Consumers across the world have been waiting for the recent launches of new Apple iPhone 14 devices and the Samsung Galaxy Z Fold4. With new chipsets and technologies, Ookla® was curious to see how much faster these devices were performing against previous models, so we used Speedtest Intelligence® to look at data from select countries during the first few weeks after launch. We compared how the iPhone 14 devices are performing against their iPhone 13 counterparts over 5G and how the Samsung Galaxy Z Fold4 is performing against the Galaxy Z Fold3 over 5G.
Note that device data differs across markets due to a variety of factors, including: 5G investments by governments and mobile operators, different 5G spectrum allocations by operator, 5G Availability, the number of 5G deployments, and other differences, including mobile 5G plans. Furthermore, it should be noted that the iPhone 14 Pro Max and Pro models launched in select markets on different days than the iPhone 14, which is why the date ranges differ slightly in each market in our analysis.
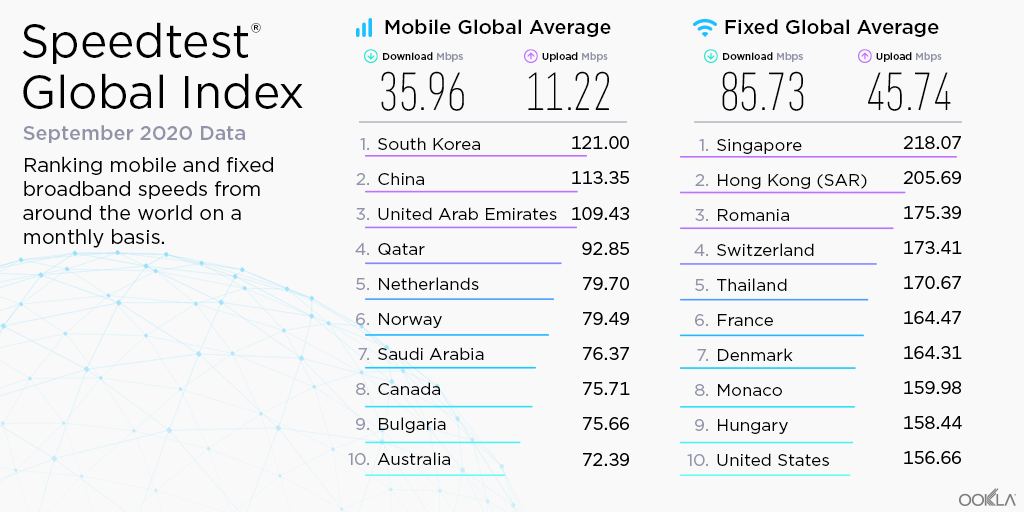
Key takeaways:
- The Samsung Galaxy Z Fold4 outperformed the Galaxy Z Fold3 in every country we surveyed except Australia, and performed about the same as the Fold3 in South Korea and Taiwan.
- The new Apple iPhone 14 models outperformed their iPhone 13 counterparts in every country.
Key improvements to the new Galaxy Z Fold4 and iPhone 14
Consumers almost always want to know if the newest technology is worth the upgrade when they’re investing in a costly new phone. Each of these devices has various upgrades, but when it comes to performance, here’s a quick list of what’s different between the new and older models.
Samsung Galaxy Z Fold4 vs. Galaxy Z Fold3
- The Samsung Galaxy Z Fold4 has the Qualcomm Snapdragon 8+ Gen 1 chipset as well as the Qualcomm Snapdragon X65 5G modem whereas the Galaxy Z Fold3 has the older Snapdragon 888 5G chipset.
- The Fold4 has an upgraded Octa-core (1×3.19 GHz Cortex-X2 & 3×2.75 GHz Cortex-A710 & 4×1.80 GHz Cortex-A510) and the Fold3 has an Octa-core (1×2.84 GHz Cortex-X1 & 3×2.42 GHz Cortex-A78 & 4×1.80 GHz Cortex-A55).
Apple iPhone 14 vs. iPhone 13
- The Apple iPhone 14 Pro and Pro Max have Apple A16 CPU chipsets, which we expect to be faster than the iPhone 13s, whereas the iPhone 14 has the Apple A15 CPU chipset.
- The iPhone 14 Pro and Pro Max have the new Qualcomm Snapdragon X65 chipset for 5G, which also supports the 2.4 GHz n53 band for satellite, while the iPhone 14 has a Qualcomm Snapdragon X60 for 5G, which the iPhone 13 Pro Max and 13 Pro also use.
- The Apple iPhone 13 models have 4 GB of memory, whereas the newer iPhone 14 models have 6 GB of memory.
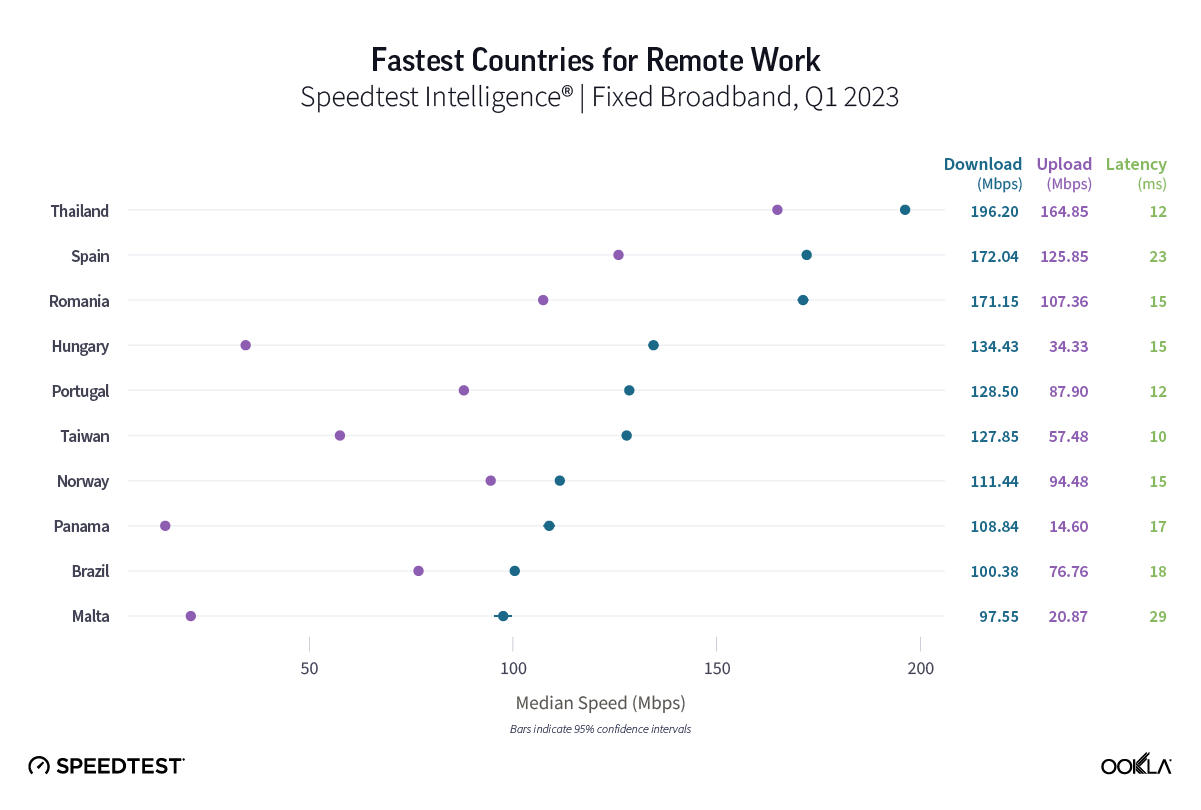
Australia
Samsung Galaxy Z Fold
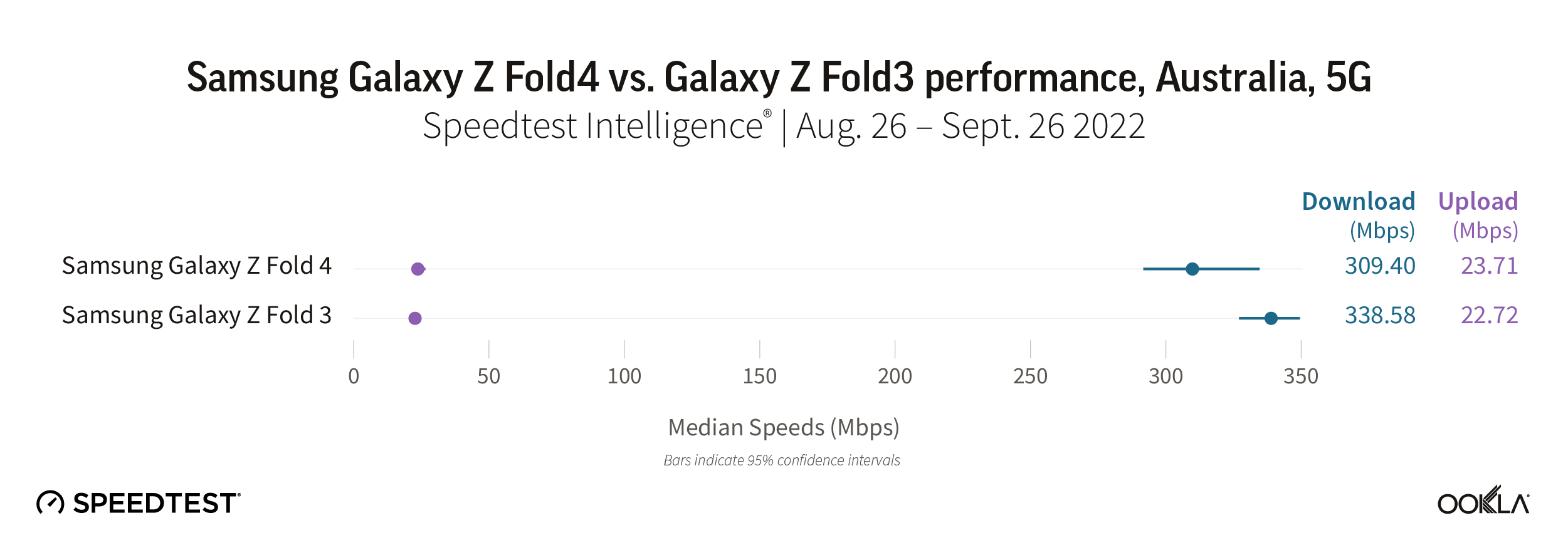
Speedtest Intelligence shows the Galaxy Z Fold4 was not statistically faster than the Fold3 in Australia. The Galaxy Z Fold3 had a median 5G download speed at 338.58 Mbps and the Fold4 at 309.40 Mbps. The median upload speed was roughly the same, with the Fold4 achieving 23.71 Mbps and the Fold3 at 22.72 Mbps.
Recommendation: Australian Galaxy Z Fold3 users may want to wait to upgrade their phone until speeds improve, unless you really want other new features the Fold4 offers.
Apple iPhone
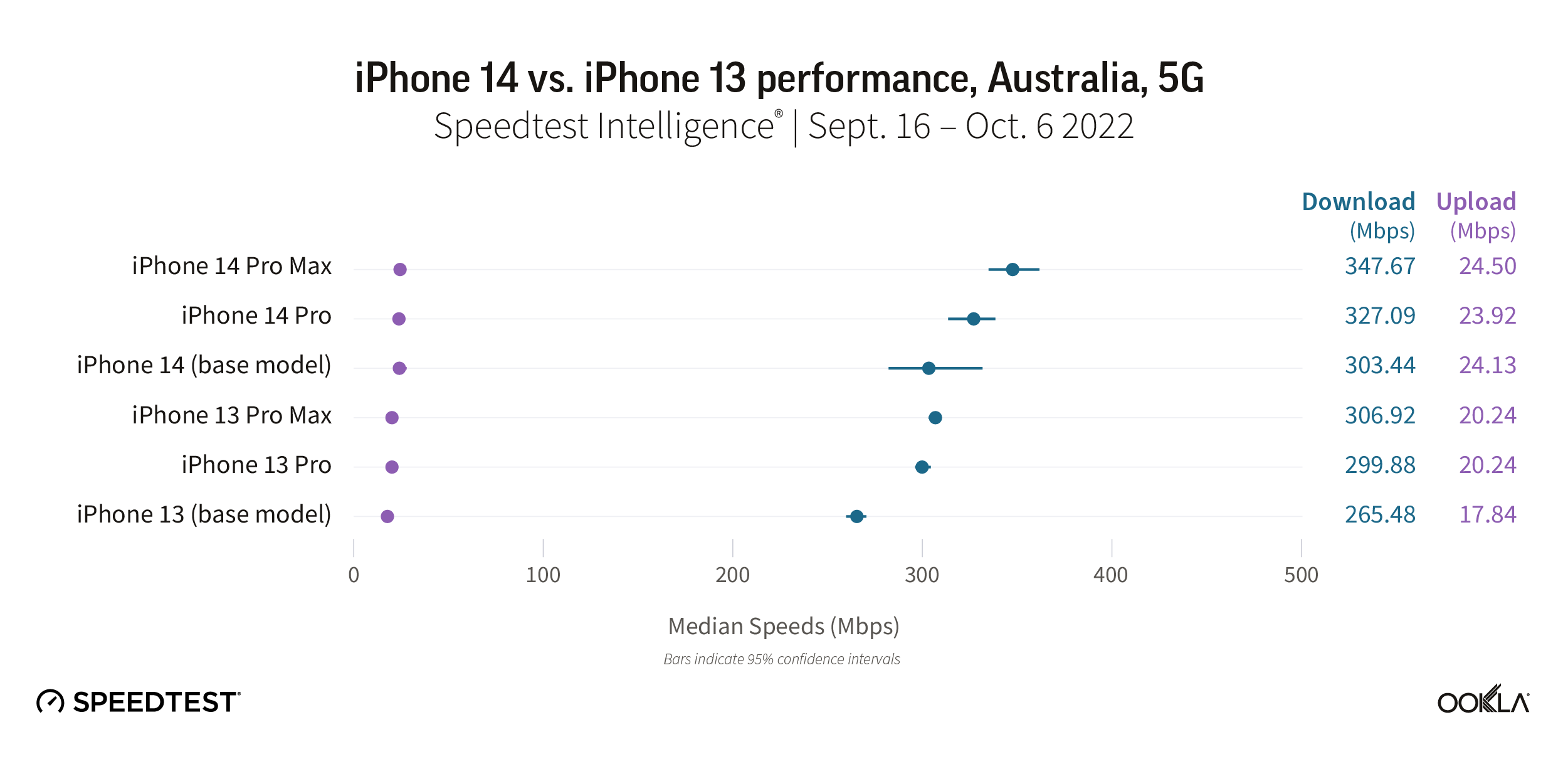
Our data shows every new iPhone 14 model offering faster median download speeds than their iPhone 13 counterparts in Australia. The iPhone 14 Pro Max had the fastest median 5G download speed at 347.67 Mbps, followed by the iPhone 14 Pro (327.09 Mbps). Even the iPhone 14 base model was comparable to the iPhone 13 Pro Max at 303.44 Mbps to 306.92 Mbps, as well as the iPhone 13 Pro (299.88 Mbps). The iPhone 13 base model “lagged” behind at a fast 265.48 Mbps.
Upload speeds were generally similar, with the iPhone 14 models ranging slightly faster from 23.92 Mbps to 24.50 Mbps, and the iPhone 13 models ranging from 17.84 Mbps to 20.24 Mbps.
Recommendation: iPhone 13 users in Australia who want faster speeds should consider upgrading their phone to a new iPhone 14 model.
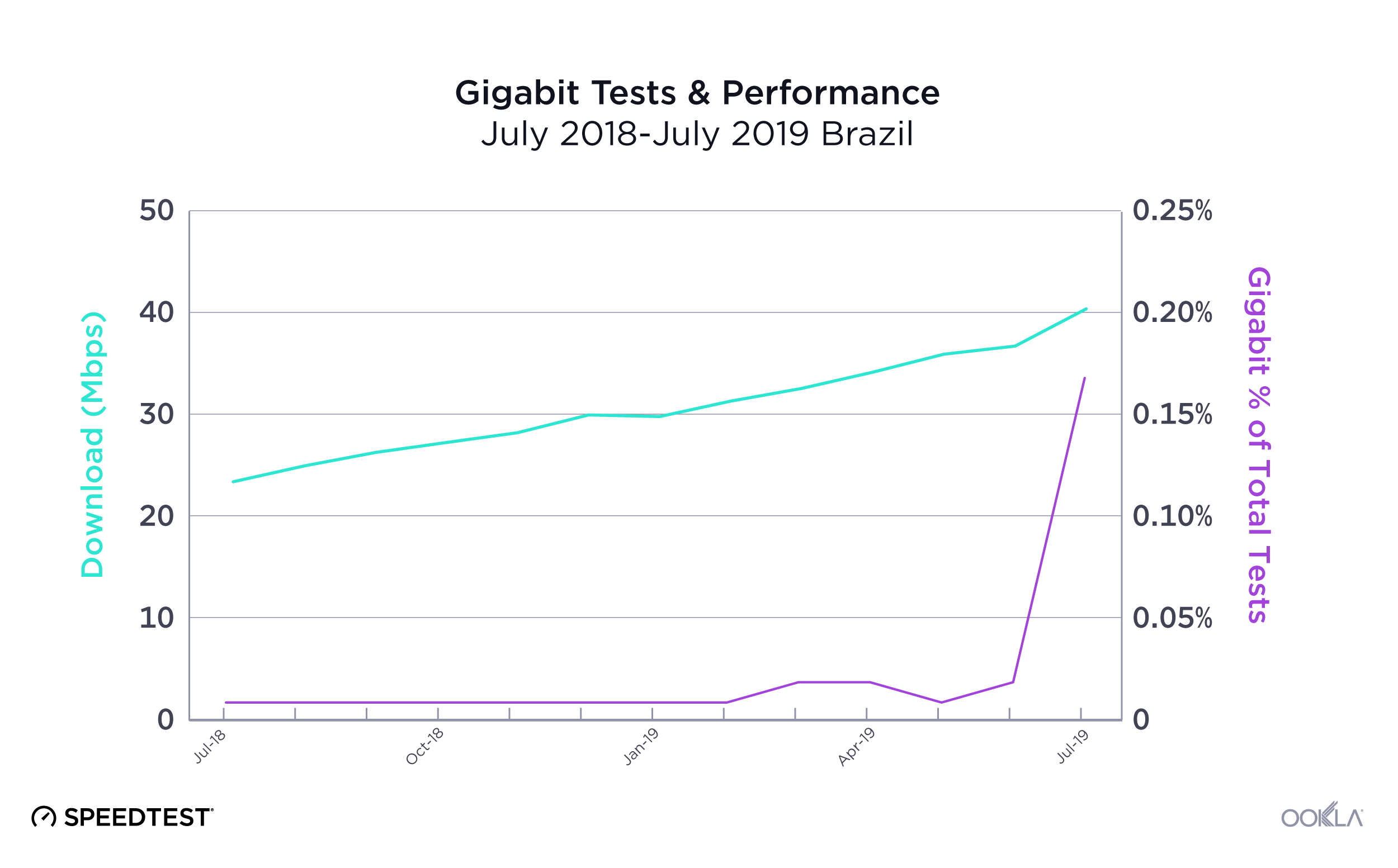
Brazil
Samsung Galaxy Z Fold
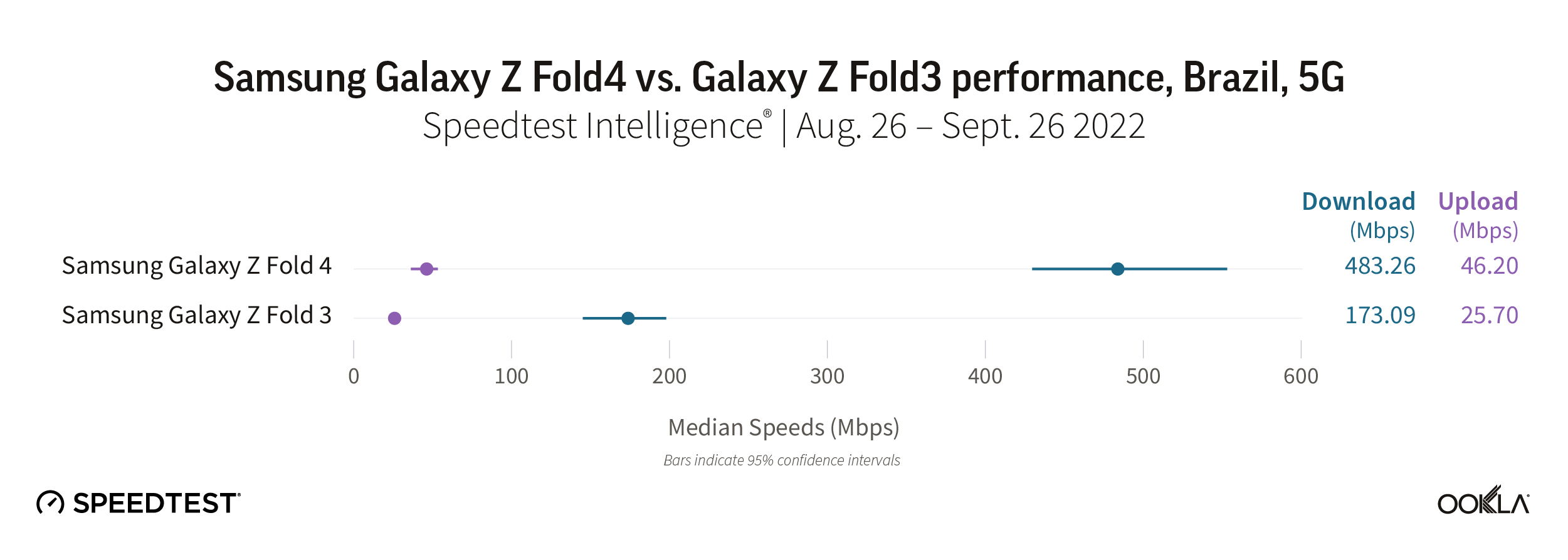
During the first month of the Galaxy Z Fold4’s launch, Brazilian 5G consumers who upgraded saw tremendous improvements over the Galaxy Z Fold3. The Fold4 dramatically outpaced the Fold3 with a median download of 483.26 Mbps and median upload of 46.20 Mbps to the Fold3’s 173.09 Mbps download and 25.70 Mbps upload.
Recommendation: Galaxy Z Fold3 users in Brazil should upgrade their phone to the Galaxy Z Fold4 if they have access to 5G.
Apple iPhone
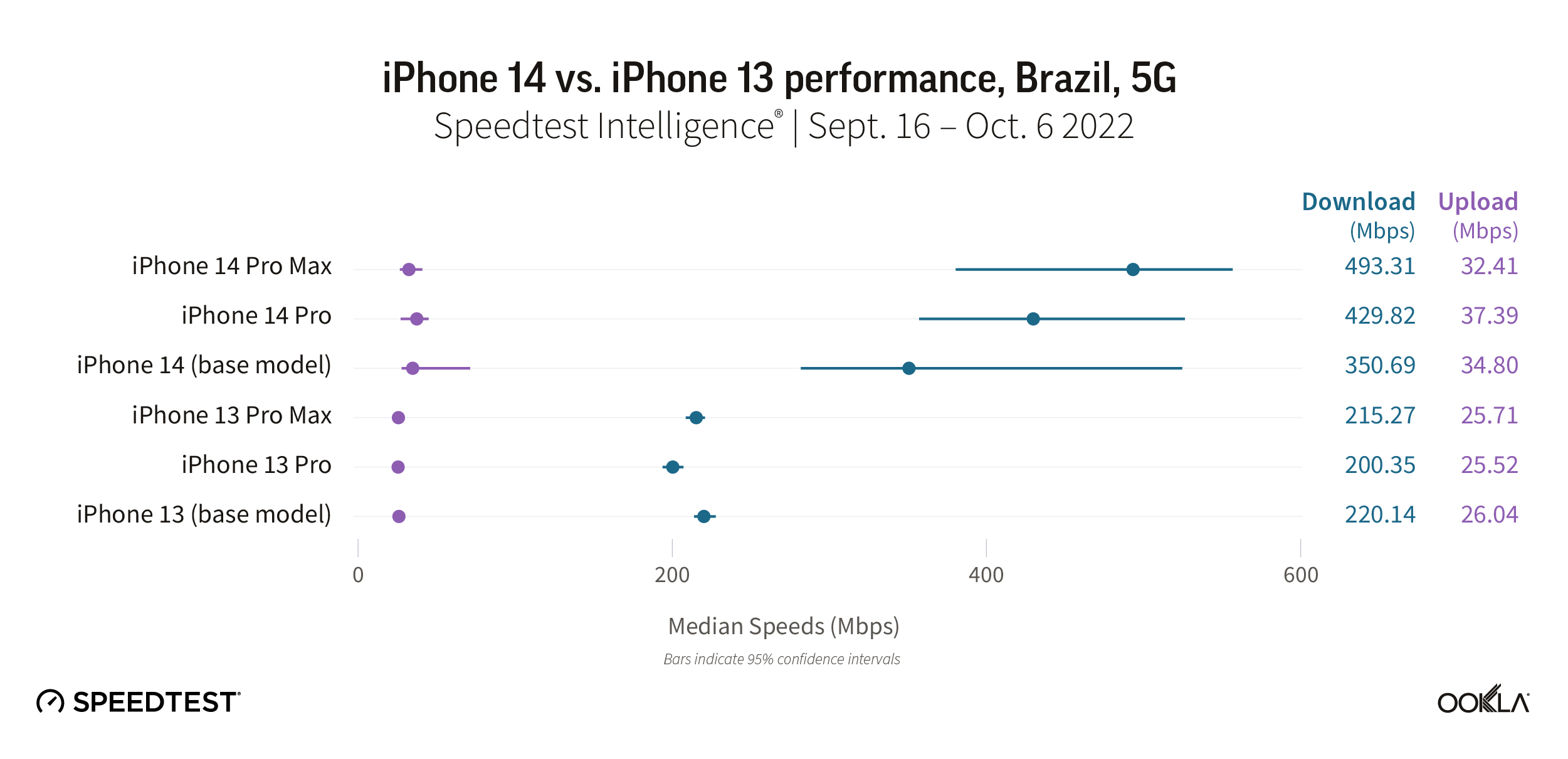
Speedtest Intelligence reveals that every iPhone 14 model performed much faster than their iPhone 13 counterparts on 5G in Brazil. The iPhone 14 Pro Max raced ahead at 493.31 Mbps, then the iPhone 14 Pro (429.82 Mbps), and iPhone 14 (350.69 Mbps). The iPhone 13 (220.14 Mbps), iPhone 13 Pro Max (215.27 Mbps), and iPhone 13 Pro (200.35 Mbps) trailed behind.
Upload speeds were faster on the iPhone 14 models, ranging from 32.41 Mbps to 37.39 Mbps, whereas the iPhone 13 models ranged from 25.52 Mbps to 26.04 Mbps.
Recommendation: Brazilian iPhone 13 users should absolutely consider an upgrade to the new iPhone.
Canada
Samsung Galaxy Z Fold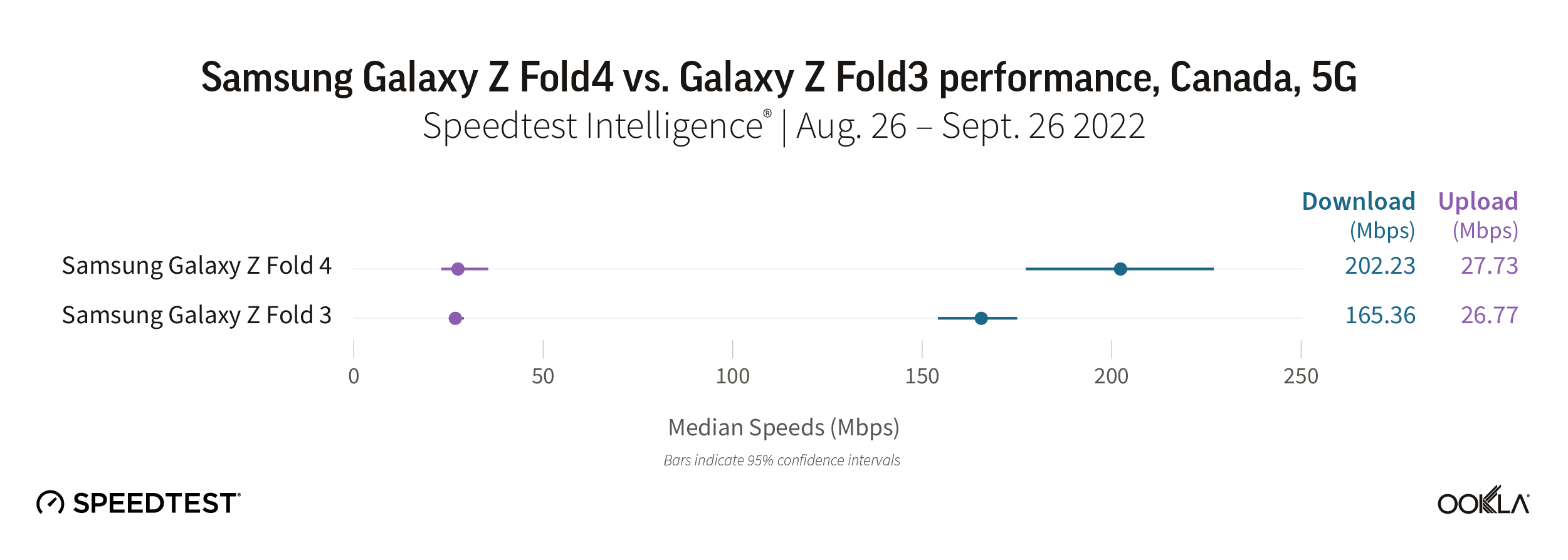
Canadian consumers saw a moderate increase in 5G download speed if they upgraded their phone from the Galaxy Z Fold3 to the Fold4, with the Fold4 achieving a median download speed of 202.23 Mbps to the Fold3’s 165.36 Mbps. Upload speed remained relatively flat between the two models with the Fold4 achieving 27.73 Mbps and the Fold3 26.77 Mbps.
Recommendation: Canadian Galaxy Z Fold3 users should feel confident that upgrading their phone to the Fold4 will give them a faster 5G experience.
Apple iPhone
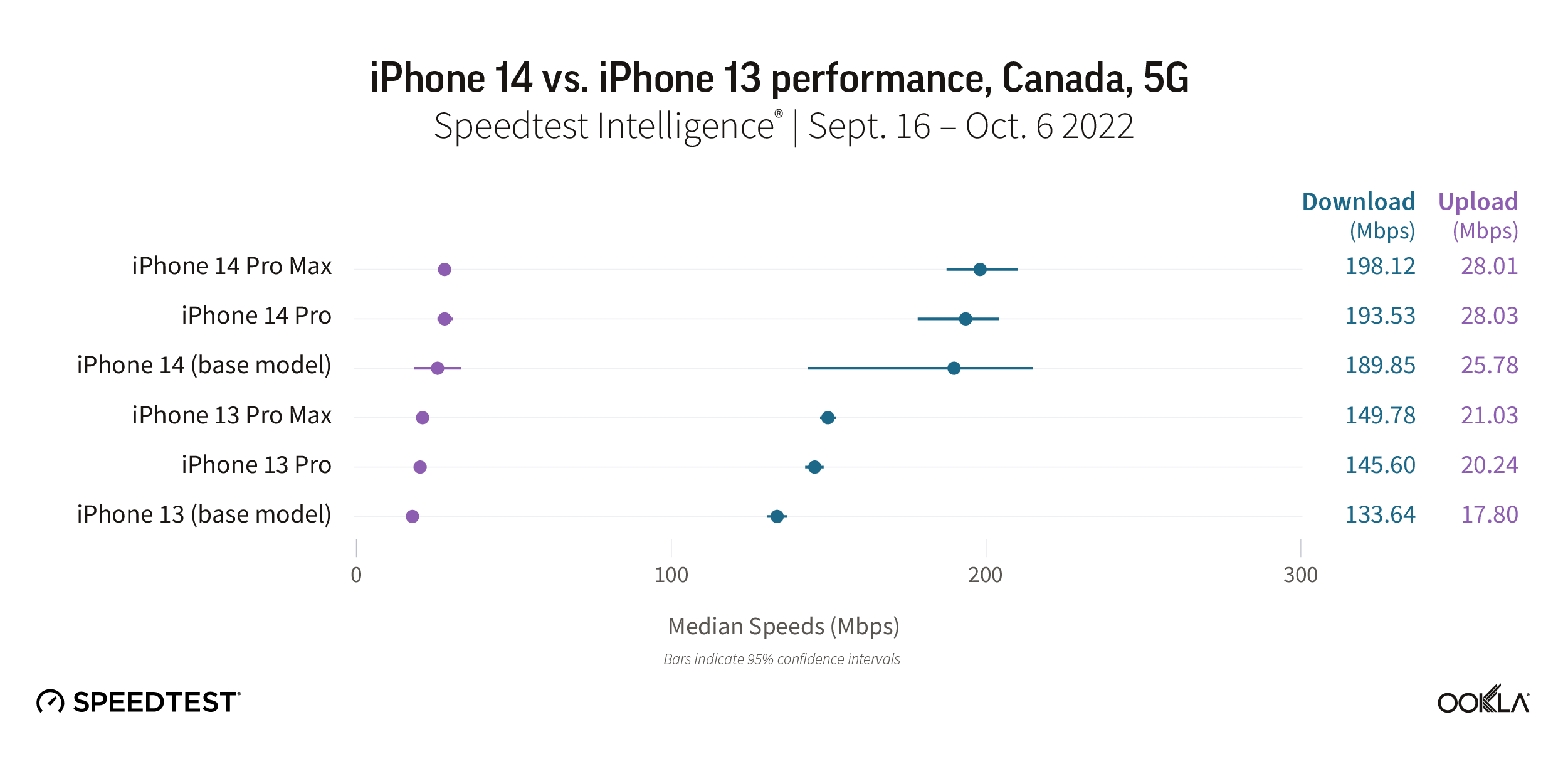
The new iPhone 14 models raced ahead of their iPhone 13 counterparts in Canada. The iPhone 14 Pro Max achieved a median 5G download speed of 198.12 Mbps, followed by the iPhone 14 Pro (193.53 Mbps), and then iPhone 14 (189.85 Mbps). The iPhone 13 Pro Max was the fastest iPhone 13 model at 149.78 Mbps, followed by the iPhone 13 Pro (145.60 Mbps), and iPhone 13 (133.64 Mbps).
The iPhone 14 models were also faster for median upload speed ranging from 25.78 Mbps to 28.01 Mbps, whereas the iPhone 13 models ranged from 17.80 Mbps to 21.03 Mbps.
Recommendation: Canadian iPhone 13 users should beeline straight to their mobile operator to upgrade to a new iPhone 14 model.
France
Samsung Galaxy Z Fold

Speedtest Intelligence revealed that French consumers saw a jump in speeds over the past month if they upgraded from the Galaxy Z Fold3 to the new Fold4, which achieved a median download speed of 290.83 Mbps over 5G. The Fold3 was far behind with a median download speed at 217.18 Mbps. 5G upload speeds were similar with the Fold4 at 15.81 Mbps and the Fold3 at 14.58 Mbps.
Recommendation: French Galaxy Z Fold3 users shouldn’t hesitate to immediately upgrade to the Fold4 for a faster 5G experience.
Apple iPhone
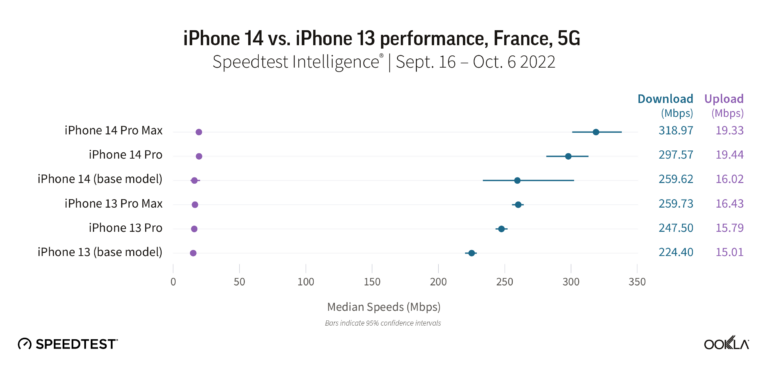
The iPhone 14 models were all faster than their iPhone 13 counterparts in France. The iPhone 14 Pro Max and iPhone 14 Pro models had the fastest median 5G download speeds at 318.97 Mbps and 297.57 Mbps, respectively, while the iPhone 14 followed at 259.62 Mbps. The iPhone 13 Pro Max was the fastest iPhone 13 model at 259.73 Mbps, with the iPhone 13 Pro (247.50 Mbps) and iPhone 13 (224.40 Mbps) following.
Upload speeds remained relatively similar, with all of the iPhone 14 models ranging between 16.02 Mbps to 19.44 Mbps, and the iPhone 13 models ranging from 15.01 Mbps to 16.43 Mbps.
Recommendation: iPhone 13 users in France should absolutely consider upgrading their phone to a new iPhone 14 model for faster speeds and new features.
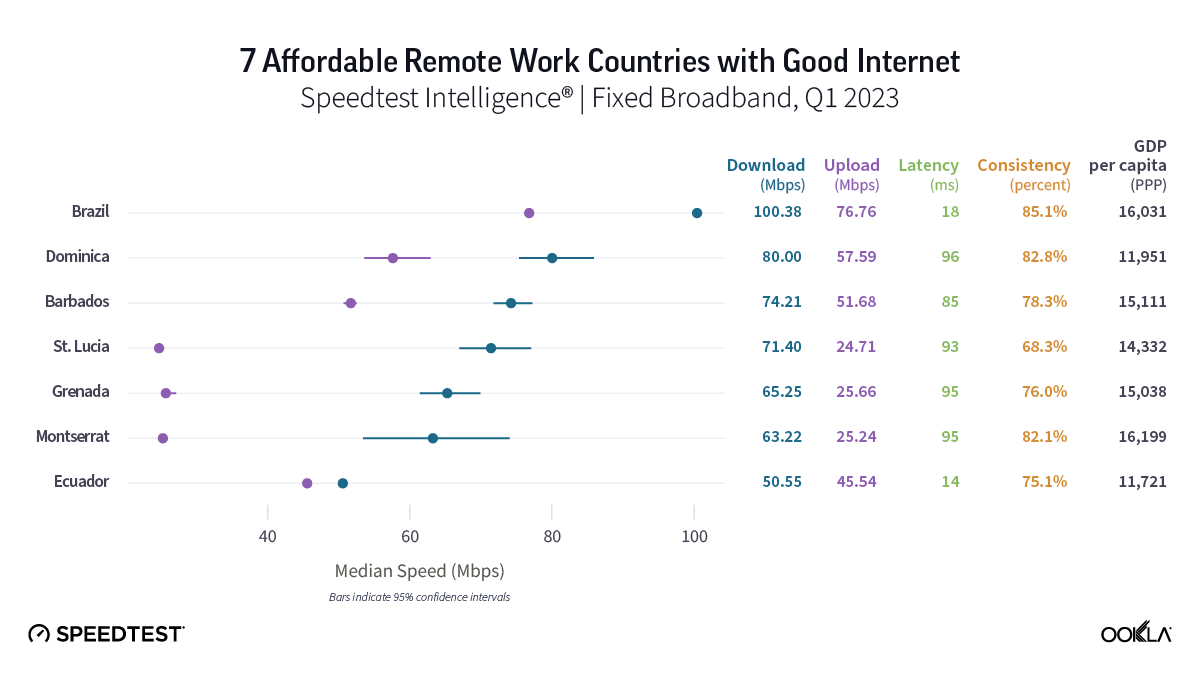
Saudi Arabia
Samsung Galaxy Z Fold
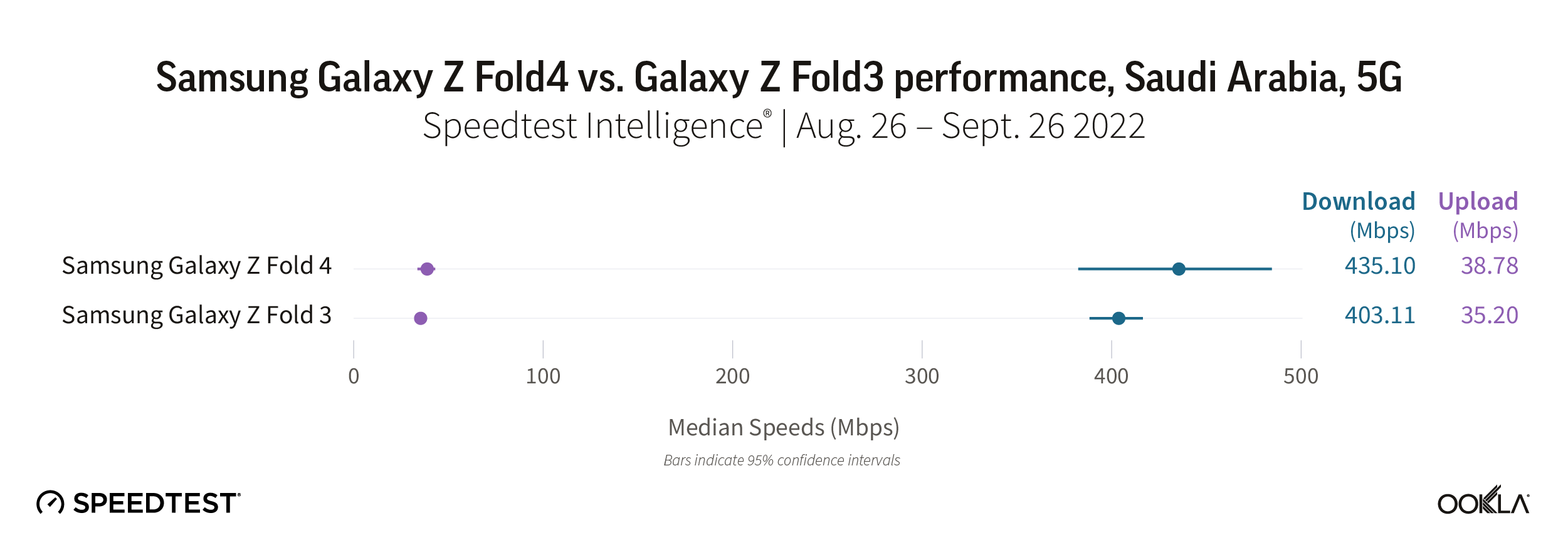
Saudi consumers who upgraded to the Galaxy Z Fold4 might not have noticed a marked improvement on their already blazing fast 5G speeds, with the Fold4 achieving a median 5G download speed of 435.10 Mbps to the Fold3’s 403.11 Mbps. Even on upload, the speeds were roughly the same at 38.78 Mbps and 35.20 Mbps for the Fold4 and Fold3, respectively.
Recommendation: Galaxy Z Fold3 users in Saudi Arabia don’t really need to upgrade your phones for great speeds. Base your decision on whether you want the other new features the Fold4 offers.
Apple iPhone
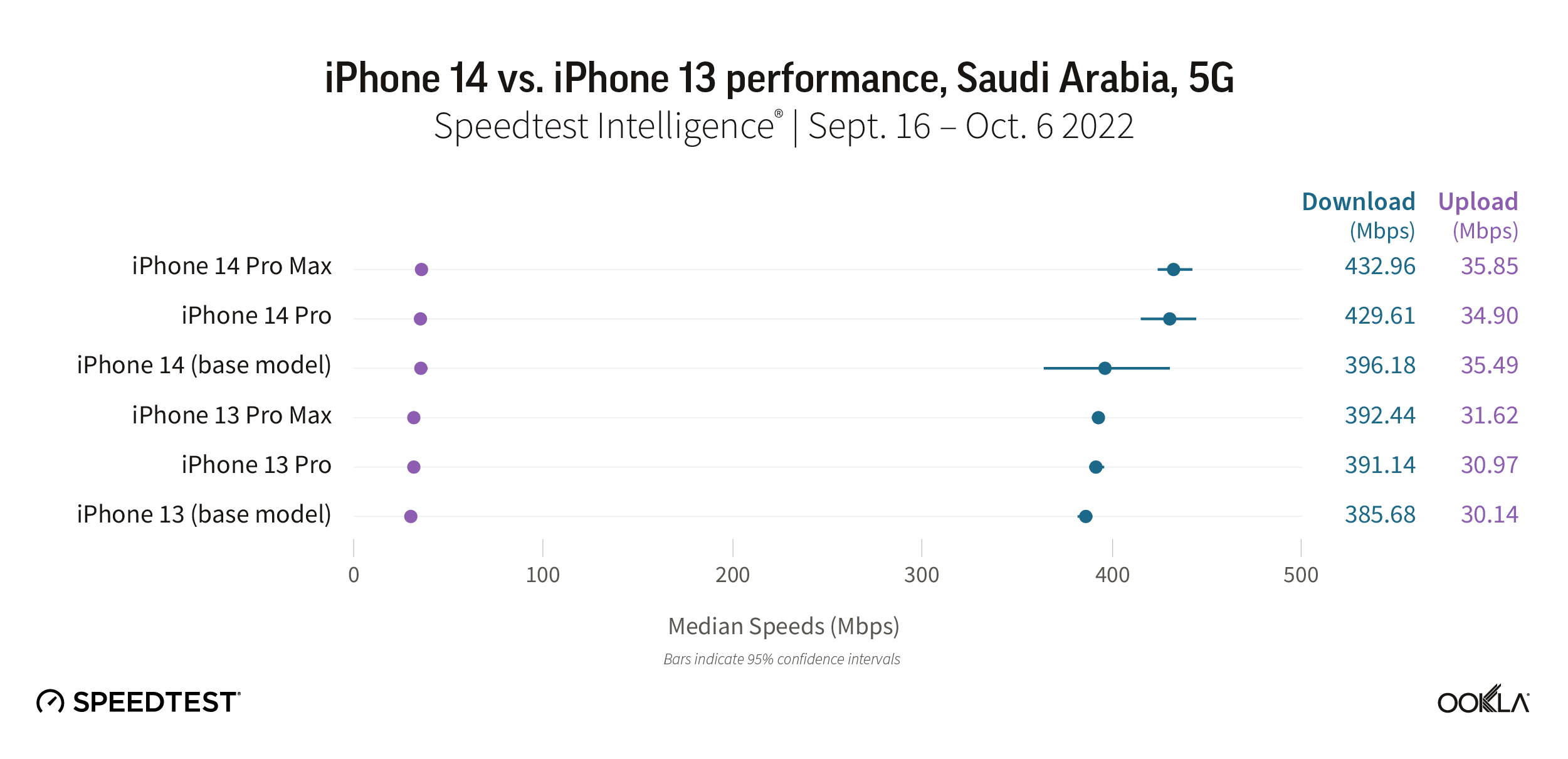
The launch of the new iPhone 14 models showed a similar story in Saudi Arabia as the Samsung Galaxy Z Fold. The new iPhone 14 models were all faster than their iPhone 13 counterparts, but all of the iPhones we looked at were very fast on 5G. The new iPhone 14 Pro Max and iPhone 14 Pro models had the fastest download speeds at 432.96 Mbps and 429.61 Mbps, respectively, while the iPhone 14 base model was next at 396.18 Mbps. The iPhone 13 Pro Max and Pro followed at 392.44 Mbps and 391.14 Mbps, respectively, while the base iPhone 13 model was next at 385.68 Mbps.
Upload speeds were faster on the iPhone 14 models, which ranged from a median speed of 34.90 Mbps to 35.85 Mbps, while the iPhone 13 models ranged from 30.14 Mbps to 31.62 Mbps.
Recommendation: Saudi iPhone 13 users should consider upgrading their phone to a new iPhone 14 model for faster speeds and new features, but most iPhone 13 users still experience very fast speeds.
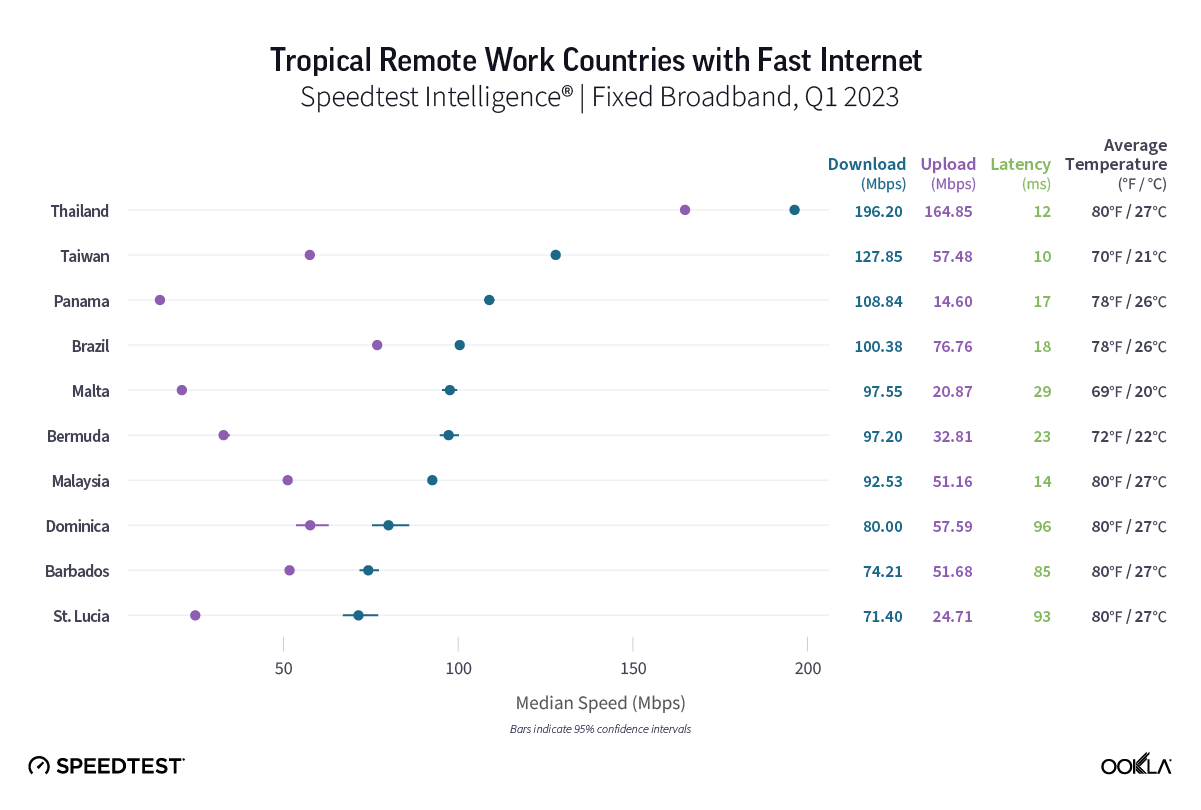
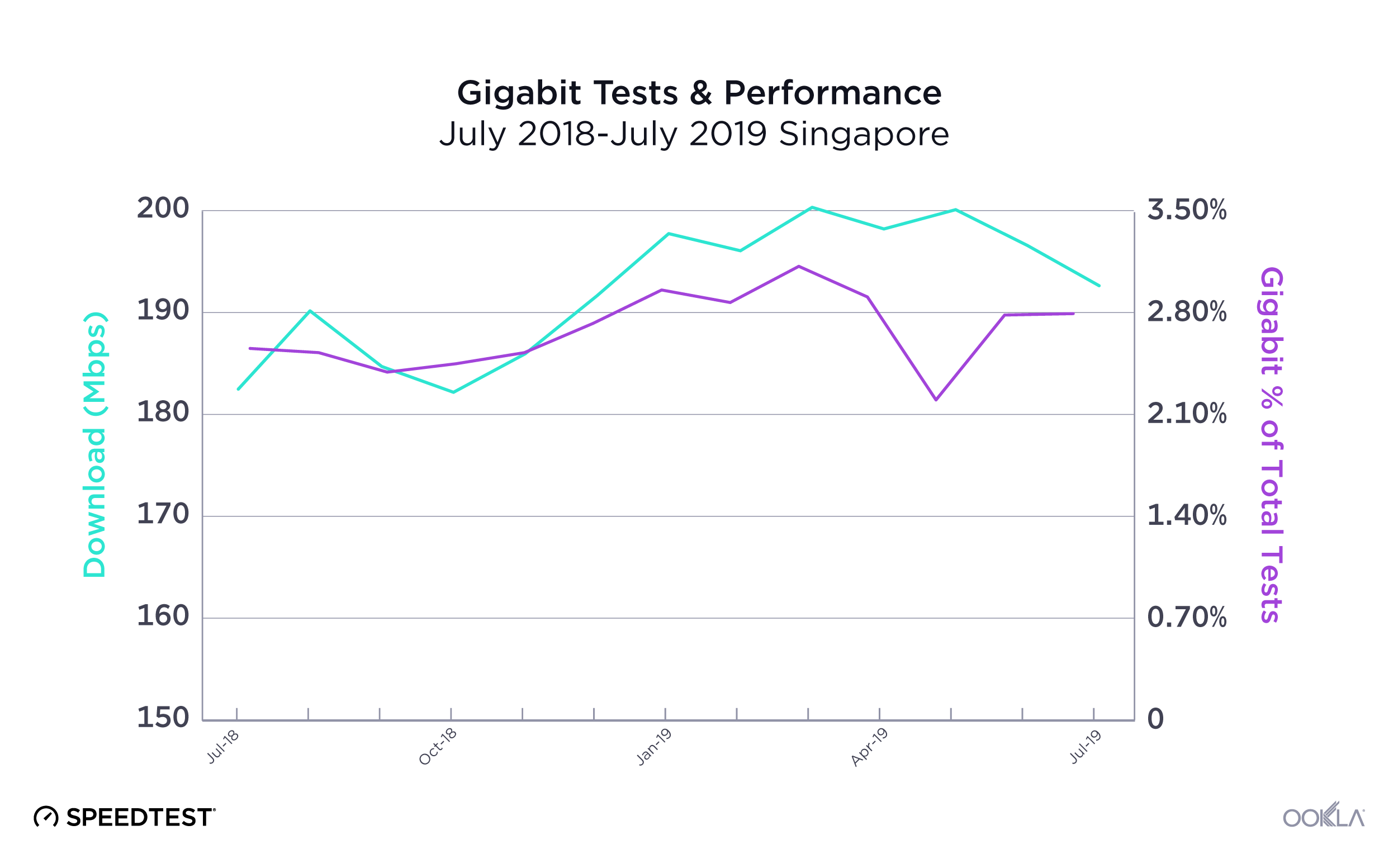
Singapore
Samsung Galaxy Z Fold
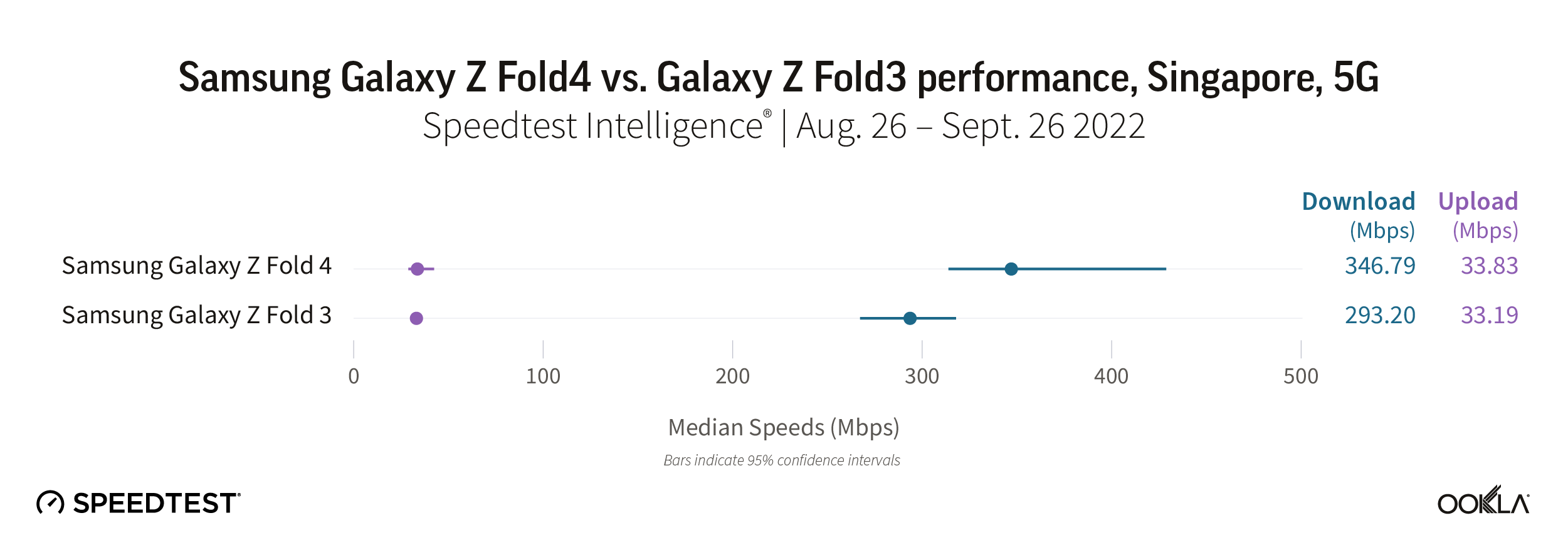
Consumers in Singapore saw a noticeable increase in median 5G download speeds by upgrading to the Galaxy Z Fold4 during the first month after its launch. The Fold4 outpaced the Fold3 346.79 Mbps to 293.20 Mbps for median 5G download speed. Upload speeds remained almost exactly the same with the Fold4 reaching a 5G median download speed at 33.83 Mbps to the Fold3’s 33.19 Mbps.
Recommendation: Galaxy Z Fold3 users in Singapore should rush to see how they can upgrade their phone to the Fold4 for faster speeds and new features.
Apple iPhone
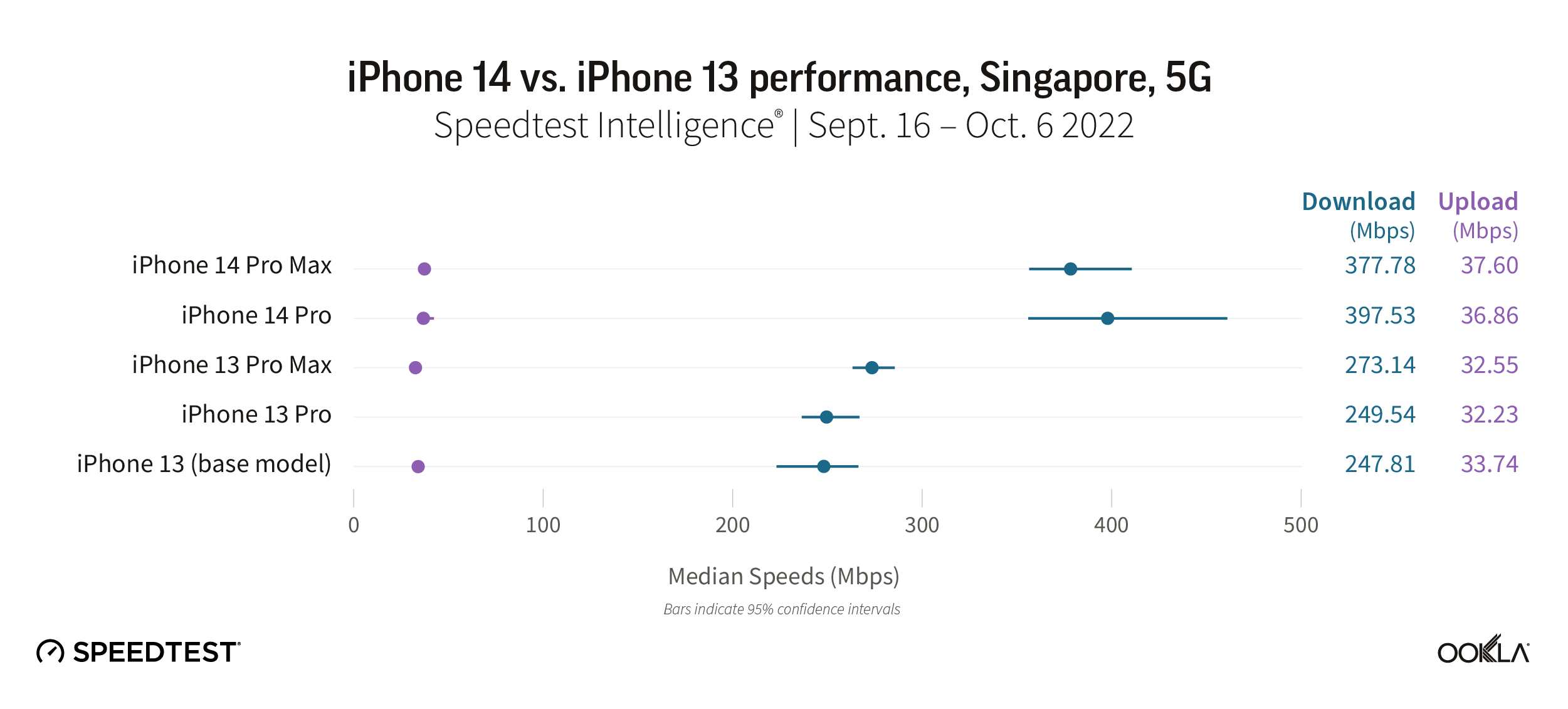
Speedtest Intelligence reveals that in Singapore the iPhone 14 Pro Max and Pro models had much faster median 5G download speeds than their already fast iPhone 13 counterparts. The iPhone 14 Pro Max and Pro models achieved median download speeds of 377.78 Mbps and 397.53 Mbps, respectively. However, iPhone 13 model users are still experiencing fast speeds. The iPhone 13 Pro Max achieved 273.14 Mbps, the iPhone 13 Pro at 249.54 Mbps, and the iPhone 13 at 247.81 Mbps. The iPhone 14 base model didn’t record enough samples to be included in our survey for Singapore.
Speedtest Intelligence also showed that upload speeds over 5G didn’t vary too significantly, with the iPhone 14 Pro Max and Pro models achieving 37.60 Mbps and 36.86 Mbps, respectively, and the iPhone 13 models ranging from 32.23 Mbps to 33.74 Mbps.
Recommendation: iPhone 13 users in Singapore won’t regret upgrading their phone to a new iPhone 14 model for faster speeds, but most iPhone 13 users already experience fast speeds.
South Korea
Samsung Galaxy Z Fold
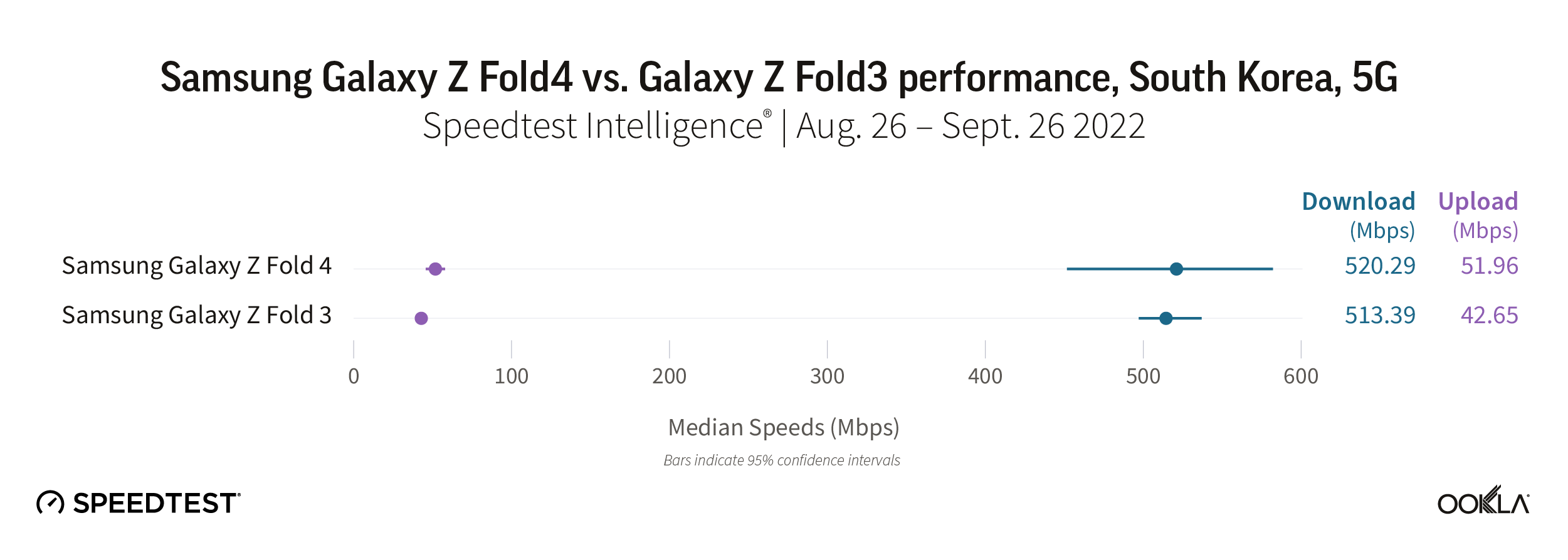
Home to Samsung’s headquarters, South Korea has some of the fastest 5G speeds in the world. However, consumers who upgraded from the Fold3 to the Fold4 haven’t yet seen a noticeable improvement upon their already super fast internet experience. The Galaxy Z Fold4 reached a similar median 5G download speed as the Fold3 at 520.29 Mbps to 513.39 Mbps, respectively. However, the Fold4 was just faster than the Fold3 for upload speed at 51.96 Mbps to 42.65 Mbps.
Recommendation: It’s hard to say “wait to upgrade” to South Korean Galaxy Z Fold3 users, but with such ridiculously fast speeds on the Fold3 that are comparable to the Fold4, users should consider waiting — unless you really want other new features the Fold4 offers.
Apple iPhone

We’re jealous of iPhone users in South Korea, who experienced lightning fast 5G download speeds on every model of iPhone we surveyed, which ranged from 570.01 Mbps to 663.43 Mbps. While we didn’t find a statistically significant fastest median 5G download speed, the iPhone 14 Pro had a median download speed of 663.43 Mbps, the iPhone 14 Pro Max at 635.23 Mbps, the iPhone 13 Pro Max at 602.17 Mbps, the iPhone 13 Pro at 596.18 Mbps, and the iPhone 13 at 570.01 Mbps. The base model of the iPhone 14 didn’t have enough samples to be included.
Median 5G upload speeds for the iPhone 14 models were also very fast, ranging from 37.14 Mbps to 62.46 Mbps. However, the iPhone 13 models still had very fast upload speeds, which ranged from 41.96 Mbps to 43.45 Mbps.
Recommendation: South Korean iPhone 13 users who want to upgrade their phone to a new iPhone 14 model should do so for the new features — 5G speeds are extremely fast no matter what model you have.
Switzerland
Samsung Galaxy Z Fold

Speedtest Intelligence shows that Swiss Samsung Galaxy Z Fold4 users only saw a moderate increase in median 5G download speed when upgrading from the Fold3, with the Fold4 achieving a median download speed of 232.70 Mbps to the Fold3’s 202.69 Mbps. The Fold4 was faster than the Fold3 for median upload speed at 49.31 Mbps to 39.76 Mbps during the same time period.
Recommendation: Swiss Galaxy Z Fold3 users have a tough decision: Speeds aren’t much faster yet for the new model, so unless you really want other new features the Fold4 offers, you may want to wait.
Apple iPhone
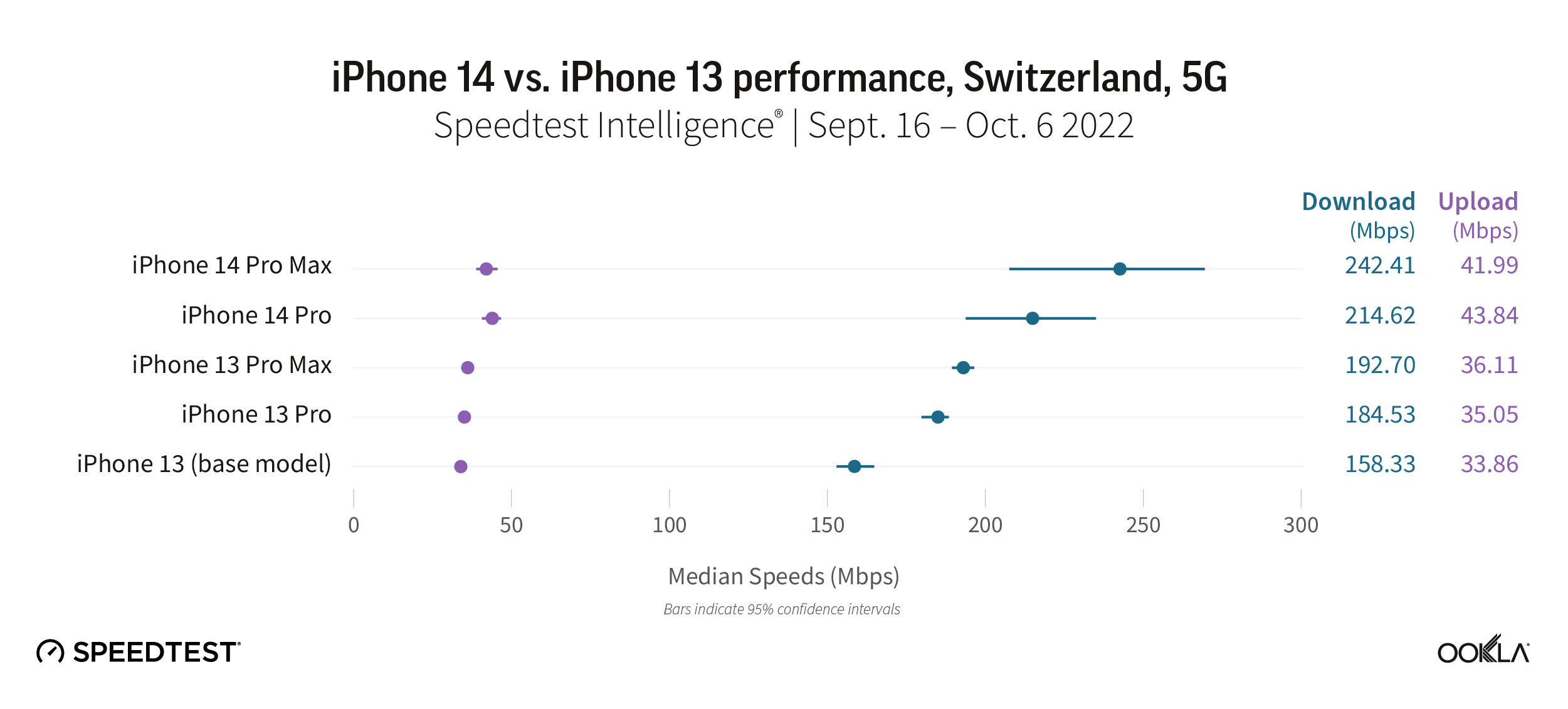
iPhone consumers in Switzerland waiting to see how the new iPhone 14 performs can rest easy. The new iPhone 14 Pro Max and Pro models are faster than their iPhone 13 predecessors, achieving median 5G download speeds at 242.41 Mbps and 214.62 Mbps, respectively. The iPhone 13 Pro Max and Pro models only achieved 192.70 Mbps and 184.53 Mbps, respectively, during the same time period. While there weren’t enough samples to evaluate the iPhone 14, the iPhone 13 had a median 5G download speed at 158.33 Mbps.
The iPhone Pro Max and Pro had faster upload speeds than their iPhone 13 counterparts at 41.99 Mbps and 43.84 Mbps, respectively, while the iPhone 13 Pro Max and Pro models achieved 36.11 Mbps and 35.05 Mbps, respectively.
Recommendation: iPhone 13 users in Switzerland who want faster speeds shouldn’t hesitate to upgrade their phone to a new iPhone 14 model and new features.
Taiwan
Samsung Galaxy Z Fold
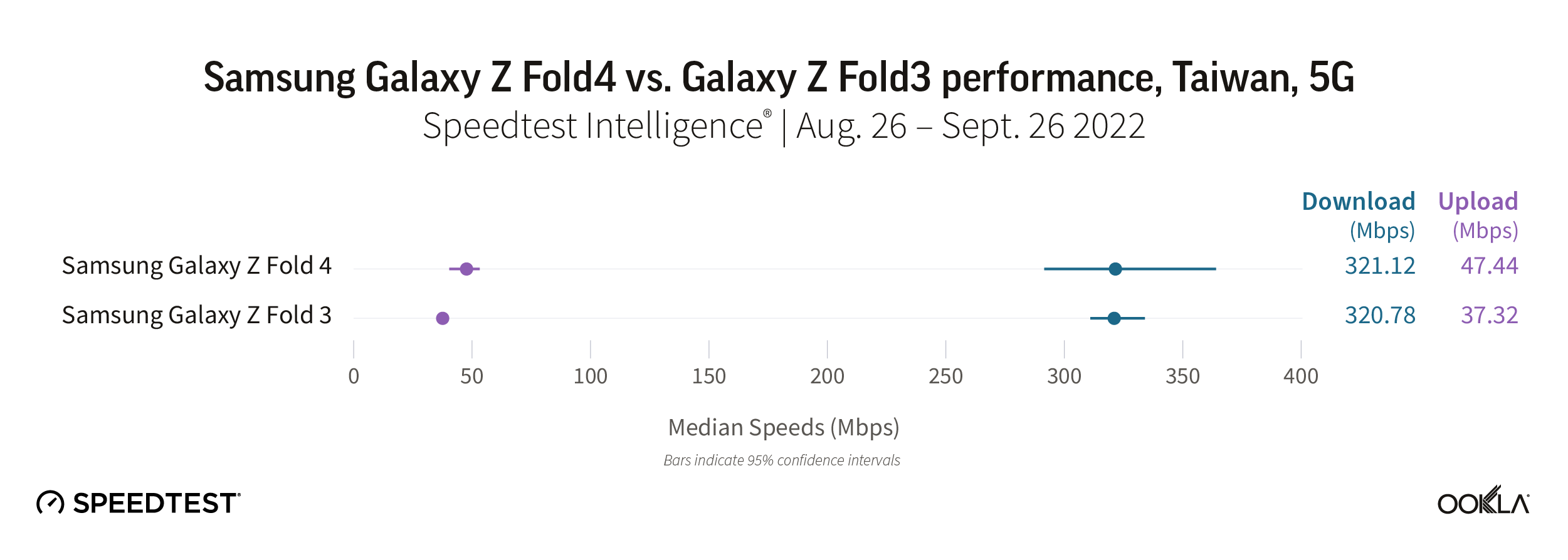
Taiwanese consumers experienced roughly the same median 5G download speed for the Galaxy Z Fold4 and Fold3 at 321.12 Mbps and 320.78 Mbps, respectively. If you’re concerned about upload speed, the Fold4 does pull ahead of the Fold3 on 5G, 47.44 Mbps to 37.32 Mbps.
Recommendation: We noticed operator speed makes a large difference to device performance in Taiwan, so check our Ookla Market Report™ to see what kind of speeds you should expect from your operator. If your operator makes the cut, you should consider upgrading your phone. Other Galaxy Z Fold3 users may want to wait to upgrade their phone until speeds improve, unless you really want other new features the Fold4 offers.
Apple iPhone
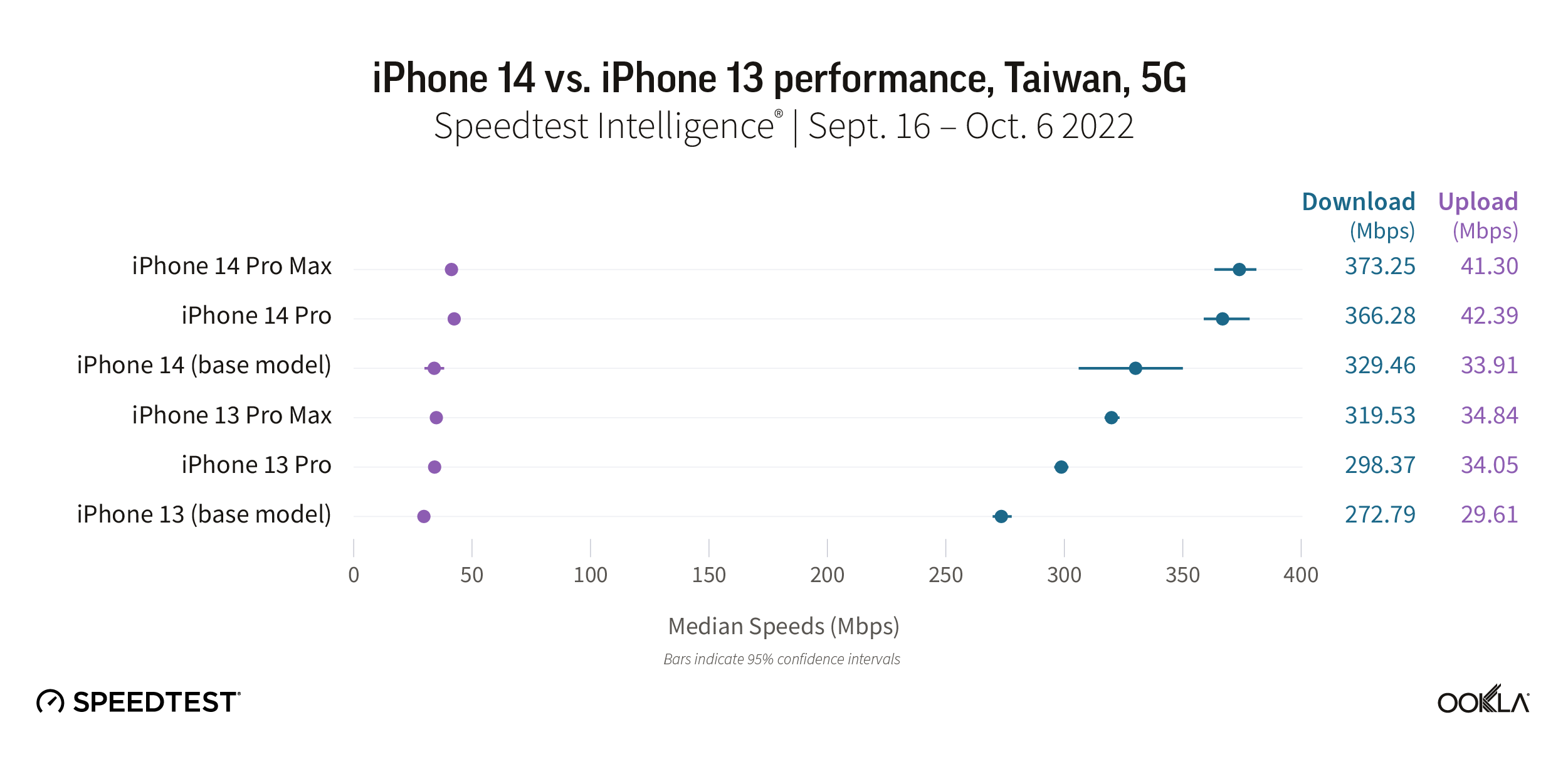
Speedtest Intelligence reveals that iPhone 14 models in Taiwan were much faster than iPhone 13 models, which were already very fast. The iPhone 14 Pro Max and 14 Pro had the fastest median 5G download speed at 373.25 Mbps and 366.28 Mbps, respectively, while the iPhone 14 followed at 329.46 Mbps. The iPhone 13 Pro Max was the fastest iPhone 13 model at 319.53 Mbps, followed by the iPhone 13 Pro (298.37 Mbps) and iPhone 13 (272.79 Mbps).
Download speeds for the iPhone 14 Pro Max and Pro were fast at 41.30 Mbps and 42.39 Mbps, respectively.The iPhone 14 (33.91 Mbps) was more on par with the iPhone 13 Pro Max (34.84 Mbps) and iPhone 13 Pro (34.05 Mbps). The iPhone 13 trailed behind at 29.61 Mbps.
Recommendation: Most iPhone 13 users in Taiwan aren’t lacking for 5G speeds, but iPhone 13 users should upgrade their phone to a new iPhone 14 model for faster speeds and new features.
United States
Samsung Galaxy Z Fold
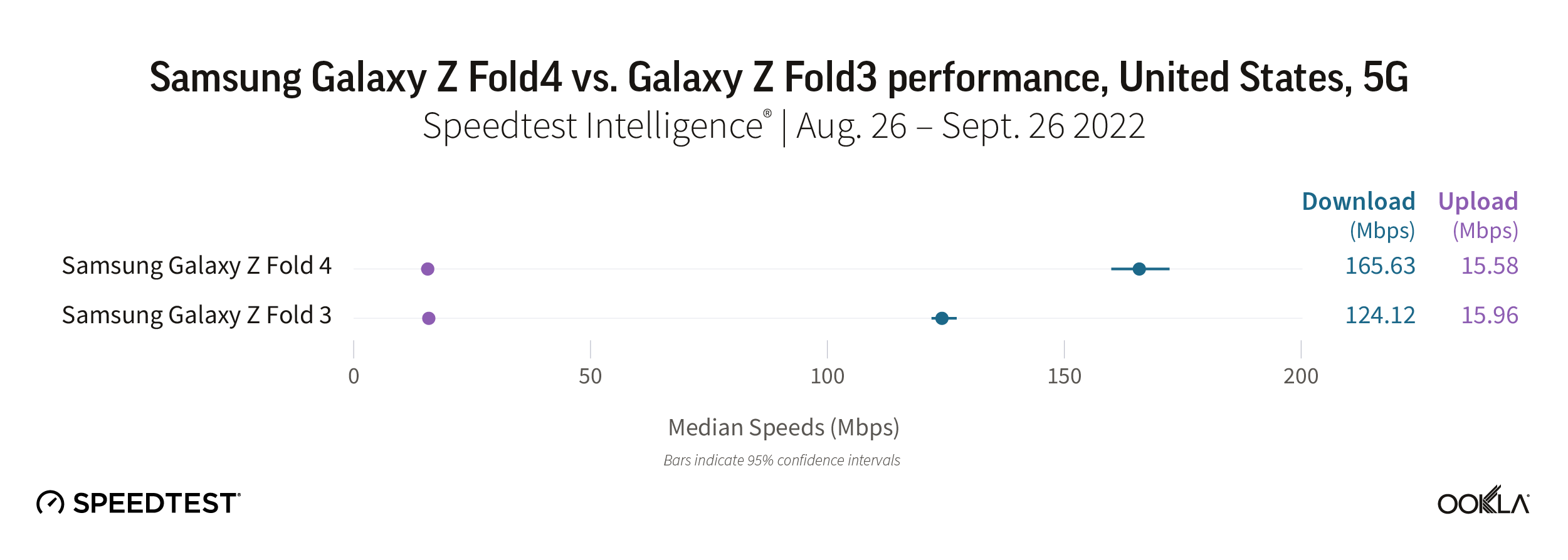
According to Speedtest Intelligence, the Fold4 outperformed the Fold3 in the U.S. with a median 5G download speed of 165.63 Mbps to 124.12 Mbps. Upload speeds were roughly the same with the Fold4 at 15.58 Mbps and the Fold3 at 15.96 Mbps.
Recommendation: Galaxy Z Fold3 users in the U.S. should embrace the Fold4 with open arms. Not only will you experience new features, you’ll continue to see faster speeds, especially as providers expand in 5G investments across the country.
Apple iPhone
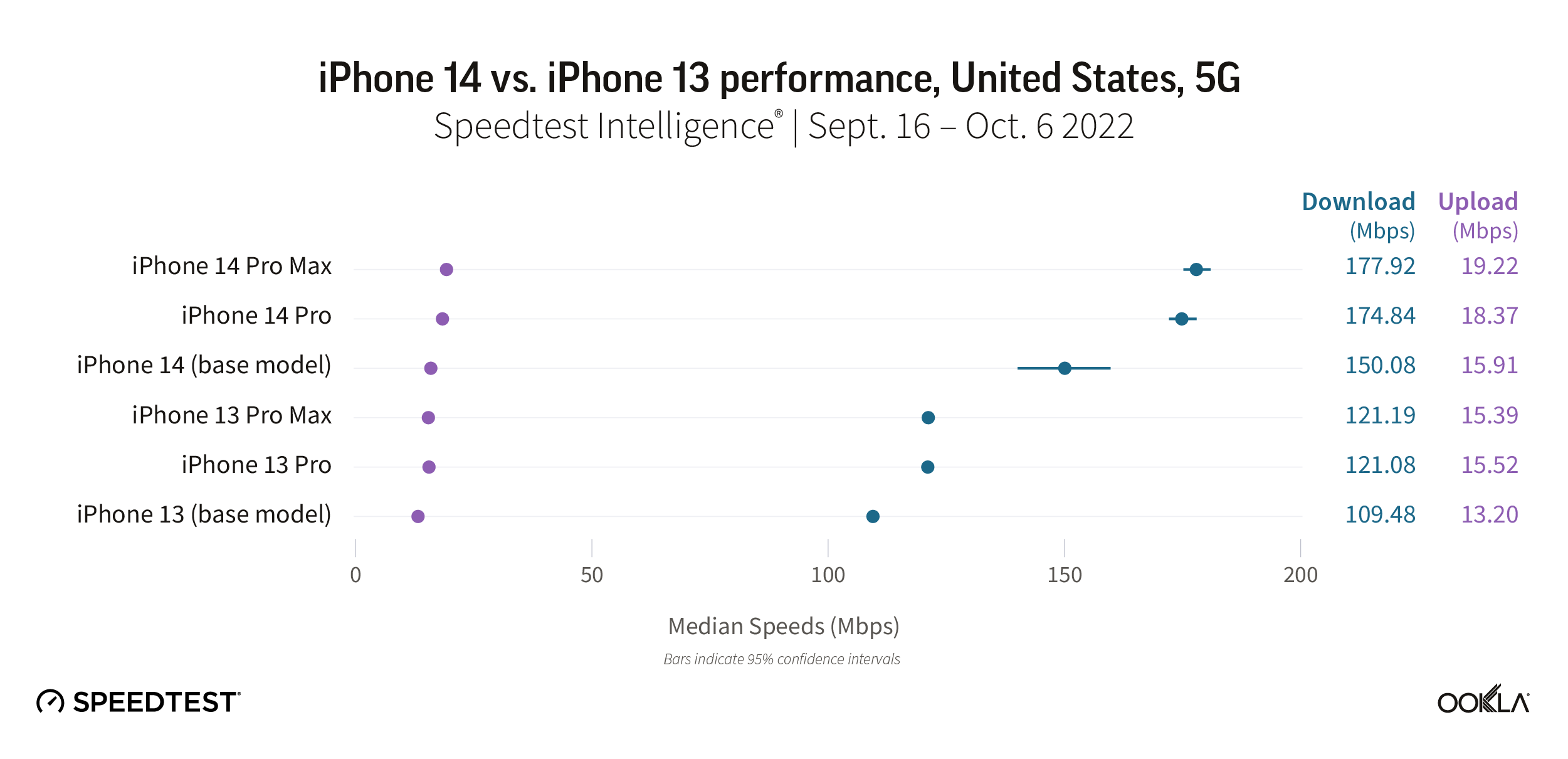
Even the base model of the iPhone 14 substantially outperformed every iPhone 13 model in the U.S. The iPhone 14 Pro Max and Pro models led the way for fastest median 5G download speed at 177.92 Mbps and 174.84 Mbps, respectively, while the iPhone 14 was at 150.08 Mbps. The iPhone 13 Pro Max and Pro models followed behind at 121.19 Mbps and 121.08 Mbps, respectively, and the iPhone 13 trailed at 109.48 Mbps.
Upload speeds were relatively similar, with the iPhone 14 Pro Max and Pro models reaching median 5G upload speeds of 19.22 Mbps and 18.37 Mbps, respectively. The iPhone 14 followed at 15.91 Mbps. The iPhone 13 models weren’t much further behind, ranging from 13.20 Mbps to 15.39 Mbps.
Recommendation: iPhone fans in the U.S. who are waiting to see how the iPhone 14 performs should feel confident in taking the plunge to upgrade their phones.
Ookla will continue monitoring how devices are performing
After blazing fast launches which already saw the iPhone 14 models race ahead in the U.S. and other markets on the Ookla Market Reports™, we’ll eagerly be watching results for the rest of the year. If you recently upgraded your phone, be sure to download the iOS or Android Speedtest® app to make sure you are getting the speeds you need along with up to 2 GB of free VPN browsing every month and access to video testing.