The new Samsung Galaxy S23, S23+, and S23 Ultra models launched February 17 and Ookla® is here today to see how they’ve performed over 5G against their predecessor S22 models. Our analysis looks at data from the first month after launching in 12 of the largest mobile markets with an established 5G market and the highest number of connected mobile devices during Q4 2022 according to GSMA. Previously, in October 2022, we used Speedtest Intelligence® to look at 5G performance data right after the launches of the iPhone 14 and Samsung Galaxy Z Fold4 in various countries.
Note that device data differs across markets due to a variety of factors, including: 5G investments by governments and mobile operators, different 5G spectrum allocations by operator, 5G Availability, the number of and different kinds of 5G deployments, and other differences, including mobile 5G plans. Read on to learn more and see whether or not you should upgrade your Samsung S22 to a newer model.
Key takeaways:
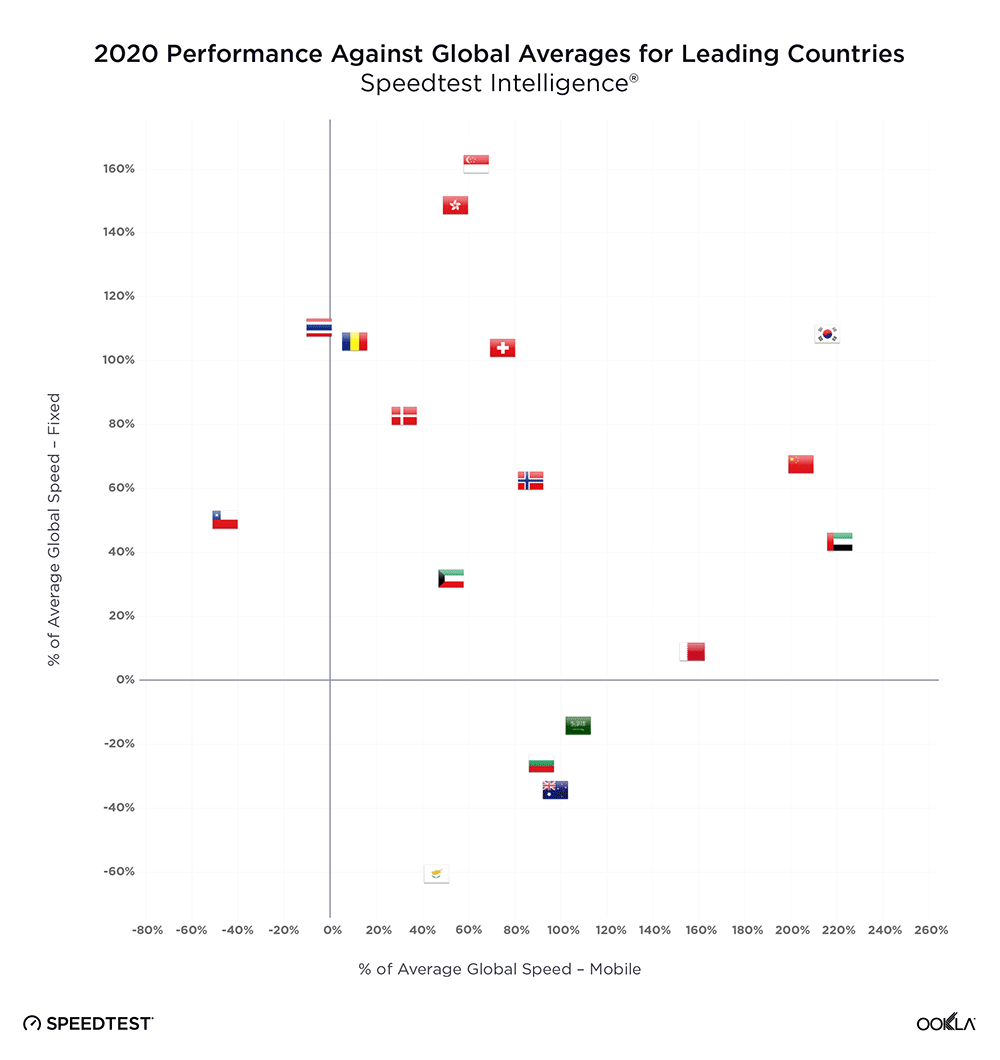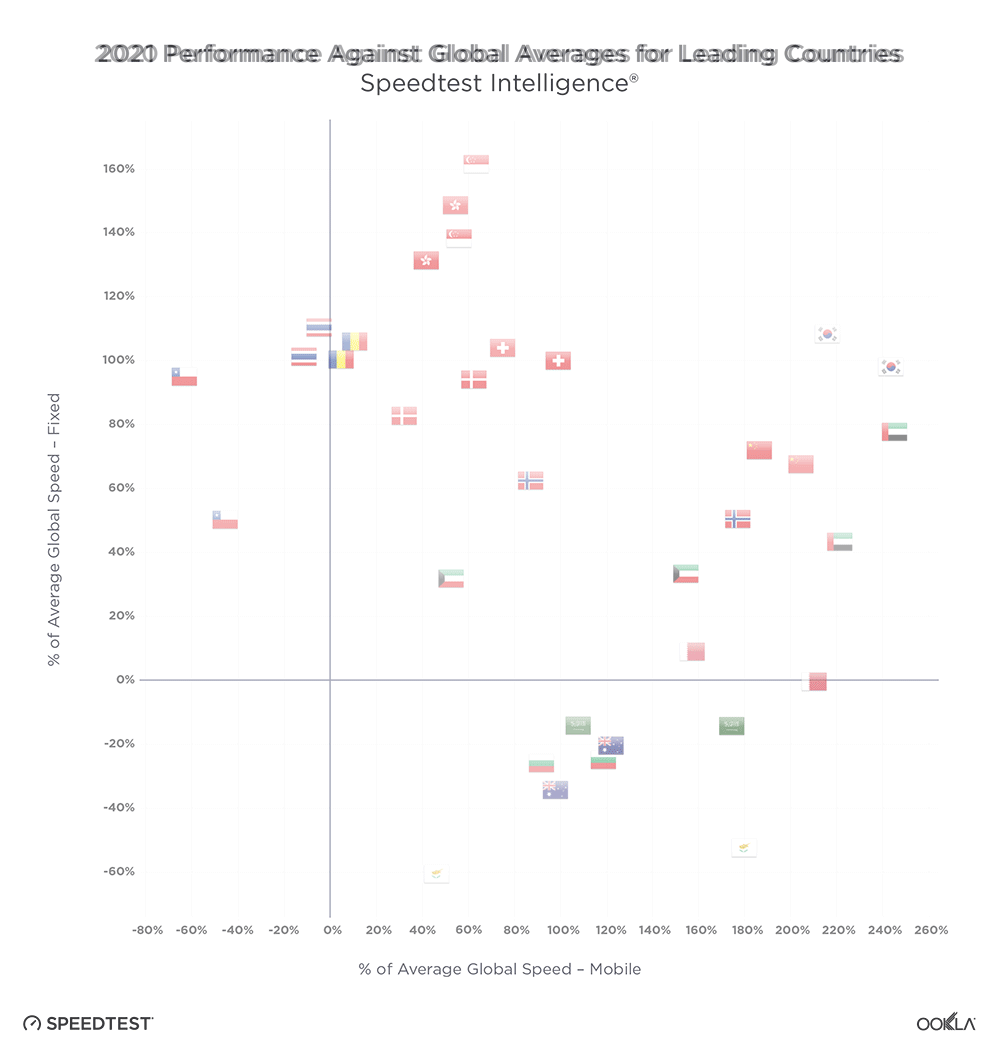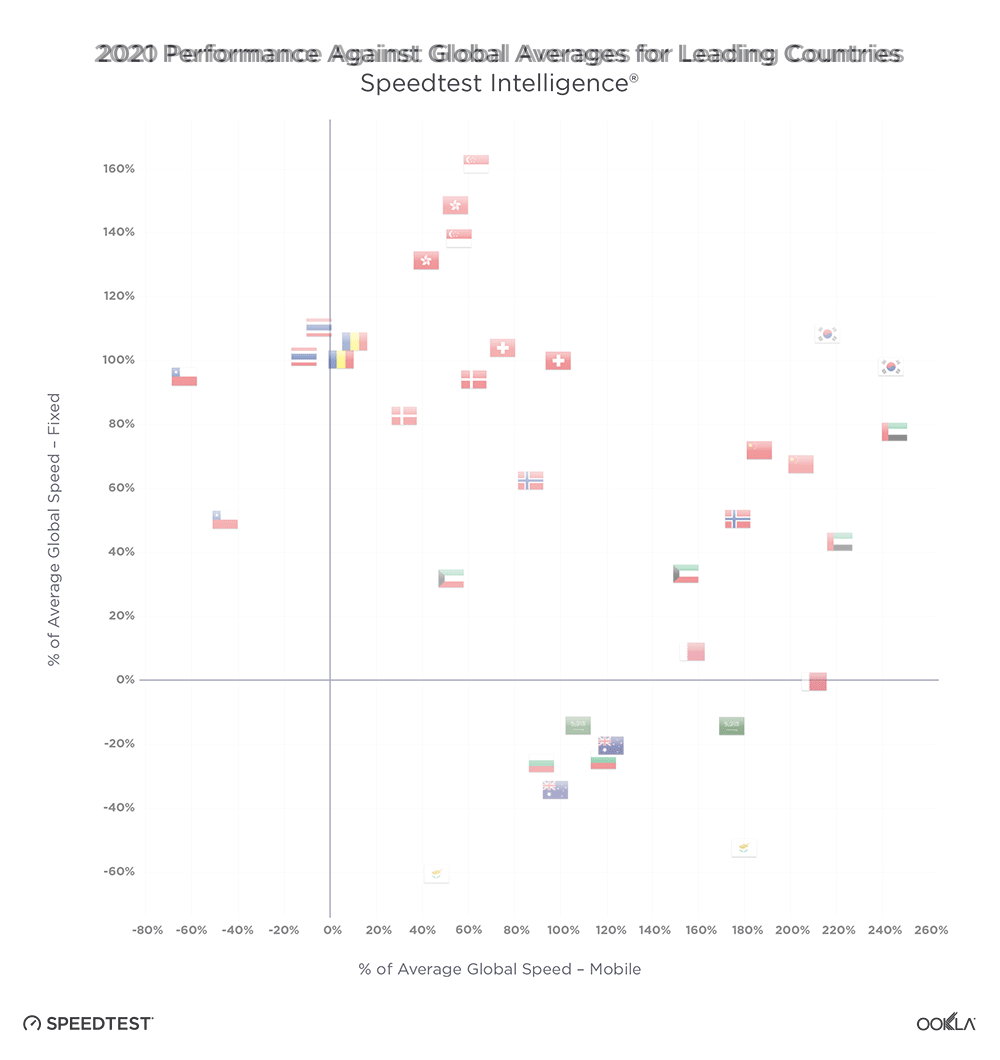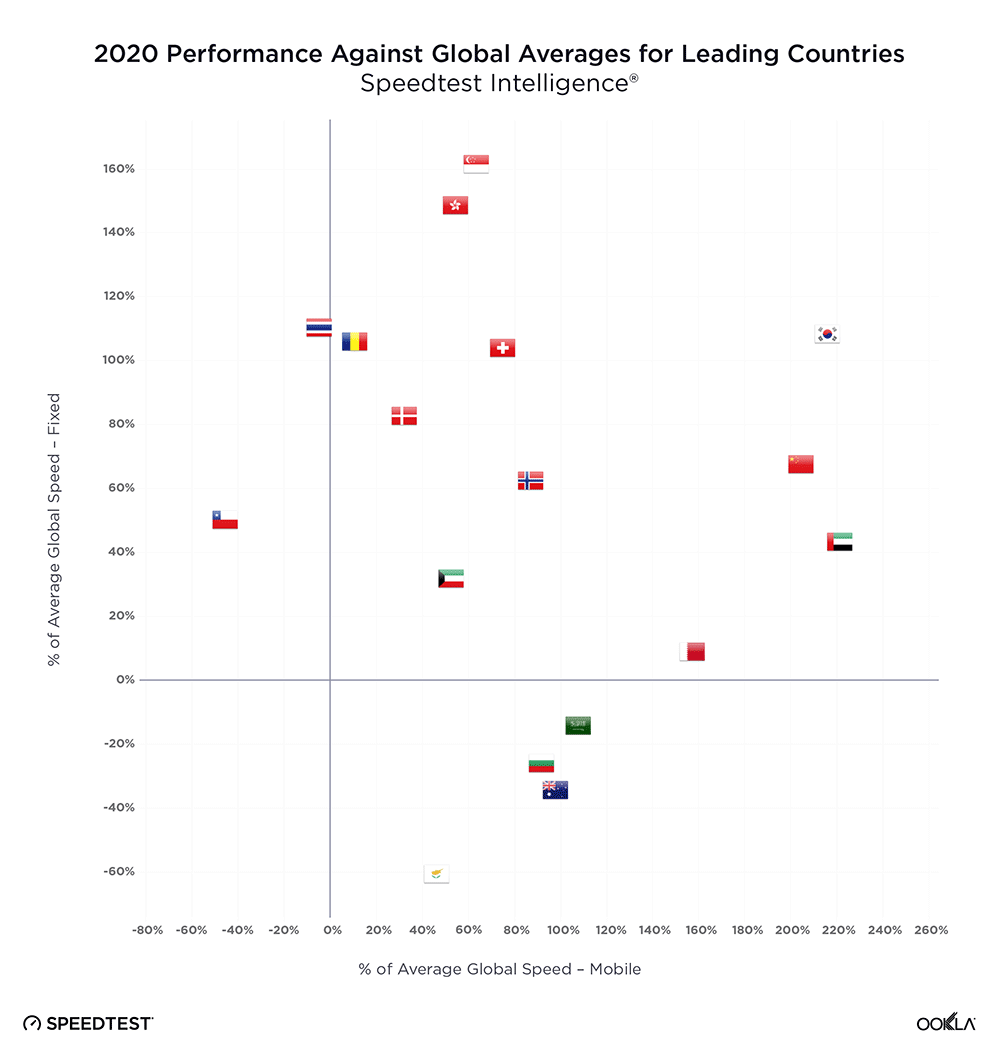
- The Samsung S23 models only statistically outperformed corresponding S22 models in Germany and two out of three models in the United States for 5G download speed, but the S23 looks poised to be faster as further 5G adoption and build out continues and more spectrum is allocated for 5G across the C-band and mmWave frequencies.
Key improvements to the new Galaxy S23 models
You want to know if the latest technology is worth the price of an upgrade when you’re looking for a new phone. The S23, S23+, and S23 Ultra have various upgrades, but when it comes to performance, here’s a quick list of what’s different between the new and older models.
All Samsung Galaxy S23 vs. S22 models
- The Samsung S23 models have a Qualcomm Snapdragon 8 Gen 2, while the Samsung S22 models have a Samsung Snapdragon 8 Gen 1
- The S23 models have a Qualcomm Snapdragon X70 modem, while the S22 models have an X65 modem
- The S23 models have an upgraded GPU
Samsung Galaxy S23 vs. S22 base models
- The S23 has a bigger battery capacity at 3,900 mAh over the S22’s 3,700 mAh
- The S23 has slightly better ultra-wide and front cameras and video recording capabilities
Samsung Galaxy S23+ vs. S22+ models
- The S23+ has expanded storage capacity at a base level of 256 GB (which can be upgraded to 512 GB) over the S22+’s base of 128 GB
- The S23+ has a bigger battery capacity at 4,700 mAh over the S22+’s 4,500 mAh
- The S23+ has slightly better ultra-wide and front cameras and video recording capabilities
Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra vs. S22 Ultra models
- The S23 Ultra has expanded storage capacity at a base level of 256 GB (which can be upgraded to 512 GB) over the S22 Ultra’s base of 128 GB
- The S23 Ultra has much better main camera, with up to 200 MP vs. the S22 Ultra’s maximum of 108 MP
Samsung Galaxy S23 performance in the world’s largest mobile device markets
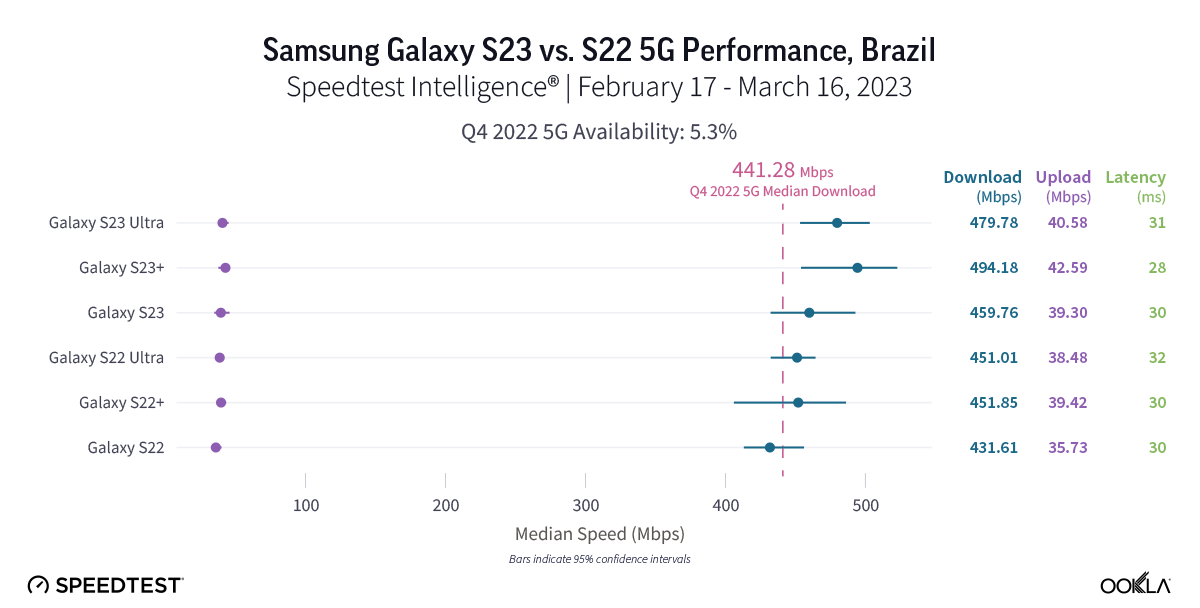
Brazilian S22 and S23 users saw seriously fast 5G speeds (even though 5G Availability remains low)
Speedtest Intelligence shows that the new S23 models were not yet statistically faster than the older S22 models in Brazil during the first month of launch, but they did exceed the median 5G download speed in Brazil during Q4 2022. Despite that, every S22 and S23 model had blazing fast speeds in Brazil, with median 5G download speeds faster than 400 Mbps. The S22 had a median download speed of 431.61 Mbps, the S22 Ultra was at 451.01 Mbps, and the S22+ at 451.85 Mbps. While the S23 models were not statistically faster than their S22 counterparts, the S23 had a median download speed of 459.76 Mbps, the S23 Ultra at 479.78 Mbps, and the S23+ at 494.18 Mbps. 5G upload speeds showed a similar trend, with no statistically faster S22 or S23 model, but with S22 models ranging from 35.73 Mbps to 39.42 Mbps and S23 models ranging from 39.30 Mbps to 42.59 Mbps. Multi-server latency — the latency you should expect to encounter more generally when your network is not under heavy load — ranged from 28.01 ms to 31.78 ms across all models over 5G.
Recommendation: Brazilian Galaxy S22 users should consider upgrading your phone if you can get 5G access; you’re going to get fast speeds and the new features of the S23, especially the camera of the S23 Ultra, may be worth it alone.
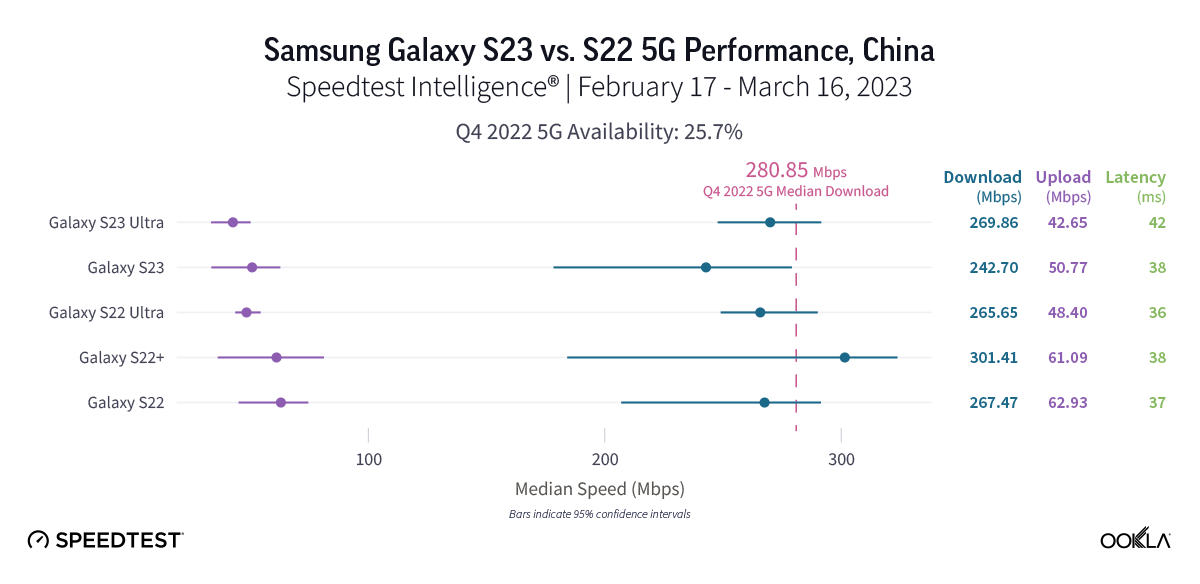
Chinese S23 users haven’t quite seen an improved 5G experience over S22 users
Data from the first month since the Samsung S23 launching illuminates that S23 models did not statistically outperform S22 models over 5G in China, and S23 models also didn’t quite exceed the Q4 2022 median 5G download speed. The S22 had a median 5G download speed of 267.47 Mbps, the S22 Ultra was similar at 265.65 Mbps, and the S22+ was at 301.41 Mbps. The S23 showed a median 5G download speed at 242.70 Mbps, while the S23 Ultra had a median download speed of 269.86 Mbps. 5G upload speeds on S22 models ranged from 48.40 Mbps to 62.93 Mbps, while the S23 and S23 Ultra were at 50.77 Mbps and 42.65 Mbps, respectively. While the S23 models showed lower median multi-server latency over 5G, there was no statistical winner between the S22 and S23 models. The S23+ did not meet the statistical threshold for inclusion in our analysis in China.
Recommendation: Chinese Galaxy S22 users should wait to upgrade your phone until speeds improve, unless the new S23 model hardware upgrades have you wanting a new phone.
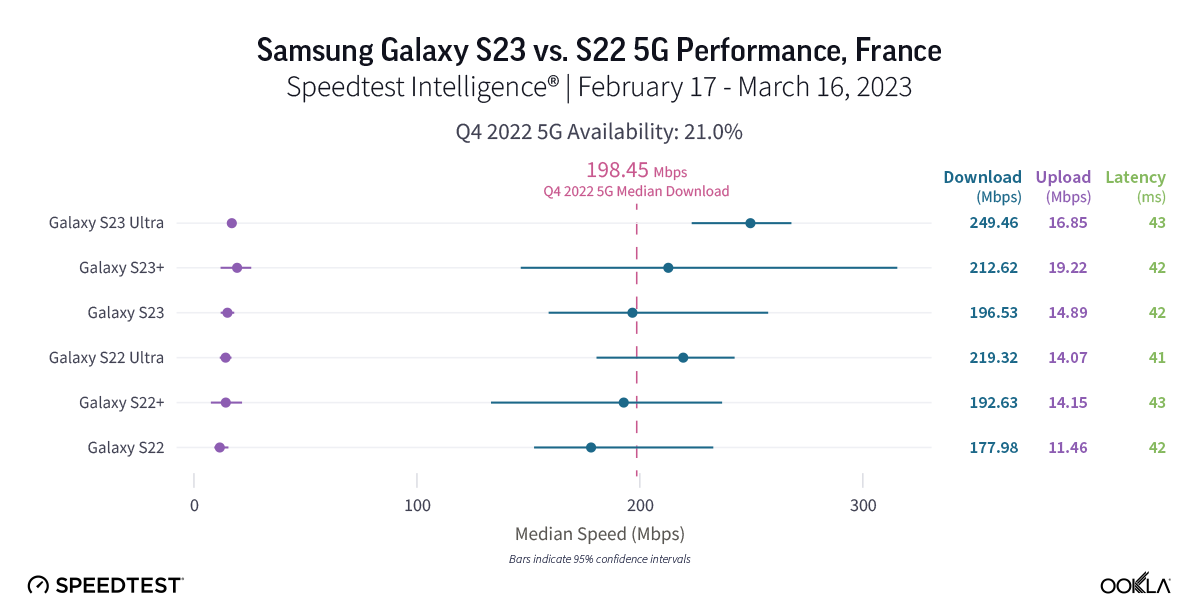
French S23 users saw promising 5G results, S22 users might want to wait to upgrade
There was no statistically faster Samsung Galaxy S22 or S23 model over 5G in France during the first month of the S23’s release. However, median 5G download speeds for the S22 models ranged from 177.98 Mbps to 219.32 Mbps, while the S23 models ranged from 196.53 to 249.46 Mbps. 5G upload speeds showed a similar story, with no statistical winner. Upload speeds on S22 models ranged from 11.46 Mbps to 14.15 Mbps, and upload speeds on S23 models ranged from 14.89 Mbps to 19.22 Mbps. 5G multi-server latency was virtually the same for both models, which all ranged from 41.40 ms to 43.24 ms.
Recommendation: French Galaxy S22 users who want faster speeds might want to wait to upgrade your phone, but the new features of the S23 may make upgrading very tempting.
German Samsung Galaxy S22 users should feel confident upgrading to S23 models
Speedtest Intelligence reveals that German S23 users experienced faster 5G download speeds than their S22 counterparts during the first month of S23 availability across all models. The S23 outperformed the S22 for median 5G download speed, 147.26 Mbps to 112.01 Mbps, the S23 Ultra outperformed the S22 Ultra 141.56 Mbps to 124.45 Mbps, and the S23+ outperformed the S22+ 174.74 Mbps to 128.69 Mbps. Upload speeds had a bit more parity with the S22 models showing a range of 5G upload speeds from 20.47 Mbps to 26.10 Mbps, while the S23 models showed a range from 23.59 Mbps to 31.64 Mbps. Multi-server latency over 5G showed no statistical winner for either model but ranged from 36.76 ms to 38.58 ms.
Recommendation: Germany Galaxy S22 users shouldn’t hesitate to run to your operator to immediately upgrade your phone to an S23 model for faster speeds and better features.
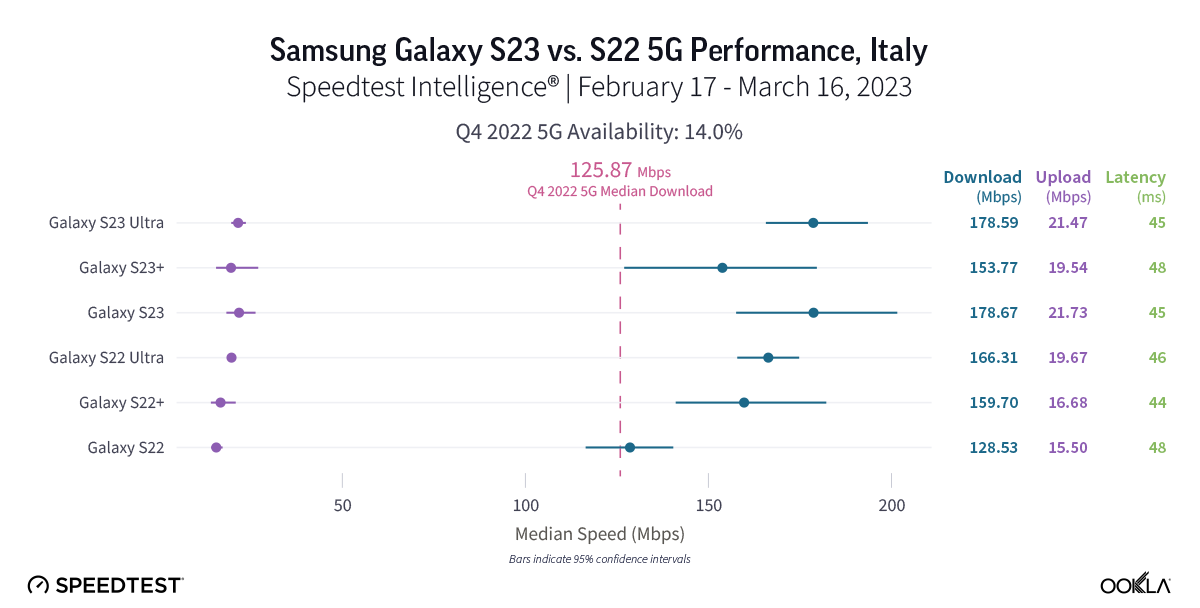
Samsung Galaxy S23 users in Italy saw mixed 5G results after launch
New Speedtest Intelligence data reveals that while the basic S23 model outperformed the S22 model over 5G in Italy for median download speed 178.67 Mbps to 128.53 Mbps during the first month after launch, the S23 Ultra and S23+ models didn’t statistically outperform their S22 counterparts. That held true for upload speeds as well, with the S23 recording a median 5G upload speed of 21.73 Mbps to the S22’s 15.50 Mbps, while the S23 Ultra and S23+ weren’t statistically faster than the S22 Ultra and S22+, respectively. All of the S23 and S22 models during the first month of the S23 launch, except the S22 base model, were statistically faster than the 5G median download speed in Italy during Q4 2022. Median multi-server latency showed closer parity, with S22 models ranging from 45.02 ms to 47.79 ms, and S23 models ranging from 43.50 ms to 48.24 ms.
Recommendation: Unless you want a basic Galaxy S23 model and have consistent 5G access in Italy, you might want to wait to upgrade your phone to the S23 models unless you really want the new features.
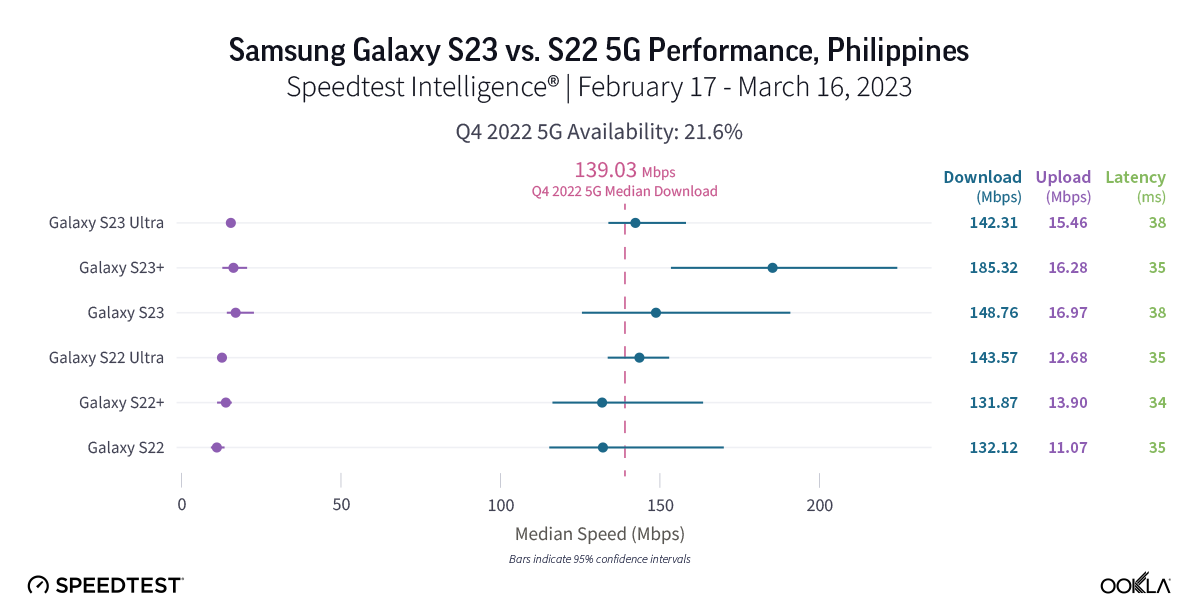
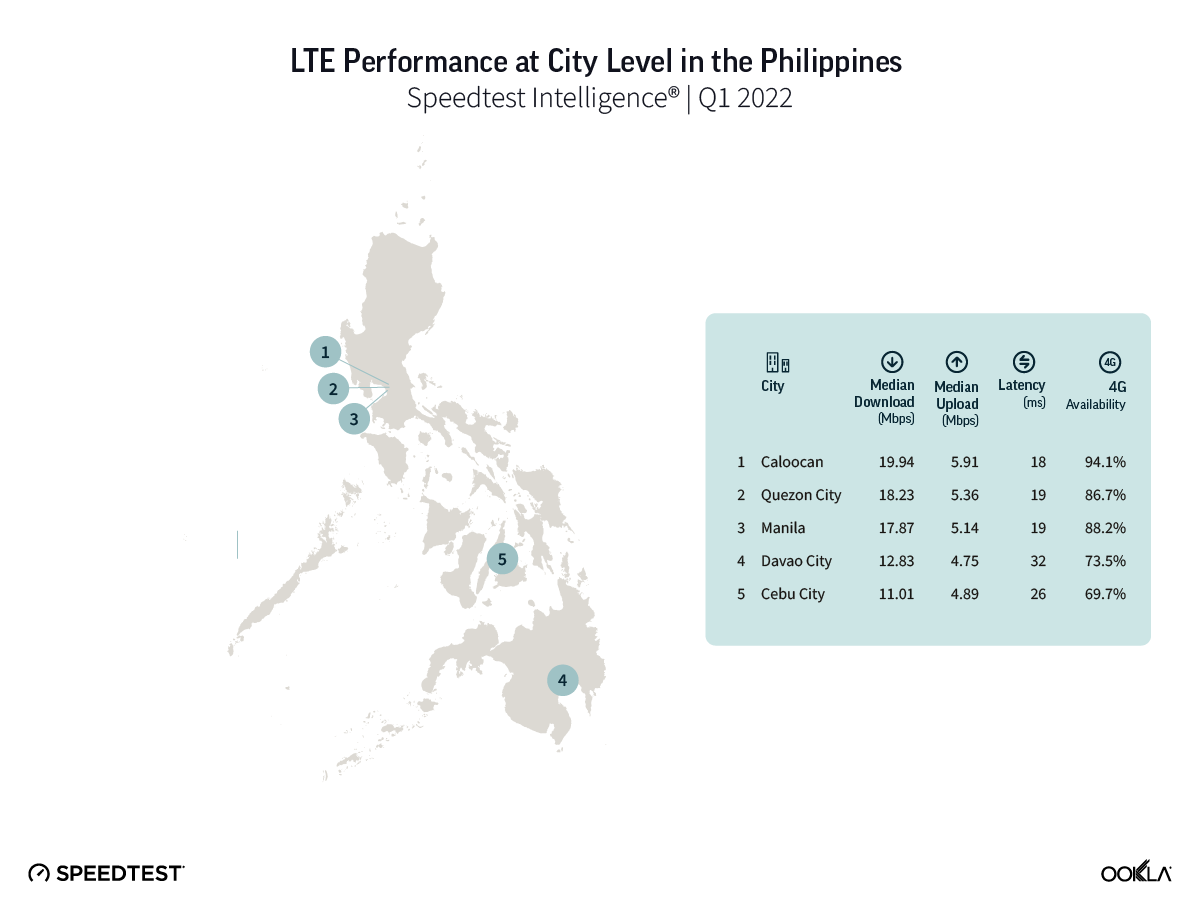
Samsung Galaxy S23 showed 5G potential in the Philippines
Fresh data from Speedtest Intelligence shows that while the S23 and S23+ had faster median 5G download speeds than their S22 counterparts during the first month of the S23’s launch, there were no statistical winners between the models in the Philippines. The S23 models’ median 5G download speeds ranged from 142.31 Mbps to 185.32 Mbps, while the S22 models ranged from 131.87 Mbps to 143.57 Mbps. Median 5G upload speed for the S23 Ultra was faster than its S22 Ultra counterparts at 15.46 Mbps to 12.68 Mbps, respectively. There were no statistical winners for median multi-server latency over 5G, though the S22 models ranged from 35.42 ms to 38.39 ms, while the S23 models ranged from 34.29 ms to 35.31 ms.
Recommendation: Filippino Galaxy S22 users should upgrade their phones to the S23 models if they want new features, but shouldn’t expect faster speeds and a better experience quite yet.
Polish Samsung S23 models had a promising debut over 5G
Speedtest Intelligence data shows Poland had some of the slowest median 5G download speeds on Samsung S23 and S22 models among the countries we surveyed. While the new S23 models had a higher median 5G download speed than their counterparts during the first month after launching, there were no statistically significant faster speeds. The S23 models ranged from 83.74 Mbps to 98.99 Mbps, while the S22 models ranged from 75.70 Mbps to 80.43 Mbps. Upload speeds were similarly faster, but not statistically so, with S22 models ranging from 16.89 Mbps to 19.62 Mbps and S23 models ranging from 19.94 Mbps to 24.25 Mbps. Median multi-server latency over 5G was a mixed bag, with the new S23+ actually having a higher latency than the S22+ 44.25 ms to 38.37 ms, respectively. The other two models were too close to call.
Recommendation: Polish Galaxy S22 users can upgrade their phones to the S23 models for the new features, but might not yet experience faster 5G speeds on the new models.
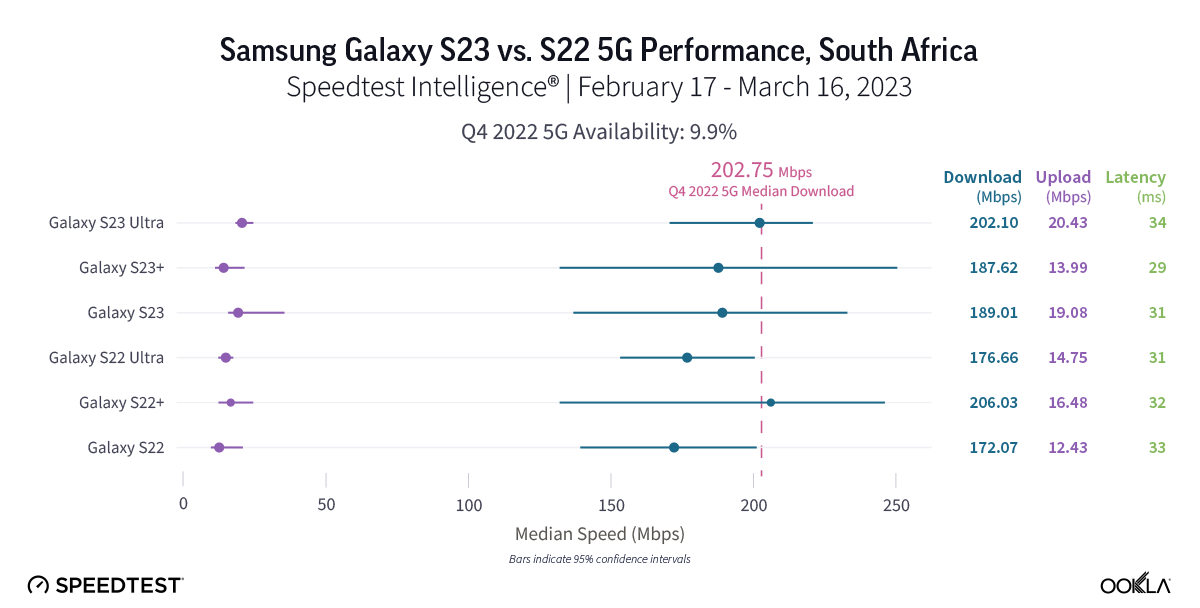
Samsung S23 models in South Africa don’t live up to the hype just yet
Speedtest Intelligence reveals that the new S23 models weren’t yet statistically faster than their S22 counterparts over 5G in South Africa during the first month after launch. S22 models had median 5G download speeds that ranged from 172.07 Mbps to 206.03 Mbps, while the S23 models ranged from 187.62 Mbps to 202.10 Mbps. There was one bright note — the median 5G upload speed for the S23 Ultra was faster than the S22 Ultra 20.43 Mbps to 14.75 Mbps. Median multi-server latency showed parity over 5G for the S22 models and S23 models. The S22 models ranged from 29.06 ms to 33.75 ms, while the S23 models ranged from 31.41 ms to 32.92 ms.
Recommendation: South African Galaxy S22 users should probably wait to upgrade their phones to the S23 models if they are looking for faster 5G experience, but the S23 features may outweigh the parity in speeds between models.
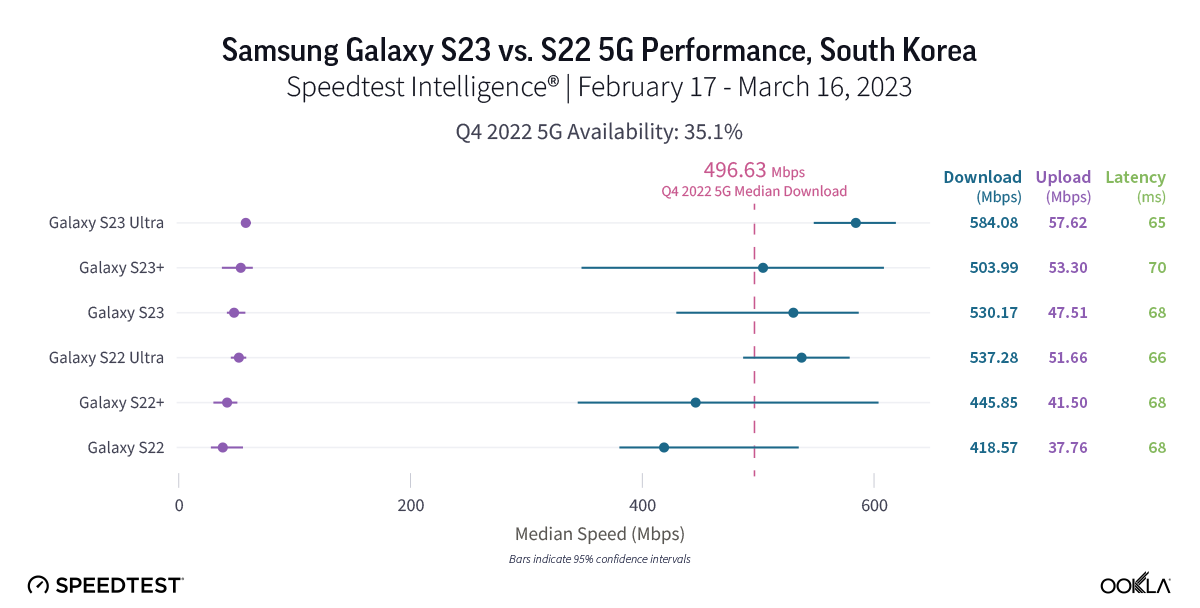
South Koreans saw fast 5G speeds on the new Samsung Galaxy S23 models
Home to Samsung, South Korea showed some of the fastest 5G speeds on our list. Every S23 model had a faster median 5G download speed than the corresponding S22 models, but statistical winners remained elusive during the first month after launch, which we expect will probably change upon more adoption in the near future. S22 models recorded median 5G download speeds between 418.57 Mbps and 537.28 Mbps, while the S23 models ranged from 503.99 Mbps and 584.08 Mbps. Upload speeds were similarly impressive — though with no statistically faster median 5G upload speeds than another — with S22 models ranging from 37.76 Mbps to 51.66 Mbps over 5G, and S23 models ranging from 47.51 Mbps to 57.62 Mbps. Median multi-server latency over 5G showed ranges from 65.00 ms to 69.81 ms for the S22 models, and a range of 66.13 ms to 68.15 ms for the S23 models.
Recommendation: If you’re a South Korean Galaxy S22 user, you can probably expect slightly faster speeds if you upgrade to the new S23 models, but an upgrade for the new features, especially for the new S23 Ultra camera, might be more justified.
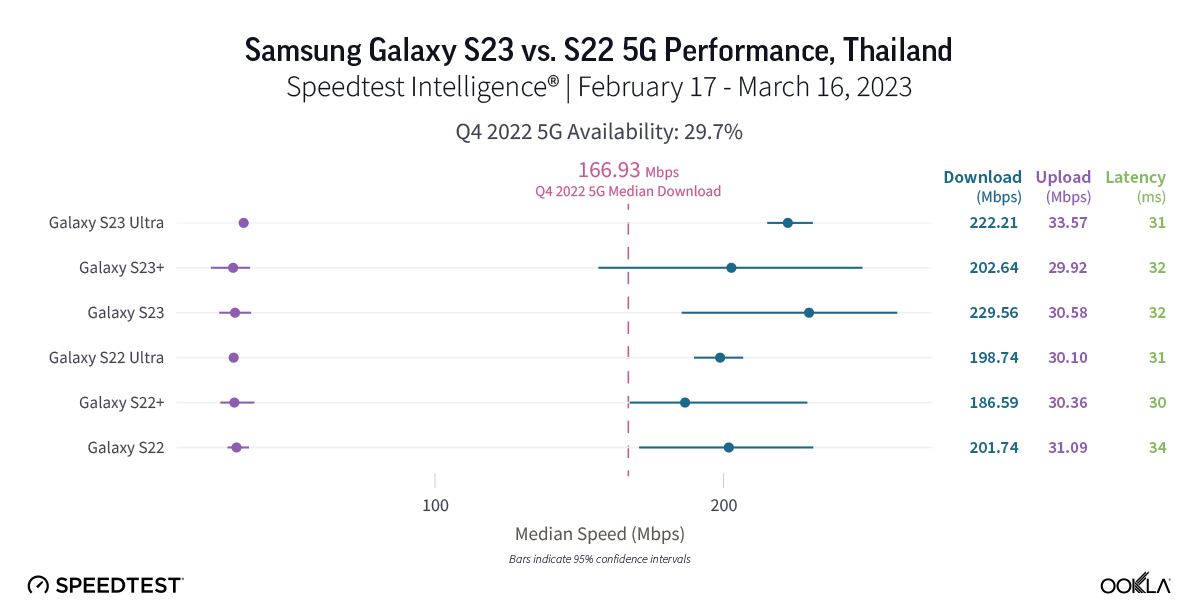
Thai Samsung Galaxy S22 and S23 users saw faster 5G speeds than the median average during Q4 2022
Speedtest Intelligence shows that the Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra was the only S23 model to achieve faster median 5G speeds than its predecessor in Thailand during the first month after launching. The S23 Ultra outperformed the S22 Ultra 222.21 Mbps to 198.74 Mbps over 5G for download speed and 33.57 Mbps to 30.10 Mbps for upload speed, respectively. The S23 and S23+ were not statistically faster, though the S23+ and S23 had median 5G download speeds of 202.64 Mbps and 229.56 Mbps, respectively. Median 5G multi-server latency showed close parity with the S22 ranging from 31.06 ms to 32.34 ms and the S23 ranging from 30.40 ms to 34.14 ms.
Recommendation: Thai Galaxy S22 Ultra users should feel confident in upgrading your phones to the S23 Ultra, especially for the new features. If you are a S22 and S22+ 5G user, you should absolutely consider upgrading, but might not yet see faster speeds.
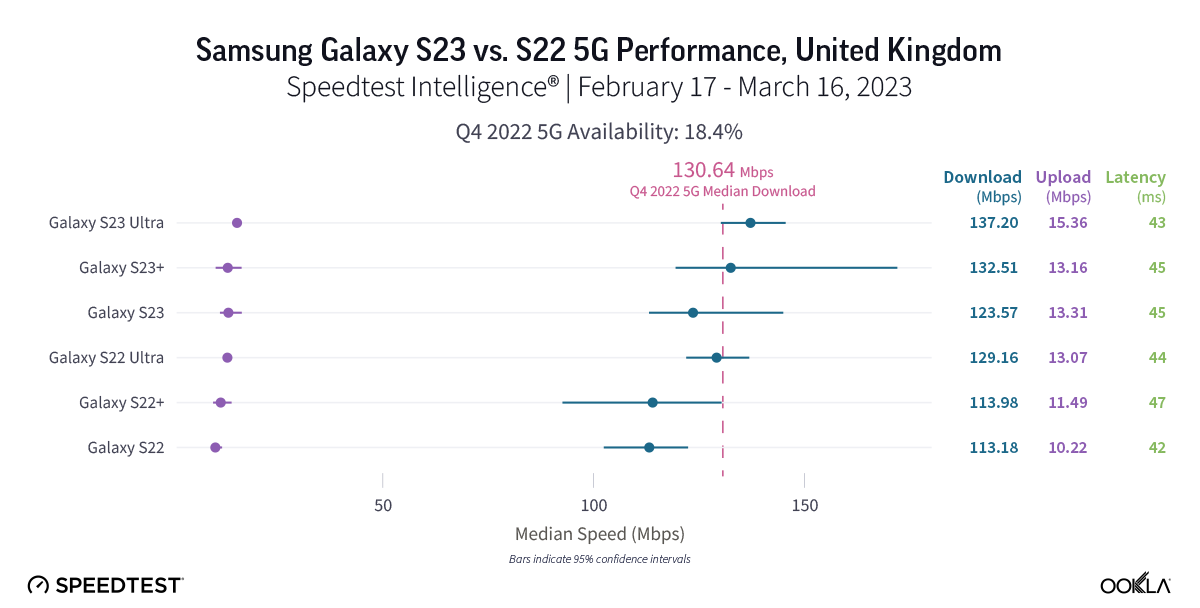
Samsung Galaxy S23 results showed potential in the United Kingdom, but you still may want to wait to upgrade
New 5G data from the U.K. reveals that while the new Samsung Galaxy S23 models have higher median download speeds, the S23 models are not statistically faster than the S22 models. The S22 models had median 5G download speeds that ranged from 113.18 Mbps to 129.16 Mbps, and the S23 models ranged from 123.57 Mbps to 137.20 Mbps. 5G download speeds in the U.K. weren’t the slowest we saw among the countries we surveyed, but they were quite close to Poland’s bottom-tier results. The S23 Ultra was one stand-out performer, which had a faster median 5G upload speed than the S22 Ultra at 15.36 Mbps to 13.07 Mbps, though the other models weren’t significantly faster, but came close. Median multi-server latency over 5G was too statistically close to call, with the S22 models between 43.04 ms and 45.09 ms, and the S23 models between 41.77 ms and 46.63 ms.
Recommendation: U.K. Samsung Galaxy S22 users should wait to upgrade their phones to the S23 models unless you’re dying for the S23’s new features. But don’t expect faster results quite yet, especially as the U.K. continues to lag behind other more mature 5G markets around the world.
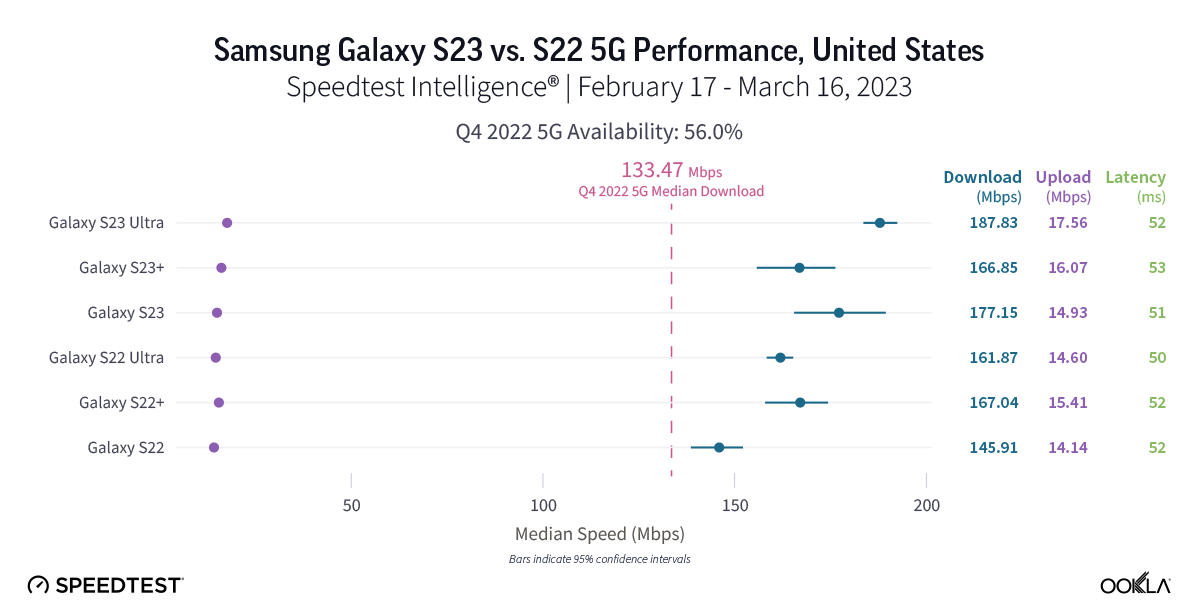
If you have 5G and a Samsung Galaxy S22 in the United States, don’t hesitate to upgrade to an S23 model
New data from Speedtest Intelligence reveals that during the first month of the Samsung Galaxy S23 series’ availability, the S23 and S23 Ultra outperformed the S22 and S22 Ultra for 5G download speeds, respectively, while the S23+ and S22+ were statistically too close to call. The S23 raced ahead of the S22 177.15 Mbps to 145.91 Mbps, and the S23 Ultra was faster than the S22 Ultra at 187.83 Mbps to 161.87 Mbps. All of the S22 and S23 models outperformed the median 5G download speed in the U.S. during Q4 2022. The Samsung S23 Ultra was the only S23 model to statistically outperform its counterpart for median 5G upload speeds, with an upload speed of 17.56 Mbps to 14.60 Mbps. The S23 and S23+ were too close to call. Looking at median multi-server latency over 5G, the S23 Ultra edged ahead of its S22 Ultra counterpart 50.44 ms to 51.52, while the other S23 didn’t have a statistical leg up.
Recommendation: U.S. Samsung Galaxy S22 users shouldn’t hesitate to upgrade to the S23 models, especially for the new features and hardware — particularly if you want the S23 Ultra’s 200 MP camera. With 5G networks increasingly getting faster, we suspect the S23 models have yet to see their full potential in the U.S., too.
The Speedtest® Android app can help benchmark your device’s 5G performance
After promising launches that have seen the Samsung Galaxy S23 models pull ever-so-slightly ahead in the U.S. and Germany, you can track how the Samsung Galaxy S23 performs on our next release of Ookla Market Reports™. If you recently upgraded your phone, be sure to download the Android Speedtest app to make sure you are getting the speeds you need along with access to video testing. We’ll be back throughout the year with fresh data on new phone launches, so if you’re considering upgrading your phone, be on the lookout for a new Ookla® device report.
Ookla retains ownership of this article including all of the intellectual property rights, data, content graphs and analysis. This article may not be quoted, reproduced, distributed or published for any commercial purpose without prior consent. Members of the press and others using the findings in this article for non-commercial purposes are welcome to publicly share and link to report information with attribution to Ookla.