Polski
Key takeaways
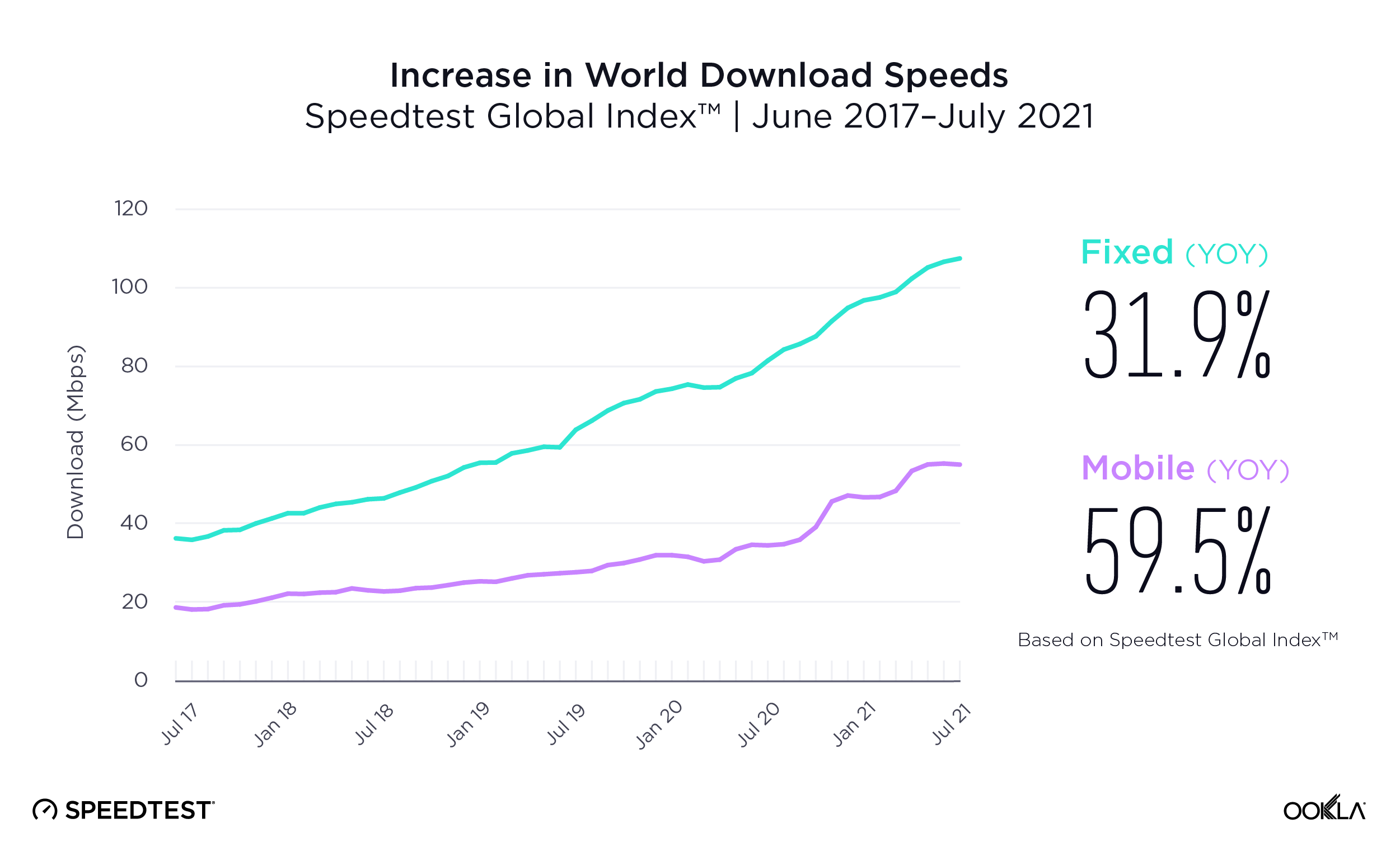
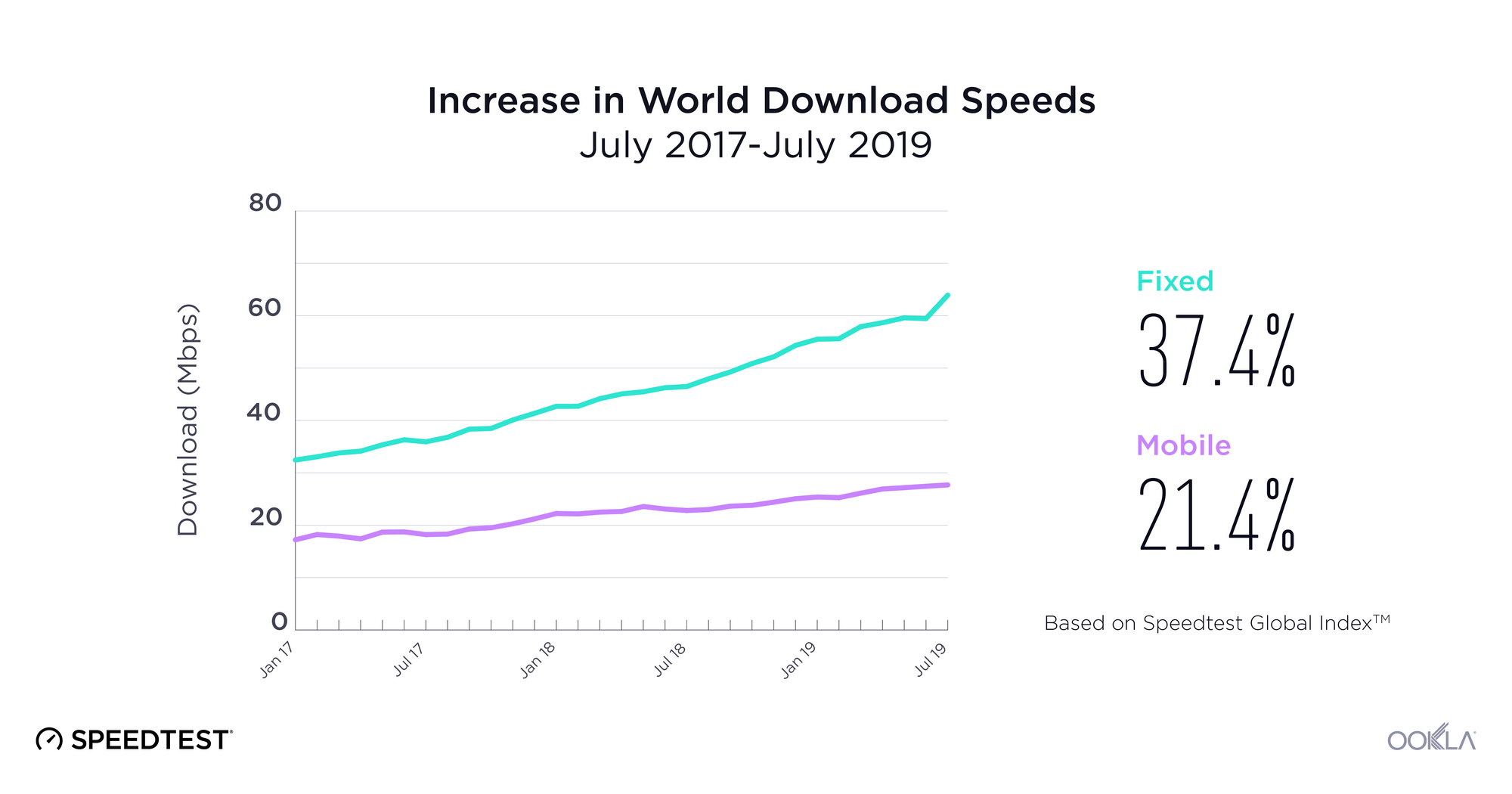
- The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the need for digital transformation, part of the EU-level funding will be available to drive digital transformation.
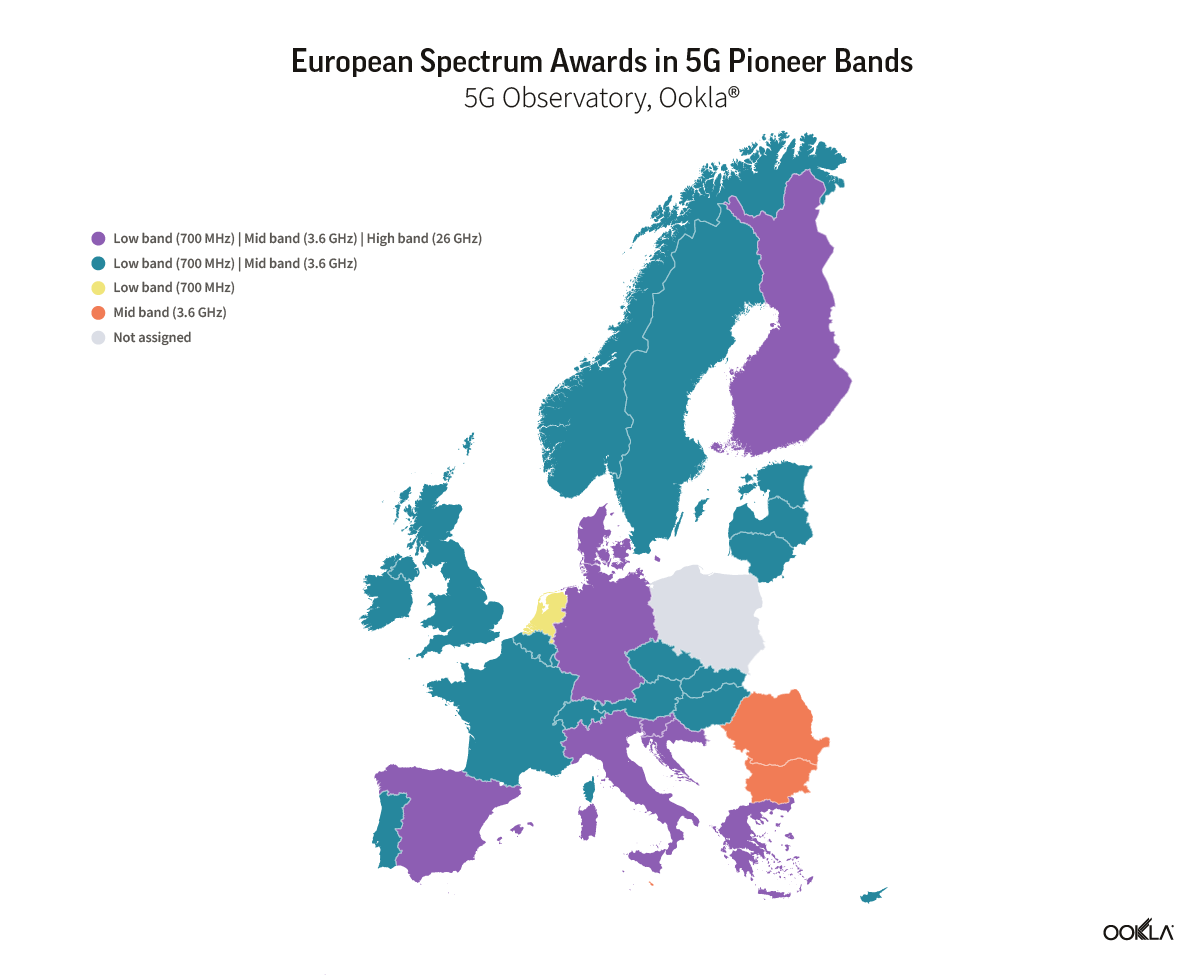
- Spectrum auctions have been delayed across the region. While Slovenia and Croatia have already completed spectrum auctions across all of the 5G pioneer bands, Poland lacks clear timelines and risks being left behind.
- Bulgaria leads in 5G median download speeds and 5G Availability. Its capital, Sofia, takes the top spot across the capital cities when it comes to median 5G speed and 5G Availability.
- Poland doesn’t fare well compared to other CEE countries. Poland came last in the median 5G download speeds ranking and its 5G speeds were just over double that of 4G. More importantly, though, it also seems that Polish end users don’t see the additional benefits 5G can bring, which depresses demand.
- Plus has the fastest median 5G speeds while Play wins 5G Availability. Łódź has the fastest 5G network among major Polish cities.
The EU funds set to stimulate digital transformation
An unprecedented amount of funding available to European Union member states has been approved to mitigate the economic and social impact of the COVID-19 pandemic. The NextGenerationEU recovery fund totals €750 billion. The vast majority, €672.5 billion, is allocated to the Recovery and Resilience Plans (RRP), distributed between loans (€360 billion) and grants (€312.5 billion). All funds must be spent by 2026.
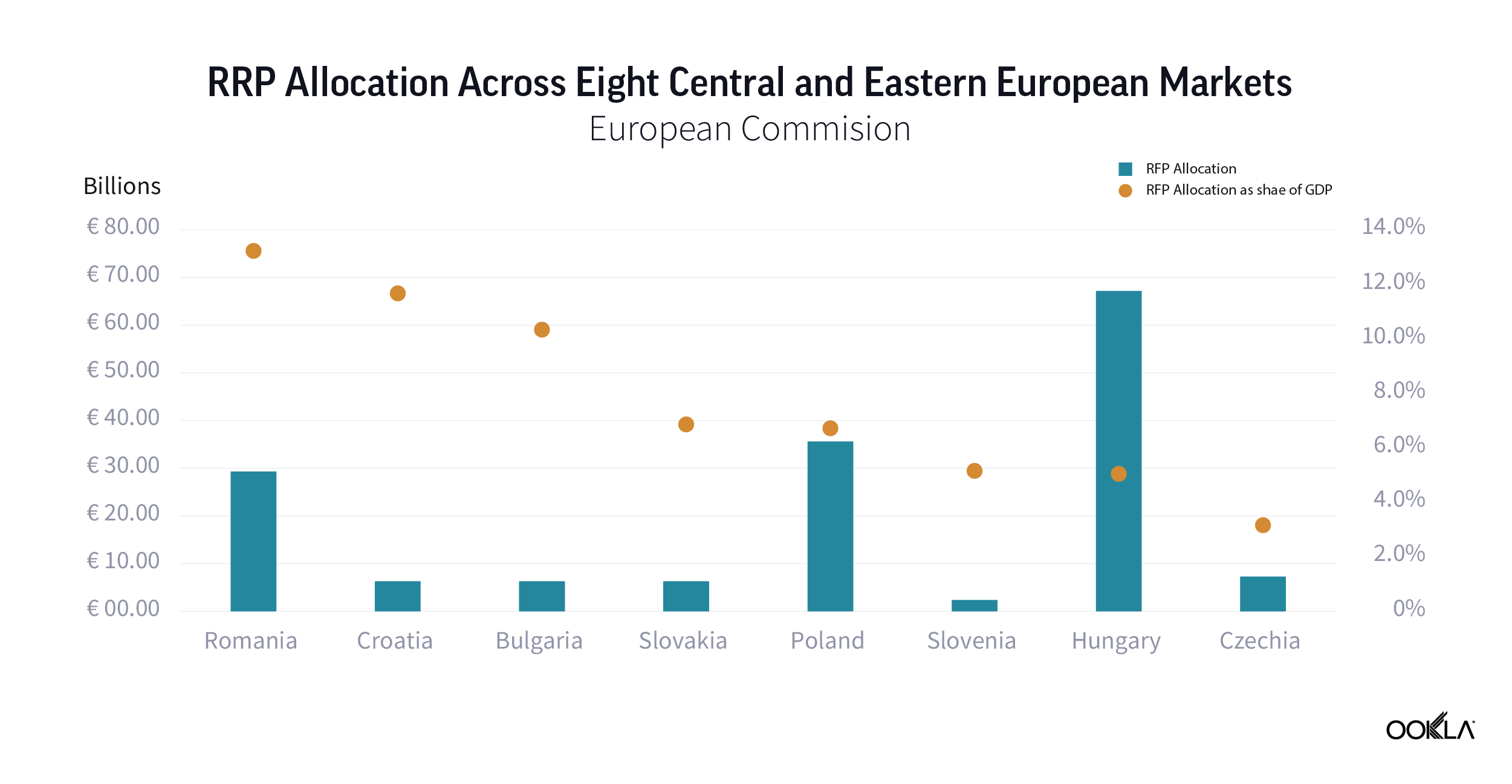
While not all these funds will drive investment into telecoms, some will have indirect impact such as green technology — see our thoughts on the discussions around Net Zero at MWC 2022. There are six pillars, one of which is digital transformation, which has over 20% of the national RRPs funding allocated. Digital transition projects include investment in R&D, deployment of new digital technologies including expansion of ultrafast broadband and 5G connectivity, and the digital transformation of the economy. The money is there for the taking, it is up to the countries to take advantage of it and funnel it into technology such as 5G to underpin economic growth.
Mid-band is most assigned spectrum across Central and Eastern Europe
We have reflected on the progress across Europe in this article. Now, we turn our attention to Central Eastern European (CEE) countries. According to GSMA Intelligence data, the vast majority of operators across the eight CEE countries — 24 out of 31 — have already launched 5G services.
As per the EC 2016 5G Action Plan, countries across the EU were meant to make low-band spectrum available for use by June 30, 2020, and mid- and high-band spectrums by December 31, 2020. At the EU level, there are three 5G pioneer bands as follows:
- Low-band: 700 MHz (703 – 733 MHz and 758 – 788 MHz)
- Mid-band: 3.6 GHz (3,400 – 3,800 MHz)
- High-band: 26 GHz (at least 1000 MHz within 24,250 – 27,500 MHz)
The delays related to spectrum assignment range from the impact of COVID-19 on schedules to cross-border coordination with non-EU countries to weak demand from the operators’ side. However, most countries included in this analysis have already assigned at least one band for 5G, with a notable exception of Poland.
Poland is yet to carry out a 5G spectrum auction — the planned sale of a C-band spectrum in Poland was postponed multiple times for various reasons. In March 2020, Poland announced the 3.6 GHz spectrum auction to be awarded by June 30, 2020. However, due to the pandemic, Polish authorities suspended all administrative proceedings, and the current holdup is due to legislative issues.
Furthermore, Poland is also exploring a controversial law to establish a state-owned 5G network, which would be operated by a state run operator — Exatel — in the 700 MHz band. The 700 MHz band is problematic because it requires coordination across the eastern borders (Belarus, Russia and Ukraine), which will delay spectrum assignment.
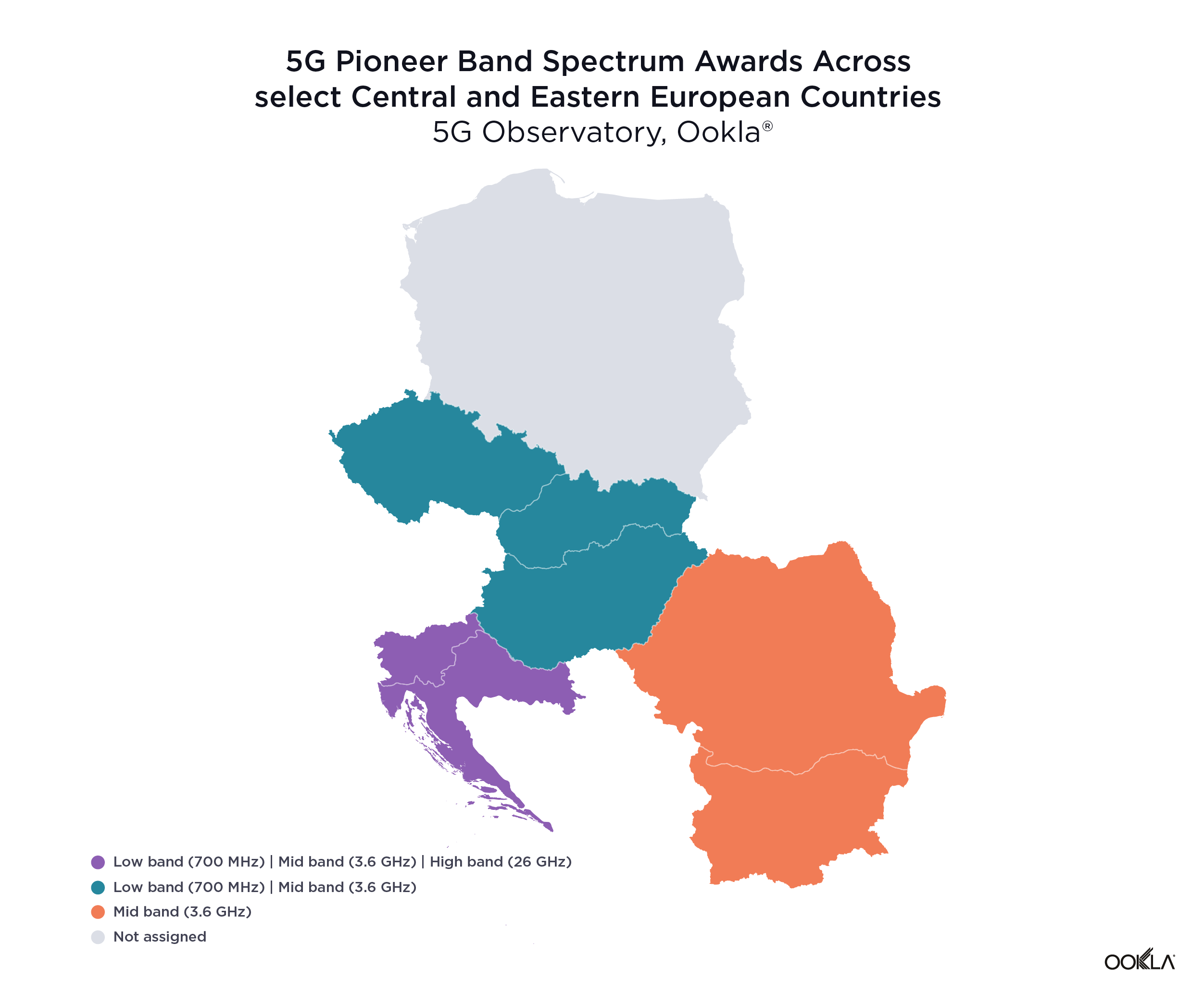
Slovenia and Croatia have forged ahead and become the only two countries that have already completed spectrum auctions across all of the 5G pioneer bands. In April 2021, Slovenia’s Agency for Communications Networks and Services (Akos) concluded the sale of frequencies in the 700 MHz, 1500 MHz, 2100 MHz, 2300 MHz, 3500 MHz and 26 GHz bands. In August 2021, the Croatian Regulatory Agency (Hakom) auctioned frequencies in the 700 MHz, 3600 MHz and 26 GHz bands. Furthermore, Miran Gosta, director of Hakom, recently announced that a new auction is being prepared for the frequencies that are already in use and will expire in 2024 such as 800 MHz, 900 MHz, 1800 MHz, 2100 MHz and 2600 MHz bands.
Bulgaria leads 5G speeds
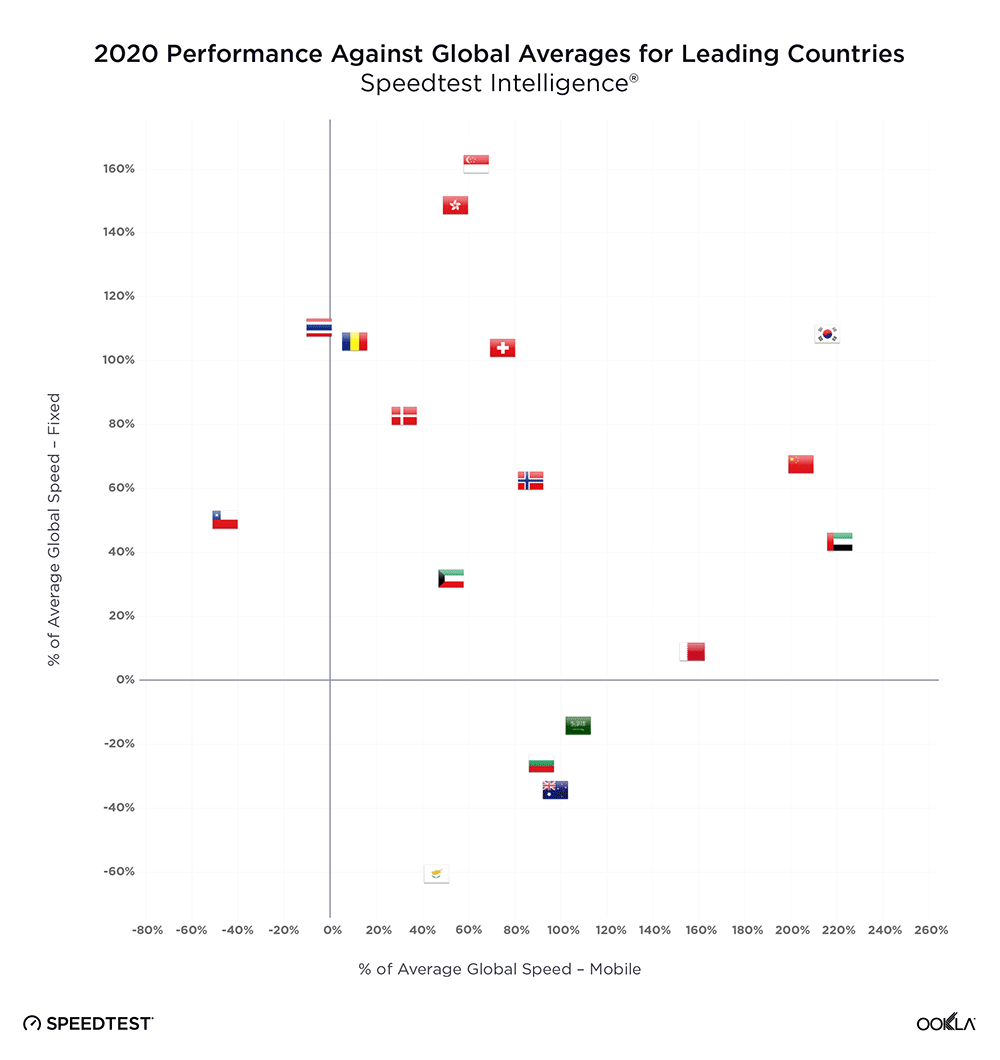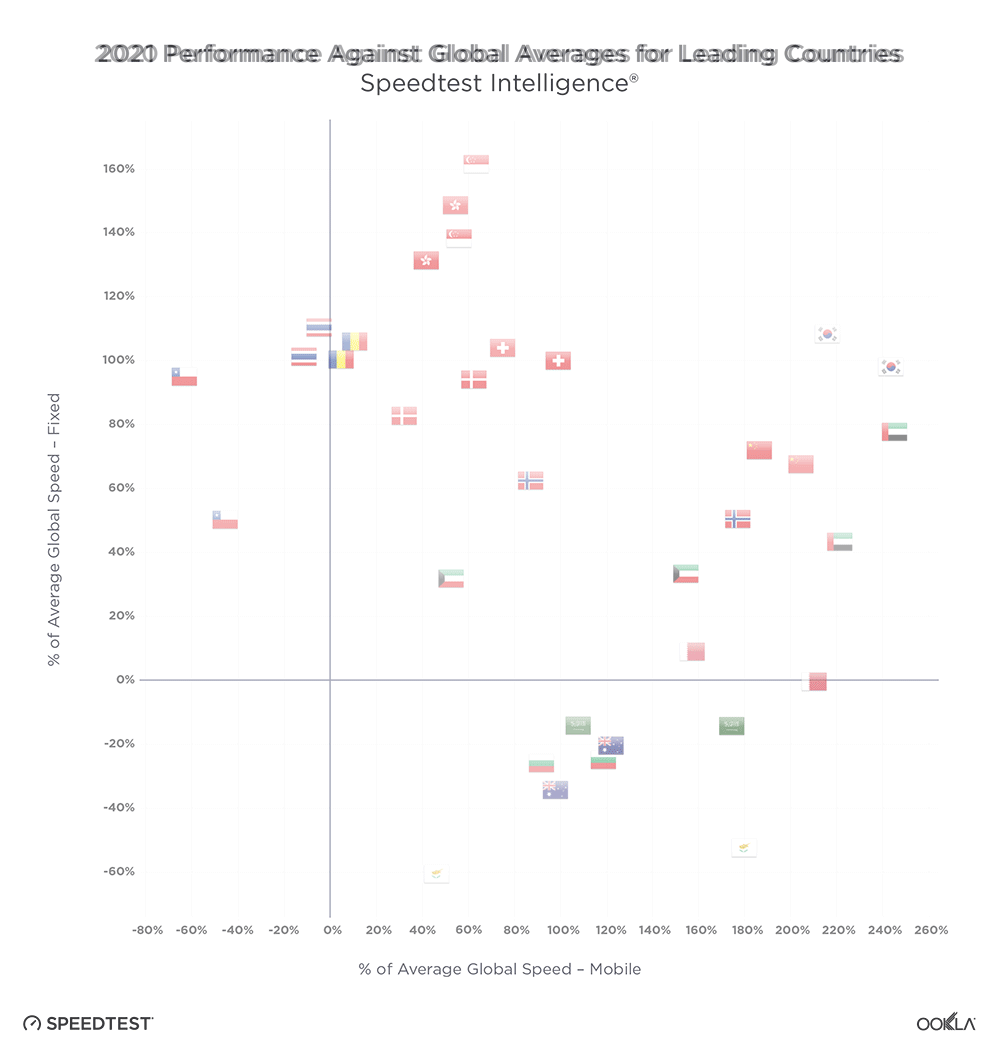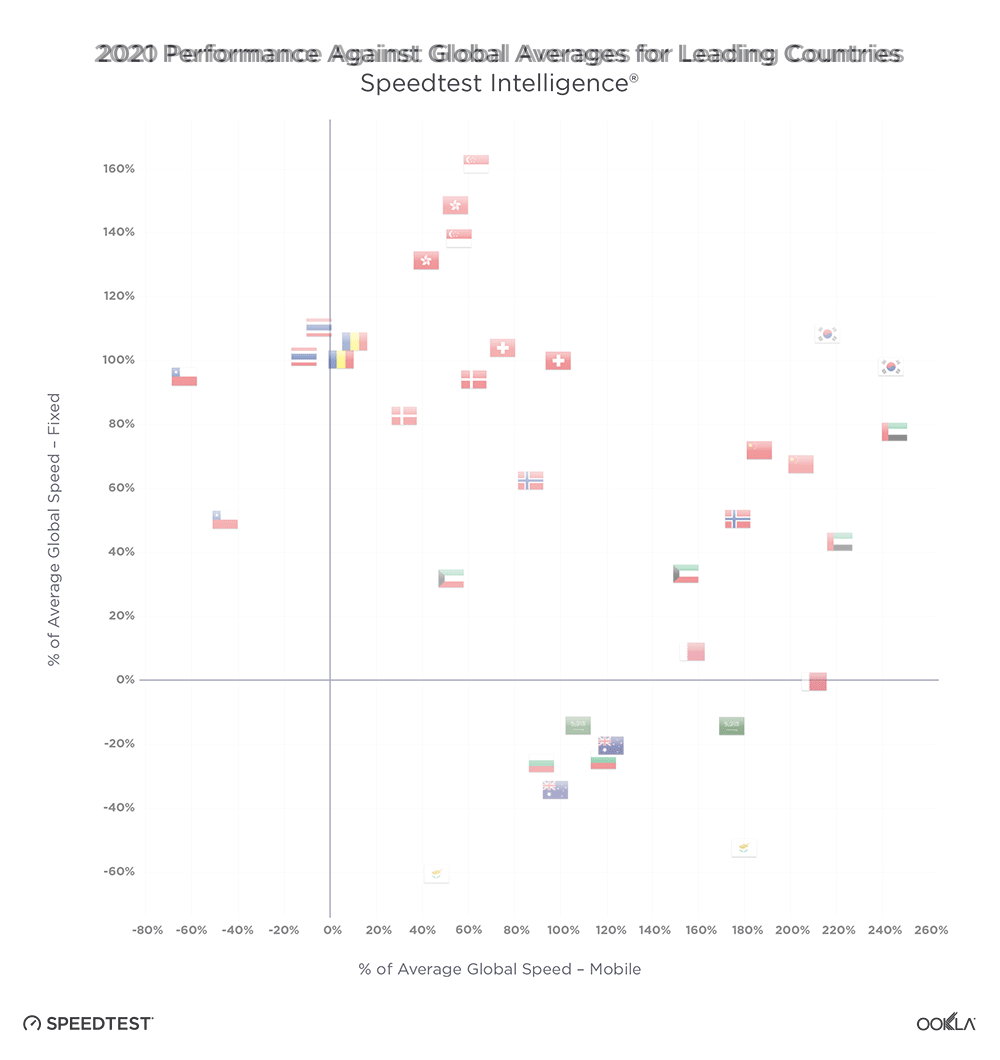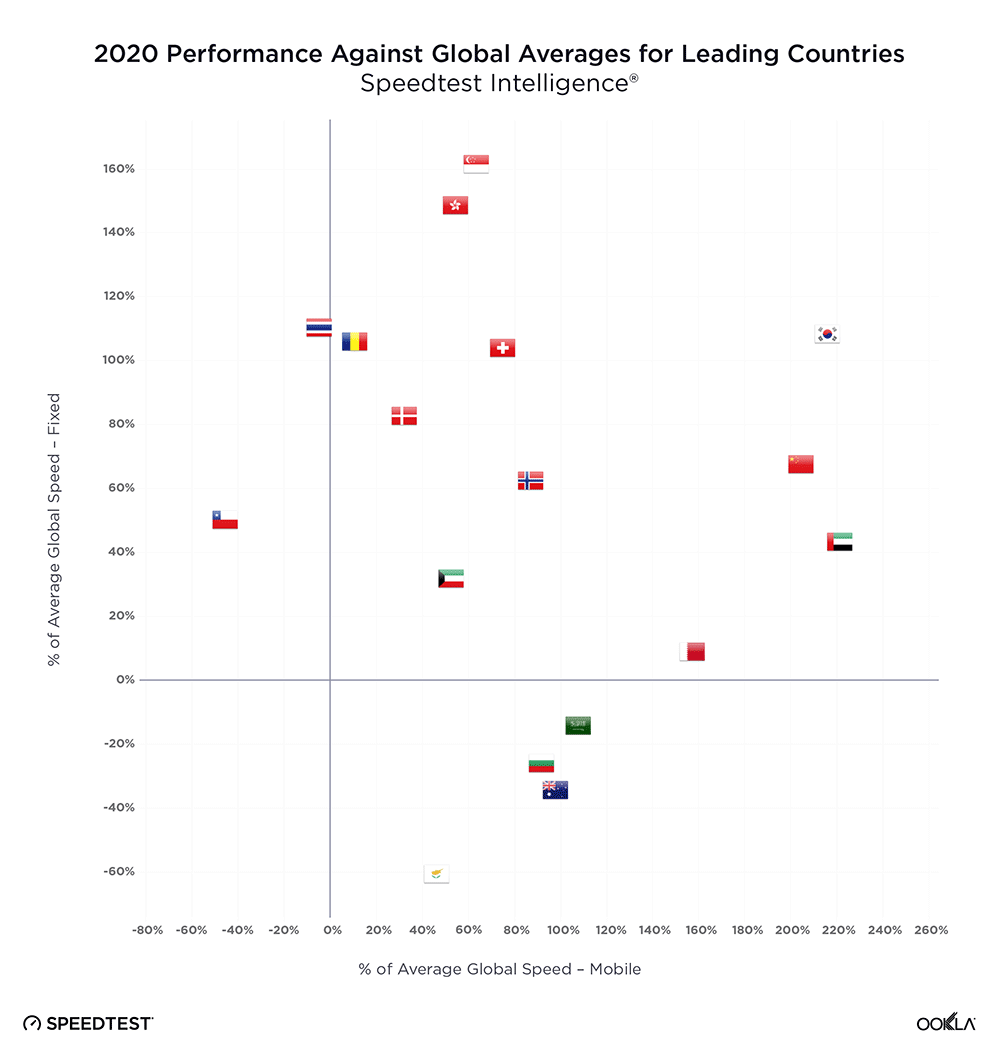
The important question is whether delays in spectrum assignments and supporting multiple network generations have affected the operators’ ability to deliver on 5G’s promise of faster speeds. According to Speedtest Intelligence®, the 5G median download speeds across the eight countries range from 73-407 Mbps. Bulgaria is the fastest at 406.97 Mbps, followed by Croatia, Hungary, Romania, Slovenia, and Slovakia. Czechia and Poland are trailing behind, at 112.53 Mbps and 73.12 Mbps, respectively.
Bulgarian operators took an active role in spearheading 5G development. In September 2020, Vivacom launched the first commercial 5G network via Dynamic Spectrum Sharing (DSS) in 1,800 MHz and 2,100 MHz, followed by A1 in Sofia using 3,600 MHz, and Telenor in early June 2021 in the biggest cities in Bulgaria in the 3,600 MHz band.
In April 2021, Vivacom Bulgaria won 100 MHz in the 3.7-3.8 GHz band for BGN4.6 million (€2.35 million) but it had already launched the 5G network before with a temporary license in November 2020. András Pali, Vivacom CTO stated in an interview that the operator plans to invest €120 million in infrastructure in 2021. Vivacom utilizes DSS, combining frequencies in 1.8, 2.1 and 3.6 GHz bands for 5G, so there is no compromise between coverage and speed. A1 Bulgaria, on the other hand, uses a dedicated 100 MHz band. Between the commercial launch in April and October 2021, A1 Bulgaria has seen the number of active users rise by 448% and the traffic generated by them by 771%, in excess of 90 terabytes (TB) in October 2021.
Furthermore, Bulgaria’s recovery and resilience plan assigned 26% of the €6.3 billion budget to digital transition. The plan includes measures to stimulate digital transformation, including significant investments and reforms in digital connectivity to increase the coverage of very high capacity networks in rural and sparsely populated areas and to create a favorable environment for the deployment of 5G networks and digital infrastructure.
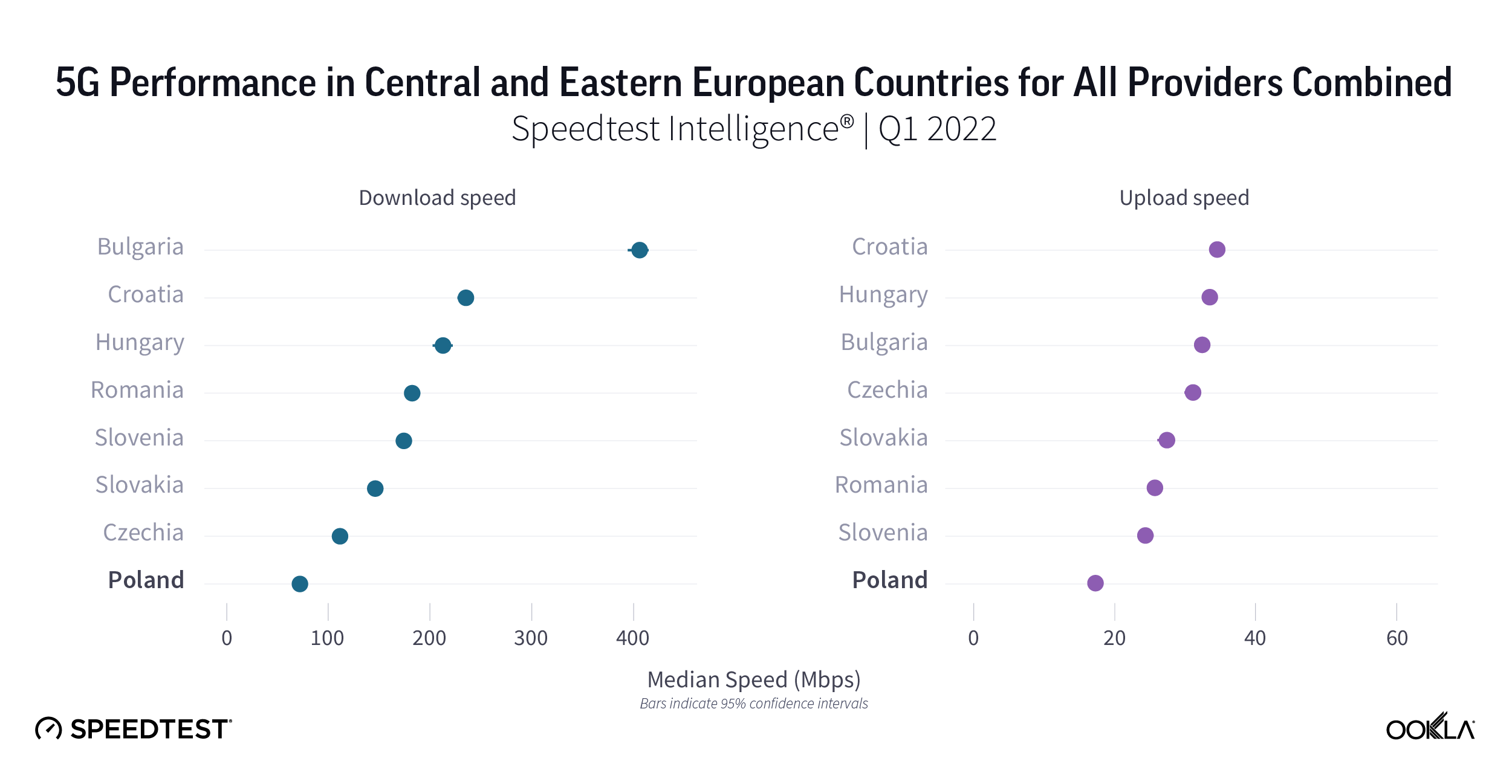
A few operators have rolled out 5G networks before having access to a dedicated 5G spectrum holding, instead using their existing spectrum holdings via DSS or temporarily allocated spectrum. Looking at the data for Poland, there is a link between lack of dedicated spectrum and median download speed. 5G speeds in Poland are just double the speeds of 4G, compared to Romania, Slovakia, Hungary, and Slovenia where 5G speeds are over five times faster than 4G. Since operators in Poland deployed 5G utilizing their existing spectral assets — in 2.6 GHz and 2.1 GHz — they are not able to take advantage of the benefits that mid-band spectrum brings to 5G deployments. We have reflected on how mid-band spectrum boosted 5G speeds and coverage in the U.S.
5G Availability skyrocketed in Bulgaria during 2021
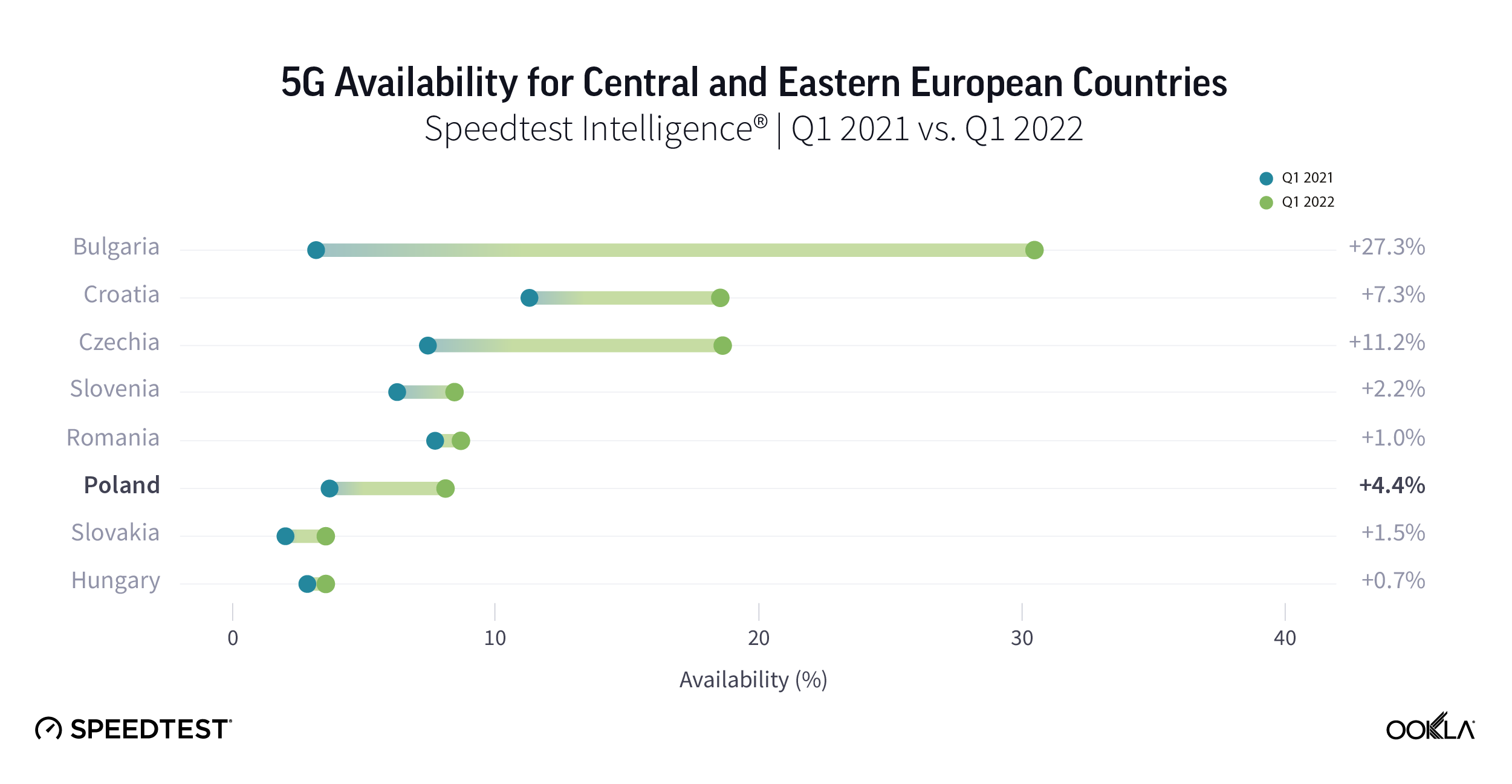
Speedtest Intelligence data put Bulgaria first in terms of 5G Availability (the proportion of users of 5G-capable devices who spend a majority of their time on 5G networks) within its regional peers. During 2021, 5G Availability in Bulgaria increased ten-fold, from 3.0% in Q1 2021 to 30.5% as of Q1 2022. This is partially thanks to operators broadening their portfolio of 5G capable devices, e.g. in June 2021, 55% of Telenor’s (now Yettel) smartphones on offer were 5G capable and offering 5G tariffs at no additional cost.
Croatia performed relatively well when it comes to 5G Availability, which increased from 11% in Q1 2021 to 18.5% in Q1 2022.The Croatian operators’ 5G license comes with coverage obligations amounting to 90% of urban areas, 99% of highways and 95% of railways by 2025. Furthermore, the license obligations include 25% rural areas coverage by 2025 and 50% by 2027. According to Hakom, 5G coverage and availability is at 60-70%.
However, five countries still had 5G Availability below 10% in Q1 2022, down from seven in Q1 2021. In Hungary, there is a public initiative in support of 5G uptake in a tune of HUF 5 billion (€13.15 million) to help consumers migrate away from 3G devices to 4G/5G smartphones in face of the upcoming 3G network sunset. On May 9, 2022 the Hungarian telecom regulator — NMHH — began a second phase of its mobile phone subsidy: owners of 2G or 3G devices can claim HUF 20,000 (€52.26) towards a purchase of a new 4G or 5G smartphone.
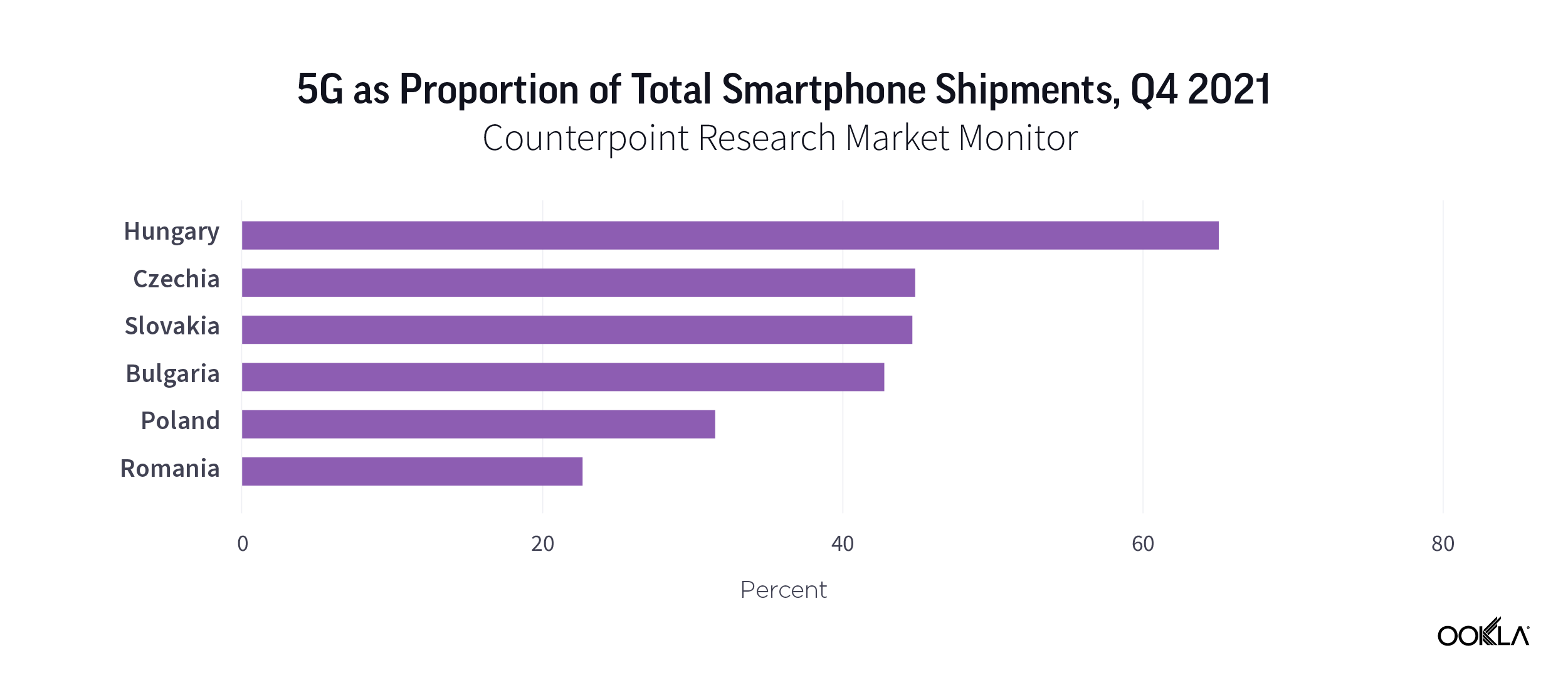
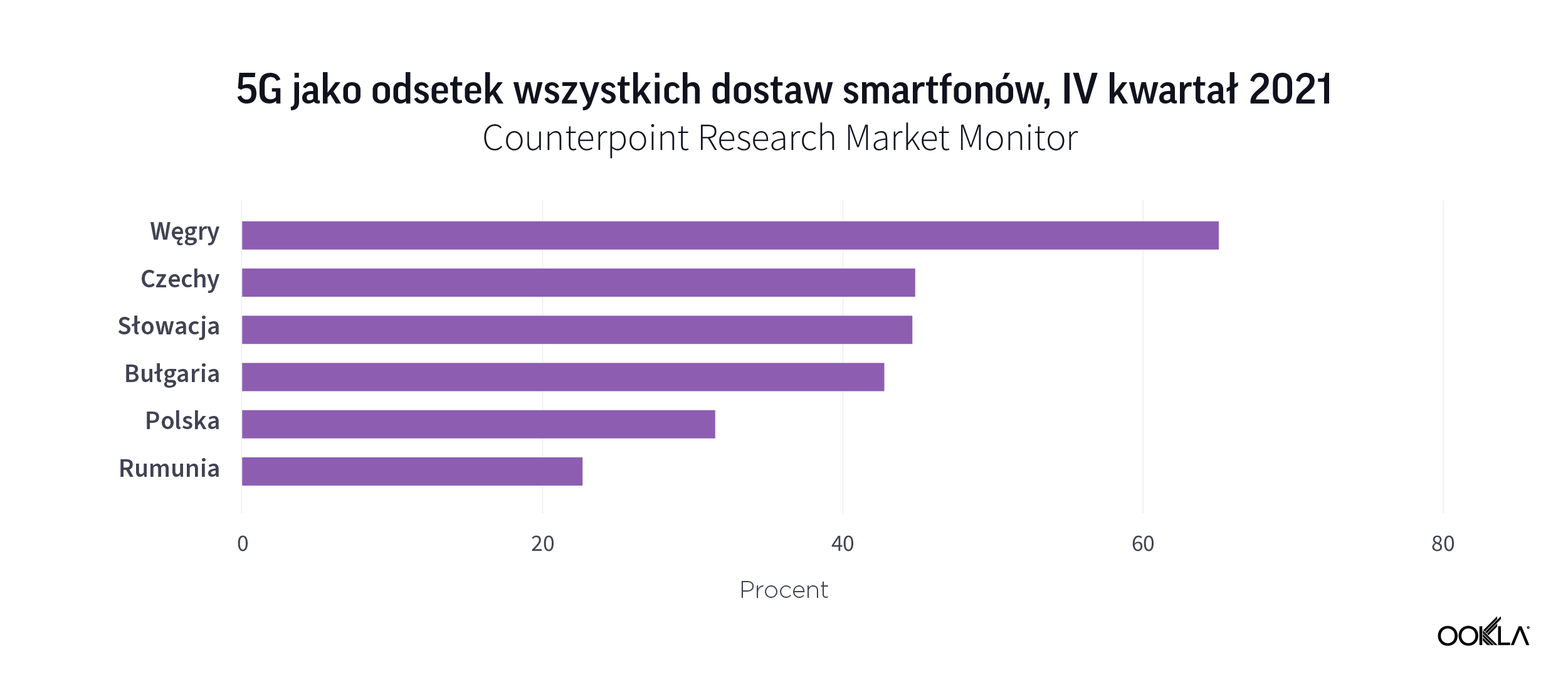
It isn’t surprising to see that Hungary came first when it comes to 5G smartphone shipments across a number of CEE countries. According to Counterpoint Research, 5G smartphones accounted for 65.1% of total smartphone shipments in Hungary in Q4 2021. In Czechia, Slovakia and Bulgaria, 5G smartphones account for two in five smartphones shipped. In Poland, this is almost one in three. Romania comes last. Although, these figures do not directly translate into direct sales to customers as shipments refer to selling into retail channels and point to an increased appetite for 5G devices. A key driving factor behind this is a growing availability of lower price tiers 5G smartphones. For instance, realme is seeing success with affordable 5G smartphones in Europe.
Sofia comes first in 5G median download speed and 5G Availability
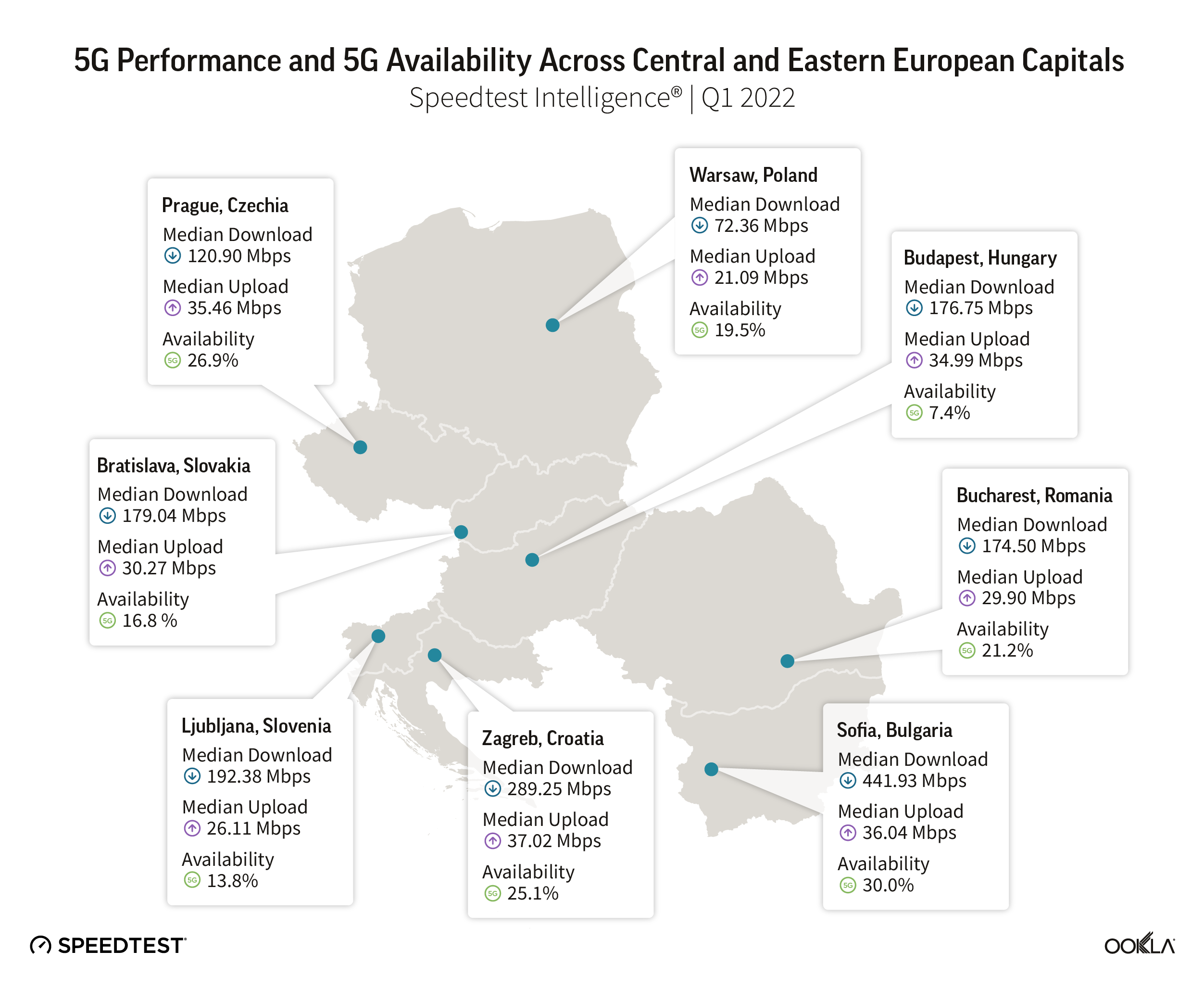
Given that Bulgaria had the fastest 5G and the best 5G Availability among its peers, it isn’t surprising its capital came first as well in the ranking of regional capitals, at 441.93 Mbps median download speed and 30% 5G Availability in Q1 2022. A1 Bulgaria started a test run already at the end of November 2020 in Sofia and Burgas, and they became the first 5G city in the country with an outdoor population coverage of over 90%.
Prague performed well when it comes to 5G Availability. In April 2022, the Prague metro area was fully covered by 5G networks thanks to a cooperation between Czech operators: T-Mobile, Vodafone, O2 and CETIN, and the Prague municipality. All of the Czech operators sunset 3G networks in 2021 to refarm the frequencies for 4G and 5G. The largest operator by number of connections, T-Mobile Czechia had more than 600 5G base stations covering 10.4% of the population in September 2021, and it planned to increase coverage to 25% by the end of the year. T-Mobile uses Ericsson and Huawei for its 5G network, which utilizes the 1800 MHz, 2100 MHz, and 700 MHz bands. The smallest operator, Vodafone Czechia, covered 70% of the population with a 5G network reaching 7 million Czechs in May 2022. Vodafone is committed to extending its network reach, at the moment it uses 3.5 GHz for 5G, but shortly it will start using the 700 MHz band as well as the refarmed 3G spectrum.
Poles need more education on the benefits of 5G
When it comes to 5G performance, Poland doesn’t fare well compared to other CEE countries. Poland came last in the median 5G download speeds ranking and its 5G speeds were just over double that of 4G. It is the only country that has not yet awarded 5G spectrum. More importantly, though, it also seems that Polish end users don’t see the additional benefits 5G can bring, which depresses demand.
According to the UKE’s enterprise survey, 78.2% of enterprises in Poland have heard of 5G. Good. However, the majority of enterprises claim that the current mobile parameters are enough to carry out their business activities across three measures: speed (88.6%), reliability (86.7%), and performance (85.9%). Given that the current 5G networks in Poland do not deliver on gigabit speed promises, this isn’t surprising.
From a Polish consumer point of view, 73.8% are familiar with the term 5G. This comes with a downside, though, just over half of respondents (57.4%) believe that 5G poses health risks.
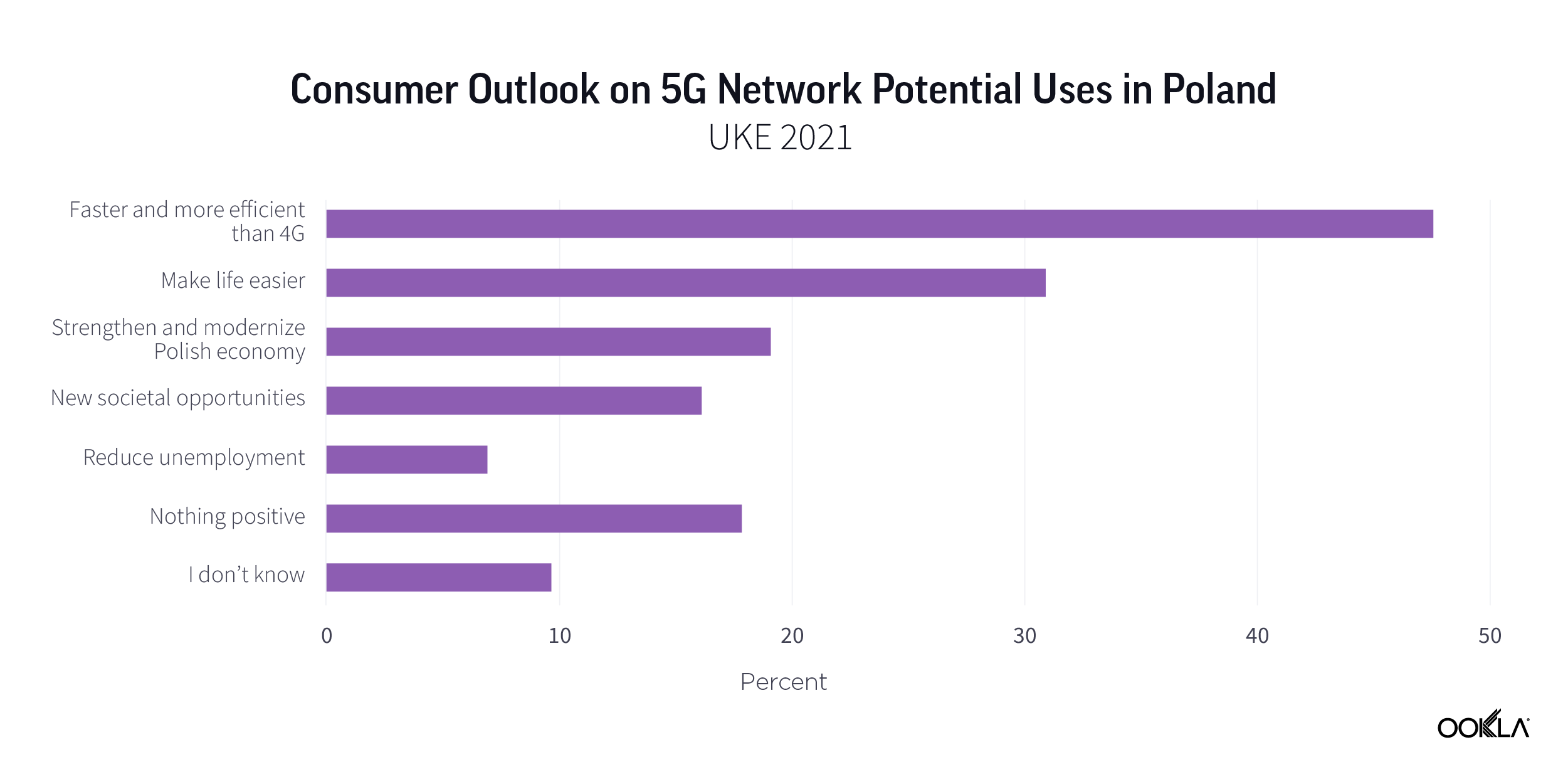
Asked what are the key benefits of 5G networks, almost half of respondents (47.5%) state that 5G will be faster and more efficient than 4G. Less than a third (31%) see 5G networks making people’s lives easier. The third preferred option is 5G’s ability to strengthen and modernize the Polish economy. Still, 18% do not see any positive outlook for using a 5G network. This can partially explain why 5G Availability in Poland is sub-10%.
5G is not only about speeds. 5G is seen as an avenue to bring additional value to the economy and society. According to a study from Ericsson Poland, the Polish economy could gain over €17 billion from 5G implementation by 2040. Considering the lack of a clear timeline for the 5G auction, the risk that Poland will fall further behind its peers is real.
Plus led on 5G download speed in Poland
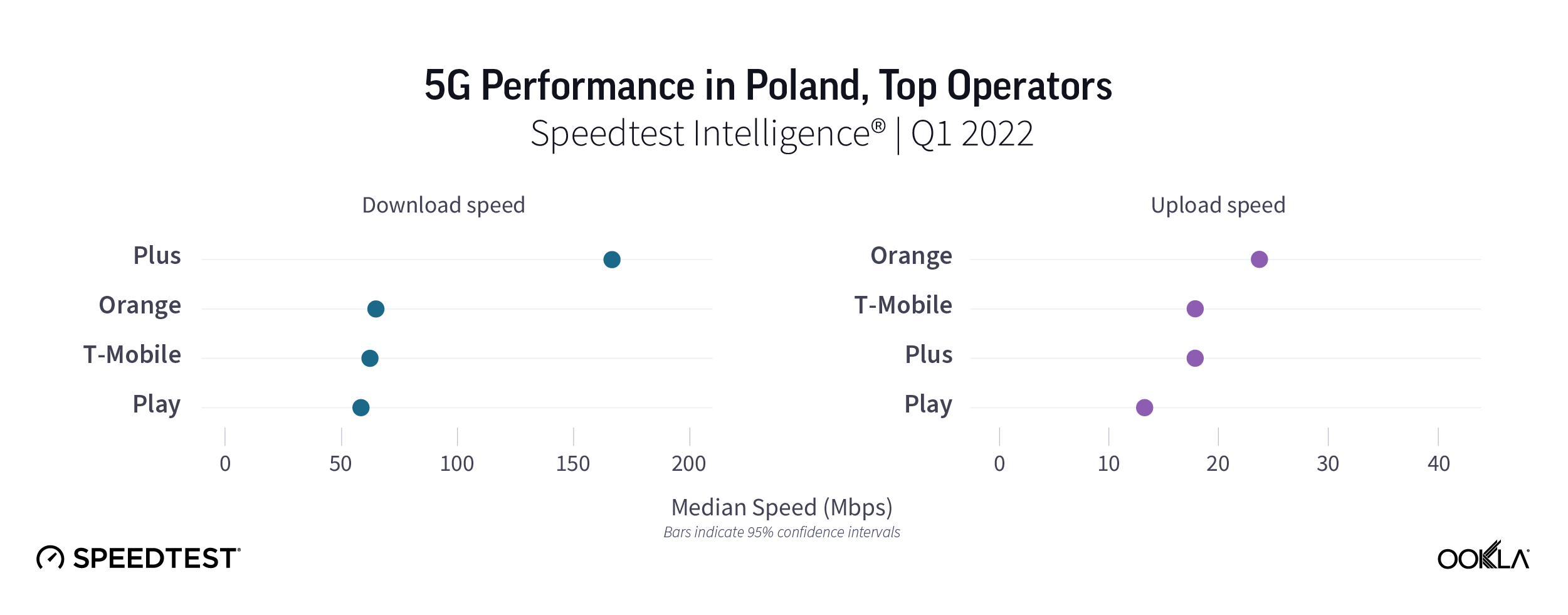
We compared 5G performance across Polish operators using Speedtest Intelligence. Plus was a clear winner, reaching median download speeds of 167.37 Mbps speeds in Q1 2022, ahead of Orange, T-Mobile, and Play. There isn’t a substantial difference in median upload speeds across the operators.
All of the Polish MNOs rolled out 5G networks tapping into their existing spectrum in a Non Standalone (NSA) mode, which relies on the underlying 4G/LTE technology. The 5G auction is now dependent on ongoing consultations about the National Cybersecurity Law Project, to be discussed by the Polish Parliament. The Law may impact network equipment decisions amongst the players, e.g. Play is using Huawei and Ericsson for base stations.
Polkomtel, trading under the Plus brand, launched the country’s first commercial 5G network in the 2.6 GHz band, utilizing 50 MHz of spectrum in May 2020. Apart from Plus, all other operators deployed 5G using DSS in the 2.1 GHz spectrum band, which can partially explain why they have lower speeds.
Orange Poland, like other countries within Orange Group, will roll out 5G Standalone (5G SA) in partnership with Ericsson. This will enable 5G network slicing and private networks development. In anticipation of the 5G auction, and to stimulate new 5G use cases, the operator launched Orange 5G Lab testing services such as AR, AI utilizing the spectrum allocated by the UKE for testing 5G in the 3.6 GHz band.
Play had the best 5G Availability in Poland
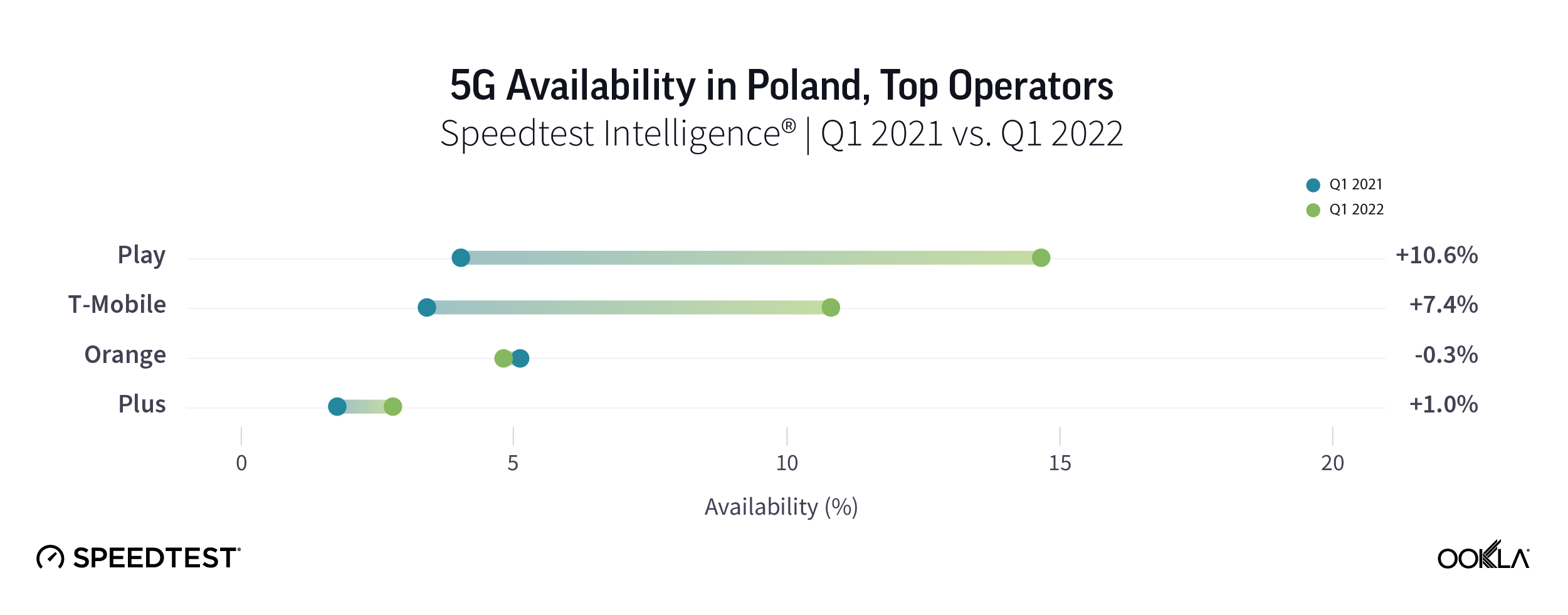
According to Counterpoint Research, smartphone shipments in Poland have almost tripled during 2021, driven by the challenger brands such as realme, OPPO and Xiaomi (including Redmi and POCO). Polish operators also continue to promote the sale of 5G-capable devices. 5G smartphones as a proportion of smartphone sales ranged between 36% for Orange, 40% for T-Mobile, and 45% for Play. Yet, Play has sprinted ahead the pack when it comes to 5G Availability, and T-Mobile is catching up leaving Orange and Plus behind.
This is surprising because the Play’s 5G network doesn’t necessarily have the widest reach. As of year-end 2021, Plus’ 5G network extended to 19 million people, followed by Play with over 13 million, T-Mobile (11 million) and Orange (6.3 million). Translating this into population coverage using 2021 census data (38.18 million people), this equates to 50%, 34%, 29%, and 17% population coverage.
Play, part of the Iliad Group, had the best 5G Availability, likely because of aggressive marketing and discounts combined with a large portfolio of 5G devices and the cheapest tariffs. Recently, Play had secured a PLN 500 million (€107 million) credit facility under the Operational Programme Digital Poland (POPC) from BGK, which will also use to roll out 5G services.
The mobile operators continue to invest in 5G network rollouts. For instance, T-Mobile extended its partnership with Nokia to include the modernization of RAN as well as rollout of 5G services. The operator plans to use 4G and 5G DSS on the lower band and. when available, the 3.5 GHz band for dense urban areas. T-Mobile targets to finish 2022 with 3,500 5G base stations and 30% population coverage. T-Mobile shut down its 3G network in the 2,100 MHz frequency band in October 2021. It has also embarked on the 3G network shutdown, aiming to realize the 900 MHz used for 3G and refarm it to LTE and 5G in 2023.
The spanner in the works to achieve wide 5G availability is the controversy around 5G auctions. In October 2019, the four leading mobile operators (Plus, Orange, Play and T-Mobile), the state-owned telecom operator Exatel and the Polish Development Fund (PFR) signed a memorandum of understanding to build a nationwide infrastructure. This will be owned by the state via a special-purpose entity called Polskie 5G. The Polish regulator has proposed to assign the entire 700 MHz band (2×30 MHz) to this new entity, with a view to first provide connectivity for public protection and disaster relief services, while making it available to all operators. Reserving spectrum for vertical use is not new, we have discussed this in our recent article; the novelty here is the band and amount. The 700 MHz band is key for providing wide coverage and in-building penetration. In our recent webinar, Eric Brands from KPN explained that KPN scores well in 5G Availability, partially because they have access to low band 5G spectrum (700 MHz).
Łódź has the fastest 5G network among major Polish cities
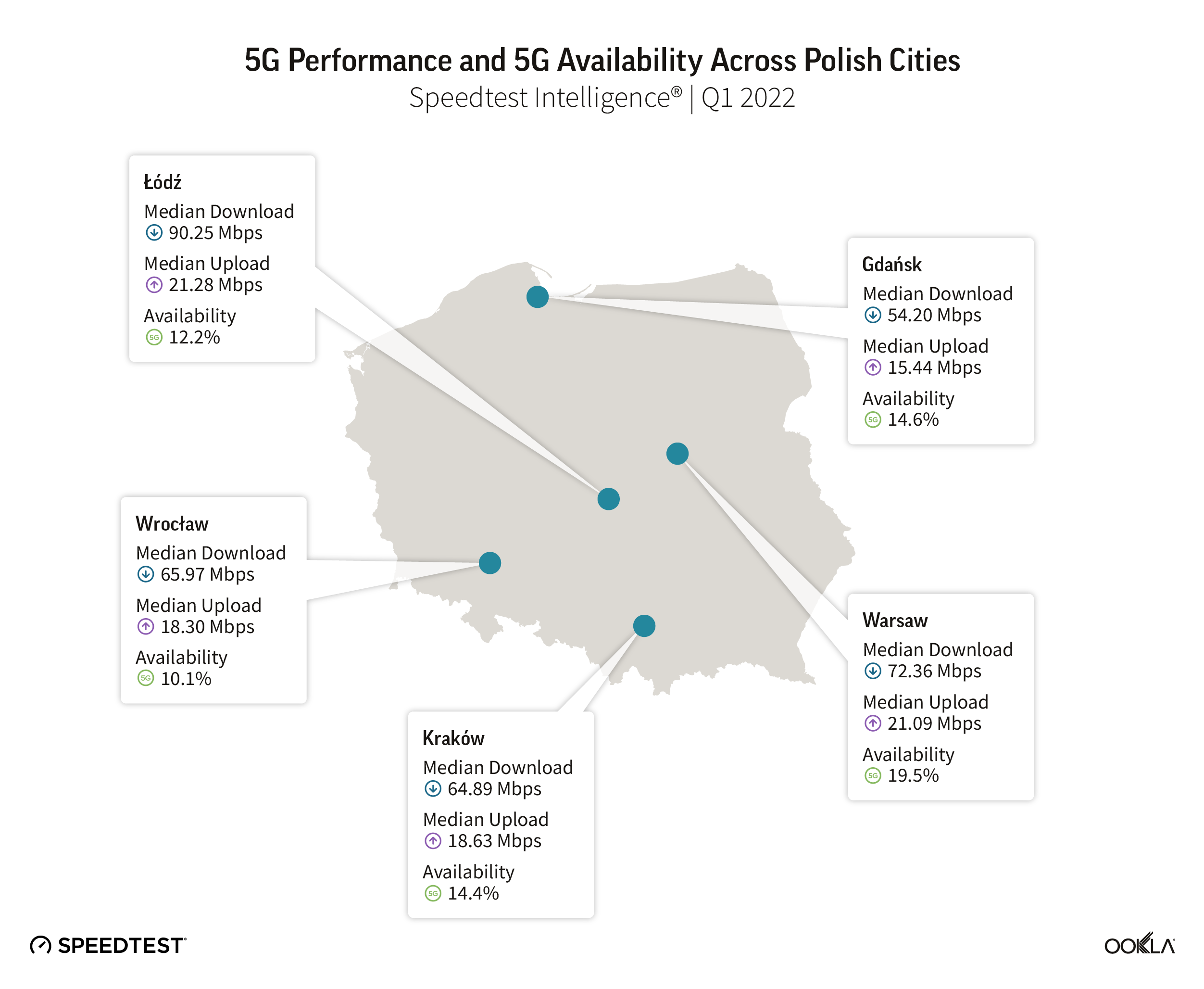
Łódź came top as the fastest city in Poland with 90.25 Mbps in Q1 2022, it is also a hotspot for operators’ innovation. Orange deployed a 5G campus network in the Lodz Special Economic Area where 40 start-ups working in the accelerator will be able to use the infrastructure. Ericsson has provided the infrastructure for the economic area: ten antennas working on the 3.6 GHz and 2,100 MHz bands, covering approx.1,000 square meters.
T-Mobile is testing 5G SA in Łódź to enable new services for both consumer and B2B customers, including VoNR (Voice over New Radio) services on the 5G network. The 5G SA network is utilizing the 2,600 MHz band.
The Polish capital, Warsaw, is just slightly ahead of the rest in terms of 5G Availability.
We’ll be watching 5G performance closely in Poland using Speedtest Intelligence. If you want to learn more about how Speedtest Intelligence can help you benchmark your 5G performance against competitors, please inquire here.
Kluczowe wnioski
- Pandemia COVID-19 podkreśliła potrzebę transformacji cyfrowej, część funduszy unijnych zostanie przeznaczona na jej realizację.
- Aukcje pasma zostały opóźnione w całym regionie. Podczas gdy Słowenia i Chorwacja zakończyły już aukcje pasma we wszystkich pionierskich pasmach 5G, Polsce brakuje jasnych harmonogramów i istnieje ryzyko pozostania w tyle.
- Bułgaria jest liderem pod względem mediany szybkości pobierania i 5G Availability. Jej stolica, Sofia, zajmuje pierwsze miejsce wśród stolic pod względem mediany prędkości 5G i 5G Availability.
- Polska nie wypada dobrze na tle innych krajów Europy Środkowo-Wschodniej. Polska zajęła ostatnie miejsce w rankingu mediany prędkości pobierania 5G, a jej prędkości 5G były nieco ponad dwukrotnie wyższe niż 4G. Co jednak ważniejsze, wydaje się również, że polscy użytkownicy końcowi nie dostrzegają dodatkowych korzyści, jakie może przynieść 5G, co zmniejsza popyt.
- Plus ma największą średnią prędkość 5G, a Play wygrywa pod względem 5G Availability. Łódź ma najszybszą sieć 5G wśród największych polskich miast
Fundusze unijne mają stymulować transformację cyfrową
W celu złagodzenia gospodarczych i społecznych skutków pandemii COVID-19 została zatwierdzona bezprecedensowa kwota środków dostępnych dla państw członkowskich Unii Europejskiej. Fundusz naprawczy The NextGenerationEU wynosi 750 mld euro. Zdecydowana większość środków, 672,5 mld euro, jest przeznaczona na Plany odbudowy i zwiększania odporności (ang. Recovery and Resilience Plans, RRP) i podzielona między pożyczki (360 mld euro) i dotacje (312,5 mld euro). Wszystkie środki muszą zostać wydane do 2026 r.
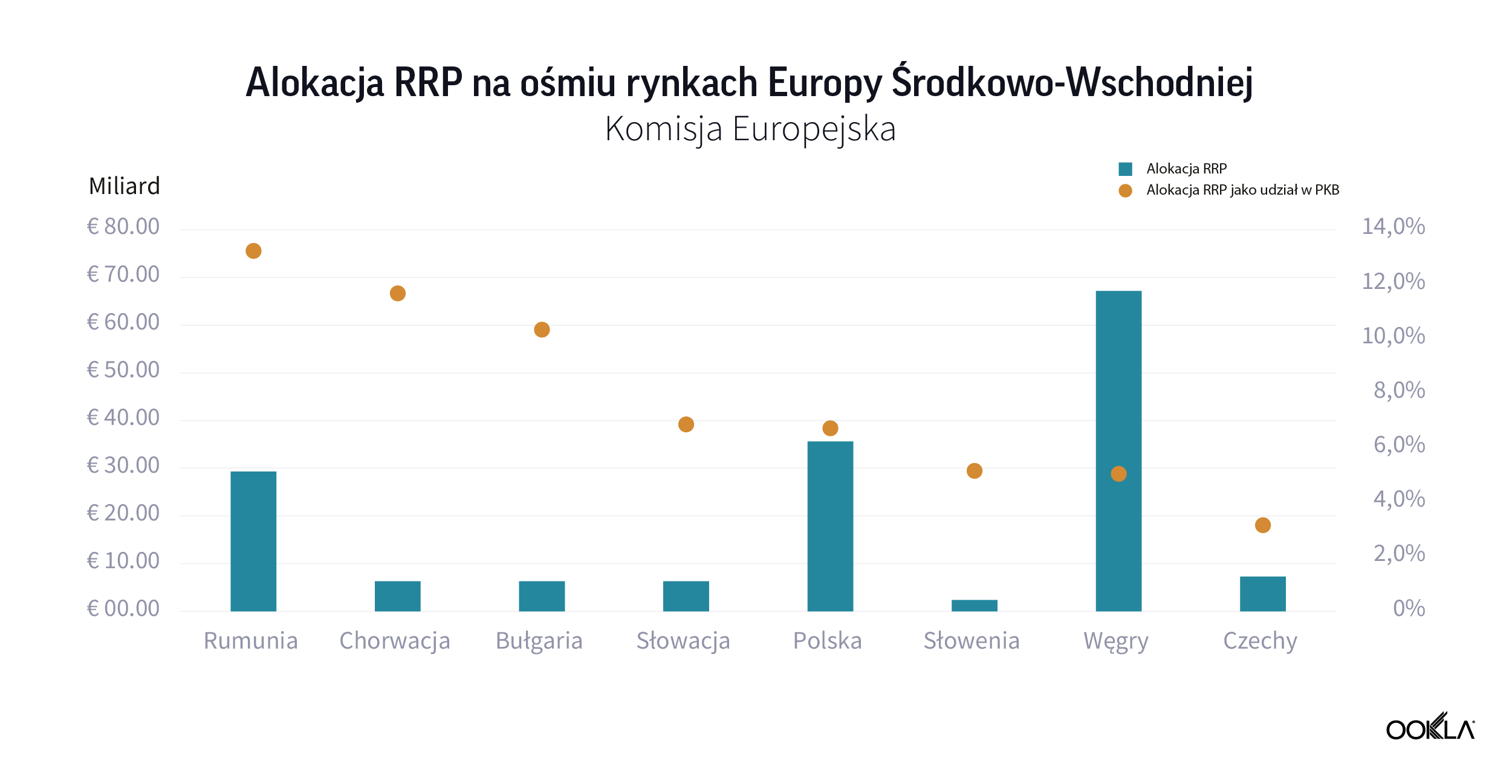
Chociaż nie wszystkie te fundusze będą napędzać inwestycje w telekomunikację, niektóre będą miały pośredni wpływ, np. zielone technologie — zobacz nasze przemyślenia na temat dyskusji na temat Net Zero na MWC 2022. Istnieje sześć filarów, z których jednym jest transformacja cyfrowa, która ma ponad 20% przydzielonego finansowania krajowych programów RRP. Projekty transformacji cyfrowej obejmują inwestycje w badania i rozwój, wdrażanie nowych technologii cyfrowych, w tym rozwój ultraszybkiej łączności szerokopasmowej i łączności 5G oraz cyfrową transformację gospodarki. Pieniądze są dostępne. To od krajów zależy, czy je wykorzystają i przekierują je do technologii, takich jak 5G, aby wesprzeć wzrost gospodarczy.
Średnie pasmo to najczęściej przydzielane pasmo w Europie Środkowo-Wschodniej
W tym artykule zastanowiliśmy się nad postępami w Europie. Teraz zwracamy uwagę na kraje Europy Środkowo-Wschodniej (CEE). Według danych GSMA Intelligence zdecydowana większość operatorów w ośmiu krajach Europy Środkowo-Wschodniej — 24 z 31 — uruchomiła już usługi 5G.
Zgodnie z planem działania KE na rzecz 5G z 2016 r., kraje w całej UE miały udostępnić do 30 czerwca 2020 r. pasmo niskich częstotliwości, a do 31 grudnia 2020 r. pasmo średnich i wysokich częstotliwości. Na poziomie UE istnieją trzy pionierskie pasma 5G, które przedstawiają się następująco:
– Dolne pasmo: 700 MHz (703 – 733 MHz i 758 – 788 MHz)
– Średnie pasmo: 3,6 GHz (3400 – 3800 MHz)
– Wysokie pasmo: 26 GHz (co najmniej 1000 MHz w zakresie 24 250 – 27 500 MHz)
Opóźnienia związane z przydziałem pasma wahają się od wpływu COVID-19 na harmonogramy, przez transgraniczną koordynację z krajami spoza UE, po słaby popyt ze strony operatorów. Jednak większość krajów uwzględnionych w tej analizie przypisała już co najmniej jedno pasmo dla 5G, z godnym uwagi wyjątkiem Polski.
Polska ma jeszcze przeprowadzić aukcję pasma 5G — planowana sprzedaż pasma C w Polsce była wielokrotnie przekładana z różnych powodów. W marcu 2020 r. Polska ogłosiła, że aukcja pasma 3,6 GHz zostanie rozstrzygnięta do 30 czerwca 2020 r. Jednak w związku z pandemią polskie władze zawiesiły wszelkie postępowania administracyjne, a obecne wstrzymanie spowodowane jest kwestiami legislacyjnymi.
Co więcej, Polska bada również kontrowersyjne prawo dotyczące utworzenia państwowej sieci 5G, która byłaby obsługiwana przez państwowego operatora — Exatel — w paśmie 700 MHz. Pasmo 700 MHz jest problematyczne, ponieważ wymaga koordynacji przez granice wschodnie (Białoruś, Rosja i Ukraina), co opóźni przydział pasma.
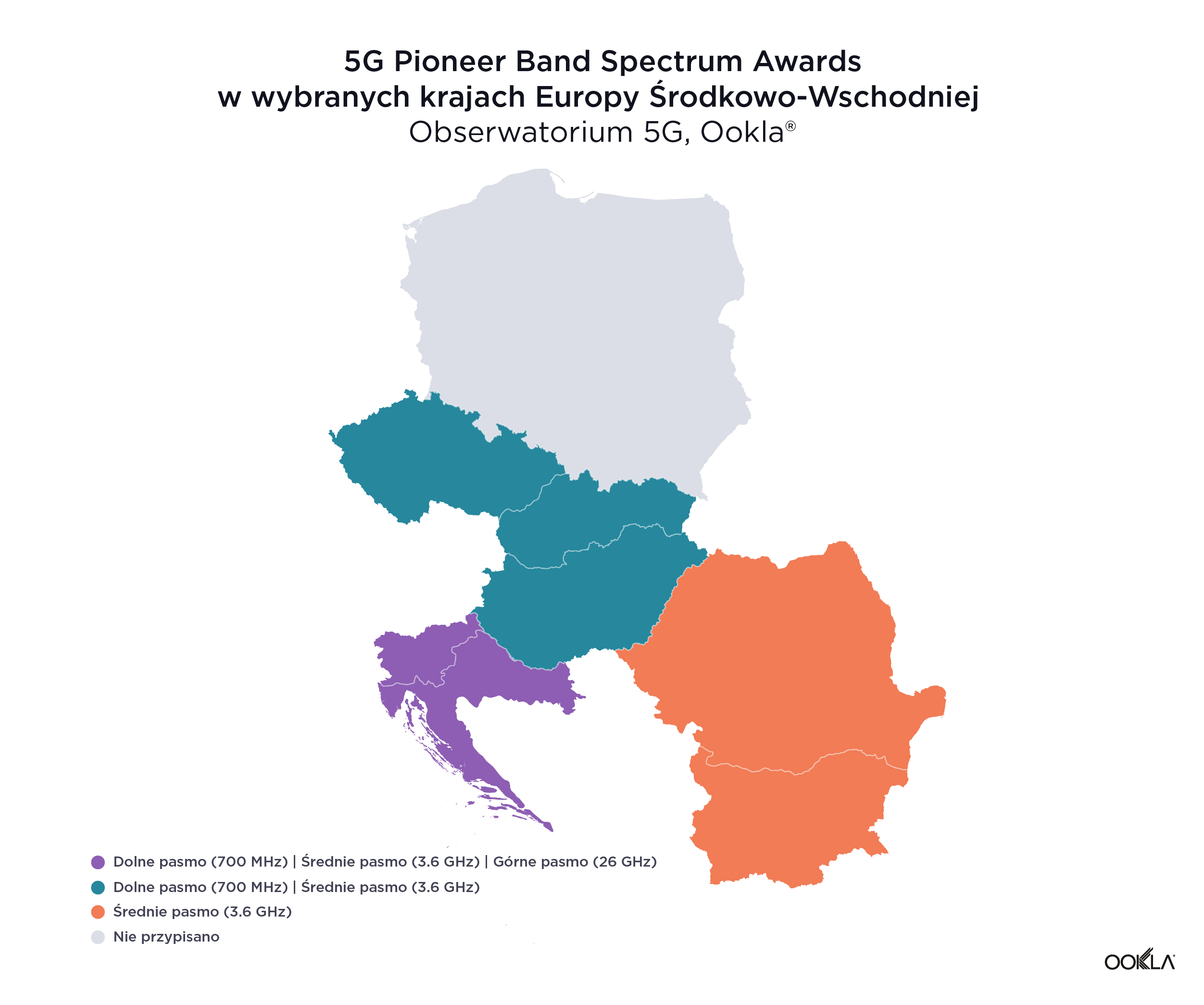
Słowenia i Chorwacja posunęły się naprzód i stały się jedynymi krajami, które zakończyły już aukcje pasma we wszystkich pionierskich pasmach 5G. W kwietniu 2021 r. słoweńska Agencja ds. Sieci i Usług Komunikacyjnych (AKOS) sfinalizowała sprzedaż częstotliwości w pasmach 700 MHz, 1500 MHz, 2100 MHz, 2300 MHz, 3500 MHz i 26 GHz. W sierpniu 2021 r. Chorwacki Urząd Regulacji Branży Sieciowej (HAKOM) sprzedał na aukcji częstotliwości z pasm 700 MHz, 3600 MHz i 26 GHz. Co więcej, Miran Gosta, dyrektor HAKOM-u, ogłosił niedawno, że przygotowywana jest nowa aukcja na częstotliwości, które są już w użyciu i wygasną w 2024 roku, takie jak pasma 800 MHz, 900 MHz, 1800 MHz, 2100 MHz i 2600 MHz.
Bułgaria liderem prędkości 5G
Ważnym pytaniem jest, czy opóźnienia w przydziałach częstotliwości i obsługa wielu generacji sieci wpłynęły na zdolność operatorów do spełnienia obietnicy 5G dotyczącej większych prędkości. Według Speedtest Intelligence®, mediana prędkości pobierania 5G w ośmiu krajach waha się w granicach 73-407 Mb/s. Bułgaria jest najszybsza z 406,97 Mb/s, za nią plasują się Chorwacja, Węgry, Rumunia, Słowenia i Słowacja. Czechy i Polska pozostają w tyle, z prędkością odpowiednio 112,53 Mb/s i 73,12 Mb/s.
Bułgarscy operatorzy brali aktywny udział w inicjowaniu rozwoju 5G. We wrześniu 2020 roku Vivacom uruchomił pierwszą komercyjną sieć 5G za pośrednictwem Dynamic Spectrum Sharing (DSS) w 1800 MHz i 2100 MHz, następnie A1 w Sofii z wykorzystaniem 3600 MHz, a Telenor na początku czerwca 2021 w największych miastach Bułgarii w paśmie 3 600 MHz.
W kwietniu 2021 r. firma Vivacom Bulgaria zdobyła 100 MHz w paśmie 3,7-3,8 GHz za 4,6 mln BGN (2,35 mln euro), ale już wcześniej uruchomiła sieć 5G z tymczasową licencją w listopadzie 2020 r. András Pali, dyrektor ds. technicznych Vivacom w wywiadzie oznajmił, że operator planuje zainwestować 120 milionów euro w infrastrukturę w 2021 roku. Vivacom wykorzystuje DSS, łącząc częstotliwości w pasmach 1,8, 2,1 i 3,6 GHz dla 5G, więc nie ma kompromisu między zasięgiem a prędkością. Z kolei A1 Bulgaria korzysta z dedykowanego pasma 100 MHz. Między komercyjnym uruchomieniem w kwietniu a październikiem 2021 r. liczba aktywnych użytkowników A1 Bulgaria wzrosła o 448%, a generowany przez nich ruch o 771%, przekraczając 90 terabajtów (TB) w październiku 2021 r.
Ponadto w planie naprawy i zwiększenia odporności Bułgarii, 26% z budżetu wynoszącego 6,3 mld euro przeznaczono na transformację cyfrową. Plan obejmuje środki stymulujące transformację cyfrową, w tym znaczne inwestycje i reformy łączności cyfrowej w celu zwiększenia zasięgu sieci o bardzo dużej przepustowości na obszarach wiejskich i słabo zaludnionych oraz stworzenia sprzyjającego środowiska dla wdrażania sieci 5G i infrastruktury cyfrowej.

Kilku operatorów wdrożyło sieci 5G przed uzyskaniem dostępu do dedykowanego pakietu pasm 5G, zamiast tego wykorzystując swoje istniejące zasoby pasma za pośrednictwem DSS lub tymczasowo przydzielonego pasma. Patrząc na dane dla Polski, istnieje związek między brakiem dedykowanego pasma a medianą prędkości pobierania. Prędkości 5G w Polsce są dwukrotnie wyższe niż prędkości 4G w porównaniu z Rumunią, Słowacją, Węgrami i Słowenią, gdzie prędkości 5G są ponad pięć razy szybsze niż 4G. Ponieważ operatorzy w Polsce wdrożyli 5G, wykorzystując swoje istniejące zasoby pasmowe — w 2,6 GHz i 2,1 GHz — nie są w stanie wykorzystać korzyści, jakie dla wdrożeń 5G niesie ze sobą średnie pasmo. Zastanowiliśmy się, w jaki sposób pasmo średnie zwiększyło prędkości i zasięg 5G w USA.
5G Availability wzrosła w Bułgarii w 2021 r.
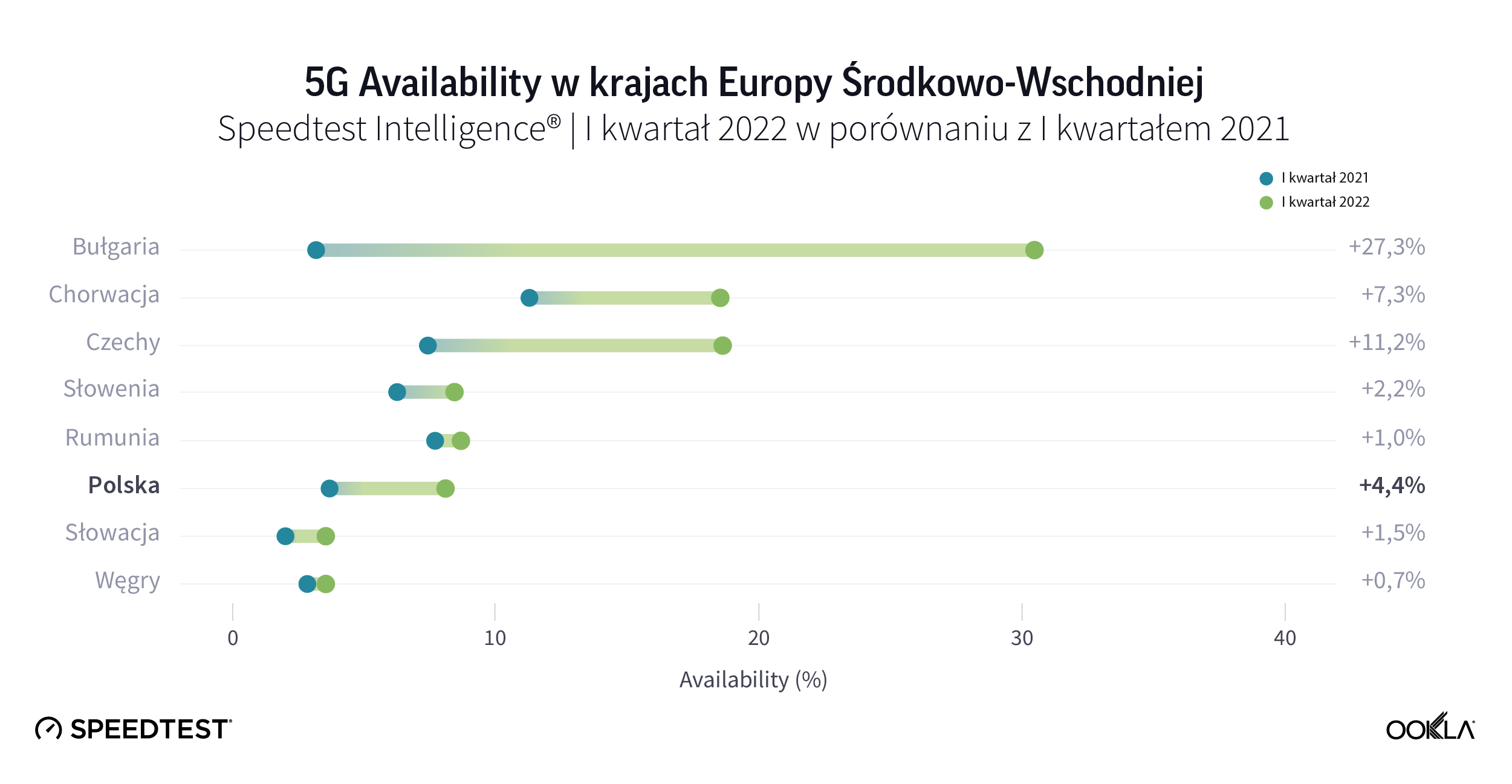
Dane Speedtest Intelligence stawiają Bułgarię na pierwszym miejscu pod względem 5G Availability (odsetek użytkowników urządzeń obsługujących 5G, którzy spędzają większość czasu w sieciach 5G) wśród swoich regionalnych partnerów. W 2021 r. 5G Availability w Bułgarii wzrosła dziesięciokrotnie, z 3% w I kwartale 2021 r. do 30,5% w I kwartale 2022 r. Jest to częściowo zasługą operatorów poszerzających portfolio urządzeń obsługujących 5G, m.in. w czerwcu 2021 r. 55% oferowanych przez Telenor (obecnie Yettel) smartfonów obsługiwało 5G i oferowało taryfy 5G bez dodatkowych kosztów.
Chorwacja radziła sobie stosunkowo dobrze, jeśli chodzi o 5G Availability, która wzrosła z 11% w I kwartale 2021 r. do 18,5% w I kwartale 2022 r. Licencja 5G chorwackich operatorów obejmuje zobowiązania dotyczące zasięgu wynoszące 90% obszarów miejskich, 99% autostrad i 95 % kolei do 2025 r. Ponadto obowiązki licencyjne obejmują 25% zasięgu obszarów wiejskich do 2025 r. i 50% do 2027 r. Według Hakom zasięg i 5G Availability wynosi 60-70%.
Jednak pięć krajów nadal miało 5G Availability poniżej 10% w I kwartale 2022 r., w porównaniu z siedmioma w I kwartale 2021 r. Na Węgrzech istnieje publiczna inicjatywa wsparcia upowszechnienia 5G na kwotę 5 mld HUF (13,15 mln EUR), konsumentom w migracji z urządzeń 3G na smartfony 4G/5G w obliczu zbliżającego się zaniku sieci 3G. 9 maja 2022 r. węgierski regulator telekomunikacyjny — NMHH — rozpoczął drugą fazę dotacji na telefony komórkowe: właściciele urządzeń 2G lub 3G mogą ubiegać się o 20 000 HUF (52,26 EUR) na zakup nowego smartfona 4G lub 5G.
Nie jest zaskoczeniem, że Węgry zajęły pierwsze miejsce, jeśli chodzi o dostawy smartfonów 5G w wielu krajach Europy Środkowo-Wschodniej. Według Counterpoint Research smartfony 5G stanowiły 65,1% wszystkich dostaw smartfonów na Węgrzech w IV kwartale 2021 r. W Czechach, Słowacji i Bułgarii smartfony 5G stanowią dwa na pięć sprzedanych smartfonów. W Polsce to prawie co trzeci. Rumunia jest ostatnia. Chociaż liczby te nie przekładają się bezpośrednio na sprzedaż bezpośrednią do klientów, ponieważ dostawy odnoszą się do sprzedaży w kanałach detalicznych i wskazują na zwiększony apetyt na urządzenia 5G. Kluczowym czynnikiem jest rosnąca dostępność smartfonów 5G z niższej półki cenowej. Na przykład firma realme odnosi sukcesy dzięki przystępnym cenowo smartfonom 5G w Europie.
Sofia zajmuje pierwsze miejsce pod względem mediany prędkości pobierania i 5G Availability
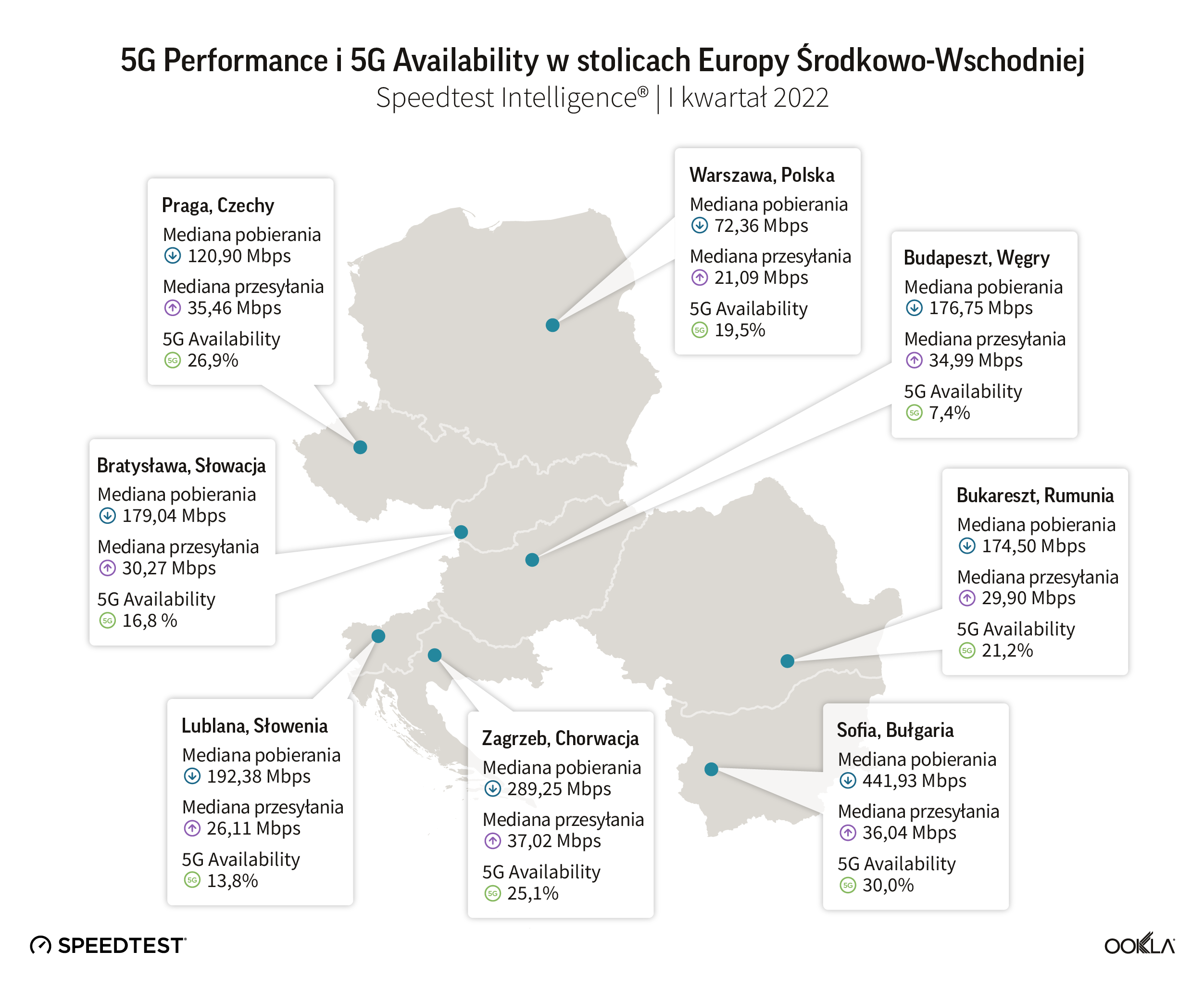
Nie dziwi więc fakt, że stolica Bułgarii zajęła również pierwsze miejsce w rankingu stolic regionalnych, z medianą prędkości pobierania 441,93 Mb/s i 30% dostępnością 5G w I kwartale 2022 r. A1 Bulgaria rozpoczęła testy już pod koniec listopada 2020 r. w Sofii i Burgas, które stały się pierwszymi miastami 5G w kraju z zasięgiem ponad 90% populacji na zewnątrz.
Praga spisała się dobrze, jeśli chodzi o 5G Availability. W kwietniu 2022 r. obszar praskiego metra został w pełni pokryty sieciami 5G dzięki współpracy czeskich operatorów: T-Mobile, Vodafone, O2 i CETIN oraz władzami samorządowymi Pragi. Wszyscy czescy operatorzy zrezygnowali z sieci 3G w 2021 r., aby zmienić częstotliwości na 4G i 5G. Największy operator pod względem liczby połączeń, T-Mobile Czechy, miał we wrześniu 2021 r. ponad 600 stacji bazowych 5G obejmujących 10,4% populacji, a do końca roku planował zwiększyć zasięg do 25%. T-Mobile używa Ericssona i Huawei do swojej sieci 5G, która wykorzystuje pasma 1800 MHz, 2100 MHz i 700 MHz. Najmniejszy operator, Vodafone Czechia, objął 70% populacji siecią 5G docierającą do 7 milionów Czechów w maju 2022 roku. Vodafone jest zdeterminowany do poszerzenia zasięgu swojej sieci, w tej chwili używa 3,5 GHz dla 5G, ale wkrótce zacznie używać pasmo 700 MHz oraz refarmowane pasmo 3G.
Polacy potrzebują więcej edukacji na temat korzyści 5G
Jeśli chodzi o prędkość 5G, Polska nie wypada najlepiej na tle innych krajów Europy Środkowo-Wschodniej. Polska zajęła ostatnie miejsce w rankingu mediany prędkości pobierania 5G, a jej prędkości 5G były nieco ponad dwukrotnie wyższe niż 4G. To jedyny kraj, który nie przyznał jeszcze pasma 5G. Co jednak ważniejsze, wydaje się również, że polscy użytkownicy końcowi nie widzą dodatkowych korzyści, jakie może przynieść 5G, co zmniejsza popyt.
Według badania przedsiębiorstw UKE, 78,2% przedsiębiorstw w Polsce słyszało o 5G. To dobry wynik. Jednak większość przedsiębiorstw twierdzi, że obecne parametry mobilne są wystarczające do prowadzenia działalności biznesowej w trzech miarach: szybkości (88,6%), niezawodności (86,7%) i wydajności (85,9%). Biorąc pod uwagę, że obecne sieci 5G w Polsce nie spełniają obietnic dotyczących szybkości gigabitowej, nie jest to zaskakujące.
Z punktu widzenia polskiego konsumenta termin 5G zna 73,8%. Ma to jednak wadę, ponieważ nieco ponad połowa respondentów (57,4%) uważa, że 5G stanowi zagrożenie dla zdrowia.
Na pytanie, jakie są kluczowe zalety sieci 5G, prawie połowa respondentów (47,5%) twierdzi, że 5G będzie szybsze i wydajniejsze niż 4G. Mniej niż jedna trzecia (31%) widzi, że sieci 5G ułatwiają ludziom życie. Trzecią preferowaną opcją jest zdolność 5G do wzmocnienia i modernizacji polskiej gospodarki. Jednak 18% nie widzi pozytywnych perspektyw korzystania z sieci 5G. To może częściowo tłumaczyć, dlaczego 5G Availability w Polsce wynosi poniżej 10%.
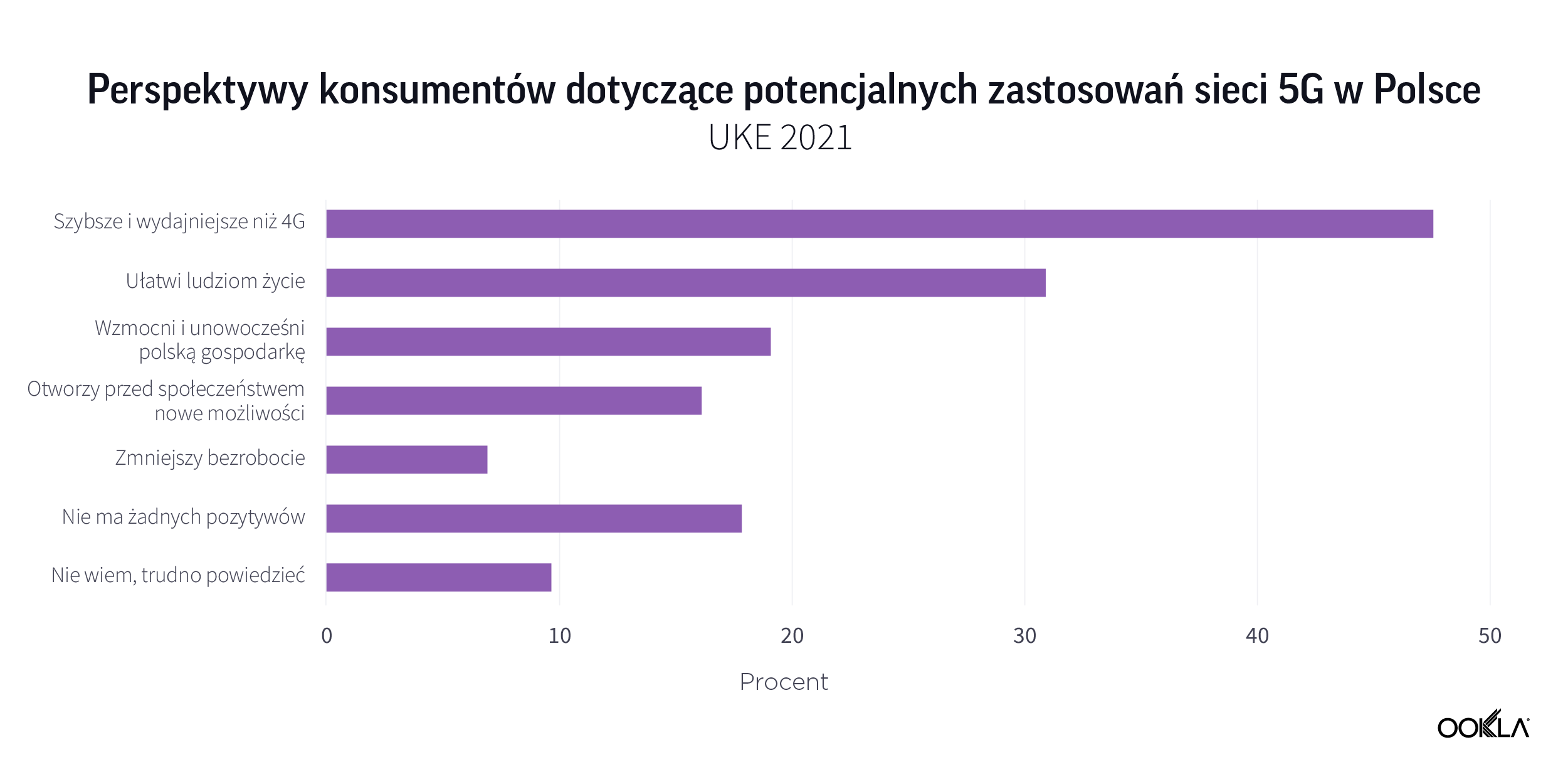
W 5G nie chodzi tylko o szybkość. 5G jest postrzegane jako sposób na wniesienie dodatkowej wartości do gospodarki i społeczeństwa. Według badania przeprowadzonego przez Ericsson Polska, polska gospodarka może zyskać ponad 17 miliardów euro na wdrożeniu 5G do 2040 roku. Biorąc pod uwagę brak jasnego harmonogramu aukcji 5G, ryzyko, że Polska będzie dalej odstawać od swoich konkurentów jest realne.
Plus prowadzi w prędkości pobierania 5G w Polsce

Porównaliśmy prędkość 5G u polskich operatorów za pomocą Speedtest Intelligence. Operator Plus był wyraźnym zwycięzcą, osiągając medianę prędkości pobierania 167,37 Mb/s w I kwartale 2022 r., wyprzedzając Orange, T-Mobile i Play. Nie odnotowano znaczącej różnicy w medianie prędkości wysyłania u operatorów.
Wszyscy polscy operatorzy sieci komórkowych uruchomili sieci 5G, wykorzystując istniejące częstotliwości w trybie Non Standalone (NSA), który opiera się na bazowej technologii 4G/LTE. Aukcja 5G jest obecnie uzależniona od trwających konsultacji dotyczących projektu ustawy o krajowym systemie cyberbezpieczeństwa, który ma być przedmiotem obrad polskiego parlamentu. Ustawa może wpłynąć na decyzje dotyczące sprzętu sieciowego wśród graczy, np. Play używa Huawei i Ericsson dla stacji bazowych.
Polkomtel, działający pod marką Plus, w maju 2020 roku uruchomił pierwszą w kraju komercyjną sieć 5G w paśmie 2,6 GHz, wykorzystującą pasmo 50 MHz. Oprócz Plusa, wszyscy pozostali operatorzy wdrożyli 5G z wykorzystaniem DSS w paśmie 2,1 GHz, co może częściowo wyjaśniać, dlaczego mają niższe prędkości.
Orange Polska, podobnie jak inne kraje Grupy Orange, wdroży 5G Standalone (5G SA) we współpracy z firmą Ericsson. Umożliwi to “krojenie sieci” (ang. network slicing) 5G i rozwój sieci prywatnych. W oczekiwaniu na aukcję 5G oraz w celu stymulowania nowych zastosowań 5G, operator uruchomił usługi testowe Orange 5G Lab, takie jak AR, AI wykorzystujące pasmo przydzielone przez UKE do testowania 5G w paśmie 3,6 GHz.
Play miał najlepszą 5G Availability w Polsce
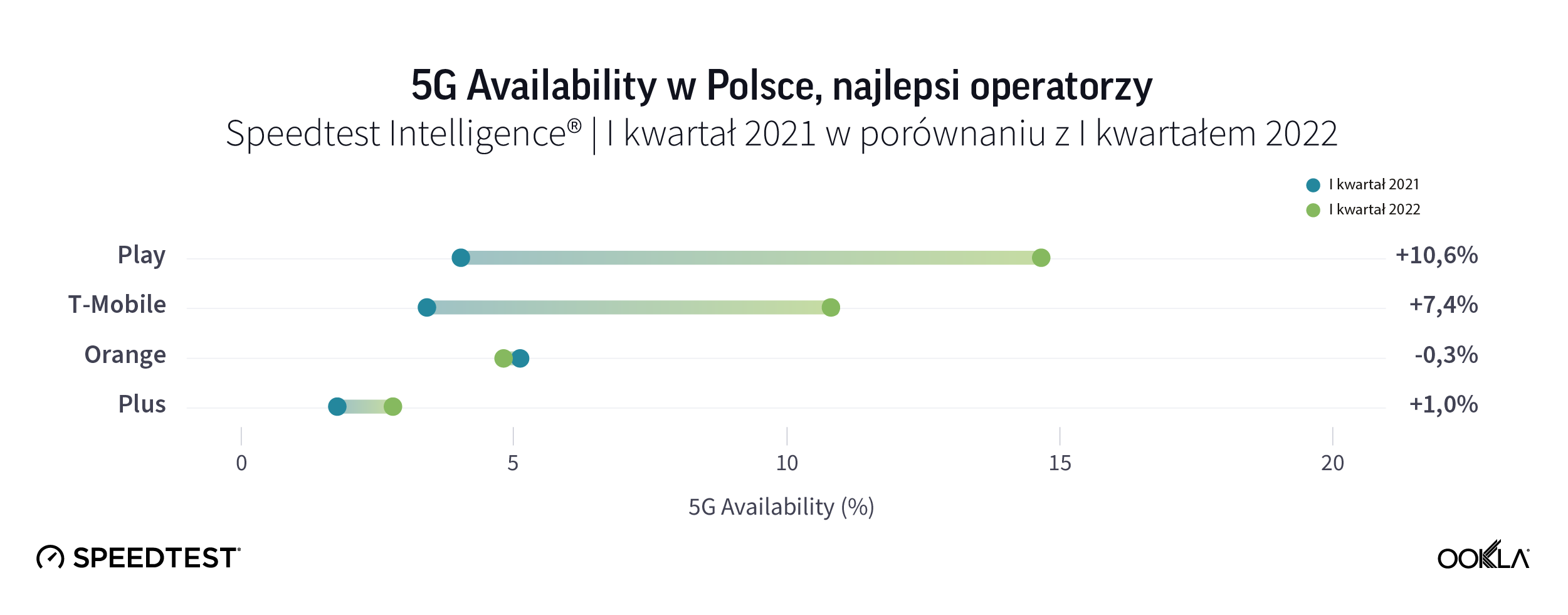
Według Counterpoint Research, w 2021 r. dostawy smartfonów w Polsce prawie się potroiły, napędzane przez konkurencyjne marki, takie jak realme, OPPO i Xiaomi (w tym Redmi i POCO). Polscy operatorzy również w dalszym ciągu promują sprzedaż urządzeń obsługujących 5G. Smartfony 5G jako udział w sprzedaży smartfonów wahały się od 36% dla Orange, 40% dla T-Mobile oraz 45% dla Play. Jednak Play wyprzedził konkurencję, jeśli chodzi o 5G Availability, a T-Mobile nadrabia zaległości, pozostawiając w tyle Orange i Plus.
Jest to o tyle zaskakujące, że sieć 5G Play niekoniecznie ma największy zasięg. Na koniec 2021 r. sieć 5G Plusa powiększyła się do 19 mln osób, następny był Play z ponad 13 mln, T-Mobile (11 mln) i Orange (6,3 mln). Przekładając to na pokrycie populacji przy użyciu danych ze spisu powszechnego z 2021 r. (38,18 mln osób), oznacza to pokrycie populacji 50%, 34%, 29% i 17%.
Play, część Grupy Iliad, miał najlepszą 5G Availability, prawdopodobnie ze względu na agresywny marketing i rabaty w połączeniu z dużym portfolio urządzeń 5G i najtańszymi taryfami. Niedawno Play pozyskał z BGK kredyt w wysokości 500 mln zł (107 mln euro) w ramach Programu Operacyjnego Polska Cyfrowa (POPC), który posłuży również do uruchomienia usług 5G.
Operatorzy komórkowi nadal inwestują w rozwój sieci 5G. Na przykład T-Mobile rozszerzył swoją współpracę z Nokią o modernizację sieci RAN, a także wdrożenie usług 5G. Operator planuje wykorzystanie 4G i 5G DSS w dolnym paśmie oraz gdy będzie to możliwe, w paśmie 3,5 GHz na gęstych obszarach miejskich. T-Mobile planuje zakończyć 2022 rok z 3500 stacjami bazowymi 5G i 30% pokryciem populacji. T-Mobile wyłączył swoją sieć 3G w paśmie częstotliwości 2100 MHz w październiku 2021 roku. Rozpoczął również zamykanie sieci 3G, mając na celu wykorzystanie 900 MHz dla 3G i zmianę jej na LTE i 5G w 2023 roku.
Przeszkodą w osiągnięciu szerokiej dostępności 5G są kontrowersje wokół aukcji 5G. W październiku 2019 r. czterej czołowi operatorzy komórkowi (Plus, Orange, Play i T-Mobile), państwowy operator telekomunikacyjny Exatel oraz Polski Fundusz Rozwoju (PFR) podpisali porozumienie w sprawie budowy ogólnopolskiej infrastruktury. Będzie on własnością państwa za pośrednictwem jednostki specjalnego przeznaczenia – Polskie 5G. Polski regulator zaproponował przydzielenie temu nowemu podmiotowi całego pasma 700 MHz (2×30 MHz), z myślą o zapewnieniu w pierwszej kolejności łączności dla służb porządkowych i ratowniczych, a jednocześnie udostępnienie go wszystkim operatorom. Zarezerwowanie pasma do użytku pionowego nie jest niczym nowym, omówiliśmy to w naszym ostatnim artykule; nowością jest tu pasmo i ilość. Pasmo 700 MHz ma kluczowe znaczenie dla zapewnienia szerokiego zasięgu i penetracji wewnątrz budynków. W naszym ostatnim webinarze Eric Brands z KPN wyjaśnił, że KPN osiąga dobre wyniki w zakresie 5G Availability, częściowo dlatego, że ma dostęp do niskiego pasma 5G (700 MHz).
Łódź ma najszybszą sieć 5G wśród największych polskich miast
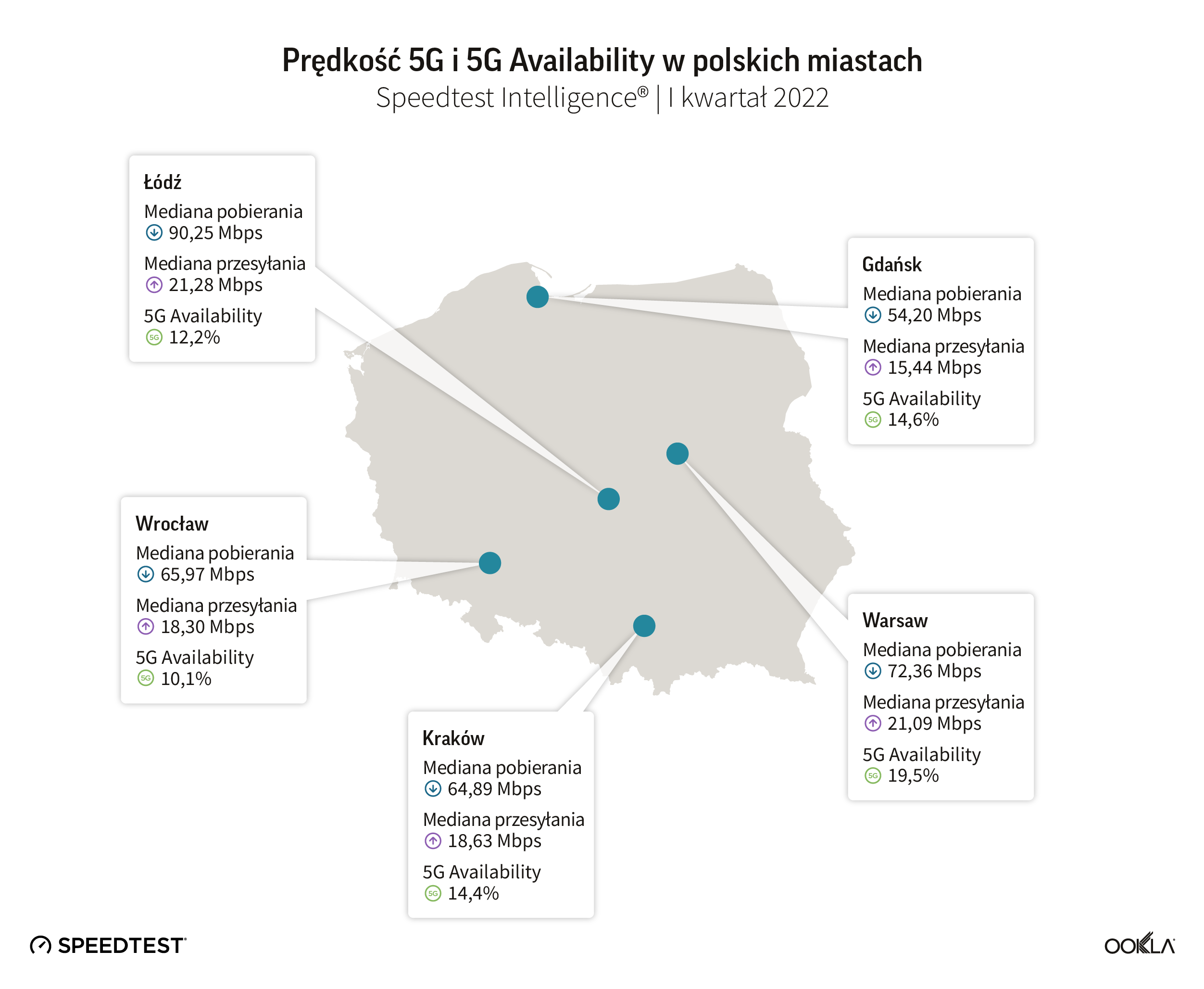
Łódź zajęła pierwsze miejsce jako najszybsze miasto w Polsce z prędkością 90,25 Mb/s w I kwartale 2022 r., jest także hotspotem dla innowacji operatorów. Orange wdrożył kampusową sieć 5G na terenie Łódzkiej Specjalnej Strefy Ekonomicznej, gdzie 40 start-upów pracujących w akceleratorze będzie mogło korzystać z infrastruktury. Ericsson dostarczył infrastrukturę dla obszaru gospodarczego: dziesięć anten pracujących w pasmach 3,6 GHz i 2100 MHz, obejmujących około 1000 m2.
T-Mobile testuje 5G SA w Łodzi, aby umożliwić nowe usługi zarówno klientom indywidualnym, jak i klientom B2B, w tym usługi VoNR (Voice over New Radio) w sieci 5G. Sieć 5G SA wykorzystuje pasmo 2600 MHz.
Stolica Polski, Warszawa, nieznacznie wyprzedza resztę pod względem 5G Availability.
Będziemy uważnie obserwować prędkość 5G w Polsce za pomocą Speedtest Intelligence. Jeśli chcesz dowiedzieć się więcej o tym, jak Speedtest Intelligence może pomóc Ci porównać prędkość 5G z konkurencją, zapytaj tutaj.