The rapid expansion of 5G in countries across the globe was a bright spot in a year that needed one. But just how great is the news? We examined Speedtest Intelligence® data from over 60.5 million Speedtest® results during Q3 2020 to see how much speeds have improved, where download speeds are the fastest at the country and capital level, where 5G deployments have increased and what worldwide 5G coverage looks like now. We also looked at countries where 5G doesn’t yet reach to understand where good news might be on the horizon.
We have only included countries with commercially available 5G on these lists in order to provide a more accurate view of the performance consumers can reasonably expect. While our data shows results for many countries where 5G is not yet commercially available, these tests are likely results from engineers testing their own networks. In addition, we’re only providing analysis for countries with more than 200 samples during Q3 2020. The bars shown in our charts are 95% confidence intervals, which represent the range of values in which the true value is likely to be. Countries marked in tables with an asterisk first launched 5G commercially in 2020.
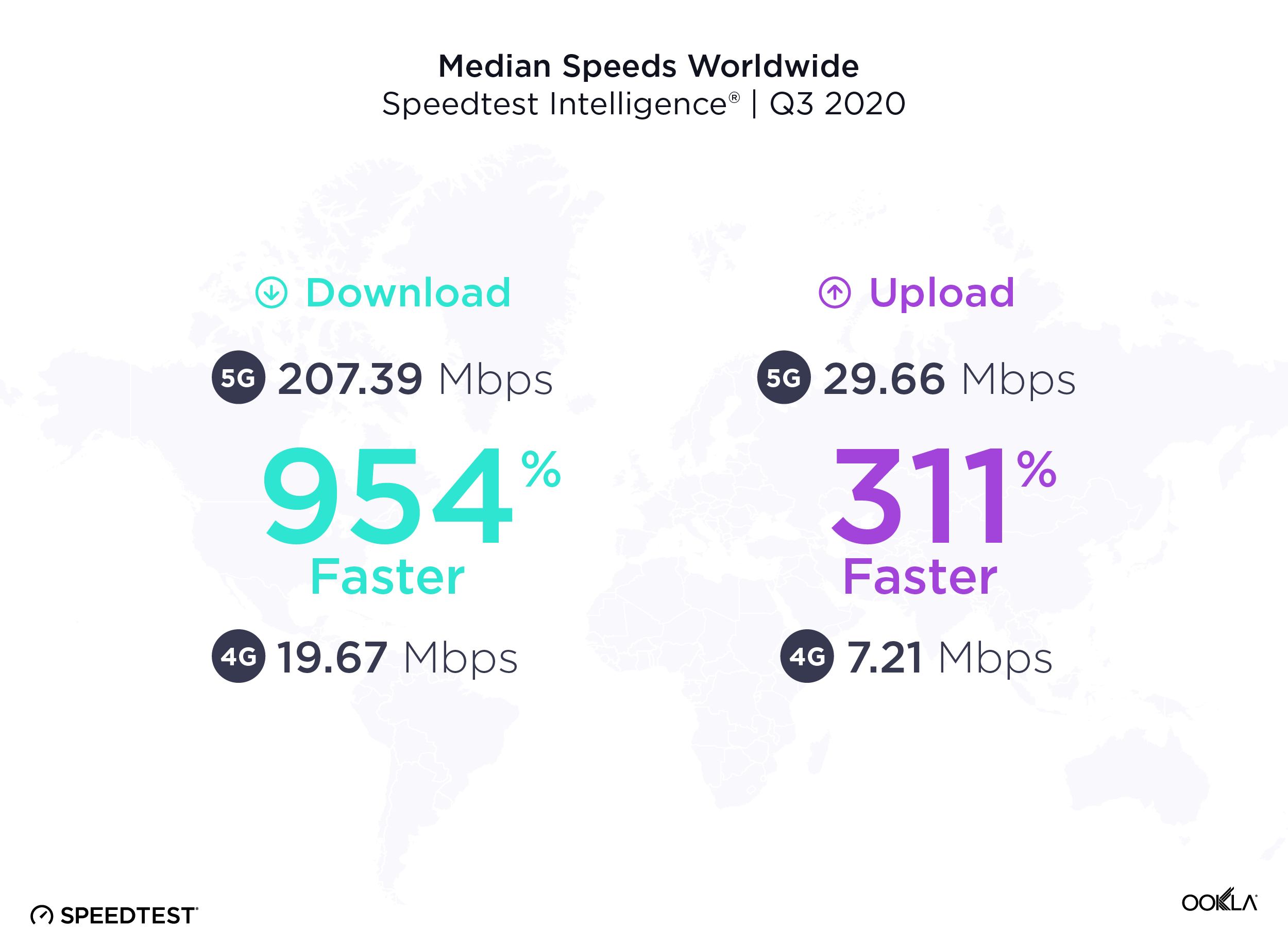
5G downloads were 954% faster than 4G at the global level
The worldwide median download speed over 5G was 954% faster than that over 4G during Q3 2020. Median upload speed over 5G was 311% faster than that over 4G. Consumers are eagerly adopting the new technology and many have wanted to measure the full throughput capacity of their network connection. In Q3 2020 alone, there were 4,324,788 Speedtest results over 5G.
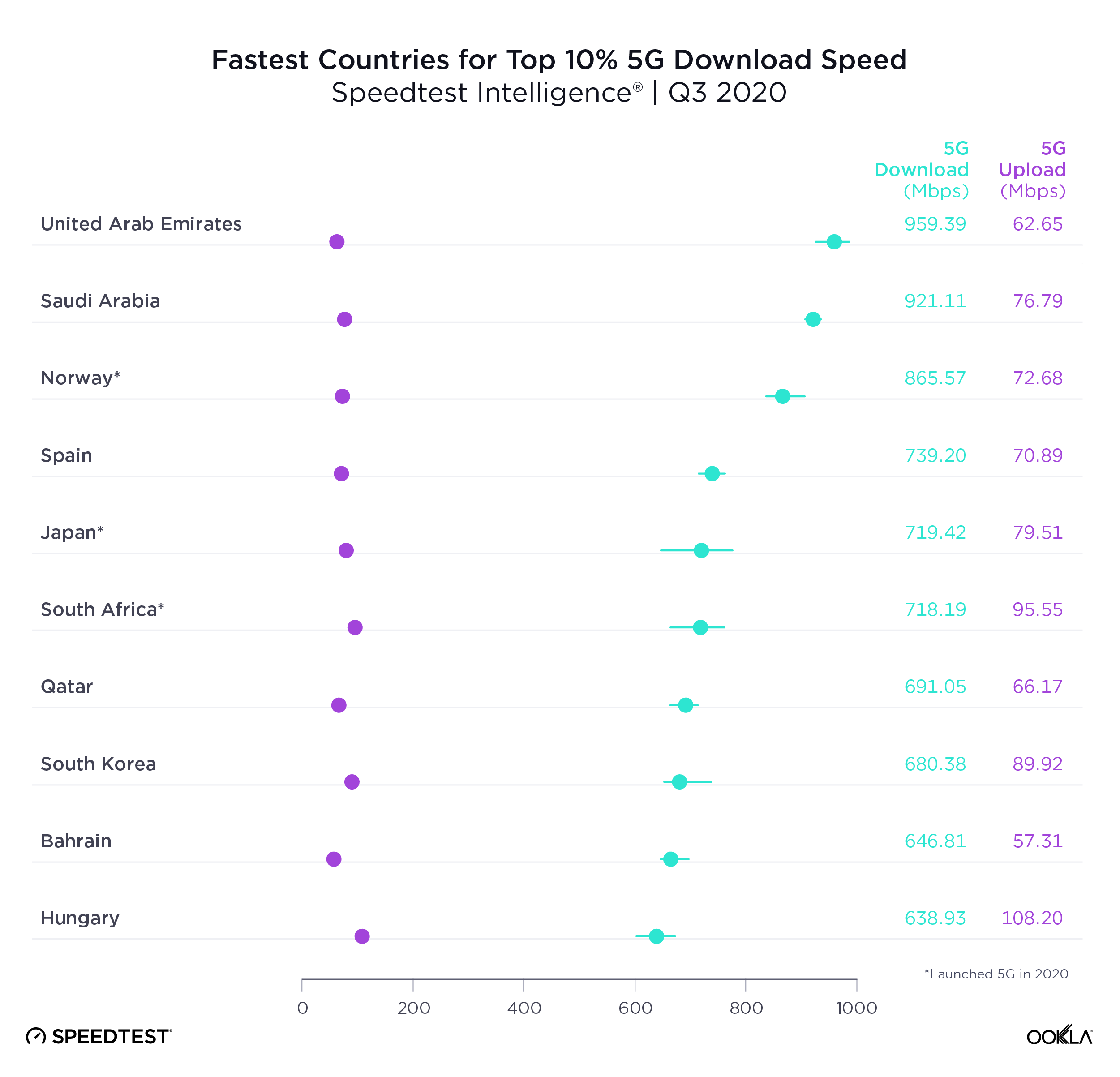
United Arab Emirates had the fastest 5G
United Arab Emirates topped the list of countries with the fastest top 10% 5G download speed in Q3 2020. Top 10% (or 90th percentile) measures the speeds seen by the fastest 10% of users and is a way to gauge what each country’s networks are capable of. Saudi Arabia was second for top 10% 5G download speed, Norway third, Spain fourth and Japan fifth.
Another way to measure 5G performance is to look at median 5G download speed, which is a better predictor of the kind of performance most 5G customers can expect. Norway was the country with the fastest median download speed over 5G during Q3 2020. U.A.E. was second in this category, South Africa third, Saudi Arabia fourth and Spain fifth.
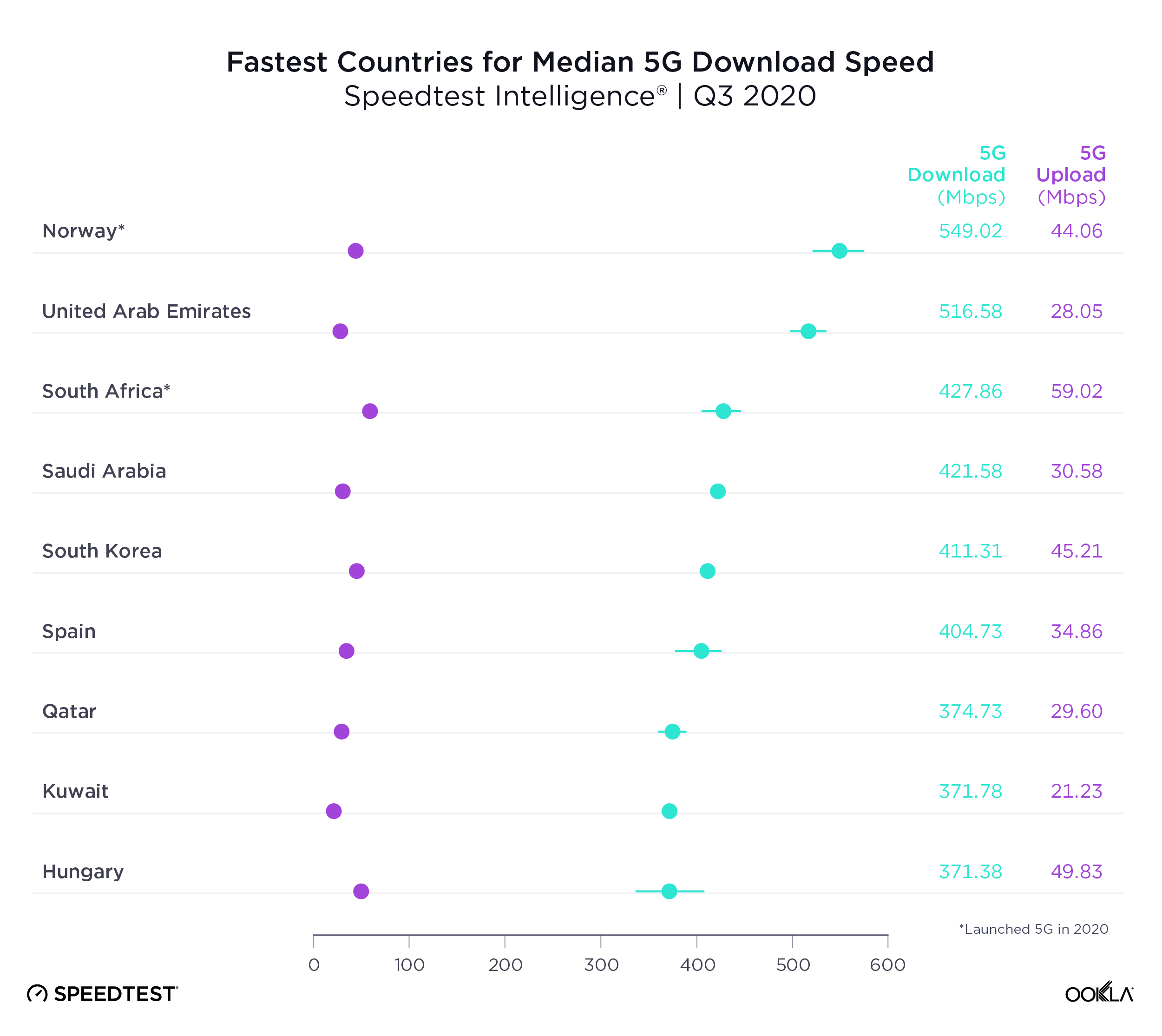
It’s notable that Japan was on the list of 10 countries with the fastest top 10% 5G download speed but not on the list of 10 countries with the fastest median download speed over 5G. No matter how fast a country’s mobile infrastructure is, many other factors go into median 5G speeds, including device adoption and spectrum allocation.
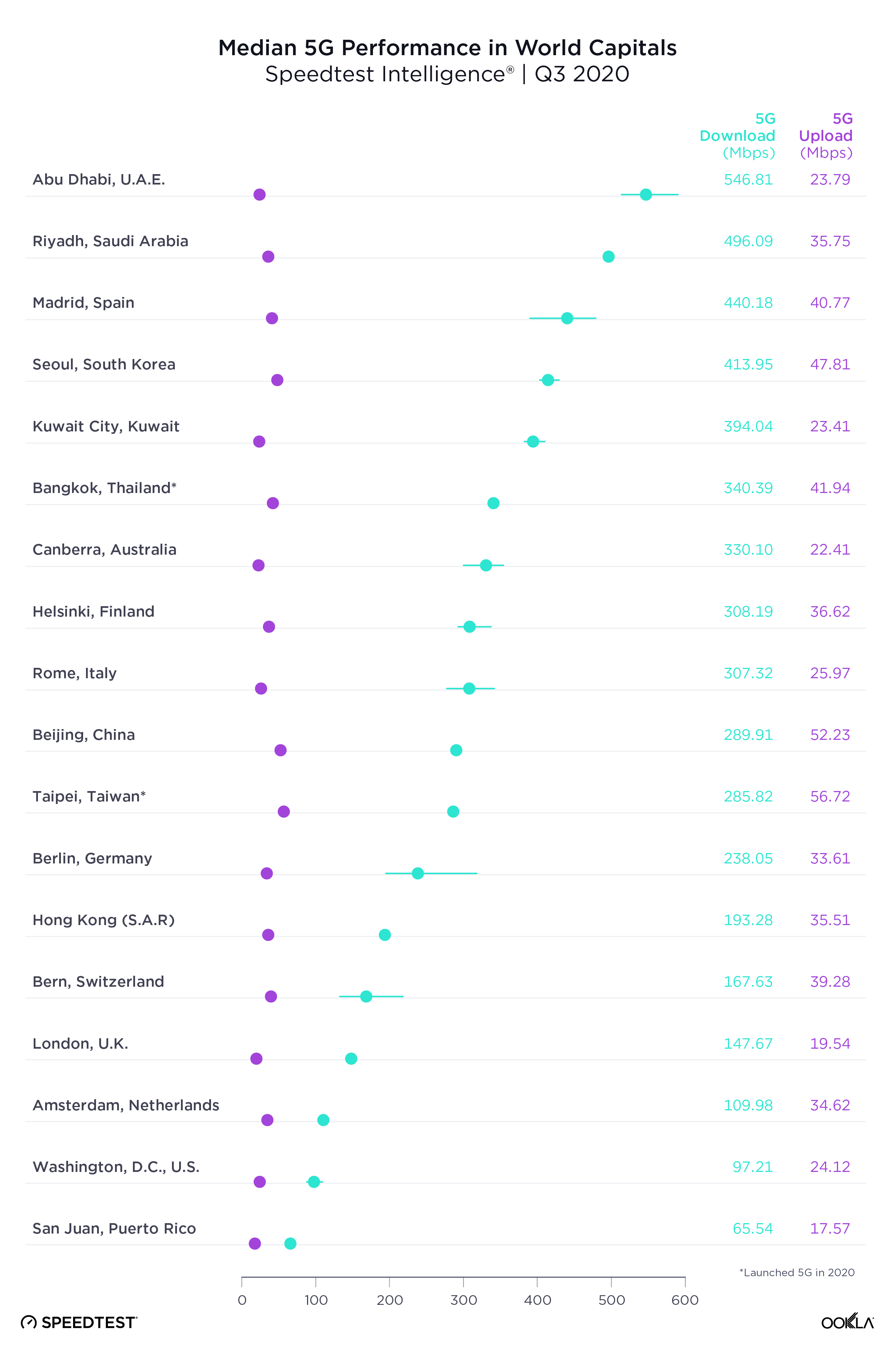
Abu Dhabi tops list of 5G speeds in world capitals
Our examination of 5G performance for 18 world capital cities with 5G during Q3 2020 found that Abu Dhabi had the fastest median download speed over 5G at 546.81 Mbps. Riyadh was second, Madrid third, Seoul fourth and Kuwait City fifth. As we saw at the country level, median upload speed was much lower than download speed.
We looked more closely at 5G performance across several intergovernmental organizations and trade blocs to get a better sense of how countries are performing in comparison to their neighbors and trade partners. We also calculated Time Spent on 5G, the proportion of time that users with 5G-capable devices spent on 5G, for each country.
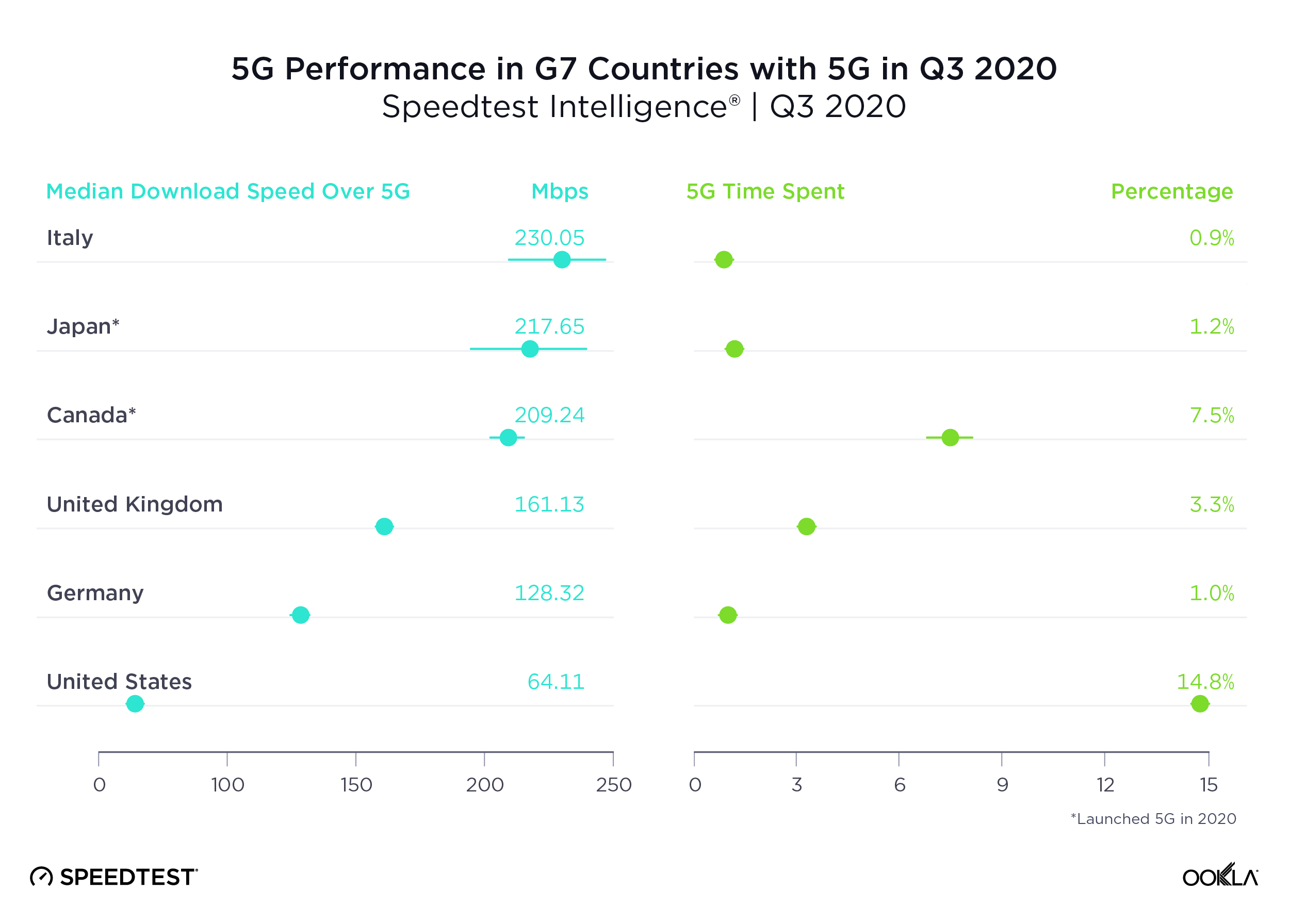
Italy had the fastest 5G among G7 countries, U.S. the slowest
Italy had the fastest median download speed over 5G of all the G7 countries. Japan was second, Canada third, the U.K. fourth and Germany fifth. The U.S. had the highest Time Spent on 5G, followed by Canada. For a deeper analysis of 5G in the U.K., read our previous coverage. Because France launched commercially available 5G only within the last couple of weeks, we have not included it on this table.
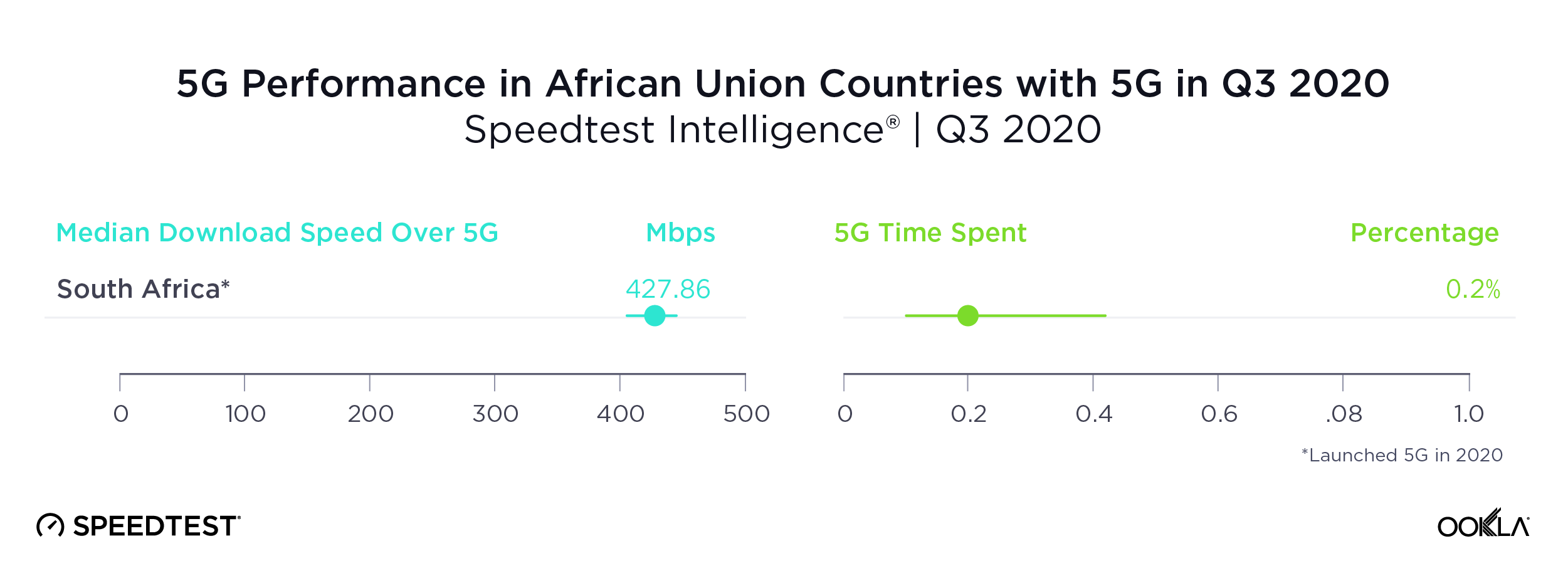
South Africa was the only country in the African Union with sufficient 5G to rate
As we saw above, South Africa’s impressive median download speed over 5G ranked the country third in the world during Q3 2020. South Africa was only one of two countries in the African Union to have commercially available 5G during Q3 2020. The other, Madagascar, did not have sufficient samples to properly analyze. Time Spent on 5G in South Africa was very low, an indication that 5G is not yet widely available there.
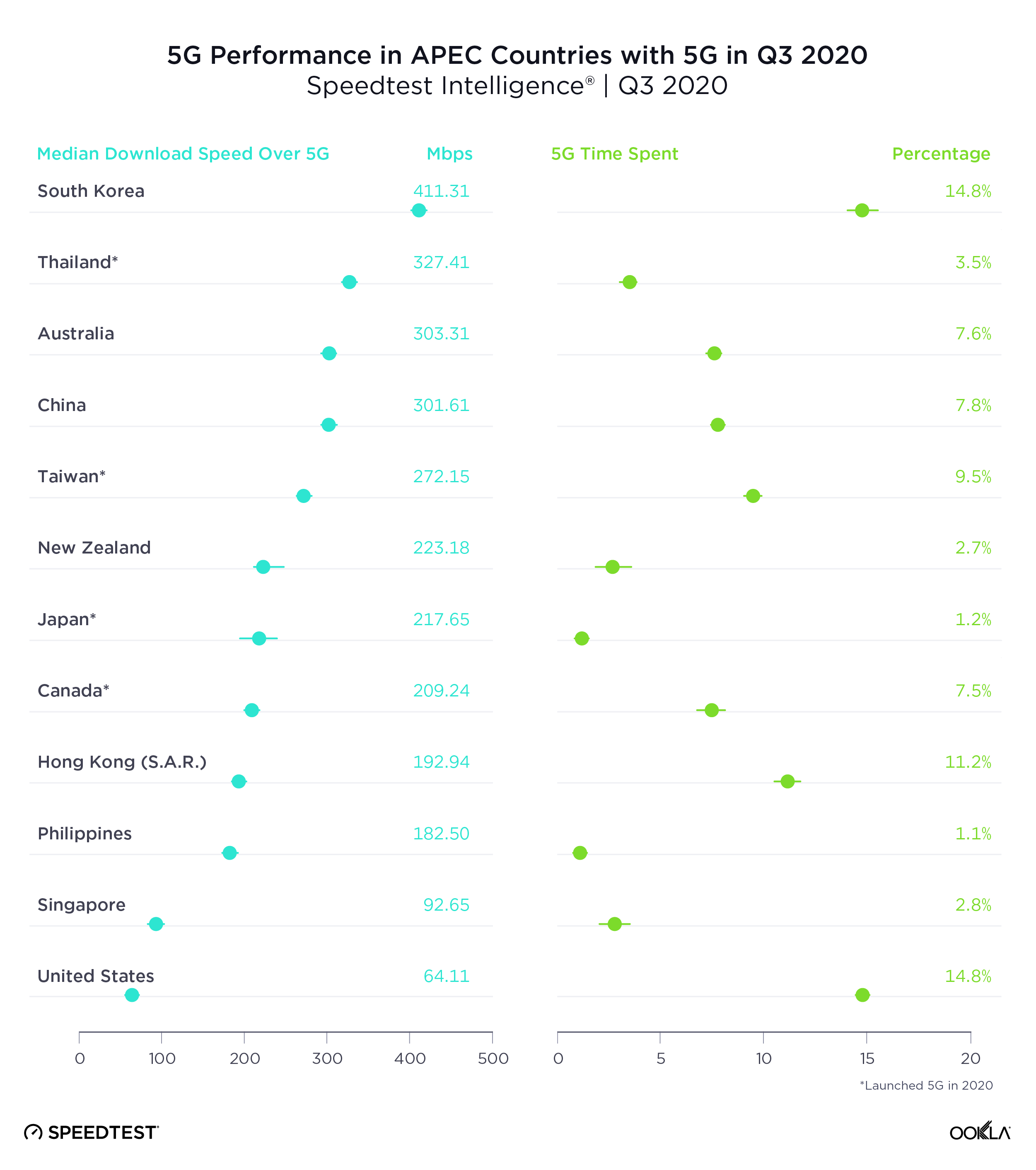
South Korea had the fastest 5G in APEC countries, U.S. the slowest
A median download speed over 5G of 411.11 Mbps put South Korea comfortably at the top of Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) countries with the fastest 5G during Q3 2020. Thailand was second, Australia third, China fourth and Taiwan fifth. 5G speeds represented the largest improvement over 4G in the Philippines where the median download speed over 4G during Q3 2020 (9.36 Mbps) was substantially lower than that of other countries on this list.
South Korea and the U.S. tied for highest Time Spent on 5G among APEC countries during Q3 2020, followed by Hong Kong and Taiwan.
Spain had the fastest 5G in the E.U., Poland the slowest
Spain showed the fastest median download speed over 5G among the 11 European Union (E.U.) countries with sufficient 5G samples to rank during Q3 2020. Hungary was second, Finland third, Romania fourth and Ireland fifth. Spain’s median download speed over 5G also represented the largest gain over 4G among all of these countries, partially because Spain had the second slowest median download speed over 4G. France is not included on this list because 5G did not become commercially available in the country until after Q3 2020.
The Netherlands had the highest Time Spent on 5G among E.U. countries during Q3 2020, indicating that customers with 5G phones are able to spend far more time on 5G there than in other E.U. countries. Denmark was second for Time Spent on 5G among EU countries in Q3 2020 and Finland third.
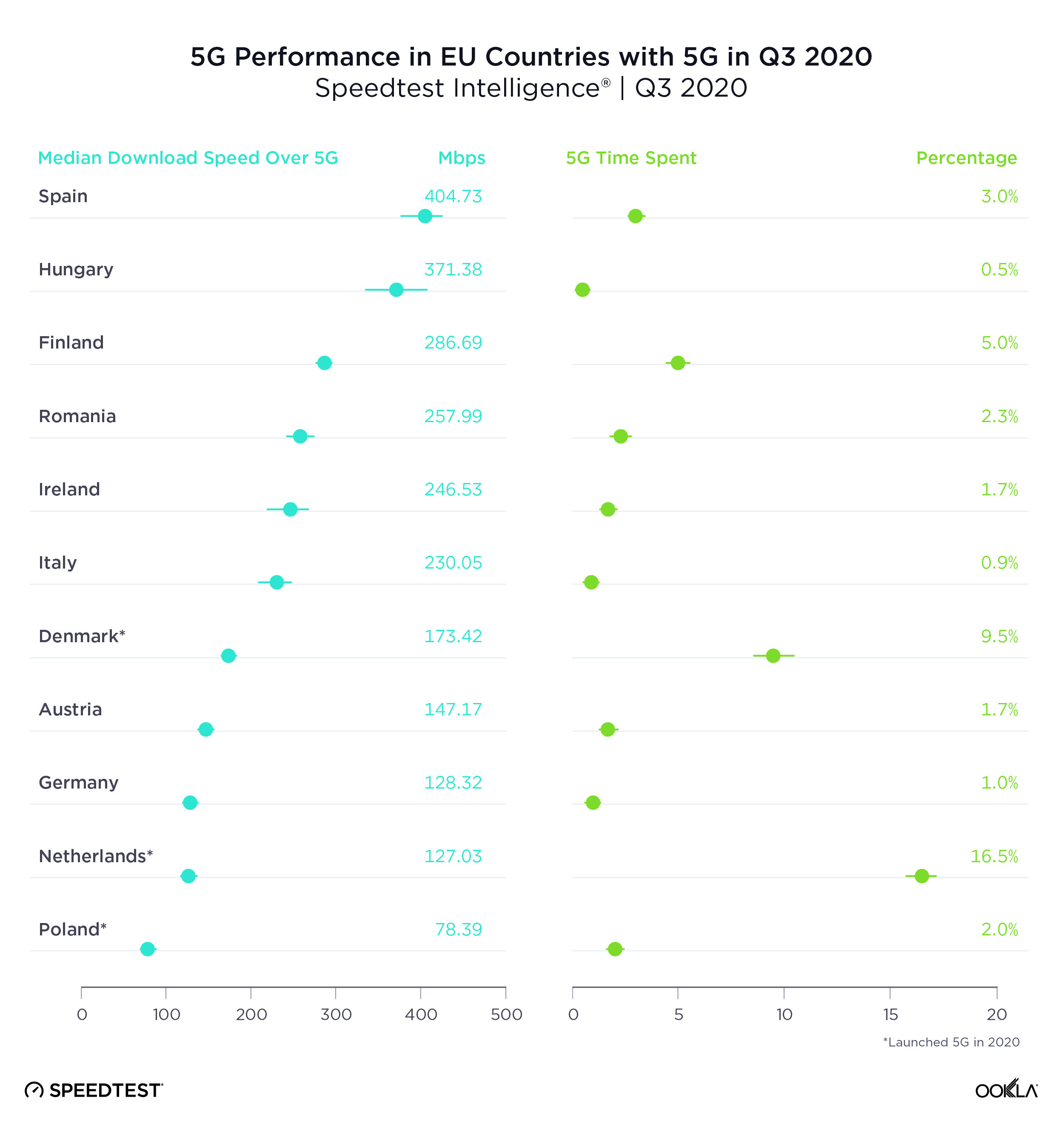
U.A.E had the fastest 5G in Gulf Cooperation Council Countries
With the second fastest median download speed over 5G in the world, U.A.E. was also the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) country with the fastest 5G during Q3 2020. Saudi Arabia was second and Qatar third. While Oman does have commercially available 5G, there were insufficient samples in the country during Q3 2020 to properly analyze performance.
5G represented the largest improvement over 4G in Kuwait and Bahrain, countries that had slower median download speeds over 4G than their neighbors.
Time Spent on 5G was relatively high in all the GCC countries on this list, except Bahrain, when compared to other countries in the world during Q3 2020. Qatar showed the highest Time Spent on 5G among GCC countries in Q3 2020 at 16.0%. U.A.E. was second and Saudi Arabia third.
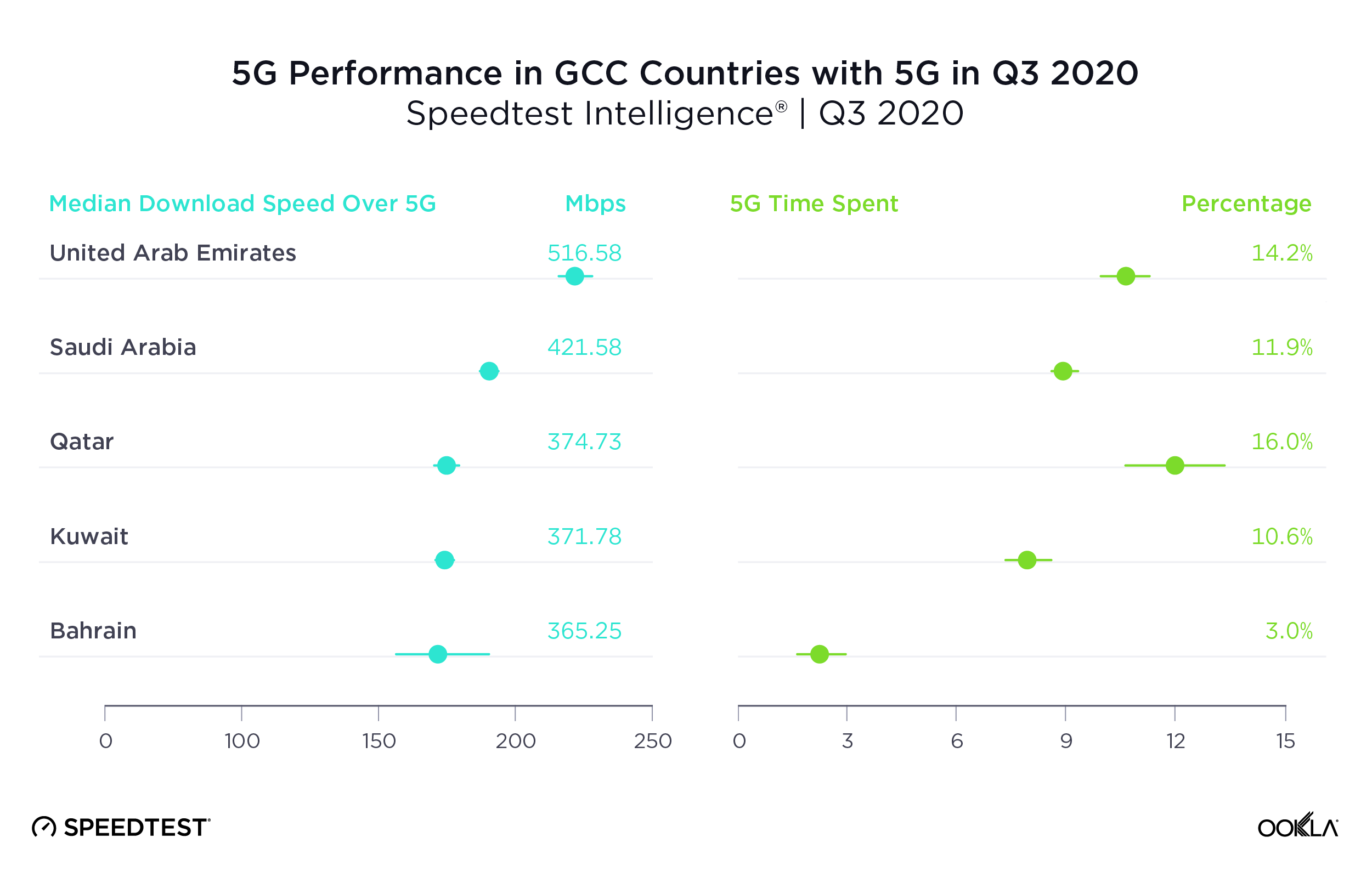
Brazil was the only MERCOSUR country with sufficient 5G to rate
Brazil’s median download speed over 5G of 84.60 Mbps during Q3 2020 may not seem fast for 5G, but it still puts Brazil well ahead of other countries in the Southern Common Market (MERCOSUR), most of which do not yet have 5G at all. We did see 5G results in Colombia, but there were insufficient samples to properly compare.
Time Spent on 5G in Brazil during Q3 2020 was not quite one percent, indicating that customers do not have much access to 5G yet.
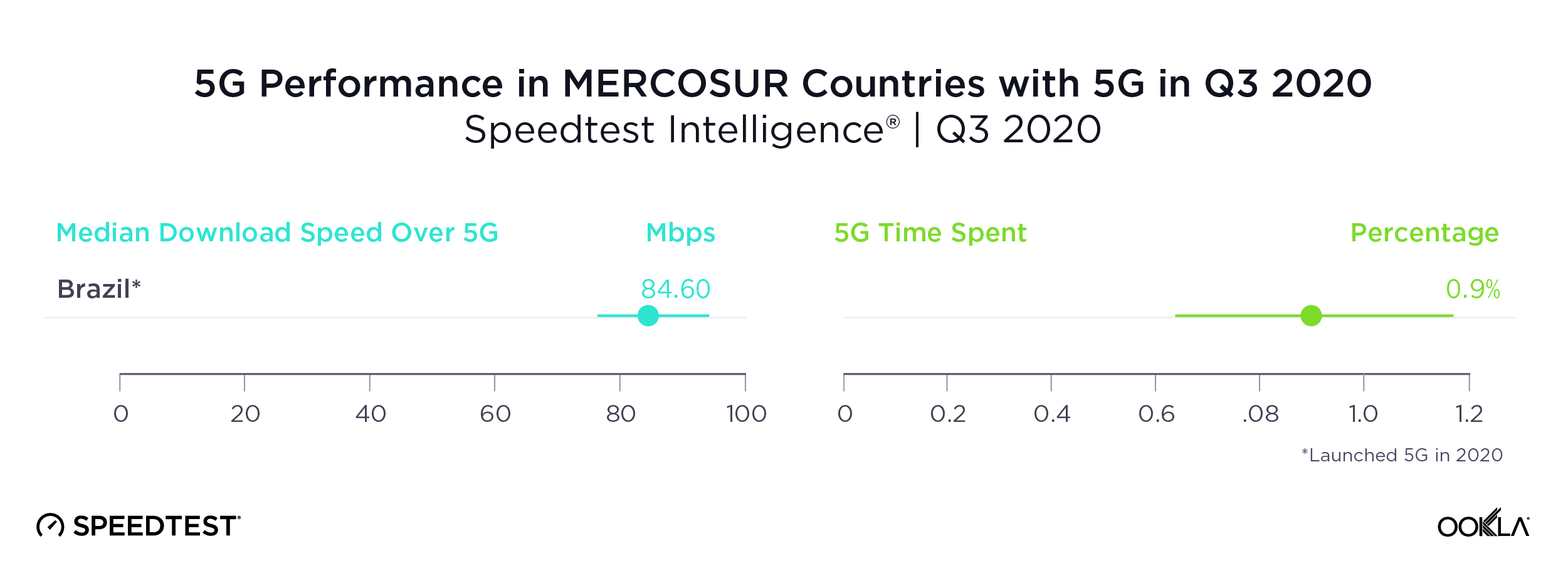
The U.S., Europe and Asia see widespread 5G coverage
Data from Cell Analytics™ shows a global view of 5G coverage in Q3 2020. This map, based on 5G connectivity data for opted-in Speedtest users, shows that 5G is spreading rapidly across the U.S., Europe, the Arabian Peninsula and Asia. In other regions, 5G is primarily available in larger cities, if at all.
99 countries worldwide had 5G, in 14,643 total cities
The number of countries with 5G deployments increased 62.3% between Q3 2019 and Q3 2020, with 99 countries having 5G deployments at the end of Q3 2020, according to the Ookla 5G Map™. There were 14,643 cities worldwide with 5G deployments at the end of Q3 2020, a 1,671% increase over Q3 2019. The total number of deployments worldwide was 17,046. The counts here and throughout this section include commercially available 5G as well as 5G networks with limited availability and those in pre-release.
| Country |
Numbers of Cities with 5G |
| United States |
7,583 |
| Germany |
2,312 |
| Austria |
1,104 |
| Netherlands* |
1,009 |
| Switzerland |
554 |
| Thailand* |
325 |
| Ireland |
214 |
| Puerto Rico |
187 |
| United Kingdom |
169 |
| Kuwait |
97 |
The U.S. had the most cities with 5G deployments at the end of Q3 2020 with 7,583. Germany was second, Austria third, the Netherlands fourth and Switzerland fifth. A deployment is when a provider has some level of 5G presence in a city. A city can have multiple deployments when more than one provider is present.
| Country |
5G Deployments as of Q3 2020 |
% Change Q3 2020 vs Q3 2019 |
| Netherlands* |
1,071 |
50,350% |
| Thailand* |
451 |
32,401% |
| United States |
7,808 |
21,566% |
| Germany |
2,417 |
11,460% |
| Canada* |
93 |
7,600% |
| Austria |
1,173 |
4,918% |
| Ireland |
236 |
4,180% |
| Poland |
81 |
3,150% |
| Japan* |
75 |
2,050% |
| Oman |
50 |
2,000% |
The Netherlands showed the largest percentage change in the number of 5G deployments between Q3 2019 and Q3 2020 with a 50,350% jump from two deployments in Q3 2019 to 1,071 in Q3 2020. Thailand saw the second largest percentage increase, the U.S. third, Germany fourth and Canada fifth.
Most early trials and commercial deployments of 5G spectrum allocations around the world have been centered around fallow swaths of the mid-band (3.3 GHz – 4.2 GHz) spectrum. With the recent commercialization of Dynamic Spectrum Sharing (DSS) across all major 5G infrastructure vendors, there is now increasing demand for 5G support on many existing 4G frequencies, ranging from 600 MHz to 2.5 GHz. In unique 5G markets like Japan, there is an additional need for the 4.5 GHz band as well as the millimeter wave (FR2).
In the United States, early deployments leveraged millimeter wave frequency bands in the 28 GHz and the 39 GHz, which delivered impressive speeds in a very constrained footprint. The rapid 5G deployment in the 600 MHz band has added a substantial nationwide 5G footprint — and with that, much wider 5G availability for many more Americans. With the recent merger between T-Mobile and Sprint, the deployment of 2.5 GHz spectrum has been significantly accelerated, which should improve both network efficiency and user experience on T-Mobile’s network. Additionally, next year’s availability of 5G Carrier Aggregation will allow T-Mobile to combine 600 MHz with 2.5 GHz to deliver improved 5G speeds on top of the existing nationwide footprint. In addition, DSS has recently been deployed by AT&T and Verizon, which allows operators to choose from existing low-band spectrum assets (850 MHz) and deliver both LTE and 5G at the same time. This feature alone doesn’t add a significant boost in perceived user experience, but will certainly improve the 5G footprint.
China showed the highest percentage of 5G test samples
Another way to measure 5G adoption is to look at the proportion of samples taken over 5G relative to the total number of samples on all technologies. Speedtest Intelligence is uniquely positioned to measure global growth in 5G because of the worldwide adoption of Speedtest apps. China had the highest percentage of 5G Speedtest results compared to other mobile technology types in Q3 2020 at 18.9%. South Korea was second, Hong Kong third, Puerto Rico fourth and Qatar fifth.
| Country |
5G Samples as a % of Total |
| China |
18.9% |
| South Korea |
15.8% |
| Hong Kong (S.A.R.)* |
7.9% |
| Puerto Rico |
6.7% |
| Qatar |
5.7% |
| United States |
5.5% |
| Netherlands* |
4.9% |
| United Arab Emirates |
4.6% |
| Kuwait |
4.6% |
| Australia |
4.2% |
What 5G will look like in 2021
With recently announced device chipset advancements expected in 2021, including 5G Carrier Aggregation, operators will be able to combine two 5G frequency bands in the sub-6GHz (FR1) range, allowing not only faster speeds, but also greater coverage. More importantly, the ability to combine Frequency Division Duplexing (FDD) and Time Division Duplexing (TDD) FR1 channels will enable operators to leverage low-band frequencies (sub-1GHz) for uplink transmissions (user device to cell site), while combining the low-band with the mid-band (2.5 GHz, 3.5 GHz) on the downlink. This should significantly expand the availability of fast 5G download speeds across larger geographies.
Similarly, DSS — which is a stepping stone to standalone 5G and allows for the simultaneous delivery of 4G and 5G technology on the same spectrum slice — will enable operators to combine already-deployed FDD spectrum with dedicated mid-band spectrum for an enhanced standalone 5G experience. This will unlock the full potential of 5G networks, such as ultra low latency and network slicing, while delivering an improved mobile experience to users.
Where 5G fails to reach
During Q3 2020 Speedtest Intelligence showed 55 countries in the world (with more than 200 samples) where more than 20% of samples were from 2G and 3G connections (combined). These are countries where, in many cases, 5G is still aspirational. As excited as we are about the expansion of 5G, we do not want to see these countries left behind.
| Country |
2G & 3G Samples |
4G Samples |
| Turkmenistan |
74.9% |
25.1% |
| Rwanda |
52.3% |
47.7% |
| Iraq |
49.4% |
50.6% |
| Belarus |
46.5% |
53.5% |
| Afghanistan |
46.0% |
54.0% |
| Antigua and Barbuda |
40.2% |
59.8% |
| Tajikistan |
40.2% |
59.8% |
| Suriname |
39.7% |
60.3% |
| Haiti |
37.7% |
62.3% |
| Syria |
37.5% |
62.5% |
| Ghana |
36.0% |
64.0% |
| Ethiopia |
35.0% |
65.0% |
| Mozambique |
34.7% |
65.3% |
| Benin |
34.3% |
65.7% |
| Angola |
34.1% |
65.9% |
| El Salvador |
32.5% |
67.5% |
| Moldova |
31.8% |
68.2% |
| Venezuela |
30.3% |
69.7% |
| Tanzania |
30.0% |
70.0% |
| Papua New Guinea |
29.5% |
70.5% |
| Jamaica |
29.4% |
70.6% |
| Sudan |
29.2% |
70.8% |
| Algeria |
29.0% |
71.0% |
| Namibia |
28.5% |
71.5% |
| Zimbabwe |
28.5% |
71.5% |
| Somalia |
28.4% |
71.6% |
| Nicaragua |
28.1% |
71.9% |
| Armenia |
28.1% |
71.9% |
| Bosnia and Herzegovina |
28.1% |
71.9% |
| Uzbekistan |
27.8% |
72.2% |
| Cameroon |
27.5% |
72.5% |
| Zambia |
27.4% |
72.6% |
| Uganda |
26.6% |
73.4% |
| Trinidad and Tobago |
26.6% |
73.4% |
| Honduras |
26.5% |
73.5% |
| Bangladesh |
26.3% |
73.7% |
| Burkina Faso |
26.0% |
74.0% |
| Ukraine |
25.8% |
74.2% |
| Nigeria |
25.7% |
74.3% |
| DR Congo |
24.6% |
75.4% |
| Costa Rica |
24.3% |
75.7% |
| Botswana |
24.1% |
75.9% |
| Libya |
22.9% |
77.1% |
| Azerbaijan |
22.9% |
77.1% |
| Ecuador |
22.8% |
77.2% |
| Mali |
22.4% |
77.6% |
| Mongolia |
21.8% |
78.2% |
| Maldives |
21.6% |
78.4% |
| Mauritius |
21.3% |
78.7% |
| Tunisia |
21.0% |
79.0% |
| Belize |
20.7% |
79.3% |
| Laos |
20.5% |
79.5% |
| Kenya |
20.3% |
79.7% |
| Paraguay |
20.1% |
79.9% |
| Côte d’Ivoire |
20.0% |
80.0% |
In markets where 4G layers haven’t been deployed or substantially covered, end users fall back to the circuit-switched network (2G, 3G). These decades-old network technologies should be sufficient for basic voice and texting, social media, and navigation apps, but cannot deliver rich media experiences or video calling. Unfortunately, many countries on this list are places where consumers rely primarily on mobile phones for their internet connectivity.
5G is radically changing the speeds and capabilities of mobile networks around the world. If the current growth rate continues, it won’t be long before most nations have access to 5G. But there are nations and subsets of subscribers who may not see the benefits of 5G for years to come. We will continue reporting on 5G achievements across the globe and watching speeds in general on the Speedtest Global Index™.