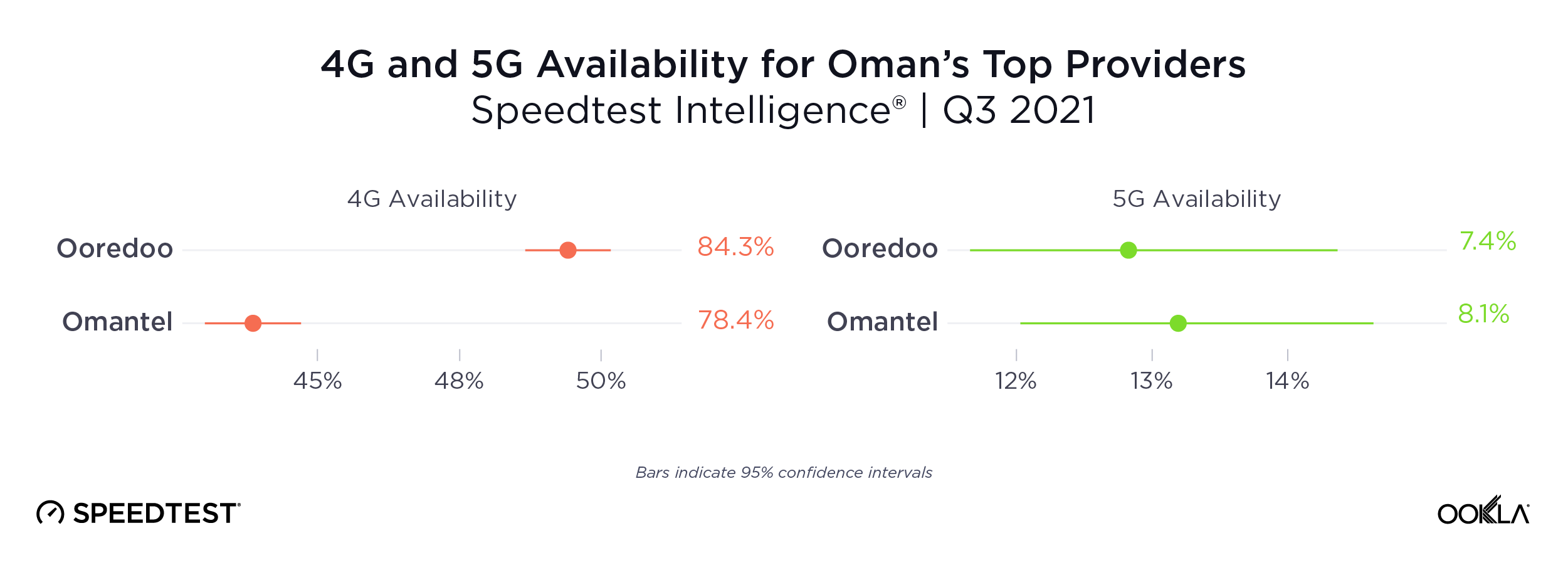
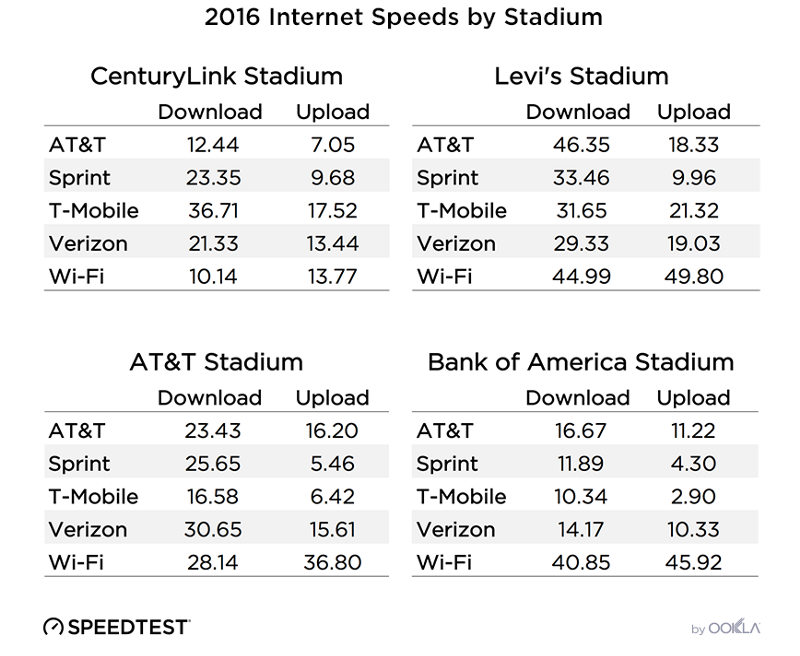
Competition for the highest 4G and 5G Availability — with 4G Availability representing the proportion of users who spend most of their time on 4G or greater networks and 5G Availability representing the proportion of users who spend most of their time on 5G networks — was also close in Oman during Q3 2021. Ooredoo had the highest 4G Availability at 84.3% to Omantel’s 78.4%. For 5G Availability there was no statistical winner, but Omantel achieved 8.1% and Ooredoo achieved 7.4% during Q3 2021.
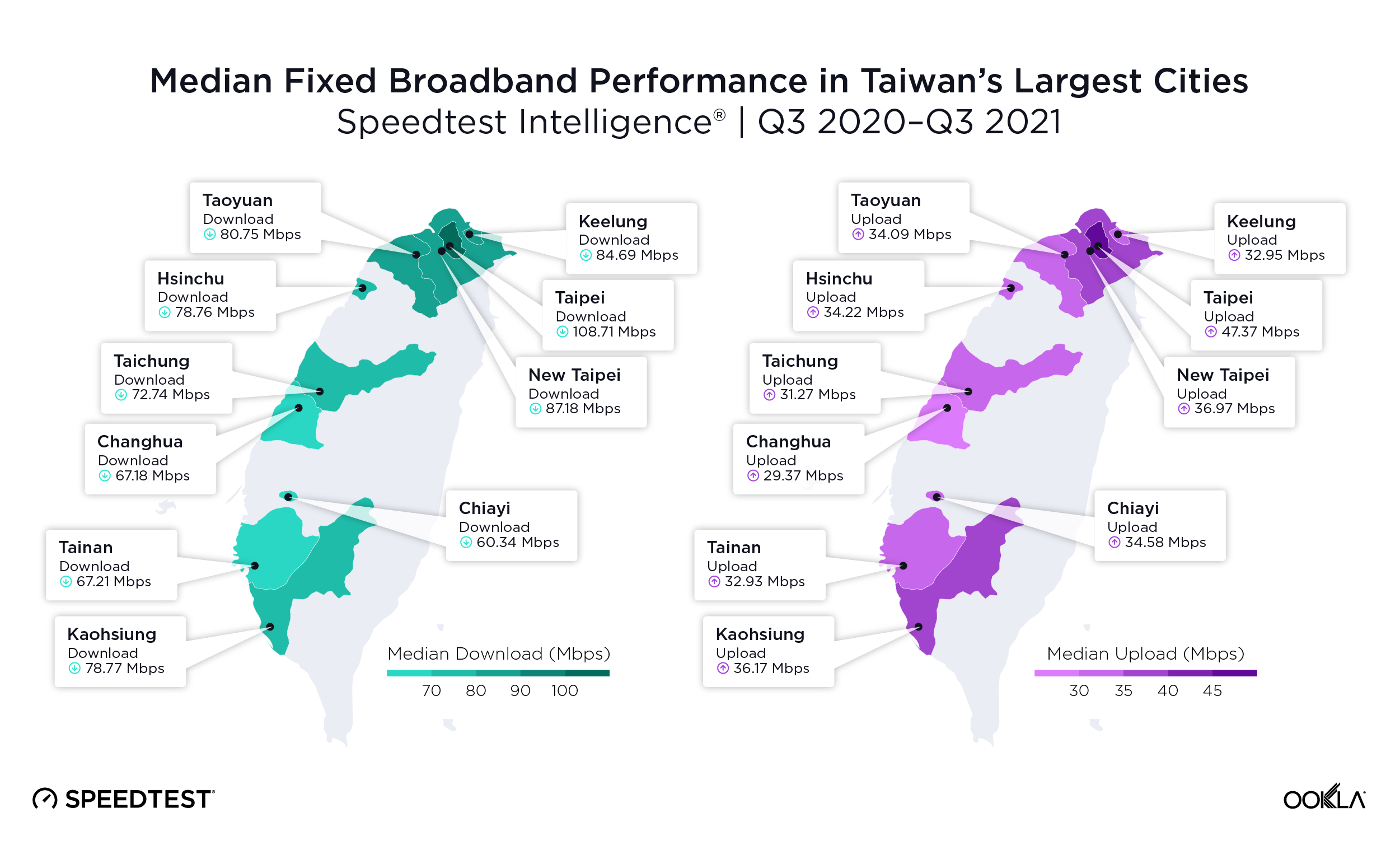
Muscat had the fastest mobile download speed among Oman’s governorates
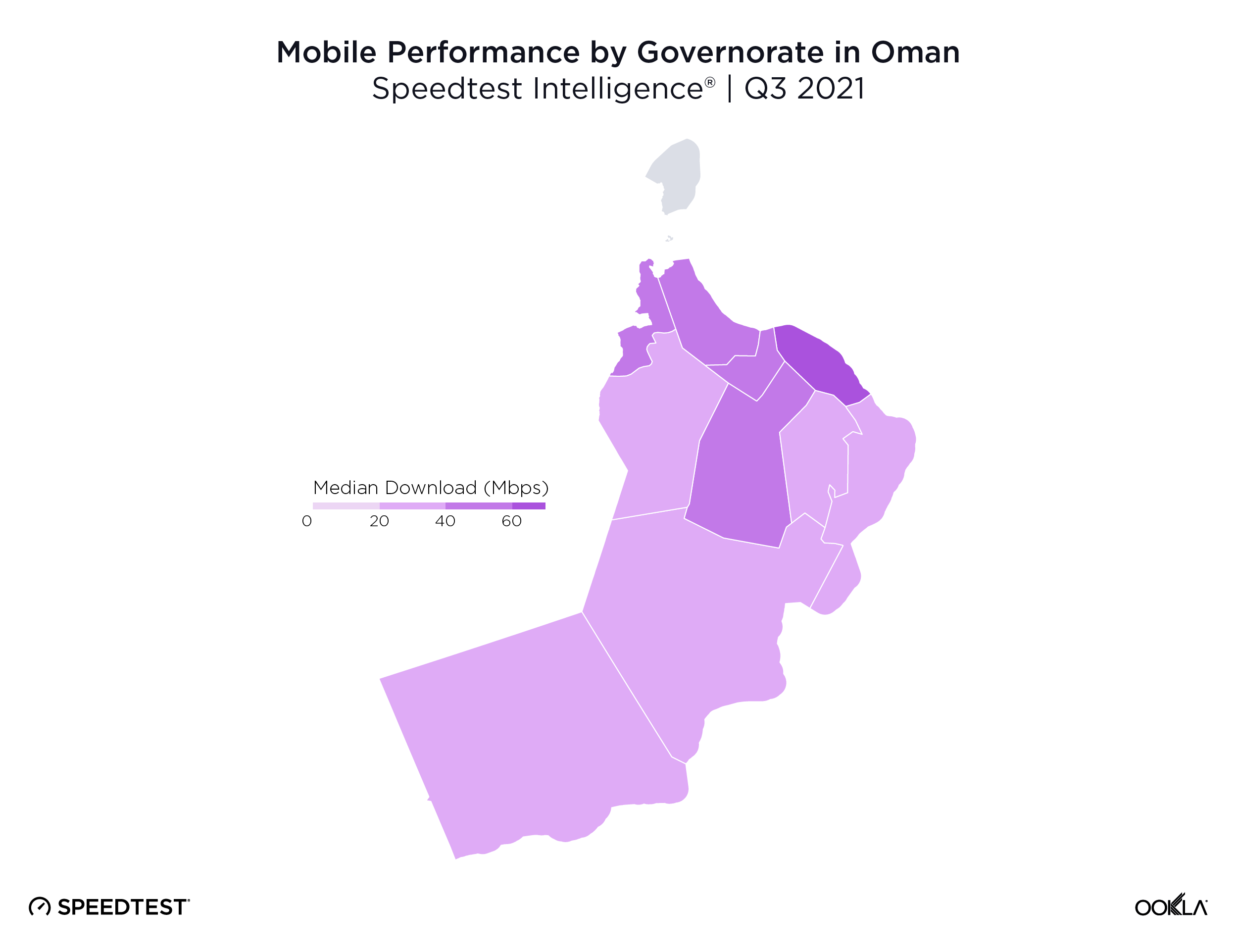
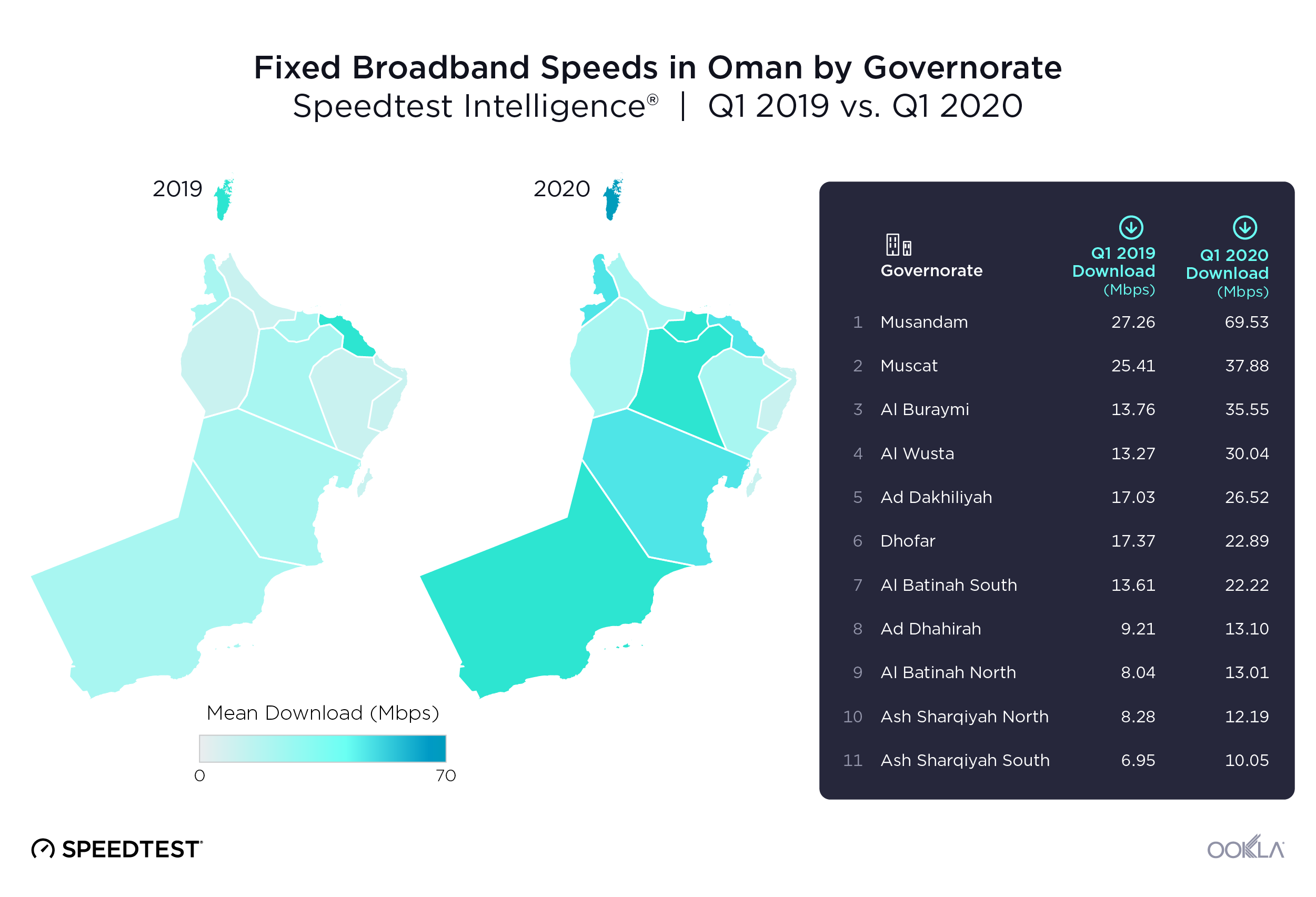
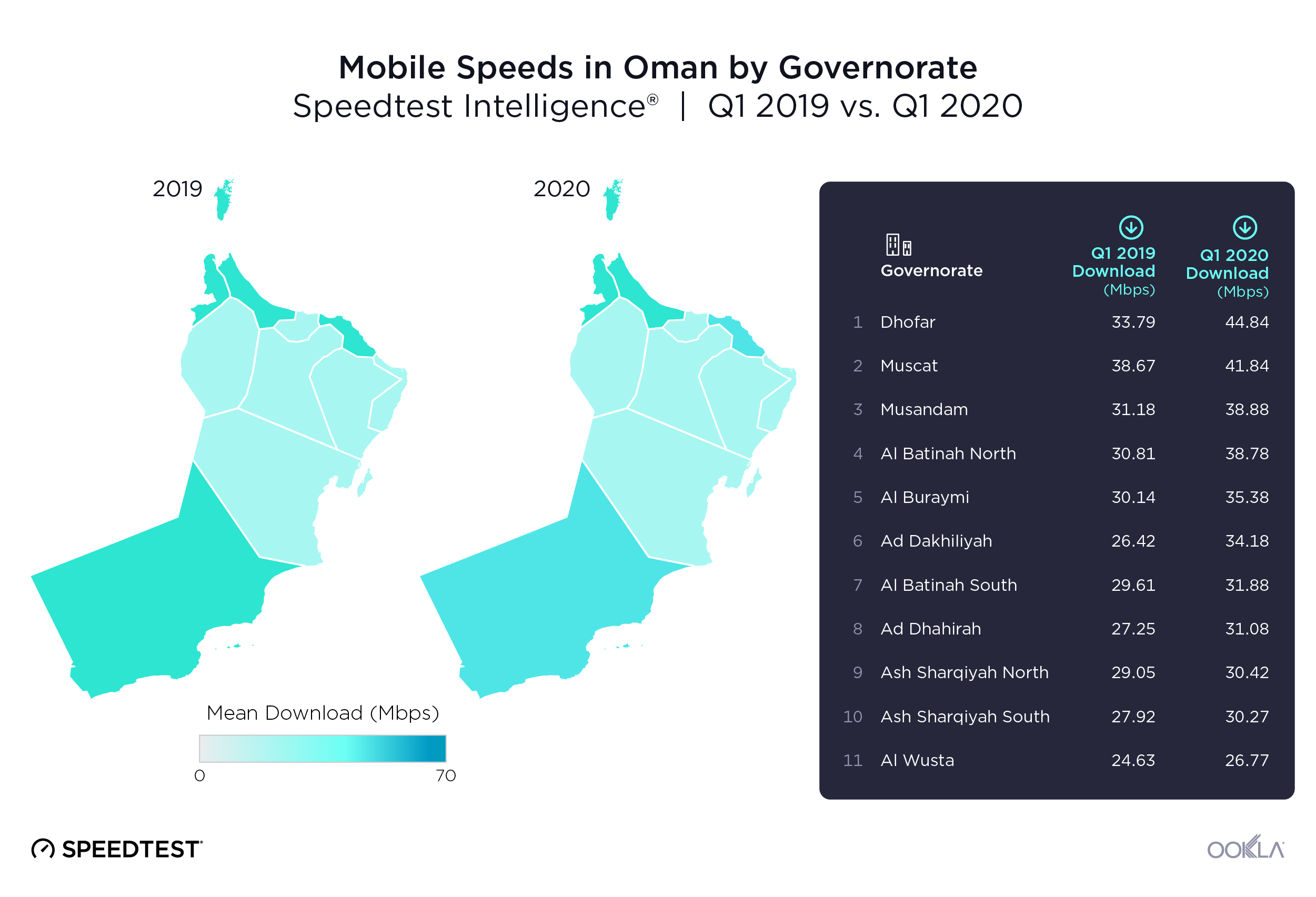
We used data from Speedtest Intelligence to examine Oman’s 11 governorates and found Muscat Governorate had the fastest median mobile download speed at 66.96 Mbps during Q3 2021. Al Buraymi Governorate was next on this list at 47.22 Mbps, followed by Al Batinah North Governorate (46.74 Mbps), Al Batinah South Governorate (44.68 Mbps) and Ad Dakhiliyah Governorate (42.49 Mbps). Ash Sharqiyah North Governorate, Dhofar Governorate and Ad Dhahirah Governorate and Ash Sharqiyah South Governorate achieved between 34.00 Mbps and 39.00 Mbps. Al Wusta Governorate had the slowest median download speed at 33.21 Mbps. Musandam Governorate lacked sufficient data for inclusion.
Four governorates achieved the 4G Availability above 80% during Q3 2021
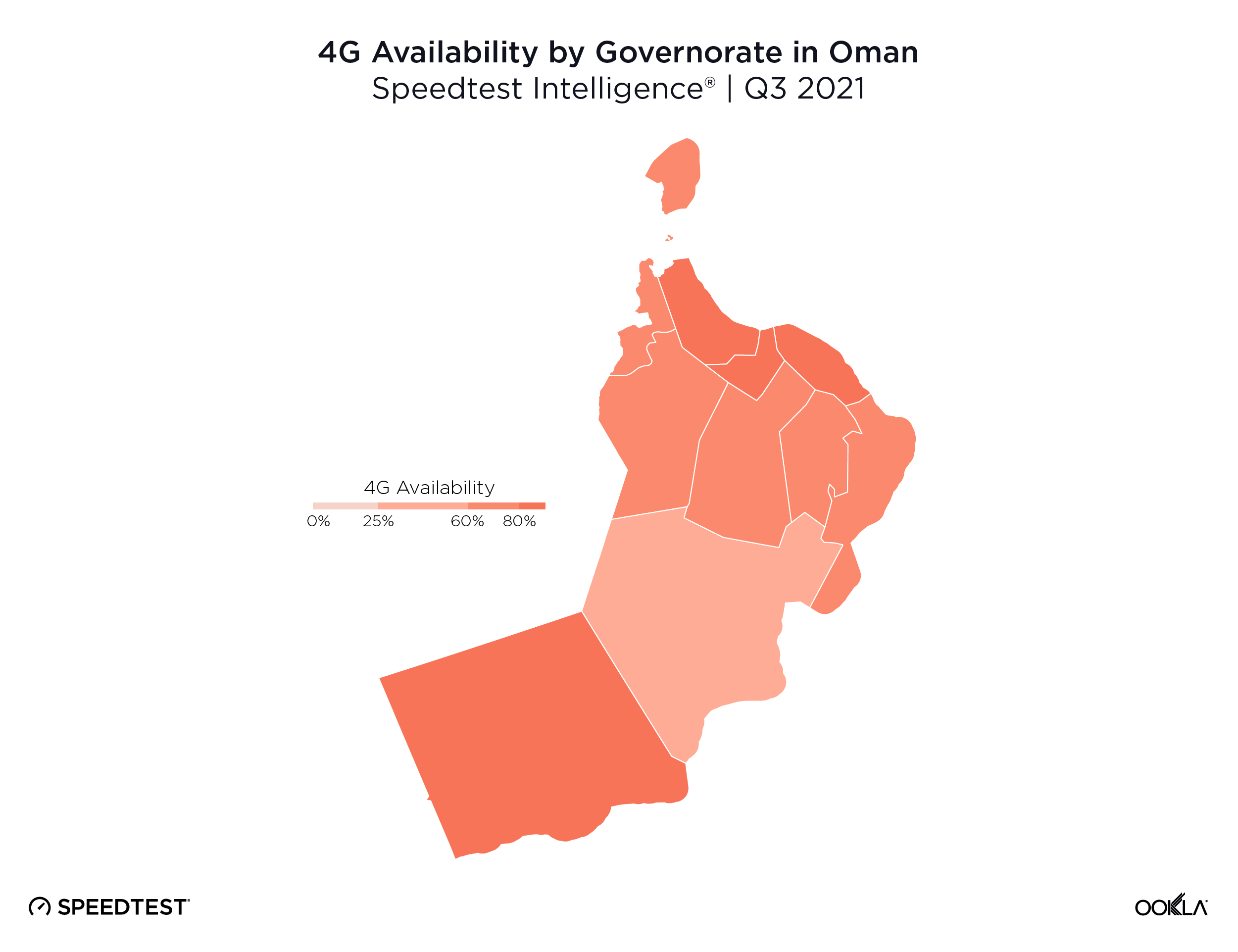
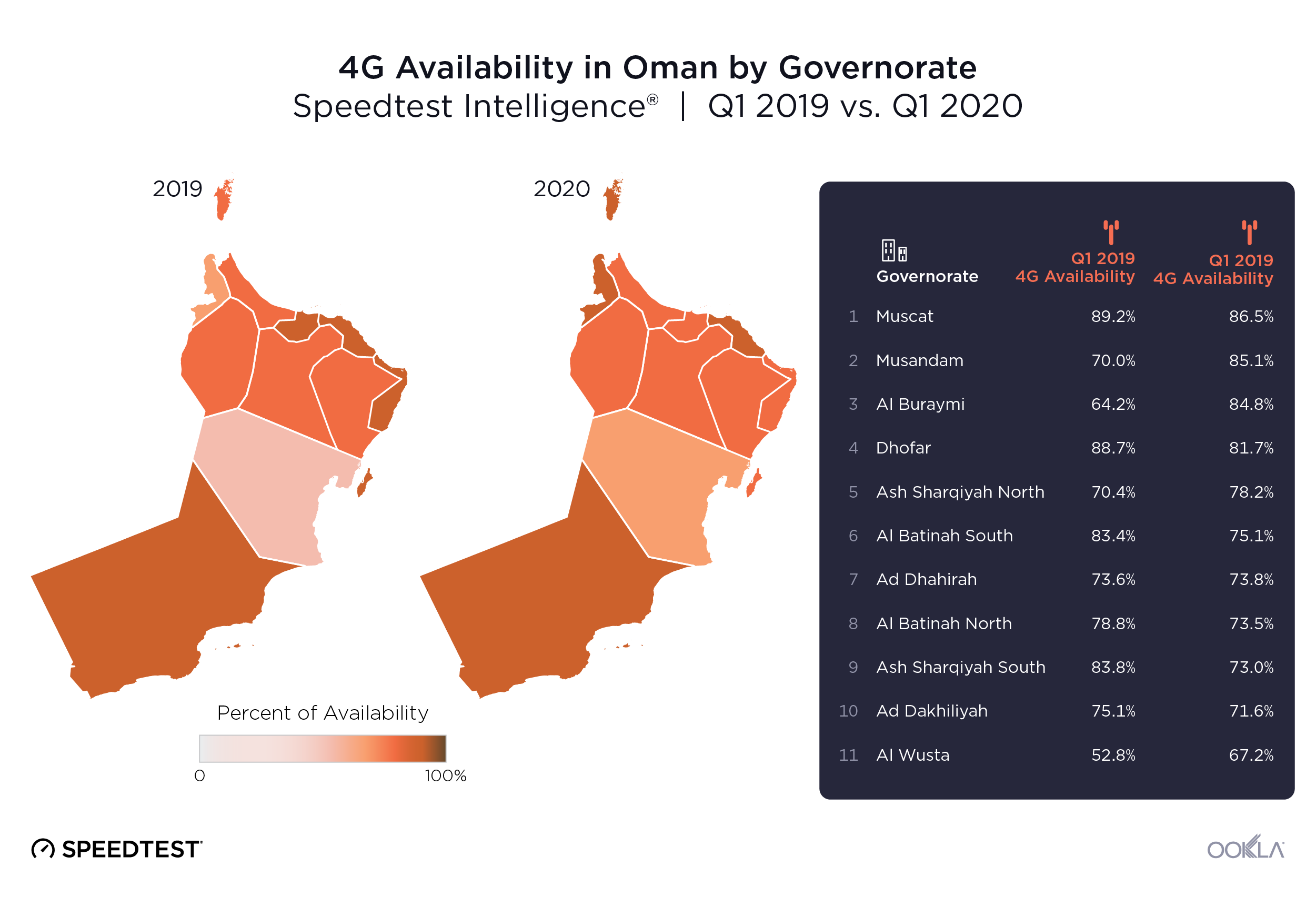
Speedtest Intelligence found that there was no statistical winner for highest 4G Availability in Oman during Q3 2021, but Muscat Governorate (84.4%), Al Batinah North Governorate (83.5%), Al Batinah South Governorate (83.0%) and Dhofar Governorate (82.8%) all achieved 4G Availability above 80%. All the rest of Oman’s governorates had 4G Availability between 72.0-80.0% except Al Wusta Governorate, which had the lowest 4G Availability in Oman at 57.9% during Q3 2021.
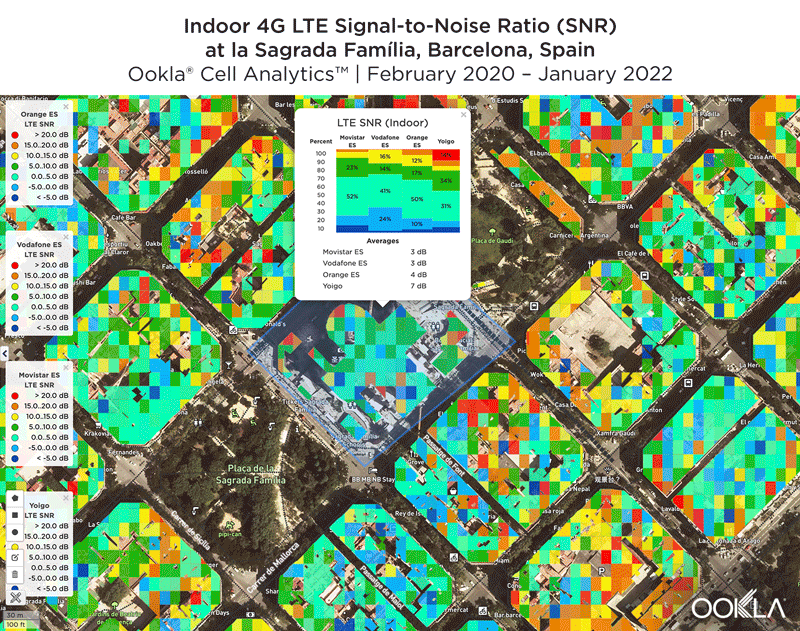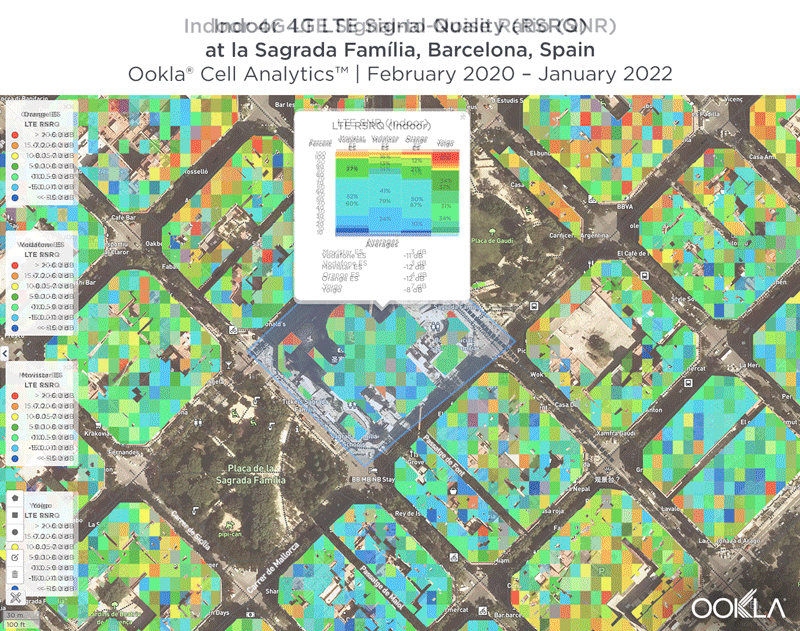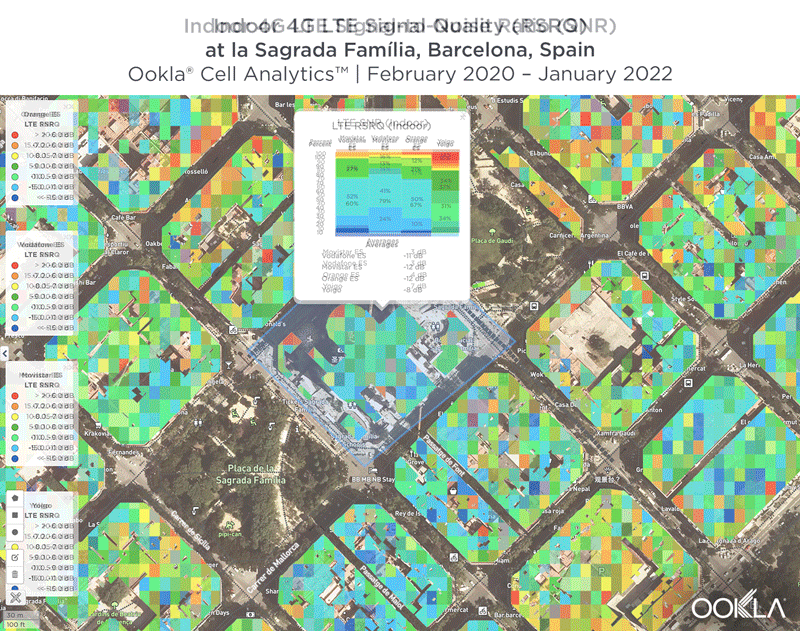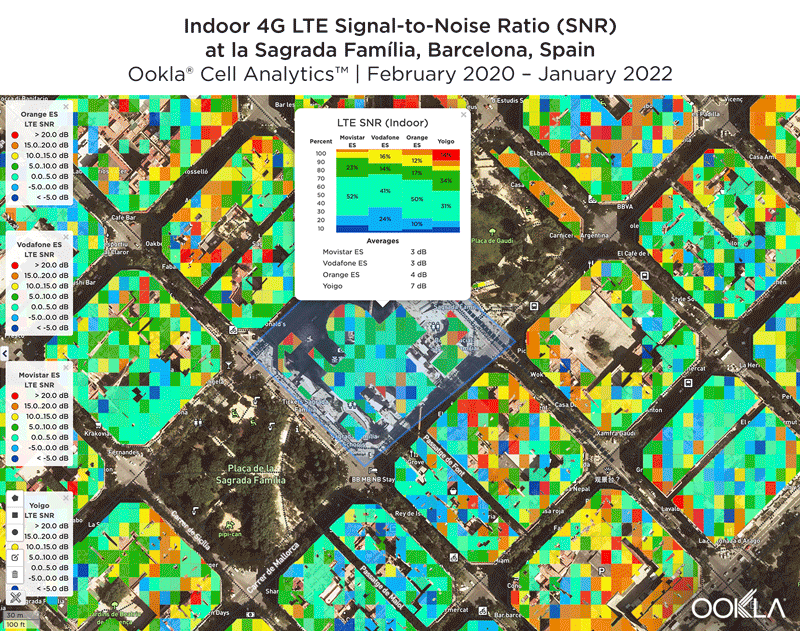
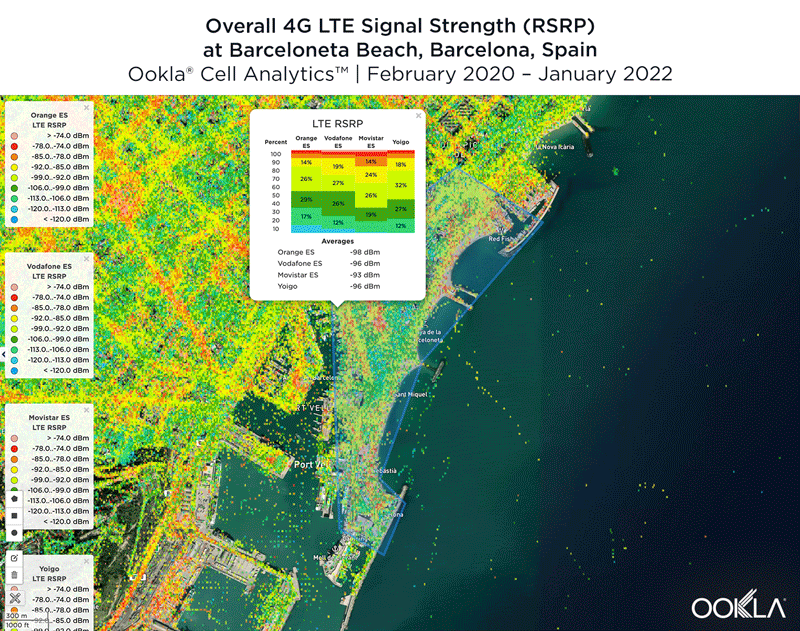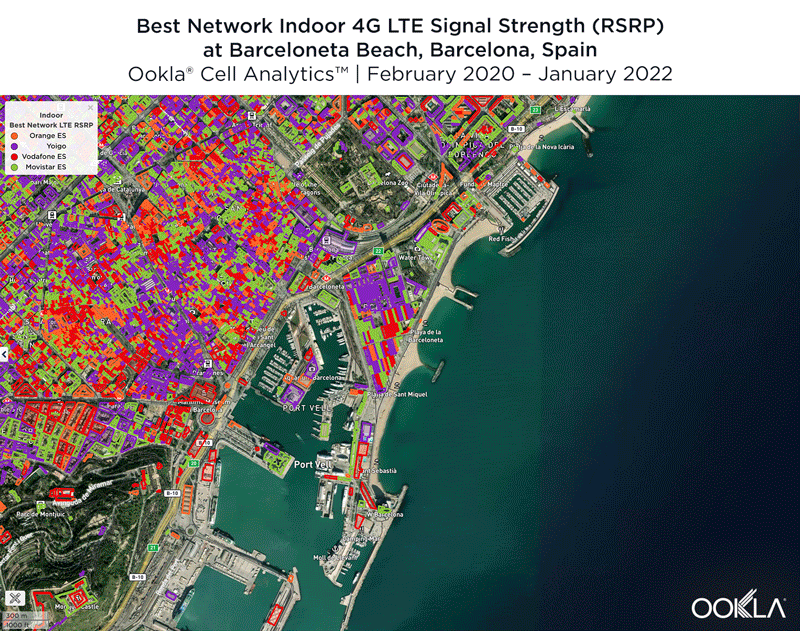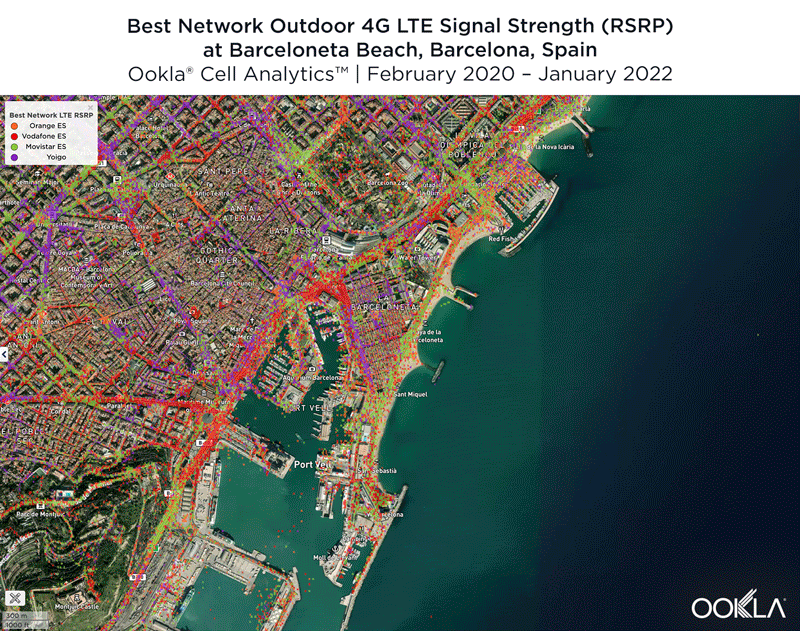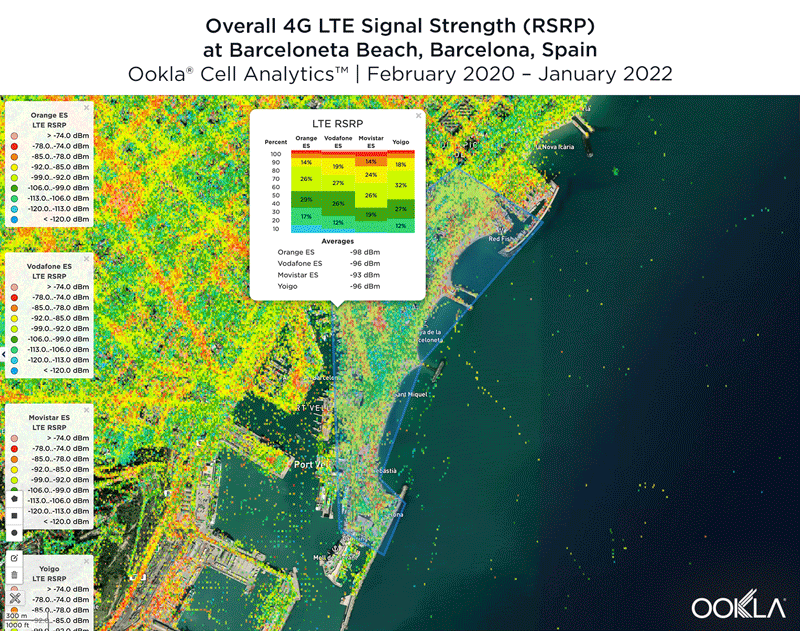
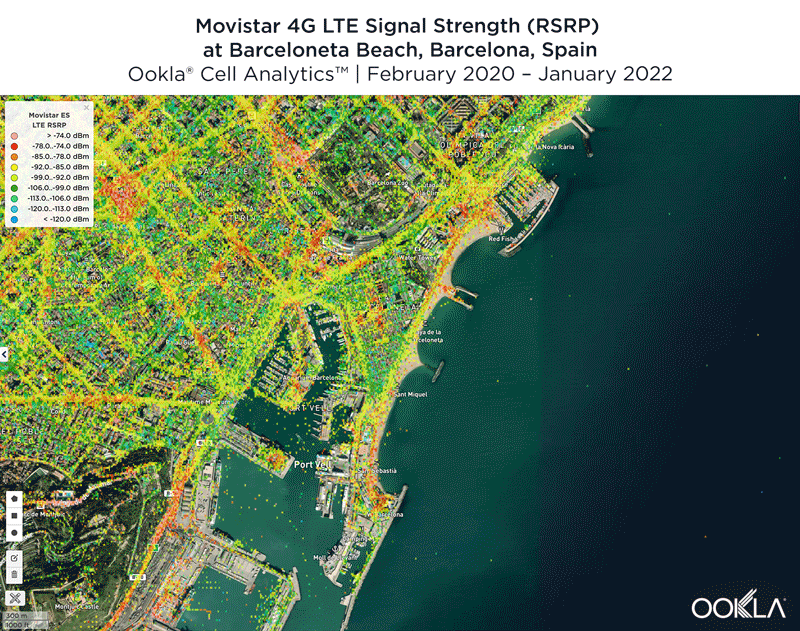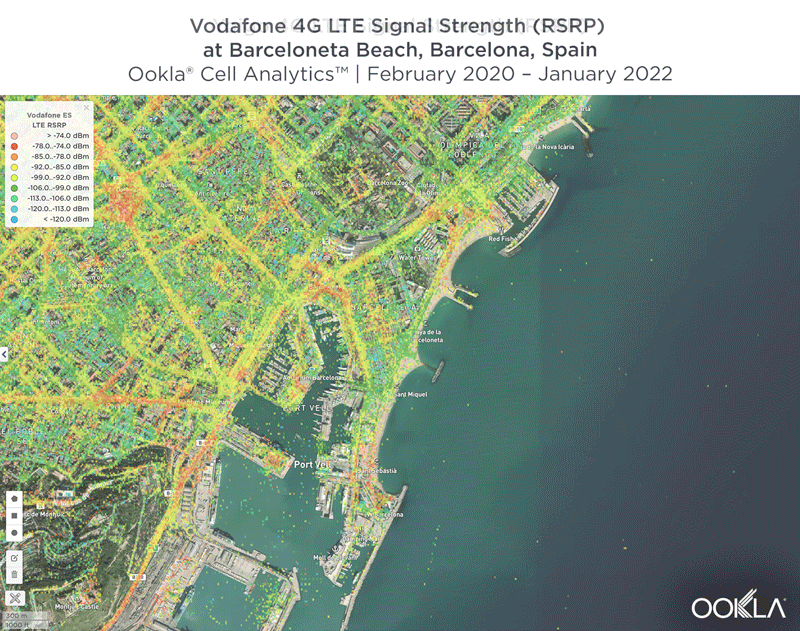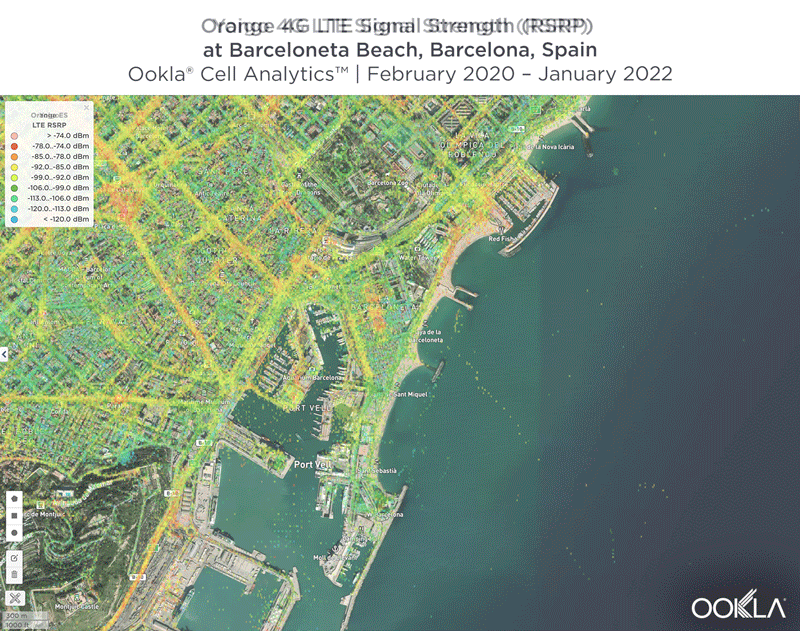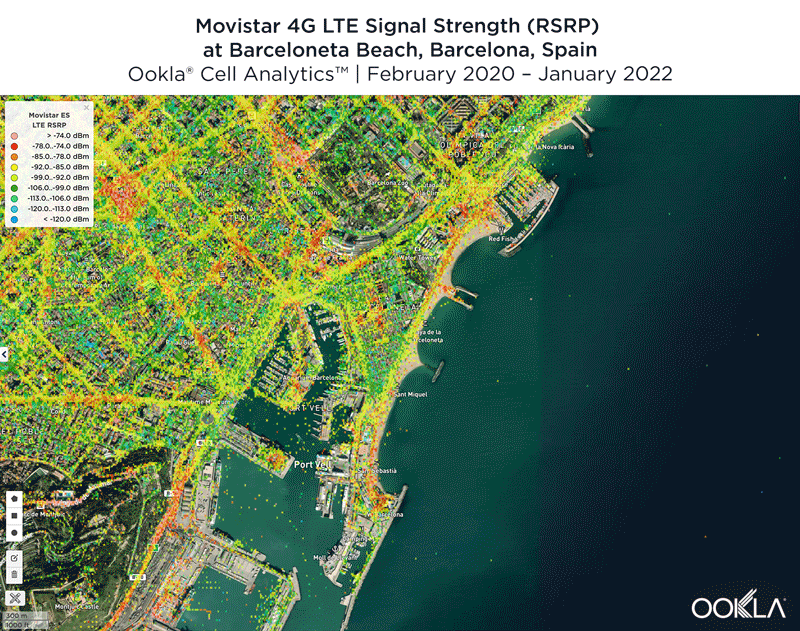
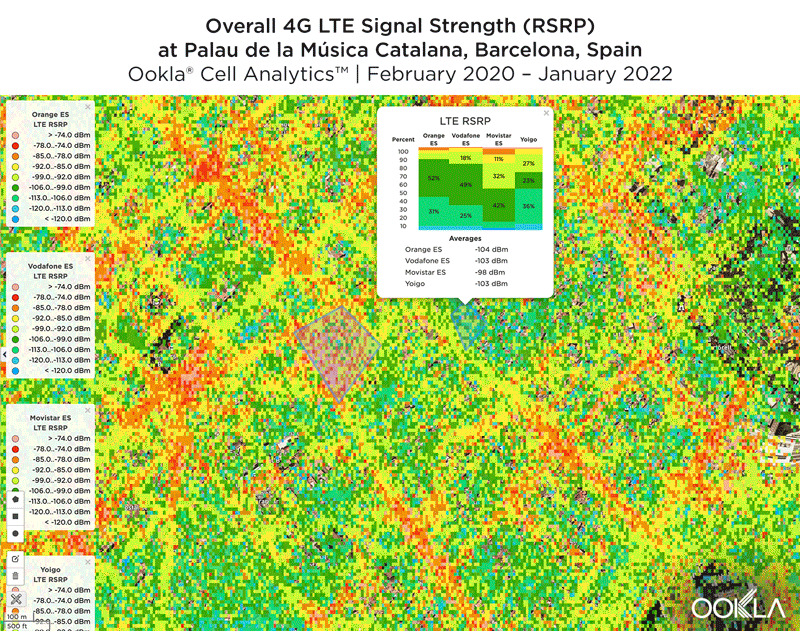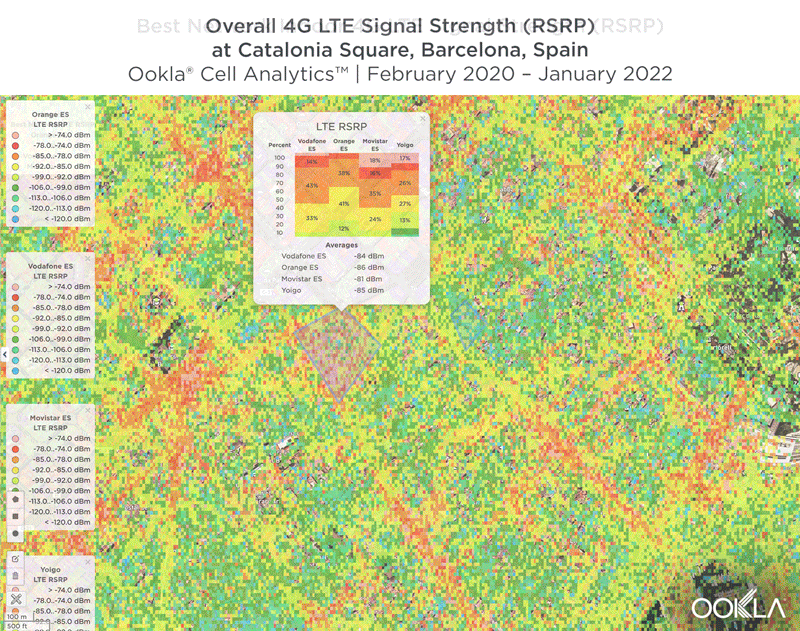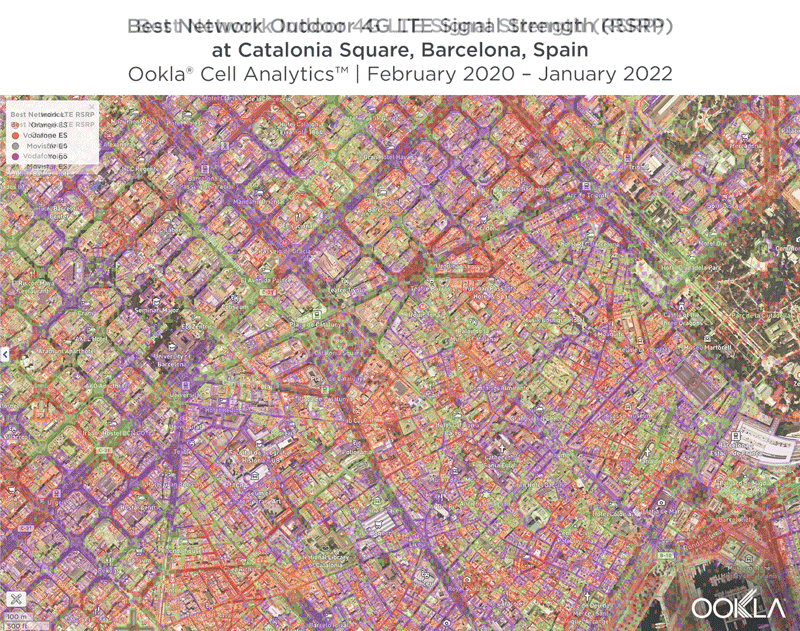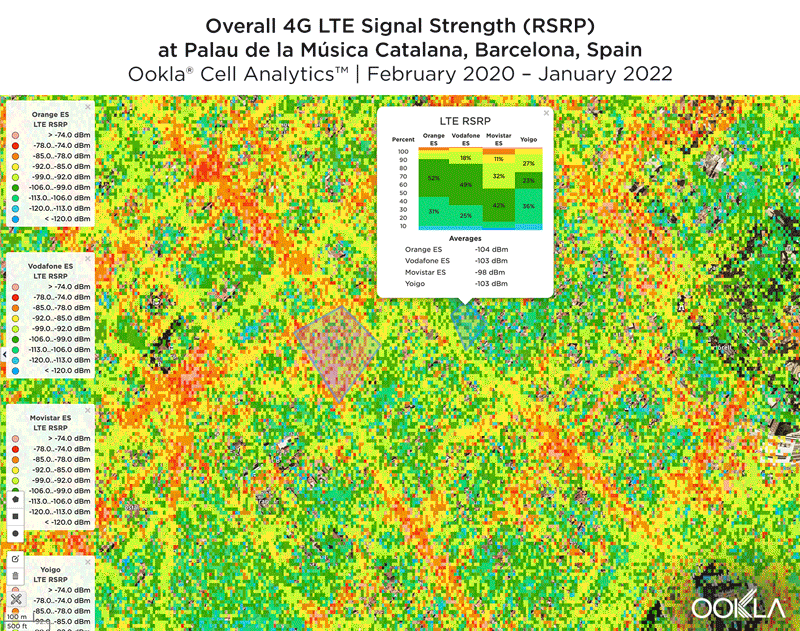
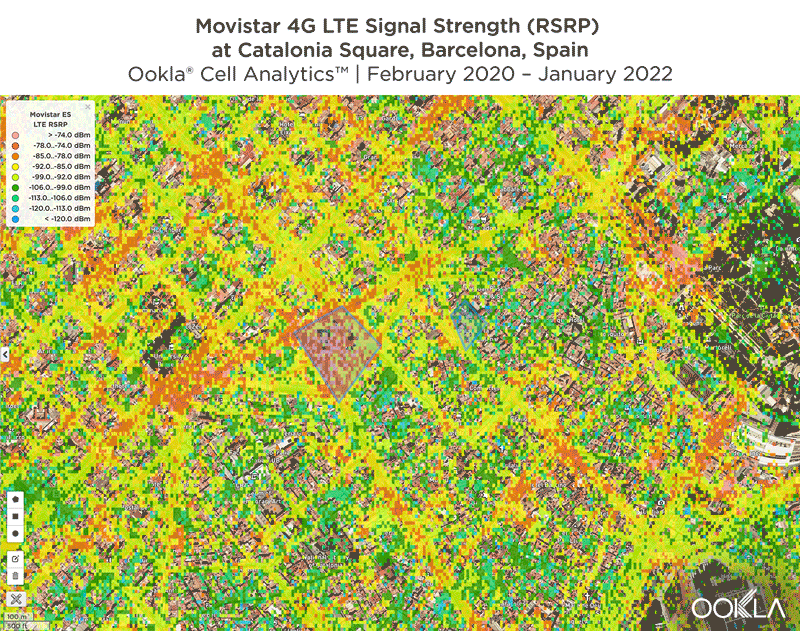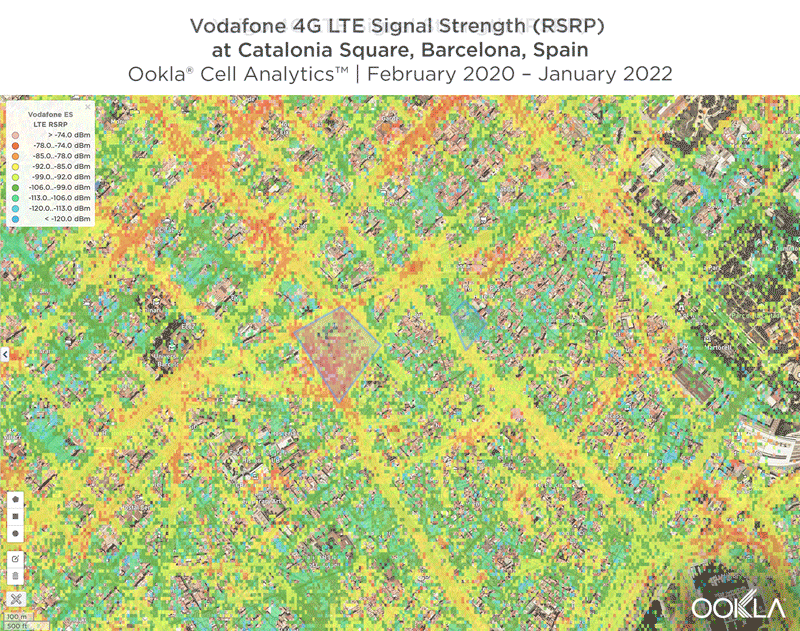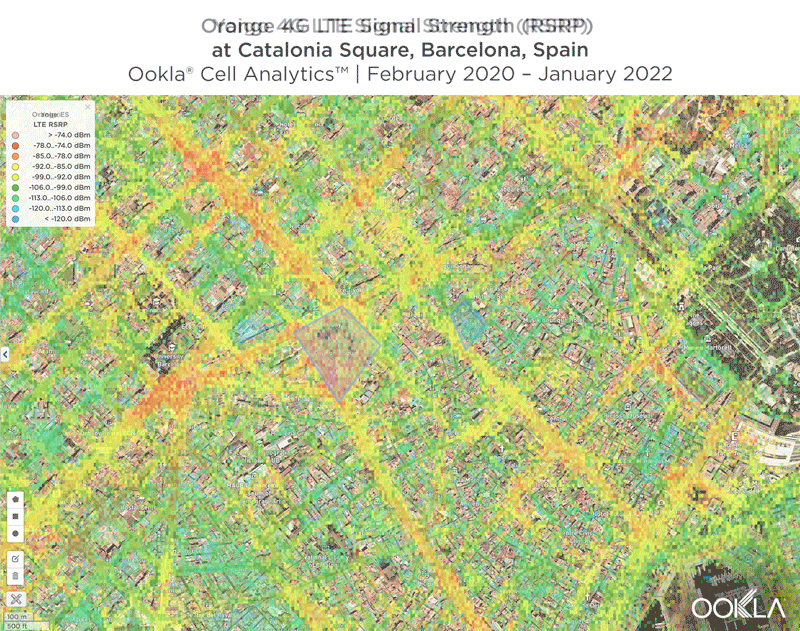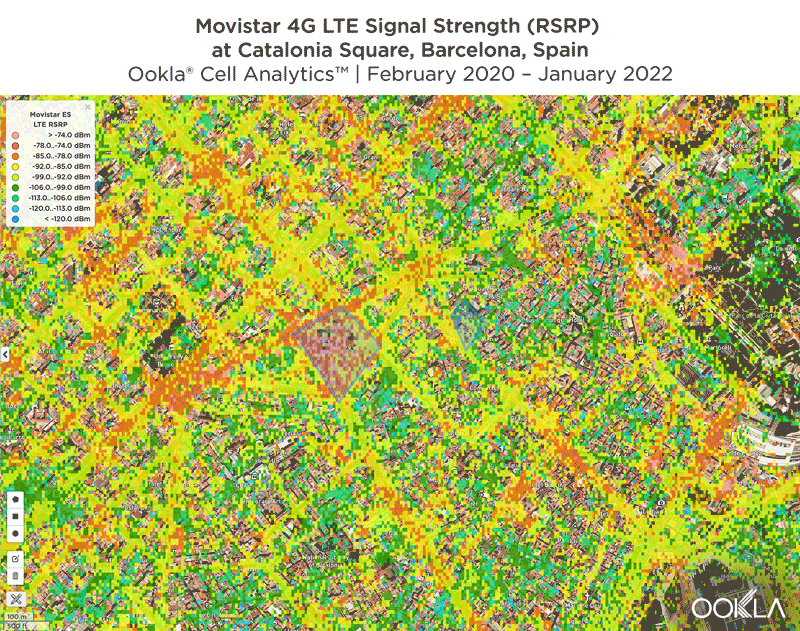
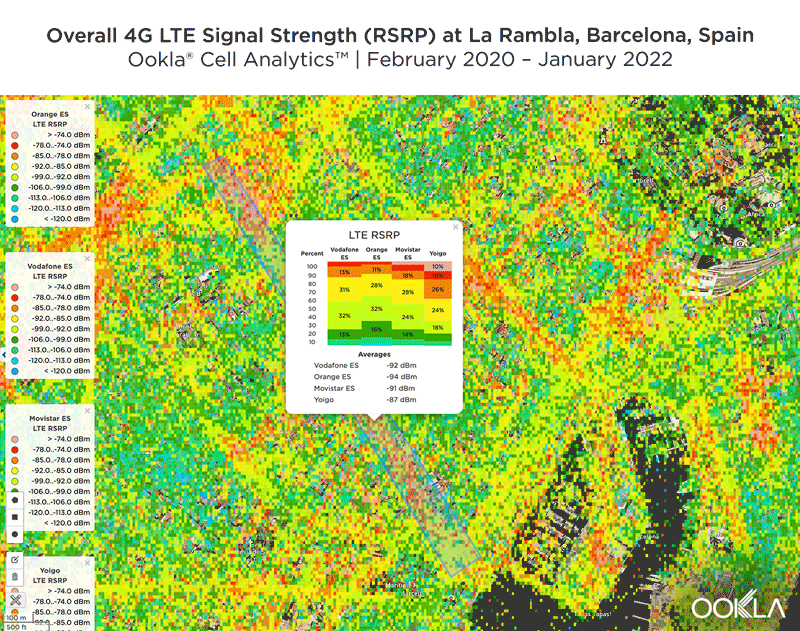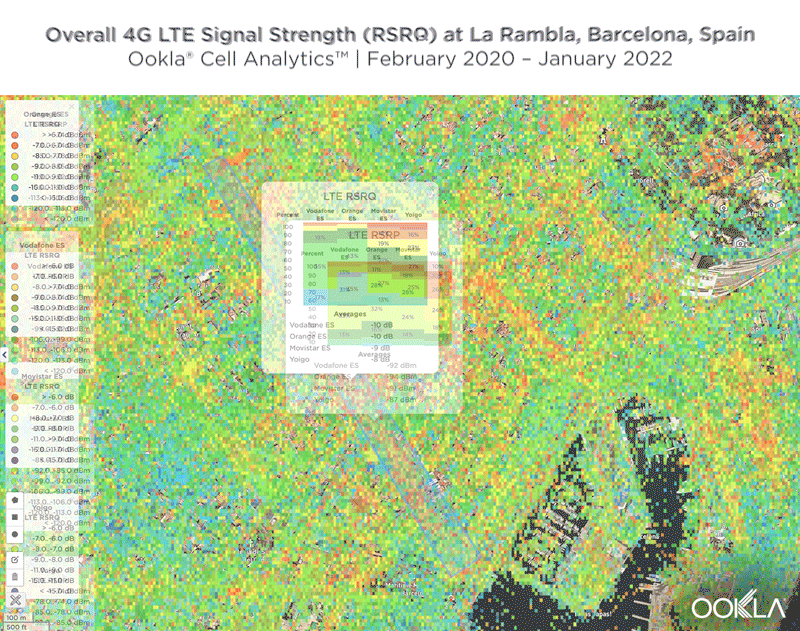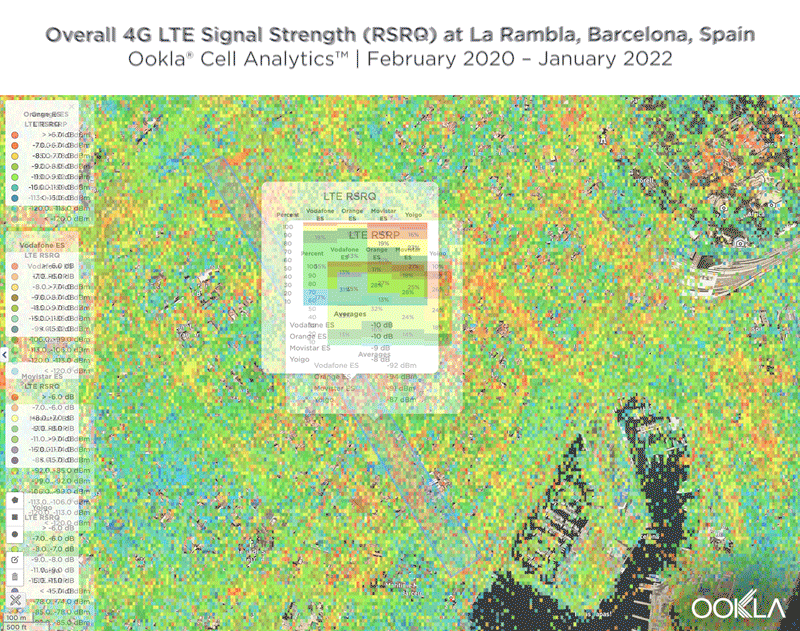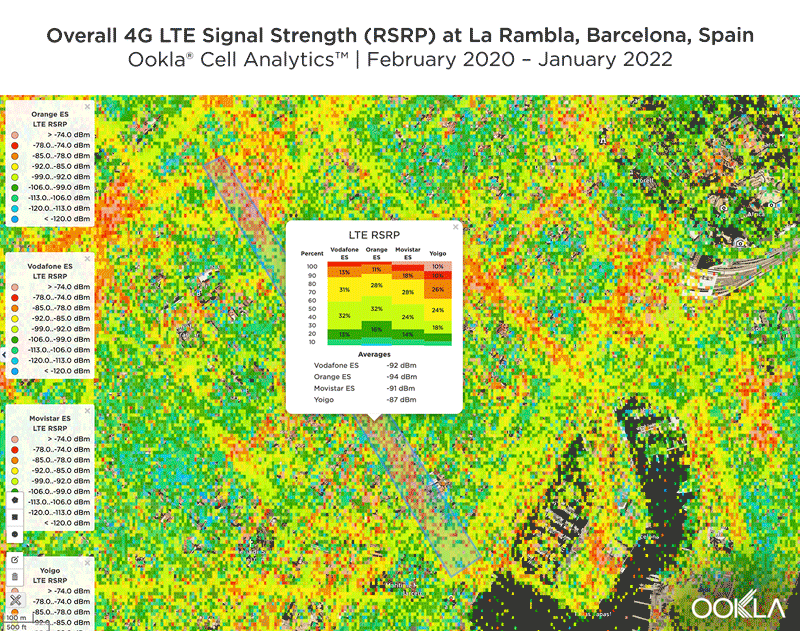
Signal strength is competitive in Muscat
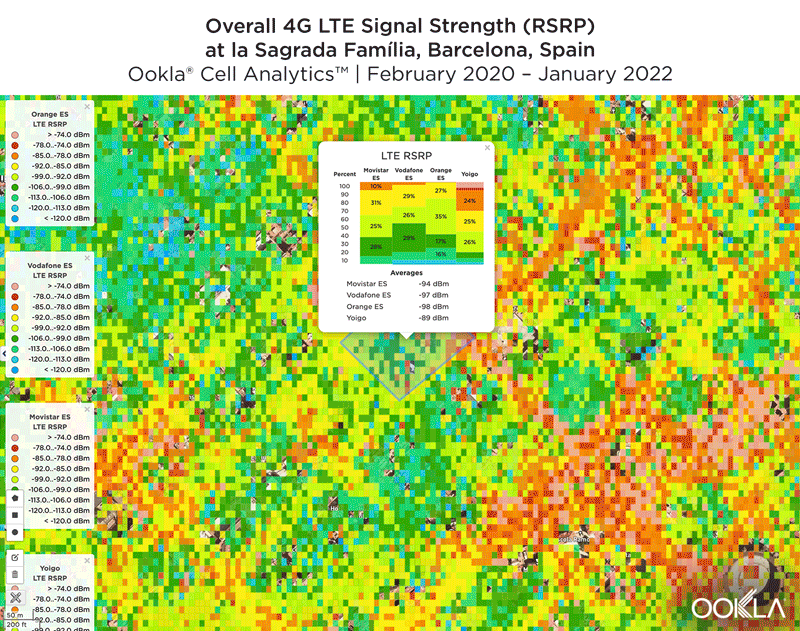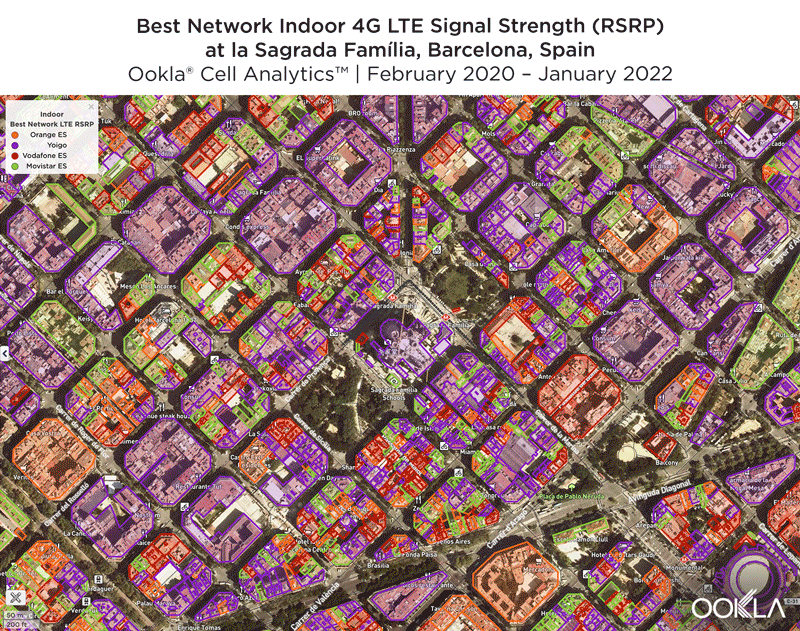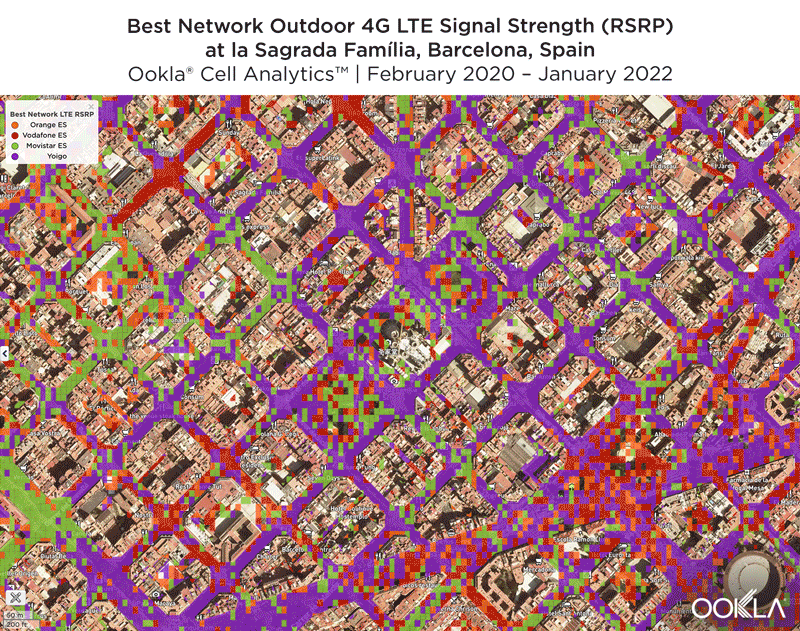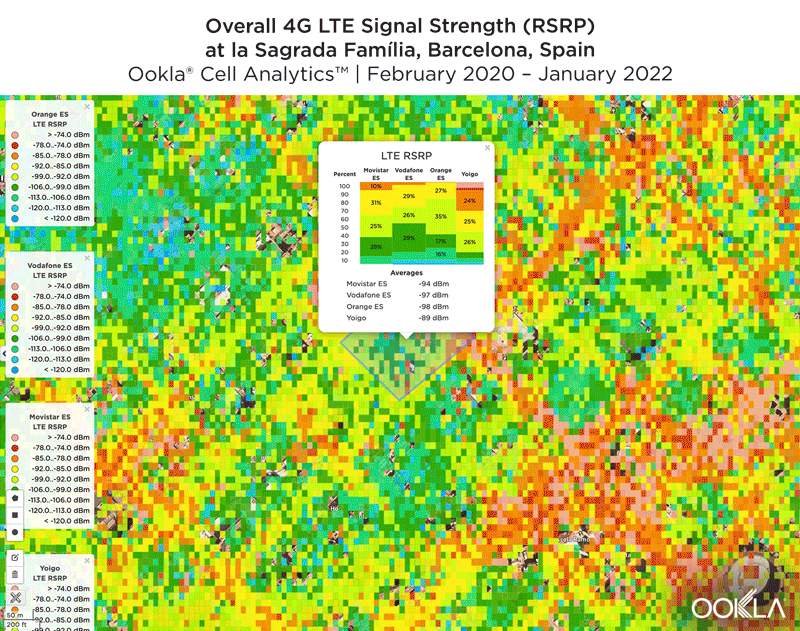
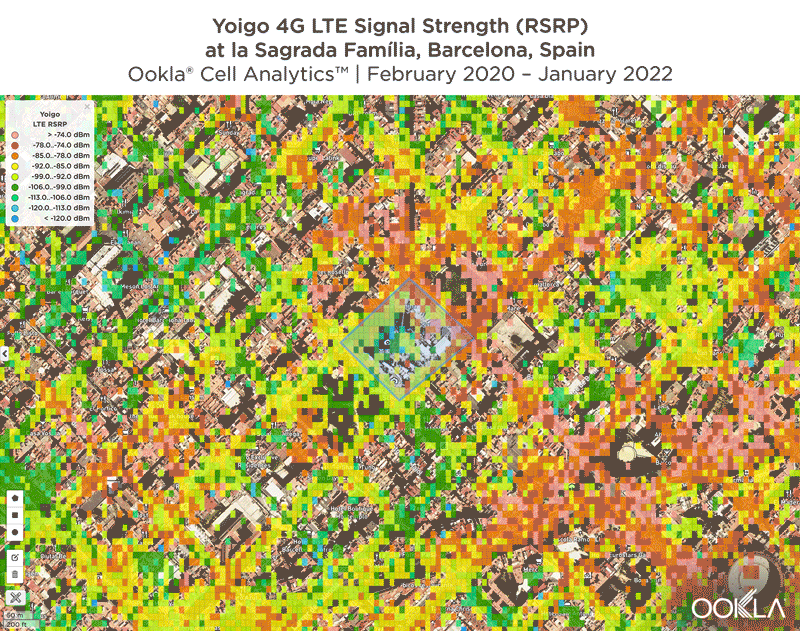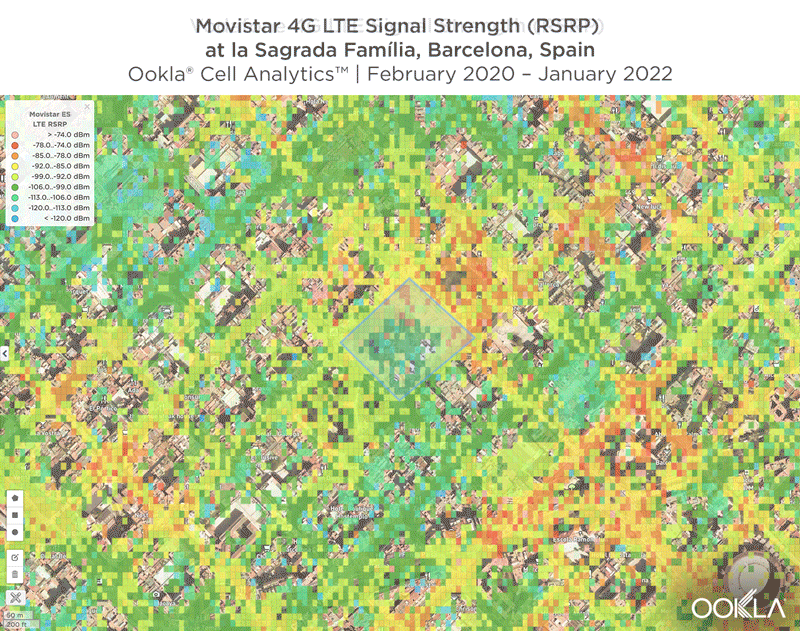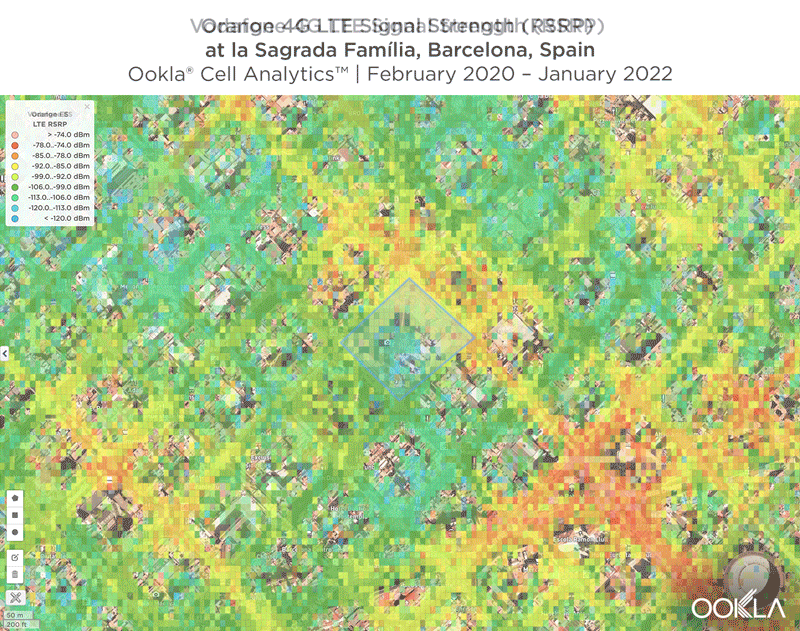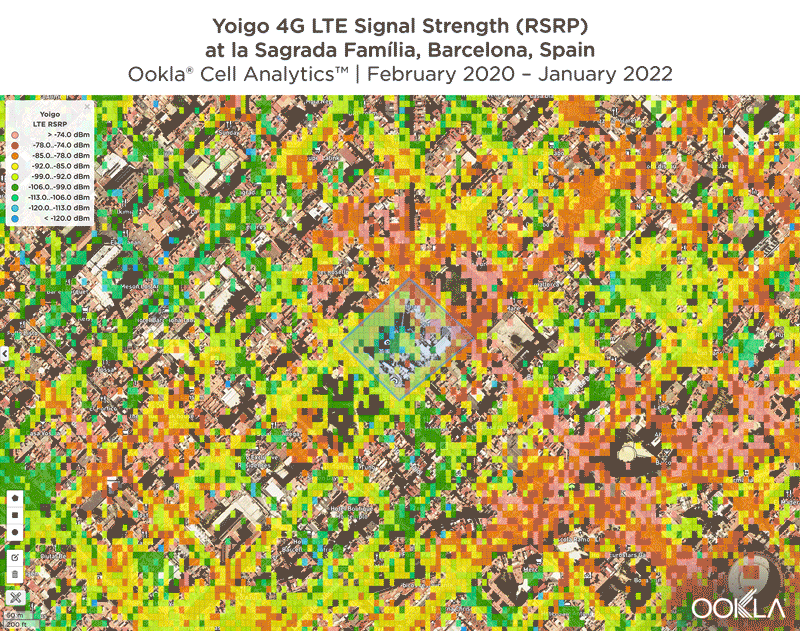
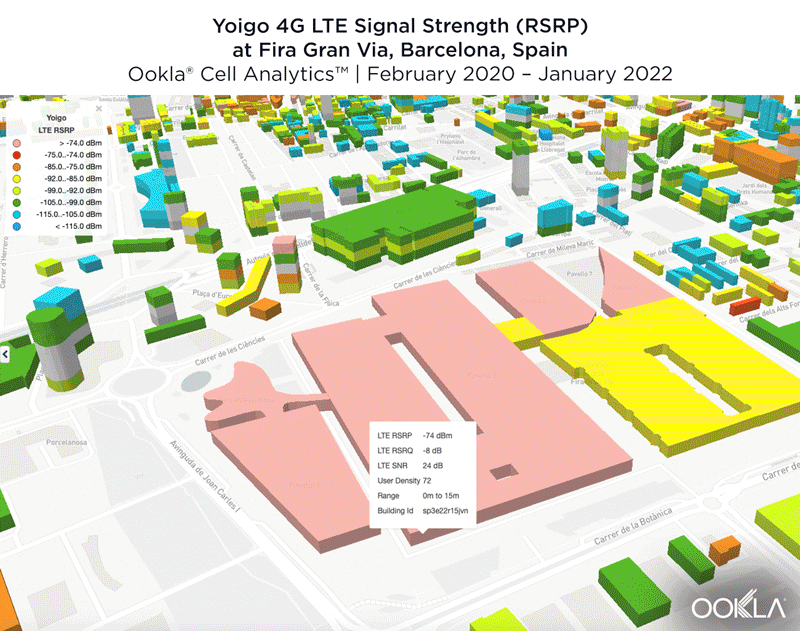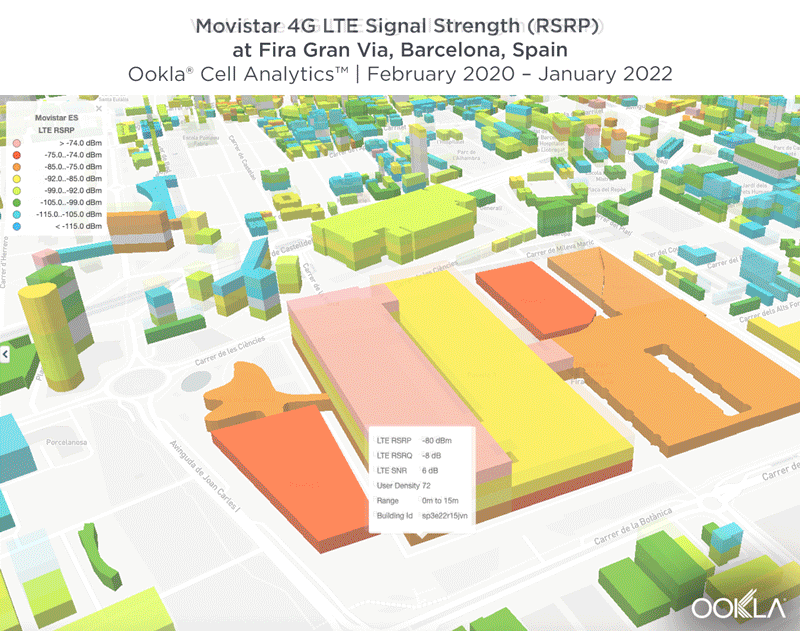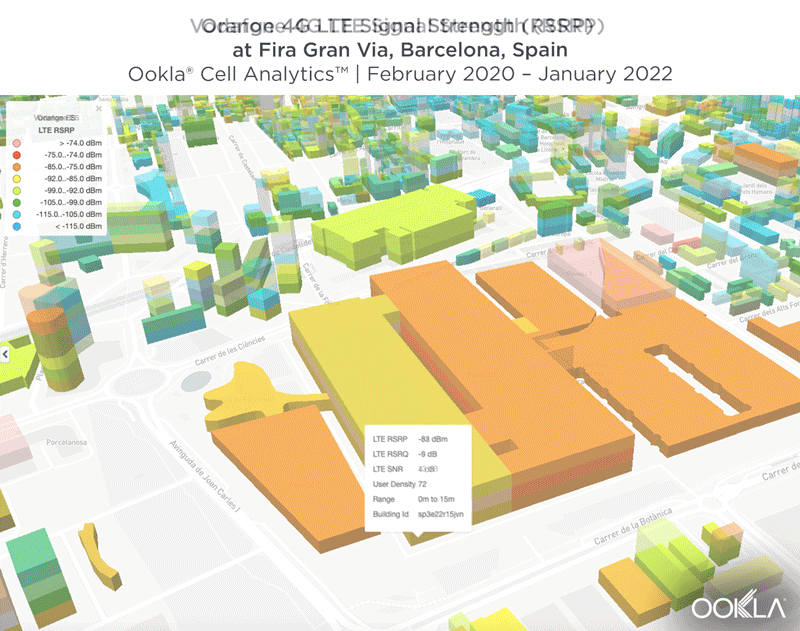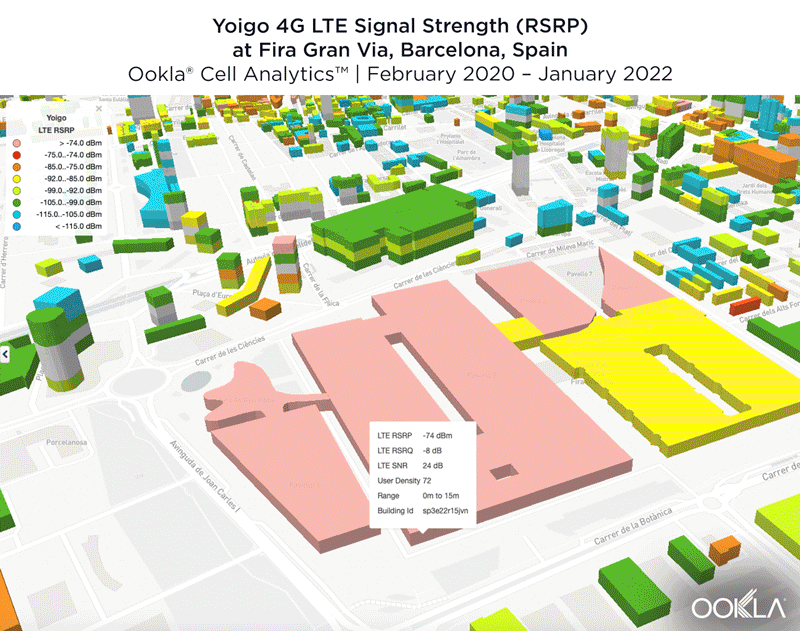
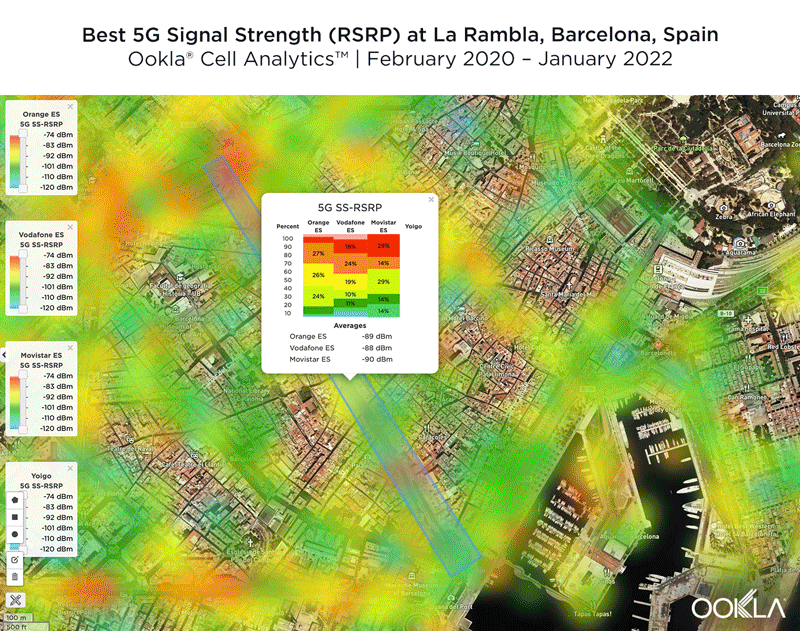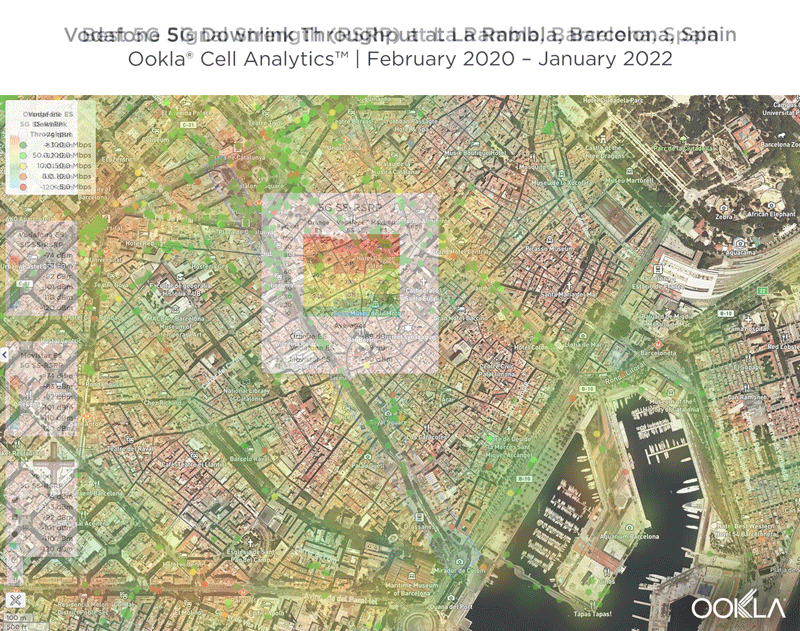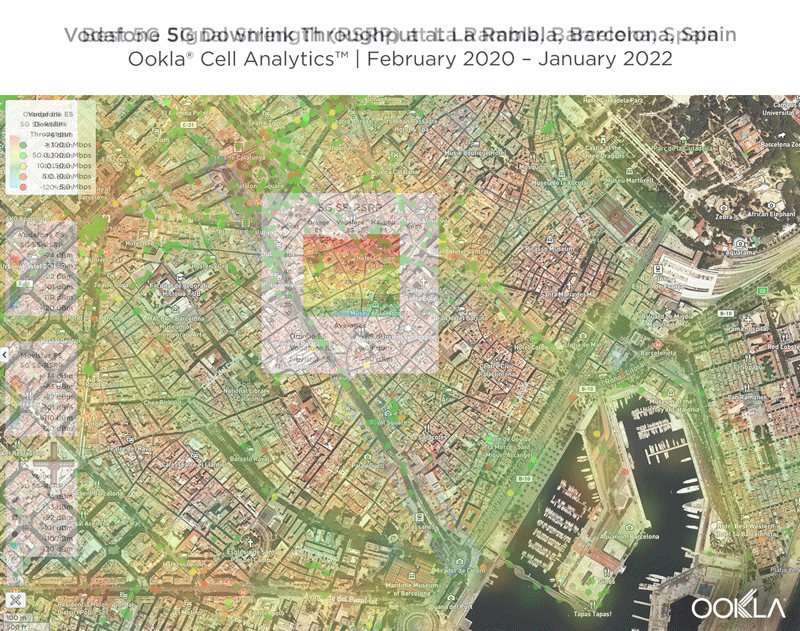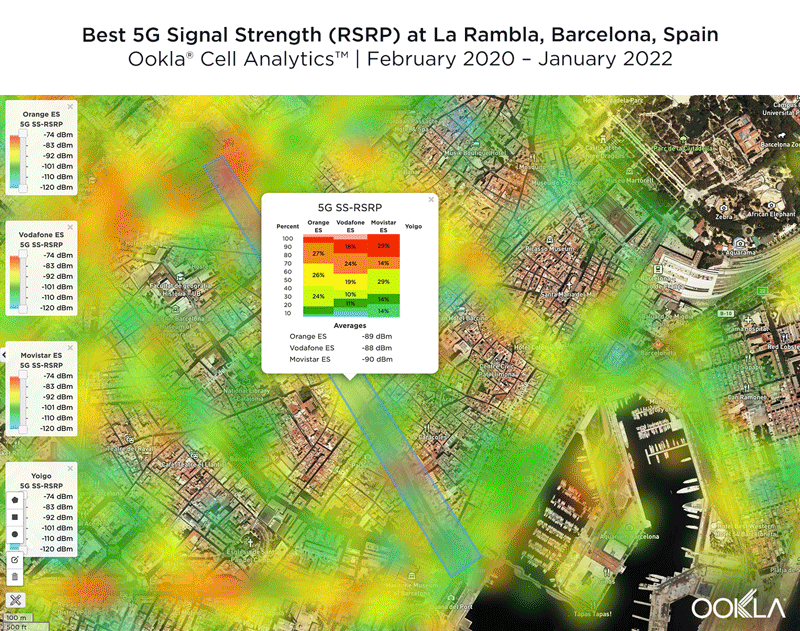
We identified several key locations in Muscat to highlight using Cell Analytics data from Q2-Q3 2021. Each of these maps shows the strongest 4G reference signal received power (RSRP) in a given area, which can help mobile operators locate areas where they can improve their networks. Cell Analytics can identify the strongest RSRP by mobile network provider for a given area if there is a statistically-significant winner and color codes that plot bin to the provider’s color. Provider-level maps show the performance of individual providers for a given area, with pink and red showing a strong signal and blue indicating a weak signal.
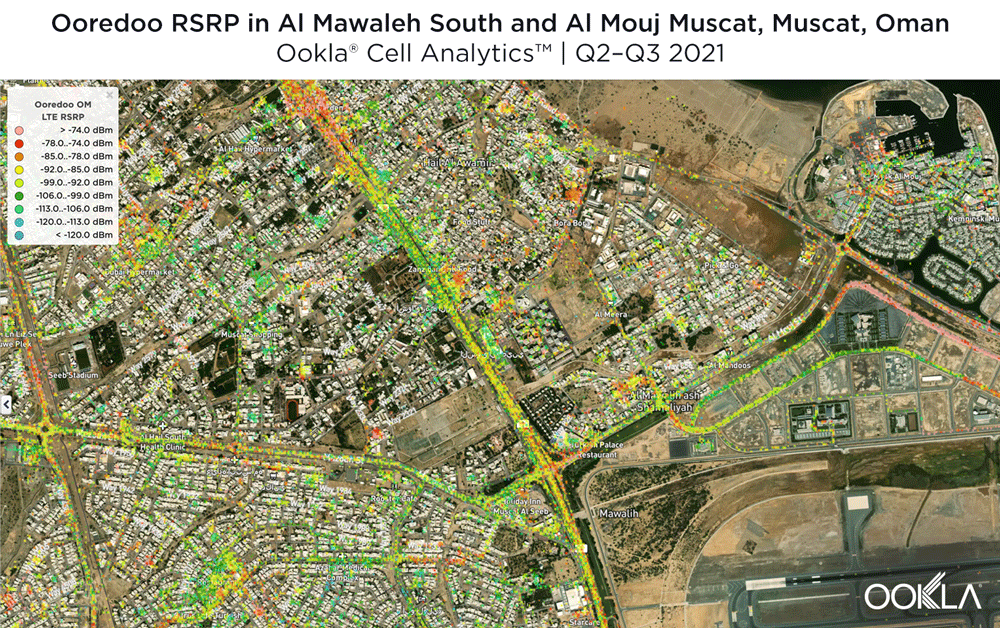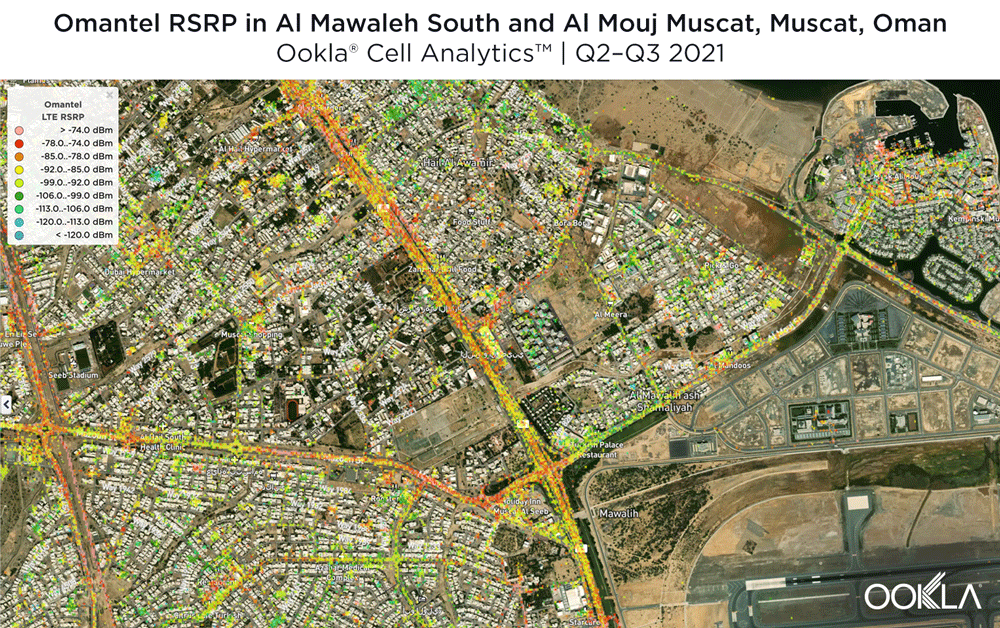
Al Mawaleh South and Al Mouj Muscat
Located west and northwest of the Muscat International Airport, Al Mawaleh South and Al Mouj Muscat are high-traffic areas frequented by many Omani residents. The image below shows the strongest 4G LTE RSRP signal strength by provider with the dark blue representing Omantel and purple representing Ooredoo. As evidenced by the bands of solid colors, Omantel and Ooredoo have a strong presence by the major throughways in this area, while competition throughout the neighborhood is tight, particularly around the City Centre Muscat mall just west of the airport.
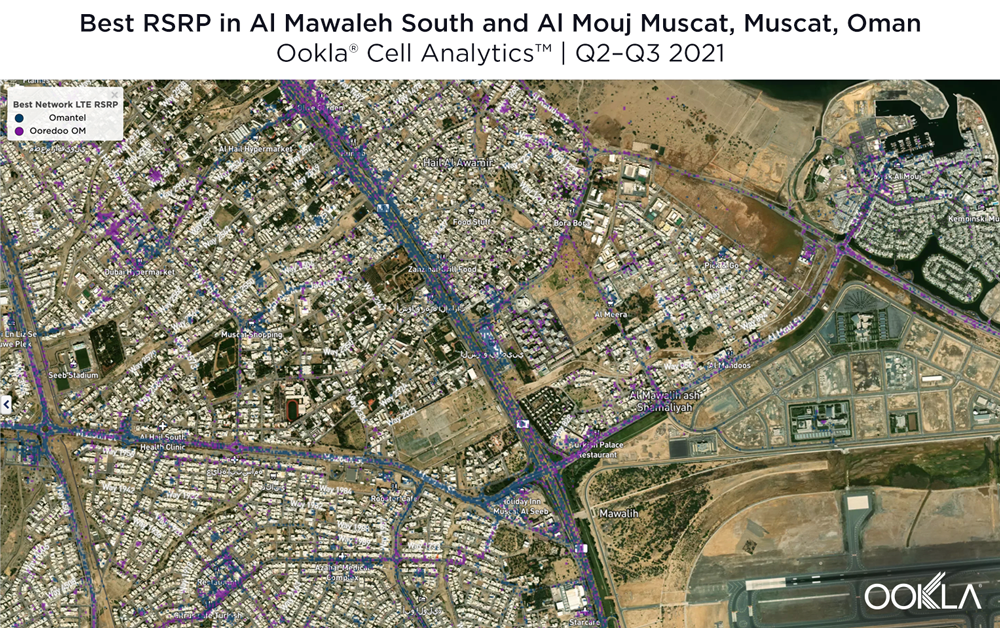
The maps below show areas where each top provider has high and low signal strength data. Omantel had areas of high signal strength (pink and red), particularly on the major throughways and crowded shopping areas. Omantel also had a strong presence near the Al Mouj Marina, as well as key locations at the Seeb Stadium and City Centre Muscat mall. Ooredoo had deployments in similar locations with a strong signal near 18th November St., just north of the airport.
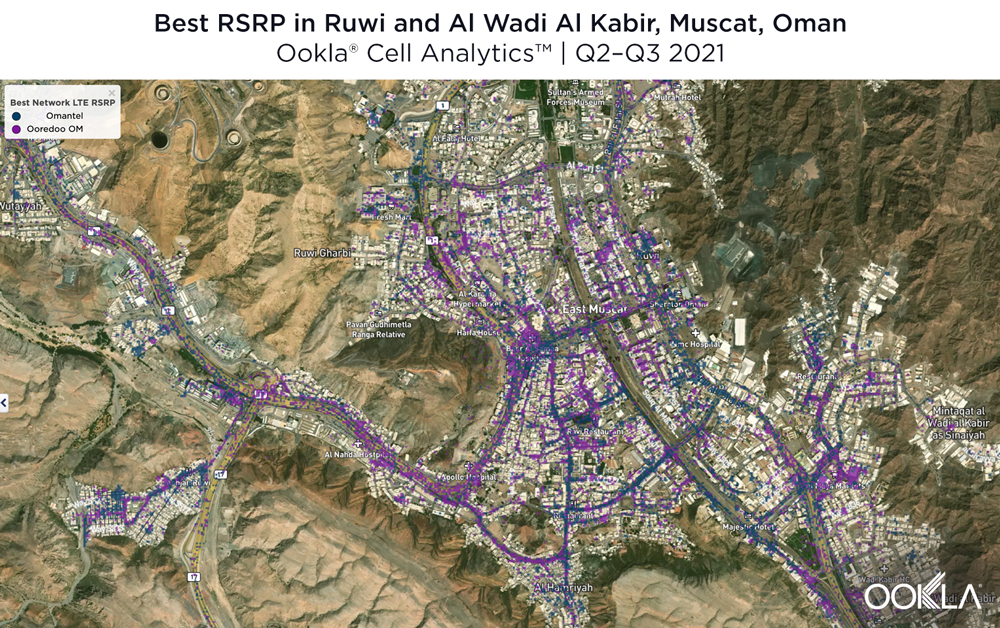
Ruwi and Al Wadi Al Kabir
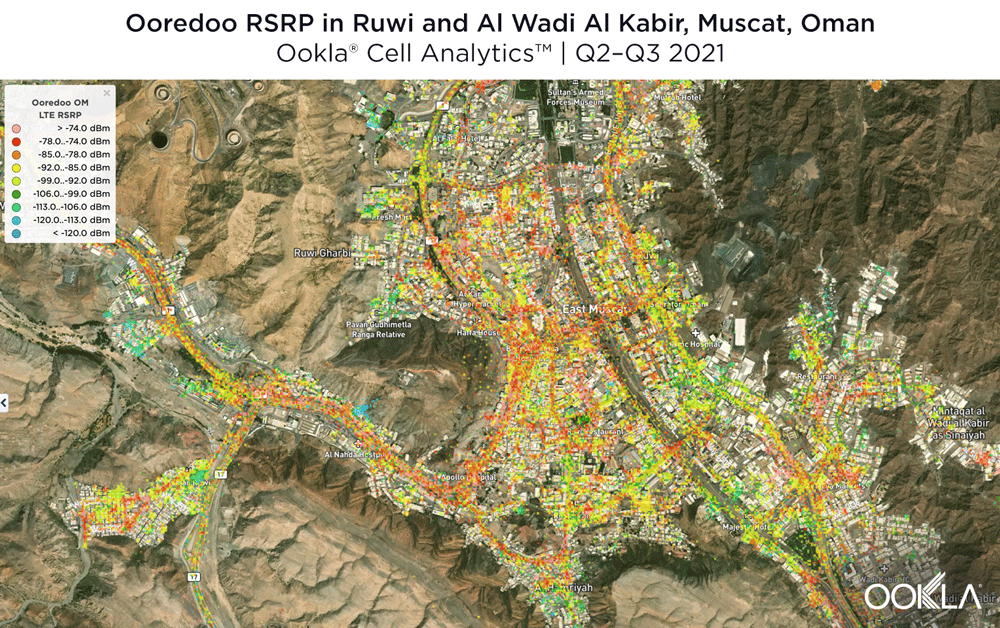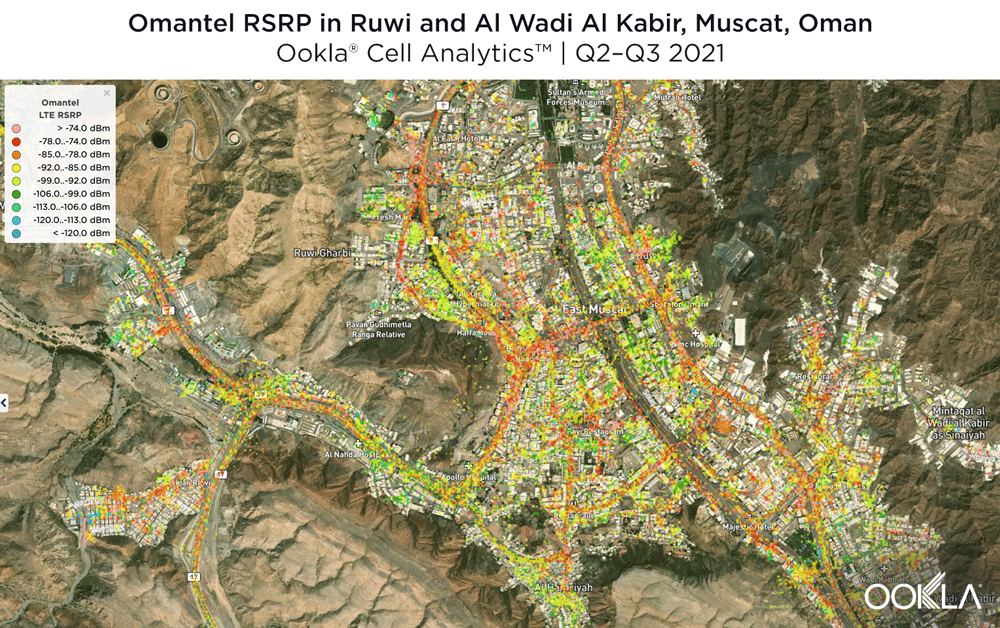
Located in central Muscat, Ruwi and Al Wadi Al Kabir Industrial Estate represent the commercial heart of Muscat. As the images that follow show, it’s clear mobile operators have recognized how valuable this valley is to Omanis. Ooredoo had a strong presence in this area during Q2-Q3 2021, particularly through the central throughways, downtown core and central Al Wadi Al Kabir Industrial Estate. Omantel had strong signal strengths along most of Bait Al Falaj St. as well as south of this map.
It comes as no surprise then that Ooredoo showed very strong 4G LTE signal strength near the central and southwest areas of this map during Q2-Q3 2021, as well as a few pockets of strong RSRP throughout. Interestingly, there were a few weaker areas between Ruwi St. and 41 Way near the center of the map. Omantel had strong signal strength near the north of this map, the southern half and central core, though there were a few areas of weaker signal strength (green and blue) in the west and center.
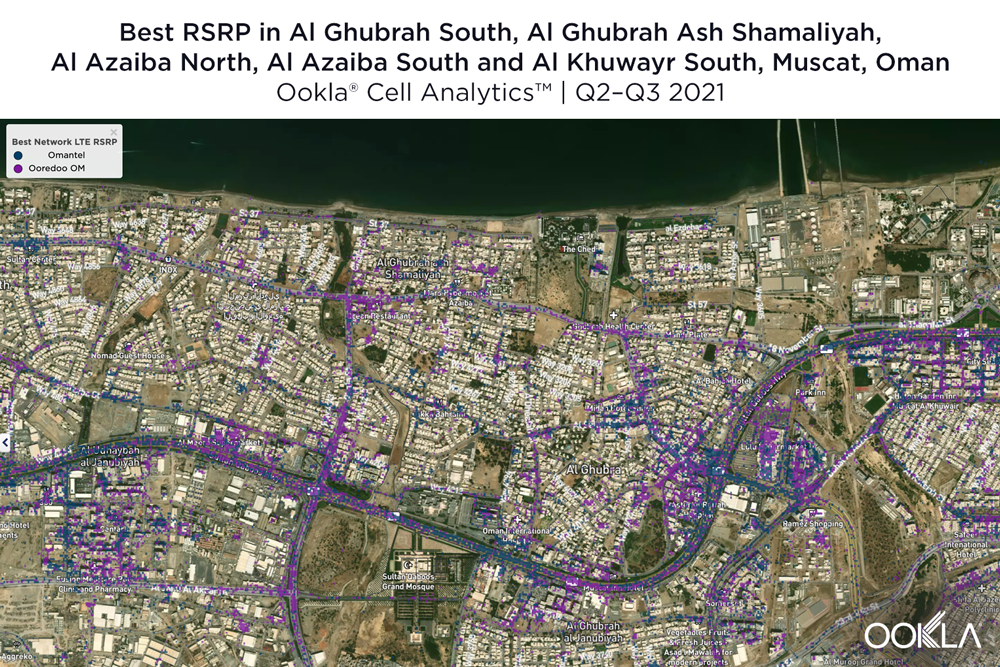
Al Ghubrah South, Al Ghubrah Ash Shamaliyah, Al Azaiba North, Al Azaiba South and Al Khuwayr South
Home to the busy downtown Muscat area as well as the Sultan Qaboos Grand Mosque, national Omani soccer stadium and beautiful beaches, this central Muscat area contains major local and international points of interest. The map below shows the provider with the strongest RSRP signal strength for a given area during Q2-Q3 2021. We saw a seemingly even competition between Ooredoo and Omantel, with each provider showing stronger RSRP signal strength in bands near the major highway and major sightseeing activities.
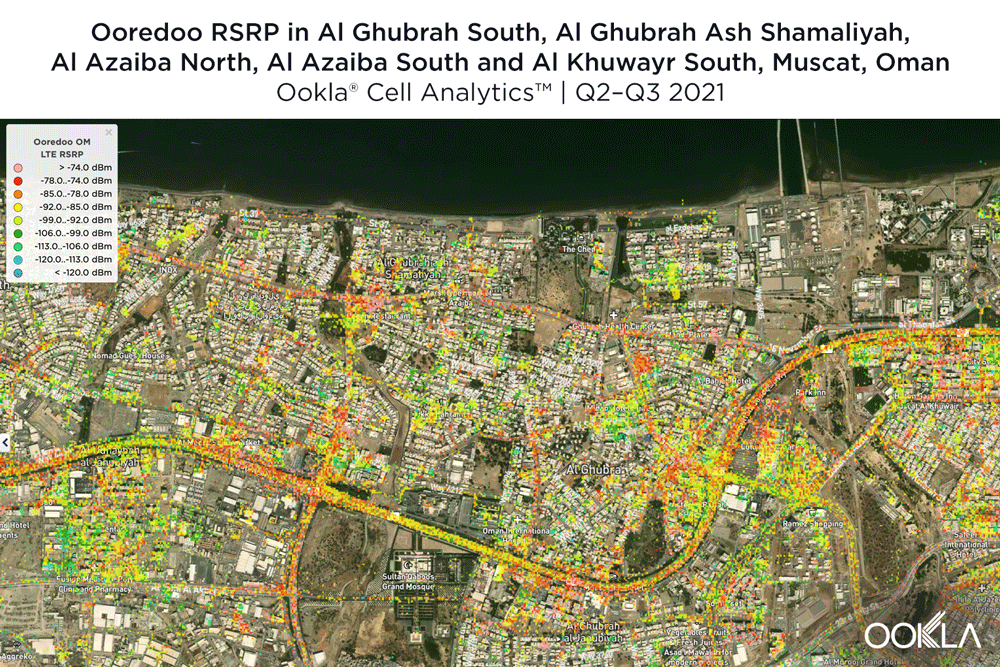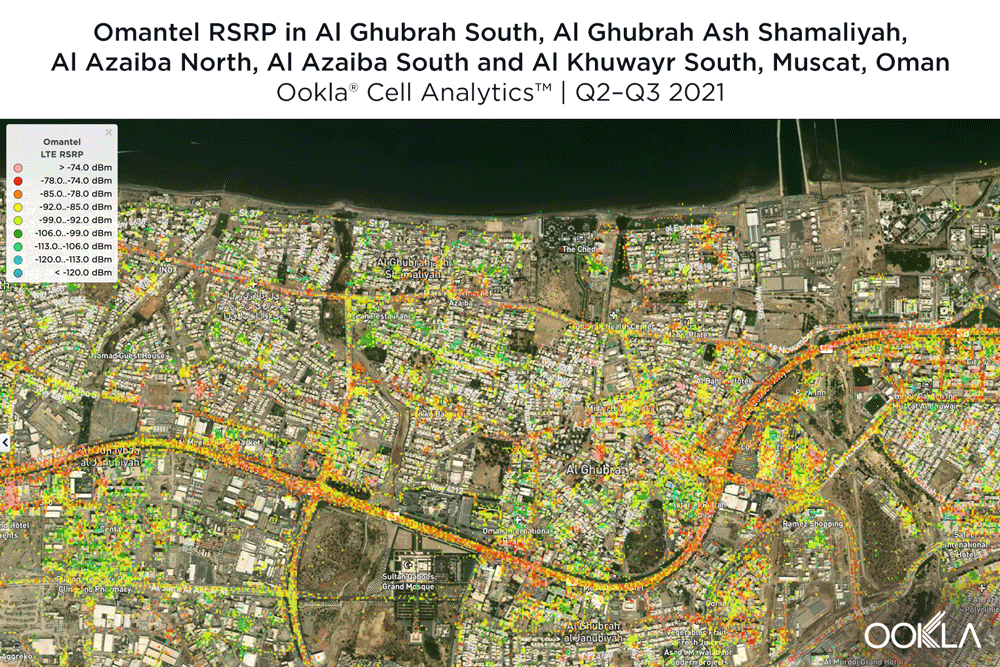
However, when we look at each individual mobile operators’ 4G LTE RSRP, we see the area on Sultan Qaboos St. that includes Oman Avenues Mall, LuLu Hypermarket-Bousher, Muscat Grand Mall, Sharaf DG Muscat Mall and IKEA Muscat was fiercely competitive. Ooredoo had strong signal strength near the north of this area while Omantel had strong signal strength near in the middle of this area, fading slightly within the shopping mall areas. Omantel also had strong signal strength along most of Qaboos St. and lower signal strength within many of the neighborhoods beyond that core roadway. In that last respect, Ooredoo seemed to be doing a little better with more red showing in some of the neighborhood areas where Omantel fell short.
Oman’s future mobile experience is faster, competitive 5G
Like many of its peers in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC), Oman has set in place a strategic vision for its economic development as it looks to diversify its economy away from a reliance on oil. Its e.Oman 2030 strategy highlights the realization of a high-speed, high density network infrastructure as a key enabling factor in achieving its goals of increased digital literacy and skills, the development and adoption of e-government services, and the digital transformation of Omani industries.
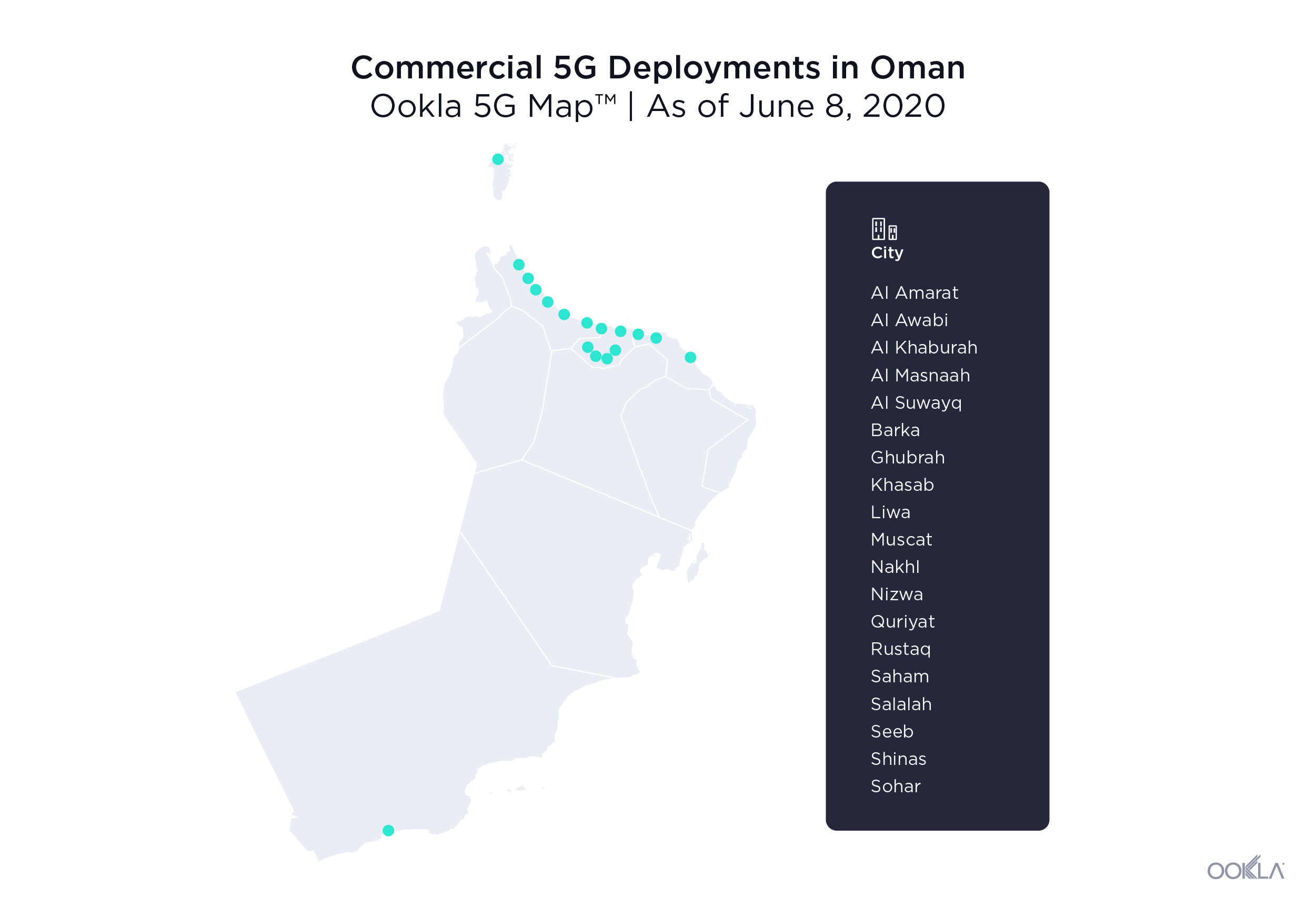
In October 2019, Oman’s Telecommunications Regulatory Authority (TRA) outlined its 5G roadmap in support of this objective. The regulator has granted Omantel and Ooredoo rights to a 100 MHz block of spectrum each in the C-band for 5G services, while reserving an additional 100 MHz block for a new entrant. The regulator also waived annual frequency fees for a year to encourage investment, while the operators undertook deploying 4,400 5G base stations over the following five years. According to the RTA, a total of 1,300 5G sites had been deployed in the market as of June 2021, equating to 5G coverage of 40% of the population. With 5G Availability in the market below 10%, it’s clear that operators need to do more to encourage 5G adoption.
Oman Future Telecommunications (OFT), operating under the Vodafone Oman brand, plans to launch commercial services in late 2021. OFT signed a strategic partnership with Vodafone in 2019 and was granted a license in 2021 to become Oman’s third network operator. OFT recently signed a managed services agreement with Ericsson to build and operate a greenfield 4G and 5G core and radio access network and already has agreements in place with Oman Tower Company and Oman Broadband to accelerate its network build. Increased competition in the market, particularly when 5G adoption is still in its early stages, will bring renewed focus on network speed as a differentiator. This is backed up by Vodafone Oman’s aggressive network rollout with Ericsson. Vodafone‘s experience in India — where the early 4G era and entrance of Reliance Jio saw price wars that led to both network operator consolidation and the amassing of large debt burdens by operators in the market — is likely to dissuade Vodafone from pursuing an aggressive pricing strategy in Oman.
Internet speeds in Oman are blazing forward and we’ll be watching closely to see how they change. Click here to learn more about Speedtest Intelligence and Cell Analytics.
Ookla retains ownership of this article including all of the intellectual property rights, data, content graphs and analysis. This article may not be quoted, reproduced, distributed or published for any commercial purpose without prior consent. Members of the press and others using the findings in this article for non-commercial purposes are welcome to publicly share and link to report information with attribution to Ookla.