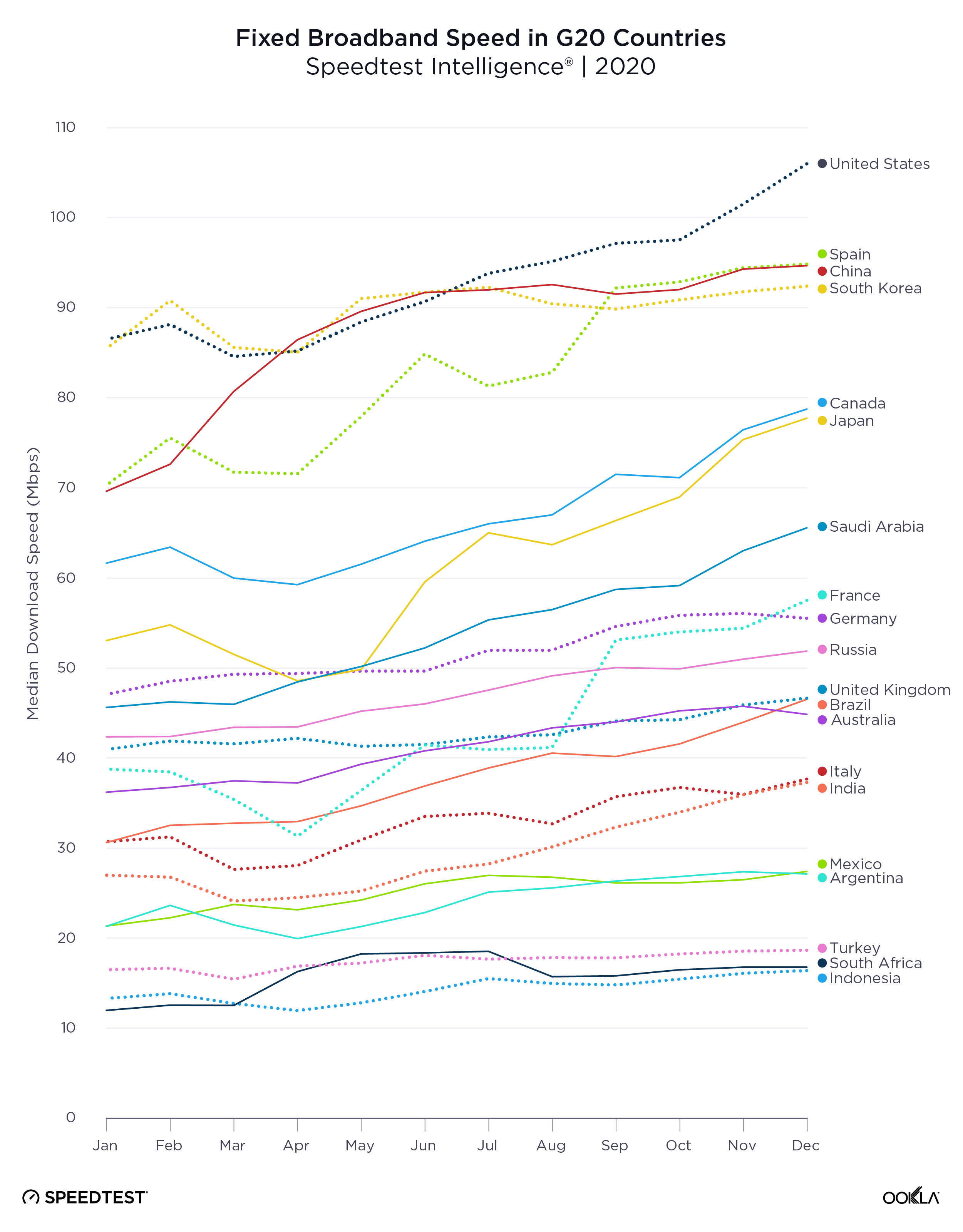
A lot has changed in the two years since 2017 when we first began ranking mobile and fixed broadband speeds of countries around the world with the Speedtest Global IndexTM. 5G is being deployed around the world and fiber continues to make gigabit speeds a reality in more and more countries. We’ve been tracking it all and are here to report on how much speeds have increased, which countries are leading internet performance and which are falling behind, and what trends we see across continents.
World mobile speed increased 21.4% with fixed broadband up 37.4%
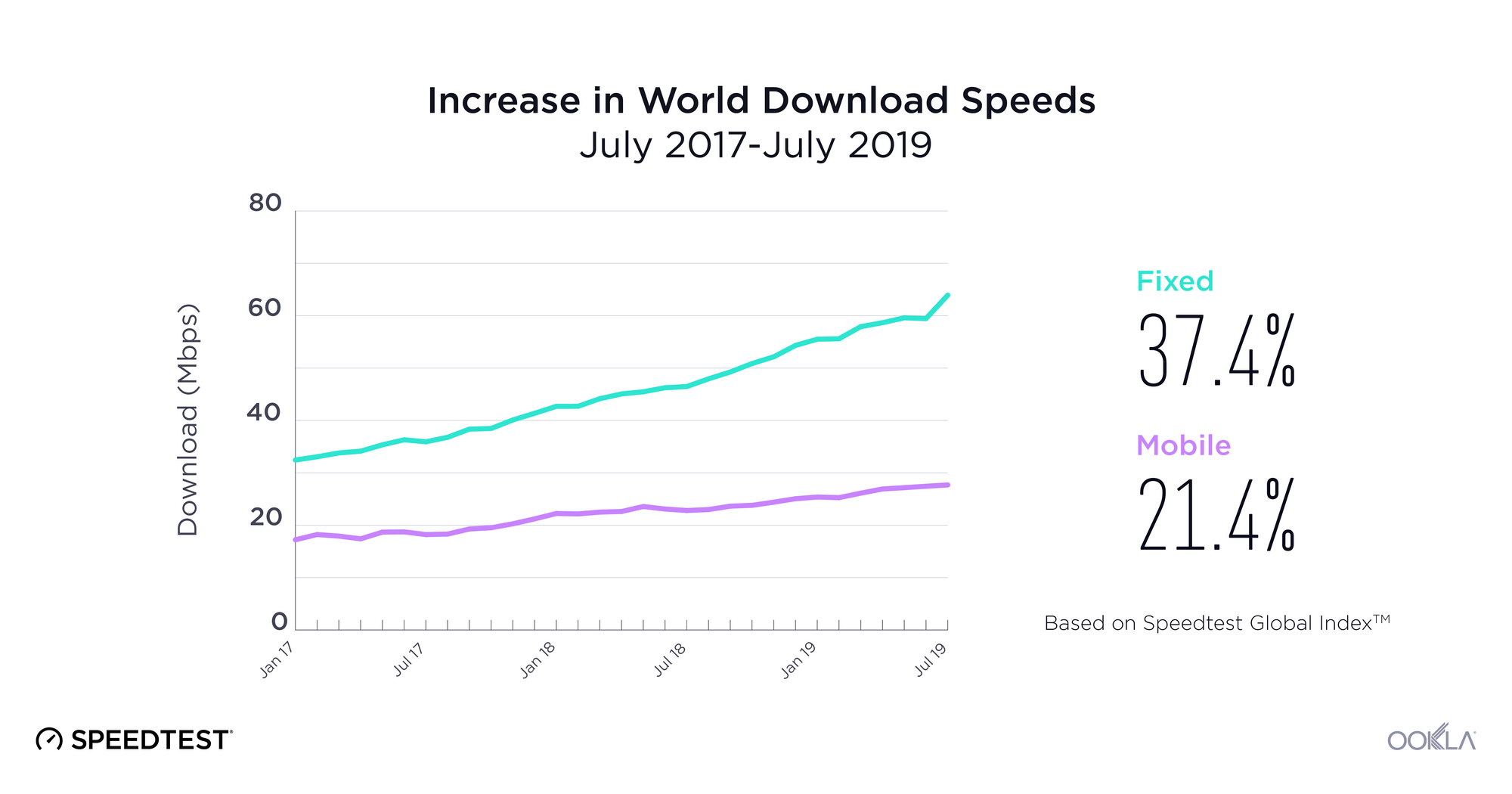
Looking just at the last year, the world’s mean download speed over mobile increased 21.4% from 22.81 Mbps in July 2018 to 27.69 Mbps in July 2019. Mean upload speed over mobile increased 18.1% from 9.13 Mbps to 10.78 Mbps. The world average for download speed over fixed broadband increased 37.4% from 46.48 Mbps in July 2018 to 63.85 Mbps in July 2019. Mean upload speed over fixed broadband increased 48.9% from 22.52 Mbps to 33.53 Mbps.
Shake-ups in the country rankings for internet performance
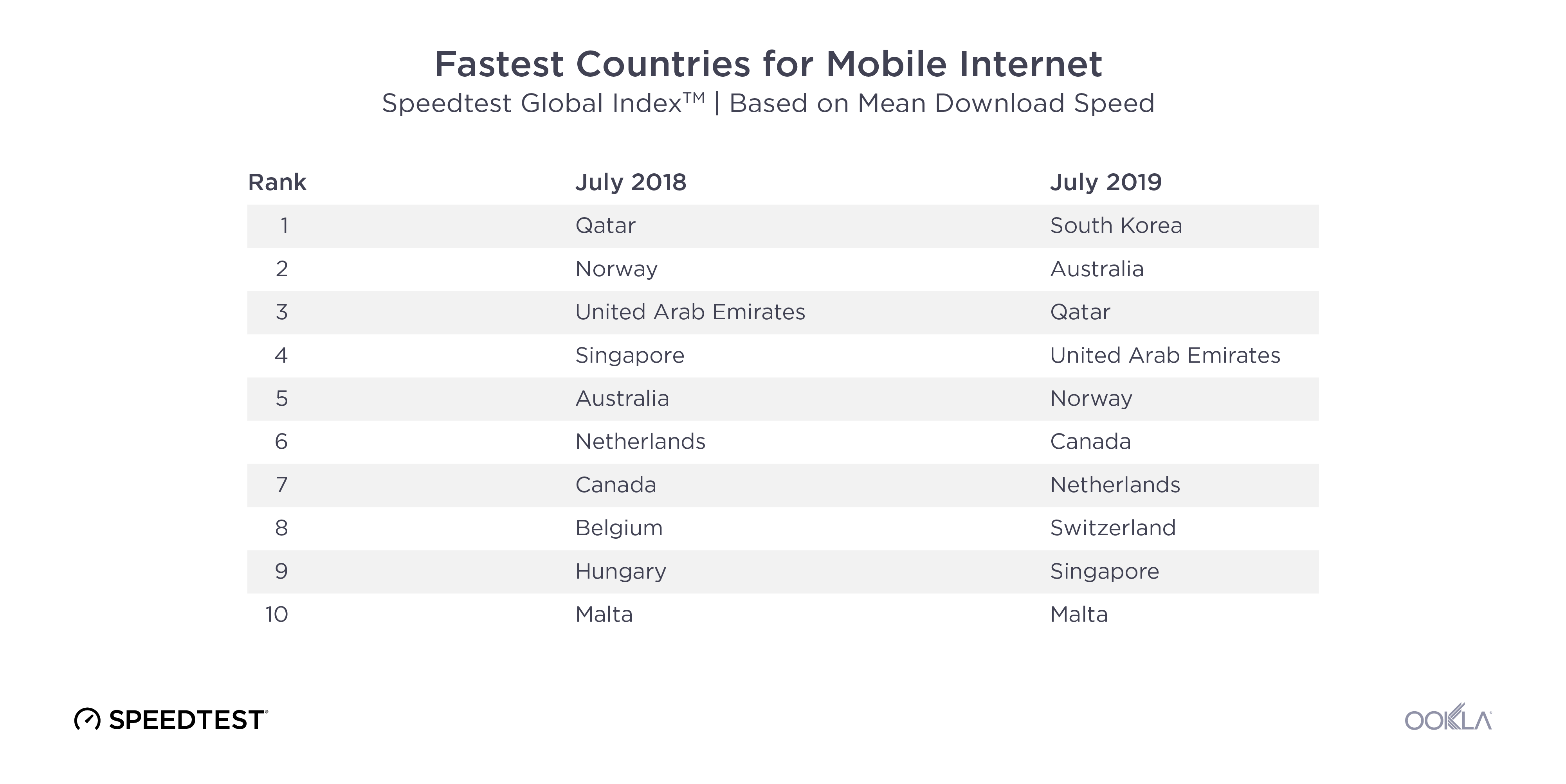
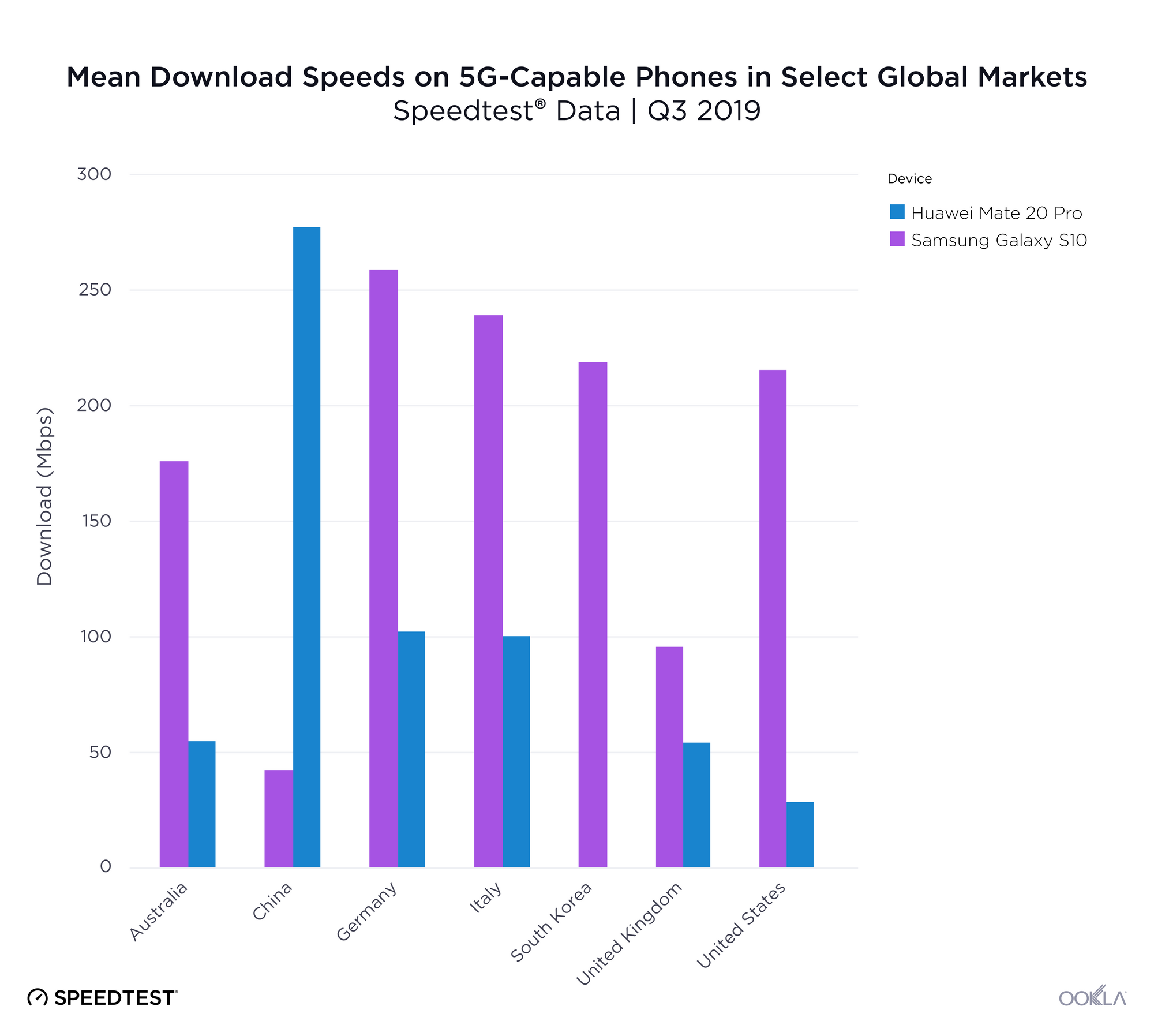
Mobile speeds in the fastest countries have skyrocketed in the past year which has dramatically shifted the rankings. South Korea, which was not even in the top ten a year ago, saw a 165.9% increase in mean download speed over mobile during the past 12 months, in large part due to 5G. Switzerland’s mean download speed increased 23.5%. Canada’s was up 22.2%, Australia 21.2%, the Netherlands 17.3%, UAE 11.1%, Malta 10.3% and Norway 5.8%. Qatar remained in the top ten, although the country’s mean download speed over mobile actually dropped 1.4% from July 2018 to July 2019.
Individual mobile operators can make a huge difference in a country’s speeds. In 2017 we were excited to see Telenor uncap their mobile speeds, which drove Norway to the top of the Speedtest Global Index. A big part of South Korea’s mobile success in the past year is the way KT, LG U+ and SK Telecom banded together to release 5G at the same time. Switzerland has also benefited from 5G and Sunrise leads the country with 262 5G deployments across the country while Swisscomm has 52.
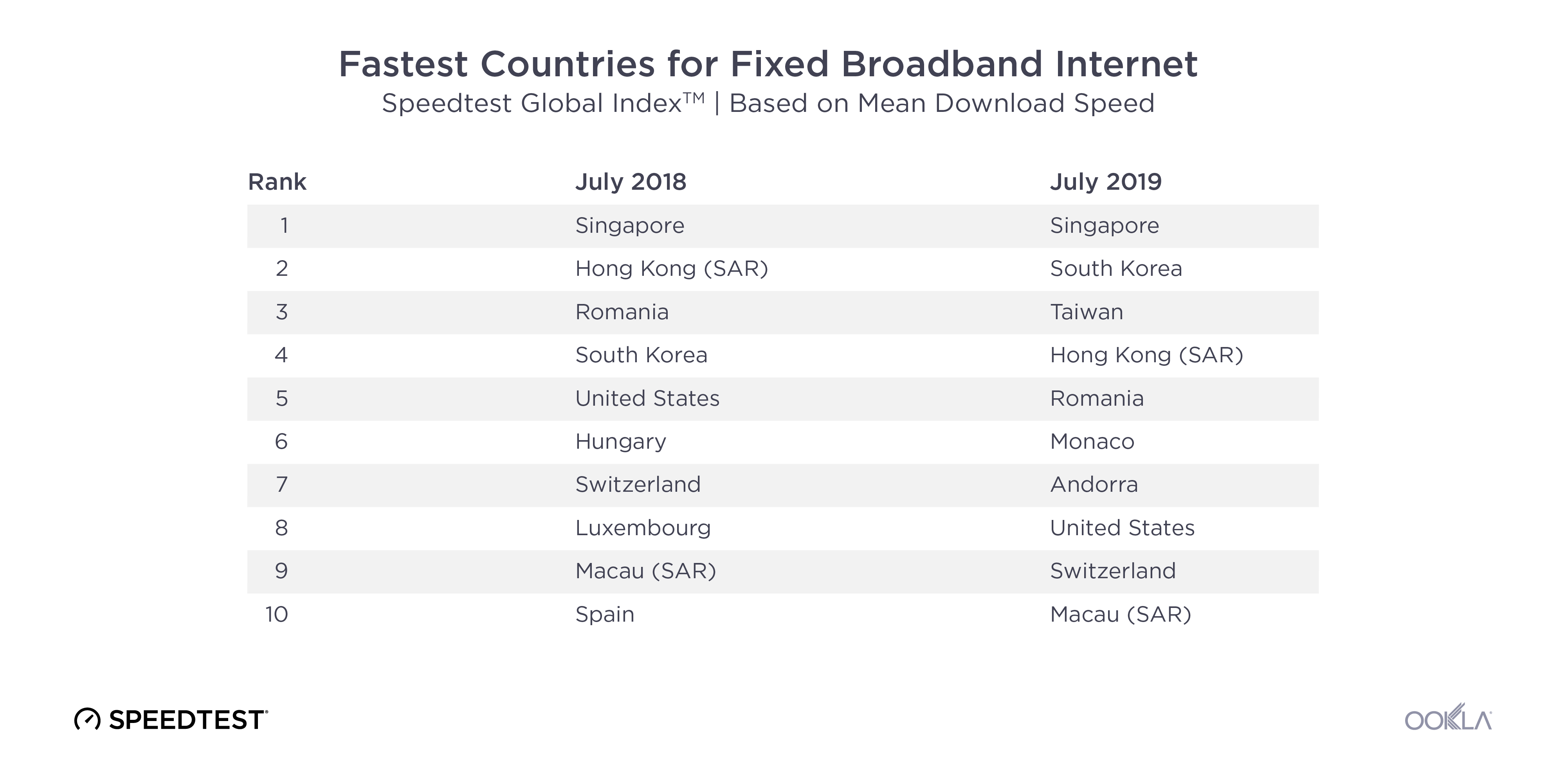
Fixed broadband rankings on the Speedtest Global Index have not changed as dramatically during the past 12 months as those on mobile. Singapore remains the fastest country with an increase in mean download speed over fixed broadband of 5.6%. Taiwan had the largest jump in speeds among the top 10 with a 166.5% improvement in fixed download speed between July 2018 and July 2019. Mean download speed over fixed broadband increased 52.4% in South Korea, 26.4% in Macau, 21.7% in Romania, 21.0% in Switzerland, 19.3% in the United States and 3.5% in Hong Kong.
Monaco and Andorra did not have enough tests to qualify for the Speedtest Global Index one year ago, but massive fixed broadband improvements in both countries inspired us to lower our test count threshold for inclusion and also share these smaller countries’ success stories.
Technologies paving the way: 5G and gigabit
The presence of 5G is not enough to change a market
As discussed above, 5G has the potential to rocket a country to the top of the mobile rankings on the Speedtest Global Index. In practice, we’ve seen 5G speeds that were over 1000% faster than those on LTE.
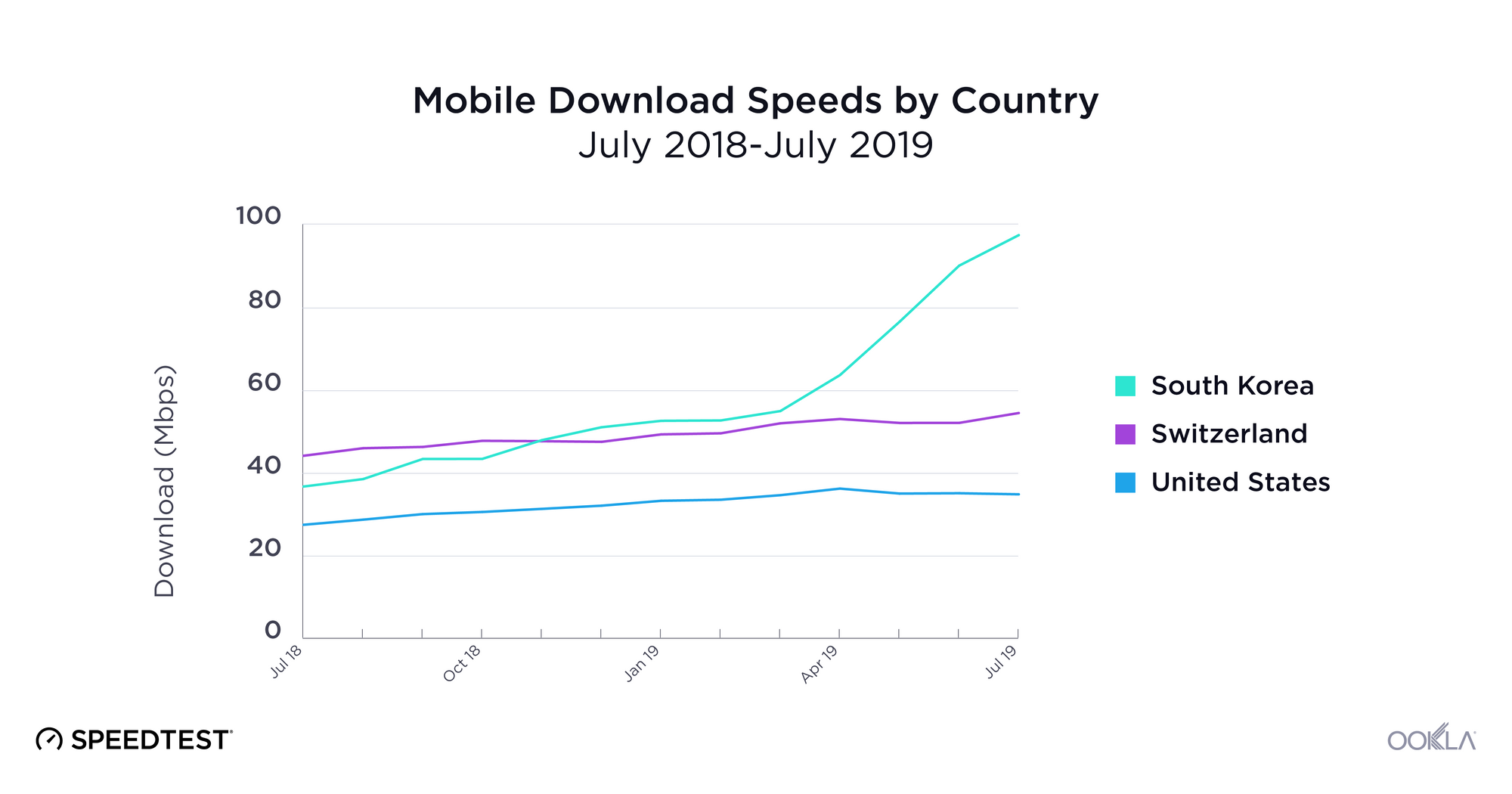
In reality, though, unless 5G is commercially available widely across a country and from all mobile operators (as was the case in South Korea), the change in speeds at the country level is not that significant. Though commercial 5G was launched widely across Switzerland by Sunrise and Swisscom in April 2019, the country’s mean download speed only increased 2.8% in the three months since. The average mobile download speed in the U.S. has actually declined slightly since 5G was initially deployed. This is because 5G is still only available in a very limited number of markets to consumers with 5G-capable devices.
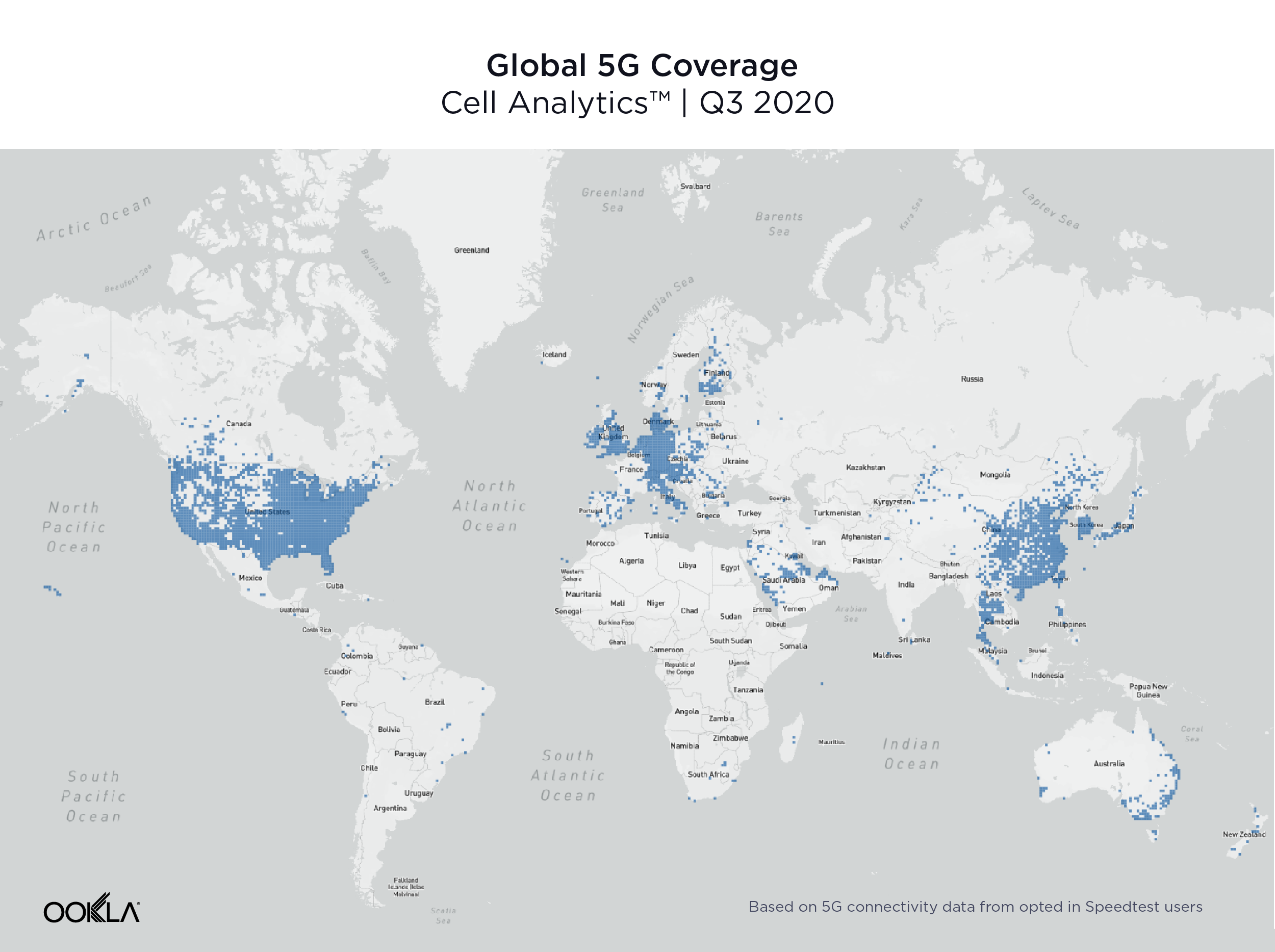
Visit the Ookla 5G Map for the latest on 5G deployments across the globe.
Gigabit is a game-changer, if you can get it
Unlike 5G, fiber connections have been rolling out since 2007, opening up the possibility of gigabit-speed fixed broadband. That said, it’s costly and time-intensive to lay miles and miles of fiber so progress has varied widely across the globe.
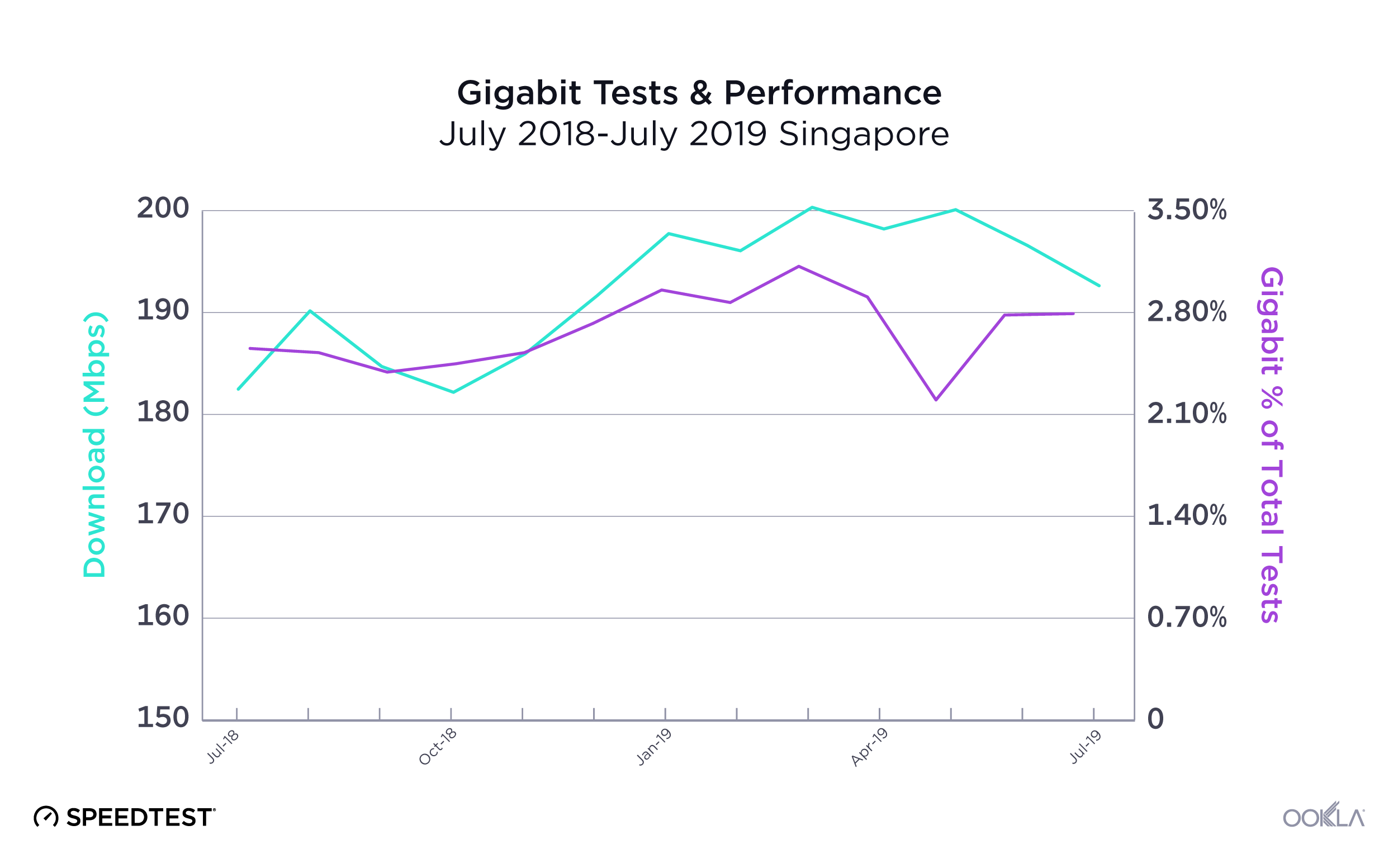
Geographically small countries like Singapore have the advantage when it comes to fiber, because It’s easier and cheaper to lay fiber optic cable across the country’s small footprint. Singaporean internet service providers (ISPs) have used this advantage to go beyond mere gigabit and offer connections as fast as 10 Gbps. This is reflected both in Singapore’s dominance of the fixed rankings on the Speedtest Global Index and in the fact that 2.87% of their total Speedtest results over fixed broadband are gigabit-speed (800 Mbps or higher).
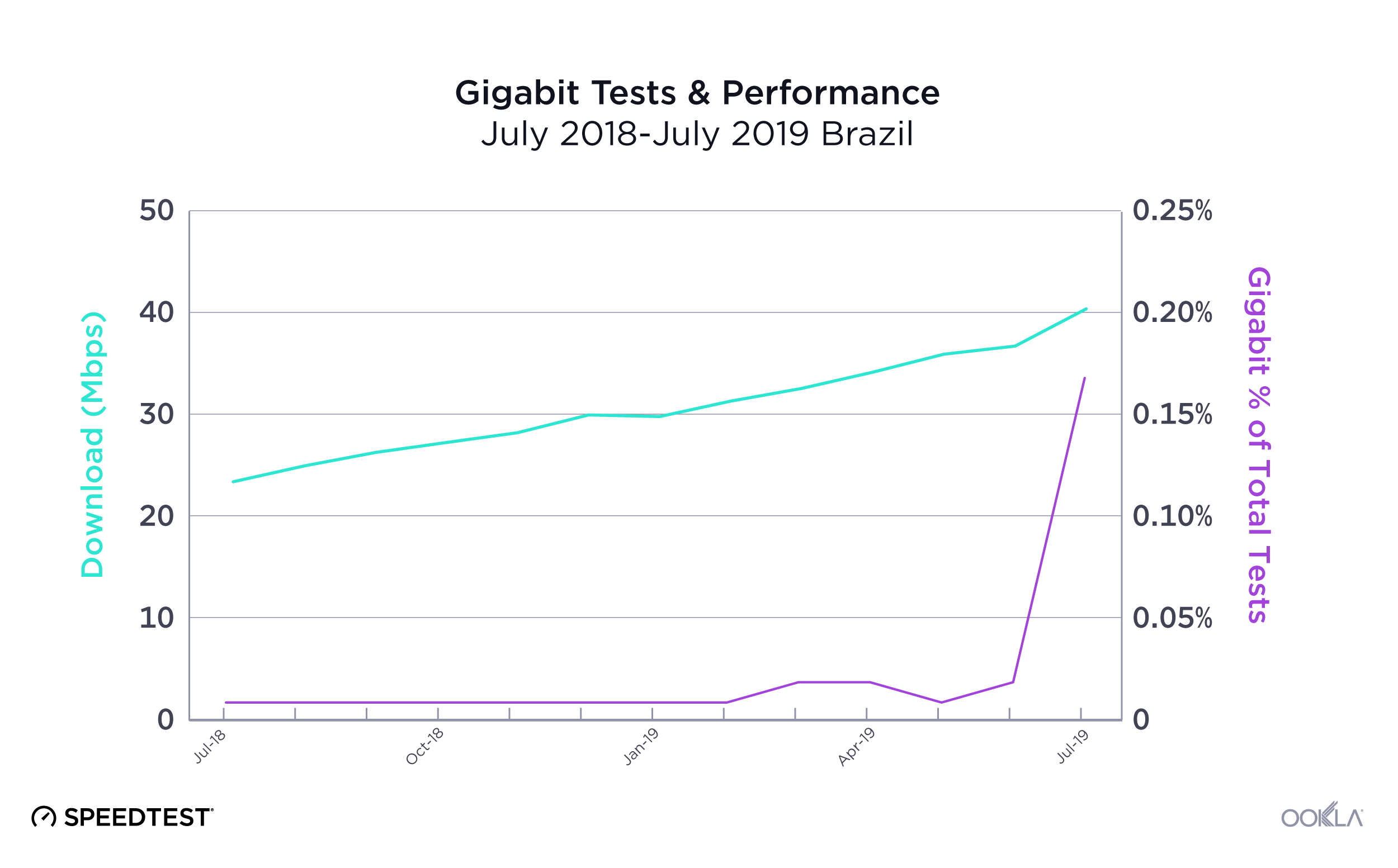
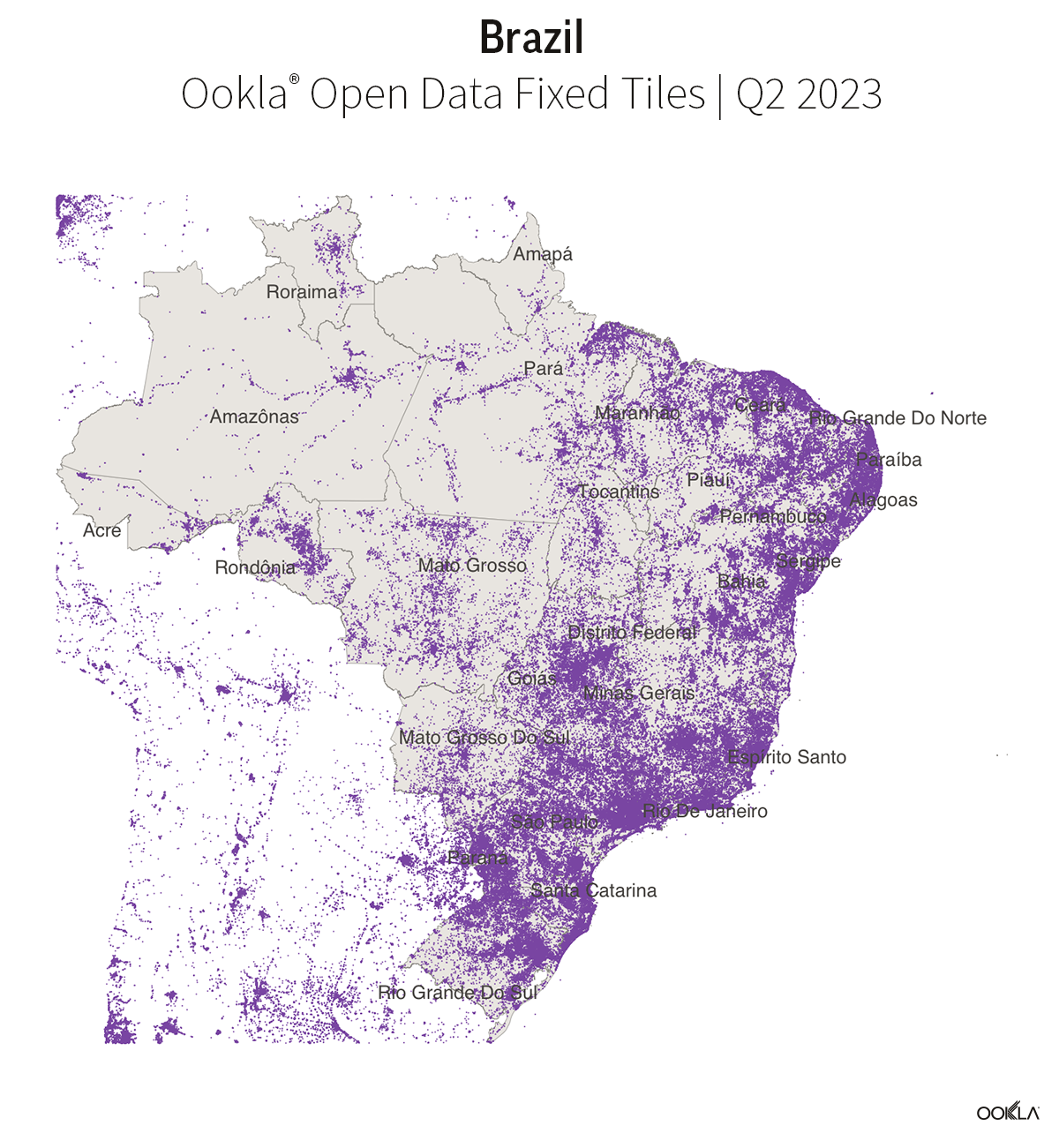
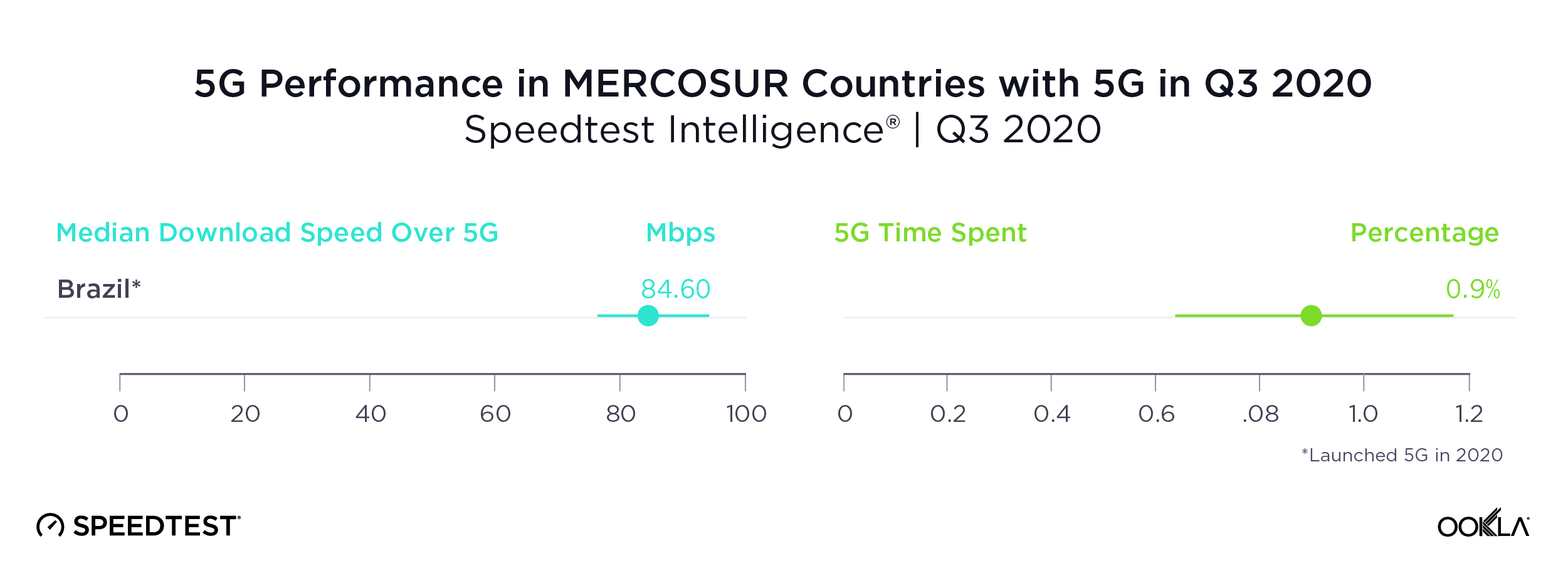
Brazil offers a good contrast for how difficult it can be for gigabit to reach the masses. While the first Brazilian ISP to offer fiber-to-the-premises (FTTP) initially did so in 2007, easy access to gigabit speeds was slow to follow. However, that may be starting to change. Between June and July 2019 we saw a large uptick in gigabit-speed results in Brazil, where the proportion of gigabit speed tests increased from 0.02% of total fixed broadband tests to 0.17%. This corresponded with a large increase in mean download speed at the country level.
Comparing world mobile and fixed broadband at a glance
We were curious to see just how different internet performance experiences were around the world, so we plotted average mobile download speed against average download speed on fixed broadband. All of the graphs below use a percentage difference from the global average, a number that changed between 2018 and 2019.
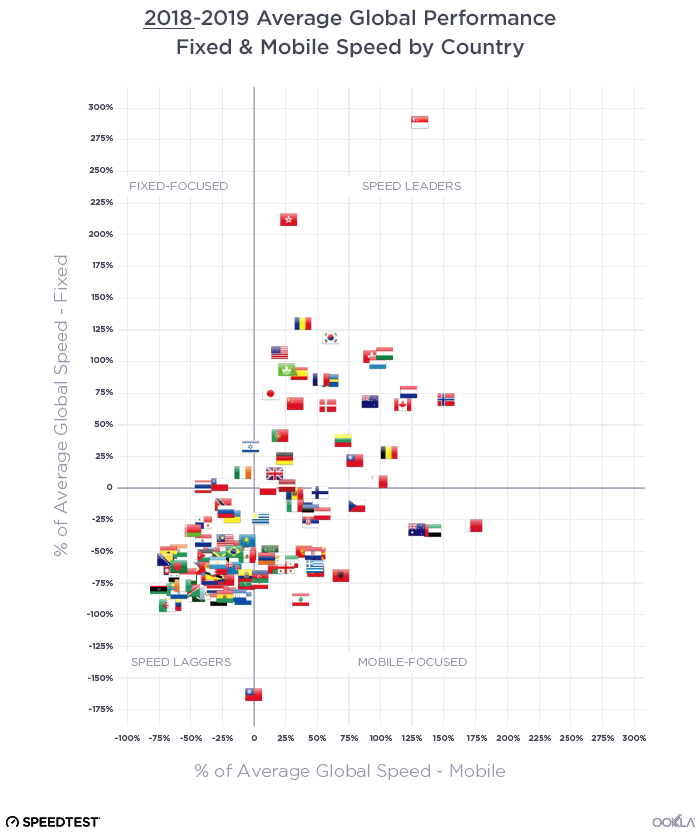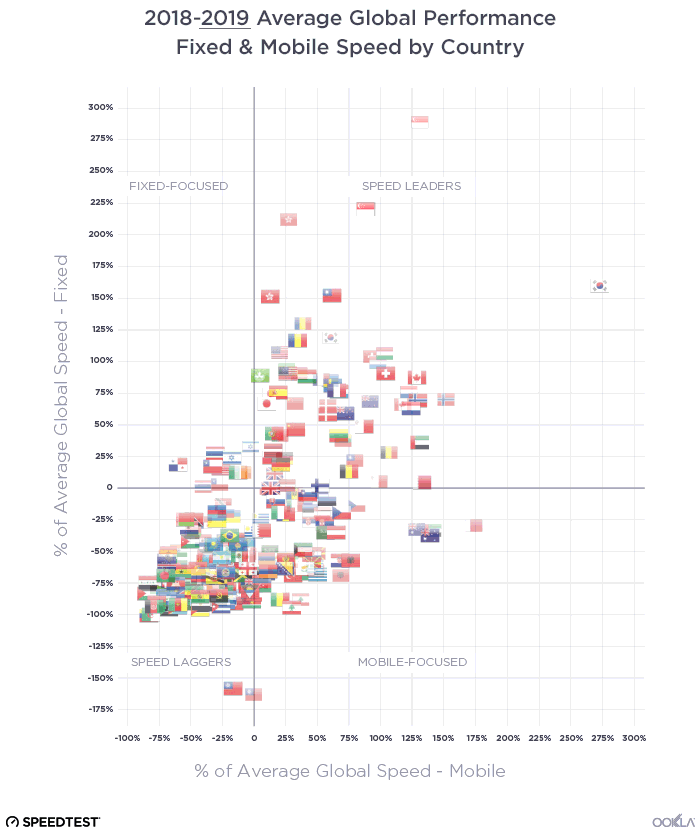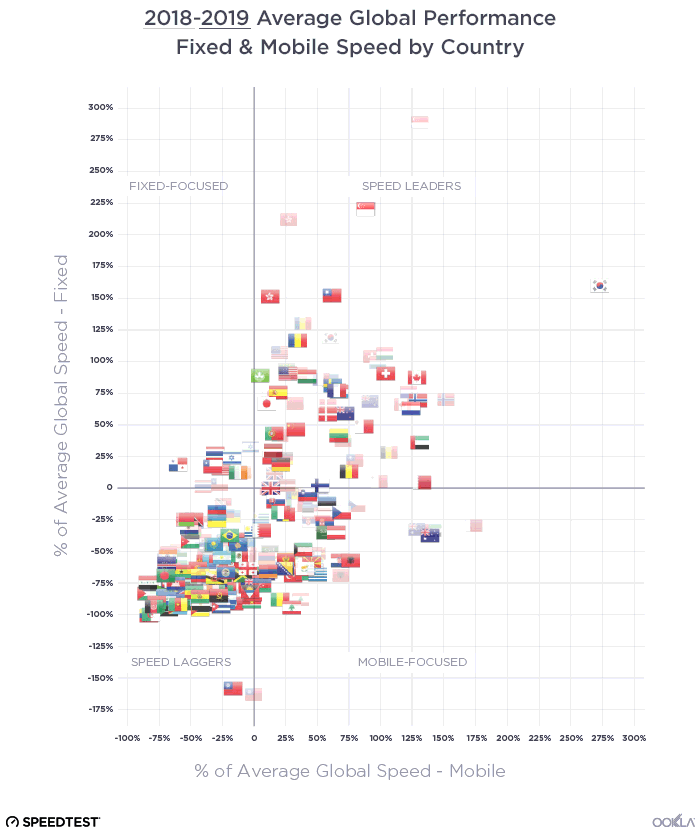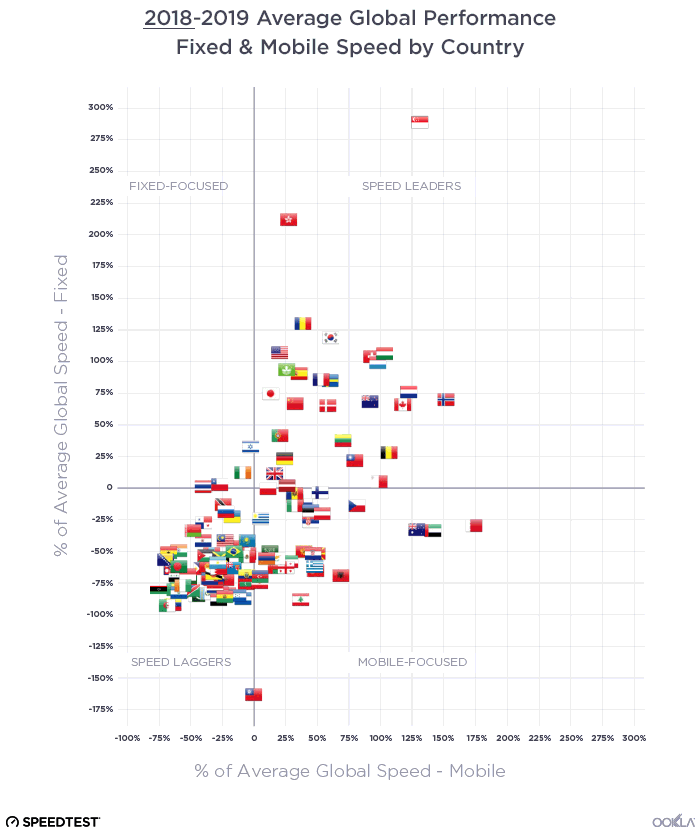
Speed Leaders
There was not much change in the list of countries that showed above-average download speeds on both mobile and fixed broadband between July 2018 and July 2019, the “Speed Leaders.” What did change was that fixed broadband speeds increased significantly enough among the group to bring the whole pack closer to Singapore and Hong Kong. On the mobile axis, South Korea’s major increase in download speed made that country more of an outlier, pushing the boundaries of what great performance can look like.
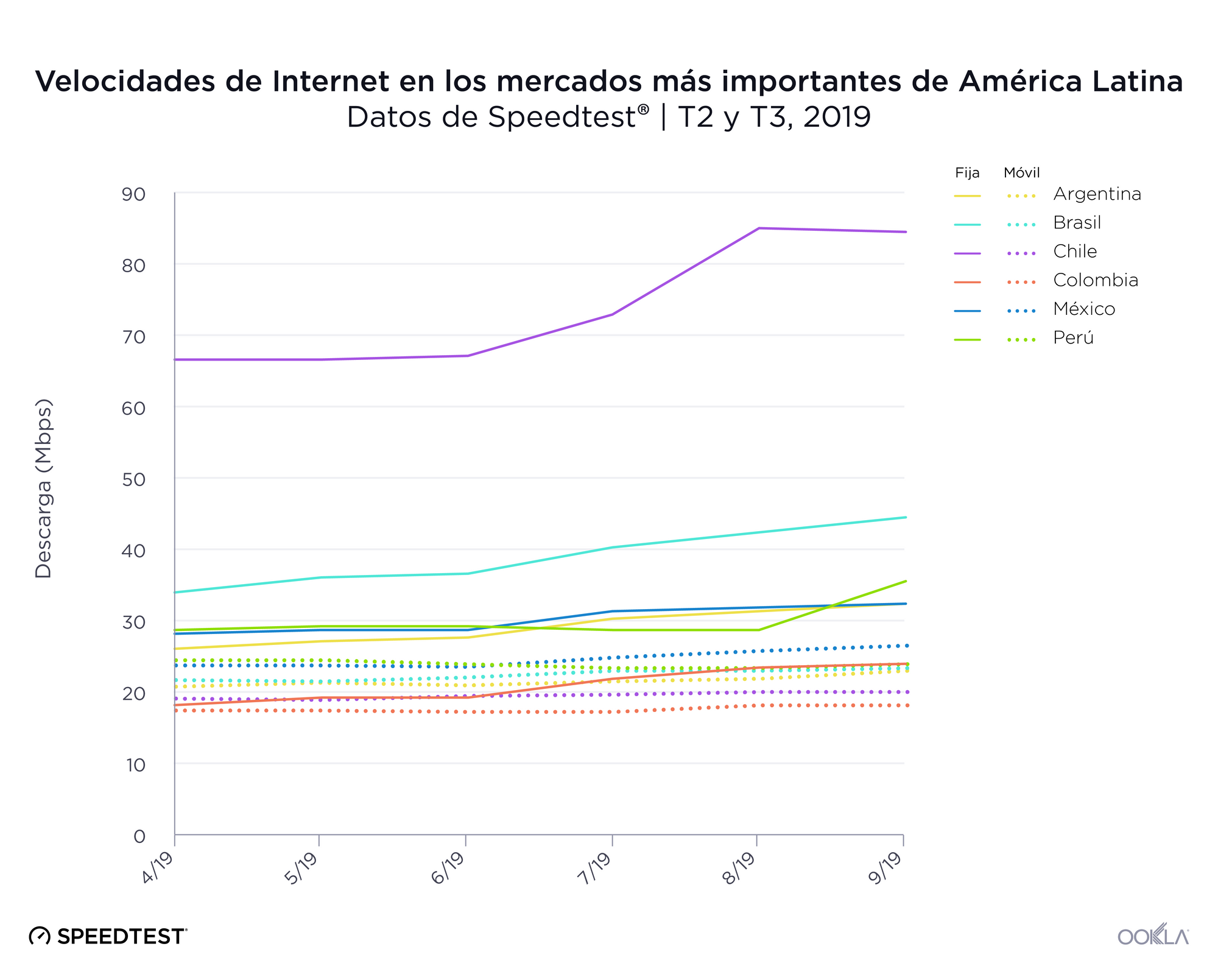
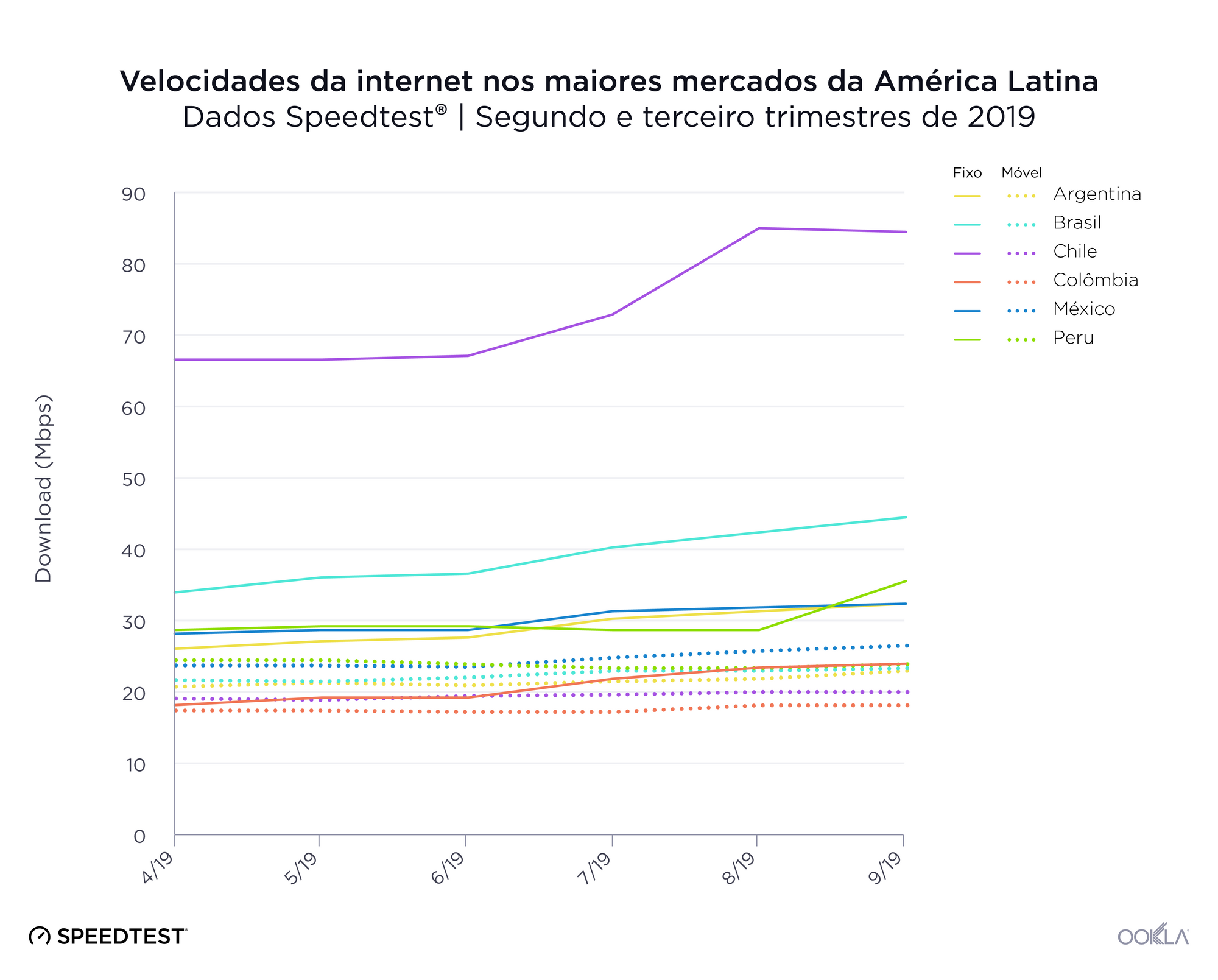
Fixed-Focused countries
Between July 2018 and July 2019 we saw the number of countries considered to be “Fixed-Focused” (having faster download speeds over fixed broadband than the world average while their average mobile download speeds were slower than average) increase. Ireland was the only country that solidly fit this category in 2018. Thailand and Chile started near the midline for fixed speeds and below-average for mobile speeds in 2018. 2019 found both countries squarely in the Fixed-Focused category. Israel also edged into this category as their mobile download speed fell between July 2018 and 2019.
Mobile-Focused countries
The “Mobile-Focused” category saw the most movement between July 2018 and July 2019 as some countries (the UAE and Qatar) increased their fixed speeds sufficiently to join the Speed Leaders. Meanwhile, Bosnia and Herzegovina’s mobile download speed increased year-over-year to move them into the Mobile-Focused quadrant. Georgia’s mobile download speed decreased enough to move them from Mobile-Focused to Speed Laggers.
It will be interesting to see how many of these Mobile-Focused countries double down on their mobile investments and explore 5G alternatives to fixed broadband.
Speed Laggers
No country wants to be in the position of having slower than average mobile and fixed broadband speeds. We saw 57 countries in this “Speed Laggers” quadrant in July 2018 and 78 in July 2019. This increase is mostly due to our expansion of the number of countries we consider for the Speedtest Global Index based on test count. There were enough countries in this category that we’ve considered them separately by continent below.
Regional views of mobile and fixed broadband performance
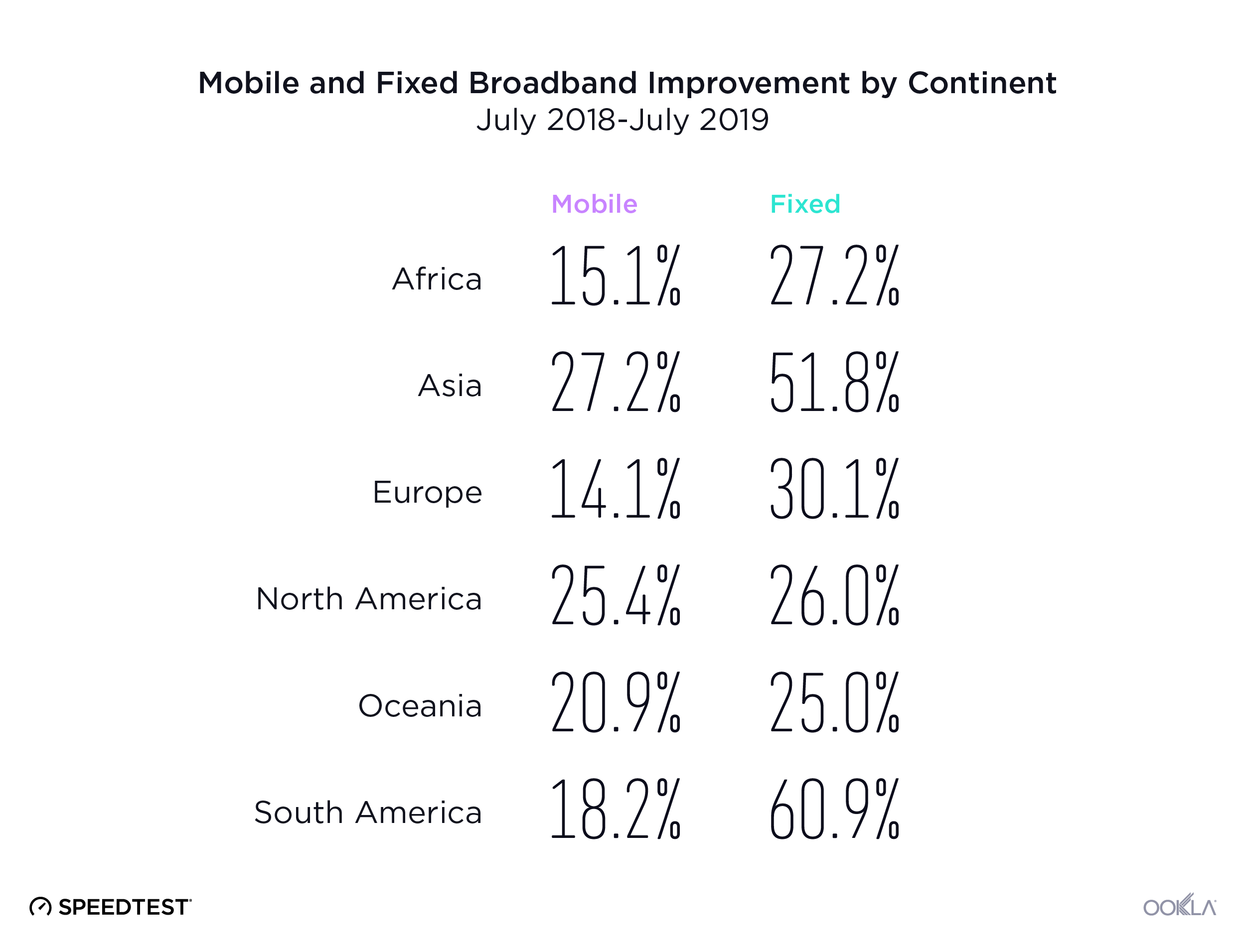
We aggregated Speedtest results by continent to analyze mobile and fixed broadband performance by continent.
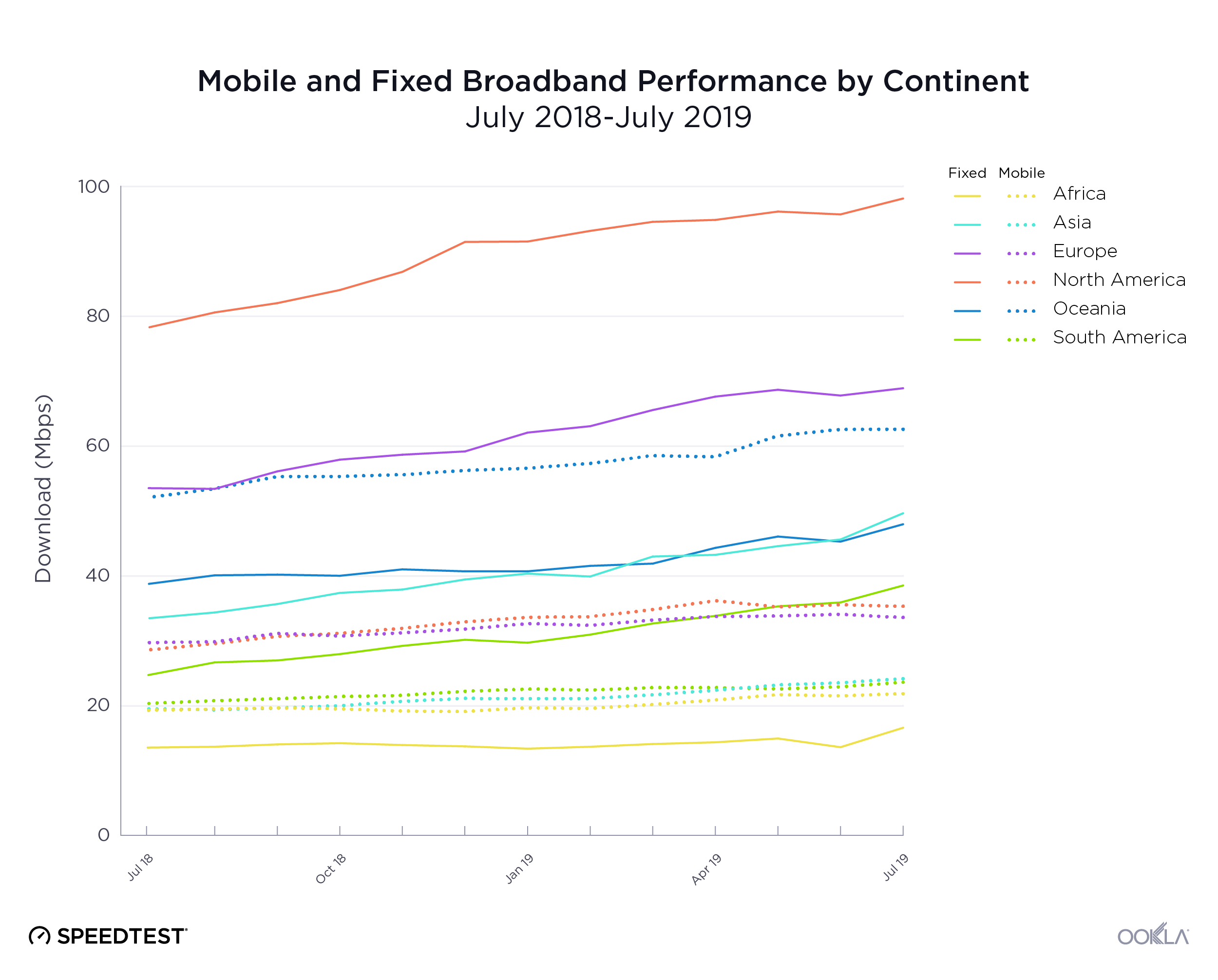
Asia had the highest percentage increase in mobile download speed followed by North America, Oceania, South America, Africa and Europe. Oceania had the fastest mean download speed in July 2019. North America placed second, Europe third, Asia fourth, South America fifth and Africa sixth.
On the fixed broadband side, South America saw the highest percentage increase in download speed. Asia came in second, Europe third, Africa fourth, North America fifth and Oceania sixth. North America had the fastest mean download speed in July 2019. Europe was second, Asia third, and Oceania fourth. As we saw with mobile, South America and Africa again ranked fifth and sixth, respectively.
A zoomed-in view of the speed quadrants separated by continent offers a more detailed view of each country’s role in these rankings.
Africa mostly lags in internet speeds
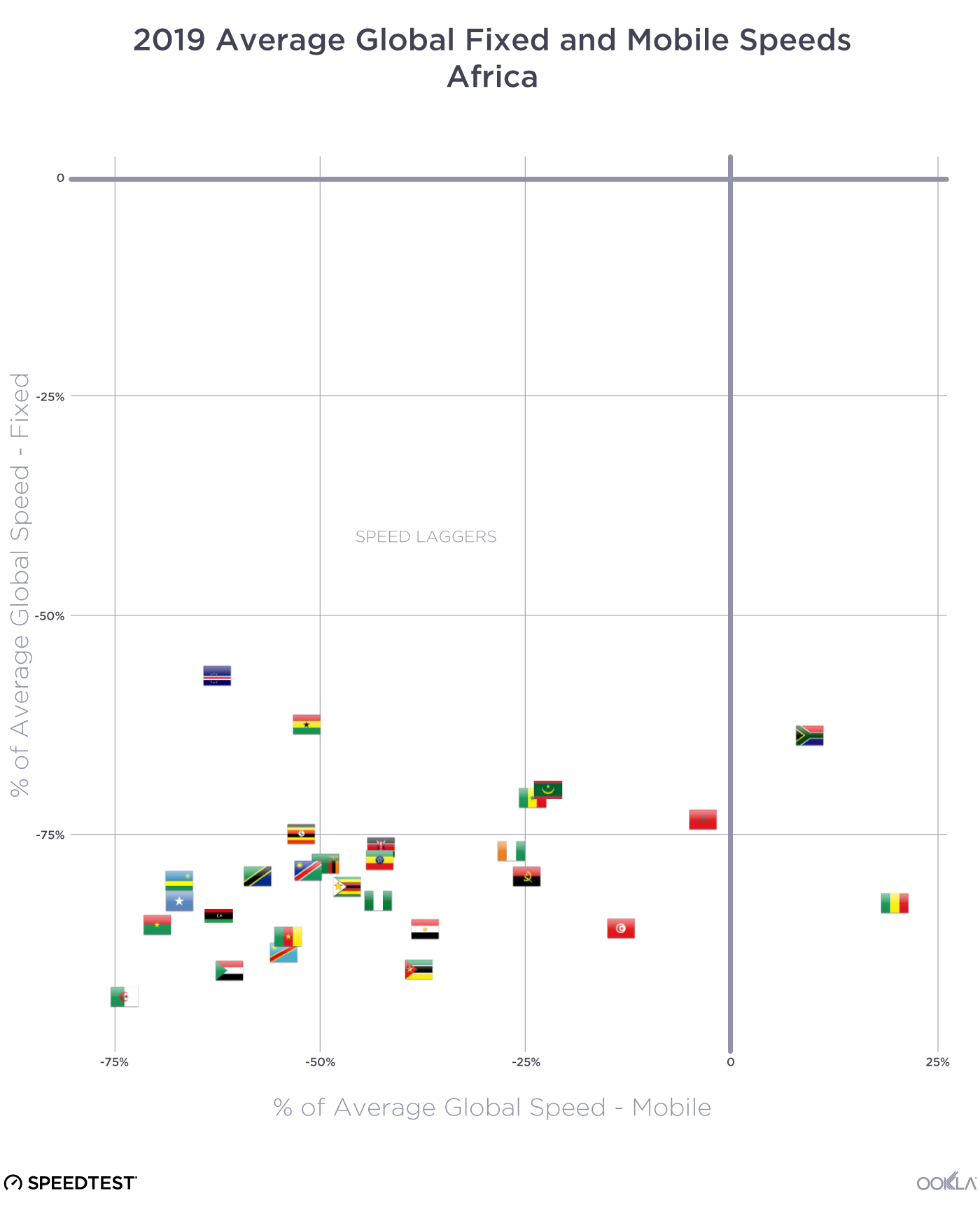
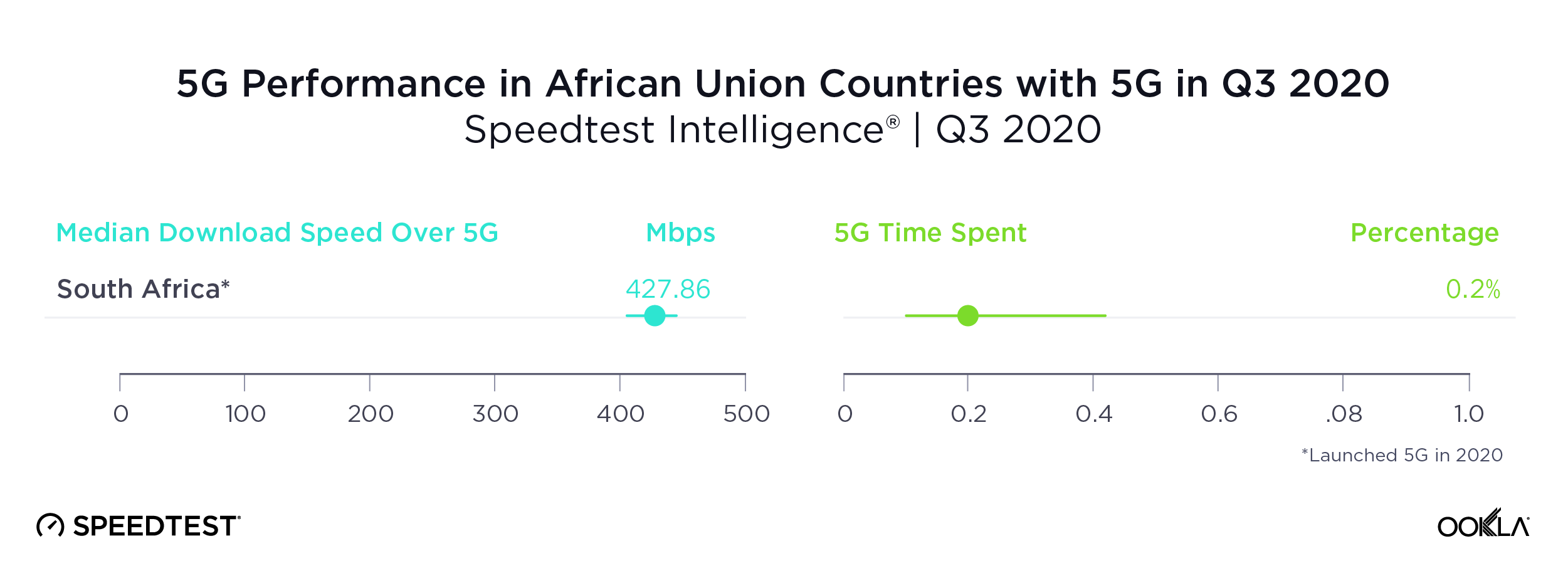
In July 2019, all but two African countries in the Speedtest Global Index fell into the Speed Laggers category, having mobile and fixed broadband speeds that were below global averages. The exceptions were South Africa and Guinea, which both had fast enough mobile speeds to place them in the mobile-focused quadrant.
Asian markets show a wide breadth of internet performance
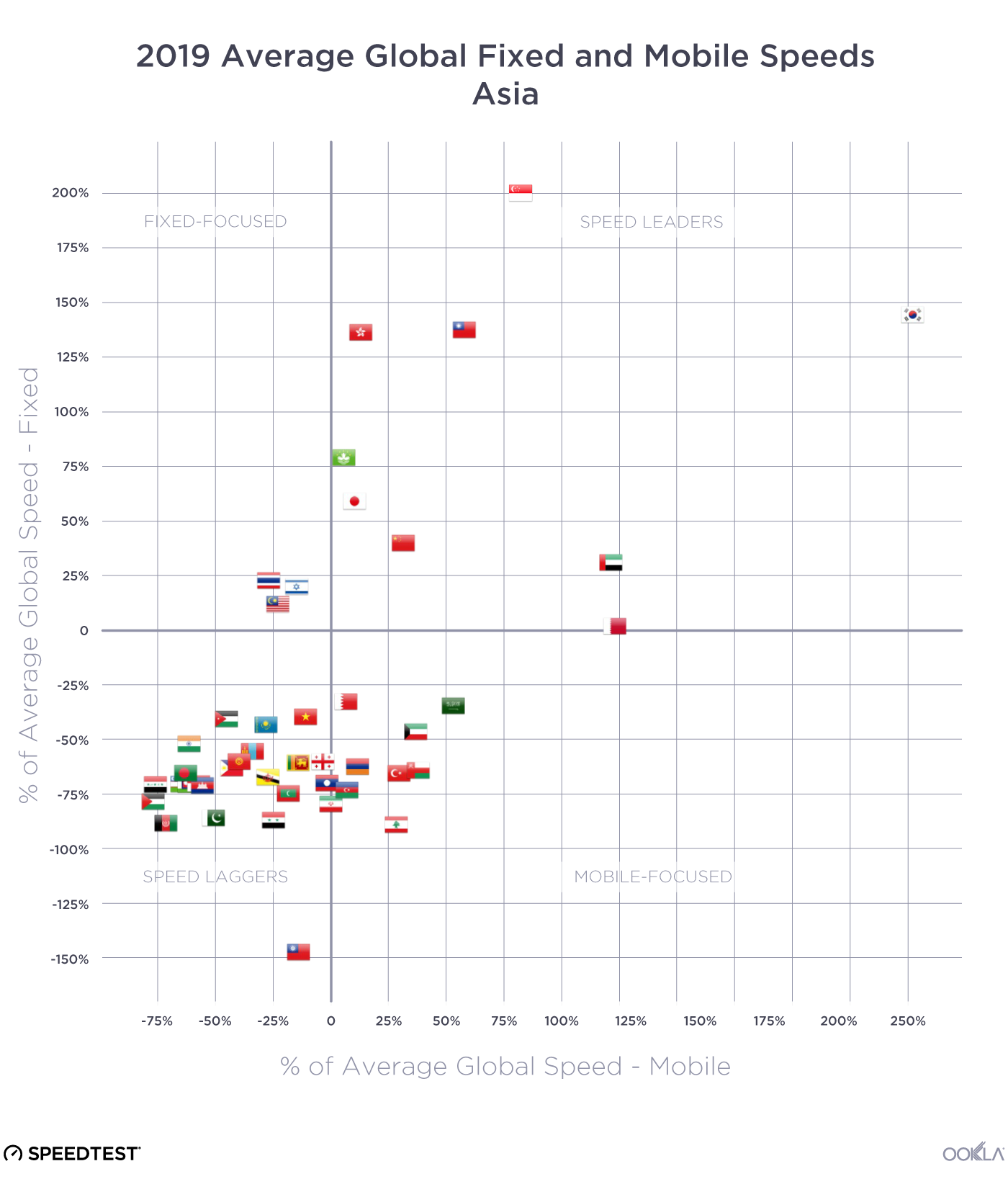
Asia was the most diverse continent we examined in terms of internet performance. We saw a plurality of countries in each of the four quadrants in July 2019. Most of the Speed Leaders were in East Asia: China, Hong Kong (SAR), Japan, Macau (SAR), South Korea, and Taiwan. If we include Singapore, another Speed Leader, these are among the wealthiest nations in Asia (using GDP per capita). Two of Asia’s Fixed-Focused countries are in Southeast Asia (Malaysia and Thailand) and one is in the Middle East (Israel).
The Speed Laggers category contained countries from South Asia (including Afghanistan, India and Pakistan), Southeast Asia (Brunei, Cambodia, the Philippines and Vietnam) and the Middle East (Jordan). Mobile-Focused countries in Asia were mostly Middle Eastern, including Kuwait, Lebanon, Oman, Saudi Arabia and Turkey.
European mobile performance is mostly strong, fixed varies
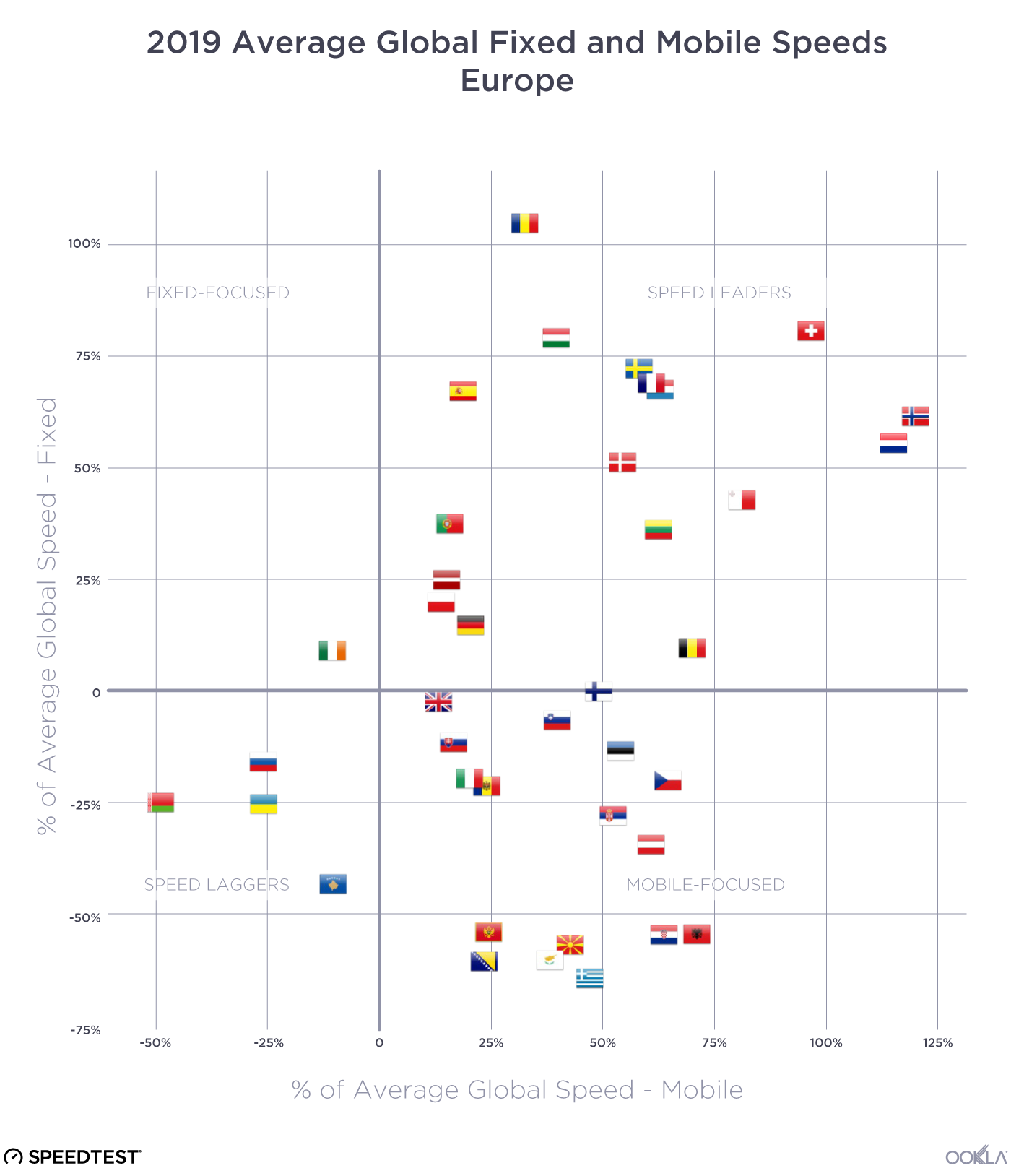
With the exception of Ireland, the European countries on the Speedtest Global Index fell into the Speed Leaders, Mobile-Focused, and Speed Laggers categories. All of the Speed Laggers (Belarus, Kazakhstan, Russia and the Ukraine) were from Eastern Europe. Countries from Southeast Europe (including Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Greece, Montenegro, Moldova, Serbia and Slovenia) and Central Europe (Austria and the Czech Republic) made up the bulk of the Mobile-Focused category.
Speed Leaders included countries from the Baltics (Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania), the Nordics (Denmark, Norway and Sweden), Central Europe (Poland and Romania), and Western Europe (including Belgium, France, Germany, the Netherlands, and Spain).
North American internet performance is sharply divided
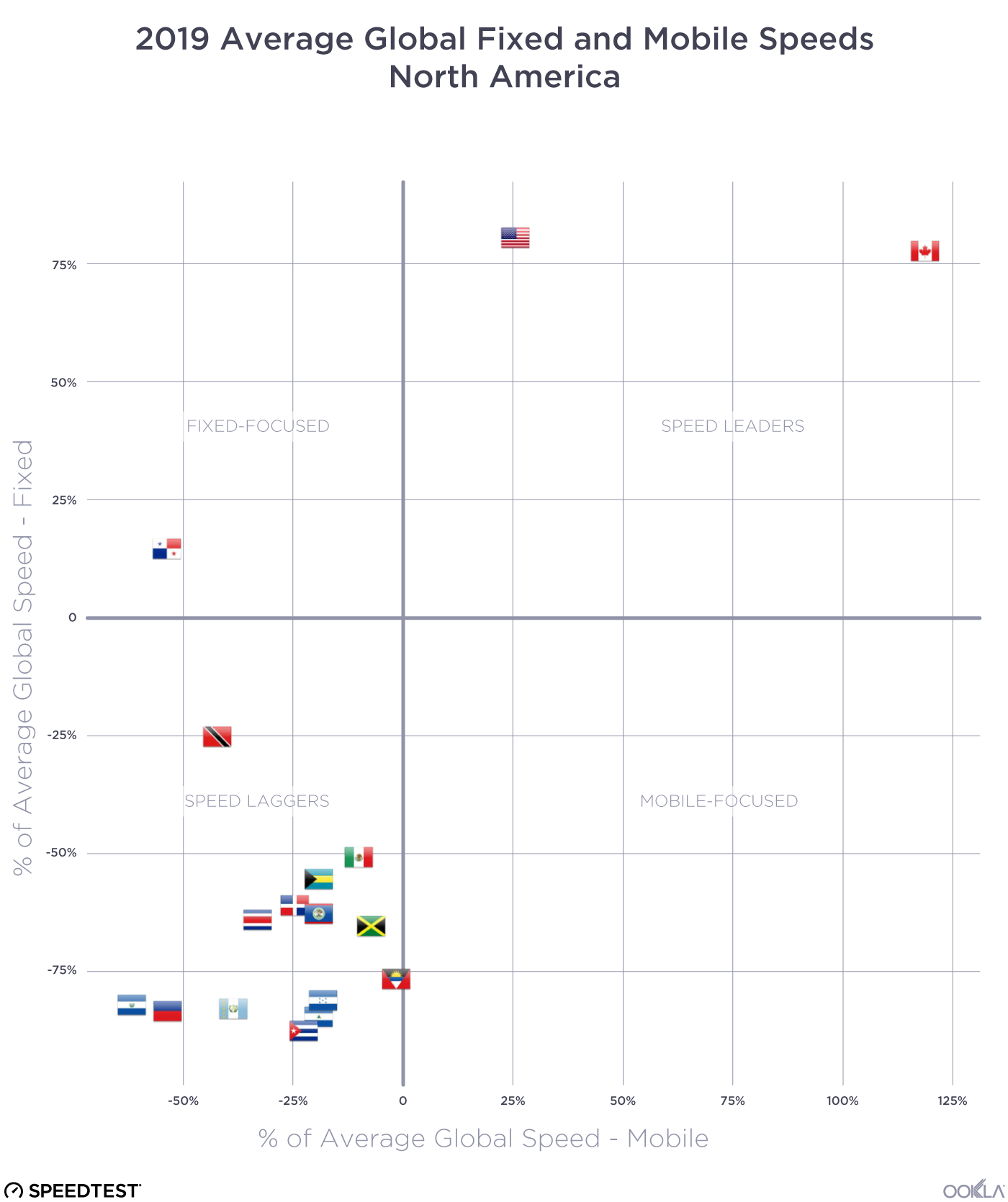
Canada and the U.S. are the only two North American countries in the Speed Leaders category. Panama is the only North American country under Fixed-Focused. Mexico and all of the Central American countries fall into the Speed Laggers category. There are no North American countries that are Mobile-Focused.
Each country in Oceania has a very different internet story
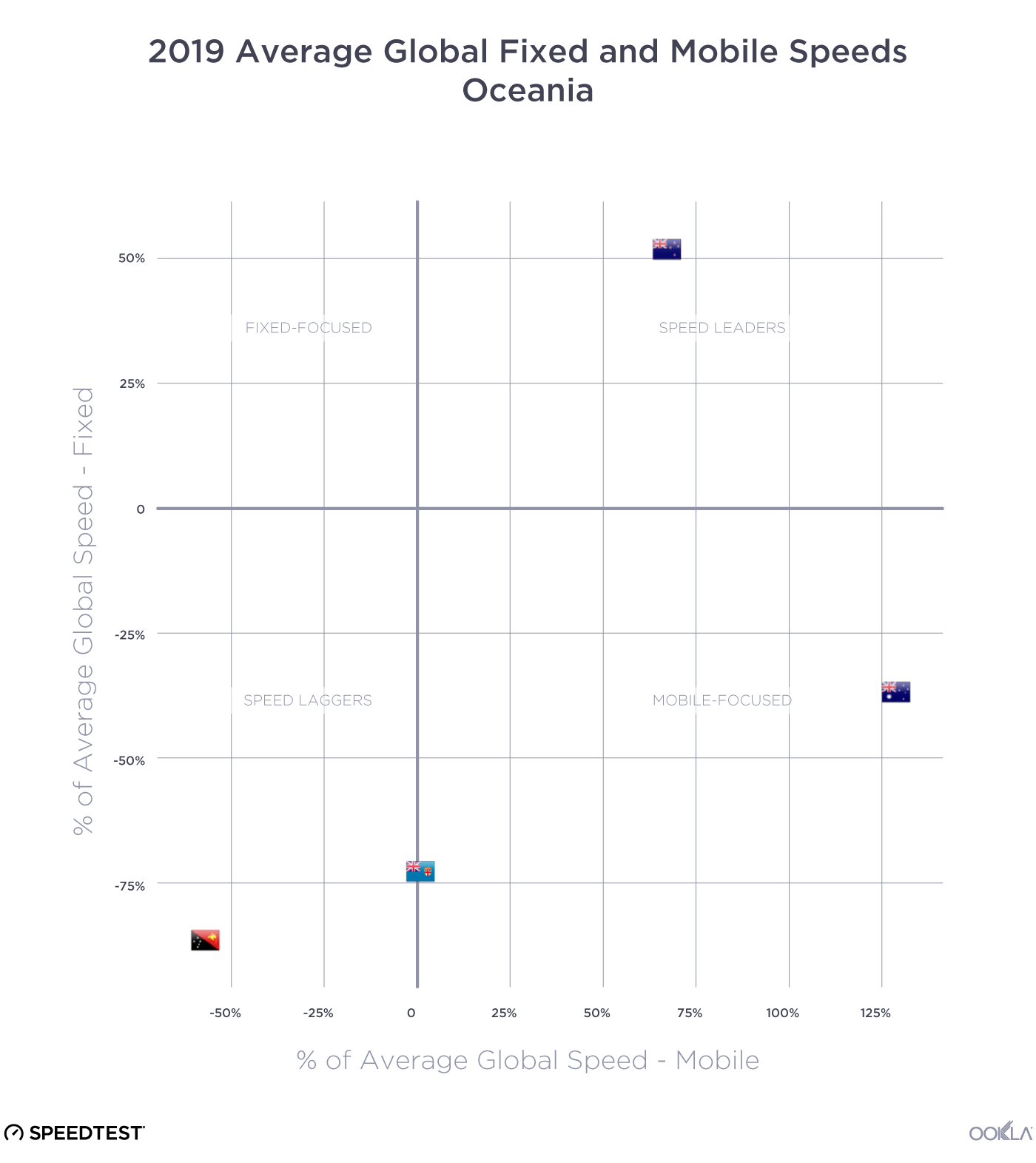
Oceania is represented in three of the four quadrants: Speed Leaders (New Zealand), Mobile-Focused (Australia) and Speed Laggers (Papua New Guinea) with Fiji straddling the divide between Speed Laggers and Mobile-Focused.
South America mostly lags in mobile and fixed internet speeds
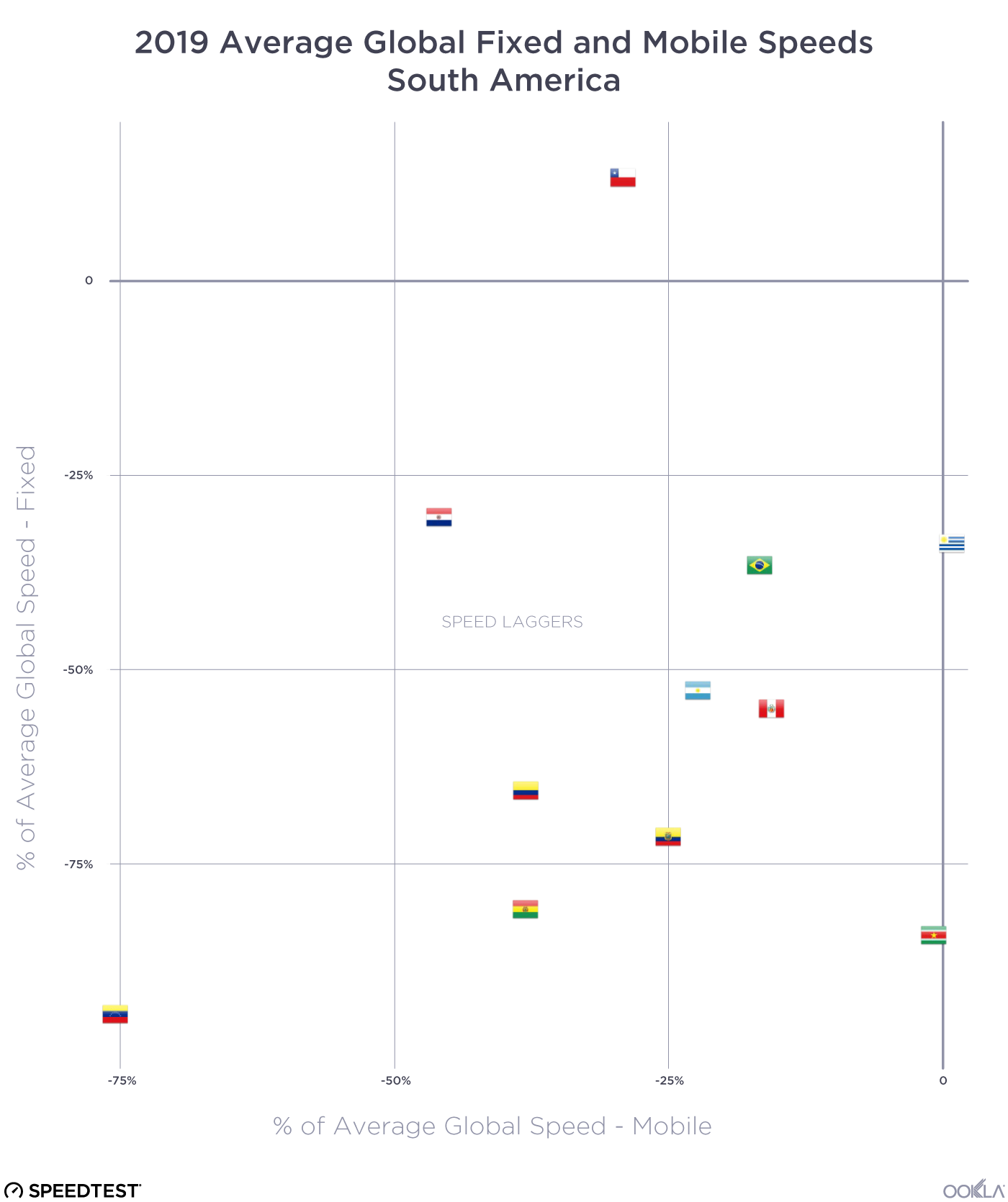
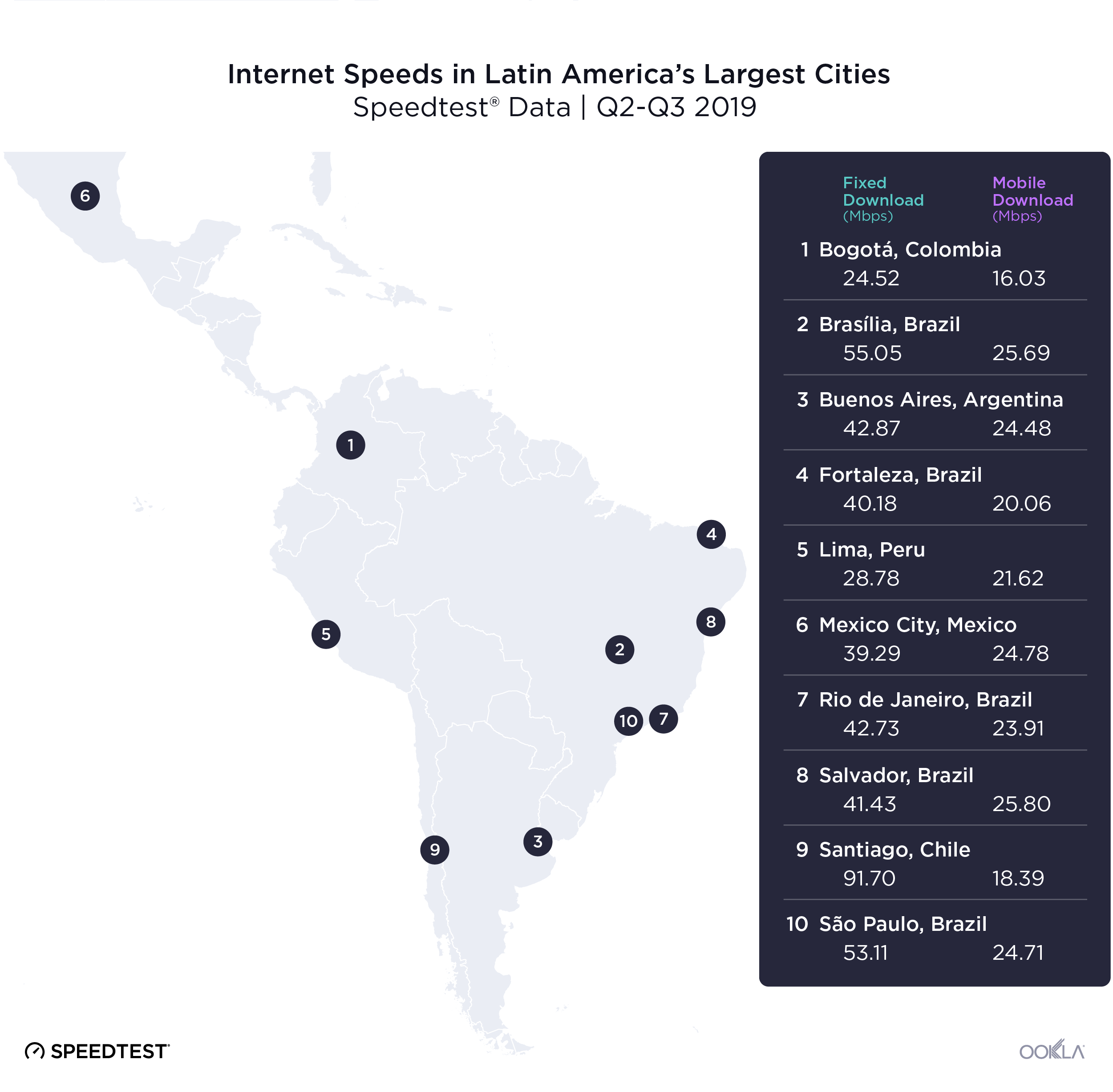
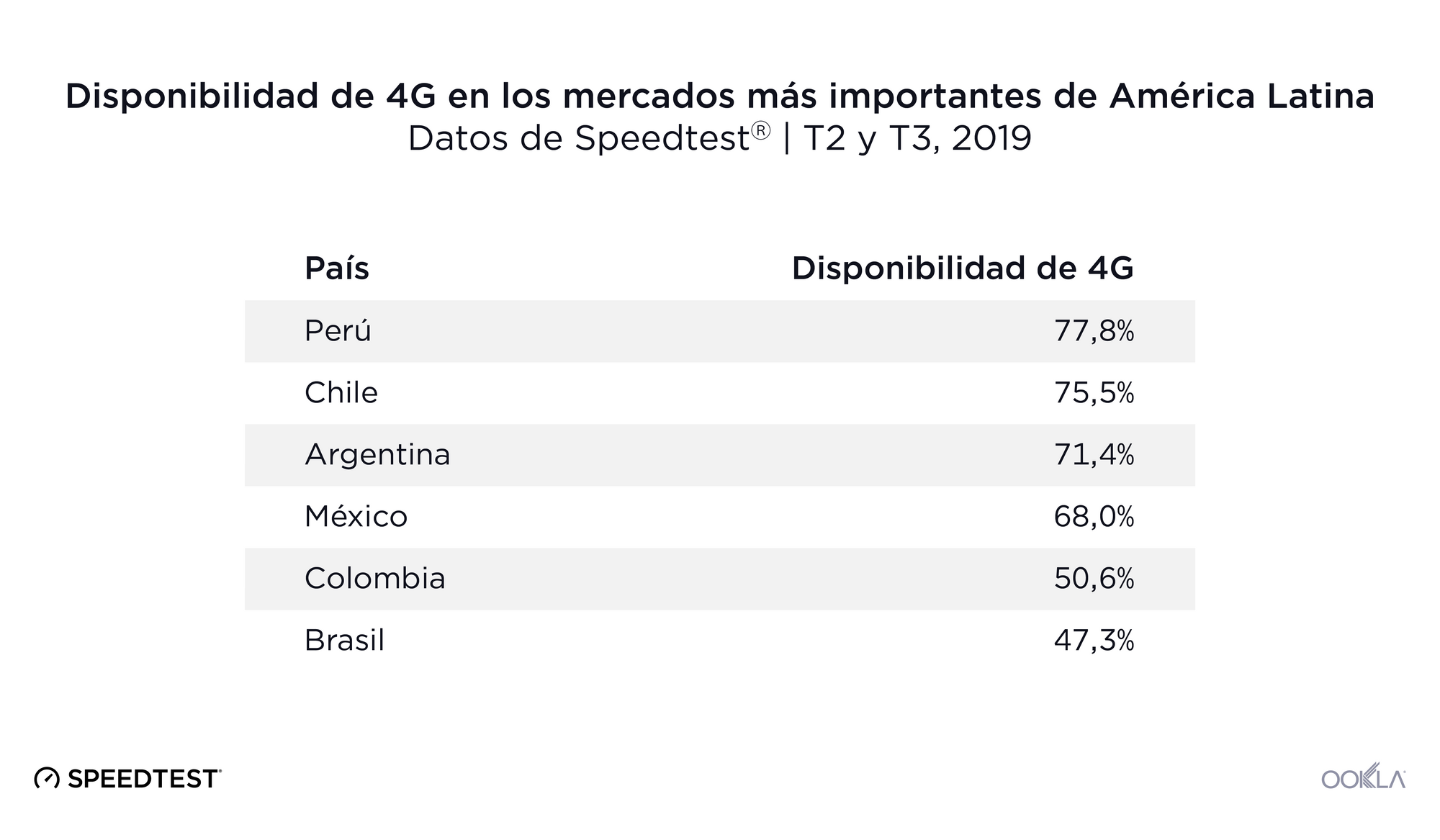
Most of the South American countries represented on the Speedtest Global Index are in the Speed Laggers quadrant (Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Paraguay, Peru, Suriname and Venezuela). Chile is an exception, being part of the Fixed-Focused group, as is Uruguay which sits in Mobile-Focused.
Global internet speeds are improving on average and 5G and gigabit are compounding those advances where available. However, not all countries are benefitting equally. We’ll be interested to see how 5G continues to push mobile speeds in the next year and also whether 5G Wi-Fi becomes a game changer for fixed broadband. Remember to check the Speedtest Global Index on a monthly basis for updated country rankings. And take a Speedtest to make sure your experience is represented in your country’s averages.
Editor’s Note: This article was edited on September 10, 2019 to correct an error in the labeling on the first image. The colors in a later image were updated for consistency.
Ookla retains ownership of this article including all of the intellectual property rights, data, content graphs and analysis. This article may not be quoted, reproduced, distributed or published for any commercial purpose without prior consent. Members of the press and others using the findings in this article for non-commercial purposes are welcome to publicly share and link to report information with attribution to Ookla.