Читати звіт українською мовою | Читать отчет на русском
As Ukraine emerged from the recession of 2016, both regulators and service providers committed to bringing high-speed internet services to more of the population and positioning the country as a seat for innovation. With recent LTE deployments from the mobile operators and fixed broadband providers building out fiber offerings, consumers in Ukraine are experiencing unprecedented access to faster internet — and the market is more competitive than ever. The mobile broadband market is currently dominated by three main competitors — Kyivstar, Vodafone Ukraine (owned by MTS) and lifecell (owned by Turkcell) — and the fixed broadband market is highly saturated, with hundreds of ISPs operating at the national, regional and local level. In this report, Ookla checked in to see how fixed broadband speed, mobile speed and 4G Availability have looked over the last two quarters in Ukraine.
Our analysis includes performance data from 1,805,450 consumer-initiated tests taken with Speedtest® and coverage data from over 623 million coverage scans on 372,690 devices during Q2-Q3 2019. The data in this analysis does not represent Crimea.
To see Ukraine’s fastest fixed broadband providers, fastest mobile providers and which providers offer the best speeds and 4G Availability in some of Ukraine’s largest cities, download the full report.
Mobile and fixed broadband speeds are increasing at the country level
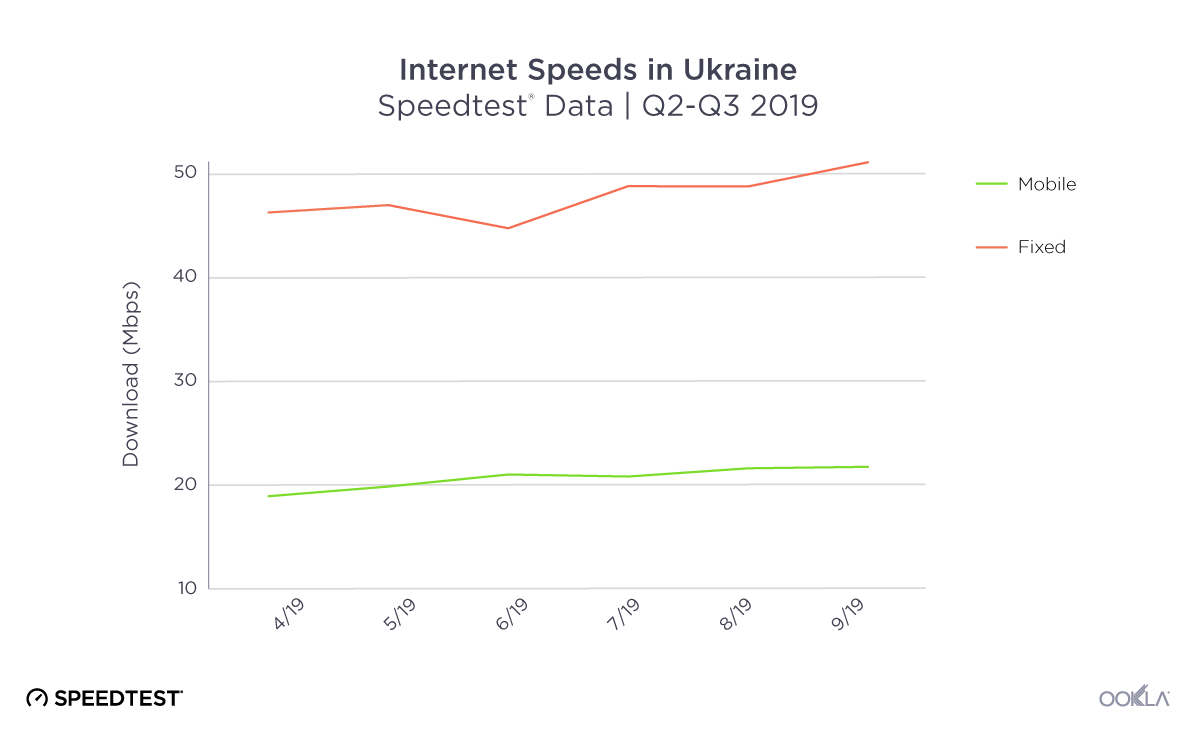
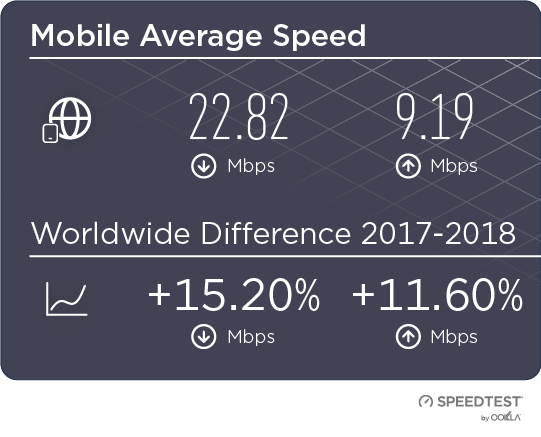
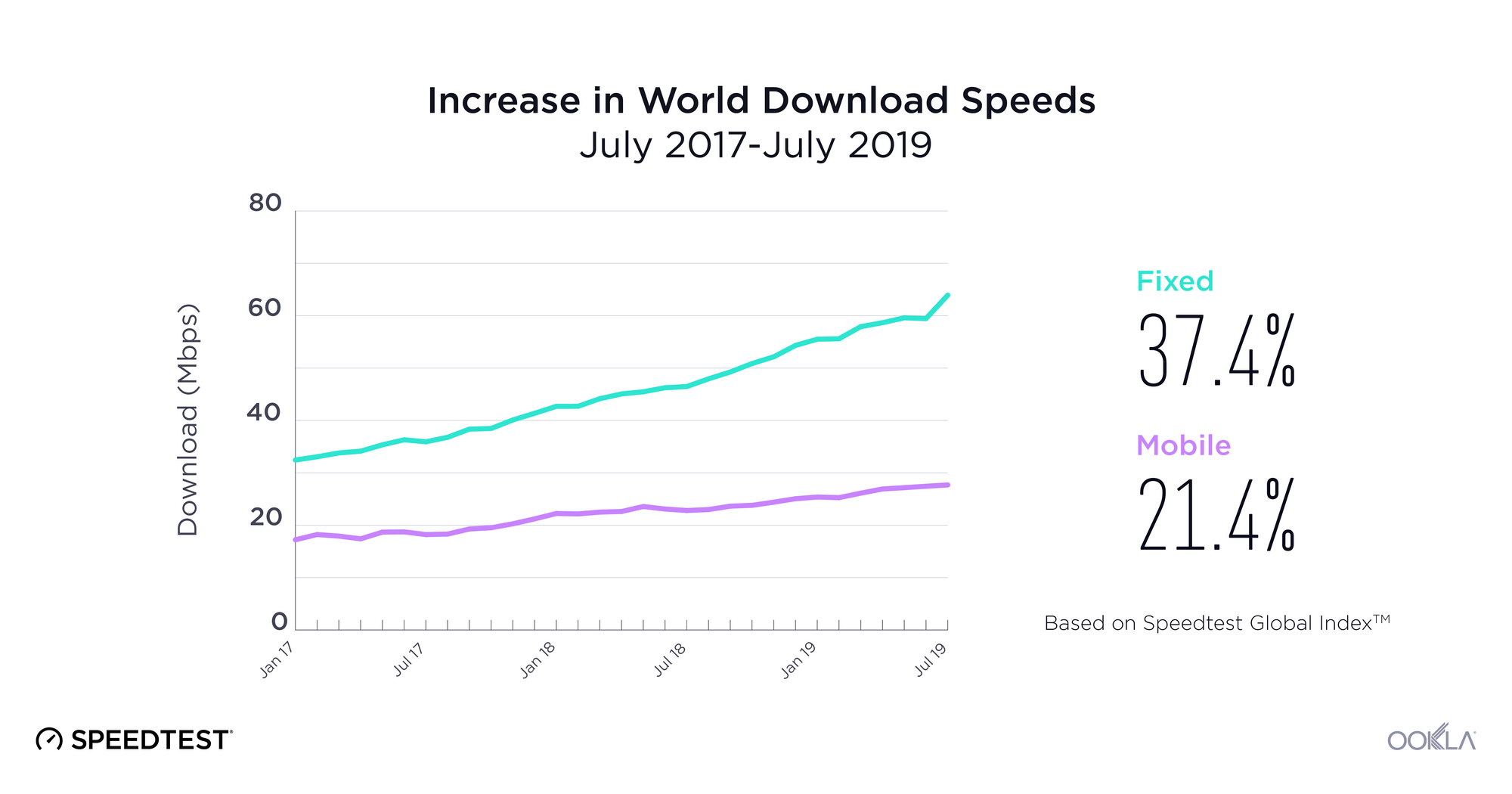
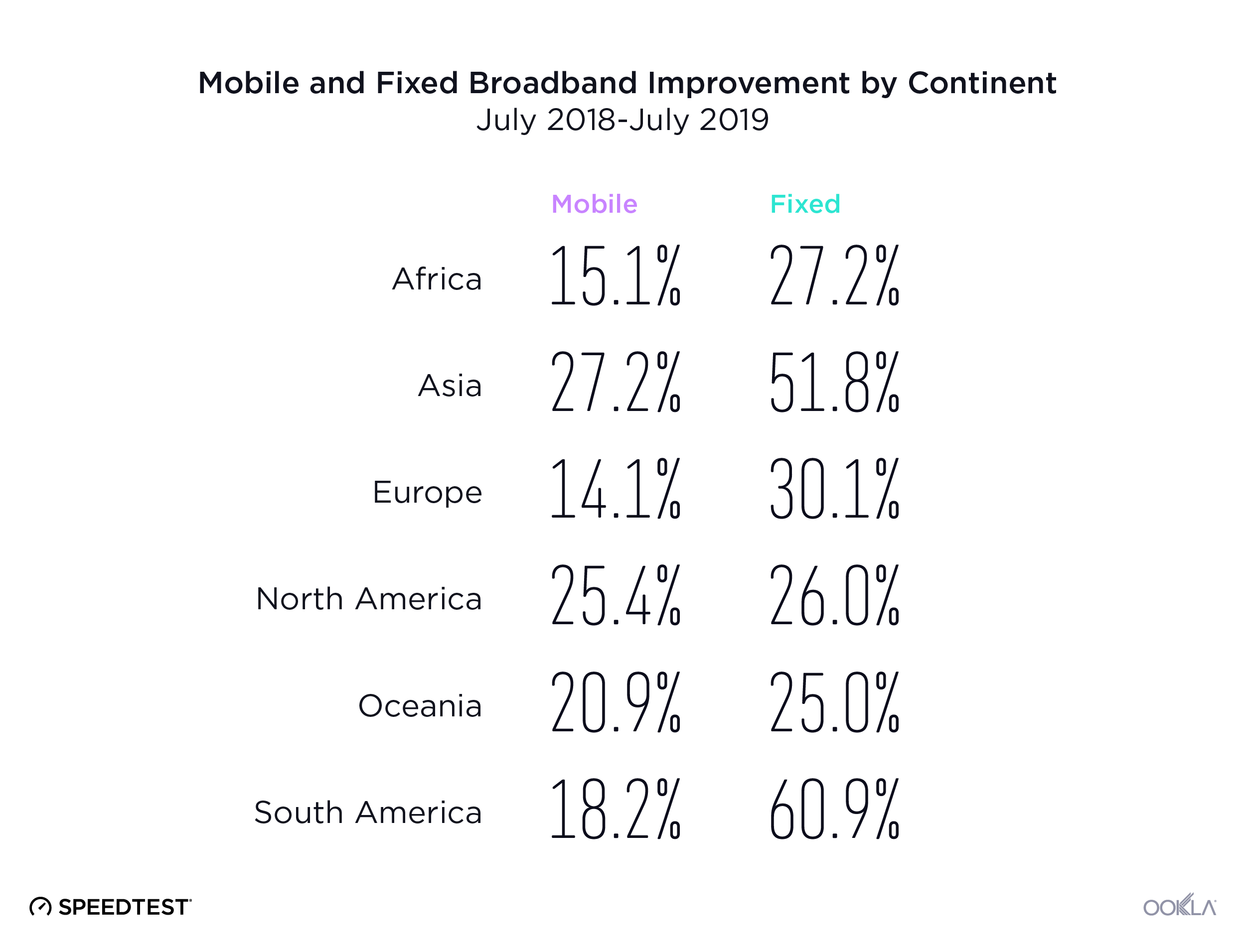
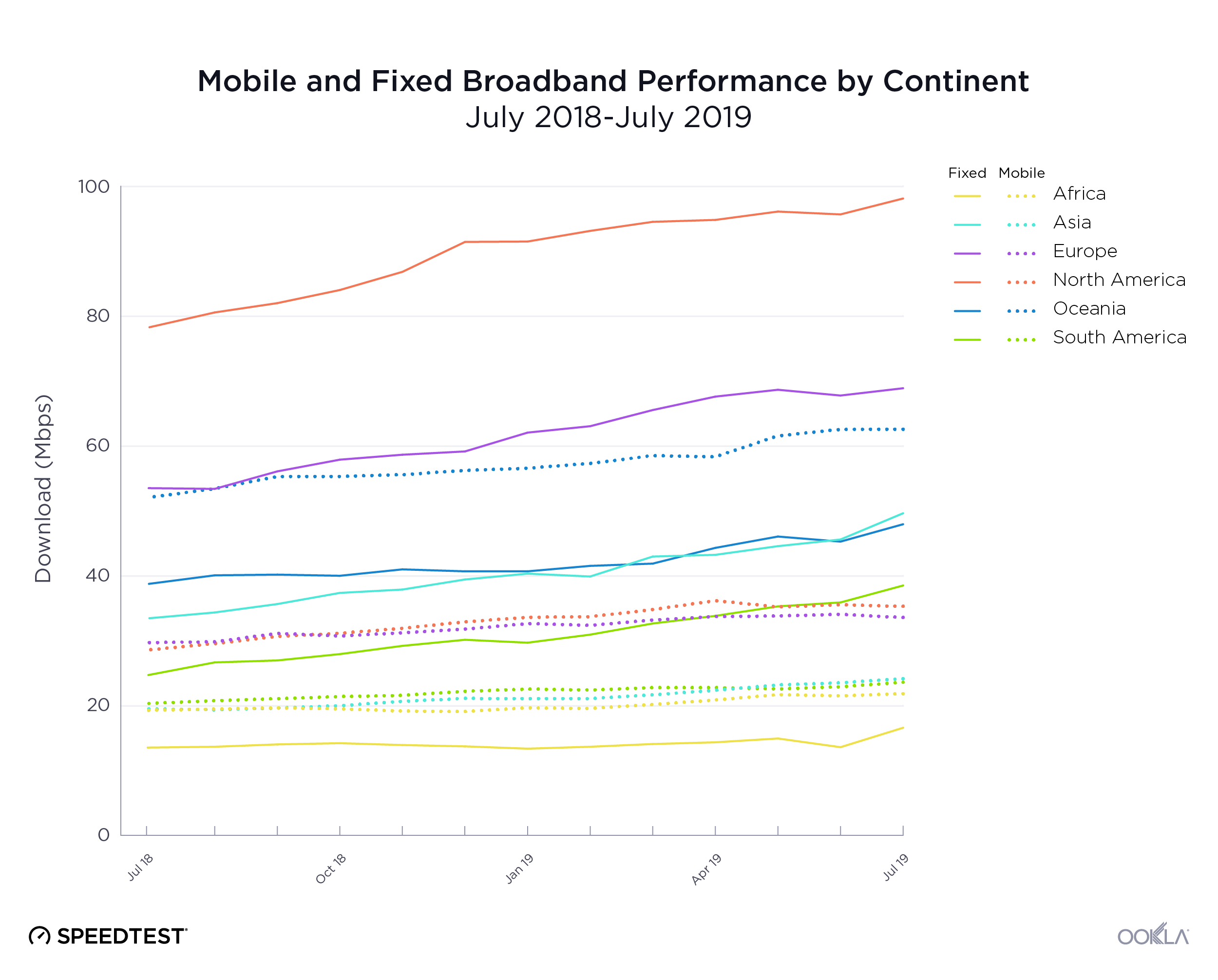
Both mobile and fixed broadband speeds saw incremental improvement at the country level during Q2-Q3 2019 in Ukraine. Average download speeds on fixed broadband increased by 10.4% during that time period to a peak of 49.99 Mbps in September. Mobile speeds were also on the rise, increasing 14.8% to 21.40 Mbps in September. As more of the country gains access to LTE service, we expect to see a continued trend of improvement in average mobile speeds.
New LTE deployments are bringing faster speeds to more of the country
The development of LTE networks has been a key priority for operators in Ukraine over the last year. NCCIR allocated new spectrum and 4G licenses to Kyivstar, lifecell and Vodafone Ukraine at the beginning of 2018 with an agreement that they would provide LTE coverage to at least 90% of the population of each regional center within 12 months, and to 90% of the population of each town with more than 10,000 residents within 42 months.
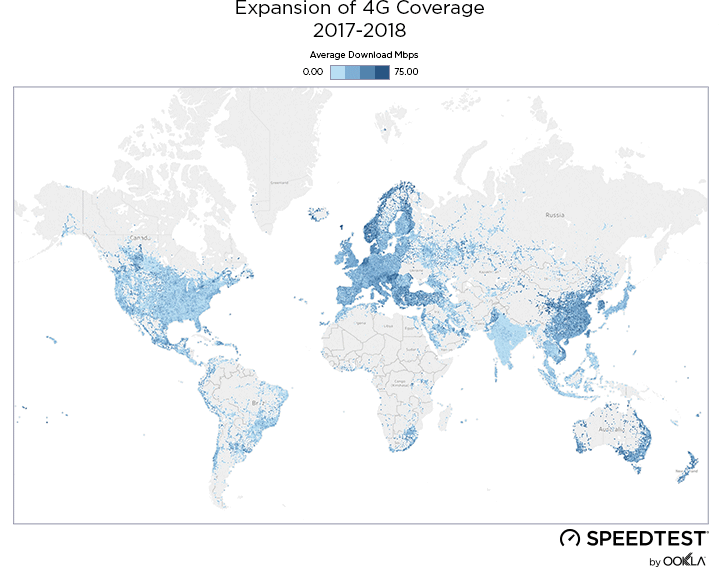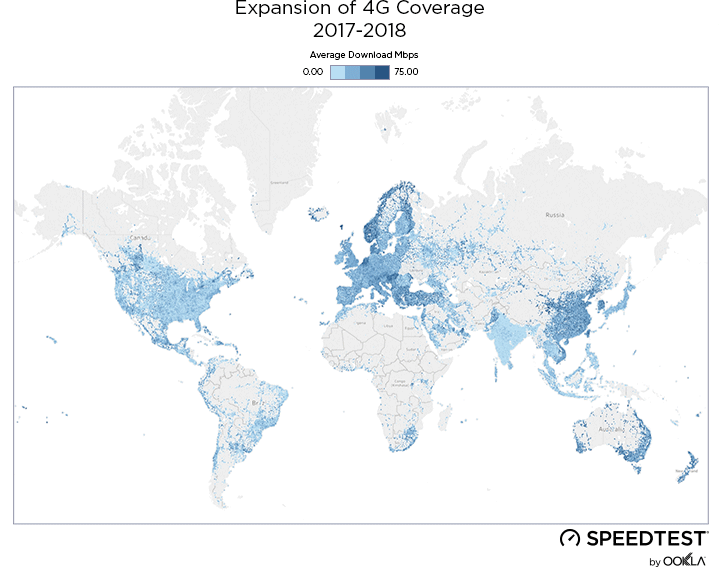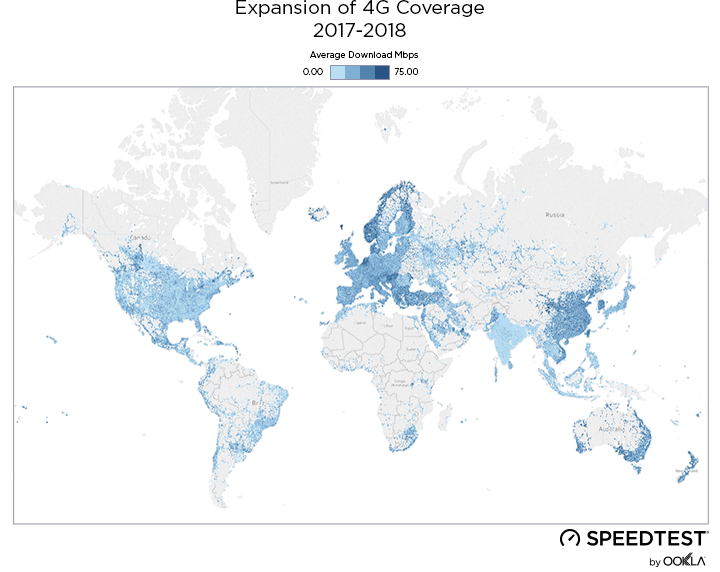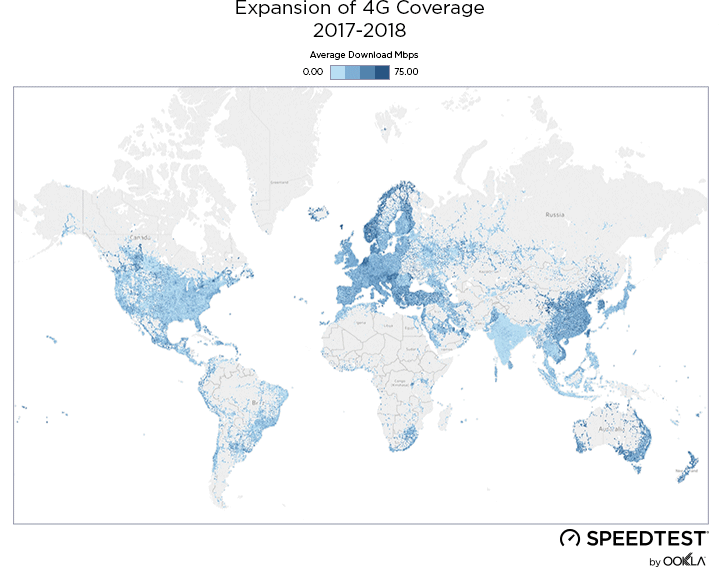
As a result of new 4G deployments, we’ve seen rapid growth in LTE coverage over the last year in Ukraine and Speedtest data reveals the country’s 4G Availability was 34.8% during Q2-Q3 2019.
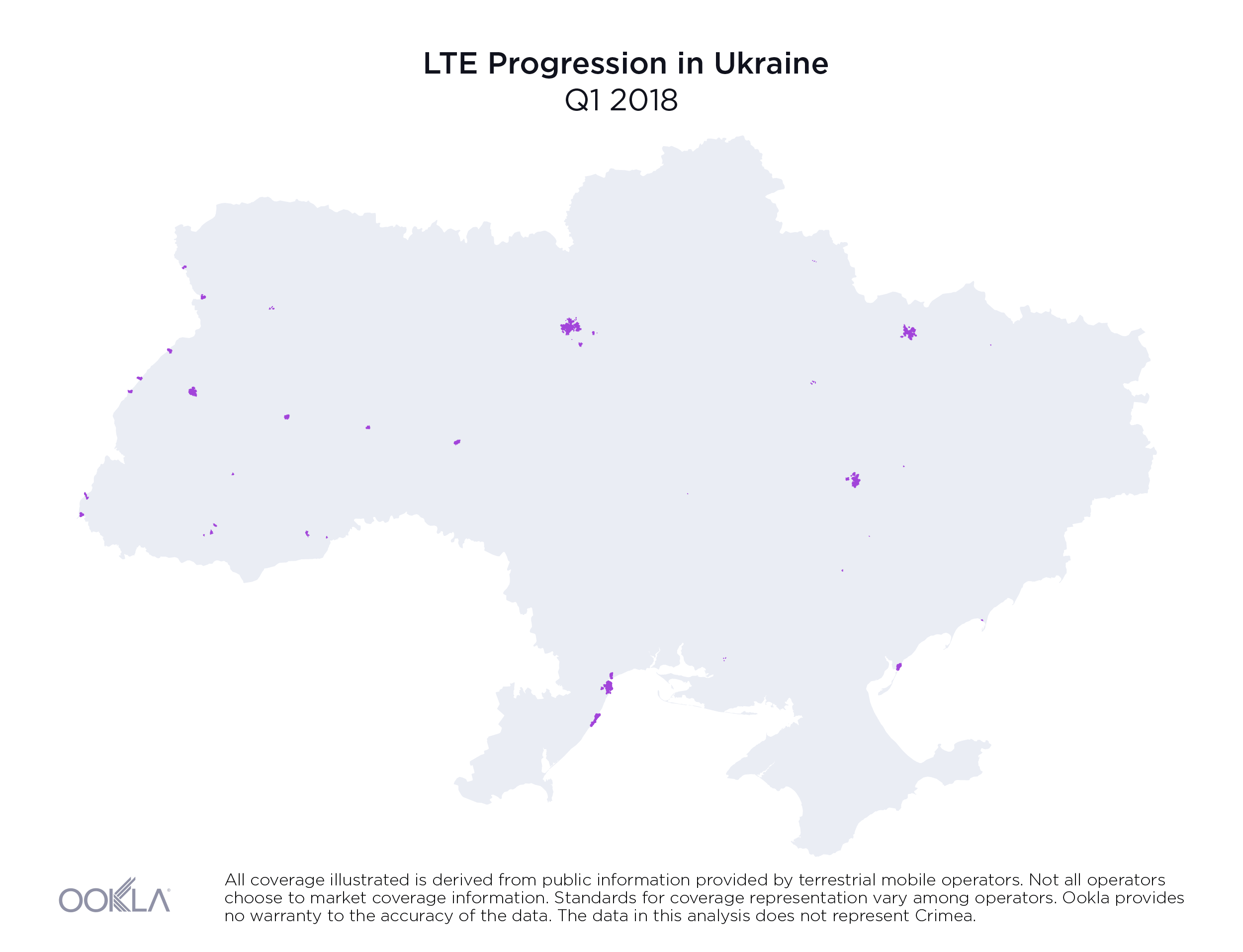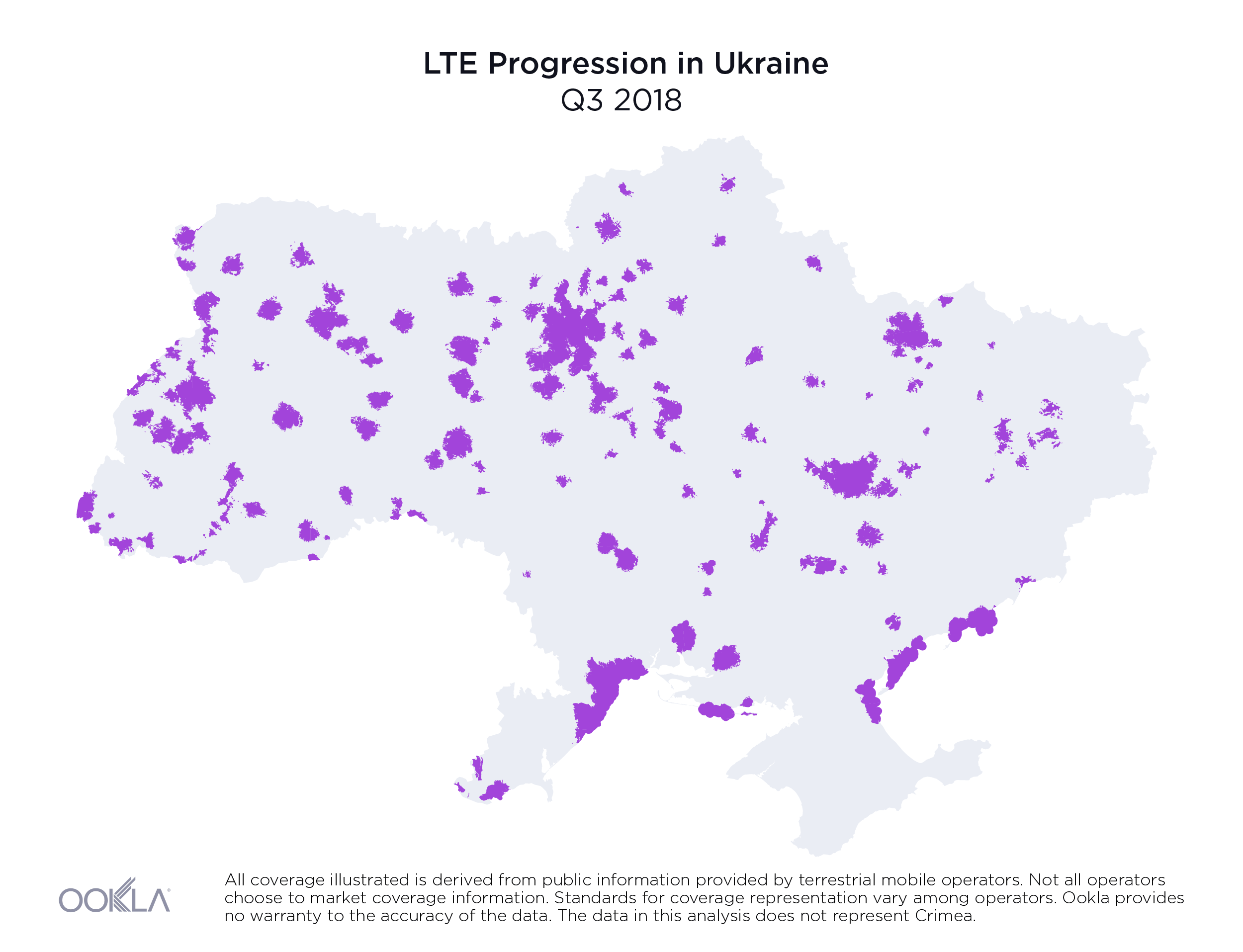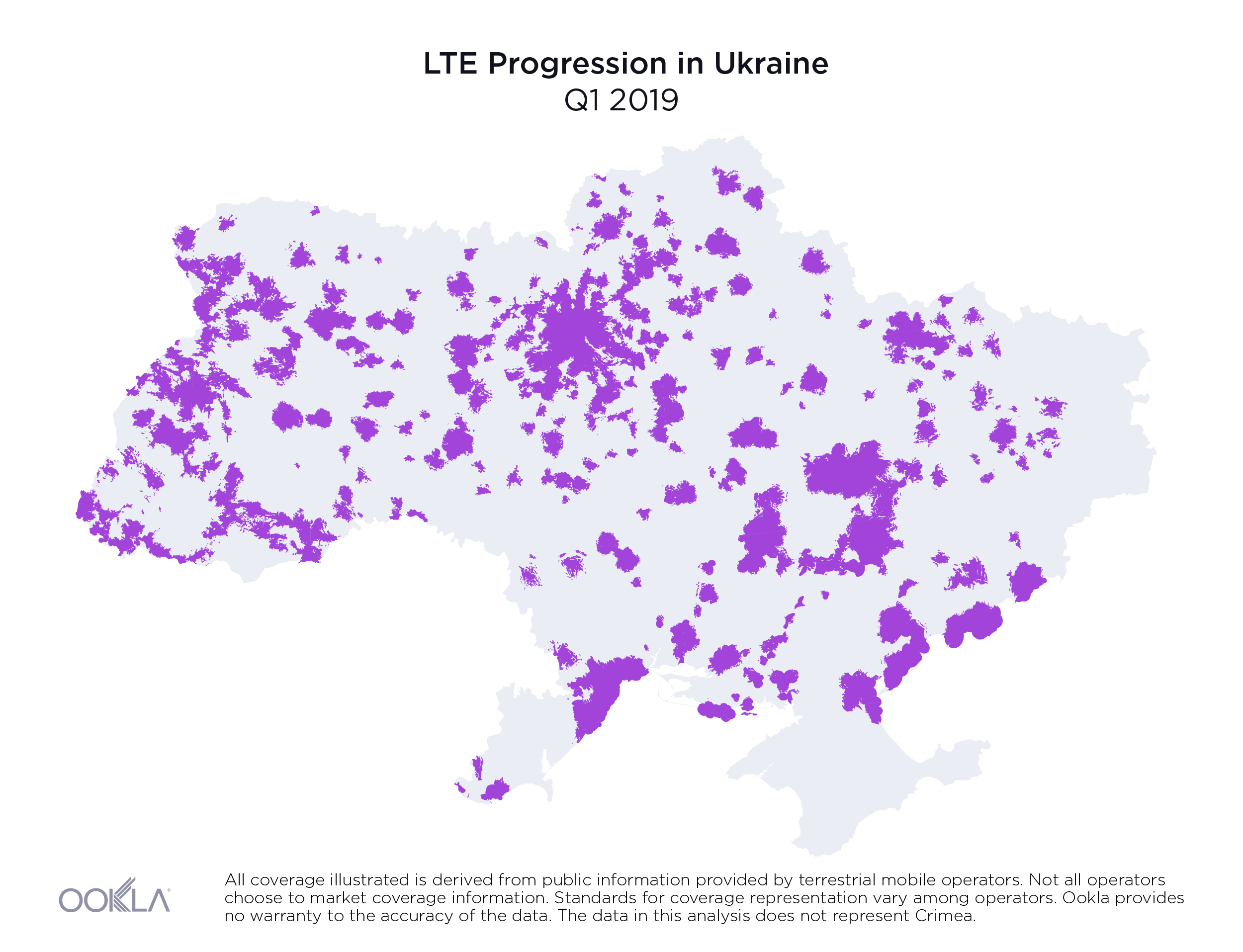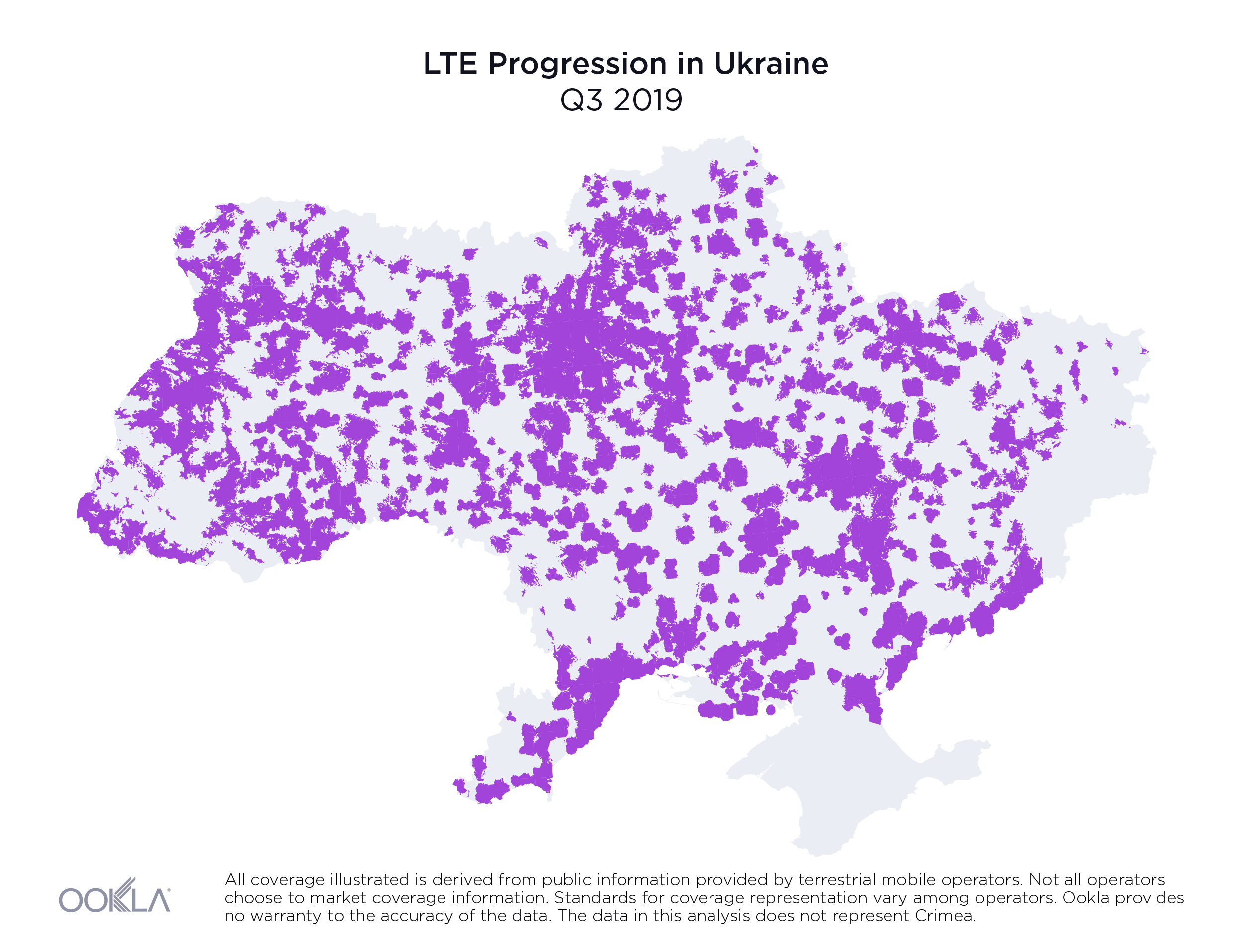
While less than 1% of the country had access to LTE service at the beginning of 2018, by the end of Q3 2019, the three largest mobile operators reported nearly 36.2% of land area in Ukraine was covered, as illustrated above.
To see Speedtest measurements of 4G Availability and speed by operator, download the full report.
Mobile speeds and 4G Availability are higher in urban areas than the country average, but fixed broadband speeds varied
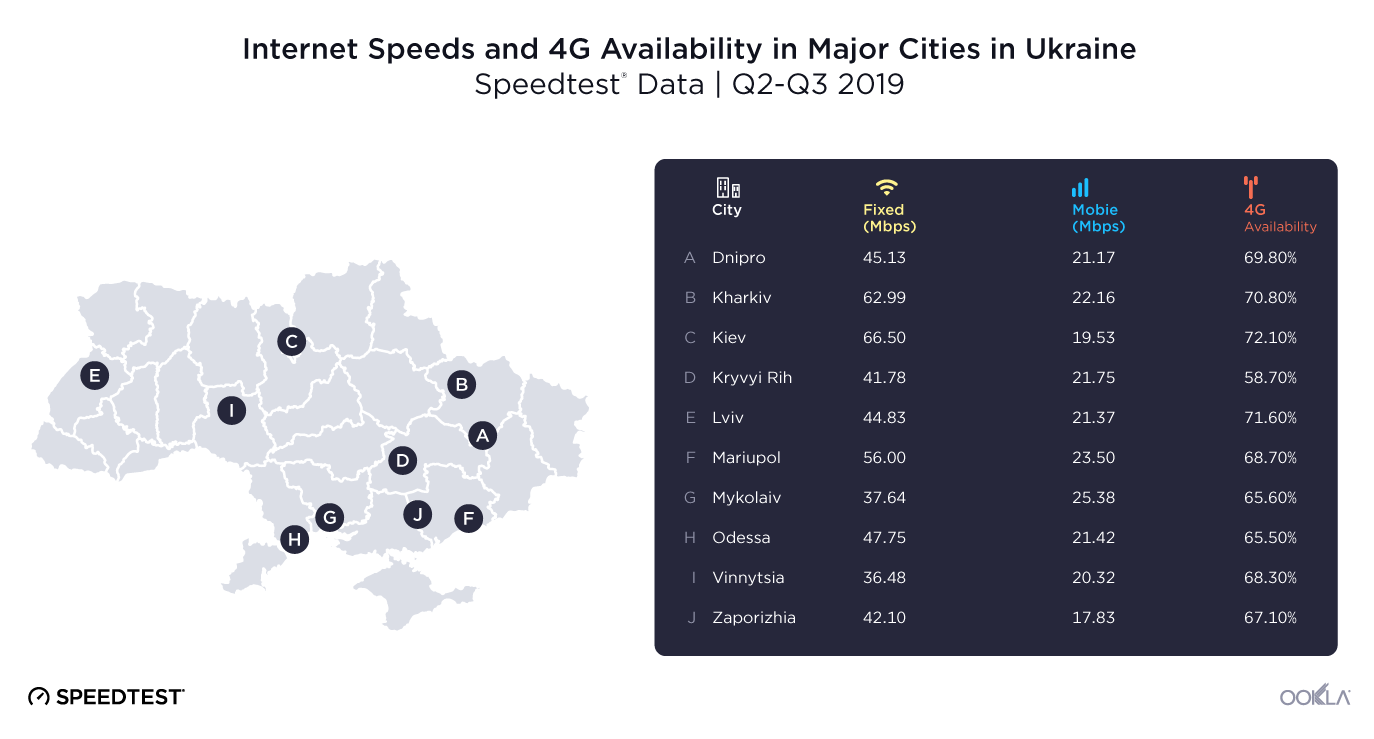
While some cities experienced fixed broadband speeds that were lower than the national average of 49.99 Mbps, Kiev (66.50 Mbps), Kharkiv (62.99 Mbps) and Mariupol (56.00 Mbps) all saw speeds that were significantly higher. The slowest speeds on our list were measured in Kryvyi Rih (41.78 Mbps), Mykolaiv (37.64 Mbps) and Vinnytsia (36.48 Mbps).
Mobile download speeds — which include all cellular technologies, not just 4G — were generally equal to or greater than the national average in the cities we looked at. Mykolaiv saw the fastest mobile download speeds, with an average of 25.38 Mbps, followed by Mariupol (23.50 Mbps) and Kharkiv (22.16 Mbps). The lowest speeds on this list were measured in Kiev (19.53 Mbps) and Zaporizhia (17.83 Mbps).
4G Availability is significantly higher in many of Ukraine’s cities than the overall country average of 34.8%, perhaps because of the operators’ commitment to bring LTE service to major population centers first. The capital, Kiev, had the best 4G Availability (72.1%) during Q2-Q3 2019, followed by Lviv (71.6%) and Kharkiv (70.8%). The other cities we measured showed a range between 65.5% and 69.8%, with the exception of Kryvyi Rih (58.7%), where there was somewhat less 4G Availability.
To see the fastest mobile and fixed broadband providers in each city, download the full report.
Editor’s note: The maps in this article were updated on November 25 to include Crimea.
Дослідження продуктивності мереж стаціонарного широкосмугового та мобільного Інтернету в Україні
Після того як Україна вийшла з економічної кризи 2016 року, регулятивні органи та постачальники послуг поставили собі за мету забезпечити надання послуг швидкісного Інтернету більшій кількості населення та позиціонувати Україну як країну, сприятливу для інновацій. Завдяки нещодавнім розгортанням LTE мобільними операторами та створенню оптоволоконних мереж постачальниками стаціонарного широкосмугового Інтернету споживачі в Україні мають безпрецедентний доступ до швидкого Інтернету, а конкуренція на ринку стала як ніколи високою. Зараз на ринку домінують три основні конкуренти: Київстар, Vodafone Україна (власником є компанія МТС) і lifecell (власником є компанія Turkcell). Ринок стаціонарного широкосмугового Інтернету дуже насичений: тут є сотні постачальників інтернет-послуг, які працюють на національному, регіональному та місцевому рівнях. У цьому звіті Ookla наведено результати перевірки швидкості стаціонарного широкосмугового та мобільного Інтернету, а також показника 4G Availability (доступність 4G) протягом останніх двох кварталів в Україні.
Ми проаналізували дані щодо продуктивності, отримані за результатами 1 805 450 тестів, проведених споживачами з використанням технологій Speedtest®, а також дані про покриття за результатами 623 мільйонів відповідних перевірок на 372 690 пристроях протягом II та III кварталів 2019 р. Дані в цьому аналізі не представляють Крим.
Щоб дізнатися, які постачальники послуг стаціонарного широкосмугового та мобільного Інтернету в Україні пропонують найшвидший доступ до Інтернету, а також про постачальників, які пропонують найшвидший доступ до мережі Інтернет і мають найкращий показник 4G Availability у великих містах України, завантажте повну версію звіту.
Швидкість мобільного та стаціонарного широкосмугового Інтернету збільшується по всій країні
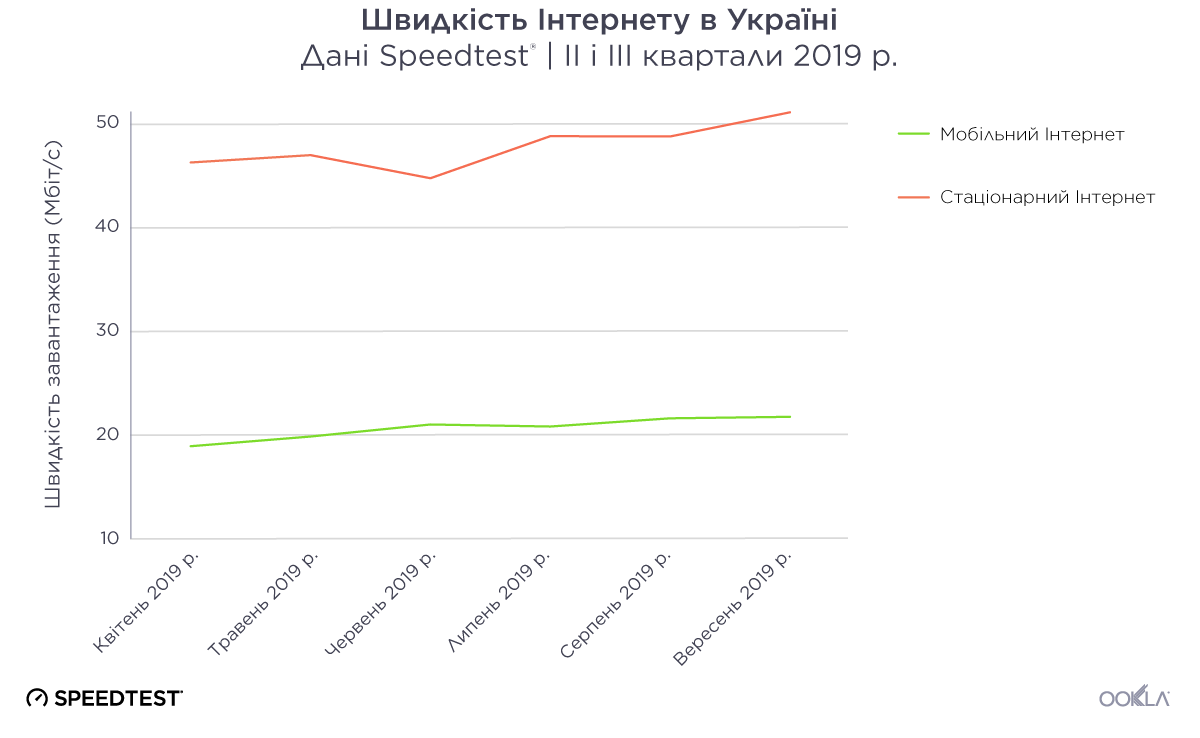
Швидкість мобільного та стаціонарного Інтернету в Україні поступово зростала протягом II і III кварталів 2019 р. Упродовж цього періоду середня швидкість завантаження стаціонарного широкосмугового Інтернету збільшилася на 10,4% до максимального значення 49,99 Мбіт/с у вересні. Швидкість мобільного Інтернету також збільшувалася: вона зросла на 14,8% й у вересні склала 21,4 Мбіт/с. Оскільки в Україні розповсюджується послуга LTE, ми очікуємо, що середня швидкість мобільного Інтернету буде безперервно зростати.
Нові розгортання LTE роблять швидший Інтернет доступнішим для більшої кількості людей
За останній рік розгортання мереж LTE було ключовим пріоритетом для операторів України. Національна комісія, що здійснює державне регулювання у сфері зв’язку та інформатизації, надала новий діапазон і ліцензії на 4G компаніям Київстар, lifecell і Vodafone Україна на початку 2018 року з домовленістю, що вони забезпечать покриття LTE принаймні для 90% населення кожного регіонального центру протягом 12 місяців і для 90% населення кожного міста, кількість жителів якого перевищує 10 000, протягом 42 місяців.
У результаті нових розгортань 4G за останній рік покриття LTE в Україні швидко зростало, а дані Speedtest свідчать про те, що показник 4G Availability протягом II та III кварталів 2019 року складав 34,8%.
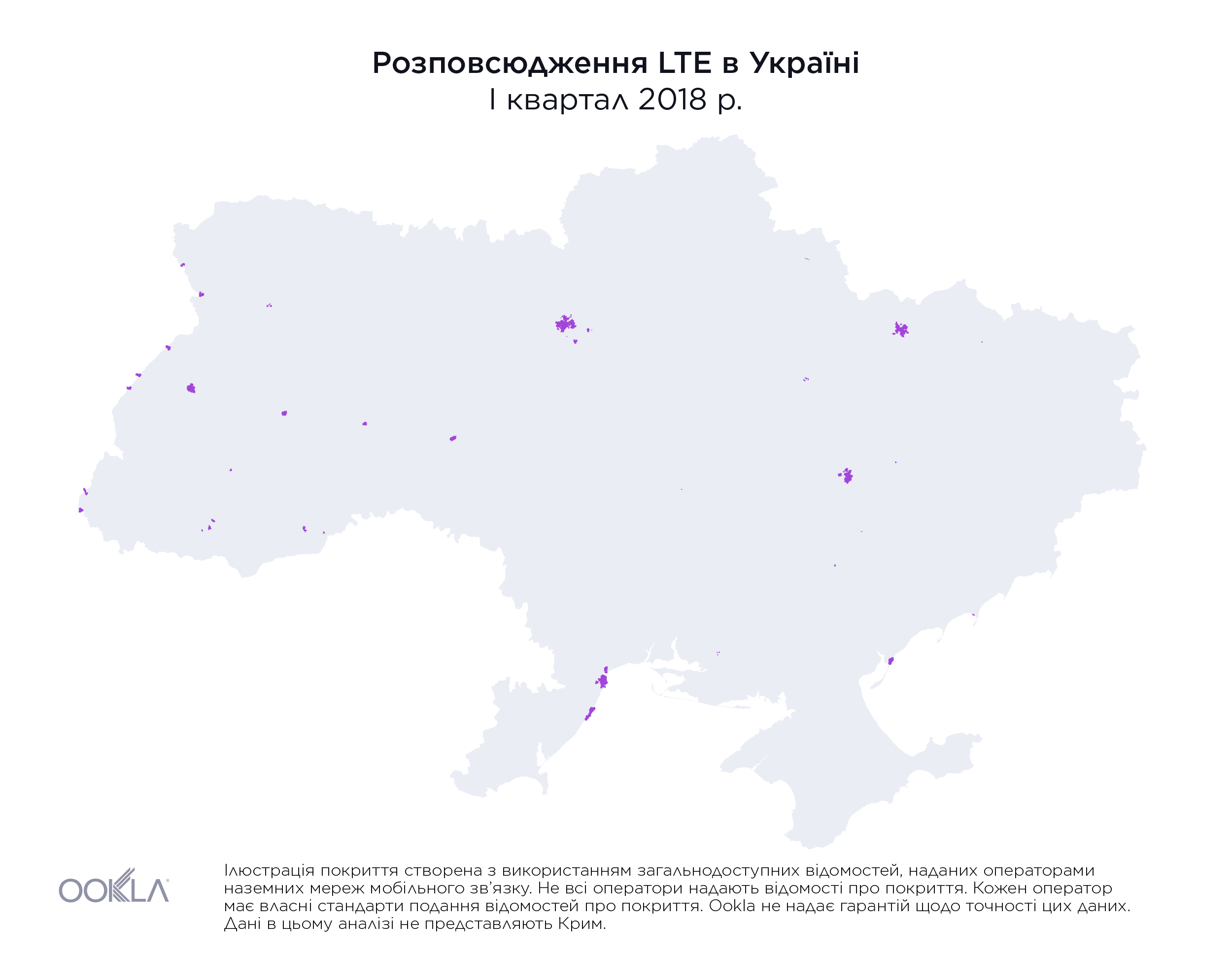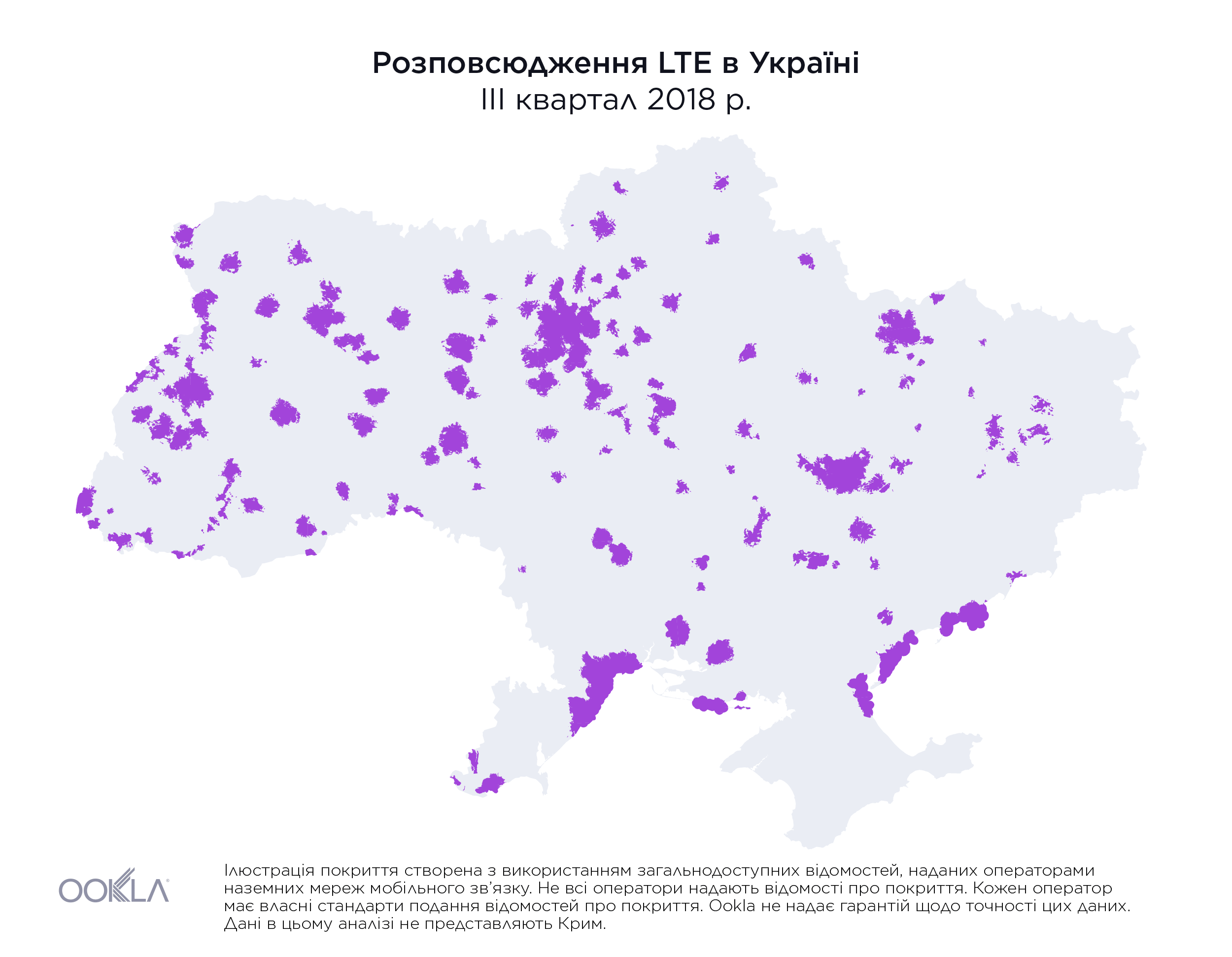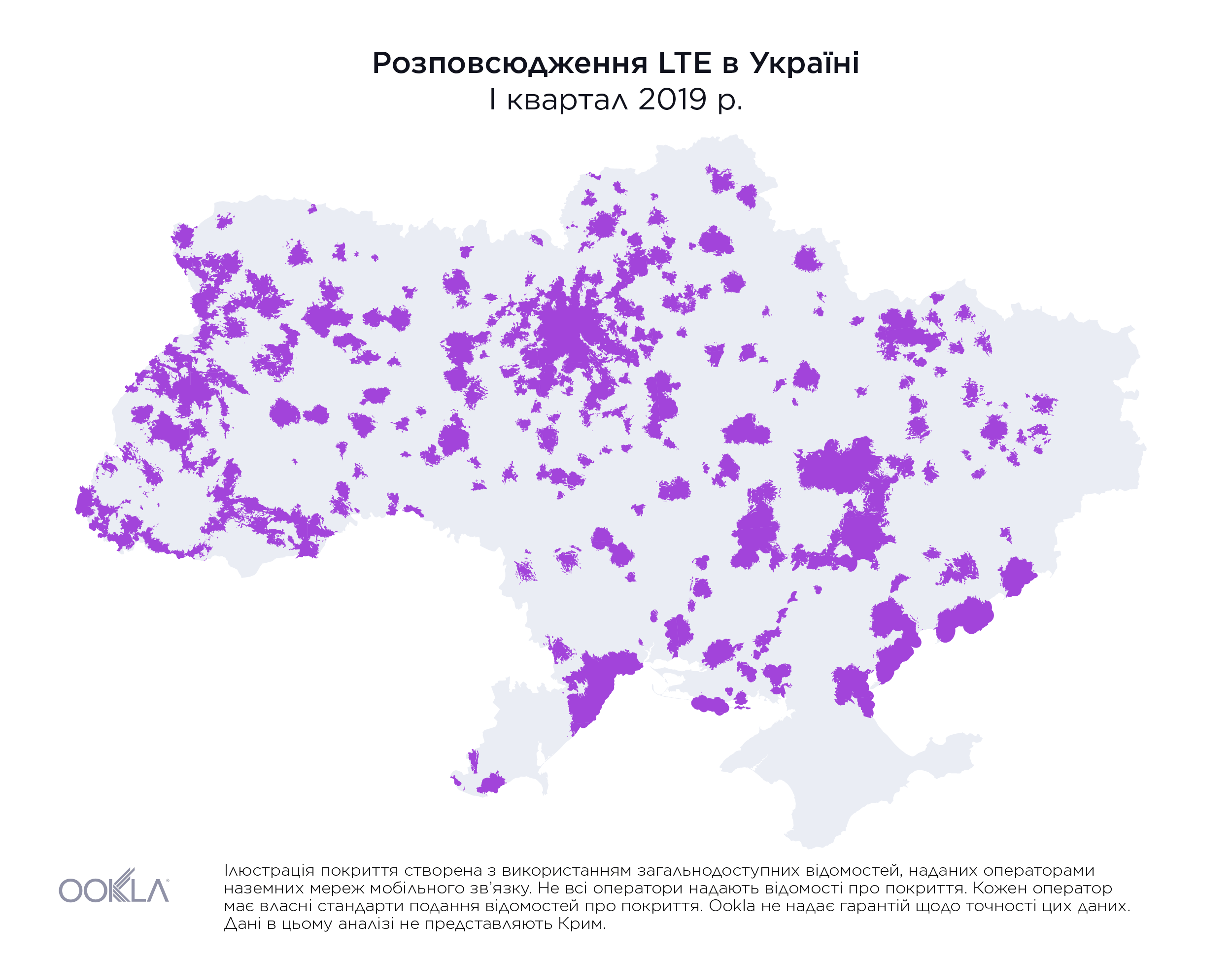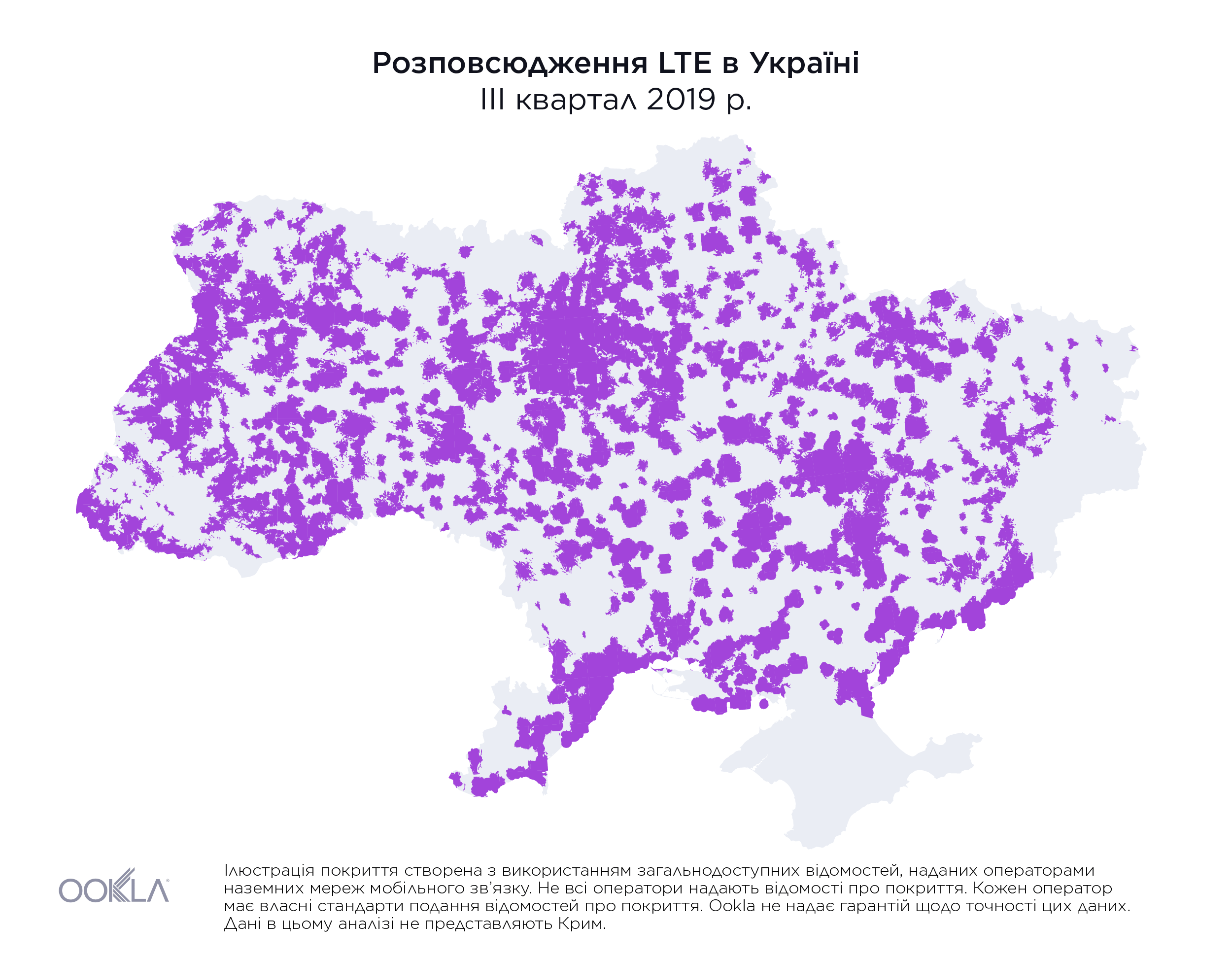
На початку 2018 року територія, на якій були доступні послуги LTE, не перевищувала 1% площі країни. Однак наприкінці III кварталу 2019 року три найбільших оператори мобільного зв’язку повідомили, що покриття вже охопило майже 36,2% материкової території України, як показано вище.
Щоб дізнатися про виконані за допомогою Speedtest вимірювання показника 4G Availability та швидкості Інтернету, який надають оператори, завантажте повну версію звіту.
У середньому швидкість мобільного Інтернету та показник 4G Availability в міських регіонах вище, ніж у середньому по країні, однак показники швидкості стаціонарного Інтернету різняться

Хоча в деяких містах швидкість стаціонарного Інтернету нижче середнього показника по країні, який дорівнює 49,99 Мбіт/с, у Києві (66,50 Мбіт/с), Харкові (62,99 Мбіт/с) і Маріуполі (56,00 Мбіт/с) швидкість Інтернету була набагато вищою. Найнижчі швидкості в містах із нашого списку були зафіксовані в Кривому Розі (41,78 Мбіт/с), Миколаєві (37,64 Мбіт/с) і Вінниці (36,48 Мбіт/с).
Швидкість завантаження в мобільних мережах (включно з усіма стільниковими мережами, а не лише 4G) зазвичай дорівнювала середньому національному показнику або перевищувала його в містах, у яких виконувалося вимірювання. У Миколаєві було зафіксовано найвищу швидкість завантаження: середній показник склав 25,38 Мбіт/с. На другому місці був Маріуполь із показником 23,50 Мбіт/с, а на третьому — Харків (22,16 Мбіт/с). Найнижчі швидкості серед міст із цього списку було зафіксовано в Києві (19,53 Мбіт/с) і Запоріжжі (17,83 Мбіт/с).
У багатьох містах України показник 4G Availability значно вищий, ніж середній показник по країні (34,8%). Імовірно, причина полягає в тому, що оператори намагаються вводити послугу LTE спочатку у великих містах. У столиці України, Києві, зафіксовано найвищий показник 4G Availability (72,1%) протягом II та III кварталів 2019 року. Друге місце за цим показником посідає Львів (71,6%), а третє — Харків (70,8%). В інших містах, у яких виконувалися вимірювання, діапазон показників склав від 65,5% до 69,8%, за винятком Кривого Рогу (58,7%), де показник 4G Availability був трохи нижчим.
Щоб дізнатися про постачальників найшвидшого мобільного та стаціонарного Інтернету в кожному місті, завантажте повну версію звіту.
Примітка редактора: Карти в цій статті були оновлені 25 листопада, щоб включити Крим.
Анализ скорости сетей мобильного и фиксированного широкополосного доступа в Интернет в Украине
После экономического спада 2016 года регулирующие органы и поставщики услуг в Украине поставили перед собой цель сделать высокоскоростной Интернет более доступным для населения и улучшить условия для внедрения инноваций в стране. Благодаря развертыванию сетей LTE операторами мобильной связи и созданию оптоволоконных сетей поставщиками фиксированного широкополосного доступа (ШПД) быстрый Интернет стал доступен для беспрецедентного количества украинских потребителей. При этом конкуренция на рынке интернет-услуг стала как никогда высокой. Ведущее положение на рынке мобильного широкополосного Интернета в настоящее время занимают три оператора: Киевстар, Vodafone Украина (принадлежит МТС) и lifecell (принадлежит Turkcell). А на рынке услуг фиксированного ШПД действуют сотни национальных, региональных и местных поставщиков. В рамках данного отчета компания Ookla рассматривает показатели скорости фиксированного ШПД и мобильного Интернета, а также 4G Availability (доступность 4G) в Украине за последние два квартала.
Наш анализ включает в себя данные о скорости за второй и третий кварталы 2019 г., полученные в результате проведения 1 805 450 потребительских тестов (с помощью Speedtest®), и данные охвата, полученные в ходе выполнения 623 млн проверок на 372 690 устройствах. Данные в этом анализе не представляют Крым.
Чтобы узнать больше о работающих в Украине поставщиках с самой высокой скоростью фиксированного ШПД и мобильного Интернета, а также ознакомиться с данными о скорости и показателями 4G Availability в некоторых из крупнейших городов Украины, скачайте полный отчет.
Скорость фиксированного ШПД и мобильного Интернета увеличивается по всей стране

В течение второго и третьего кварталов 2019 г. скорость мобильного Интернета и фиксированного ШПД немного увеличилась по всей Украине. За этот период средняя скорость скачивания с фиксированным ШПД увеличилась на 10,4% и в сентябре достигла самого высокого значения — 49,99 Мбит/с. Скорость мобильного Интернета также возросла на 14,8% — до 21,40 Мбит/с в сентябре. Так как доступ к услугам LTE получает все больше украинцев, мы ожидаем, что средняя скорость мобильного Интернета продолжит увеличиваться.
Развертывание новых сетей LTE помогает увеличить скорость Интернета по стране
За последний год развертывание сетей LTE стало одним из главных приоритетов для операторов в Украине. В начале 2018 г. НКРСИ предоставила лицензии на новые частоты и 4G операторам Киевстар, lifecell и Vodafone Украина с обязательством, что они обеспечат охват сетями LTE по меньшей мере 90% населения в каждом региональном центре в течение 12 месяцев и до 90% населения в каждом городе с населением более 10 000 жителей в течение 42 месяцев.
Новые развертывания 4G значительно расширили охват LTE в Украине за последний год, и данные Speedtest показывают, что показатель 4G Availability в стране в течение второго и третьего кварталов 2019 г. составил 34,8%.
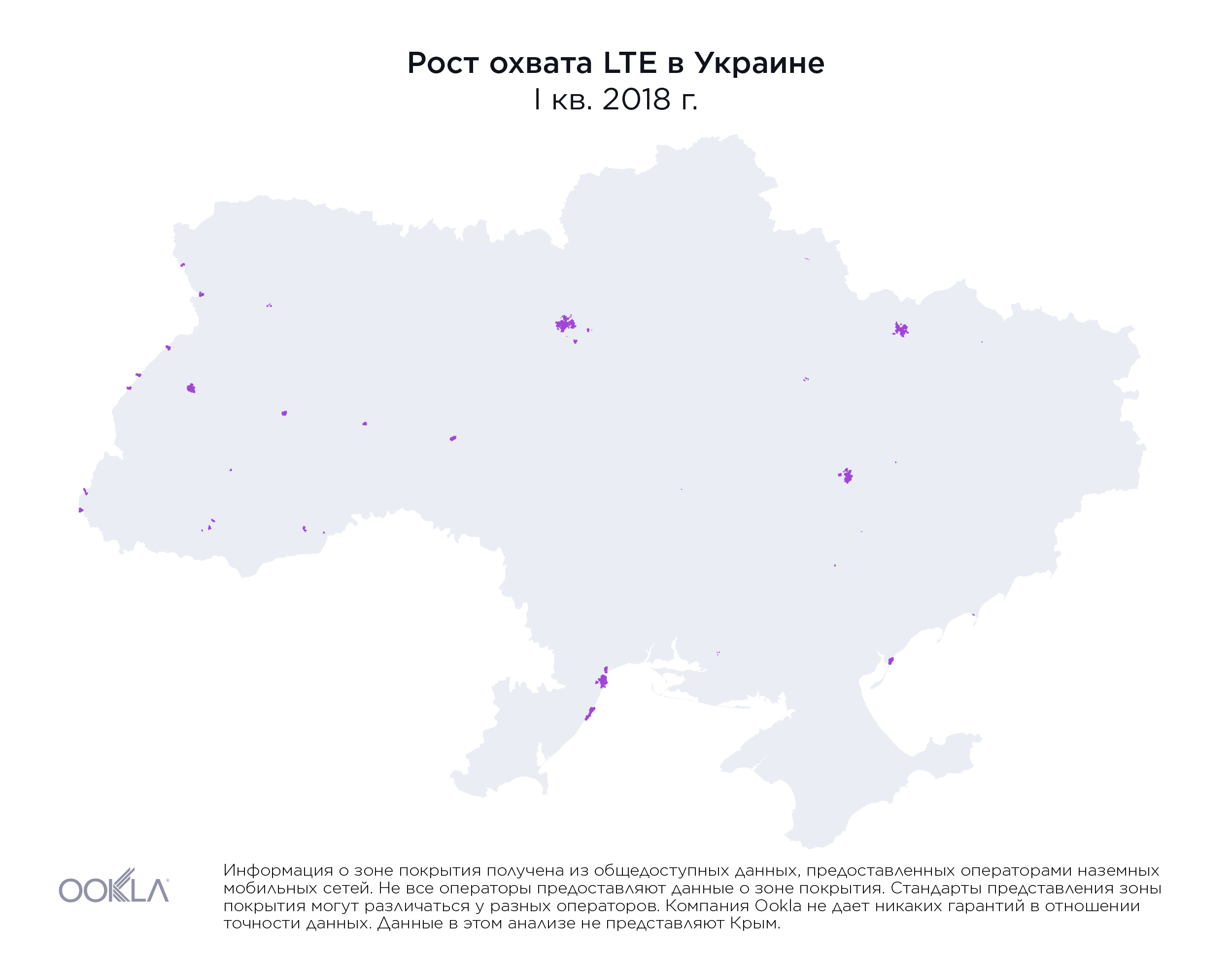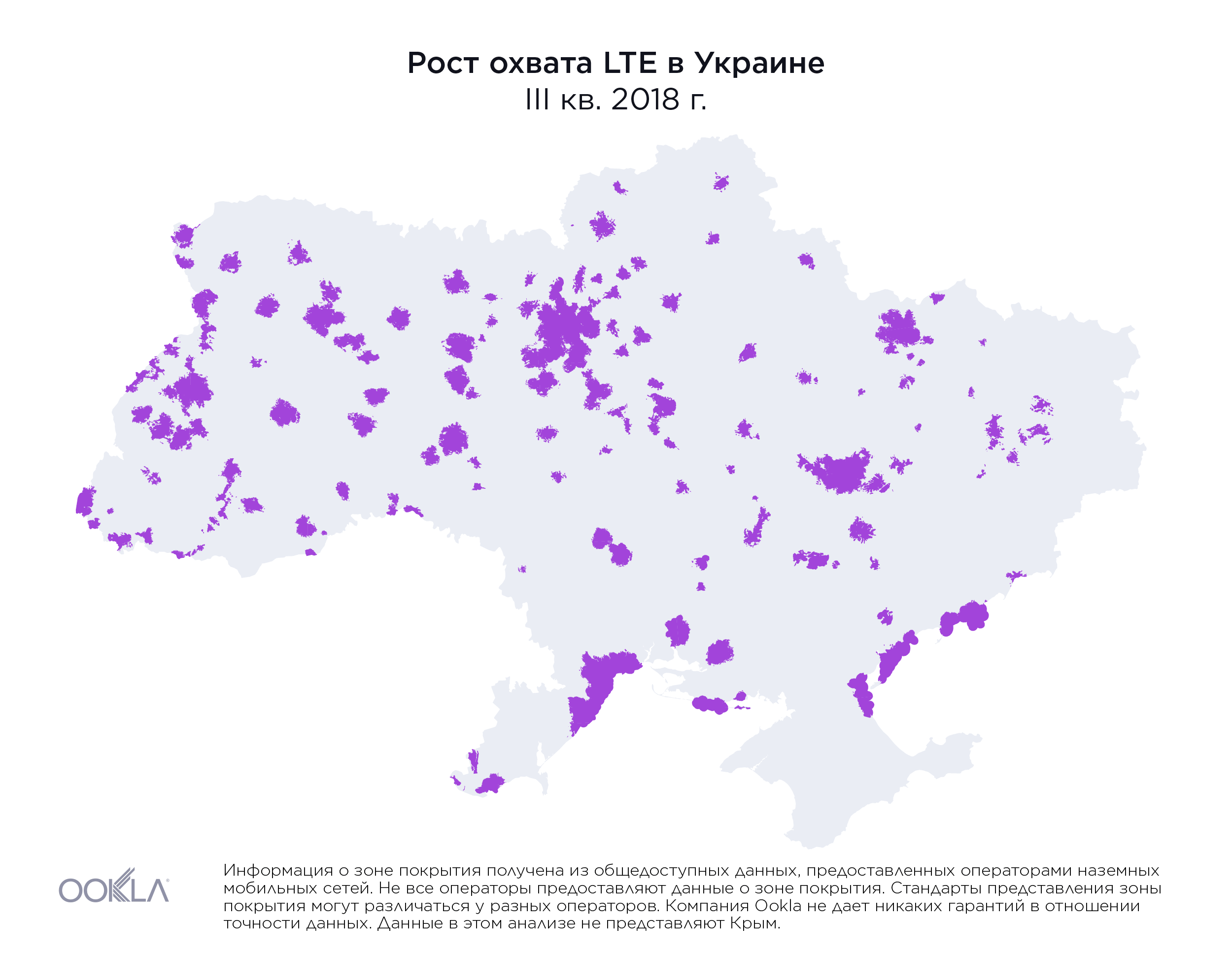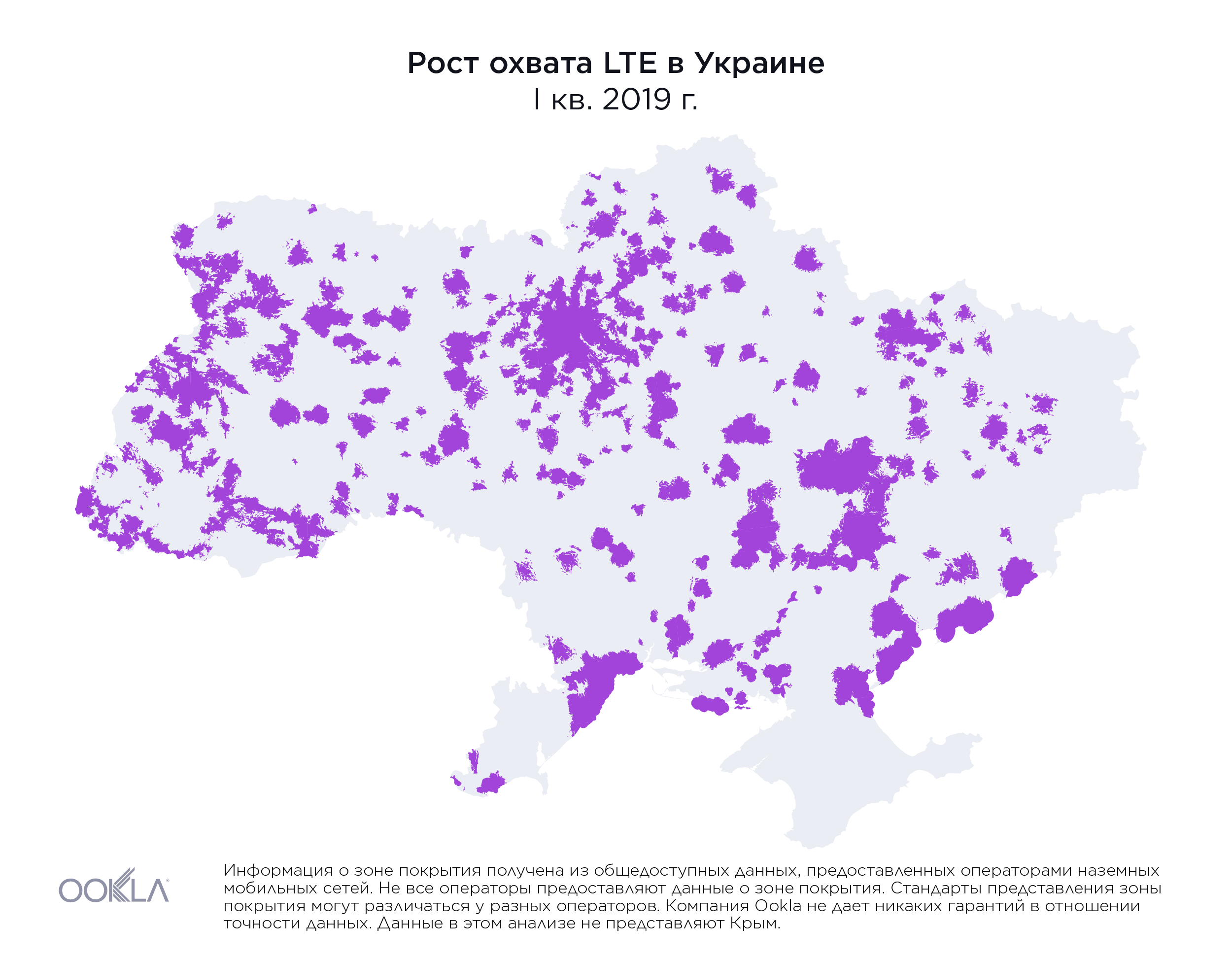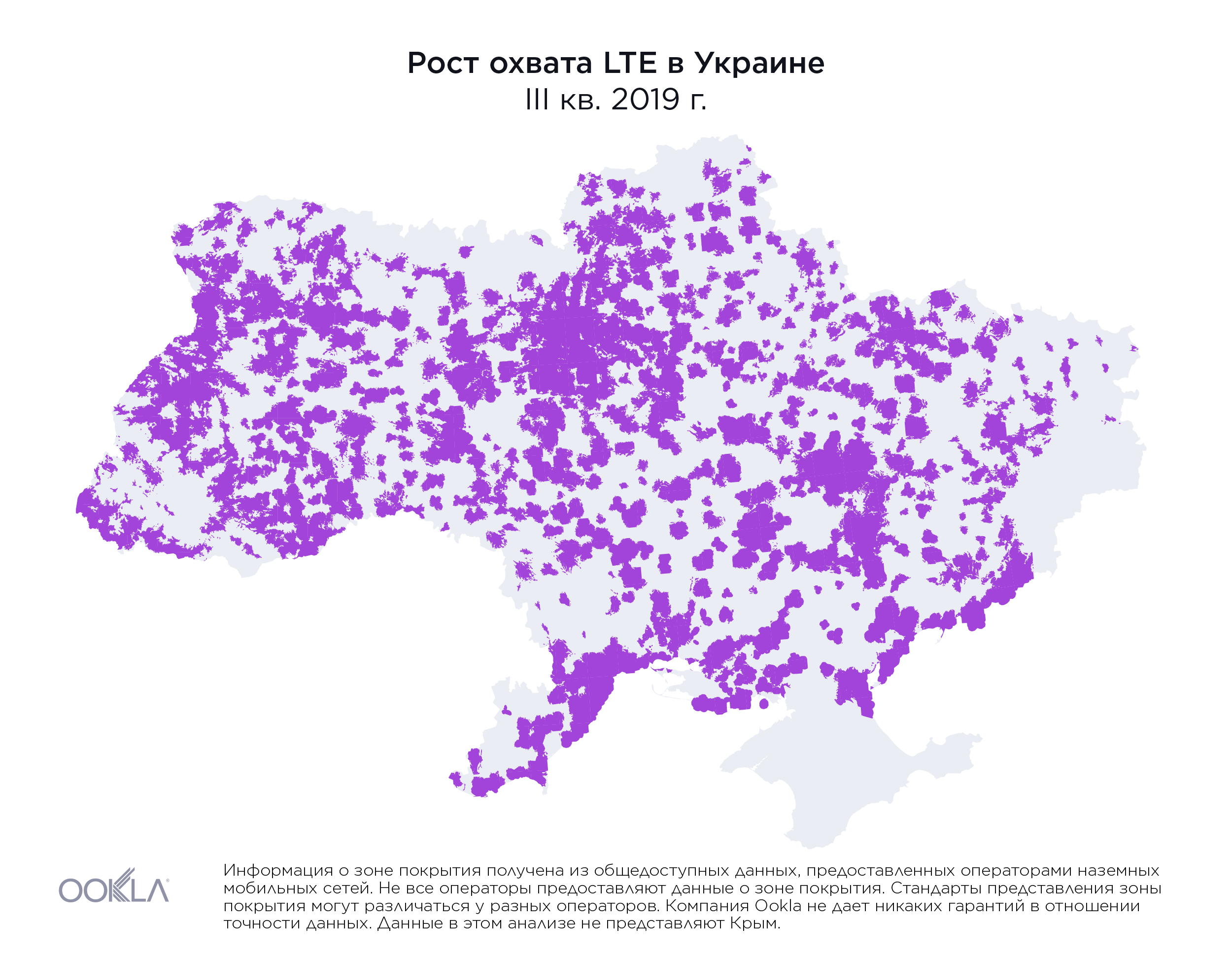
Хотя в начале 2018 года территория, на которой были доступны услуги LTE, составляла менее 1% площади страны, к концу третьего квартала 2019 г. три крупнейших мобильных оператора сообщили, что наземное покрытие обеспечено для 36,2% территории Украины, как показано выше.
Чтобы ознакомиться с данными Speedtest о показателе 4G Availability и скоростях по каждому оператору, скачайте полный отчет.
Скорость мобильного Интернета и показатель 4G Availability в городских районах выше, чем в среднем по стране, но скорость фиксированного ШПД варьировалась.

Хотя в некоторых городах скорость фиксированного ШПД была ниже, чем в среднем по стране (49,99 Мбит/с), она была значительно выше в Киеве (66,50 Мбит/с), Харькове (62,99 Мбит/с) и Мариуполе (56,00 Мбит/с). Самая низкая скорость была зарегистрирована нами в Кривом Роге (41,78 Мбит/с), Николаеве (37,64 Мбит/с) и Виннице (36,48 Мбит/с).
Скорость скачивания с мобильным Интернетом (учитывались все сотовые технологии, а не только 4G) в оцененных нами городах в целом находилась на уровне среднего значения по стране или превышала его. В Николаеве скорость скачивания с мобильным Интернетом была самой высокой — в среднем 25,38 Мбит/с. Второе место по этому показателю занял Мариуполь (23,50 Мбит/с), а третье — Харьков (22,16 Мбит/с). Самая низкая скорость зарегистрирована в Киеве (19,53 Мбит/с) и Запорожье (17,83 Мбит/с).
Показатель 4G Availability во многих городах Украины значительно выше, чем в среднем по стране (34,8%). Возможно, это связано с тем, что операторы стремятся обеспечить доступность услуг LTE в первую очередь в крупных населенных пунктах. Во втором и третьем кварталах 2019 г. столица Украины, город Киев, имела высокий показатель 4G Availability (72,1%). Второе место по этому показателю занял Львов (71,6%), а третье — Харьков (70,8%). В других городах, по которым были получены данные, этот показатель составил от 65,5% до 69,8%, за исключением Кривого Рога (58,7%), в котором показатель 4G Availability был ниже.
Чтобы ознакомиться с данными о поставщиках самого быстрого мобильного Интернета и фиксированного ШПД в каждом городе, скачайте полный отчет.
Примечание редактора: карты в этой статье были обновлены 25 ноября и теперь включают Крым.

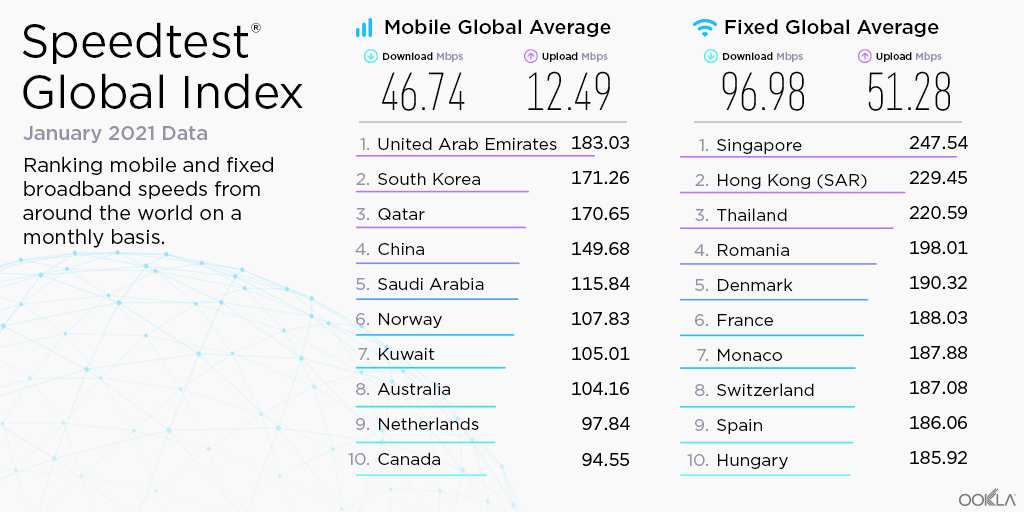









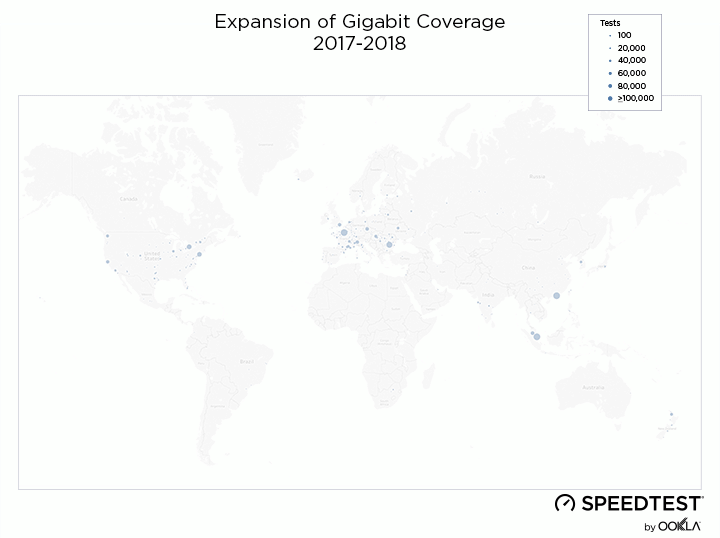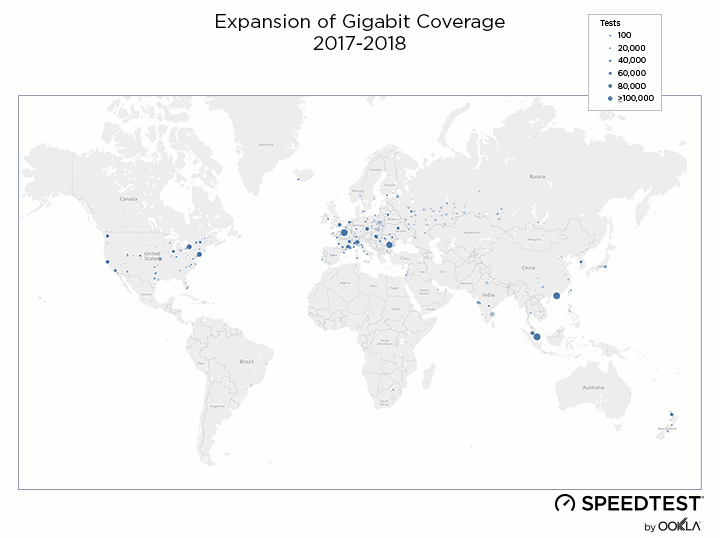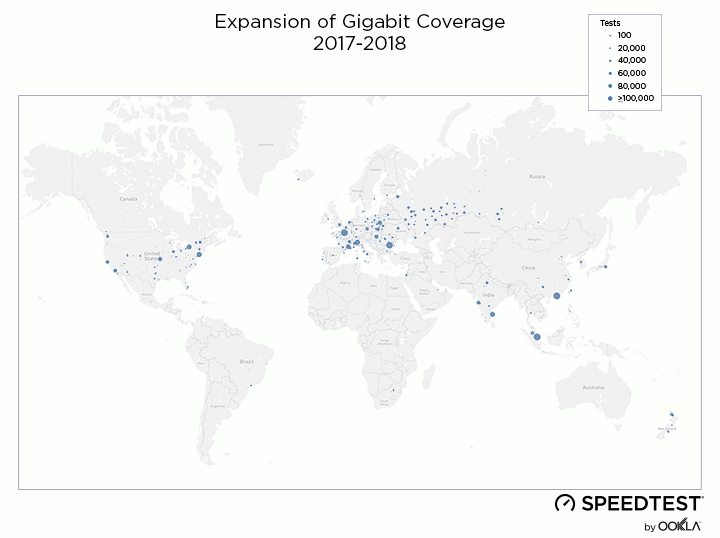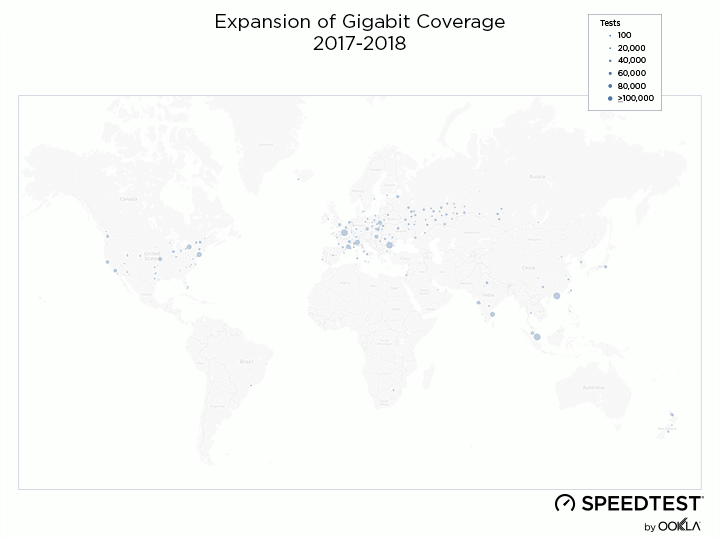
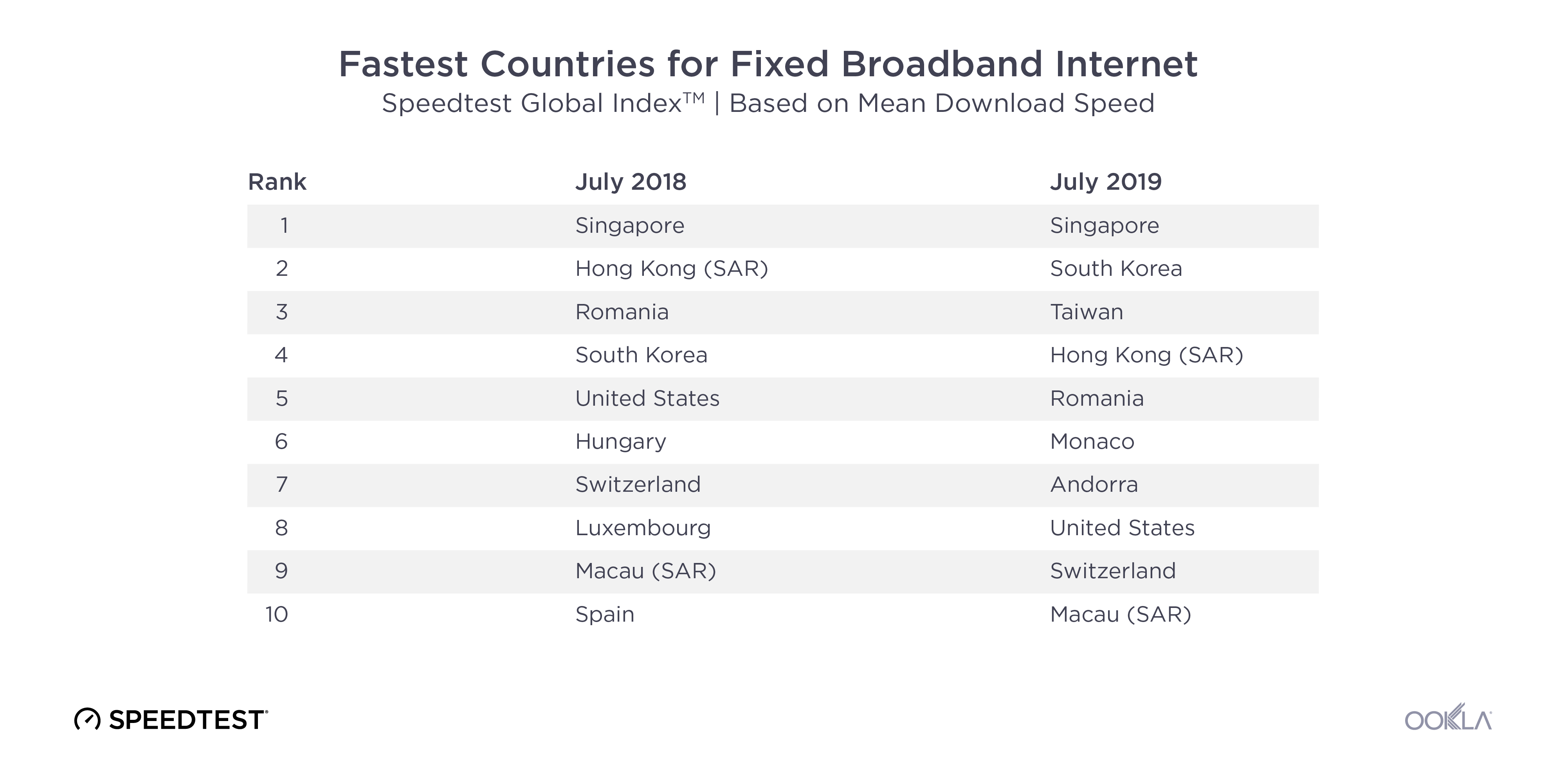
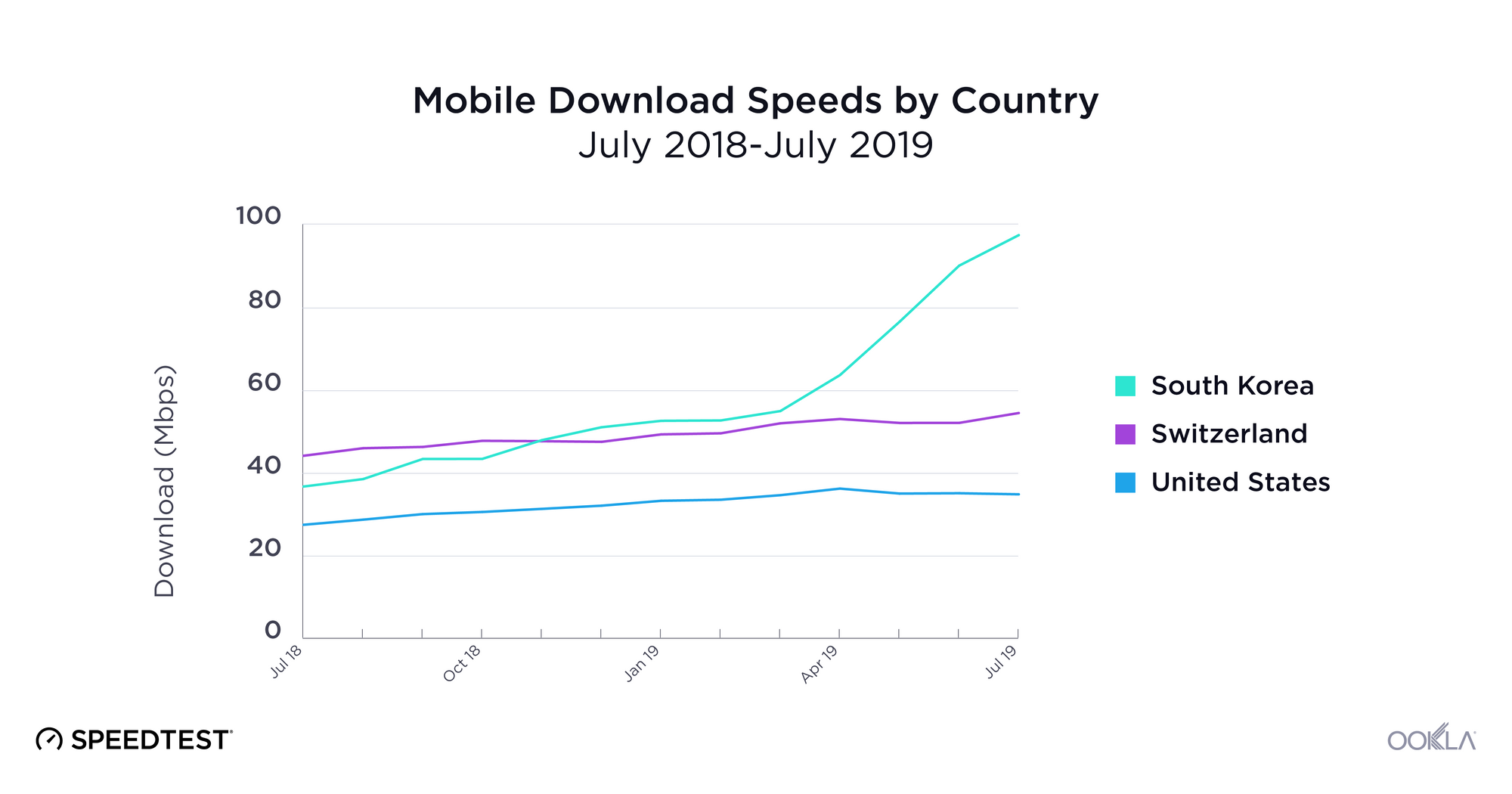
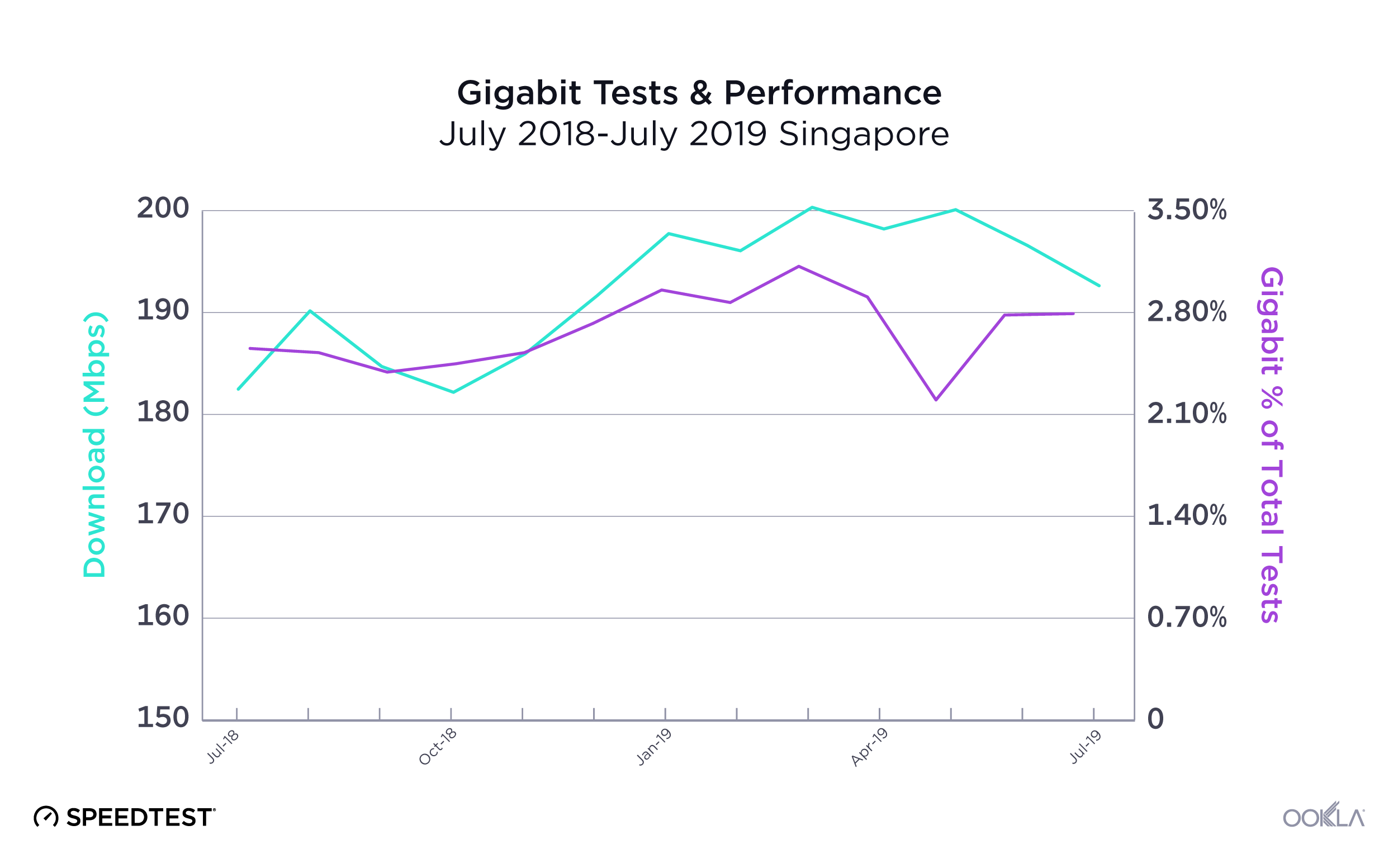
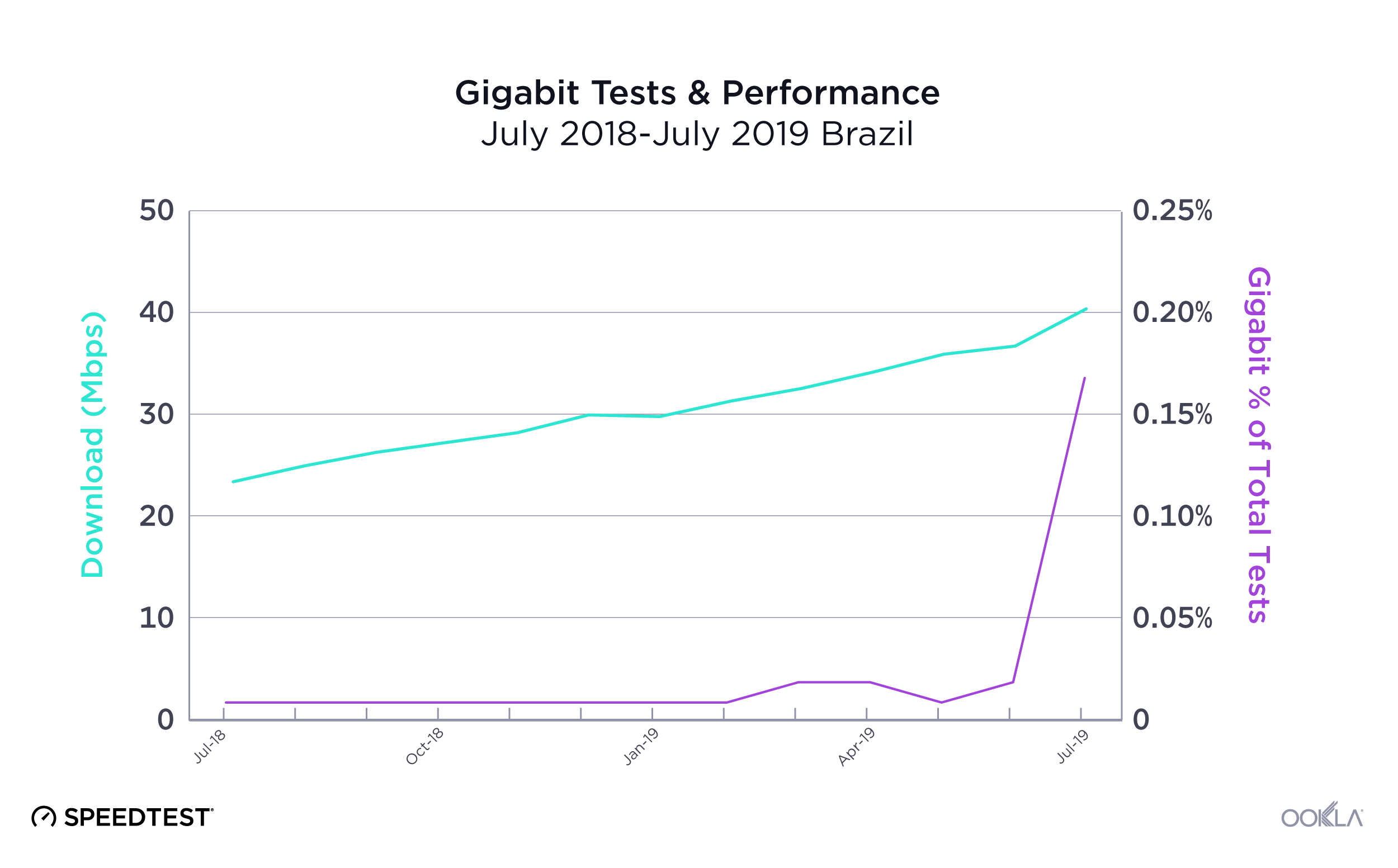
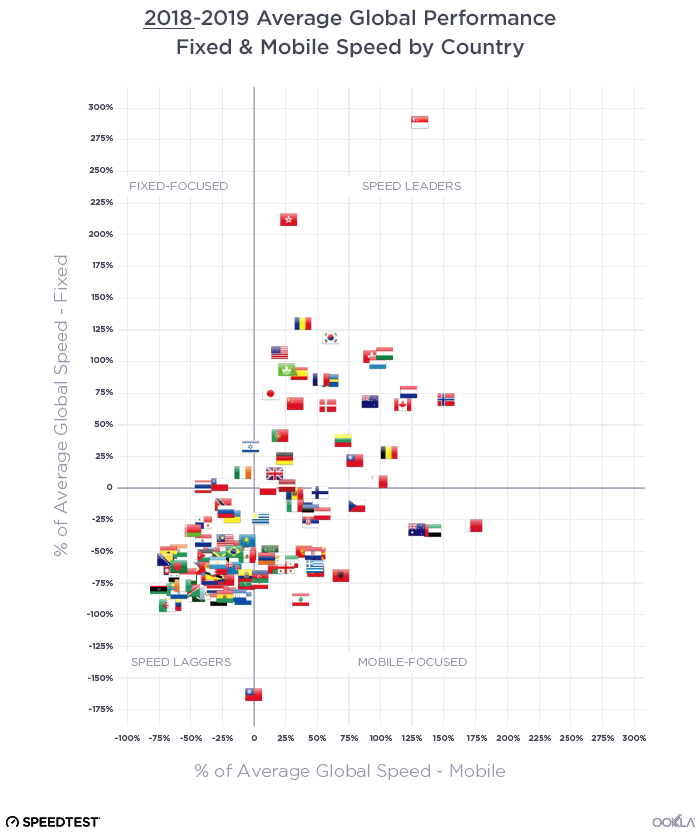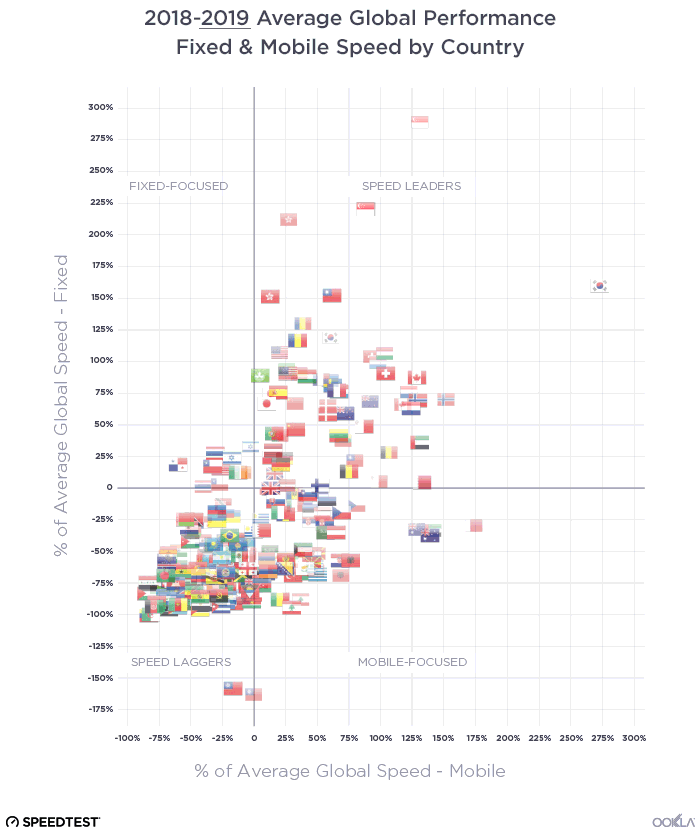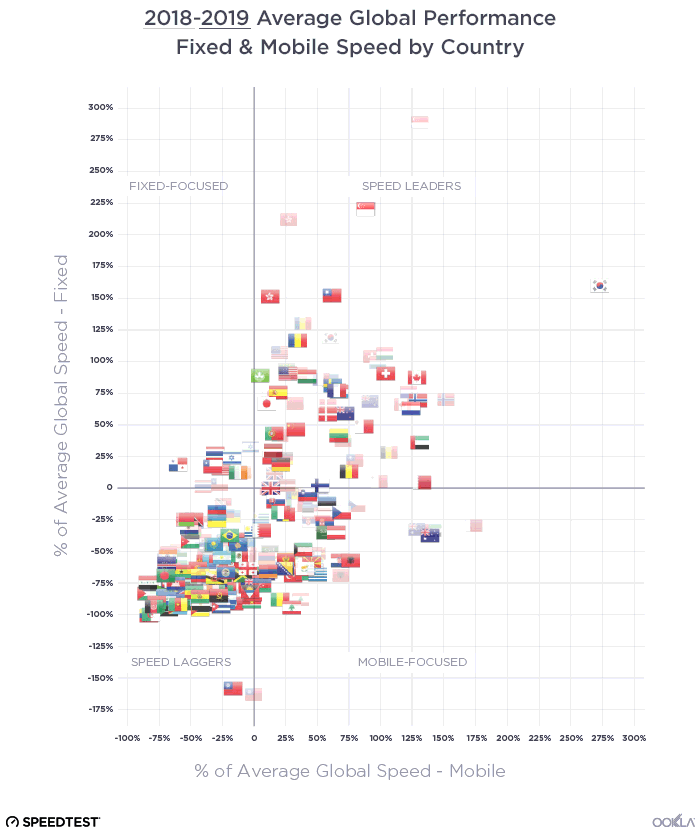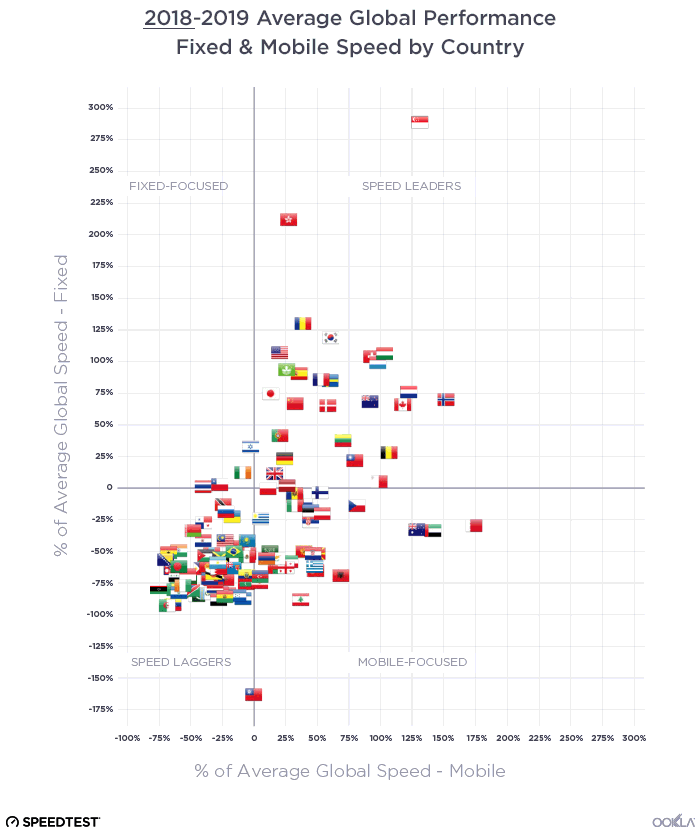
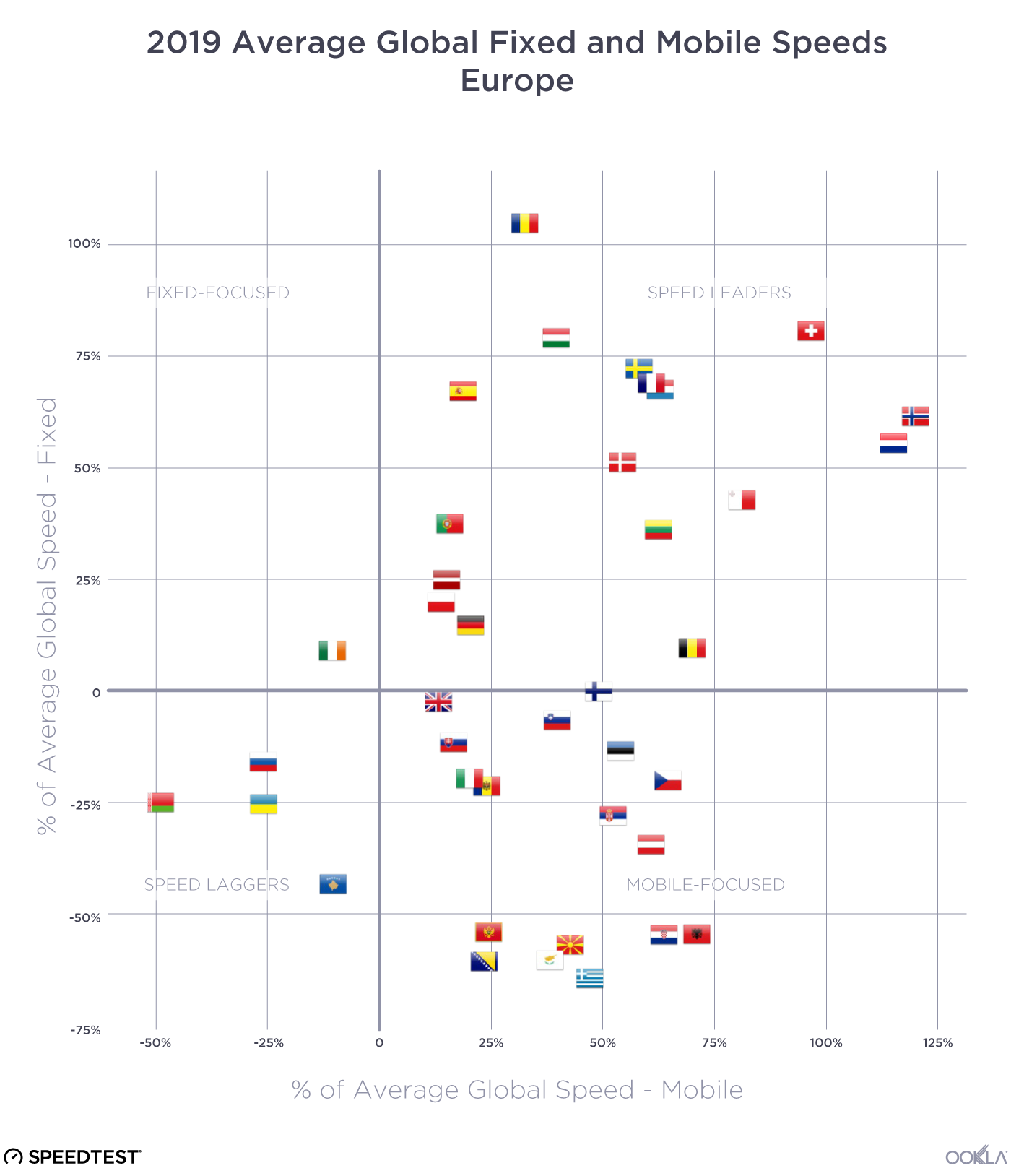
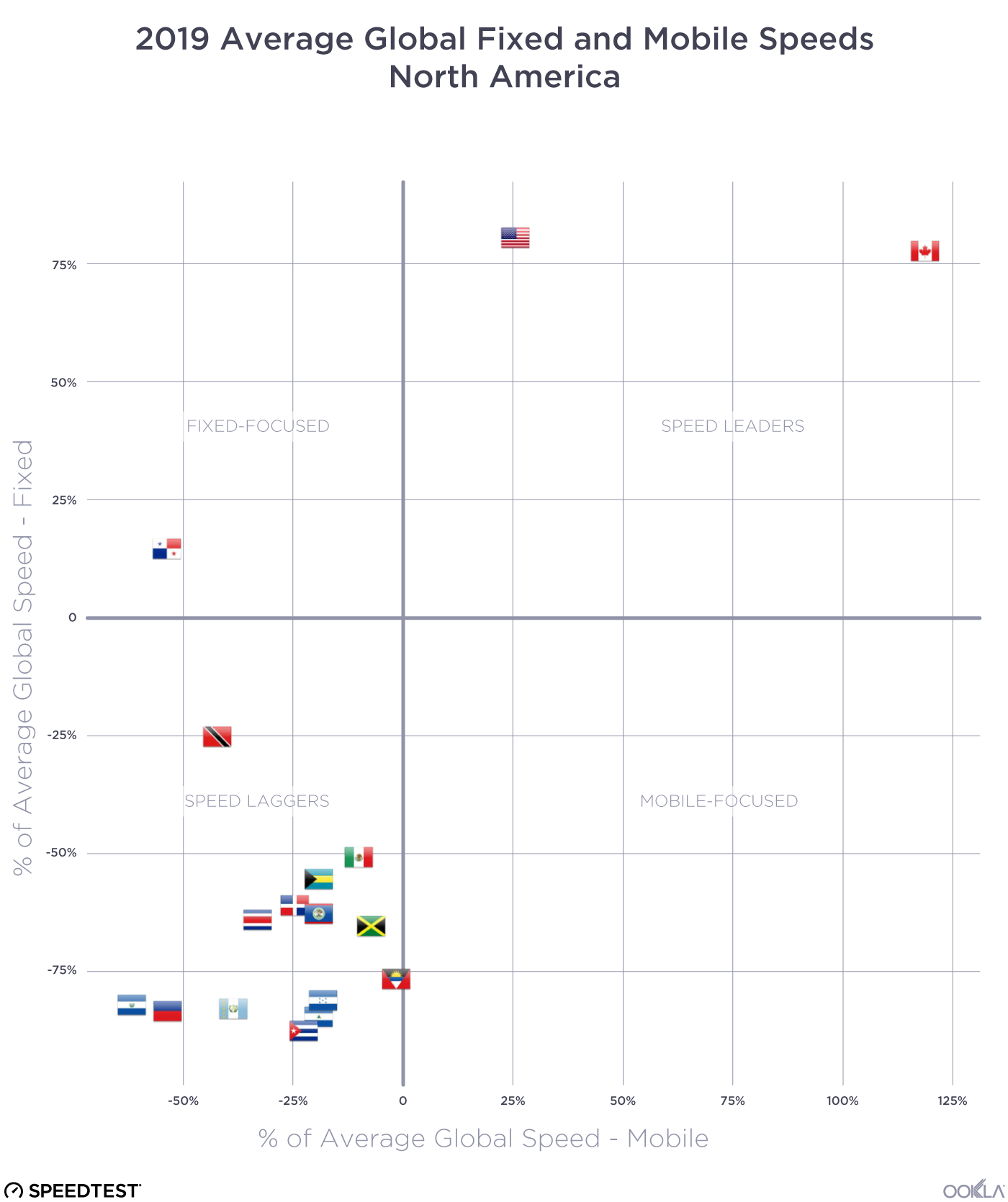
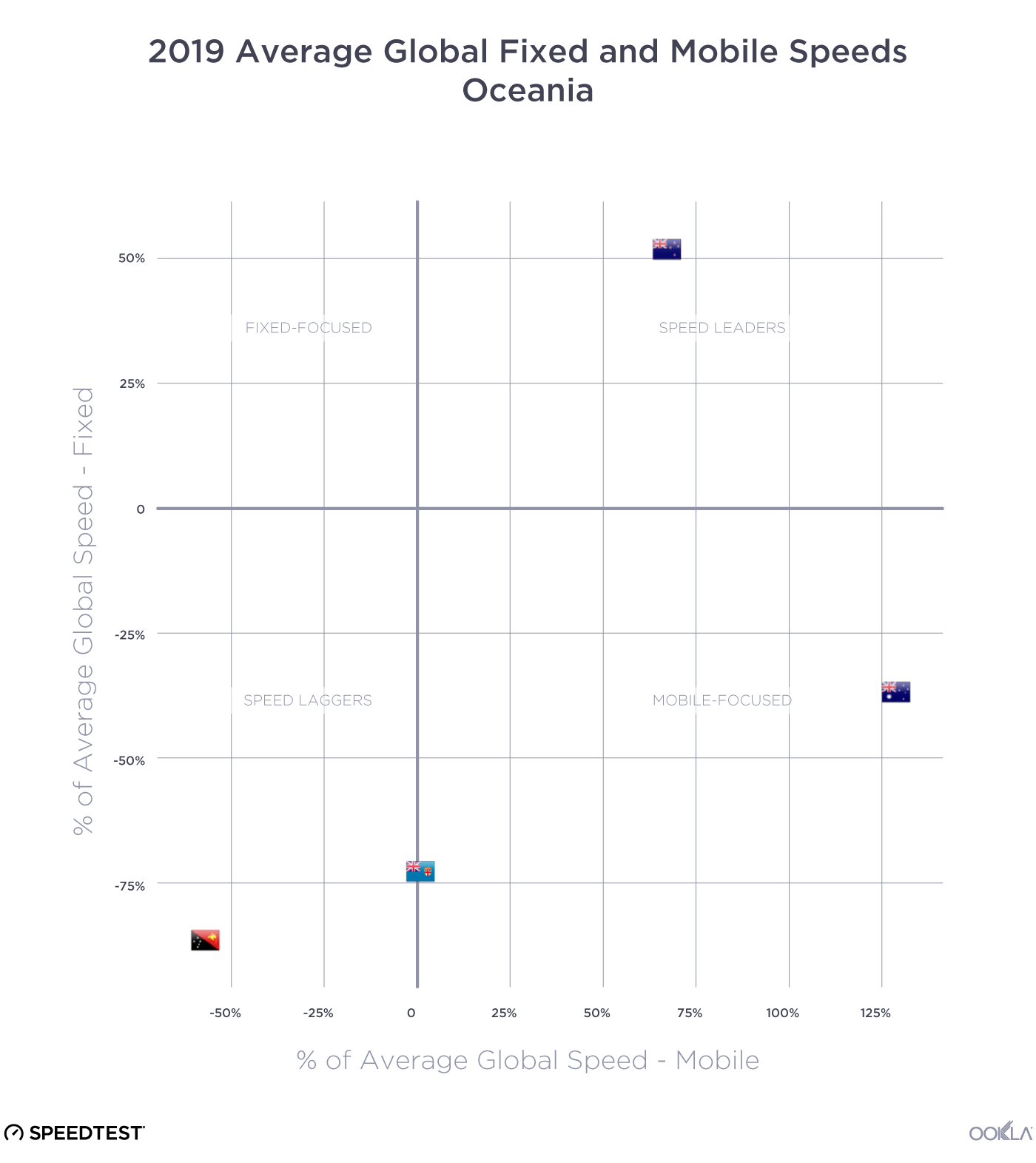
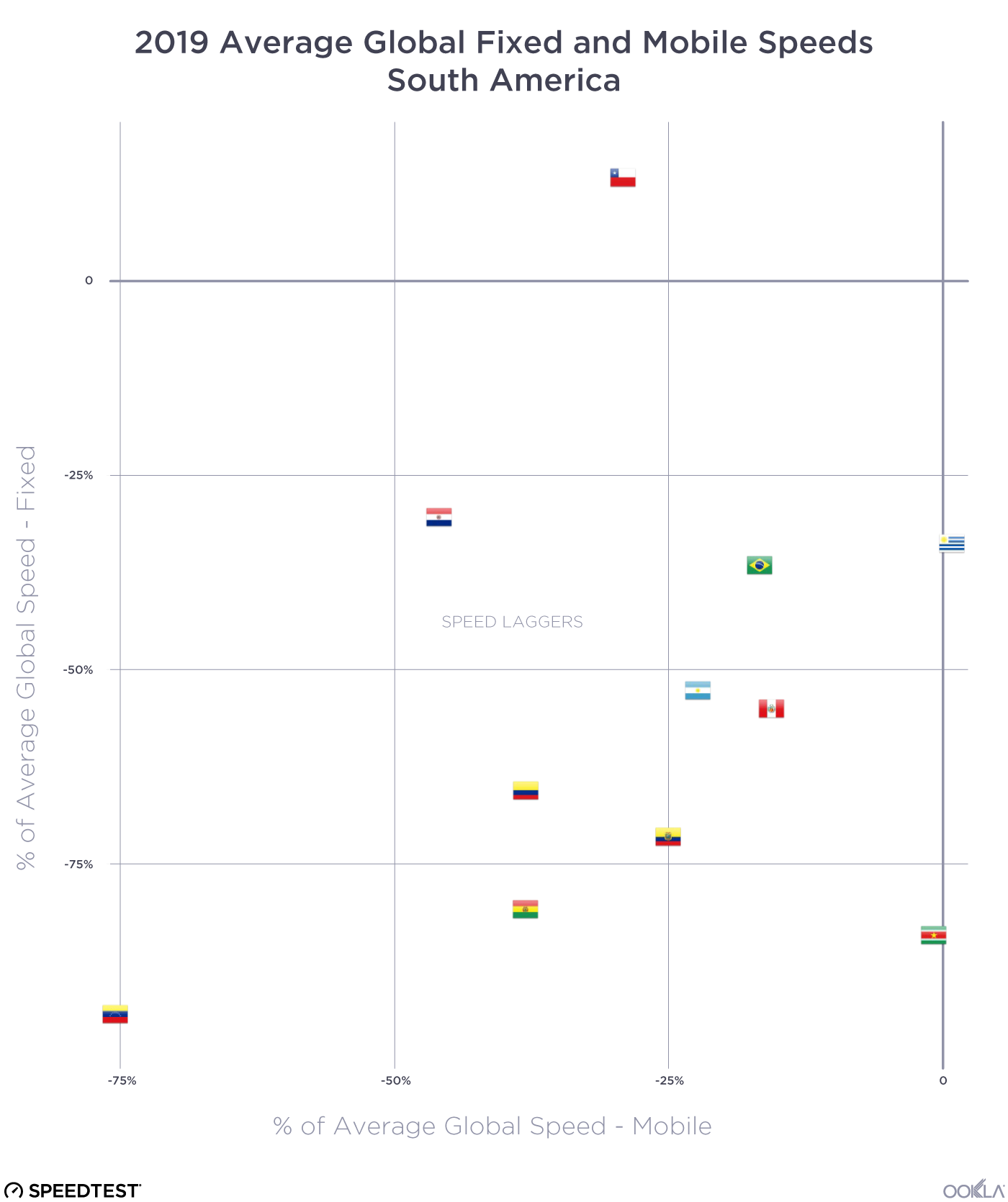
 When it comes to the internet, the news is mostly good for 2018. Download and upload speeds are increasing across the globe on both mobile and fixed broadband. 5G is on the horizon and gigabit service is expanding.
When it comes to the internet, the news is mostly good for 2018. Download and upload speeds are increasing across the globe on both mobile and fixed broadband. 5G is on the horizon and gigabit service is expanding.