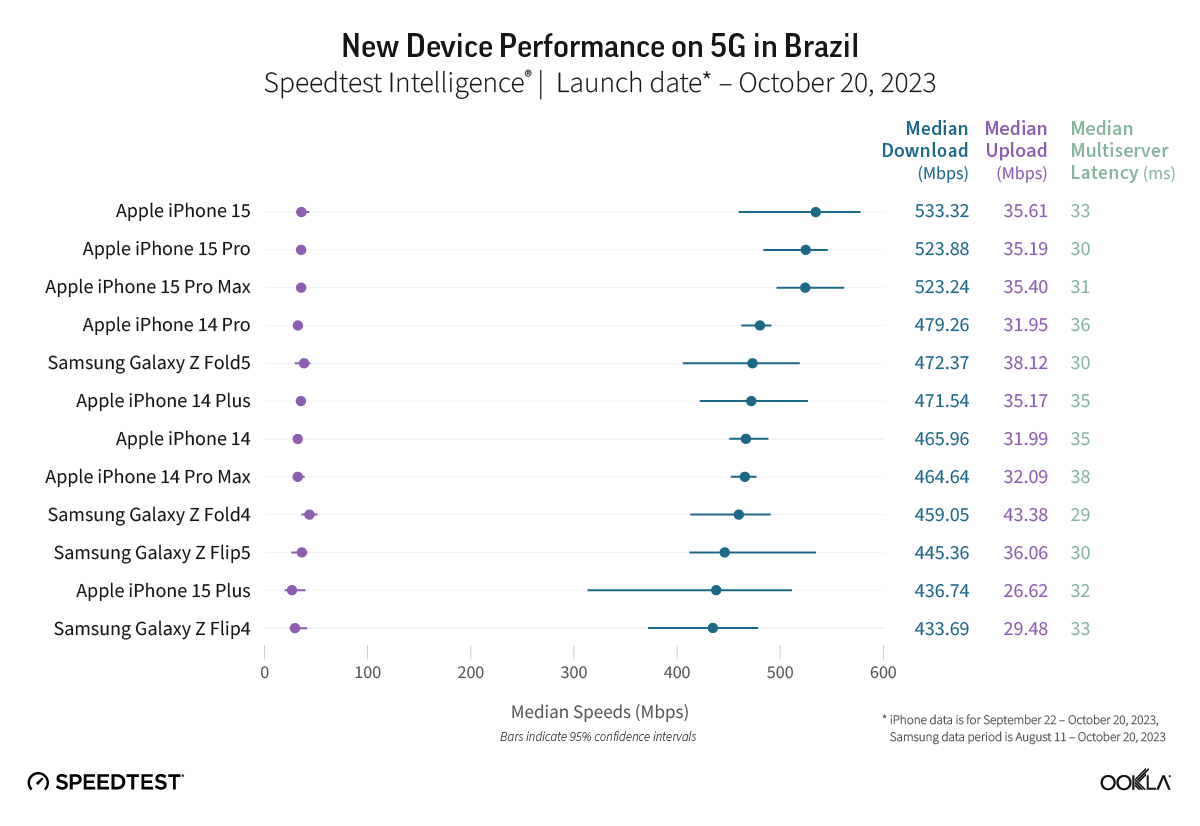
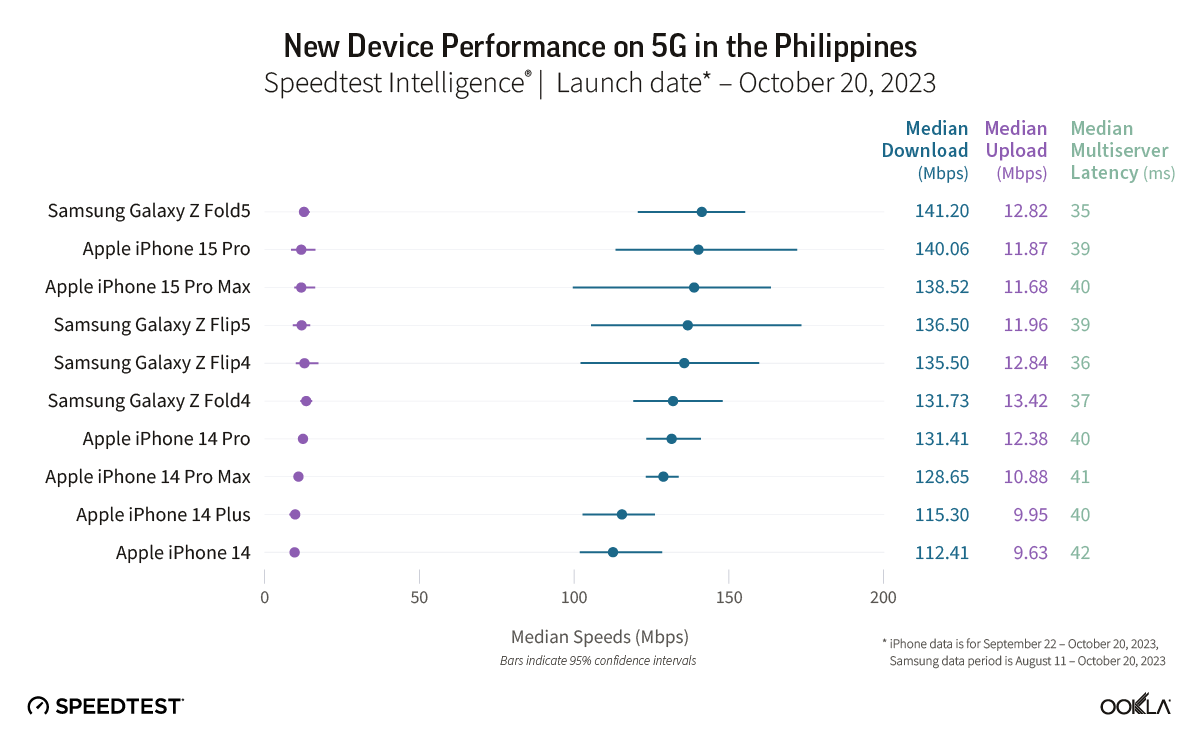
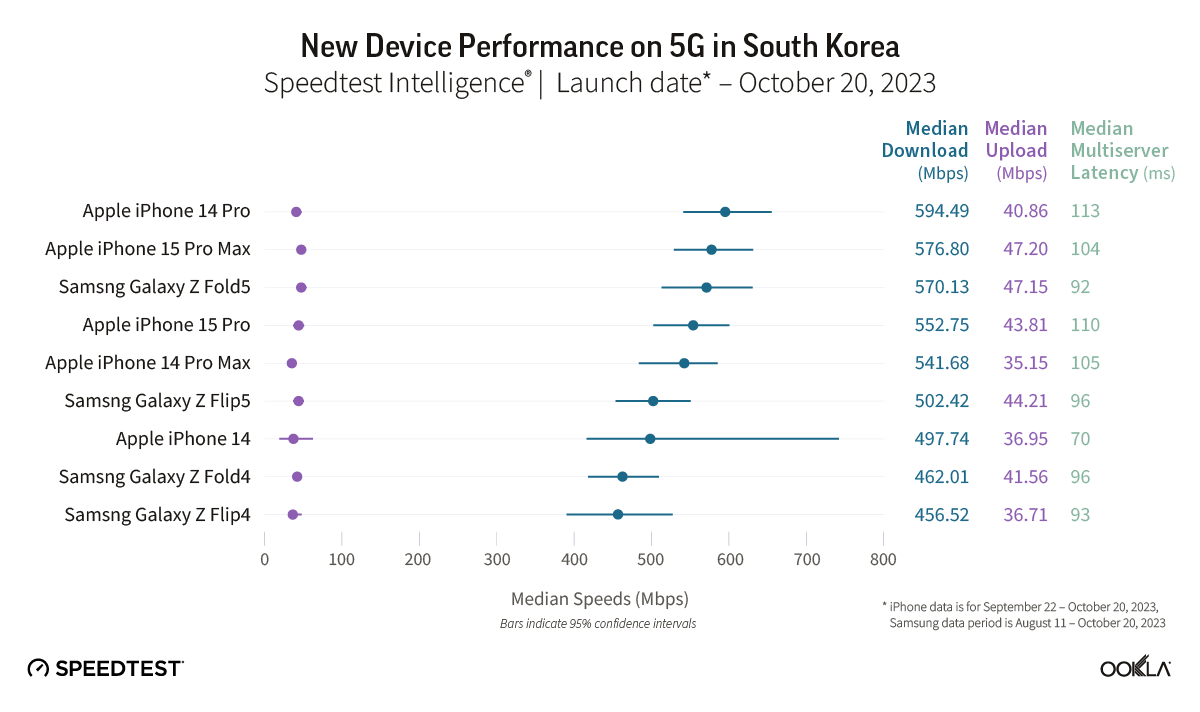
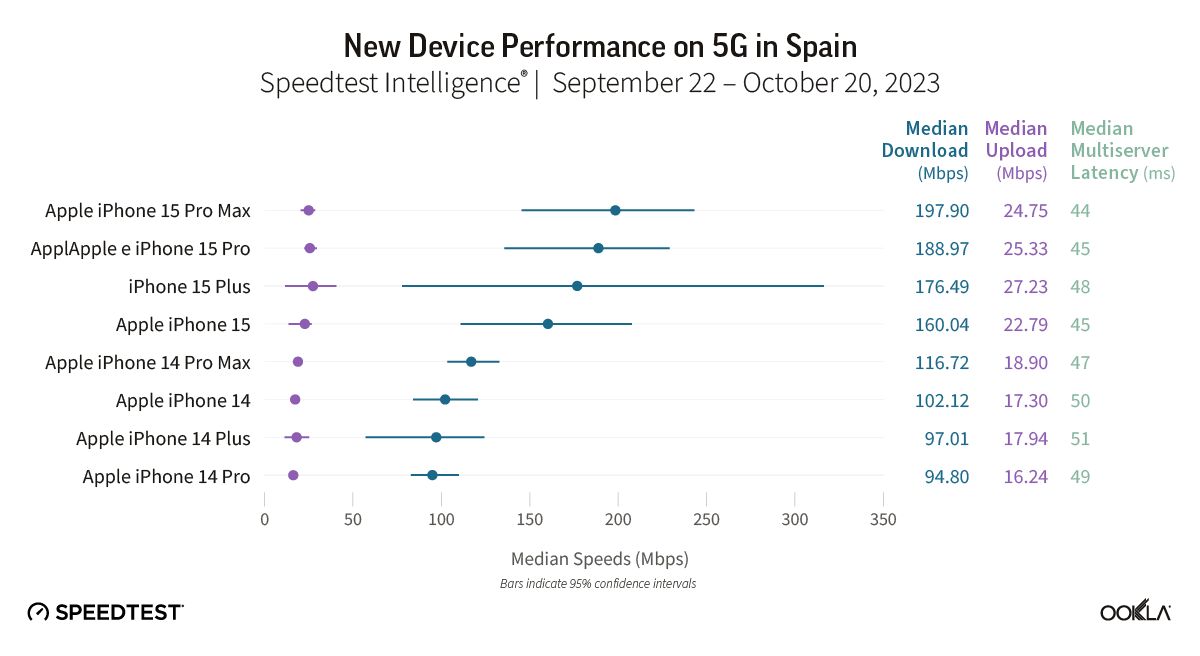
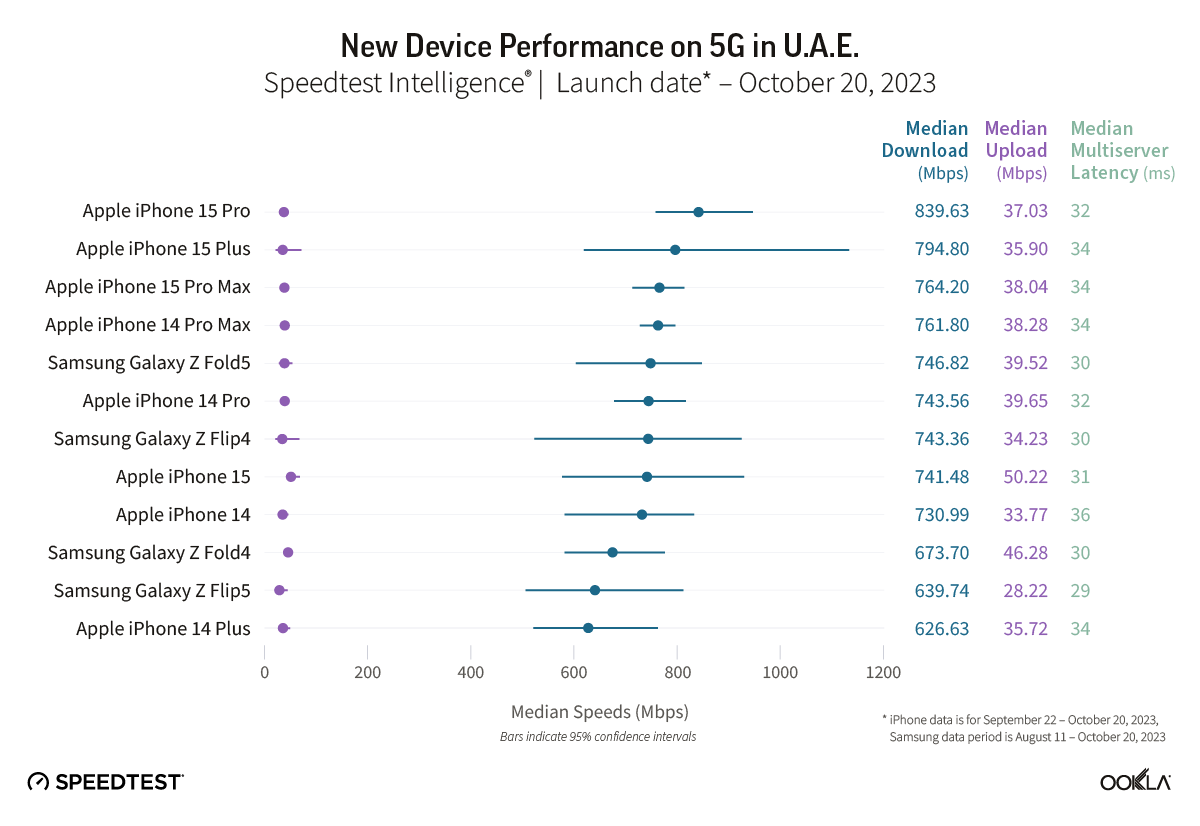
Bahrain took the lead in 5G gaming performance across the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) and the Middle East during the first half of 2023, based on Ookla Speedtest Intelligence® data. This article examines the gaming performance on Bahrain’s 5G networks, evaluates their suitability for multi-player on-device and cloud gaming services, and discusses local initiatives to position Bahrain as the regional gaming hub.
Key takeaways
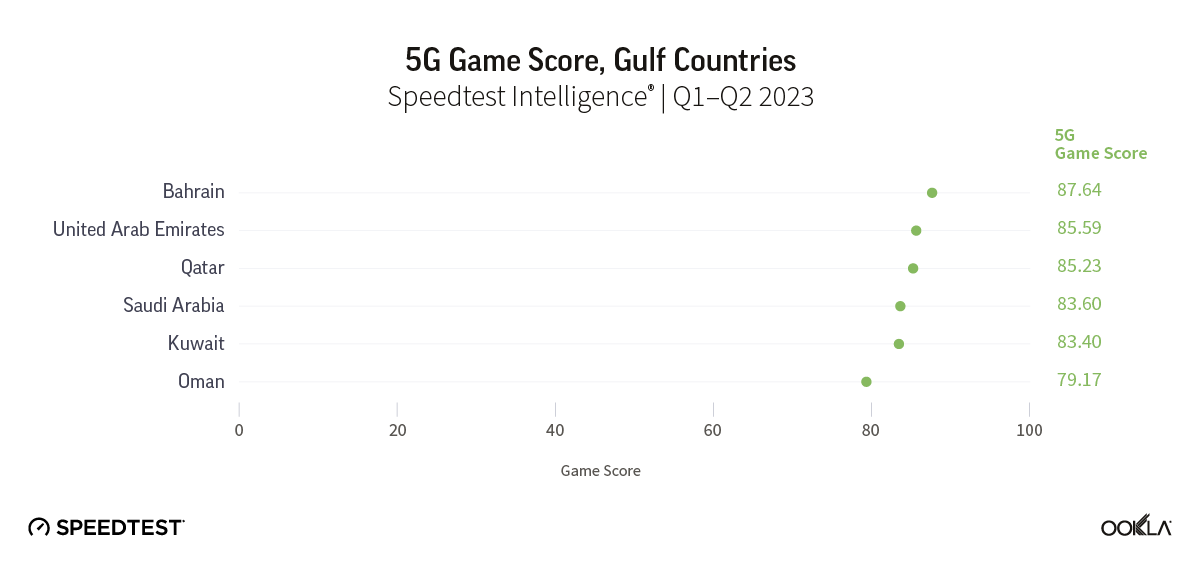
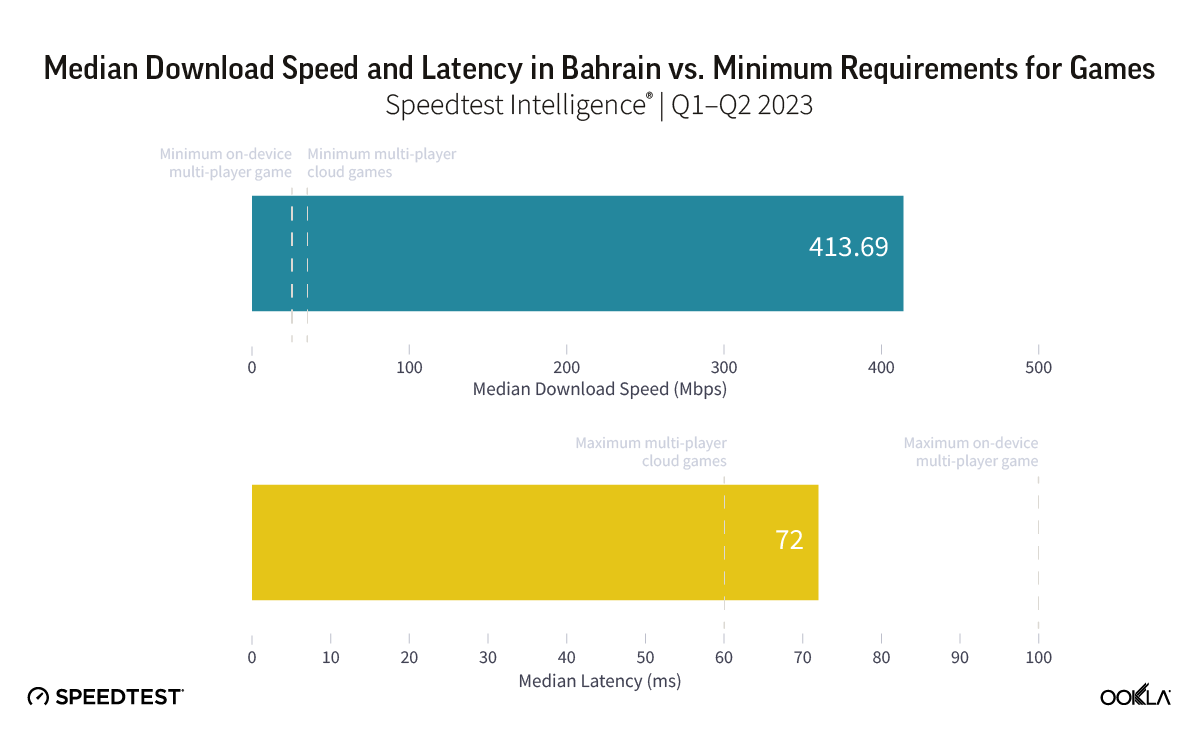
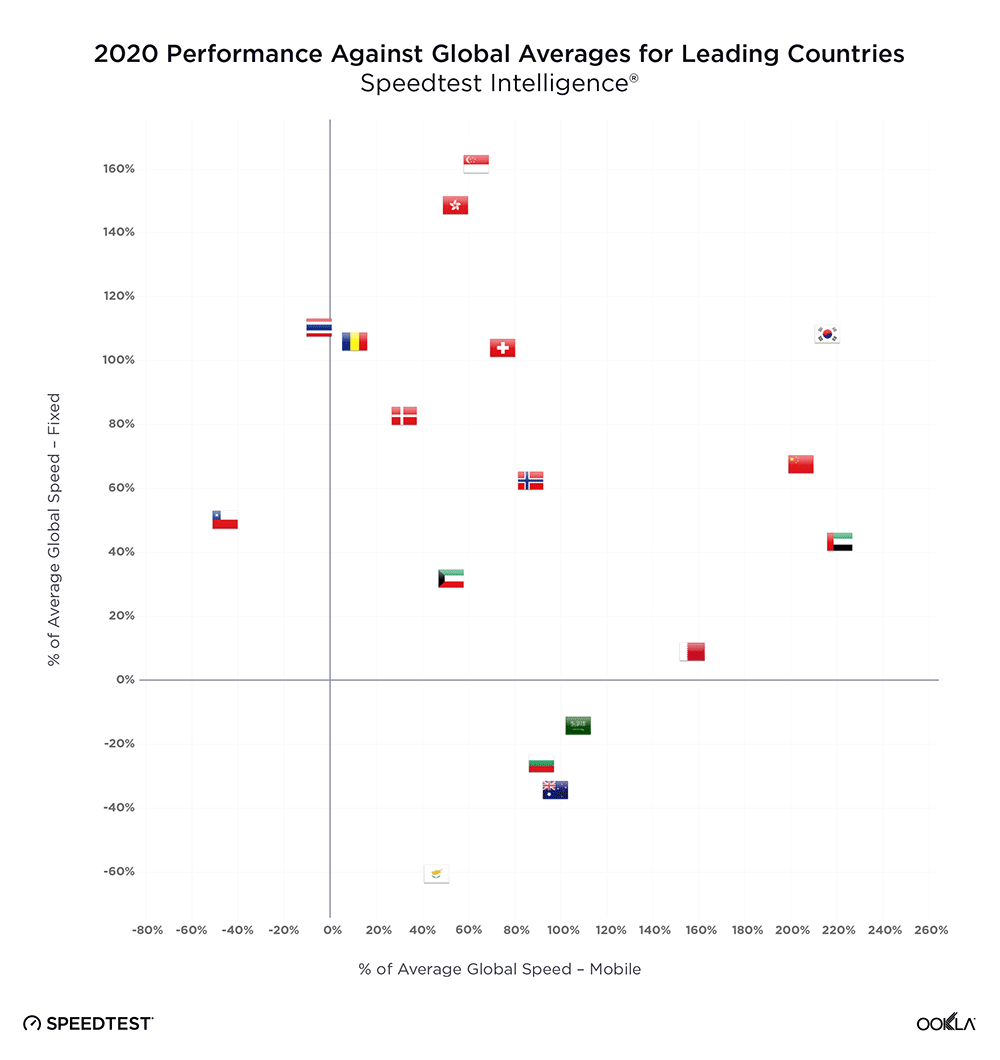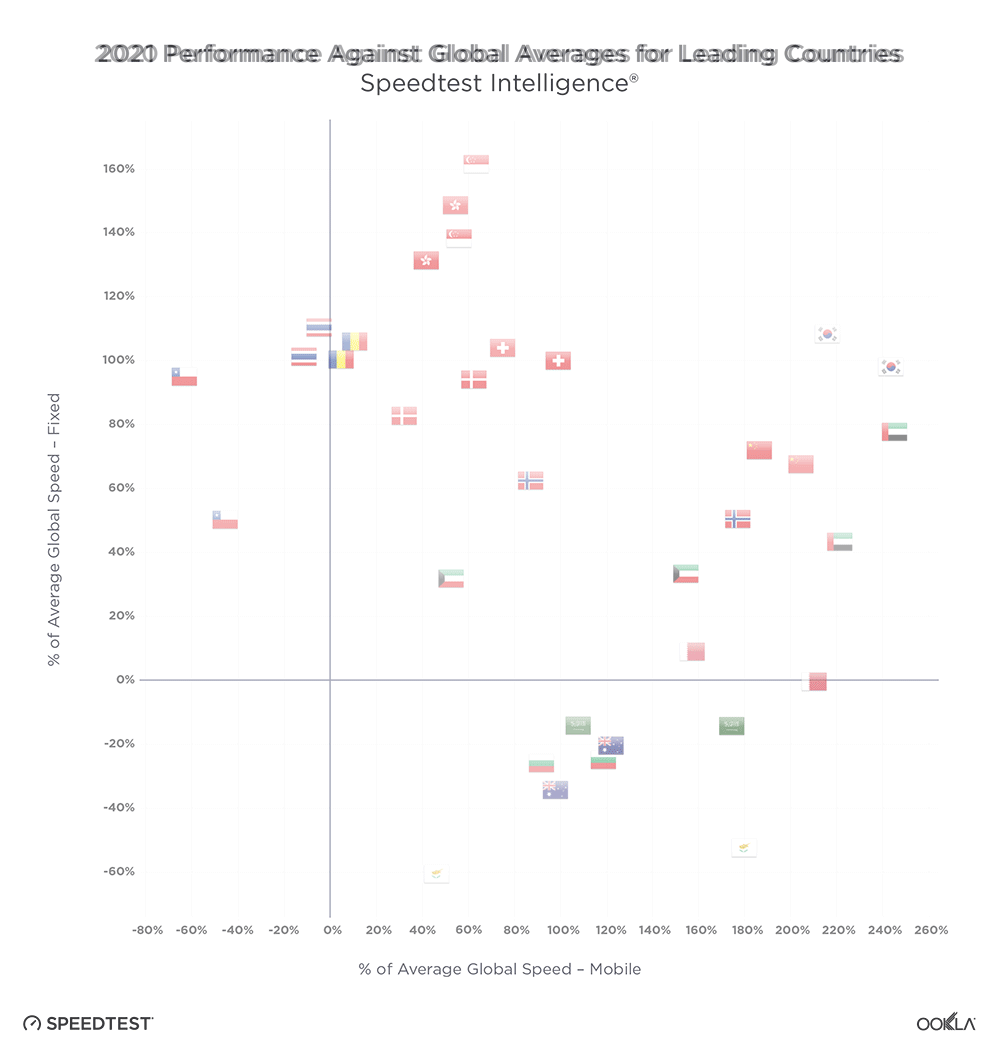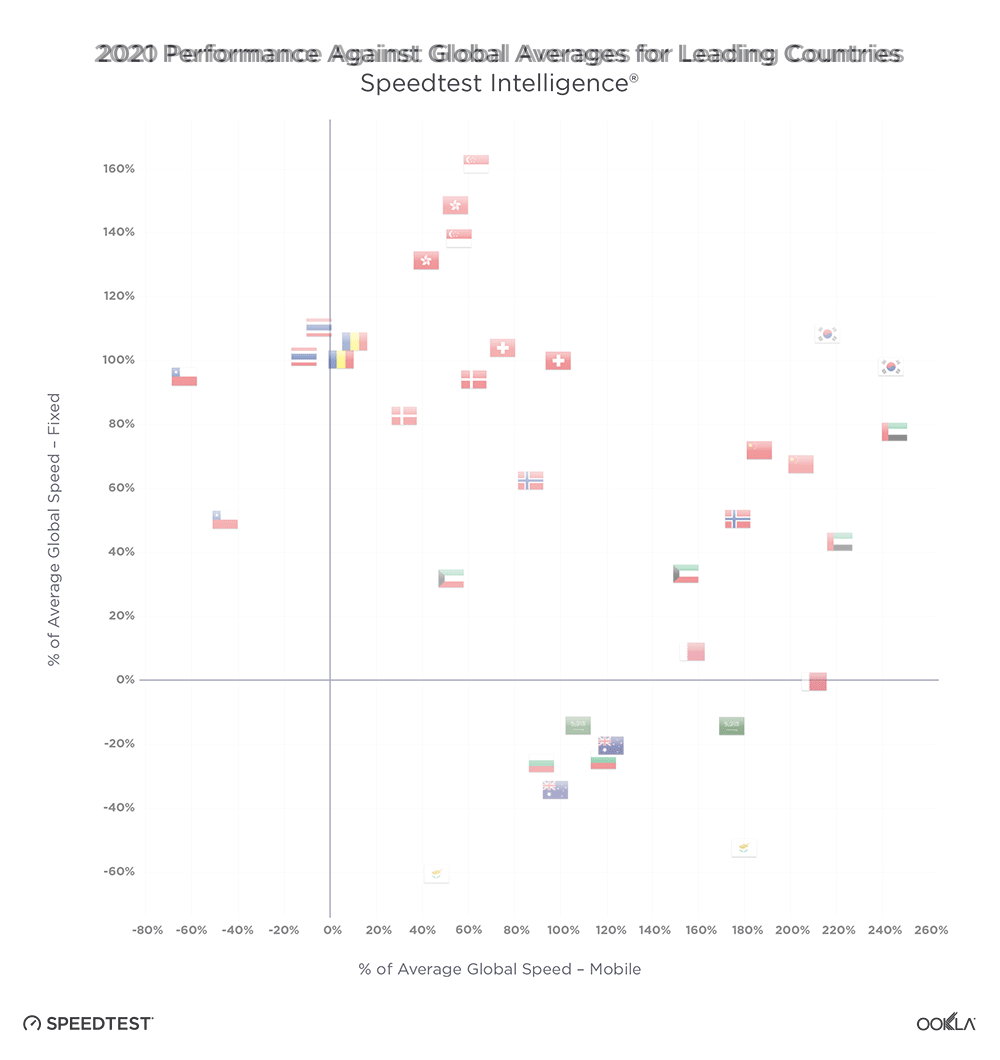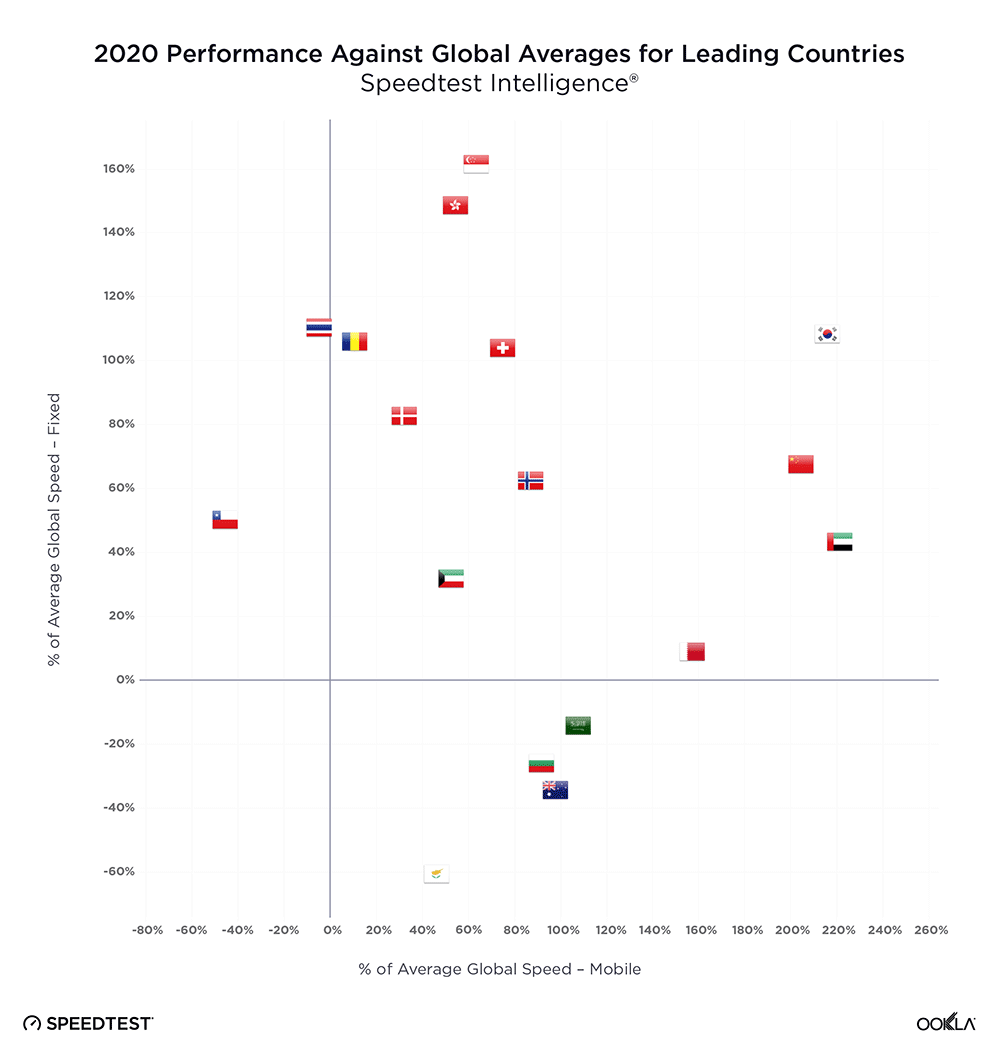
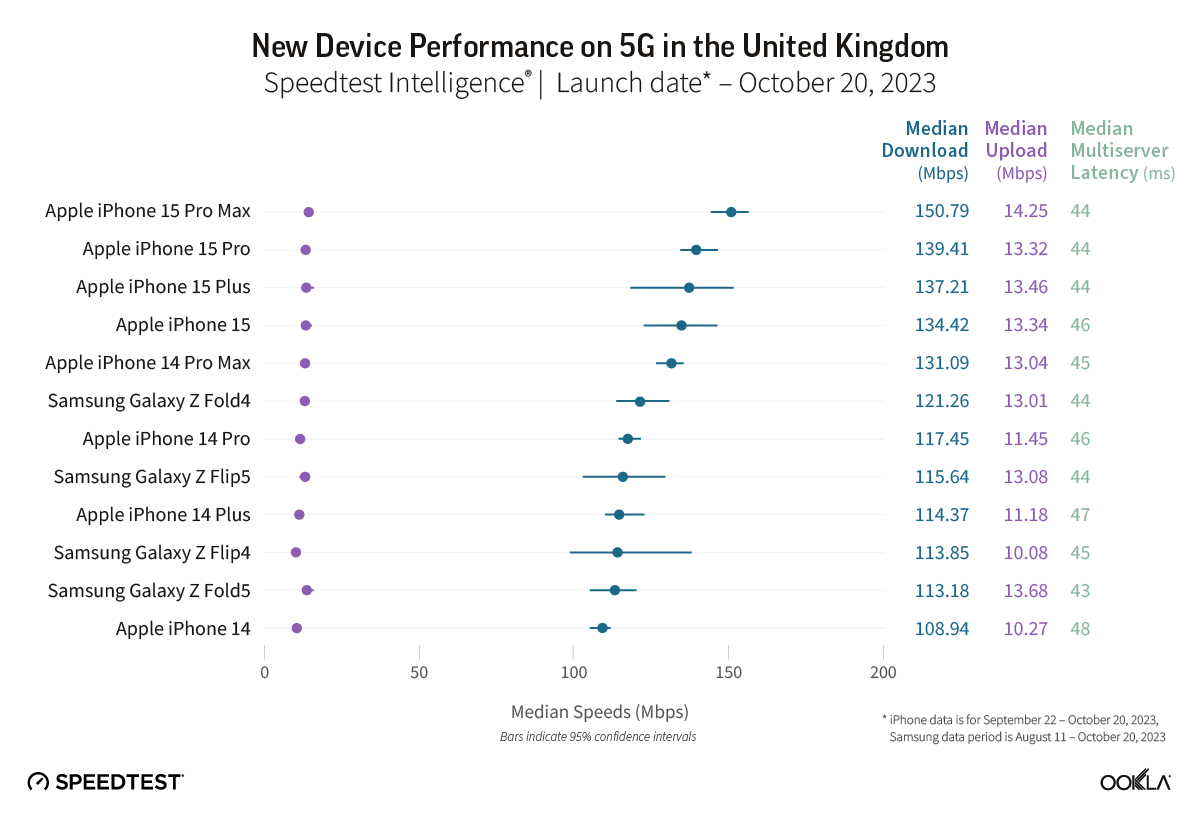
- Bahrain’s 5G Game Score™ was the highest in the Middle East at 87.64 out of 100 during Q1-Q2 2023. This exceptional network performance helps to deliver a good gaming experience. With ultra-fast 5G speeds (413.69 Mbps) and low latency (72 ms), most casual gamers can expect a top-notch multi-player gaming experience.
- Bahrain’s pro-gaming policies and initiatives helped to attract international companies and foster a burgeoning local gaming ecosystem. The vibrant start-up landscape, bolstered by supportive business-friendly policies, funding, and access to tech-savvy talent, helped to attract international gaming studios and emerge local ones.
- Bahrain faces competition from its neighbors to become a regional gaming hub. However, it can leverage its advanced networking infrastructure and reputation as a technology incubator to attract companies and entrepreneurs who want to trial new ideas and technologies for gaming and transform them into ventures that serve the region.
Bahrain leads the Middle East in terms of 5G Game Score and latency
The cellular infrastructure is critical for the growth of mobile gaming. Advanced network systems that offer speed, reliability, and low latency are pivotal to seamless gaming experiences and thus, the gaming industry. The growing popularity of mobile devices and portable gaming also pushes the boundaries of what mobile games can do.
Recognizing this, Ookla has devised a new metric, Game Score, to measure the gaming experience. This score considers various network parameters that impact gaming, including download and upload speeds, latency, and jitter. Game Score is based on Ookla’s consumer-initiated Speedtest Intelligence results for download and upload speeds, as well as Consumer QoE’s™ latency and jitter measurements taken on actual game servers.
Each component is scored on a scale of 0-100 and then combined in a weighted average to produce a Game Score. A higher score signifies a better gaming experience for the user. You can find more details about the Game Score methodology here.
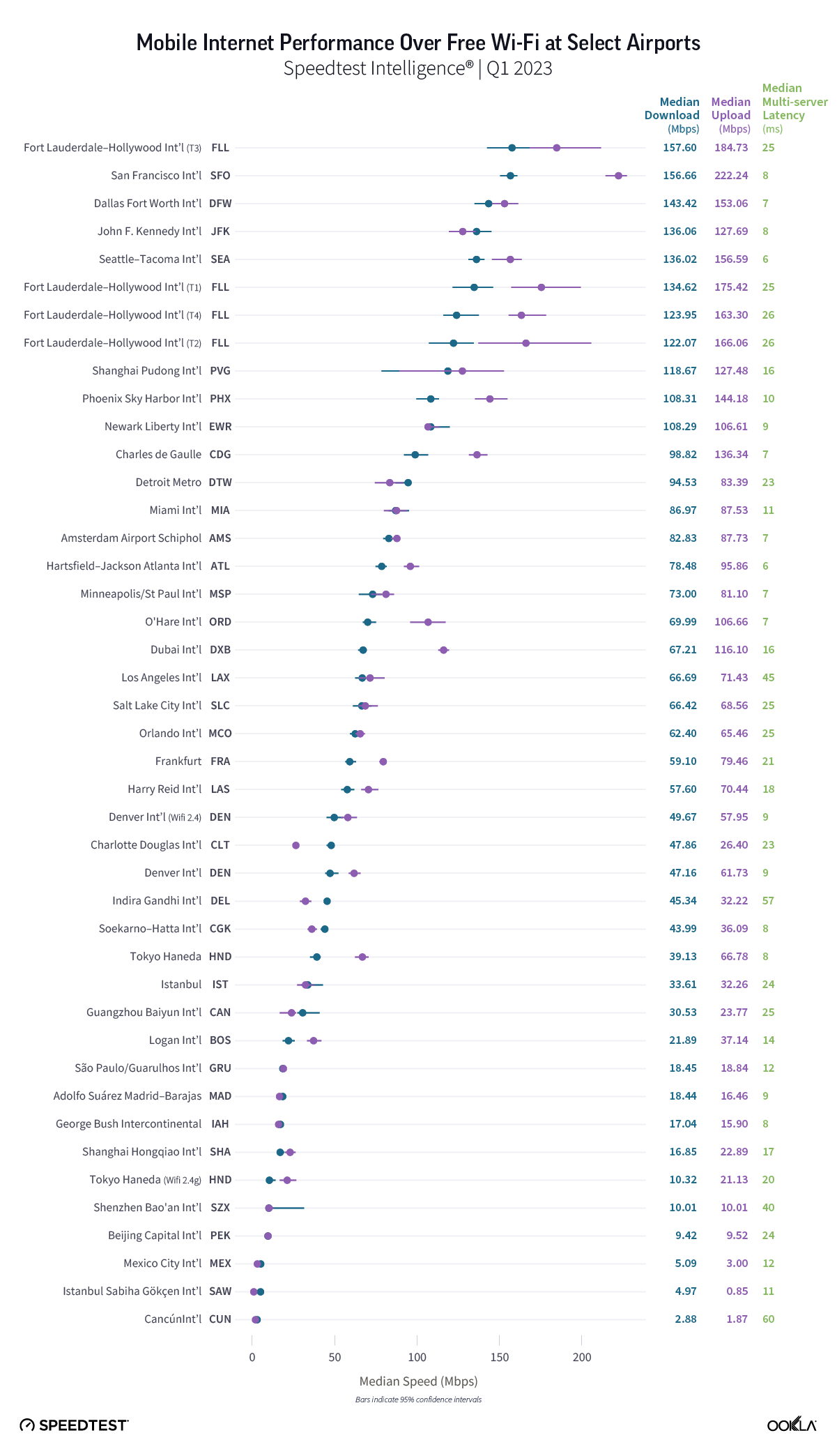
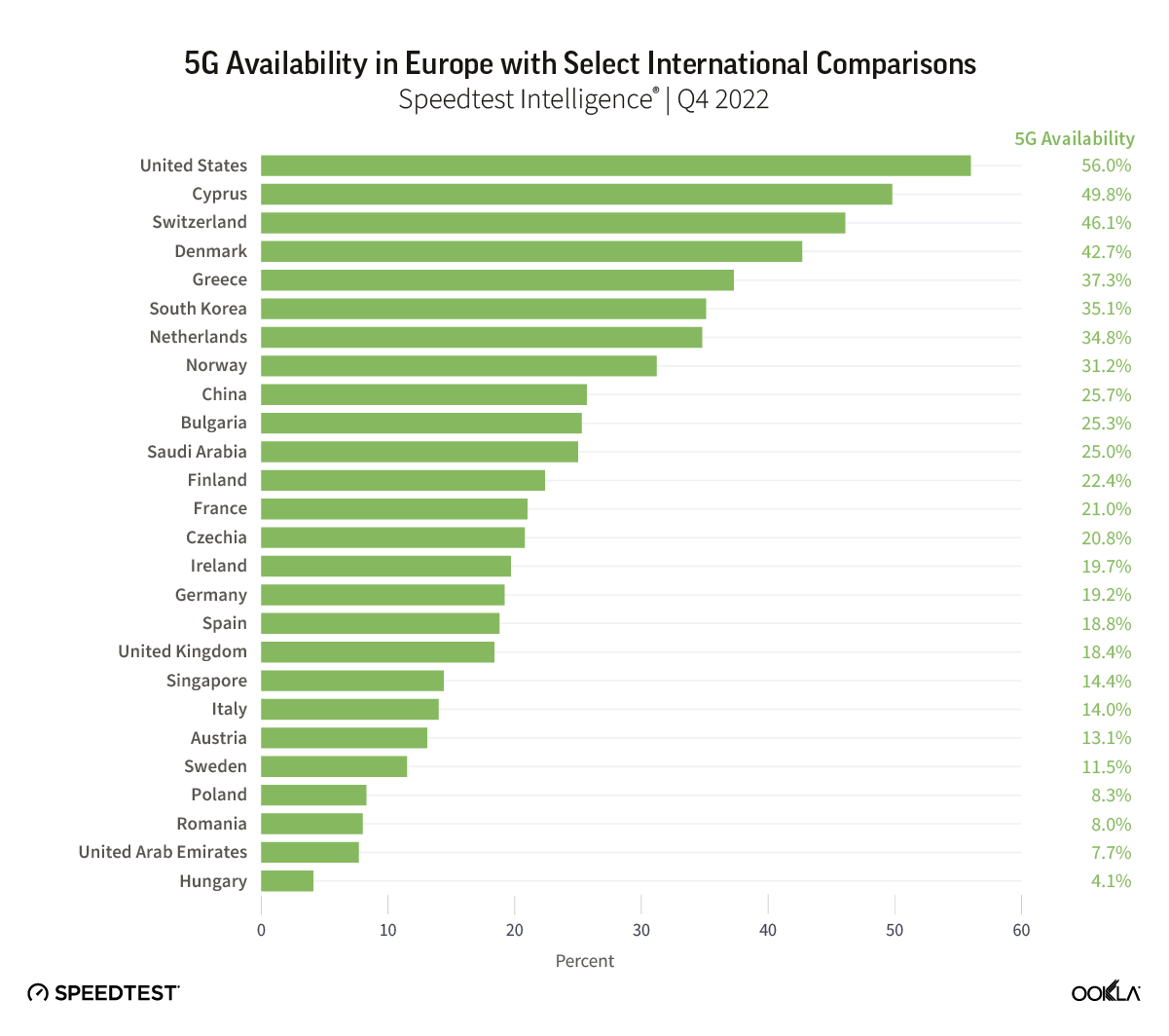
In a recent article, we presented the Game Scores for the six GCC countries. Bahrain led the Middle East region during the first half of 2023 with the highest 5G Game Score at 87.64. The U.A.E. and Qatar trailed closely with scores of 85.59 and 85.23, respectively, reflecting the high-quality mobile network performance in these markets that provides excellent gaming experiences. Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, and Oman received lower Game Scores.
Gamers in Bahrain can enjoy a great multi-player gaming experience over 5G
Looking more closely at two main components of the Game Score – download speed and game latency – we can assess how well Bahrain’s 5G network supports multi-player gaming services.
- Download speed is crucial for ensuring uninterrupted gameplay and maintaining high-quality streaming. High download speeds are also important for downloading digitally distributed games and updates. Download speed requirements for online mobile gaming vary depending on the game type (for example, cloud gaming needs higher bandwidth than a game played on a smartphone) and the gamer profile (for example, competitive gamers will require higher bandwidth than casual players)
- Game latency is a measure of latency to popular gaming server locations. It impacts the speed at which a gamer’s response is reflected in gameplay and is particularly important for games where quick reactions are crucial. Low latency also means smoother and lag-free gaming.
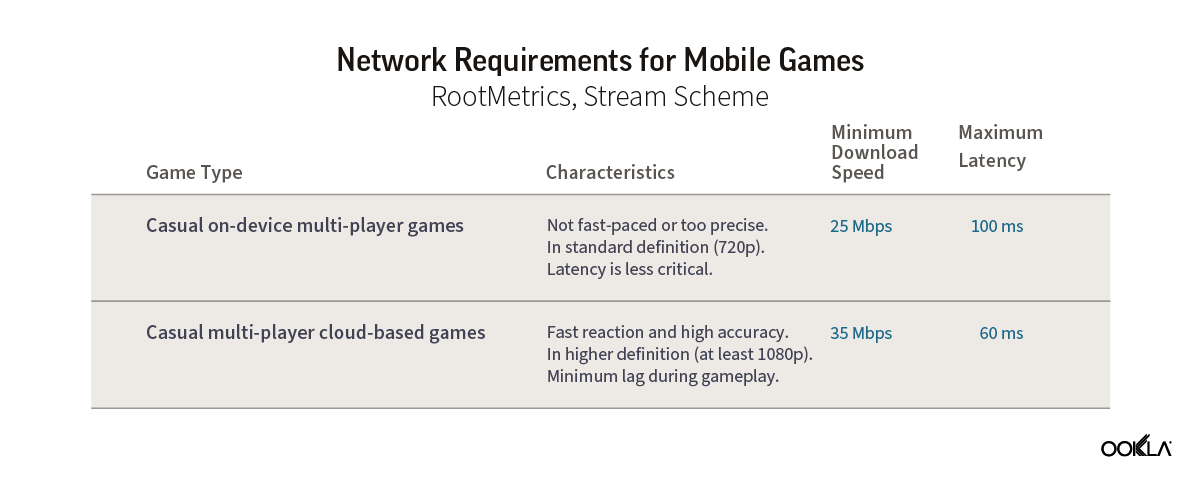
For this analysis, we consider two types of multi-player games to account for variations in network requirements and user expectations. The table below outlines the minimum requirements for casual gamers (who make up the majority of gamers) for download speed and latency for on-device and cloud games.
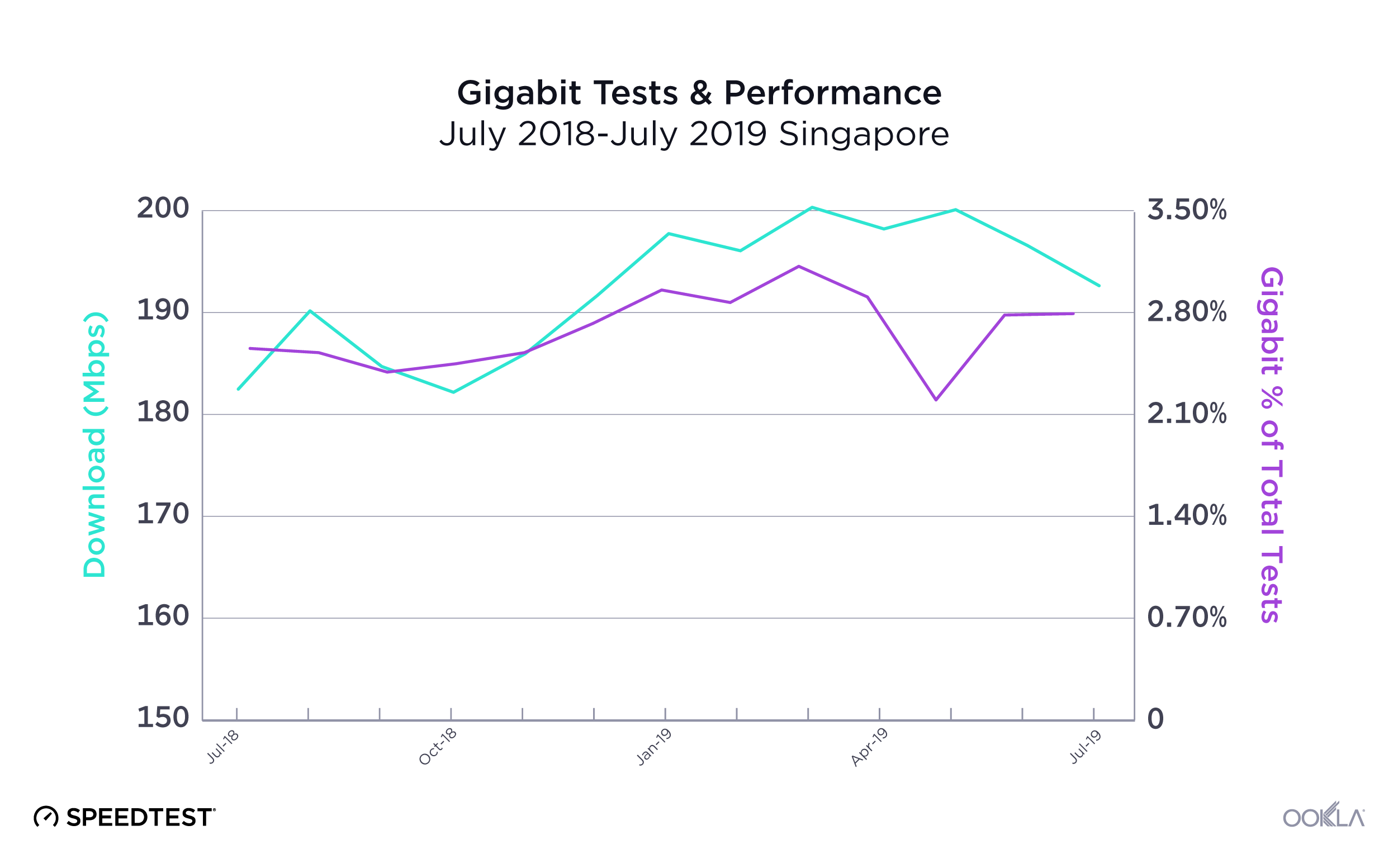
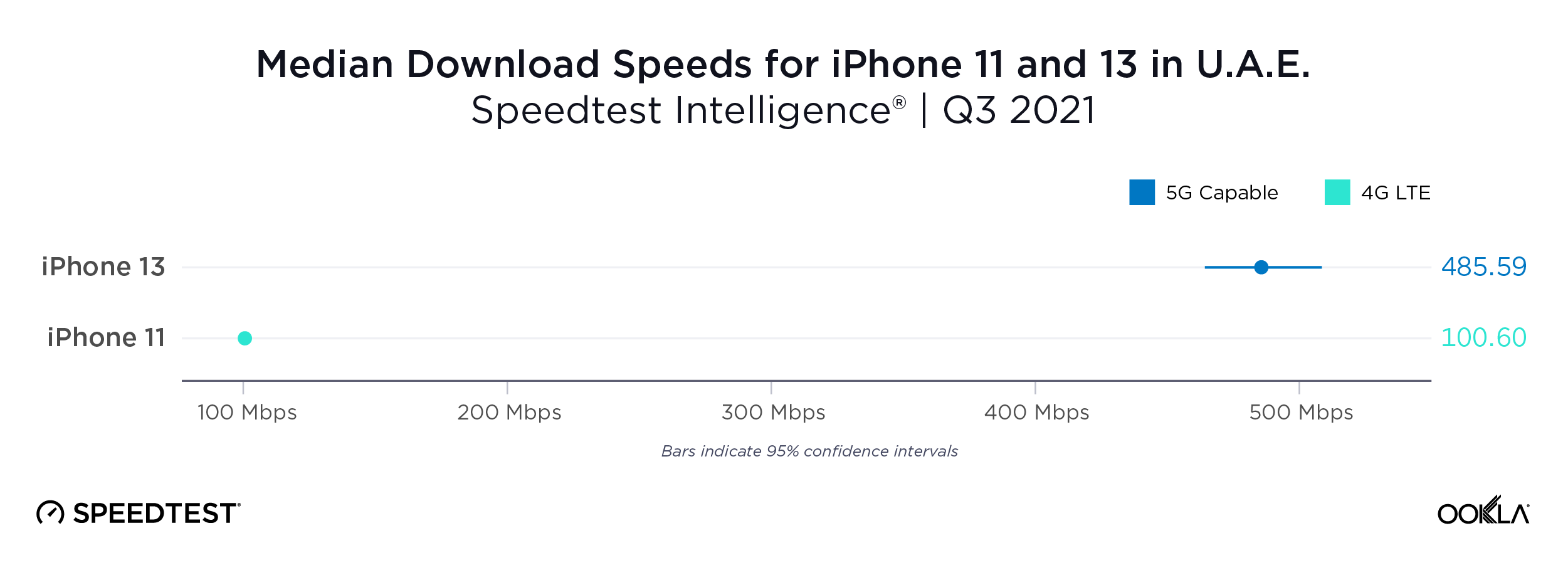
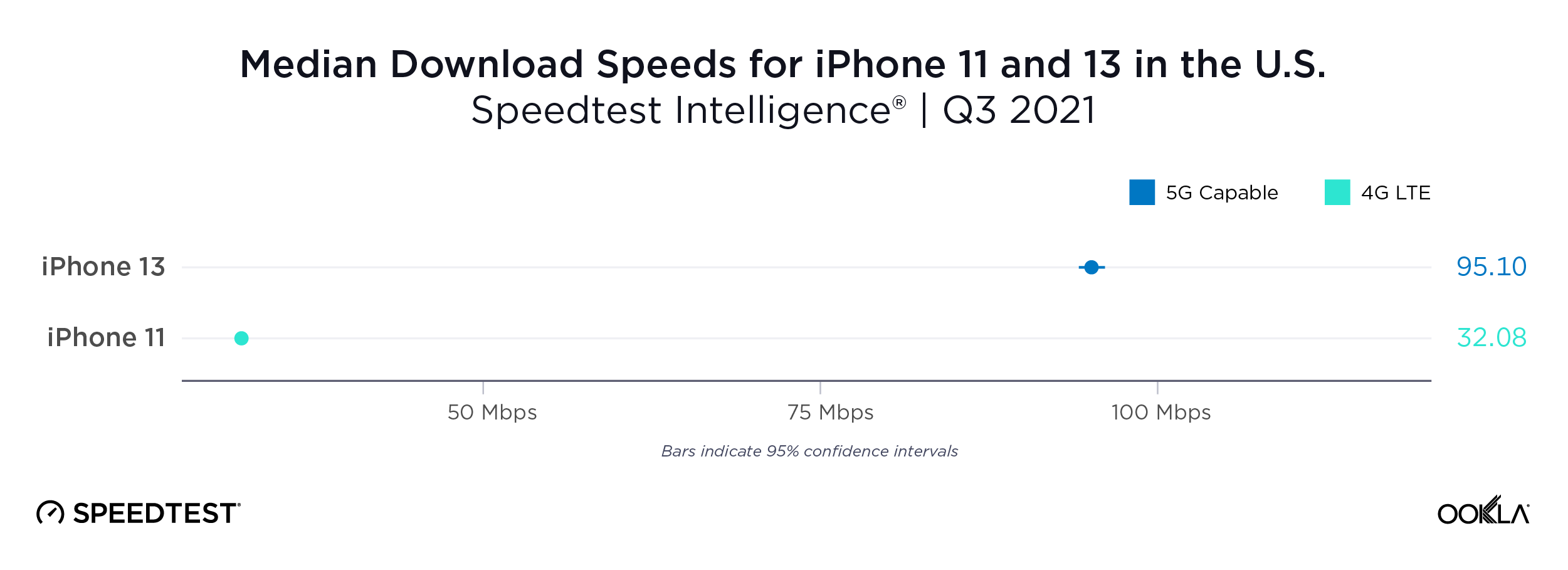
Ookla’s data shows that Bahrain significantly exceeds the speed requirement for both game types, with a median download speed of 413.69 Mbps during Q1-Q2 2023. This implies that gamers should not face delays in downloading games, loading games, or applying patches.
Bahrain has also the lowest latency in the Gulf region at 72 ms and should provide smooth gameplay for most casual games. Yet, some multiplayer shooters, racing, fighting, and multiplayer online battle arena (MOBA) games might experience some lag, particularly if streamed from a cloud server outside the country. There’s room for operators to enhance conditions for multiplayer games, especially for competitive gamers.
It should be noted that the gaming experience can be affected by other factors besides 5G network quality. The location of the game server, for example, can influence latency. If the game server is outside the country or region then the quality of international connectivity matters more. Since Bahrain has a small land mass and a high population density, game servers, and international gateways are likely to be close to gamers. This partially explains why its game-related metrics are better than those of other countries in the region.
Bahrain made the digital sector, including gaming, central to its economic expansion. The government and various regulatory authorities have fostered a favorable business environment to attract investments from global technology companies. Operators have also supported the country’s ambition to become the regional ICT hub by developing advanced digital infrastructure and nurturing local talent.
Following the COVID-19 pandemic, Bahrain prioritized ICT as a key sector for economic growth and diversification, setting targets to achieve 100% broadband coverage and increase the number of start-ups by 20% by the end of 2026. According to the Telecommunications Regulatory Authority (TRA), mobile broadband penetration of the population reached 146.0%, and fixed broadband penetration of households reached 69% in Q3 2023.
Bahrain was among the first countries in the Middle East to launch 5G in 2019. The three mobile operators, Batelco, stc, and Zain, have invested in its expansion, achieving 100% 5G commercial network coverage. Operators are also upgrading their 5G infrastructure to improve throughput and reduce latency by deploying 5G Standalone (SA) and 5G Advanced (5.5G). For example, stc tested 5G SA in May 2022 and 5G network slicing in October 2023. Batelco deployed a cloud-native 5G core and tested 5G SA in April 2022. Zain trialed 5G SA in 2022 and implemented 5G carrier aggregation using a mid-band frequency.
Furthermore, Batelco’s parent company, Beyon, announced an investment of over $250 million to support the country’s digital transformation. This includes the development of the country’s biggest data center. In 2022, stc announced that it plans the region’s largest technology park, which includes a new data center. These new facilities will supplement existing data centers and strengthen the country’s position as a regional digital infrastructure center.
The country’s extensive and high-quality network infrastructure underpinned its ‘Cloud First Policy’ which encouraged public and private organizations to migrate to the cloud. This strategy has proven successful in attracting major hyperscalers like AWS which established three ‘regional availability zones’ in 2019 in Bahrain.
Pro-graming policies and initiatives helped attract international companies and develop a local gaming ecosystem
This influx of international cloud service providers has caught the attention of game publishers eager to cater to their fans in the region. Take Epic Games, the publisher of Fortnite, as an example. They set up a local server over AWS infrastructure to boost game response times and stimulate interest in e-sports. They expected latency to improve between 20% and 50% for players in the Gulf region and India. Similarly, Riot Games set up a local server in Bahrain for its game Valorant.
Bahrain has a vibrant start-up landscape in the Middle East region bolstered by supportive government policies, funding schemes, and a pool of young, tech-savvy talent. As part of the Bahrain Economic Vision 2030, the government established Tamkeen, an agency designed to promote private sector development and digital services adoption. Tamkeen has been involved in initiatives such as setting up a training program for video game development and the creation of the ‘D11 Gaming Hub’, designed to strengthen the e-sports ecosystem in Bahrain.
Thanks to these efforts, Bahrain attracted foreign gaming studios, like The Stories Studio, to establish a local office. It has also nurtured a burgeoning local game production industry, with award-winning gaming studios, such as Juego Studios and Regnum Studio, and a host of start-ups offering a range of products, solutions, and services for the gaming industry. Bahrain also aspires to be a leading e-sports competition destination in the Middle East, having already hosted global events like the BLAST Pro Series Global Final, NVTC Tournament, and GIRLGAMER Festival.
Operators have also taken proactive steps to capitalize on the growing demand for gaming in recognition of its potential to diversify revenue, increase customer engagement, and differentiate their services. For example:
- Batelco introduced a mobile gaming portal in 2022.
- stc launched the ‘stc play’ app, hosted multiple e-sport tournaments, and bundled gaming packages with its mobile data and home services.
- Zain introduced a mobile game pass with a dedicated data allowance for popular games. It also partnered with the Bahraini Esports Federation and gaming platform provider Playhera to organize e-sports tournaments. Most recently, it launched the ‘Zain Esports Lab’ in collaboration with Tamkeen to host e-sports leagues, provide training to gamers, and offer professional opportunities for e-sports enthusiasts.
Bahrain harbors grand ambitions to strengthen its standing as a regional gaming hub
As part of the Telecommunications, ICT, and Digital Economy Sector Strategy 2022-2026, the Bahraini government aims to consolidate its reputation as a regional innovation center while continuing to lure large technology companies. Part of this strategy revolves around making the country an even more attractive destination for gaming companies to cater to the rapidly expanding base of casual gamers, e-sports enthusiasts, and professional players across the Middle East.
In November 2023, the TRA also unveiled the Sixth National Telecommunication Plan (NTP6). The plan outlines the government’s strategic three-year approach and general policies for the telecommunications sector. Bahrain’s objective is to continue to lead the way in ICT and telecommunications infrastructure development within the GCC region and aspire to be among the global top 10 in this sector.
BCG reported that the Middle East boasts the highest gaming penetration in the world, with over 60% of the population identifying as gaming enthusiasts. The audience for live-streaming games is projected to surpass 200 million in 2025, making the Middle East one of the fastest-growing regions for gaming, outpacing even China.
The GCC region is particularly ripe for growth in terms of active gamers and e-sports participants, thanks to its youthful demographic, substantial disposable income, access to affordable high-speed connectivity, and the ongoing development of gaming infrastructure. The market is bound to expand as gaming becomes more mainstream and as more female users and older demographics engage in gaming.
Statista predicts that the gaming industry in Bahrain (including in-game ads and live streaming) will generate over $38 million in 2023 and grow to over $53 million by 2027. Mobile games constitute the largest segment, with a market value nearing $12 million in 2023, expected to grow to more than $18 million by 2027. This is driven by the increasing number of players, expected to reach nearly 400,000 users by 2027.
These figures show that the domestic gaming market in Bahrain is relatively small because of the limited population. That is why the opportunity lies in serving the larger and growing gaming audience in the Middle East and fostering a local gaming ecosystem that can scale up to serve the region.
However, Bahrain faces stiff competition from its neighbors seeking to diversify their economies through digital services. For example, Saudi Arabia invested in major gaming studios such as Capcom and Activision Blizzard via the Public Investment Fund (PIF), its sovereign fund, and has a national gaming and e-sports strategy. U.A.E. encourages global gaming producers to establish a local presence and hosts major game tournaments and events.
Bahrain should leverage its unique advantages, such as its advanced connectivity infrastructure, skilled workforce, and favorable business environment. Its track record as a technology incubator can also position it as an ideal place to test new ideas, technologies, monetization models, and regulations to support innovative gaming services.
Ookla retains ownership of this article including all of the intellectual property rights, data, content graphs and analysis. This article may not be quoted, reproduced, distributed or published for any commercial purpose without prior consent. Members of the press and others using the findings in this article for non-commercial purposes are welcome to publicly share and link to report information with attribution to Ookla.