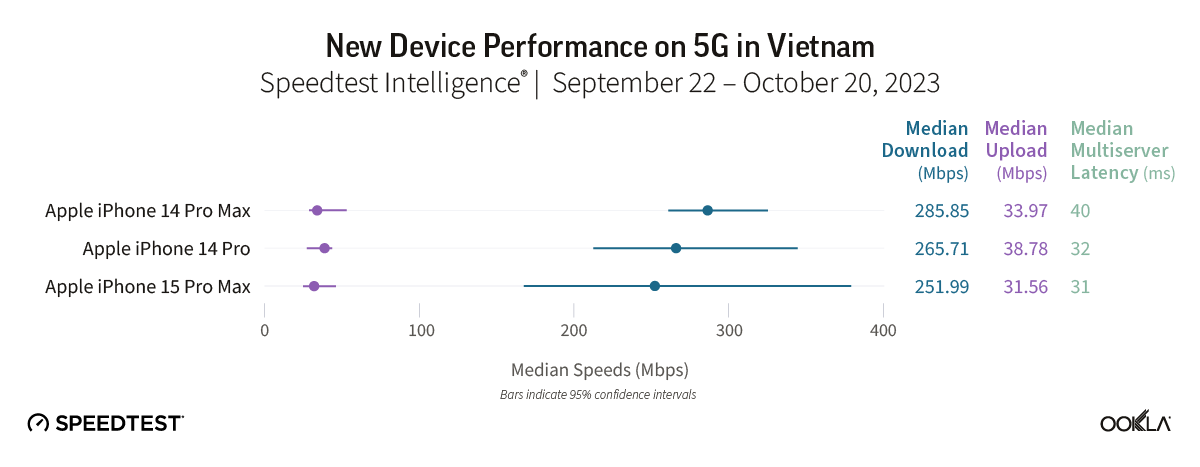
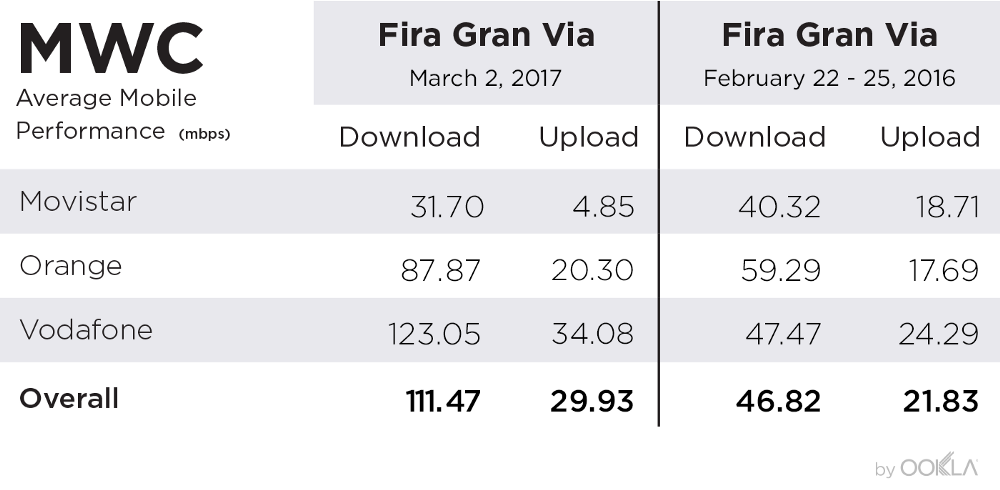
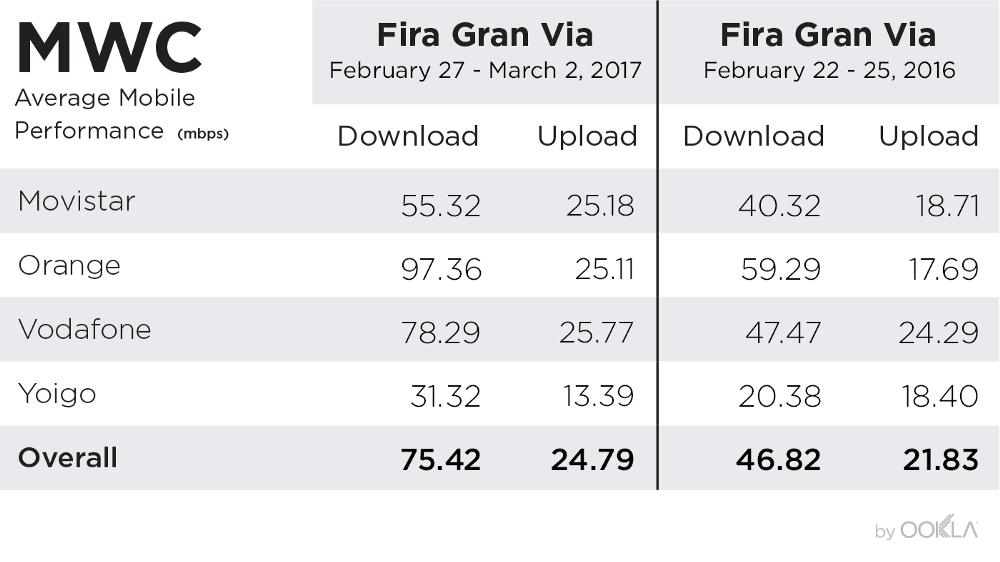
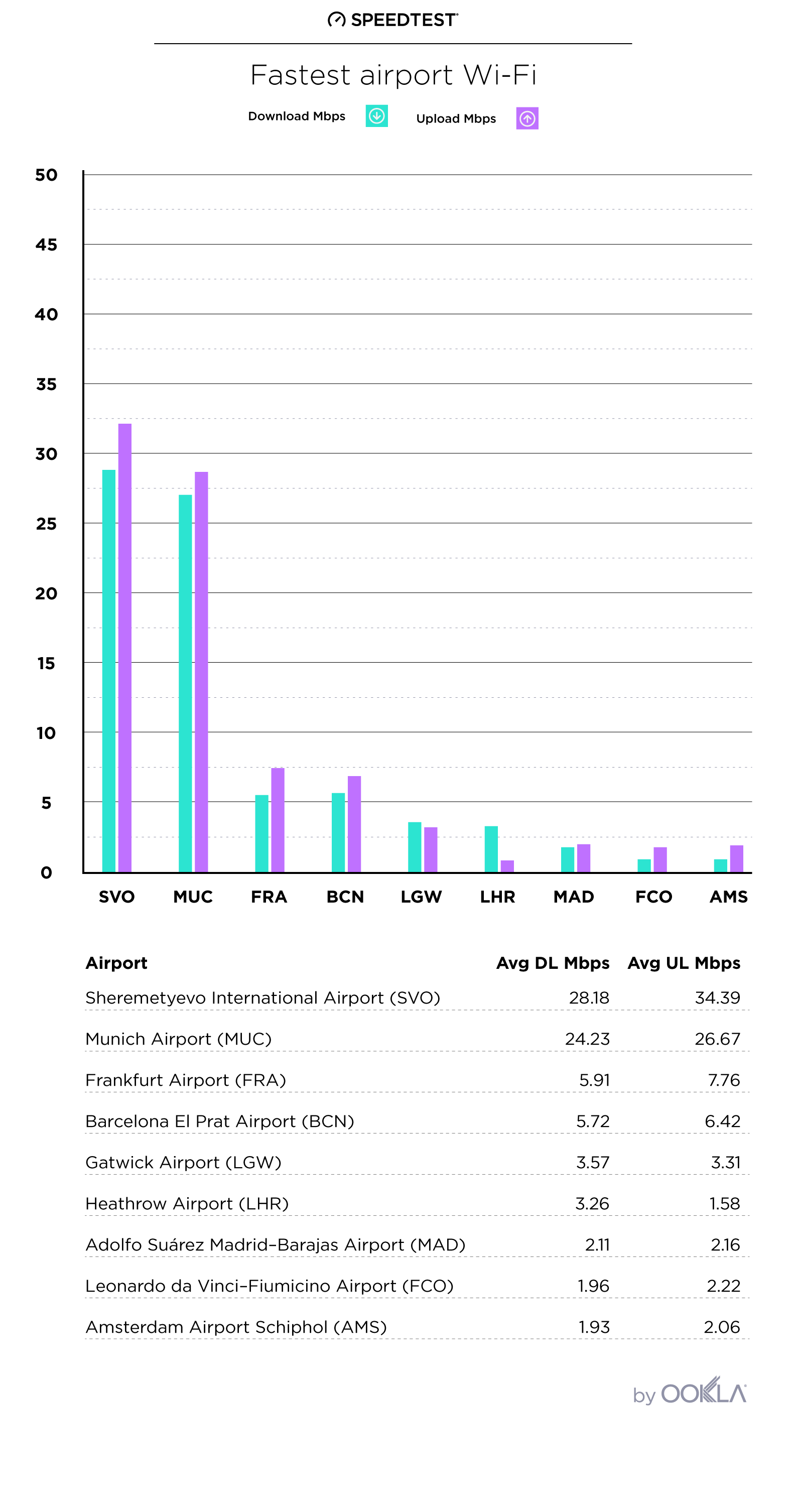
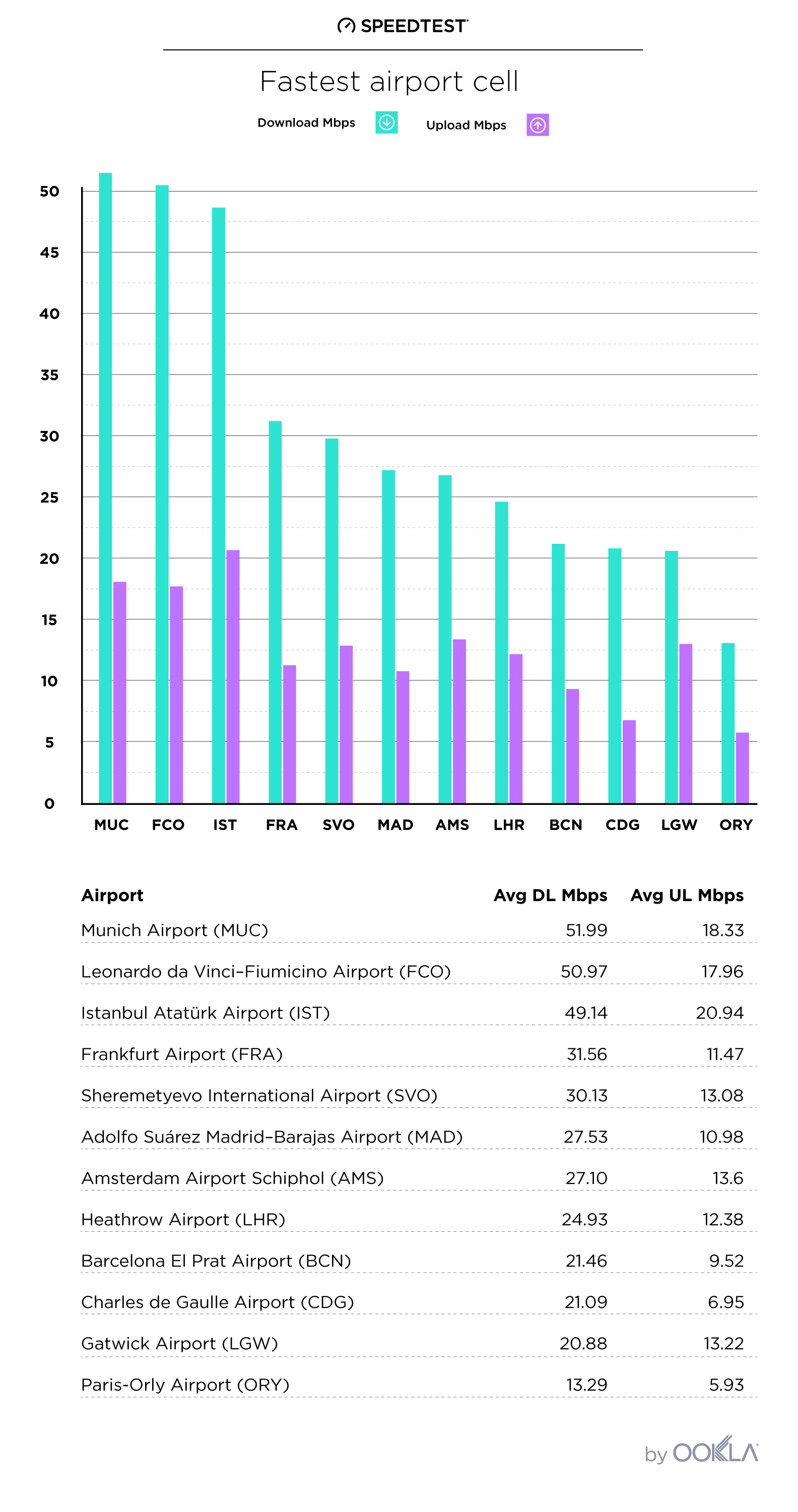
The European Commission has set forth an ambitious goal of achieving a Digital Decade 2030 strategy, also known as the Digital Compass. The aim is to expedite the digital transformation of Member States by 2030. One of the primary objectives of this strategy is to improve digital connectivity, which will be measured through specific targets such as 100 Mbps services by 2025 and gigabit coverage to all EU households by 2030. In this article, we will discuss the progress made so far, the disparities in user experience, and the challenges that need to be addressed to achieve Europe’s connectivity goals.
Key messages
- Digital Decade Ambition: The ambitious goals of the EU’s Digital Decade strategy are indeed lofty. Broadband services might promise speeds in excess of 1 Gbps, but the reality is that users rarely experience that level of speed. However, while the gap between advertised speeds and actual speeds for gigabit services is wide, speeds approaching 100 Mbps are far more common.
- Median Download Speeds and Infrastructure Development: Several European countries are making substantial progress in offering high-speed broadband. Denmark, Spain, France, and Romania have notably fast median download speeds, primarily due to their fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) infrastructure investments. The type of broadband technology used in those countries (and others) significantly influences the gap between download and upload speeds, with fiber-based networks showing more balanced speeds.
- AltNets Drive Fiber Adoption: Alternative network providers (AltNets) play a vital role in accelerating fiber adoption and addressing challenges mainstream ISPs face. Their role varies across countries and regions.
- Take-up rates remain a challenge: With the completion of fiber rollout in several countries, the focus has now shifted towards promoting fiber subscriptions. However, there are challenges that persist, such as consumer reluctance and the need for incentives. A survey conducted in rural France revealed that 42% of the respondents found their current internet sufficient, while 37% said that they would be encouraged to upgrade if offered incentives.
You can also register for our November 8 webinar, where a panel of industry experts will discuss how Europe can accelerate the expansion of gigabit-capable infrastructure. Register now.
On the road to 100 Mbps
The European Commission aims to ensure that all European households, businesses, and public institutions should have access to “high internet speeds” of at least 100 Mbps by year-end 2025. The EU is showing progress in terms of achieving that target. According to Broadband Coverage in Europe 2022, 86.6% of EU households were within 100 Mbps + coverage, meaning they had access to broadband services capable of providing at least 100 Mbps download speeds.
While having networks available does not automatically equate to real penetration or adoption rates, it is an important prerequisite. Physical accessibility to network services is a vital first step before actual usage, which is influenced by factors such as affordability, awareness, and the perceived need for the service.
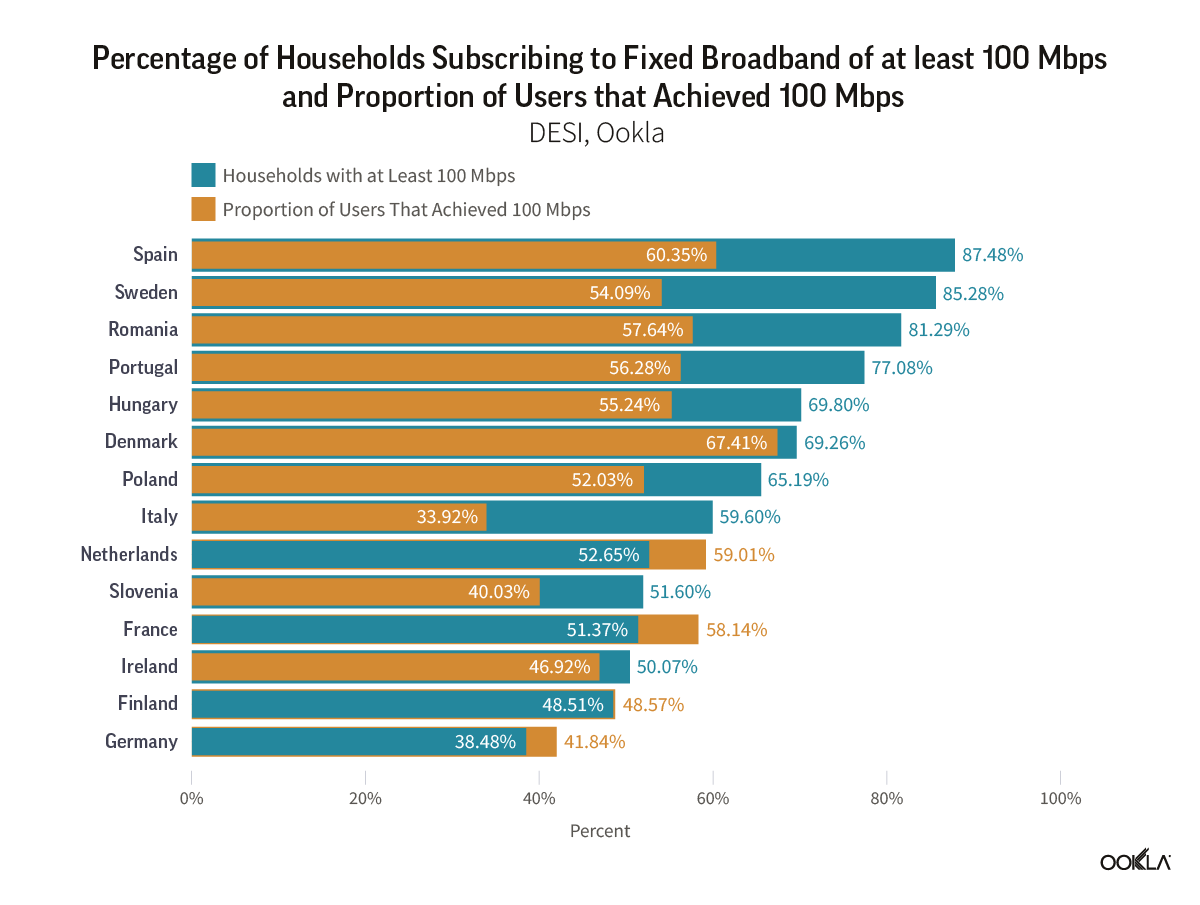
According to the Digital Economy and Society Index DESI 2023 dashboard for the Digital Decade, 55.08% of EU households had already subscribed to fixed broadband services with internet speeds of at least 100 Mbps. While this rate of subscribers is significant and an indicator of the EC’s ongoing progress, the region is still far from achieving its goal of universal, 100 Mbps coverage by 2025. Some countries like Spain, Sweden, and Romania, where over 80% of households subscribe to broadband exceeding 100 Mbps, have already made significant progress in terms of fiber coverage.
However, in those countries, there is a significant gap between what households subscribe to and what we see from Ookla® data in terms of users actually experiencing speeds above 100 Mbps. Netherlands, France, and Germany are the outliers where we see more users having “high internet speeds” compared to the speeds advertised in their broadband subscription package. This is particularly interesting because Germany still heavily relies on VDSL for high-speed access technologies. Still, there is a significant amount of work to be done before countries can deliver on their strategies to achieve the 100 Mbps target.
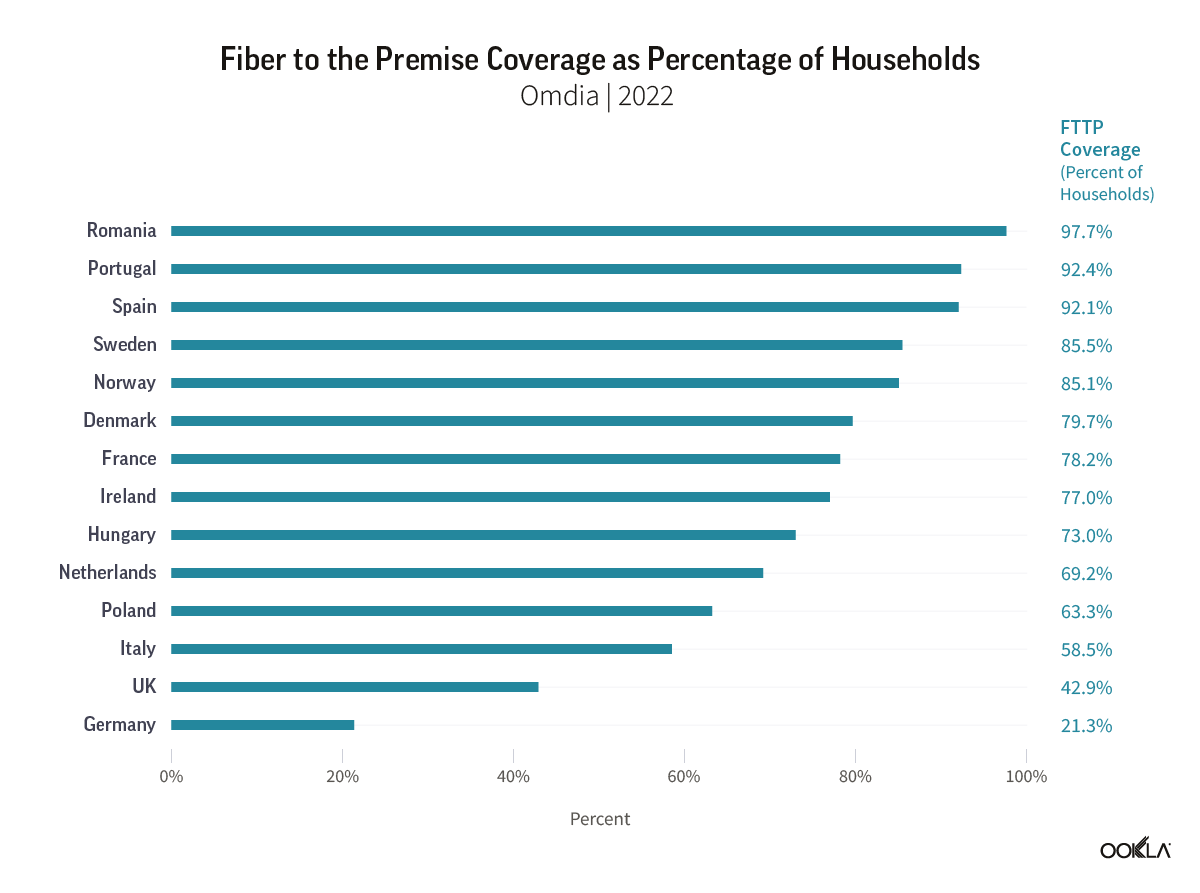
The EC’s goal of gigabit connectivity is certainly one of the driving forces behind the rollout of fiber networks in the region. So far, progress is mixed across the region in terms of fiber network rollouts and adoption. As we have discussed, regulatory incentives propel the move to fiber. For example, Romania has one of the highest Fiber to the Home/ Building (FTTP/B) penetration rates across the region — nearly 97.7% of households — which is partially driven by government-backed fixed infrastructure projects such as RoNet, and the special attention given to rural and disadvantaged areas. Portugal, which already scored high on fiber coverage, plans to launch an international public tender by the end of 2023 for a project to cover all underserved areas with fiber-optic networks to boost fiber penetration further.
The reality of gigabit speeds
The European Commission’s Digital Decade 2030 strategy seeks to extend gigabit (1 Gbps) connectivity to every European Union household by 2030. To track the progress of these objectives, the DESI plays a crucial role in tracking EC’s progress. Only 56% of households in the EU have access to the necessary fiber networks for gigabit connectivity, and the take-up rate (proportion of households that subscribe to fiber) is even lower. According to the DESI 2023 dashboard for the Digital Decade, 13.76% of households in the European Union have subscribed to fixed broadband with at least 1 Gbps as of 2022. Nevertheless, there is a significant disparity in these percentages across different EU nations. For instance, only five countries surpassed the EU value – France leading with 39.94%, Hungary second at 29.81%, followed by Romania at 23.35%, Denmark at 18.66%, and Spain at 14.57%.
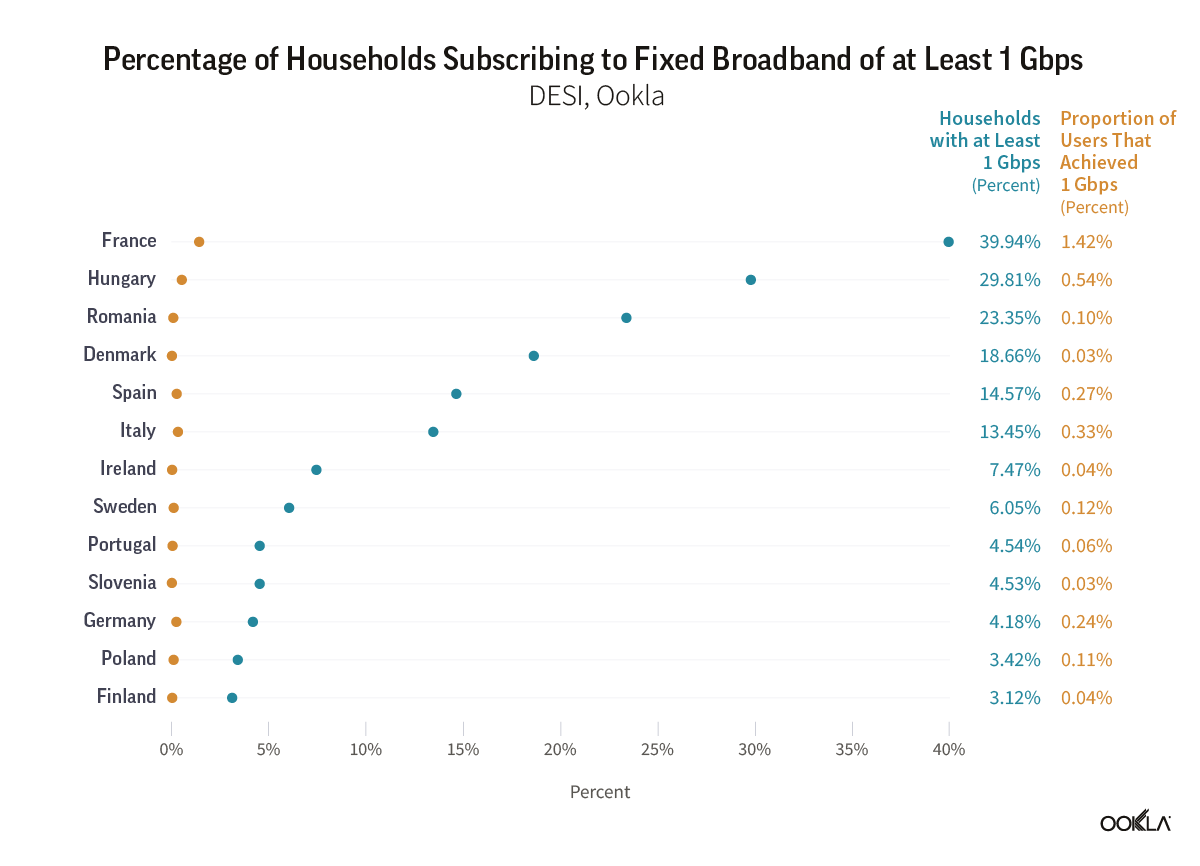
Looking at this data one might believe that many European households have access to Gigabit internet speeds. However, the reality is different as not all of them genuinely experience such high speeds. In fact, the proportion of Speedtest® users registering median download speeds of at least 1 Gbps in many countries is quite low. For example, France only had 1.42%, Hungary at 0.54%, Romania at 0.1%, Denmark at 0.03%, and Spain at 0.27%.
The significant gap between expectations and reality underscores the importance of not only rolling out gigabit-capable networks but also stimulating demand for those services. Service providers also need to pay attention to home networking equipment. Our research has shown that in markets where legacy broadband technology (such as DSL or coax cable) is being replaced by advanced cable and fiber connections, Wi-Fi performance can lag behind ethernet. Wi-Fi speeds typically range from 30-40% of ethernet, indicating a need to accelerate the adoption of more advanced Wi-Fi technologies and optimize the home network environment.
Median download and upload disparities
Median speeds are a standard metric for measuring performance, but there’s more to the story for the end-user experience. Access technology, be it DSL, cable, or fiber, as well as customer premises equipment and end-user devices, significantly influence the user experience. In our recent article, we highlighted how the persistent use of legacy and underperforming Wi-Fi standards in home networks can hamper efforts to provide the best network experience to customers despite progress in terms of fiber rollout and adoption.
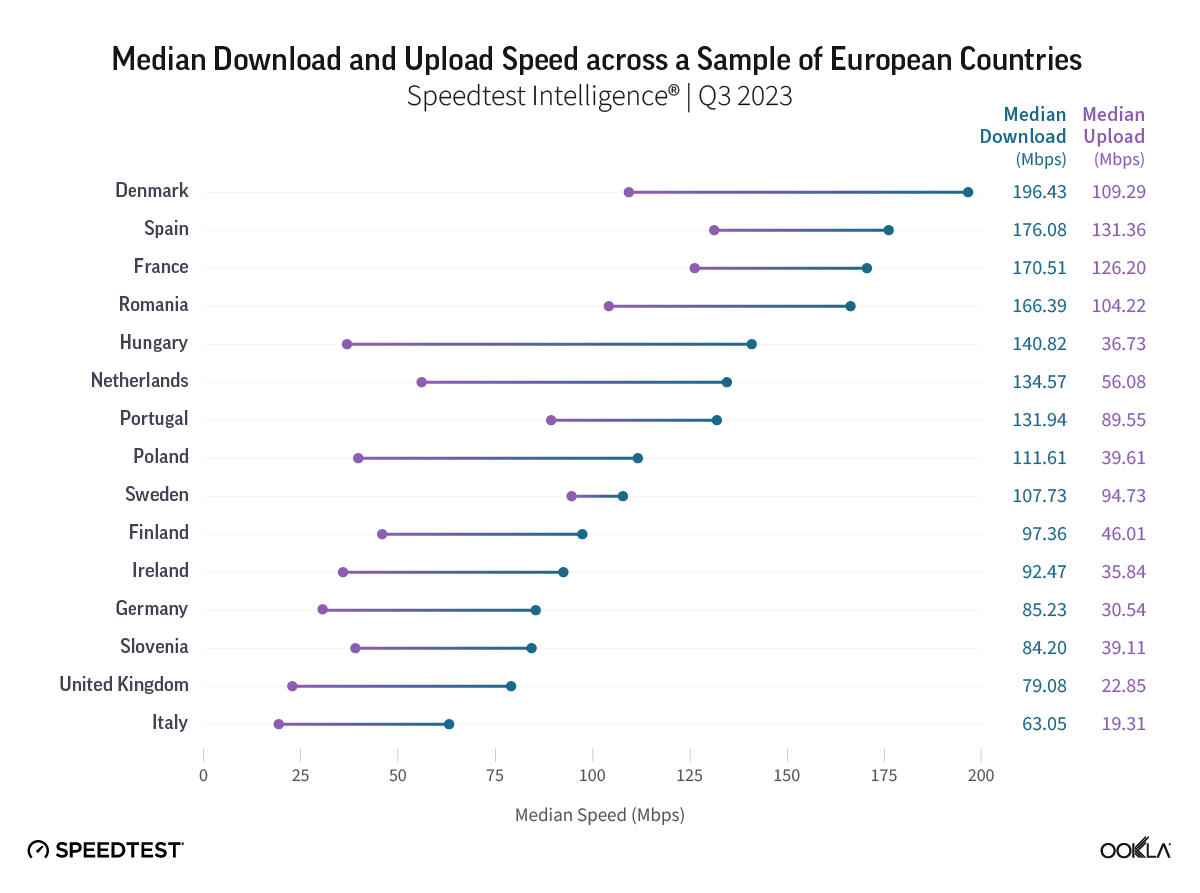
According to Speedtest Intelligence® in Q3 2023, across Europe, Denmark had the fastest median download speed for fixed broadband (196.43 Mbps), followed by Spain (176.08 Mbps), France (170.51 Mbps), and Romania (166.39 Mbps). Notably, several of those countries have a substantial gap between median download and upload speeds. The type of broadband technology implemented can heavily influence the divergence between download and upload performance. Nations still reliant on DSL and cable often exhibit lower median upload speeds and a wider gap between upload and download speeds. On one hand, the UK and Germany lag behind other countries in broadband infrastructure upgrades due to their reliance on copper-based technologies and cable networks and are at the tail end of the ranking.
On the other hand, Sweden, with a 63% Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH) penetration rate in 2022, has the narrowest gap between download and upload speeds. Forward-thinking broadband infrastructure and significant municipal involvement have positioned Sweden to reach the EC’s goals in the coming years. France, Spain, Denmark, Romania, and Portugal are also making significant progress toward achieving full-fiber coverage, with France expecting a full-fiber rollout by 2025. As fiber broadband adoption increases, the gap between download and upload speeds will narrow, mainly because fiber subscriptions are typically offered with symmetrical speeds, where users would experience the same level of speed for both download and upload usage.
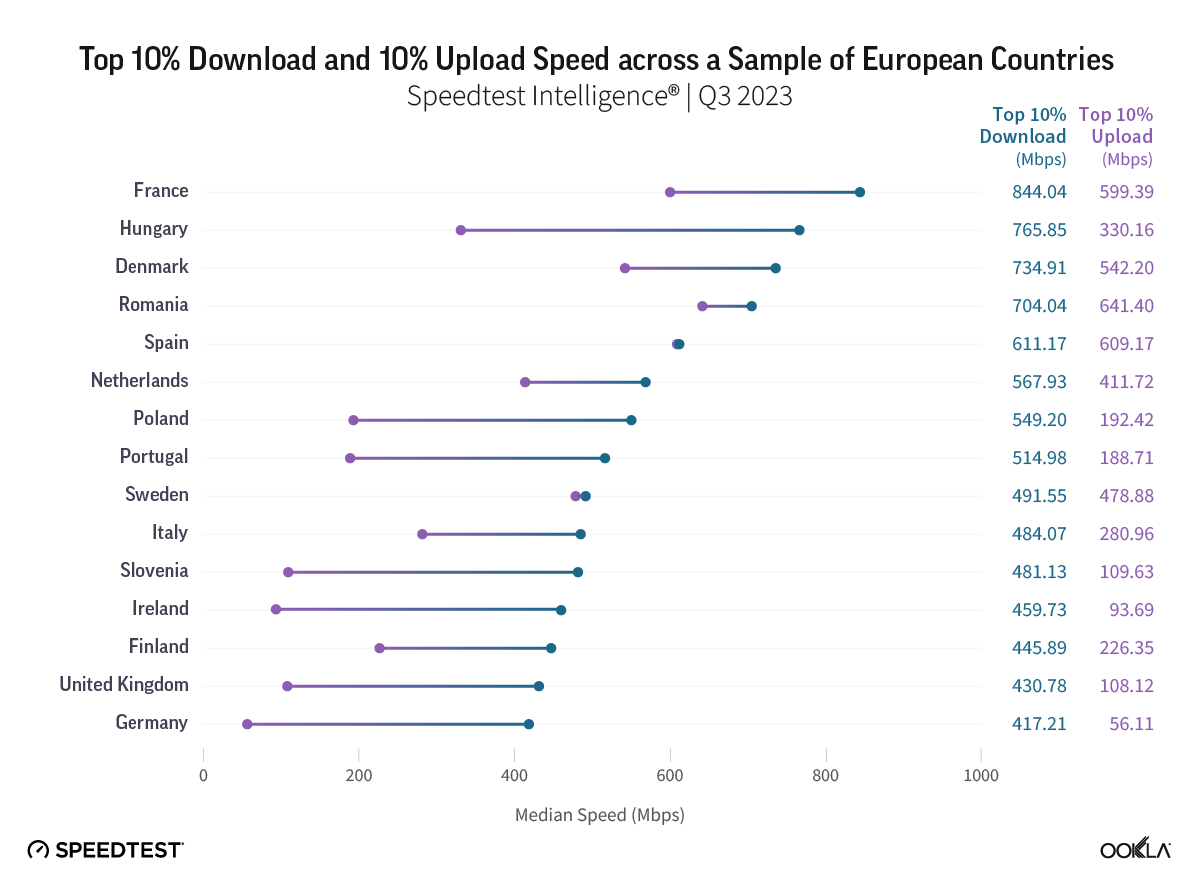
However, even when we look at “the best-connected” Speedtest users (those seeing speeds in the top 10th percentile of our results), there’s a wide range of performance. Download speeds ranged between 417.23 Mbps and 844.04 Mbps, while the range for upload speeds was even wider, with median upload speeds ranging from 57.11 Mbps to 599.39 Mbps.
When looking at speeds at the 10th percentile, only four countries topped 700 Mbps. France led with a top speed of 844.08 Mbps, followed by Hungary at 765.85 Mbps, Denmark at 734.91 Mbps, and Romania at 704.04 Mbps. Notably, three of these countries (Romania, France, and Denmark) also lead in the top 10% of upload speeds, with all three exceeding 500 Mbps.
While for most countries included in this analysis, top speeds are at least a few hundred Mbps apart, there are a few exceptions. Spain shined bright, with the top 10% of its download and upload speeds closely matched at 611.17 Mbps and 609.17 Mbps, respectively.
Beyond median speeds
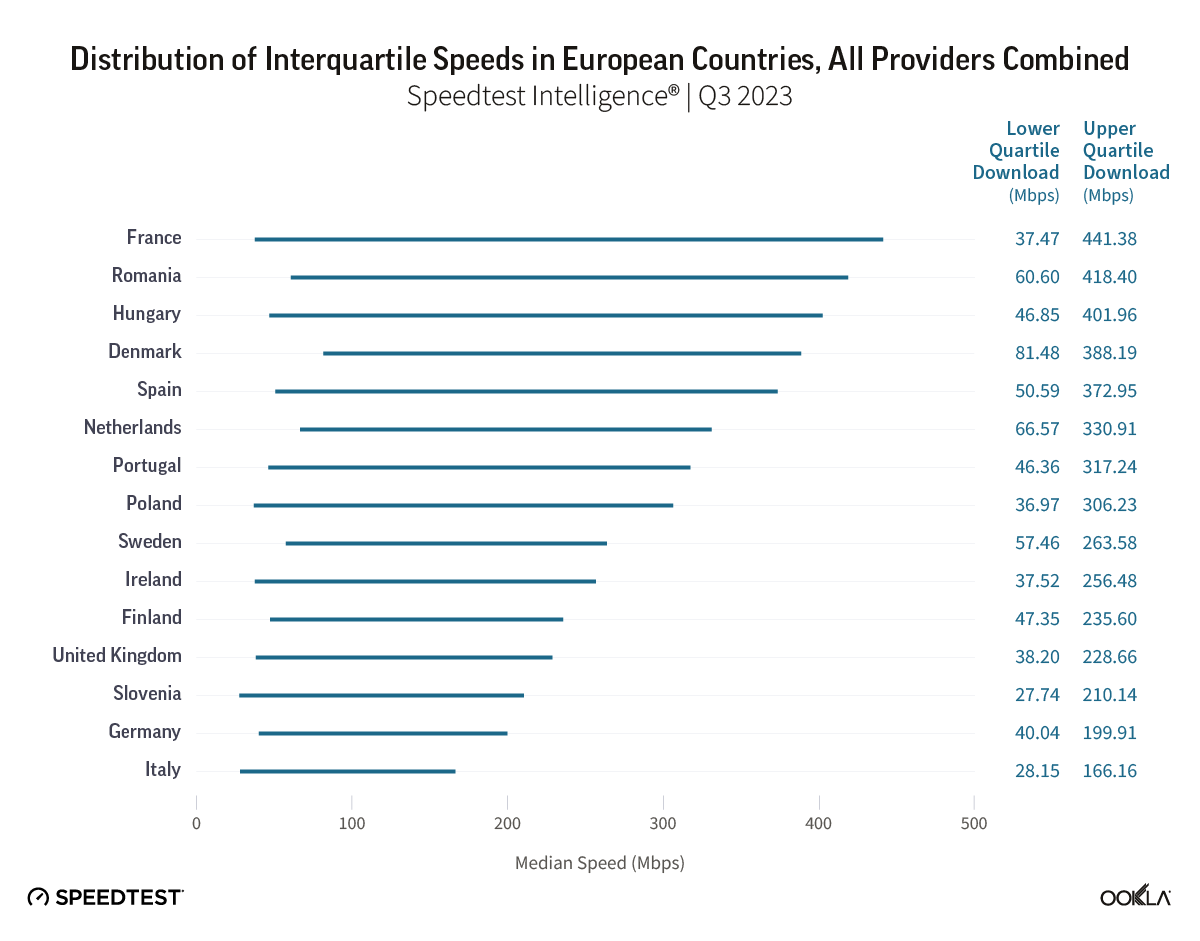
To delve deeper into the performance and reliability of internet services across different countries, it can be helpful to look at the expected speed range, i.e., the range of speeds that the majority of users experience. This middle 50% of speeds are captured by the interquartile range, with the lower value of the range, or lower quartile, indicating the bottom 25% of speeds and the upper value of the range, or upper quartile, indicating the top 25% of speeds. Examining Speedtest Intelligence data from Q3 2023, the lower quartile download speed across European countries ranged from 28.15 Mbps to 81.48 Mbps (in other words,, 25% of downloads were below that speed), while upper quartile speeds clocked in between 166.16 Mbps and 441.38 Mbps (i.e., 25% of downloads were above this speed).
Role of AltNets
According to the FTTH Council Europe, alternative operators (AltNets) are playing a significant role in the adoption of fiber in the EU39 region. The EU39 region comprises the EU27, the UK, Iceland, Israel, North Macedonia, Norway, Serbia, Switzerland, Turkey, and 4 CIS other countries. In 2021, around 56% of FTTH/B initiatives were led by AltNets, which marks a shift from 2011 when alternative ISPs had a 71% share, and incumbents accounted for only 21% of initiatives.

We looked at data from Omdia to determine whether there is a correlation between the number of active ISPs and the speed of the transition to fiber networks measured by FTTH share of all connections. The relationship is not straightforward and varies significantly depending on each country’s competitive landscape and government initiatives.
Across a number of countries fiber accounts for the majority of subscriptions – Spain comes on top with 81.8%, followed by Romania (81.7%), Sweden (77.5%), and Portugal (62.4%). Spain is a good example of a market that has been migrating to fiber away from copper ahead of the incumbent Telefonica turning off its legacy fixed network in 2024. Furthermore, Spain’s National Commission for Markets and Competition (CNMC) has simplified its ‘MARCo offer’, making it easier for alternative operators to access Telefonica’s infrastructure to launch their own fiber optic services.
It is worth noting that countries like the UK and Poland, which have many ISPs, are also leading the way in AltNet-driven fiber initiatives. In our previous article looking at the impact of AltNets in the UK, we concluded that AltNets played an important role. In fact, AltNets provided the top speeds in London, Glasgow, Liverpool, and Manchester, as well as across a number of counties. Public funding has helped facilitate the emergence of fiber ISPs in rural areas where fiber deployment is not commercially viable. Other AltNets like Hyperoptic are already well established, deploying and operating an FTTP network in high-density areas, which connects existing and new multi-dwelling buildings.
Take-up rates come with challenges
As fiber rollout nears completion in some countries, the focus shifts to selling fiber subscriptions to households that are within fiber network coverage. Sweden leads with an 80.1% consumer take-up rate (proportion of households that subscribed to and are actively using fiber-optic broadband services), but Spain, Norway, and France also boast high rates above 70%.
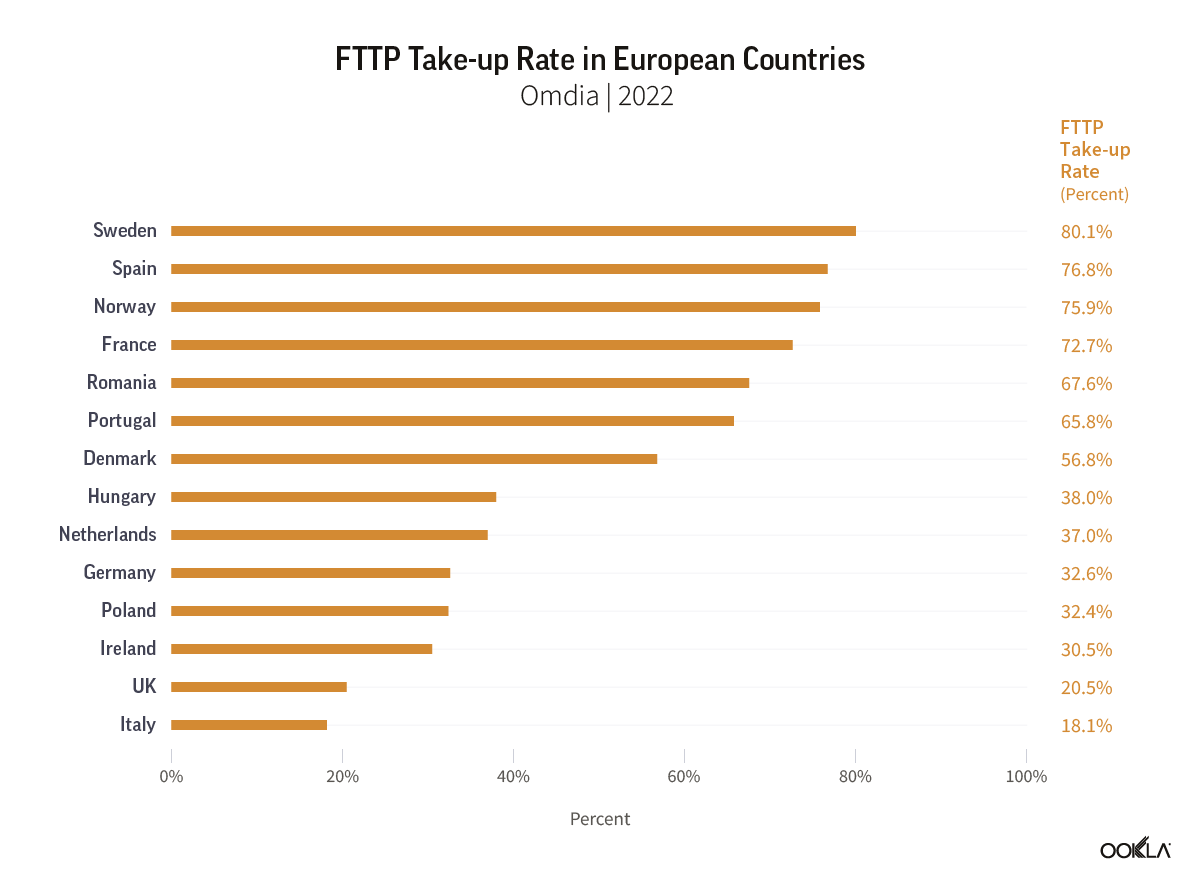
Sweden was the country that pioneered the open access model for fiber networks to drive competition and contributed to the country’s high fiber broadband penetration rates. Fiberhost, a Polish open-access network provider, is a significant beneficiary of EU funds, with 99% of funding for building the country’s fiber network in white spot areas (areas with limited or no access to high-speed internet).
There also has been notable progress in the wholesale networks market in Europe, some of which look to connect remote and rural areas. The Italian wholesale operator, Open Fiber, is partially funded by the country’s National Recovery and Resilience Plan (PNRR), with the goal of connecting the grey areas (where no other operator has plans to develop an NGA network) to gigabit speeds.
However, challenges persist in convincing consumers to switch to full fiber, even in countries with high take-up rates. For instance, a joint venture by Orange conducted a survey in rural areas of France to understand why households with FTTH access hadn’t upgraded to fiber services. The study revealed that 42% found their current internet sufficient, while 37% said incentives would encourage them to upgrade. Incentives and other initiatives are being implemented to migrate customers onto fiber networks in many countries in the region and across the world.
Future Initiatives and Investments
Fiber offers superior internet speeds, lower latency, enhanced security, and environmental sustainability – a noteworthy upgrade from copper networks and also a path forward for some cable operators (instead of DOCSIS 4.0). AltNets are making strides in driving fiber deployment across Europe, pushing toward the EC’s ambitious goals of achieving a gigabit society.
Despite progress, obstacles remain in convincing consumers to fully transition to fiber services. Comprehending consumer behavior, promoting fiber benefits, and inspiring initiatives will all play significant roles in this endeavor. Likewise, continued investments must be made to keep Europe on track to attain its connectivity targets
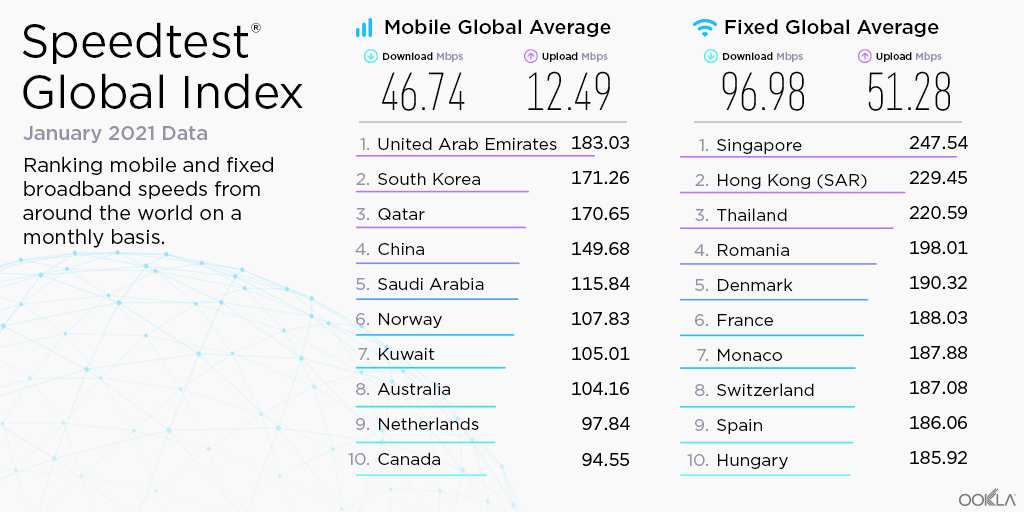
For more insightful updates on Europe’s fiber connectivity status, look forward to the Network X event in October 2023. It’ll offer a live pulse on the latest developments in fiber connectivity. We will continue to follow European countries’ progress toward Gigabit society and monitor its impact on fixed broadband speeds. If you’d like to learn more about internet speeds and speed performance in other markets around the world, visit the Speedtest Global Index™.
You can also register for our upcoming webinar, “Accelerating Europe’s Gigabit Revolution” on Wednesday, November 8 at 9 a.m. CET (GMT+1). A panel of industry experts will come together to discuss how Gigabit Society fits into Europe’s digital transformation strategy and propose strategies to ensure digital access for all. A recording will be provided for registrants who can’t join the live presentation. Register now.